A Methodological Approach to Revealing the Landscape Morphology of Heijing Village Using Fractal Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Application Background of Fractal Theory in Traditional Village Research
2.2. Theoretical Controversies and Limitations of Previous Studies
2.3. Methodological Refinement and Comparison with Alternative Approaches
3. Methods and Materials
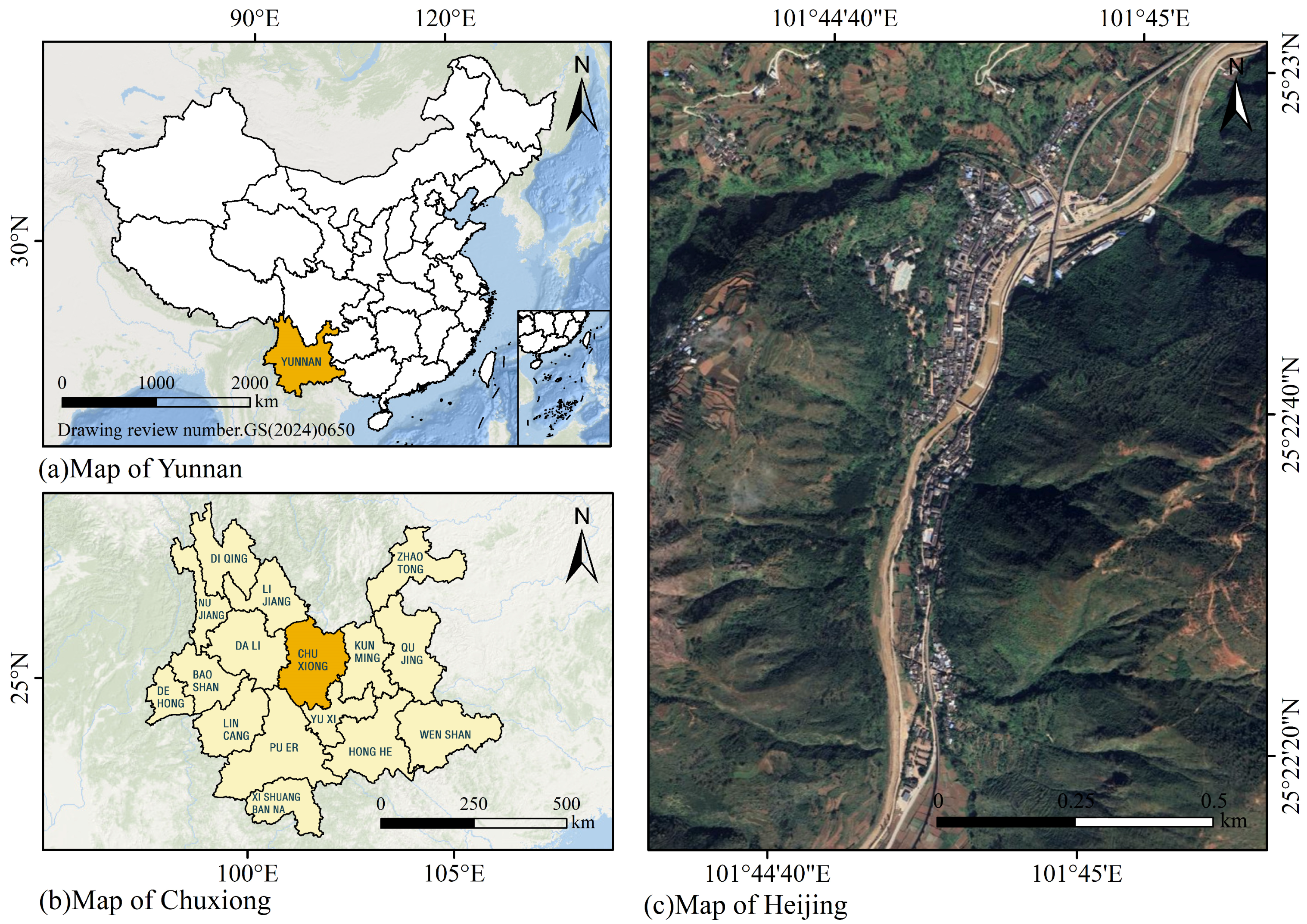
3.1. Study Area
3.2. The Relationship Between Fractal Theory and Landscape Morphology
3.2.1. Selection of Fractal Measurement Methods
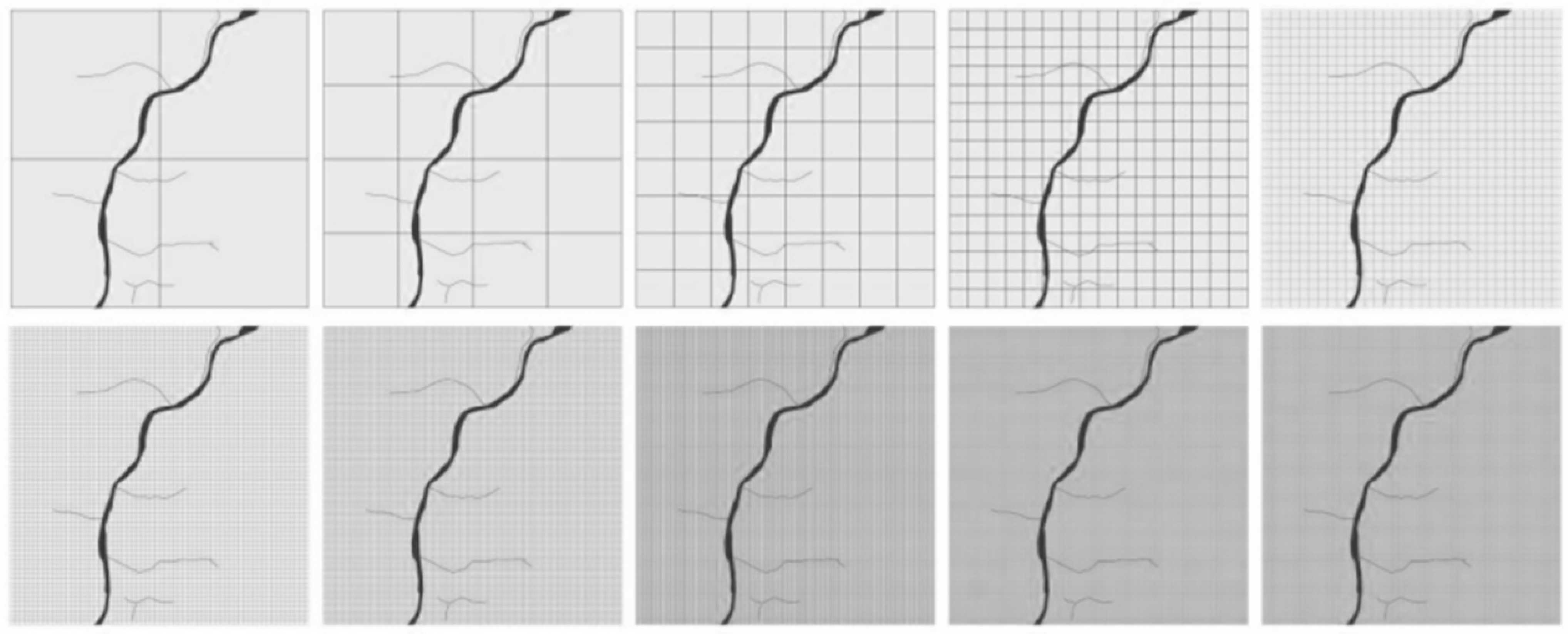
3.2.2. Fractal Dimension Grid Space Representation
3.3. Fractal Dimension Calculation of Heijing Village’s Spatial Morphology
3.4. Model Construction
- (1)
- Data Acquisition
- (2)
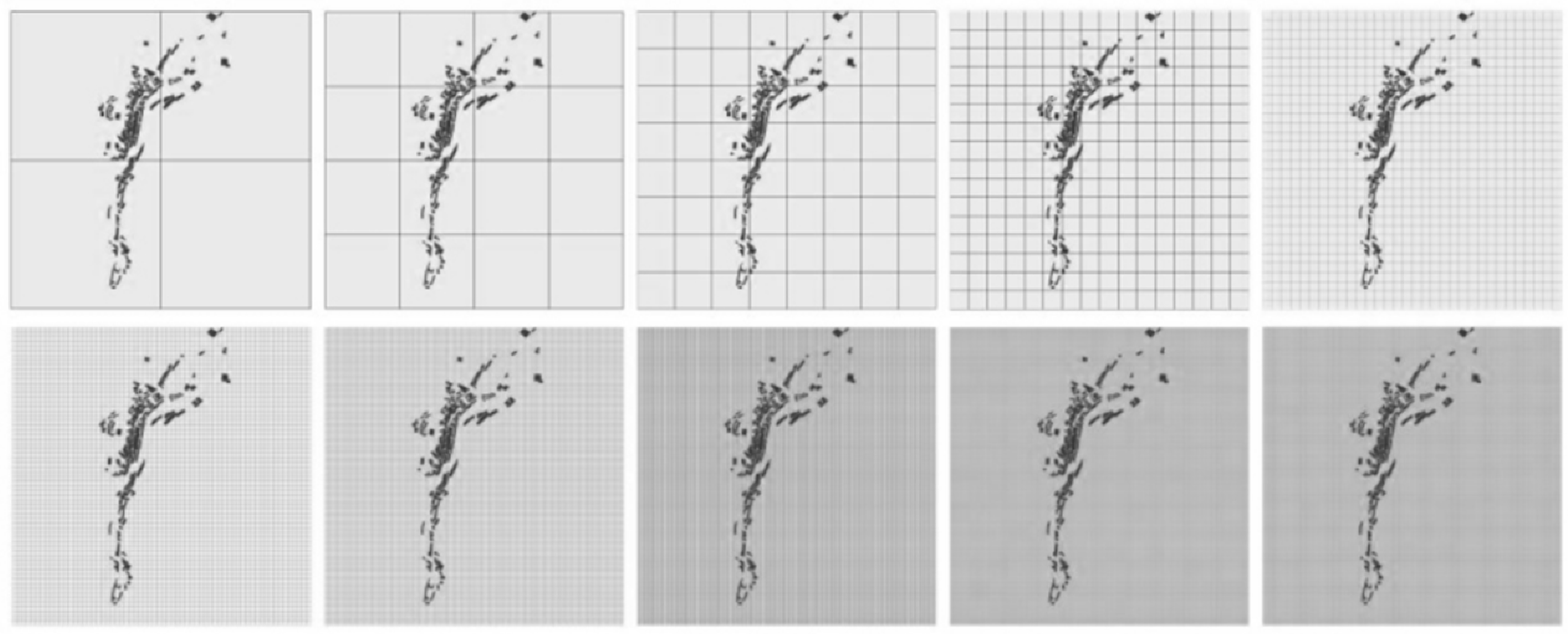
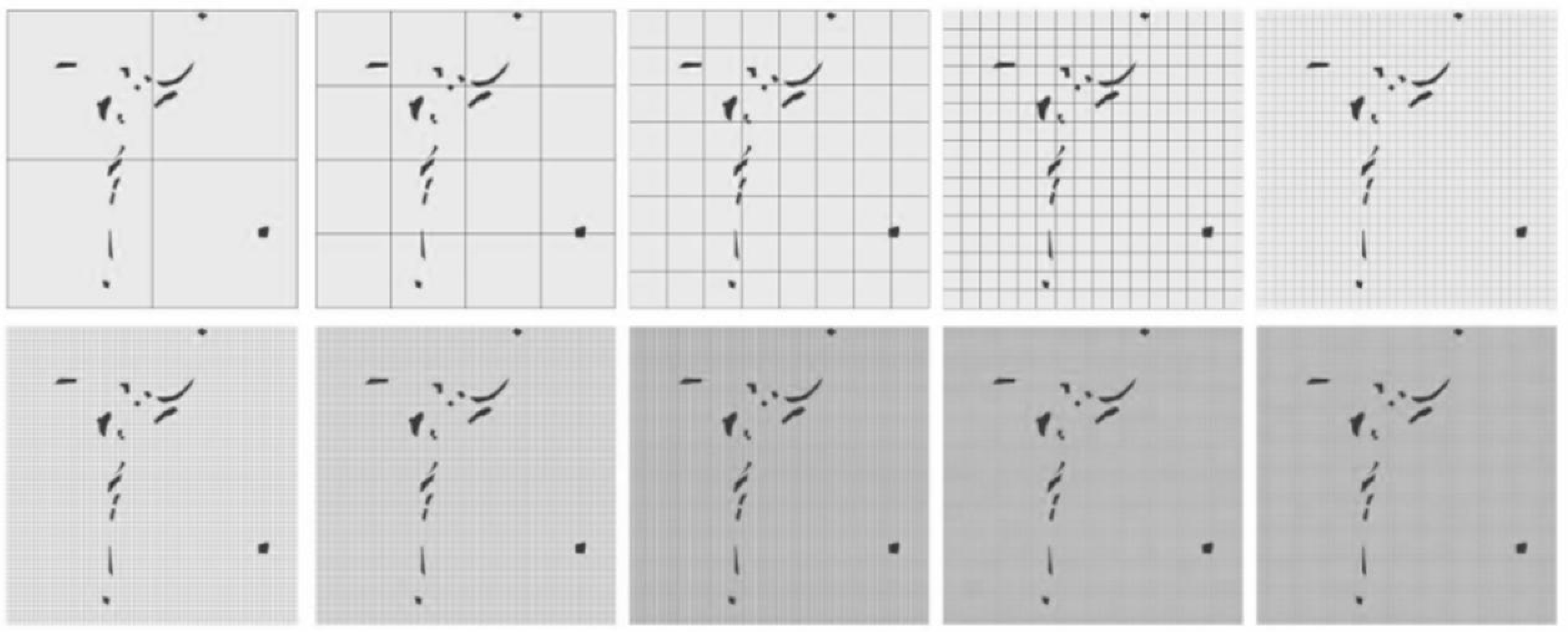
- Binarization of Fractal Images
- (3)
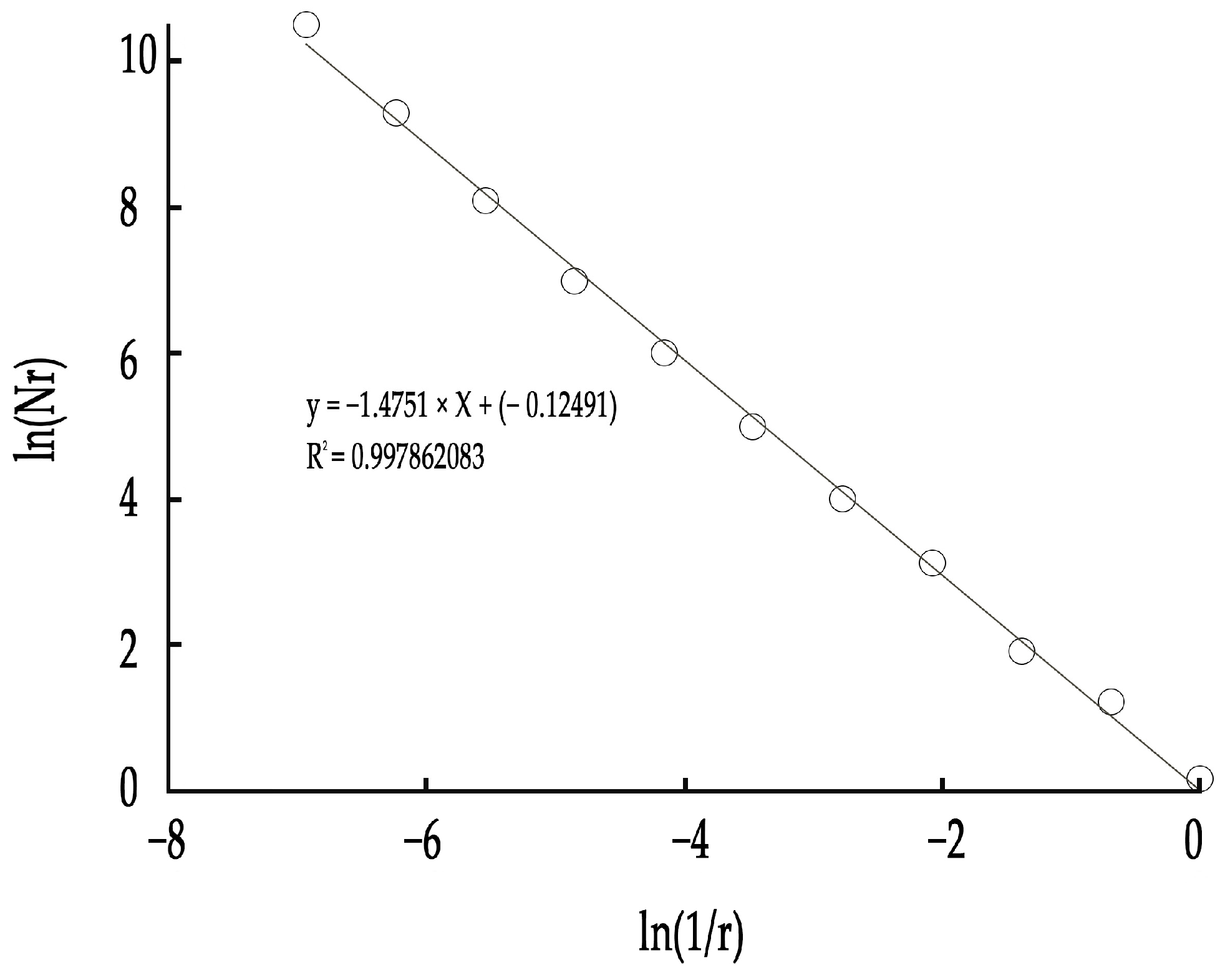
- Box-Counting Dimension Process
4. Fractal Dimension Calculation for Different Land Use Types
4.1. Residential Buildings
4.2. Village Public Service Land
4.3. Village Road Land
4.4. Village Agricultural Land
4.5. Water Bodies
4.6. Fractal Dimension Statistics of Various Land Use Types
4.7. Validity Analysis
5. Construction of the Fractal Dimension Optimization Model
5.1. Optimization Model: Methods for Reducing Human Error
5.2. Optimization Strategy for the Box-Counting Fractal Dimension Model
- (1)
- Data Processing Using the MATLAB (R2023a) Software
- (2)
- Selecting the Appropriate Image Resolution
- (3)
- Choosing Grid Division and the Number of Steps
5.3. Analysis of Optimization Data and Model Optimization Advantages of Each Land Use Type
6. Discussion and Suggestions
6.1. Discussion
6.2. Suggestions
- (1)
- Optimize Residential Land Use and Promote Compact Development
- (2)
- Enhance Spatial Integration of Public Service Facilities
- (3)
- Strengthen and Diversify Road Network Connectivity
- (4)
- Support Sustainable Agricultural Land Use through Technology and Ecological Practices
- (5)
- Implement Integrated Water Resource Management and Ecological Restoration
- (6)
- Incorporate Fractal Dimension Analysis into Ongoing Planning and Monitoring
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, S.; Wei, B. Data science based landscape ecology for traditional village landscape protection. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2021, 65, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Maliki, N.Z.B.; Yu, S. Fractal characteristics and influencing factors of landscape space of Tibetan rural in Western Sichuan: A case study of three traditional villages. Front. Urban Rural. Plan. 2023, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, H. Fractal Characteristics of the Spatial Texture in Traditional Miao Villages in Qiandongnan, Guizhou, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, K.; Jiao, K.; Li, Z. Spatio-temporal characteristics of traditional village landscape pattern and its influencing factors from the perspective of tourism development: A case study of Huangcheng Village, China. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2025, 24, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xu, K. How village leaders behave in leading vernacular heritage-based rural regeneration in traditional villages, agent or steward? Field research in traditional villages of the southeast of Chongqing, China. Habitat Int. 2025, 156, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y. The impact and transformation evaluation of art intervention in public space on ancient villages: A case study of Tengchong, Yunnan Province. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Xu, S.; Huang, J.; Ren, Y.; Song, C. Distribution patterns and driving mechanisms of land use spatial conflicts: Empirical analysis from counties in China. Habitat Int. 2025, 156, 103268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Zheng, W.; Song, Y.; Huang, X. A multi-level spatial assessment framework for identifying land use conflict zones. Land Use Policy 2025, 148, 107382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Approach to an irregular time series on the basis of the fractal theory. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1988, 31, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontier, S. Applications of fractal theory to ecology. In Develoments in Numerical Ecology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dabbagh, A.A.; Ismail, K.J.A. Fractal Geometry Tools in Studying the Formal Characteristics in the Urban Structure of the Traditional Al-Mutanabbi Street in Baghdad. J. Eng. 2025, 31, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaar, W.; Bonin, O.; Seregina, T.; Faour, G. Morphological dynamics, landscape fragmentation and climate change vulnerability of actual and predicted urban areas of Lebanon: Application of Multilayer-Perceptron Markov-Chain model. J. Urban Manag. 2025, 14, 181–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Moore, I.D.; Gallant, J.C. Fractals, fractal dimensions and landscapes—A review. Geomorphology 1993, 8, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, P.; Avnir, D. Chemistry in noninteger dimensions between two and three. I. Fractal theory of heterogeneous surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 3558–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peli, T. Multiscale fractal theory and object characterization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1990, 7, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raye, J. Fractal organisation theory. J. Organ. Transform. Soc. Change 2014, 11, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, P.; Dong, W.; Yu, S.; Gao, X. Water-Facing Distribution and Suitability Space for Rural Mountain Settlements Based on Fractal Theory, South-Western China. Land 2021, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, W.; Gepreel, K.; Li, H. A