Numerical Modeling on the Damage Behavior of Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Waterjet Cutting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Model Description
2.1. SPH–FEM Coupling Algorithm
2.2. Constitutive Model of Concrete
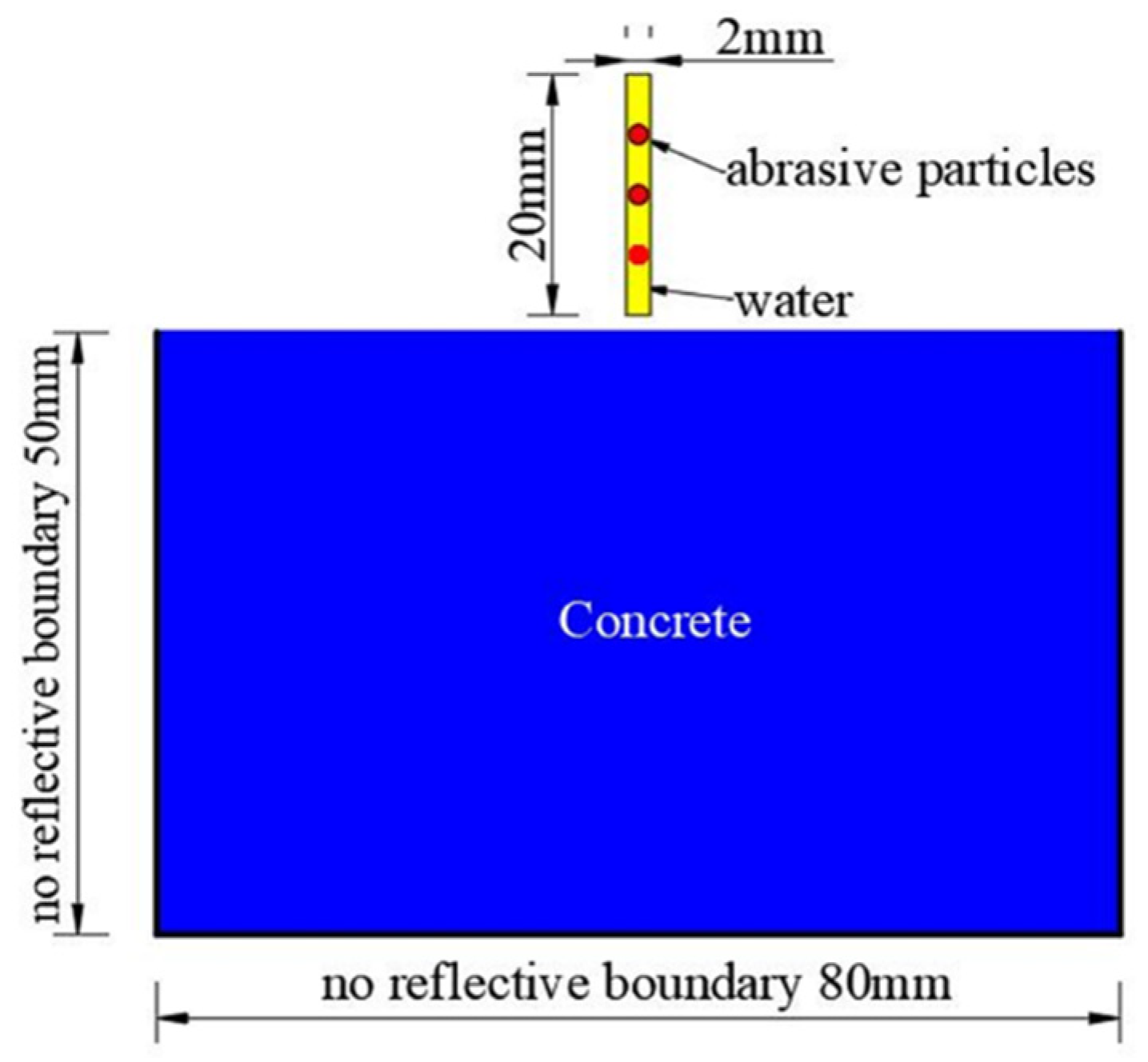
2.3. Numerical Model
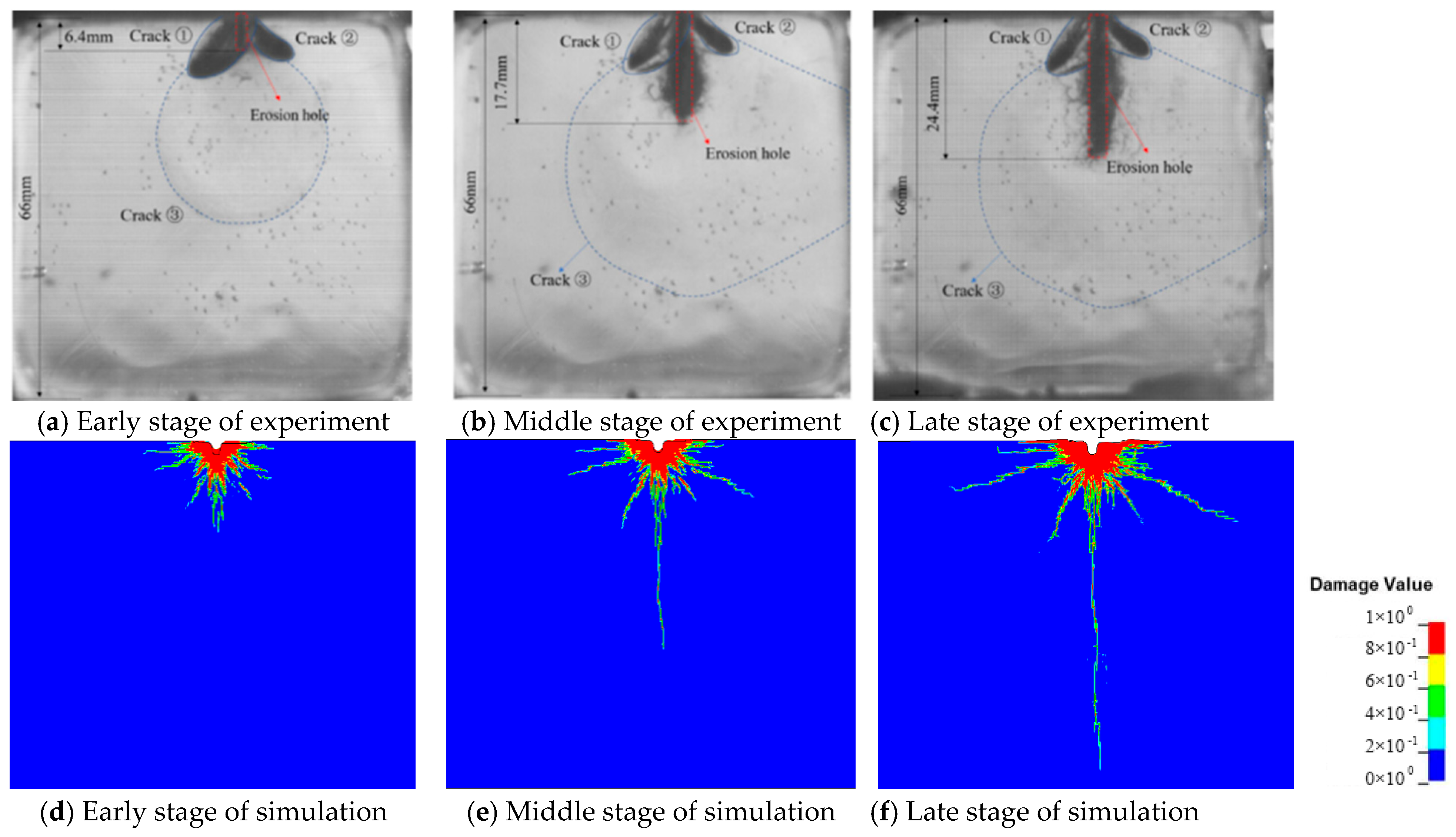
2.4. Validation of the Model
3. Results and Discussion
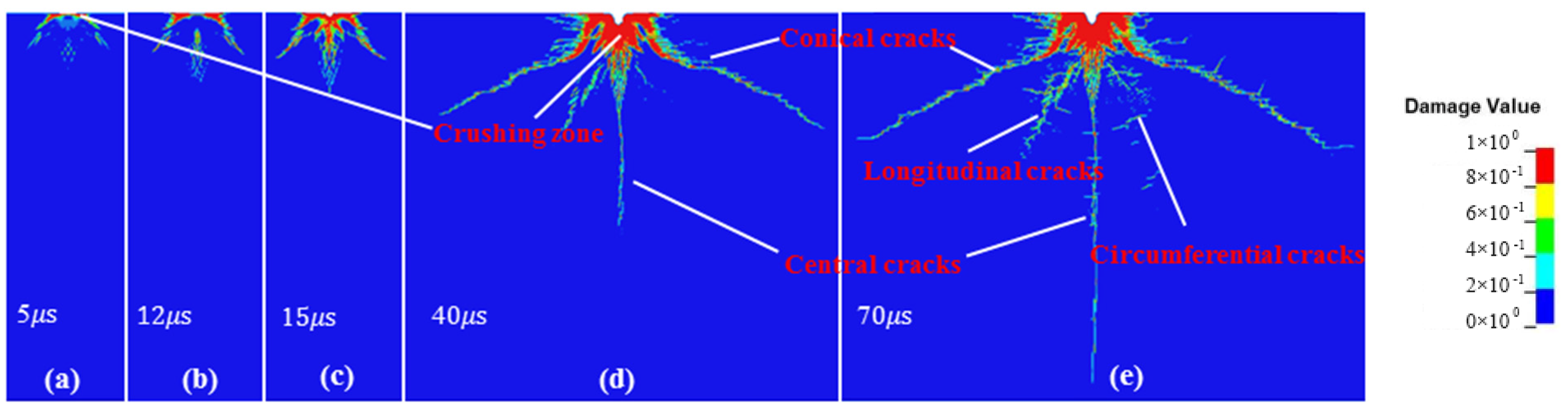
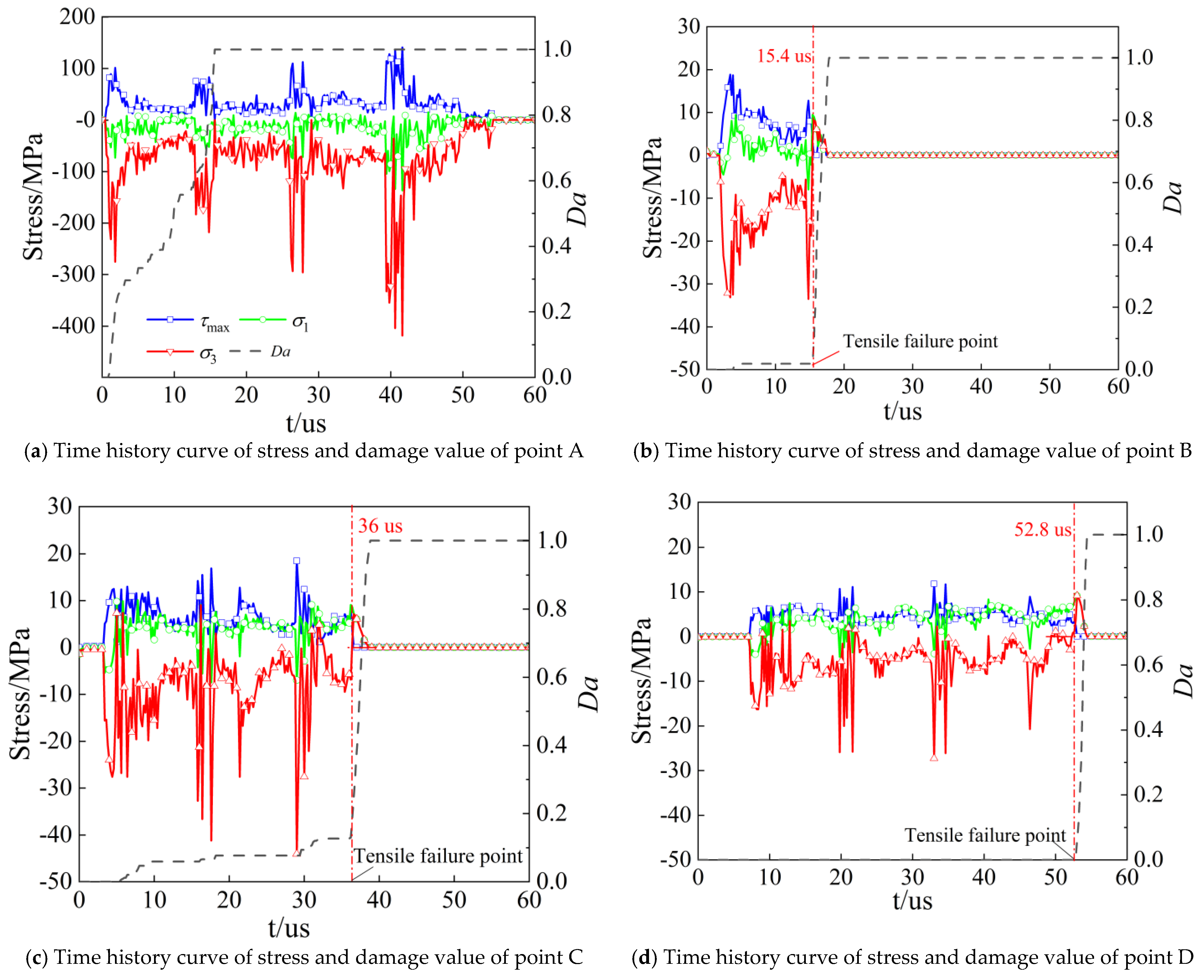
3.1. Damage Mechanism of Concrete
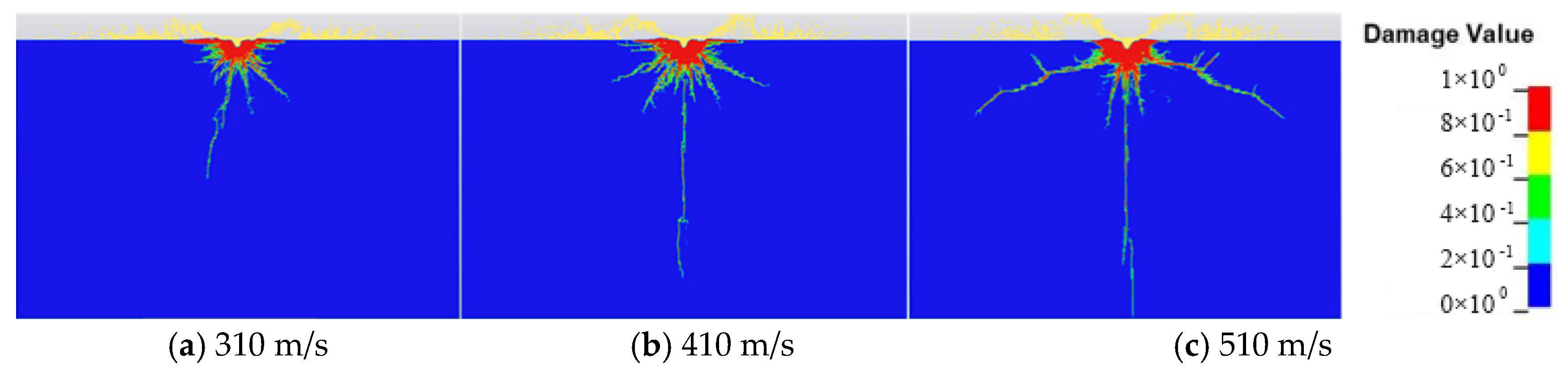
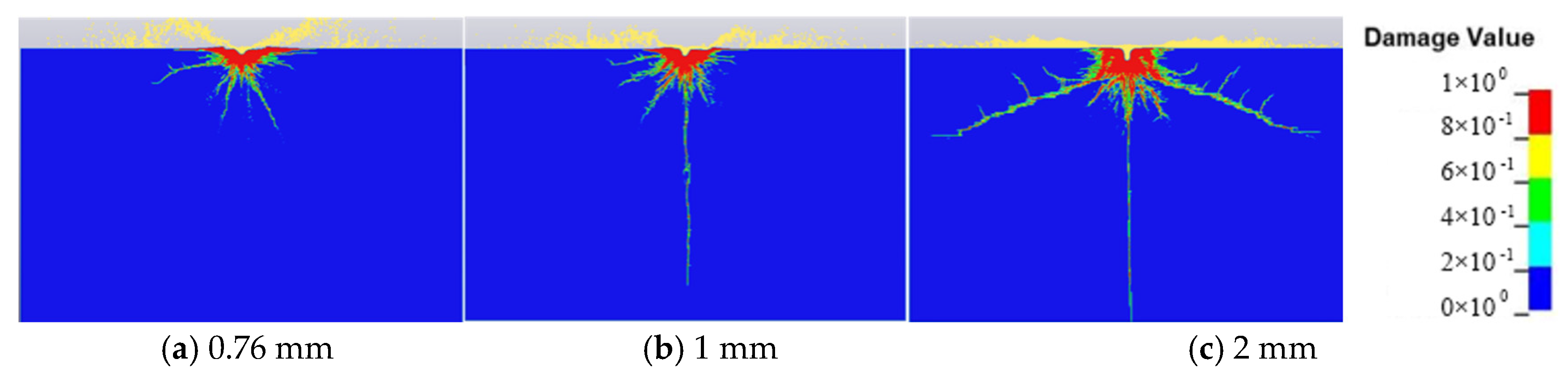
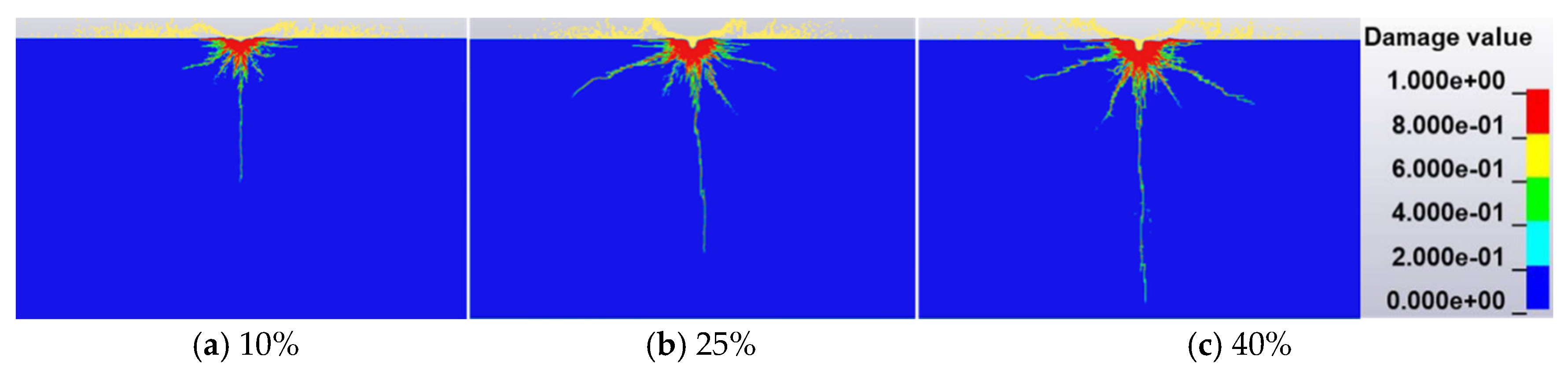
3.2. Effect of Waterjet Parameters on the Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Waterjet
3.3. Evaluation of the Optimal Combination of Jet Parameters
3.4. Parameters Configuration for Tunneling Assisted with Abrasive Waterjet
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Concrete subjected to abrasive waterjet can produce conical cracks, longitudinal cracks, circumferential cracks, and central cracks. The crushing zone and deep crater are developed in the early and middle stages of jet impact. Damage in the later stage of impact is dominated by circumferential and central cracks;
- (2)
