Steel Construction 4.0: Systematic Review of Digitalization and Automatization Maturity in Steel Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Q1—What are the advantages and limitations of using technologies and concepts related to Construction 4.0 for the manufacturing and installation of steel construction?
- Q2—What are the guidelines for future research and advancement of technologies and concepts related to Steel Construction 4.0?
- Q3—Which technologies and concepts are at the cutting edge of digitalization and automatization in the context of quality control in steel construction?
2. Materials and Methods
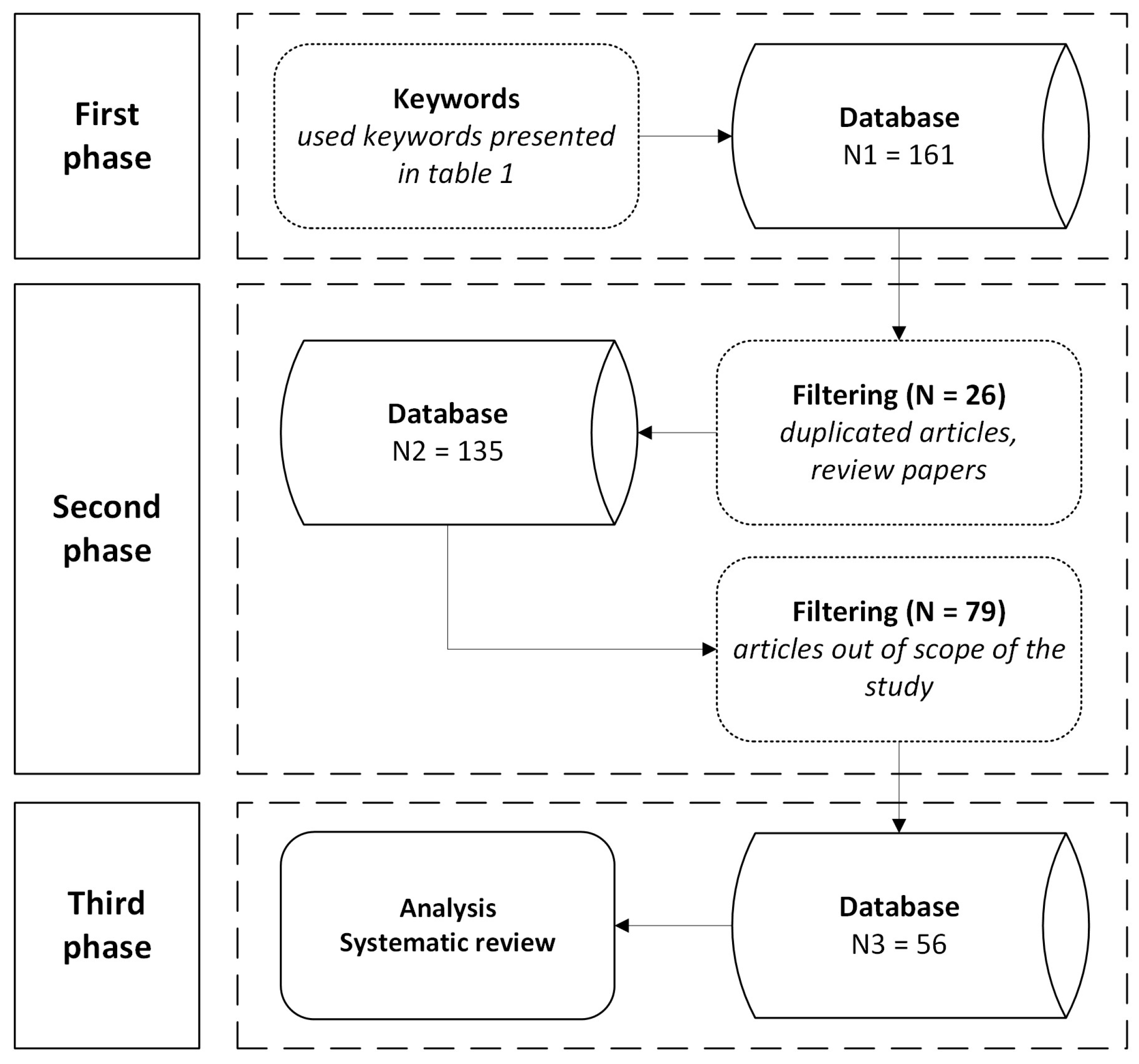
2.1. First Phase—Data Collection
2.2. The Second Phase—Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
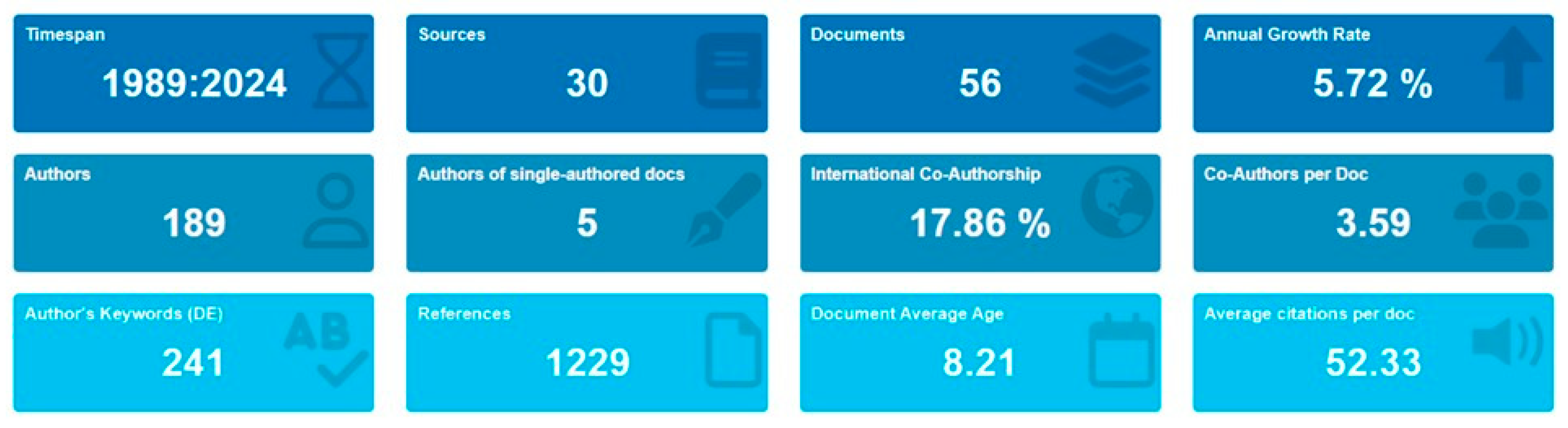
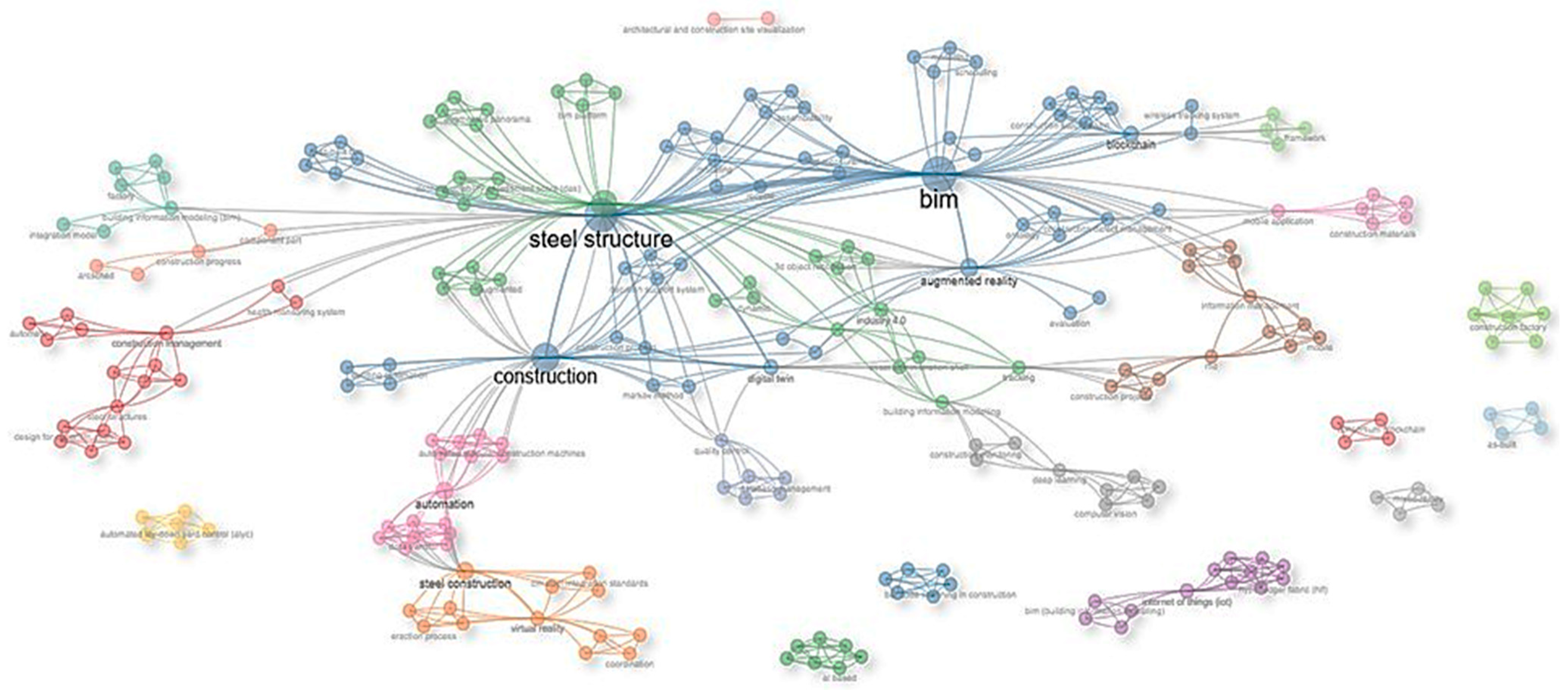
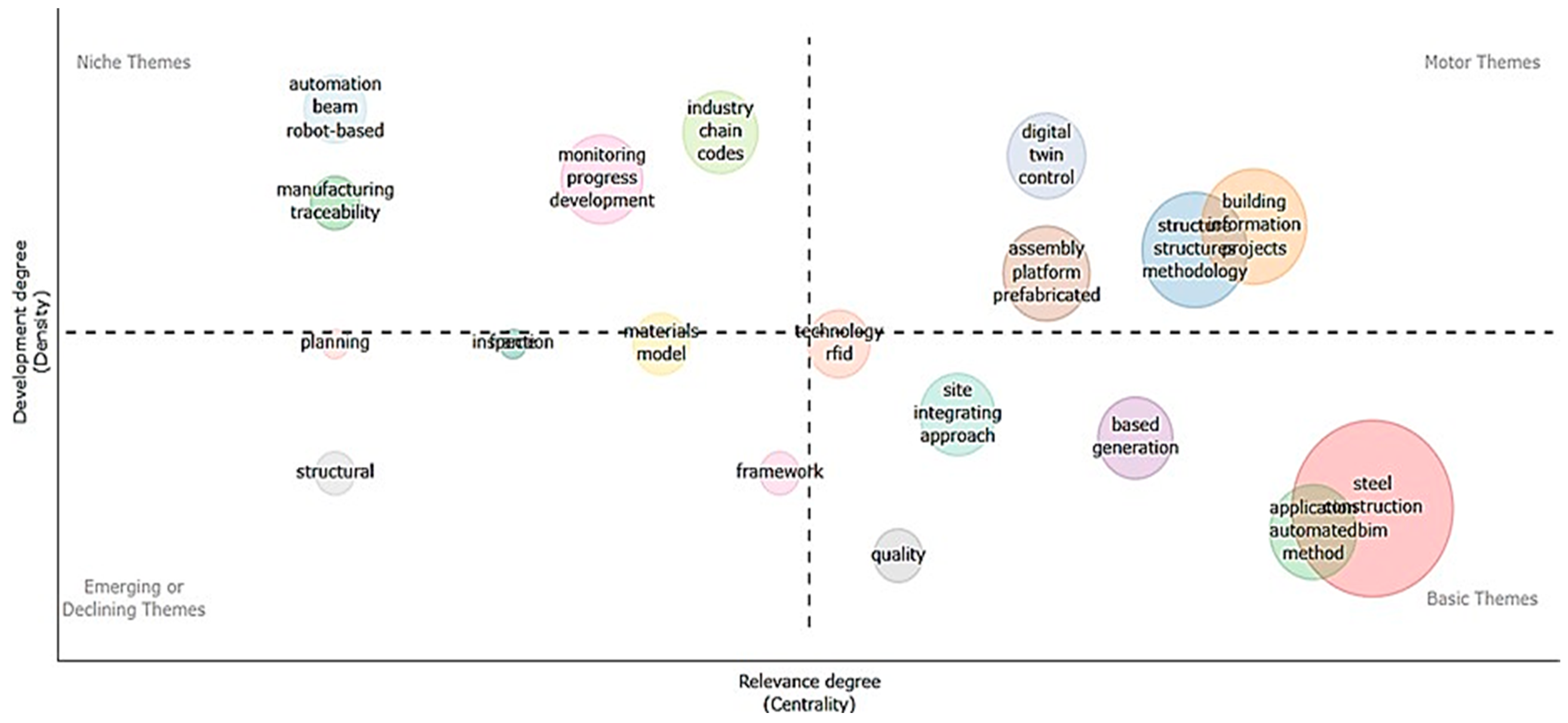
2.3. The Third Phase—Literature Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Building Information Model (BIM)
3.2. Barcodes, QR Codes, and RFID Technology
3.3. Immersive Technology
3.4. Internet of Things (IoT)
3.5. Blockchain Technology
3.6. Robotics and Deep Learning
3.7. Digital Twin
4. Discussion
4.1. Building Information Model (BIM)
4.2. Barcode, QR Code, and RFID Technology
4.3. Immersive Technology
4.4. Internet of Things
4.5. Blockchain
4.6. Robotics and Deep Learning
4.7. Digital Twin
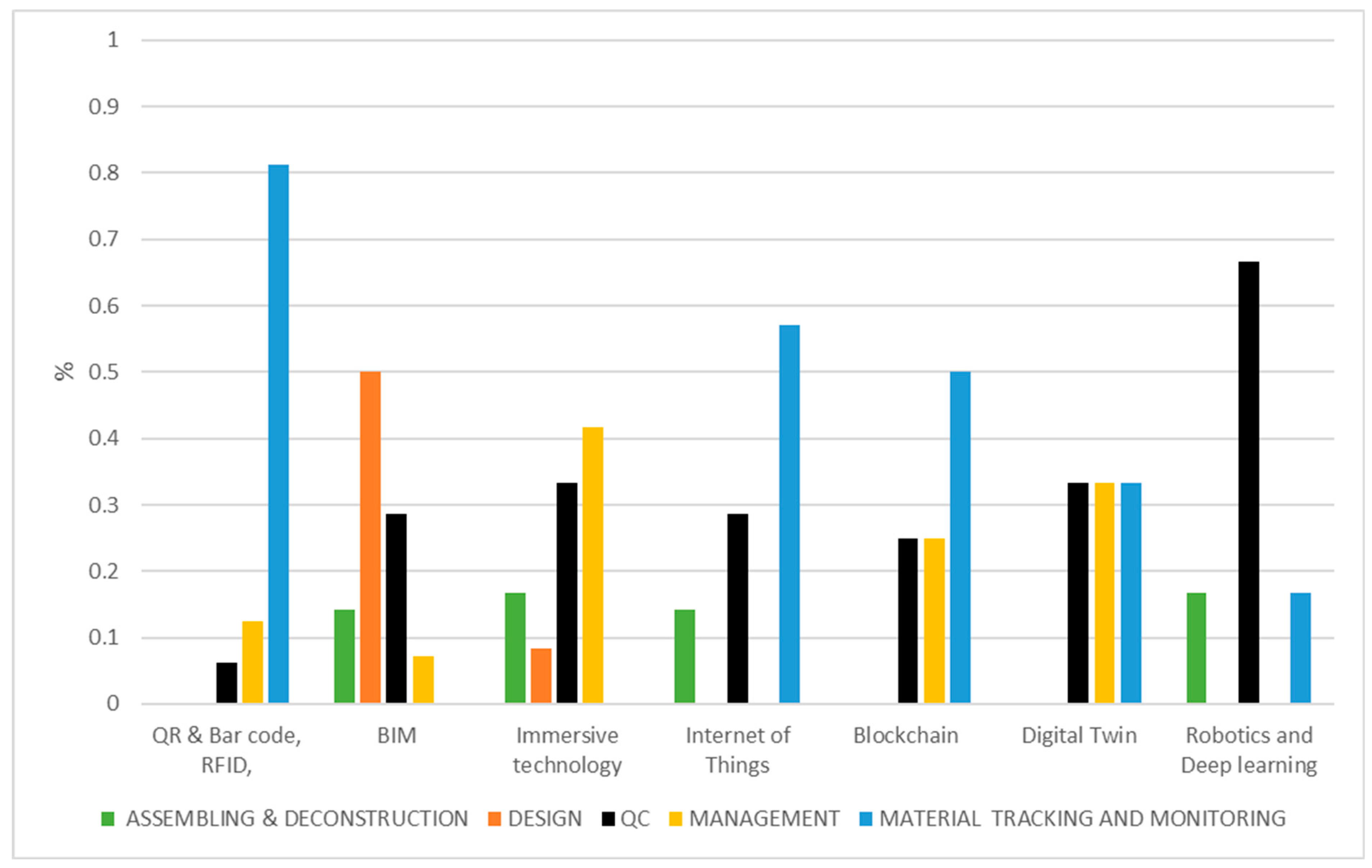
4.8. General Remarks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gajdzik, B.; Ślusarczyk, B.; Štverková, H. Digital transformation of the steel distribution sector in the context of Industry 4.0. Sci. Pap. Silesian Univ. Technol. Organ. Manag. Ser. 2023, 2023, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar, S.; Grisales, S.; Castaneda, D.I. Constructing tomorrow: A multifaceted exploration of Industry 4.0 scientific, patents, and market trend. Autom. Constr. 2023, 156, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcael, E.; Ferrari, I.; Opazo-vega, A. Construction 4.0: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, N.; Bled, A.; Bourgault, M.; Cousin, N.; Danjou, C.; Pellerin, R.; Roland, T. Construction 4.0: A survey of research trends. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2020, 25, 416–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tankova, T.; Pires, J.N.; da Silva, L.S. Industry 4.0 for Steel Construction: An Outlook. Ce/Papers 2021, 4, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbeck, P.; Löfsjögård, M.; Ansell, A. Quantitative review of construction 4.0 technology presence in construction project research. Buildings 2020, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autodesk. What Is BIM | Building Information Modelling | Autodesk. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/uk/solutions/bim (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Li, K.; Gan, Y.; Ke, G.; Chen, Z. The Analysis and Application of BIM Technology in Design of Steel Structure Joints. In Advances in Computer Science Research, Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Sensors, Measurement and Intelligent Materials, Shenzhen, China, 27–28 December 2015; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Avendaño, J.I.; Domingo, A.; Zlatanova, S. Building Information Modeling in Steel Building Projects Following BIM-DFE Methodology: A Case Study. Buildings 2023, 13, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laefer, D.F.; Truong-Hong, L. Toward automatic generation of 3D steel structures for building information modelling. Autom. Constr. 2017, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Wang, Q. Semi-automated generation of parametric BIM for steel structures based on terrestrial laser scanning data. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereiro, X.; Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; Riveiro, B. BIM methodology for cost analysis, sustainability, and management of steel structures with reconfigurable joints for industrial structures. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 77, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, A.; Serror, M.H.; Marzouk, M. A BIM-based framework for quantitative assessment of steel structure deconstructability. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galic, M.; Dolacek-Alduk, Z.; Cerovecki, A.; Glick, D.; Abramovic, M. BIM in planning deconstruction projects. In eWork and eBusiness in Architecture, Engineering and Construction; CRC Press: London, UK, 2015; pp. 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Lu, H. Development of a BIM Platform for the Design of Single-Story Steel Structure Factories. Buildings 2024, 14, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y. Virtual pre-assembly for large steel structures based on BIM, PLP algorithm, and 3D measurement. Front. Eng. Manag. 2019, 6, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; He, X.J.; He, J.; Fan, C. Virtual trial assembly of steel structure based on BIM platform. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y. Research on dynamic data monitoring of steel structure building information using BIM. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 2020, 18, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S. Applications of BIM in erecting steel structure. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 193–194, pp. 1440–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pote, N.S.; Shivaji Yele, M.; Vairagkar, M.A.; Yadav, M.V.; Jagtap, M.S.; Apurv Vairagkar, M. Planning and Scheduling of Multi Storey Building Using Bim. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2022, 9, 3014. [Google Scholar]
- Eric Lundberg, B.J.; Beliveau, Y.J. Automated Lay-Down Yard Control System-Alyc. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 1989, 115, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riurean, S. An Efficient Procedure for Materials’ Marking in Metallic Constructions Industry Based on QR Codes. MATEC Web Conf. 2019, 290, 05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Shi, J. A bim platform for the manufacture of prefabricated steel structure. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.Y.; Lee, E.B.; Jung, I.H.; Kim, C.Y. Smart-Tracking Systems Development with QR-Code and 4D-BIM for Progress Monitoring of a Steel-Plant Blast-Furnace Revamping Project in Korea. In Logistics Operations and Management for Recycling and Reuse; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 161–173. ISBN 978-3-642-33856-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tserng, H.P.; Dzeng, R.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, S.T. Mobile construction supply chain management using PDA and Bar Codes. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2005, 20, 242–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.Y.; Chen, J.C. Integrating barcode and GIS for monitoring construction progress. Autom. Constr. 2002, 11, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Yi, C.Y.; Park, Y.J. Image processing and qr code application method for construction safety management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, T.M.; Benedetta, B.; Manuele, C.; Davide, T. BIM and QR-code. A synergic application in construction site management. Procedia Eng. 2014, 85, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaselskis, E.J.; Asce, A.M.; El-Misalami, T. Implementing Radio Frequency Identification in the Construction Process. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2003, 129, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C. Enhancing construction quality inspection and management using RFID technology. Autom. Constr. 2008, 17, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.Y.L.; Tserng, H.P.; Wang, J.C.; Tsai, S.C. Developing a precast production management system using RFID technology. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.; Yoon, S.; Choi, C.; Cho, C. RFID+4D CAD for Progress Management of Structural Steel Works in High-Rise Buildings. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2008, 22, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasim, N. Intelligent materials tracking system for construction projects management. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2015, 47, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, A.F.; Thabet, W.Y. A Virtual Construction Environment for preconstruction planning. Autom. Constr. 2003, 12, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, R.; Lipman, R.R. Immersive Virtual Reality for Steel Structures; National Institute of Standards and Technology Building and Fire Research Laboratory: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, S.; Beauvais, M.; Girard-Vallée, A.; Snyder, R. A live augmented reality tool for facilitating interpretation of 2D construction drawings. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 8853, pp. 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, A.; Mahamadu, A.-M.; Mahdjoubi, L.; Manu, P. An Approach for Integrating Mixed Reality into BIM for Early Stage Design Coordination. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 312, 04001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, C.; Hakkaraine, M. Mobile Mixed Reality System for Architectural and Construction Site Visualization. In Augmented Reality—Some Emerging Application Areas; InTech: Kobe, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Dunston, P.S. Evaluation of Augmented Reality in steel column inspection. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Kwon, O.S.; Wang, X. A framework for proactive construction defect management using BIM, augmented reality and ontology-based data collection template. Autom. Constr. 2013, 33, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S.; Park, C.S.; Lim, C.R. A defect management system for reinforced concrete work utilizing BIM, image-matching and augmented reality. Autom. Constr. 2014, 46, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshokraei, M.; De Gaetani, C.I.; Migliaccio, F. A web-based BIM-AR quality management system for structural elements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.; min Park, J.; yeon Park, S.; Yilmaz, G. Low-cost mobile augmented reality service for building information modeling. Autom. Constr. 2023, 146, 104662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainggolan, F.; Siregar, B.; Fahmi, F. Design of Interactive Virtual Reality for Erection Steel Construction Simulator System Using Senso Gloves. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1542, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, H.B.; Kraus, W. Structural Steel Fabrication with Mixed Reality. Ce/Papers 2023, 6, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisari, M.; Foroughi Sabzevar, M.; Chen, P.; Irizzary, J. Integrating BIM and Panorama to Create a Semi-Augmented-Reality Experience of a Construction Site. Int. J. Constr. Educ. Res. 2016, 12, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolaković, A.; Hadžialić, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A review of enabling technologies, challenges, and open research issues. Comput. Netw. 2018, 144, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Peng, Y.; Xue, F.; Fang, J.; Zou, W.; Luo, H.; Thomas Ng, S.; Lu, W.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Huang, G.Q. Prefabricated construction enabled by the Internet-of-Things. Autom. Constr. 2017, 76, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Xue, F.; Li, X.; Hong, J.; Shen, G.Q. An Internet of Things-enabled BIM platform for on-site assembly services in prefabricated construction. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Dou, Q.; Liu, S. Internet of Things Health Detection System in Steel Structure Construction Management. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 147162–147172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Kerber, E.; Reuter, F.; Stumm, S.; Brell-Cokcan, S. The digitization of the automated steel construction through the application of microcontrollers and MQTT. Constr. Robot. 2020, 4, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandín, R.; Abrishami, S. IoT-BIM and blockchain integration for enhanced data traceability in offsite manufacturing. Autom. Constr. 2024, 159, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xia, W.; Chen, Y. Application Research on Blockchain-based Steel Structure Traceability Management. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence, MLBDBI 2020, Taiyuan, China, 23–25 October 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Bhattacharjee, P. SteelChain—Blockchain-Based Transparent Supply Chain Framework for the Steel Industry. In Advances in Thermal Engineering, Manufacturing, and Production Management; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, M.; Elghaish, F.; Brooks, T.; Pour Rahimian, F.; Park, C. Blockchain-based decentralised material management system for construction projects. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Ding, L.; Zhong, B.; Love, P.E.D.; Luo, H.; Chen, J. Construction quality information management with blockchains. Autom. Constr. 