fractal-fractional tsunami model considering near-shore fractal boundary. Fractals 2024, 32, 2450040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Du, F.; Li, H. A Study of the Spatial Form of Maling Village, Henan, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R. Multifractal characteristics of soil particle size distribution of abandoned homestead reclamation under different forest management modes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Shi, H.; Yang, R. Fractal dimension calculation of spatial morphology in Dali traditional Bai villages based on GIS. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Geology, Mapping, and Remote Sensing (ICGMRS 2024), Wuhan, China, 12–14 April 2024; Volume 13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Mumtaz, F.; Zhang, M. Spatial patterns and its influencing factors on villages around the Ji-shape bend of the Yellow River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1477693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, M.; Huang, G.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J. Tracking the impact of the land cover change on the spatial-temporal distribution of the thermal comfort: Insights from the Qinhuai River Basin, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Song, K.; Pu, F. Laws and Trends of the Evolution of Traditional Villages in Plane Pattern. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Hu, M.; Somenahalli, S.; Bian, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, Y. A Study of Spatio-Temporal Differentiation Characteristics and Driving Factors of Shaanxi Province’s Traditional Heritage Villages. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Jin, W.; Jiang, G.; Li, S.; Ma, W. Typical and atypical multifractal systems of urban spaces—Using construction land in Zhengzhou from 1988 to 2015 as an example. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisi, K.; Zakariaee, I.; Jokar, J.; Najarpoor, S. Analysis of Fractal Geometry in the Maqeli Tiled Spandrel of the Northern Iwan in Hakim Mosque in Isfahan. Mon. Sci. J. Bagh-E Nazar 2024, 21, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Fan, L.; Wang, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Deng, G. A Comparative Study on the Spatial Structure Characteristics of National-Level Traditional Villages in Liaoning, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. The Impact of Terrain on the Planar Spatial Morphology of Mountain Settlements Studied Using Fractal Dimensions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ping, X.; Fan, Q.; Li, C. Measurement of 2D and 3D Fractal Features of Urban Morphology from an Architectural View and Its Influencing Factors. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Derivation of the functional relations between fractal dimension of and shape indices of urban form. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2011, 35, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Fractal analytical approach of urban form based on spatial correlation function. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2013, 49, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Ma, X.; Sun, Q. Fractal Description of Rock Fracture Networks Based on the Space Syntax Metric. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, M.J.; Ostwald, M.J.; Lee, J.H. The Mathematics of ‘Natural Beauty’ in the Architecture of Andrea Palladio and Le Corbusier: An Analysis of Colin Rowe’s Theory of Formal Complexity Using Fractal Dimensions. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xing, H. Exploring the relationship between landscape characteristics and urban vibrancy: A case study using morphology and review data. Cities 2019, 95, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostwald, M.J. The fractal analysis of architecture: Calibrating the box-counting method using scaling coefficient and grid disposition variables. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2013, 40, 644–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankhauser, P. The fractal approach. A new tool for the spatial analysis of urban agglomerations. Popul. Engl. Sel. 1998, 10, 205–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Nie, M. Scale Characteristics and Optimization of Park Green Space in Megacities Based on the Fractal Measurement Model: A Case Study of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Xia, C. Urban landscape as a spatial representation of land rent: A quantitative analysis. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 74, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B. Fractal dimension and its metrical methods. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2004, 3, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, P. A Population-based Iterated Greedy Algorithm for the Delimitation and Zoning of Rural Settlements. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2013, 39, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Li, J. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Ecosystem Service Value Based on the Markov–FLUS Model in Ezhou City, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Hu, C.; Ma, L.; Chen, E.; Zhang, C.; Xia, G. Spatiotemporal Changes and Influencing Factors of the Coupled Production–Living–Ecological Functions in the Yellow River Basin, China. Land. 2024, 13, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Brown, G.J.; Miles, N.J. Measurement of boundary fractal dimensions: Review of current techniques. Powder Technol. 