- The damage of concrete subjected to abrasive waterjet can be divided into a crushing zone, crack formation zone and crack propagation zone. The crushing zone is caused by the shear stress. Plastic strain can cause damage accumulation, which is featured as plastic damage failure. Plastic damage failure occurs in the crack formation zone, followed by brittle damage, in which brittle damage is prominent. Brittle failure occurs in the crack propagation zone due to the large tensile stress;
- (3)
- The jet diameter has the largest effect on damage degree χ, followed by the concentration of abrasive particles. The velocity of the waterjet has the least effect. The concentration of abrasive particles has the largest effect on impact depth h, followed by the velocity of the waterjet. The jet diameter has the least effect;
- (4)
- The configuration of jet parameters in TBM assisted with waterjet for breaking rock follows the concept of higher pump pressure, larger jet diameter, and fewer abrasive particles. Shield tunneling assisted with abrasive waterjet for cutting reinforced concrete piles should follow the concept of higher pump pressure, smaller jet diameter, and more abrasive particles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Kheetan, M.J.; Al-Tarawneh, M.; Ghaffar, S.H.; Chougan, M.; Jweihan, Y.S.; Rahman, M.M. Resistance of Hydrophobic Concrete with Different Moisture Contents to Advanced Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Struct. Concr. 2021, 22, E1050–E1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthoz, N.; Branque, D.; Michalski, A.; Mohamad, W.; Bourgeois, E.; Le Kouby, A.; Szymkiewicz, F.; Rallu, A. Impact of Tunnelling on Piles in Parisian Subsoil: Dataset of in-Situ Measurements in the Ground and on Three Instrumented Piles. Data Br. 2023, 47, 108971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Sun, H. Fragmentation Pattern and Removal Mechanism of Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Water Jet Impact. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6618386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momber, A.W.; Mohan, R.S.; Kovacevic, R. Fracture Range Detection in Hydro-Abrasive Erosion of Concrete. Wear 2002, 253, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Barron, R.M.; Balachandar, R. An Experimental and Numerical Study of Water Jet Cleaning Process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tang, P.; Geng, Q.; Wang, X. Effect of Abrasive Concentration on Impact Performance of Abrasive Water Jet Crushing Concrete. Shock Vib. 2019, 2019, 3285150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Li, T.; Dai, X.; Xing, X.; Yang, X. The Effects of Inclined Particle Water Jet on Rock Failure Mechanism: Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 185, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, K. Numerical Simulation on Rock Fragmentation by Discontinuous Water-Jet Using Coupled SPH/FEA Method. Powder Technol. 