2020, 120, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Chu, B.; Hong, D. Robot-based construction automation: An application to steel beam assembly (Part II). Autom. Constr. 2013, 32, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Jung, K.; Lim, M.T.; Hong, D. Robot-based construction automation: An application to steel beam assembly (Part I). Autom. Constr. 2013, 32, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Yuvaraj, N.; Park, H.W.; Preethaa, K.R.S.; Pandian, R.A.; Lee, D.E. Investigation of steel frame damage based on computer vision and deep learning. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Automated Counting of Steel Construction Materials: Model, Methodology, and Online Deployment. Buildings 2024, 14, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Rashidi, A.; Talei, A.; Kong, D. Innovative Point Cloud Segmentation of 3D Light Steel Framing System through Synthetic BIM and Mixed Reality Data: Advancing Construction Monitoring. Buildings 2024, 14, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Ahmad, R.; Al-Hussein, M. A vision-based system for pre-inspection of steel frame manufacturing. Autom. Constr. 2019, 97, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M.; Vickers, J. Digital twin: Mitigating unpredictable, undesirable emergent behavior in complex systems. In Transdisciplinary Perspectives on Complex Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M. Virtually Perfect: Driving Innovative and Lean Products through Product Lifecycle Management; Space Coast Press: Cocoa Beach, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, C.; Anumba, C.J. Digital Twins as the Next Phase of Cyber-Physical Systems in Construction. In Computing in Civil Engineering 2019: Data, Sensing, and Analytics—Selected Papers from the ASCE International Conference on Computing in Civil Engineering 2019; American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE): Reston, WA, USA, 2019; pp. 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosse, S.; Pawlowski, D.; König, M. Industry 4.0-Based Digital Twin Approach for Construction Site Tracking Purposes. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z.; Mo, Y. Quality control method of steel structure construction based on digital twin technology. Digit. Twin 2023, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Almansa, F.; Tullini, N.; Liu, Z.; Lin, S. Digital Twin Model and Its Establishment Method for Steel Structure Construction Processes. Buildings 2024, 14, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Ray, B.R.; Karmakar, N.C. RFID localization in construction with IoT and security integration. Autom. Constr. 2024, 159, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| T&C | Variable Keywords |