1995, 84, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.R.; Benzer, W.B. On the practice of estimating fractal dimension. Math. Geol. 1991, 23, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, A.; Gong, P. Optimization on multifractal loss landscapes explains a diverse range of geometrical and dynamical properties of deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. Research on Optimization Method of Landscape Architecture Planning and Design Based on Two-Dimensional Fractal Graph Generation Algorithm. Informatica 2025, 49, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, S. Influence of Coastal Reclamation on Geomorphic Complexity and Water Ecological Environment. In International Conference on Hydraulic and Civil Engineering & Engineering Safety and Disaster Prevention Forum; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc, B.; Zucker, S.W.; Tricot, C.; Quiniou, J.F.; Wehbi, D. Evaluating the fractal dimension of surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1989, 425, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Xiao, D. Content and Method of Studying Minority Traditional Villages and Dwellings Based on Cultural Geography. J. South Archit. 2024, 1, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.; Liao, B.-Y. Correlation fractal dimension analysis mountainous traditional village settlement spatial form-case study of qiandongnan in guizhou. Environ. Soc. Manag. J./Revista Gestão Social Ambiental 2024, 18, e04741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G. Fractal dimension and fractal growth of urbanized areas. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2002, 16, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Carmona, R.; Gram-Hanssen, I.; Hochachka, G.; Sygna, L.; Rosenberg, M. Fractal approaches to scaling transformations to sustainability. Ambio 2023, 52, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Guo, L. Analysis of the impact of traditional ethnic villages in Hani area on sustainable development. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, T.; Sasaki, I. Digital Technique by Box Counting Method for Predicting Subjective Estimation of Good Scenery. J. Light. Vis. Environ. 2005, 29, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Romero, À.; Matías, M.A.; Duarte, C.M. Unravelling the universal spatial properties of coral reefs. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2025, 34, e13939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Street landscape environment design based on visual technology and entertainment robots: Computer simulation gamification landscape design. Entertain. Comput. 2025, 52, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargère, B.A.; Constantine, J.A.; Hales, T.C.; Grieve, S.W.; Johnson, S.D. A fractal framework for channel–hillslope coupling. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2025, 13, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culling, W.E.H. A new view of the landscape. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 1988, 13, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrop, M.; Van Eetvelde, V. Holistic aspects of suburban landscapes: Visual image interpretation and landscape metrics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 50, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Li, J. The correlation analysis on the landscape pattern index and hydrological processes in the Yanhe watershed, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, P.F. Landscapes and their correlation functions. J. Math. Chem. 1996, 20, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y. A Three-Dimensional Box-Counting Method to Study the Fractal Characteristics of Urban Areas in Shenyang, Northeast China. Buildings 2022, 12, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saa, A.; Gascó, G.; Grau, J.B.; Antón, J.M.; Tarquis, A.M. Comparison of gliding box and box-counting methods in river network analysis. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2007, 14, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglash, R. Ethno-biomathematics: A decolonial approach to mathematics at the intersection of human and nonhuman design. In Ubiratan D’Ambrosio and Mathematics Education: Trajectory, Legacy and Future; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fu, B. Spatial Heterogeneity of Urban Road Network Fractal Characteristics and Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y. Spatial-temporal differentiation and influencing factors of rural settlements in mountainous areas: An example of Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Southwestern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2024, 21, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, B. Changes of Spatial Characteristics: Socio-Cultural Sustainability in Historical Neighborhood in Beijing, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Q.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Self-affinity dimensions of topography and its implications in morphotectonics: An example from Taiwan. Geomorphology 2004, 62, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibo, B. Rural Spatial Form Based on 3D Simulation Model. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 2019, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasch, R. Afterword: Village Space and the Experience of Difference and Hierarchy between Normative Orders. Crit. Anthropol. 2017, 37, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, F.Y. Image Processing and Pattern Recognition: Fundamentals and Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kolahi-Azar, A.P.; Golriz, S. Multifractal topography: A tool to measure tectonic complexity in the Zagros Mountain range. Math. Geosci. 2018, 50, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laterra, P.; Orúe, M.E.; Booman, G.C. Spatial complexity and ecosystem services in rural landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 154, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İzgi, B.D. Layering Analysis of Typomorphology Dynamics in Rural Settlements Using the AHP Method. ICONARP Int. J. Archit. Plan. 2024, 12, 162–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtit, K.; Nijkamp, P.; Turk, U.; Wahlström, M. Villages in the City–Urban Planning for Neighbourhood Love. Tijdschr. Voor Econ. Soc. Geogr. 