The Effect of Cementation on Microstructural Evolution and Particle Characteristics of Calcareous Sand Under Triaxial Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
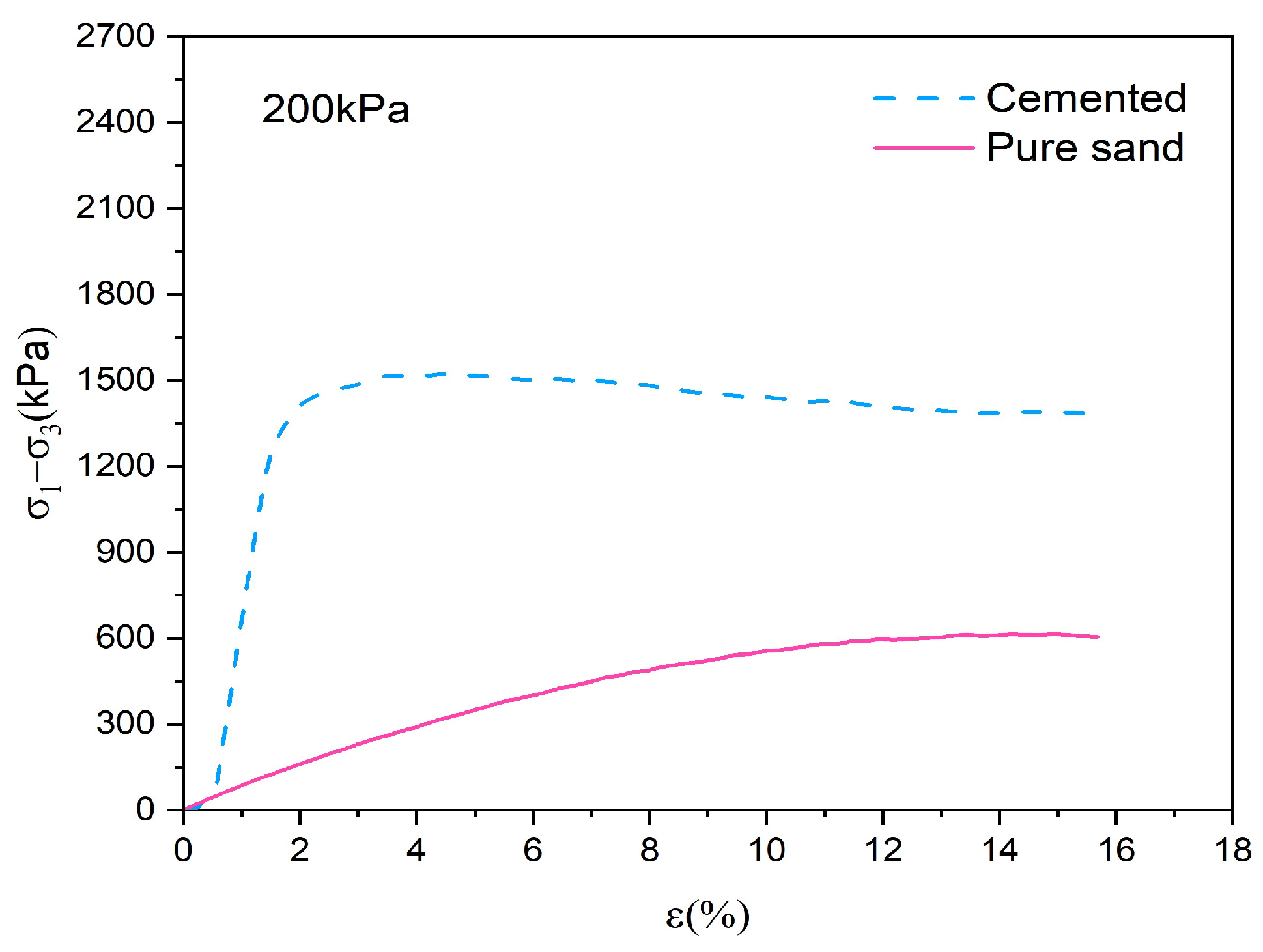
3.1. Mechanical Response and Particle Breakage for Pure and Cemented Calcareous Sand
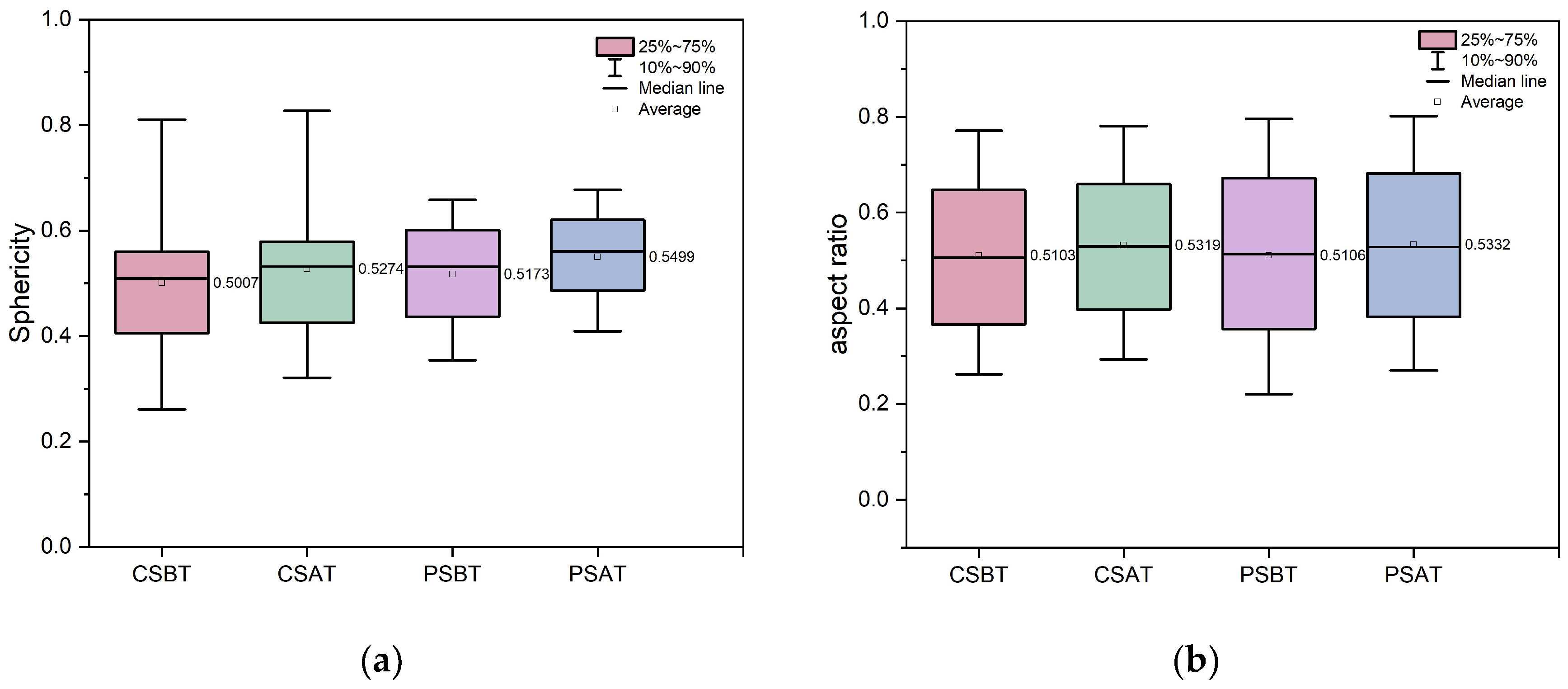