|---|---|
| Barcode and QR code, RFID | Barcode, QR code, RFID |
| Immersive technology | AR, MR, VR, Immersive technology |
| Blockchain technology | BTC, Blockchain |
| BIM | BIM, 3D modeling, Steel detailing |
| Digital Twin | Digital twin |
| Internet of Things | IoT, sensors, monitoring |
| Robotics and Deep Learning | Robotics, Machine learning, Deep learning |
| T&C | N1 | N2 | N3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barcode and QR code, RFID | 31 | 28 | 13 |
| Immersive technology | 42 | 42 | 13 |
| Blockchain technology | 16 | 11 | 4 |
| BIM | 33 | 31 | 12 |
| Digital Twin | 11 | 8 | 3 |
| Internet of Things | 17 | 8 | 5 |
| Robotics and Deep Learning | 11 | 7 | 6 |
| Year | Author | T&C | Process and Sub-Process | QC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | [20] | BIM | Assembling | - |
| 2015 | [15] | BIM | Deconstruction | - |
| 2016 | [9] | BIM | Design | - |
| 2017 | [11] | BIM + laser scan | Design | - |
| 2019 | [17] | BIM | QC | Data analysis; VTA |
| 2020 | [19] | BIM | QC | Sensors |
| 2020 | [12] | BIM + laser scan | Design; QC | Point Cloud data |
| 2020 | [14] | BIM | Design | - |
| 2022 | [18] | BIM | Assembling; QC | Data analysis; VTS |
| 2022 | [21] | BIM | Management | - |
| 2023 | [13] | BIM | Design | - |
| 2023 | [10] | BIM | Design | - |
| 2024 | [16] | BIM | Design | - |
| Year | Author | T&C | Process and Sub-Process | QC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | [22] | Barcode | Material ID and tracking | - |
| 2002 | [27] | Barcode + RF + GIS | Material ID and monitoring | Automatization; data analysis |
| 2003 | [30] | RFID | Material ID and tracking | |
| 2005 | [26] | Barcode | Material tracking | Data analysis |
| 2008 | [31] | RFID | QC | Data analysis |
| 2008 | [33] | RFID + BIM | Material tracking | - |
| 2009 | [32] | RFID | Material ID | - |
| 2014 | [29] | QR code + BIM | Management | Data analysis |
| 2015 | [34] | RFID | Material ID | - |
| 2019 | [23] | QR code | Material ID | - |
| 2020 | [24] | QR code + BIM | Material ID | Data analysis |
| 2020 | [25] | QR code + BIM | Material ID | - |
| 2021 | [28] | QR code + image processing | Safety management | - |
| Year | Author | T&C | Process and Sub-Process | QC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | [35] | VR | Management | - |
| 2003 | [36] | VR + CIS/2 | Management | - |
| 2009 | [40] | AR | QC | Digitalization |
| 2011 | [39] | BIM + AR | Management | - |