2024, 115, 518–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liang, Y.; Liu, X. Study on spatial form evolution of traditional villages in Jiuguan under the influence of historic transportation network. Herit. Sci. 2024, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan-pour, K.; Dutilleul, P.; Smith, D.L. Advances in the implementation of the box-counting method of fractal dimension estimation. Appl. Math. Comput. 1999, 105, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, J. Micro-Scale Analysis and Optimization of Rural Settlement Spatial Patterns: A Case Study of Huanglong Town, Dayu County. Land 2024, 13, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, Q.; Yu, X. Mixed-method study of the etiquette and custom cultural activity space and its construction wisdom in Bubeibu traditional Village, Yuxian County, China. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 23, 2100–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Yang, X. Reconstruction of traditional village spatial texture based on parametric analysis. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 5151421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Aziz, N.F.; Liu, J.; Huang, M.; Yu, L.; Yang, R. From text to insights: Leveraging NLP to assess how landscape features shape tourist perceptions and emotions toward traditional villages. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besussi, E.; Chin, N.; Batty, M.; Longley, P. The structure and form of urban settlements. In Remote Sensing of Urban and Suburban Areas; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkenberg, B.; Clarke, K.C. Exploring the fractal mountains. In Automated Pattern Analysis in Petroleum Exploration; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


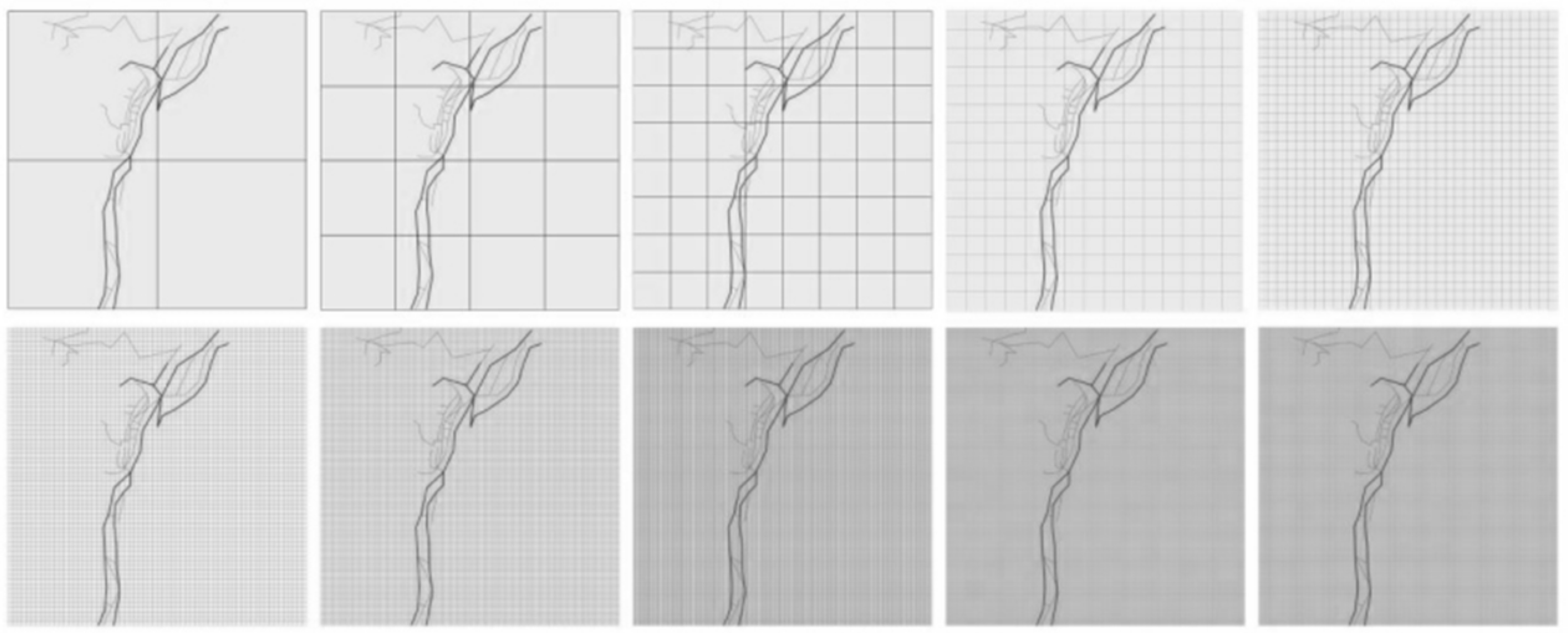




| Method | Core Focus | Strengths | Limitations | Applicability to Traditional Villages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fractal Analysis | Scale-invariance and spatial complexity | Captures organic, irregular, and multi-scale structures | Sensitive to grid size, resolution, and scale assumptions | High—ideal for unplanned and self-evolved villages |
| Space Syntax | Visual fields, spatial accessibility, and movement | Highlights visibility and connectivity in planned environments | Less effective in irregular, topographically complex settings | Moderate—best in structured street networks |
| Landscape Metrics | Land-use patterns and patch configuration | Suitable for ecological and land-cover analysis | Overly dependent on classified raster data and fixed scales | Moderate—useful for landscape-level assessments |
| Research Object | Significance in Landscape Morphology | Quantitative Indicator | Applicable Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point | Settlement Distribution | Correlation Dimension | Radius of Gyration Method |