3.2. Particle Morphology Evolution for Pure and Cemented Calcareous Sand
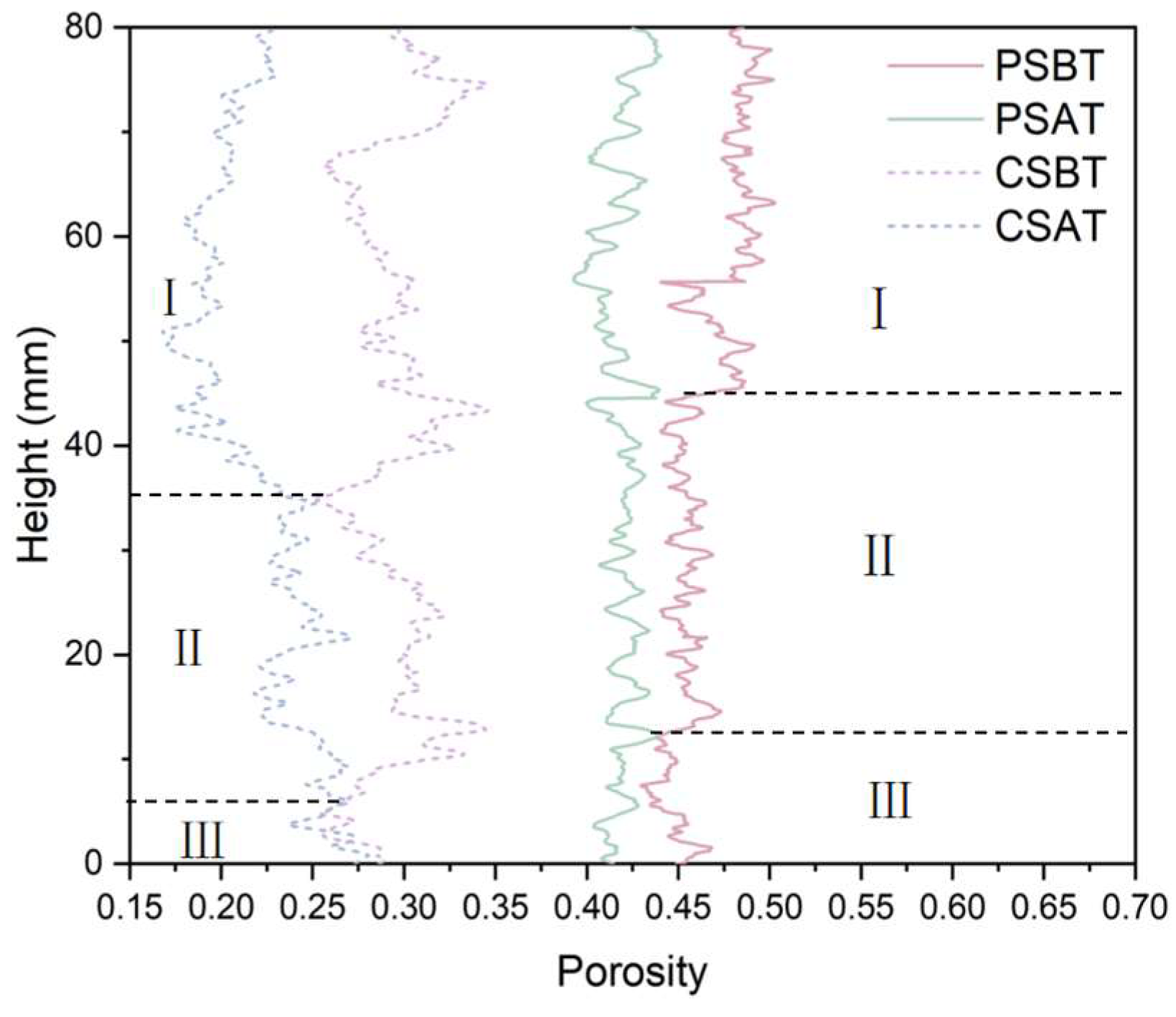
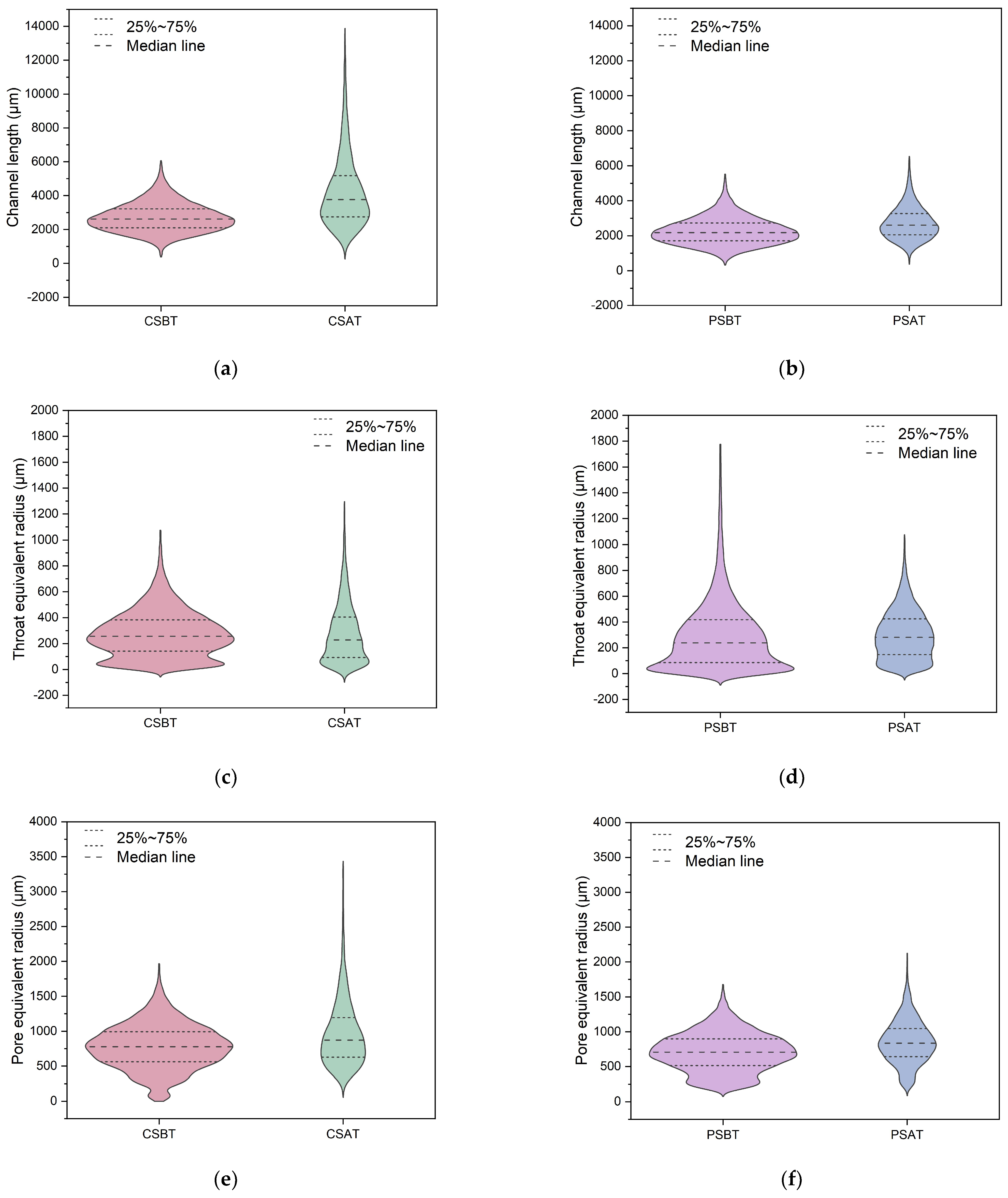
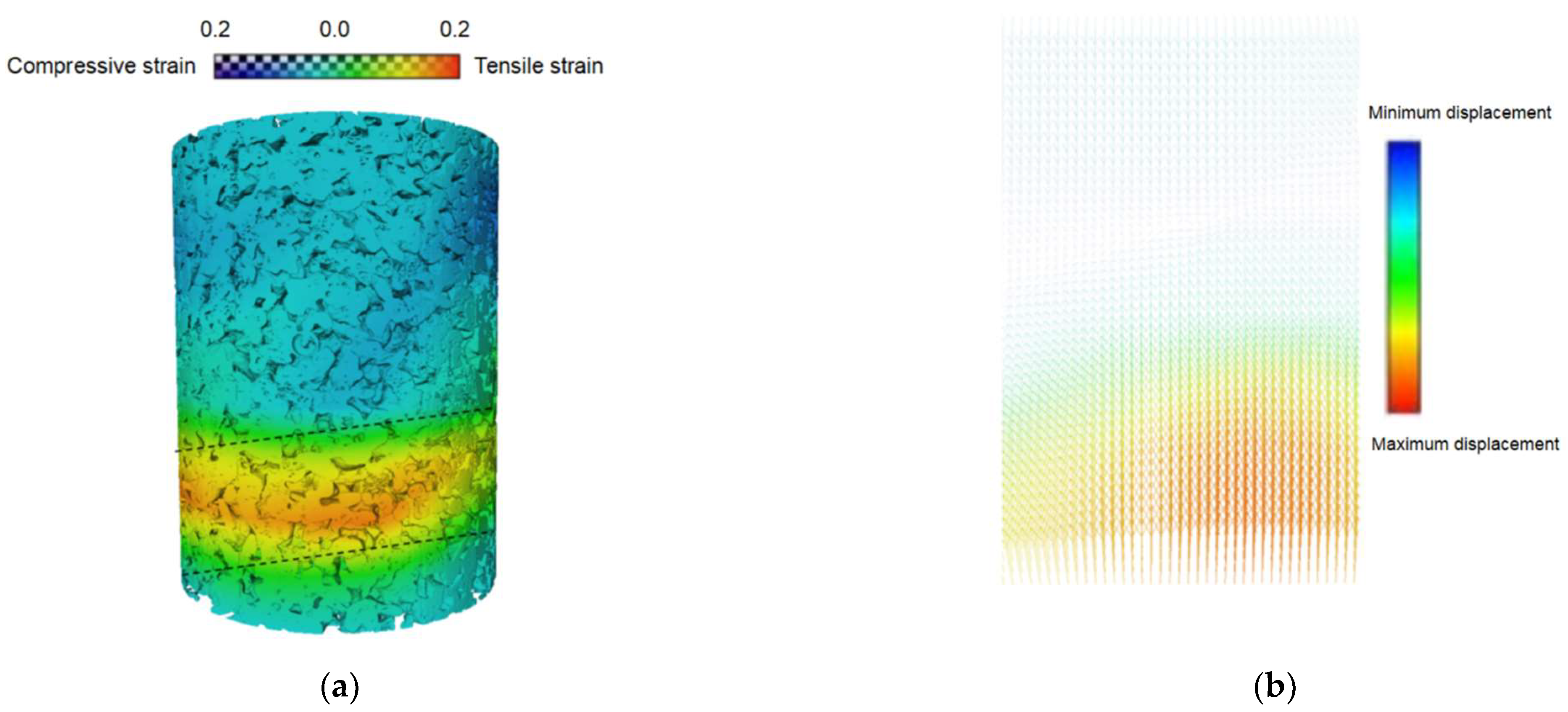
3.3. Comparison of Pore Morphology Evolution for Pure and Cemented Calcareous Sand
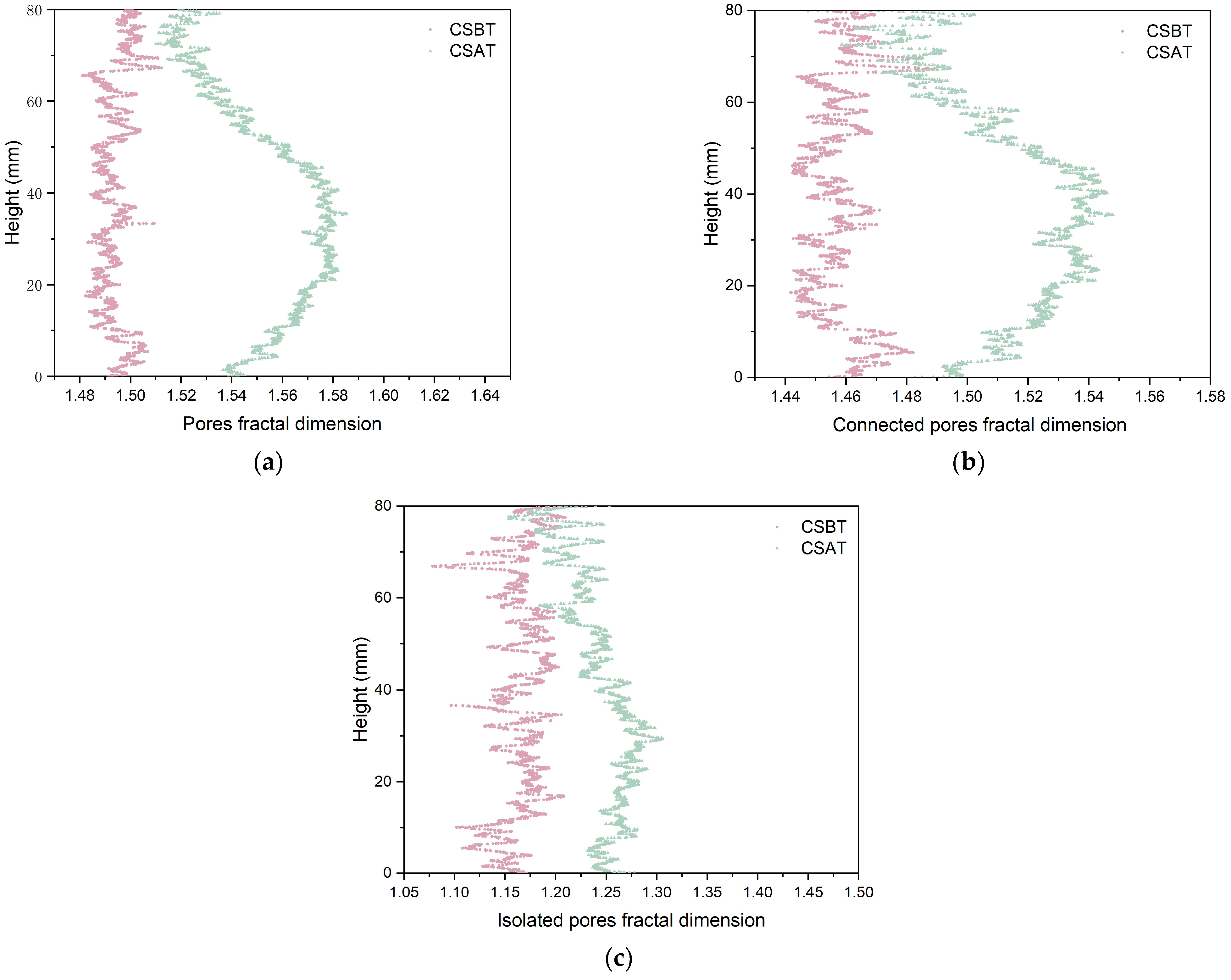