| 2013 | [41] | AR + BIM | QC | Digitalization |
| 2014 | [37] | AR + BIM | Management | - |
| 2016 | [47] | Panorama + BIM = Semi AR | Management | - |
| 2019 | [43] | AR + BIM | QC | Digitalization |
| 2020 | [38] | MR + BIM | Design | - |
| 2020 | [45] | VR | Assembling | - |
| 2023 | [44] | AR + BIM | QC | Data analysis, Digitalization |
| 2023 | [46] | MR + BIM | Assembling | - |
| Year | Author | T&C | Process and Sub-Process | QC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | [50] | IoT + BIM + RFID | Material tracking | - |
| 2018 | [51] | IoT + BIM + RFID | Material tracking | Automatization |
| 2020 | [52] | IoT | QC, monitoring | Sensors, Data analysis |
| 2020 | [53] | IoT + MQTT | Production, QC | Automatization |
| 2024 | [54] | IoT + BIM + BCT + RFID | Material tracking |
| Year | Author | T&C | Process and Sub-Process | QC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | [55] | Blockchain | Material tracking | |
| 2021 | [56] | Blockchain | Material tracking | Automatization |
| 2020 | [58] | Blockchain | QC | Data analysis |
| 2024 | [57] | Blockchain | Management |
| Year | Author | T&C | Process and Sub-Process | QC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | [59,60] | Robotics | Assembling | |
| 2019 | [64] | BIM + deep learning | QC | Automatization; Vision-based module |
| 2021 | [61] | Deep learning | QC | Automatization; Data analysis |
| 2024 | [62] | Deep learning | QC; material ID | Automatization |
| 2024 | [63] | BIM, point cloud, MR | QC | Point Cloud Data; Automatization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šokić, D.; Dolaček-Alduk, Z.; Galić, M. Steel Construction 4.0: Systematic Review of Digitalization and Automatization Maturity in Steel Construction. Buildings 2025, 15, 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132154
Šokić D, Dolaček-Alduk Z, Galić M. Steel Construction 4.0: Systematic Review of Digitalization and Automatization Maturity in Steel Construction. Buildings. 2025; 15(13):2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132154
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠokić, Dario, Zlata Dolaček-Alduk, and Mario Galić. 2025. "Steel Construction 4.0: Systematic Review of Digitalization and Automatization Maturity in Steel Construction" Buildings 15, no. 13: 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132154
APA StyleŠokić, D., Dolaček-Alduk, Z., & Galić, M. (2025). Steel Construction 4.0: Systematic Review of Digitalization and Automatization Maturity in Steel Construction. Buildings, 15(13), 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132154