2017, 312, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Si, H.; Chen, G. The Fragmentation Mechanism of Coal Impacted by Water Jets and Abrasive Jets. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsul, S.; Srinivasu, D.S. Modelling the Cross-Sectional Profile of the Kerf Generated in Overlapped Pass Erosion in Abrasive Waterjet Milling of Al6061-T6 Alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 102, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, P.; Lotfi, T.; Zitoune, R. Damage Created by Abrasive Waterjet and Conventional Drilling in Open-Hole and Assembled 3D Interlock Woven Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites Examined by Fatigue Testing and Linear Regression Analysis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 168, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdevari, S.; Sayehvand, H.; Bakhtiari Haftlang, P. Numerical Modeling of Abrasive Waterjet to Optimize Rock Cutting Parameters. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Xu, X.; Jiang, H.; Tian, Z.; Ma, T. Multicenter Hierarchical Federated Learning With Fault-Tolerance Mechanisms for Resilient Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.H.; Du, Z.J.; Chen, X.H.; Cai, C.G. Confidence Consensus-Based Model for Large-Scale Group Decision Making: A Novel Approach to Managing Non-Cooperative Behaviors. Inf. Sci. 2019, 477, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X. Value Determination Method Based on Multiple Reference Points under a Trapezoidal Intuitionistic Fuzzy Environment. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2018, 63, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. The New Similarity Measure and Distance Measure of a Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic Term Set Based on a Linguistic Scale Function. Symmetry 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, K.I.K.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.T.; Jin, Q. Reconstructed Graph Neural Network With Knowledge Distillation for Lightweight Anomaly Detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 11817–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Singh, J.; Tan, J.; Li, G. Use of Predictive Model for Identification of Overall Wear State of TBM Cutterhead Based on Tunneling Parameters. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 268, 126316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Visual Simulation of Landslide Fluidized Movement Based on Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; He, S.; Lei, X.; Bi, Y.; Liu, W.; Ouyang, C. Dynamic Process Simulation of Construction Solid Waste (CSW) Landfill Landslide Based on SPH Considering Dilatancy Effects. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonesi, M.; Franci, A.; Idelsohn, S.; Oñate, E. A State of the Art Review of the Particle Finite Element Method (PFEM). Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2020, 27, 1709–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bao, R.H.; Guo, Y.M. Waterjet Penetration Simulation by Hybrid Code of SPH and FEA. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, W.; Thoma, K.; Hiermaier, S.; Schmolinske, E. Penetration of Reinforced Concrete by BETA-B-500 Numerical Analysis Using a New Macroscopic Concrete Model for Hydrocodes. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on the Effects of Munitions with Structures, Berlin, Germany, 3–4 May 1999; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Z. Review of Concrete Dynamic Constitutive Mode. J. Tianjin Univ. 2015, 10, 853–863. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.; Axinte, D.A.; Becker, A.A. Finite Element Modelling of Abrasive Waterjet Milled Footprints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liang, C.; Tan, S. Using a High-Pressure Water Jet-Assisted Tunnel Boring Machine to Break Rock. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LS-DYNA Keyword User’s Manual Volume I; Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC): California, CA, USA, 2007.