| Line | Road Networks and Planar and Elevational Surfaces | Box-Counting Dimension, Length Dimension, and Branch Dimension | Radius of Gyration Method, Perimeter–Area Method, and Box-Counting Method |
| Surface | Overall Spatial Form | Box-Counting Dimension | Box-Counting Method |
| Land Use Type | Fractal Dimension (D) |
|---|---|
| Residential | 1.4751 |
| Public Service | 1.2846 |
| Road | 1.4011 |
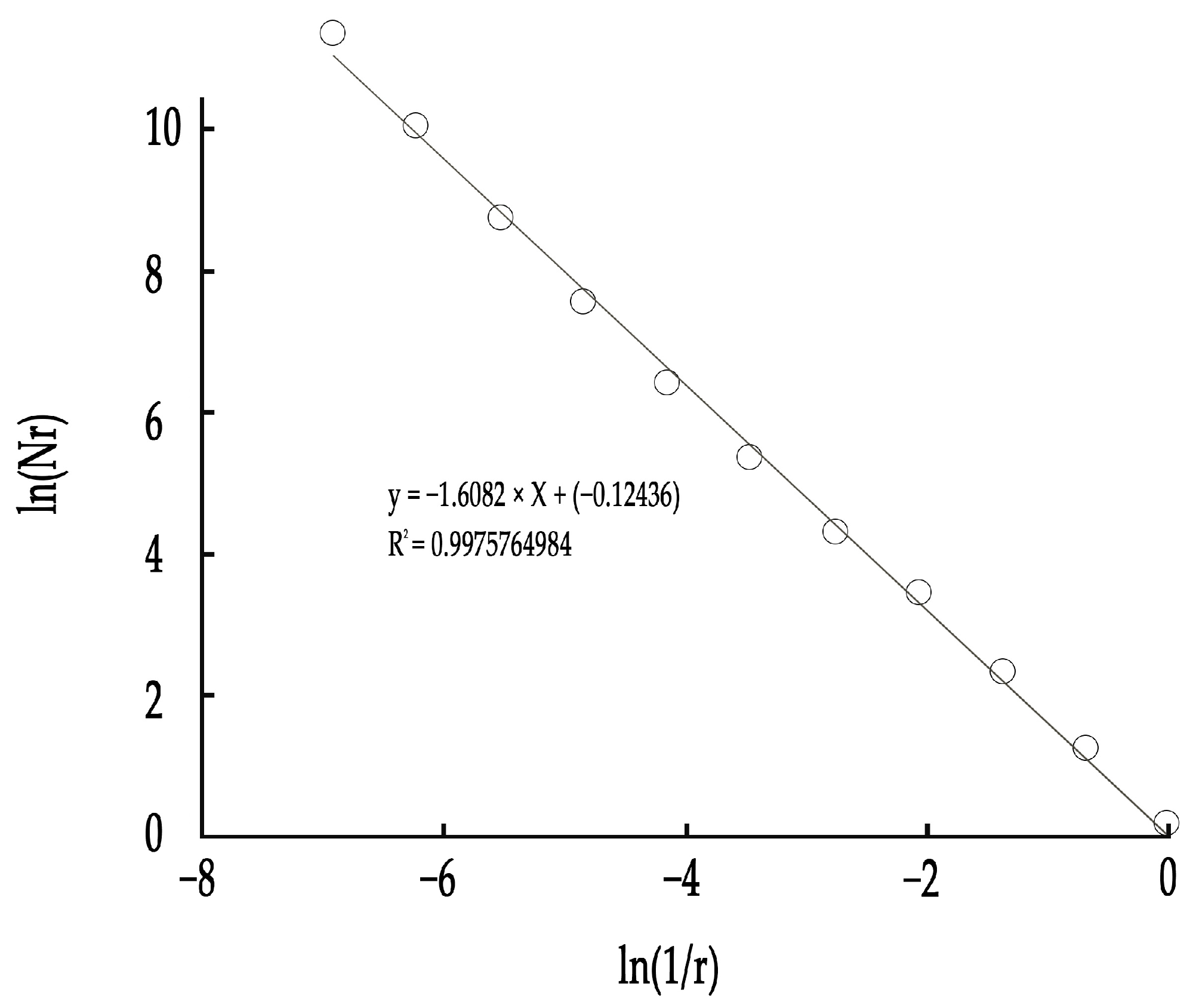
| Agricultural | 1.6082 |
| Water Bodies | 1.3886 |
| Image Type | Theoretical Dimension | Calculated Result | Relative Error (%) | Image Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 1 | 1.0544 | 5.44 | 800 × 400 |
 | 2 | 1.8793 | 6.03 | 800 × 400 |
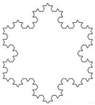 | 1.2618 | 1.3465 | 6.71 | 500 × 500 |
 | 1.585 | 1.7191 | 8.46 | 500 × 500 |
| Image Type | Theoretical Dimension | Number of Average Divisions of Scale r (n) | Calculated Result | Relative Error (%) | Image Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 1 | 9 | 1.0067 | 0.67 | 800 × 400 |
| 10 | 1.0544 | 5.44 | 800 × 400 | ||
| 11 | 1.0907 | 9.07 | 800 × 400 | ||
| 12 | 1.1306 | 13.06 | 800 × 400 | ||
 | 2 | 9 | 1.862 | 6.90 | 800 × 400 |
| 10 | 1.8793 | 6.03 | 800 × 400 | ||
| 11 | 1.8926 | 5.37 | 800 × 400 | ||
| 12 | 1.9044 | 4.78 | 800 × 400 | ||
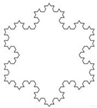 | 1.2618 | 9 | 1.3304 | 5.43 | 500 × 500 |
| 10 | 1.3465 | 6.71 | 500 × 500 | ||
| 11 | 1.3742 | 8.90 | 500 × 500 | ||
| 12 | 1.4068 | 11.49 | 500 × 500 | ||
 | 1.585 | 9 | 1.6964 | 7.00 | 500 × 500 |
| 10 | 1.7196 | 8.46 | 500 × 500 | ||
| 11 | 1.7437 | 9.96 | 500 × 500 | ||
| 12 | 1.7646 | 11.33 | 500 × 500 |
| Land Use Type | Before Optimization (D Value) | After Optimization (D Value) | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | 1.4751 | 1.5323 | 3.9% |
| Public Service | 1.2846 | 1.3453 | 4.7% |
| Road | 1.4011 | 1.4283 | 1.9% |
| Agricultural | 1.6082 | 1.6429 | 2.1% |
| Water Bodies | 1.3886 | 1.4336 | 3.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Liu, S.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y. A Methodological Approach to Revealing the Landscape Morphology of Heijing Village Using Fractal Theory. Buildings 2025, 15, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122037
Li P, Liu S, Wu P, Liu Y. A Methodological Approach to Revealing the Landscape Morphology of Heijing Village Using Fractal Theory. Buildings. 2025; 15(12):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peiyuan, Shanshan Liu, Pengjun Wu, and Yao Liu. 2025. "A Methodological Approach to Revealing the Landscape Morphology of Heijing Village Using Fractal Theory" Buildings 15, no. 12: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122037
APA StyleLi, P., Liu, S., Wu, P., & Liu, Y. (2025). A Methodological Approach to Revealing the Landscape Morphology of Heijing Village Using Fractal Theory. Buildings, 15(12), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15122037