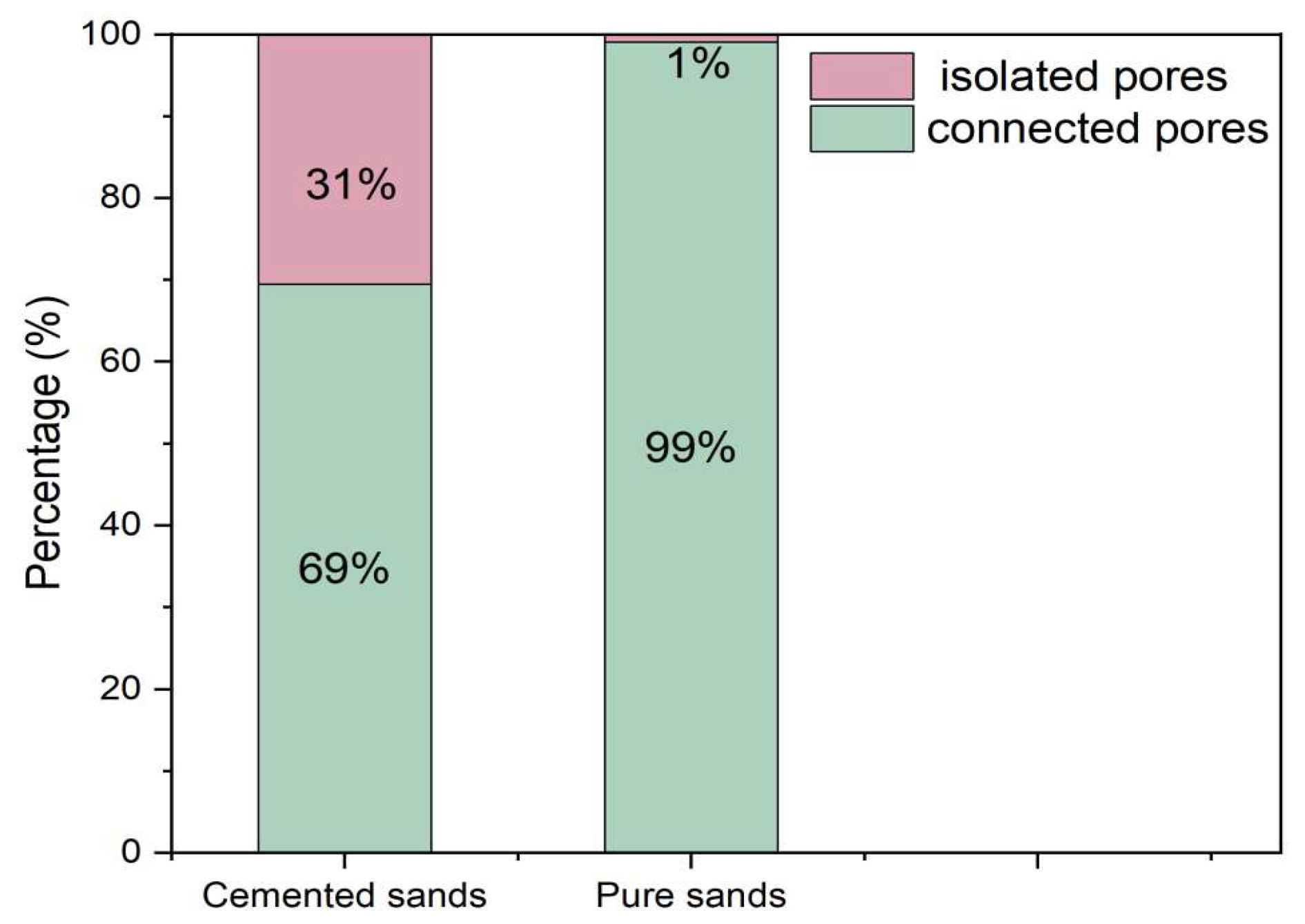
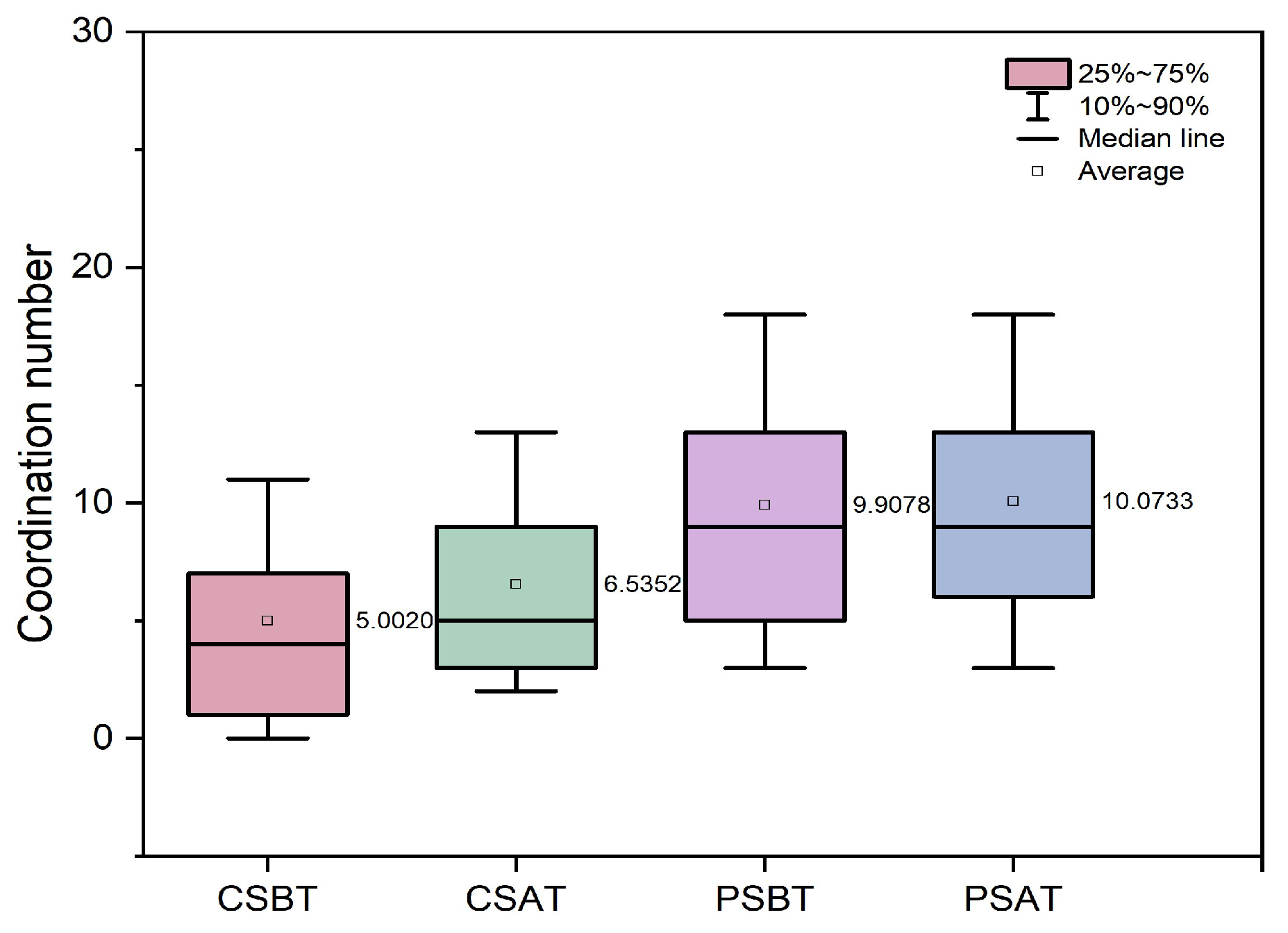
3.4. Microstructural Evolution for Pure and Cemented Calcareous Sand
4. Conclusions
- Under identical confining pressures, cemented calcareous sand exhibited higher strength–stiffness characteristics with strain-softening behavior, in contrast to pure sand. A particle size distribution analysis revealed higher particle breakage in cemented sand (Br = 9.5%) compared to pure sand (Br = 8.7%). While gypsum cementation enhanced the sample strength, it promoted shear band development, leading to stress concentration and increased particle breakage.
- Morphological analyses of particles showed greater increases in sphericity and the aspect ratio for pure calcareous sand compared to cemented specimens during triaxial tests. The presence of gypsum in cemented sand restricted sand particles’ movement and rotation, resulting in less pronounced morphological changes compared to pure calcareous sand.