- Liu, J.; Du, S.; Xue, Y. Study on the Breaking Process and Damage Characteristics of Abrasive Water Jet Impacting Concrete Based on Acoustic Emission. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Du, S. Failure Mechanism and Effect of Nozzle Parameters on Abrasive Water Jet Rock Breaking. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 6621255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.L.; Jiang, Z.H.; Han, W.F.; Li, M.L.; Wang, Y.X. Breakage Mechanism of Hard-Rock Penetration by TBM Disc Cutter after High Pressure Water Jet Precutting. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 240, 107320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccu, R.; Grosso, B. Improvement of Disc Cutter Performance by Water Jet Assistance. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, S.; Takasaki, H.; Matsui, K.; Ohashi, A.; Matsuike, T.; Sawa, Y. Application of Water Jet Cutting to Treatment for Obstructive Piles. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Tokyo, Japan, 11–13 June 1996; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qiao, S.; Wang, G.; Jiang, H.; Singh, J. Cutting Depth of Pile Materials Subjected to the Abrasive Waterjet and Its Prediction Model. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| N | BQ | Q0 | p*spall | D1 ** | D2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.6 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 1 |
| Material Parameters for Water | Material Parameters for Abrasive Particles | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model parameter | State parameter | Density (kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson ratio | Tensile failure stress (MPa) | ||||||
| ρ0 (kg/m3) | C (m/s) | S1 | S2 | S3 | γ0 | a | E0/J | ||||
| 998 | 1480 | 2.56 | −1.99 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 1.39 | 0 | 4120 | 248 | 0.3 | 150 |
| Da | 0–0.1 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.2–0.3 | 0.3–0.4 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.5–0.6 | 0.6–0.7 | 0.7–0.8 | 0.8–0.9 | 0.9–1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | A10 |
| Jet Parameters | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Velocity of water jet (m/s) | 310 | 410 | 510 |
| Jet diameter(mm) | 0.76 | 1.02 | 2 |
| Concentration of abrasive particles (%) | 10 | 25 | 40 |
| Damage Degree χ | Impact Depth h | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Velocity of Waterjet | Jet Diameter | Concentration of Abrasive Particles | Damage Degree χ (%) | Velocity of Waterjet | Jet Diameter | Concentration of Abrasive Particles | Impact Depth h/mm |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.21 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2.20 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2.24 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3.90 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5.33 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 6.55 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2.21 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5.00 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.63 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5.62 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3.75 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4.64 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3.45 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 6.22 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2.47 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4.36 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 5.99 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 8.11 |
| K1 | 2.929 | 2.291 | 2.477 | — | 4.217 | 4.473 | 3.733 | — |
| K2 | 3.197 | 2.780 | 3.481 | — | 5.087 | 4.627 | 5.670 | — |
| K3 | 3.969 | 5.024 | 4.137 | — | 6.230 | 6.433 | 6.130 | — |
| R | 1.040 | 2.733 | 1.660 | — | 2.013 | 1.960 | 2.397 | — |
| Sort | Jet diameter > Concentration of abrasive particles > Velocity of water jet | Concentration of abrasive particles > Velocity of water jet > Jet diameter | ||||||
| fj | 2 | 2 | 2 | — | 2 | 2 | 2 | — |
| Fj | 5.45 | 39.69 | 13.07 | — | 20.45 | 23.84 | 32.45 | — |
| >F0.05(2,2) | >F0.05(2,2) | >F0.05(2,2) | — | >F0.1(2,2) | >F0.05(2,2) | >F0.1(2,2) | — | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, G.; Singh, J. Numerical Modeling on the Damage Behavior of Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Waterjet Cutting. Buildings 2025, 15, 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132279
Hu X, Chen C, Wang G, Singh J. Numerical Modeling on the Damage Behavior of Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Waterjet Cutting. Buildings. 2025; 15(13):2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132279
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xueqin, Chao Chen, Gang Wang, and Jenisha Singh. 2025. "Numerical Modeling on the Damage Behavior of Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Waterjet Cutting" Buildings 15, no. 13: 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132279
APA StyleHu, X., Chen, C., Wang, G., & Singh, J. (2025). Numerical Modeling on the Damage Behavior of Concrete Subjected to Abrasive Waterjet Cutting. Buildings, 15(13), 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132279