- Pure calcareous sand exhibited a higher spatial homogeneity compared to the cemented specimens, evidenced by the lower porosity variation along specimen heights. The specimens were characterized by three distinct zones, with the top compression zone showing the most significant porosity reduction, while the middle and bottom zones experienced dilation under shear forces. In addition, cemented samples demonstrated more significant overall porosity reduction due to enhanced effective stress capacity. Pore morphology analyses indicated a slight increase in sphericity and the decreased anisotropy of pores for both specimen types. According to the change in pore fractal dimensions, a more pronounced structural evolution occurred in cemented sand (D from 1.49 to 1.55) than that in pure sand (D from 1.58 to 1.59), particularly within shear bands, suggesting more complex pore structure transformation mechanisms during loading in calcareous sand.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, X.W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.L.; Xiao, Y.; Shen, C.N. Influence of Fiber Content and Length on Engineering Properties of MICP-Treated Coral Sand. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.H.; Fang, X.W.; Yao, Z.H.; Wu, H.R.; Shen, C.N.; Zhang, Y.T. Experiment and discrete element modeling of particle breakage in coral sand under triaxial compression conditions. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2022, 41, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aal, A.A.; Nabawy, B.S. Implications of increasing the ferruginous cement on the physical and mechanical properties of the Cambro-Ordovician Wajid Sandstone in southwest Saudi Arabia: Applications for construction purposes. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 817–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabawy, B.S.; Ibrahim, E.; Kahal, A.; Alfaifi, H.J.; Lashin, A.A. Impact of authigenic iron oxides, clay content and grain size on the aquifer quality properties of the Cambrian-Ordovician Wajid Sandstone, southwest Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 172, 104000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.; Yin, M.; Meng, Q. Influence of Particle Breakage on Drained Shear Strength of Calcareous Sands. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coop, M.R.; Atkinson, J.H. The mechanics of cemented carbonate sands. Géotechnique 1993, 43, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.A.; Joer, H.A.; Randolph, M.F.; Meritt, A. Cementation of porous materials using calcite. Géotechnique 2002, 52, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, H.; Stuedlein, A.W.; Evans, T.M.; Xiao, Y. Strength, stiffness, and microstructure characteristics of biocemented calcareous sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Hu, J. Triaxial Mechanical Properties and Micromechanism of Calcareous Sand Modified by Nanoclay and Cement. Geofluids 2021, 9, 6639602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Y. Effect of particle size on the failure behavior of cemented coral sand under impact loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 149, 106884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail Mostafa, A.; Joer, H.A.; Sim, W.H.; Randolph, M.F. Effect of Cement Type on Shear Behavior of Cemented Calcareous Soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2002, 128, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Fonseca, A.V.D.; Cruz, R.C.; Heineck, K.S. Fundamental Parameters for the Stiffness and Strength Control of Artificially Cemented Sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Moraes, R.; Festugato, L. Parameters Controlling Tensile and Compressive Strength of Fiber-Reinforced Cemented Soil. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Rosa, A.D.; Corte, M.B.; Lopes, L.S.; Consoli, B.S. Porosity-Cement Ratio Controlling Strength of Artificially Cemented Clays. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.S.R.; Baxter, C.D.P.; Moran, K.; Varizi, H.; Narayanasamy, R. Strength of Weakly Cemented Sands from Drained Multistage Triaxial Tests. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y. Mechanical Behavior of Cemented Sand Considering Particle Breakage. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2016, 51, 729–735. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Dong, C. Research on Mechanical Characteristics of the Cemented Sandstone Based on 3Dimensional PFC Numerical Model. J. Chongqing Univ. 2013, 36, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Coop, M.R. The mechanics of uncemented carbonate sands. Géotechnique 1990, 40, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, A.; Coop, M.; Lancellotta, R. Influence of grading on the mechanical behaviour of Stava tailings. Géotechnique 2011, 61, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, H. Elastoplastic Constitutive Model for Rockfill Materials Considering Particle Breakage. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17, 04016041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Su, L. Particle breakage and the mobilized drained shear strengths of sand. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of calcareous sand retrieved from South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F. Particle breakage in triaxial shear of a coral sand. Soils Found. 2018, 58, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikarami, R.; Ando, E.; Gkiousas-Kapnisis, M.; Torabi, A.; Viggiani, G. Strain localisation and grain breakage in sand under shearing at high mean stress: Insights from in situ X-ray tomography. Acta Geotech. 2015, 10, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatza, Z.; And, E.; Papanicolopulos, S.-A.; Ooi, J.Y.; Viggiani, G. Evolution of deformation and breakage in sand studied using X-ray tomography. Geotechnique 2017, 68, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Gong, L.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Long, Y. Single-Particle Crushing Test of Coated Calcareous Sand Based on MICP. Materials 2024, 17, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Coop, M.R. An investigation of breakage behaviour of single sand particles using a high-speed microscope camera. Géotechnique 2016, 66, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Coop, M.R.; Viggiani, G.; Jiang, M. An investigation of single sand particle fracture using X-ray micro-tomography. Géotechnique 2015, 65, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, J. 3D quantitative shape analysis on form, roundness, and compactness with μCT. Powder Technol. 2016, 291, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhao, J. Interplays between particle shape and particle breakage in confined continuous crushing of granular media. Powder Technol. 2021, 378, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, S.; Ma, L.; Yin, M.; Meng, Q. Particle breakage and morphology changes of calcareous sands under one-dimensional compression loading. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2022, 43, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Scaringi, G.; Baudet, B.A.; Han, W. Particle shape factors and fractal dimension after large shear strains in carbonate sand. Géotech. Lett. 2018, 8, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.; O’Sullivan, C.; Coop, M.R.; Lee, P.D. Non-invasive characterization of particle morphology of natural sands. Soils Found. 2012, 52, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Li, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Liu, N. Research on the Effect of Desert Sand on Pore Structure of Fiber Reinforced Mortar Based on X-CT Technology. Materials 2021, 14, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, Y. Comparing, slurry infiltration characteristics between calcareous and silica sands based on slurry infiltration column tests and CT scanning. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 152, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xie, L.; Shen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, S. Quantitative microstructural characterization and seepage visualization of biocemented sand. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 174, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kootahi, K.; Leung, A.K.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Qi, R.; Lourenço, S.D.N.; Lai, Z.; Gao, Z. Evaluation of the Methods of Particle Morphology Characterization: CT Scanning, Digital Imaging and Light Microscopy. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 174, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Wu, K.; Meng, Q.; Gan, M.; Yi, P. Investigation of mechanical characterization and damage evolution of coral reef sand concrete using in-situ CT and digital volume correlation techniques. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, J. An investigation of the breakage behaviour of a pre-crushed carbonate sand under shear using X-ray micro-tomography. Eng. Geol. 2021, 293, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampidou, E.M.; Hall, S.A.; Stanchits, S.; Lewis, H.; Viggiani, G. Characterization of shear and compaction bands in a porous sandstone deformed under triaxial compression. Tectonophysics 2011, 503, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadell, H. Volume, Shape, and Roundness of Rock Particles. J. Geol. 1932, 40, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernlund, J.M.R. Image analysis method for determining 3-D shape of coarse aggregate. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin Bobby, O. Crushing of Soil Particles. J. Geotech. Eng. 1985, 111, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.S.; Bay, B.K.; Rashid, M.M. Digital volume correlation including rotational degrees of freedom during minimization. Exp. Mech. 2002, 42, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, K.; Tozzi, G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Tong, J.; Cossey, A.; Au, A.; Hollis, D.; Hild, F. Computation of full-field displacements in a scaffold implant using digital volume correlation and finite element analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 1298–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, M.; Ji, L.; Jiang, W.; Cao, G.; Xu, L. Multiscale pore-fracture hybrid pore network modeling for drainage in tight carbonate. Adv. Water Resour. 2023, 174, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shi, T.; Yuan, Q.; Sun, K. The creep characteristics and related evolution of particle morphology for calcareous sand. Powder Technol. 2024, 431, 119077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, S.T.A.; Chen, X.; Bao, X.; Raja, M.N.A.; Abdoun, T.; El-Sekelly, W. Data-driven intelligent modeling of unconfined compressive strength of heavy metal-contaminated soil. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
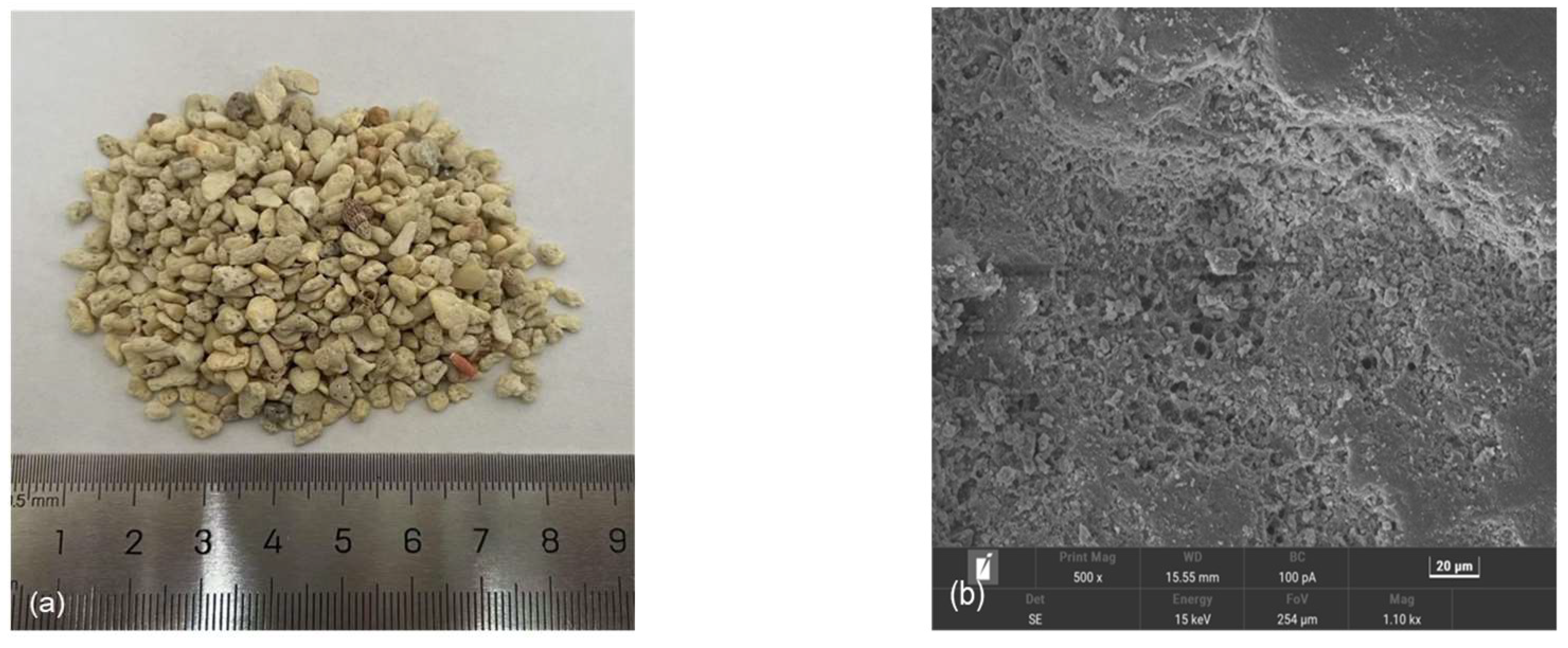


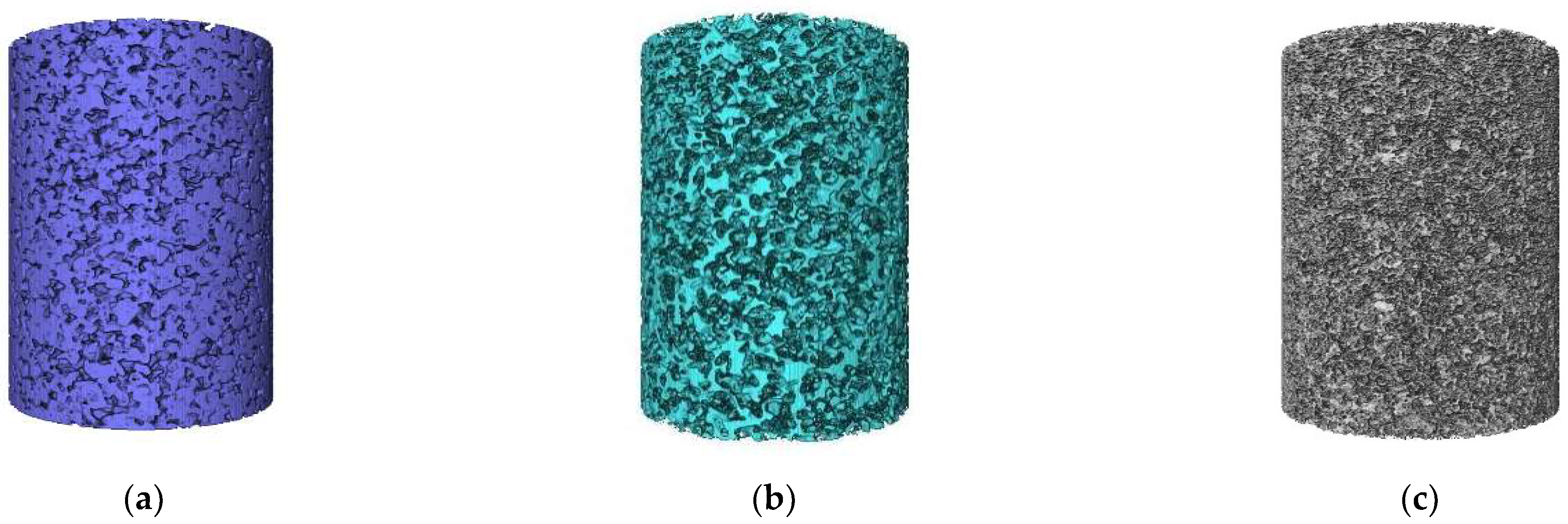
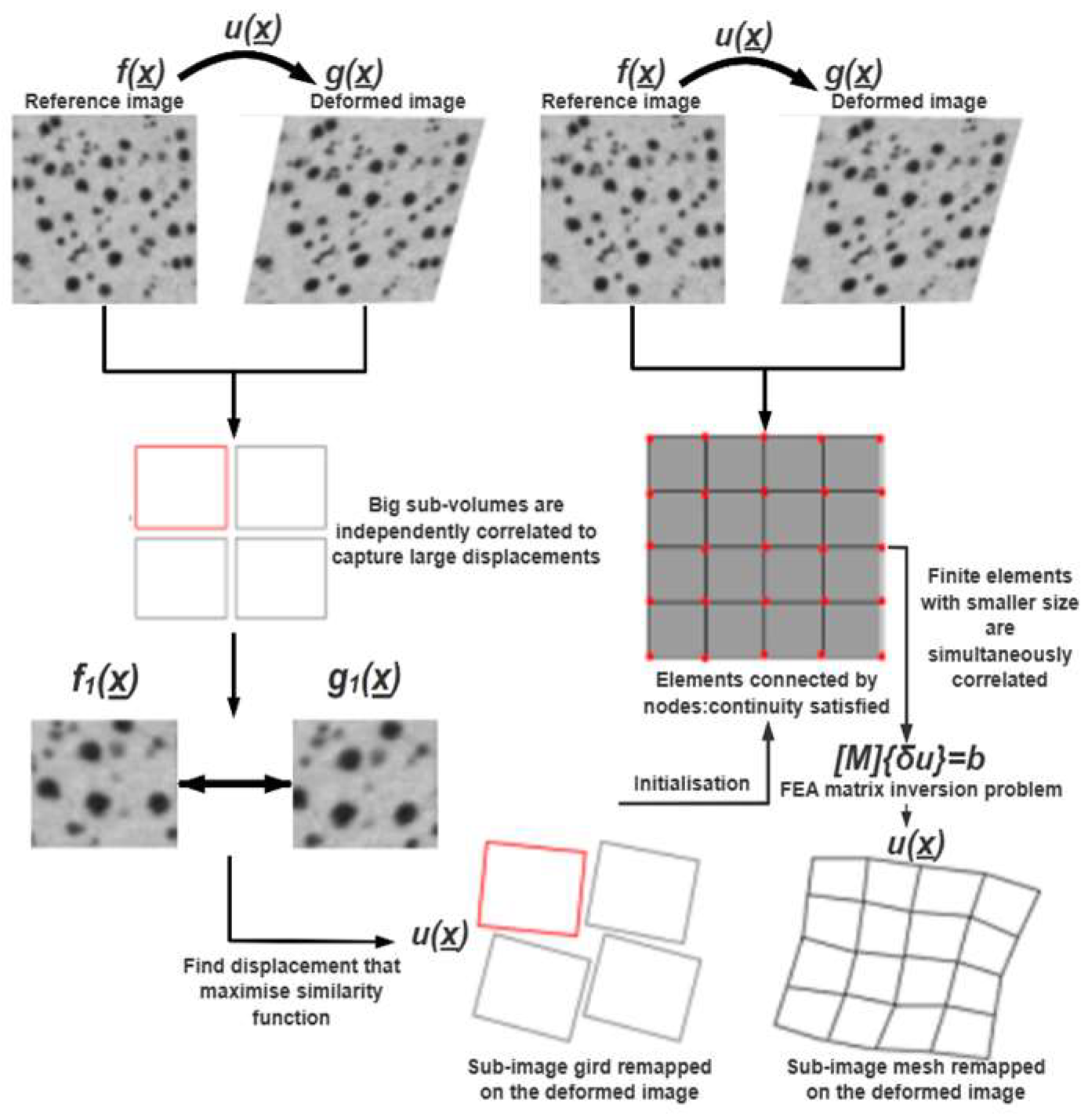




| Size (mm) | ρdmin/(g/cm3) | ρdmax/(g/cm3) | Gs | emin | emax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.18~2.36 | 0.81 | 1.33 | 2.73 | 1.06 | 2.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Huang, J.; Chen, D.; Luo, Q.; Yuan, B. The Effect of Cementation on Microstructural Evolution and Particle Characteristics of Calcareous Sand Under Triaxial Loading. Buildings 2025, 15, 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122041
Wang W, Huang J, Chen D, Luo Q, Yuan B. The Effect of Cementation on Microstructural Evolution and Particle Characteristics of Calcareous Sand Under Triaxial Loading. Buildings. 2025; 15(12):2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wanying, Jiepeng Huang, Degao Chen, Qingzi Luo, and Bingxiang Yuan. 2025. "The Effect of Cementation on Microstructural Evolution and Particle Characteristics of Calcareous Sand Under Triaxial Loading" Buildings 15, no. 12: 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122041
APA StyleWang, W., Huang, J., Chen, D., Luo, Q., & Yuan, B. (2025). The Effect of Cementation on Microstructural Evolution and Particle Characteristics of Calcareous Sand Under Triaxial Loading. Buildings, 15(12), 2041. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122041







