Degradation Behavior of the Preload Force of High-Strength Bolts after Corrosion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
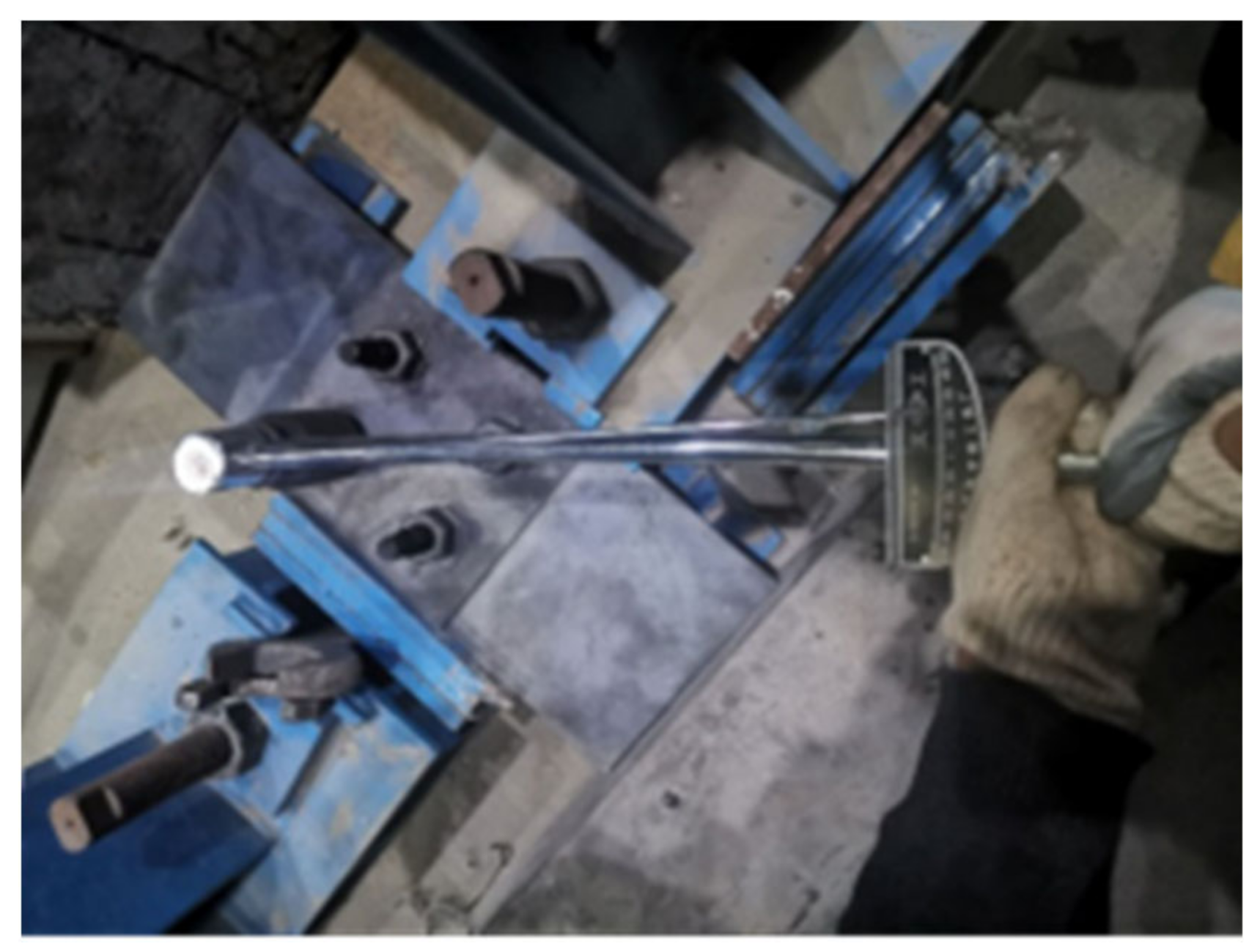
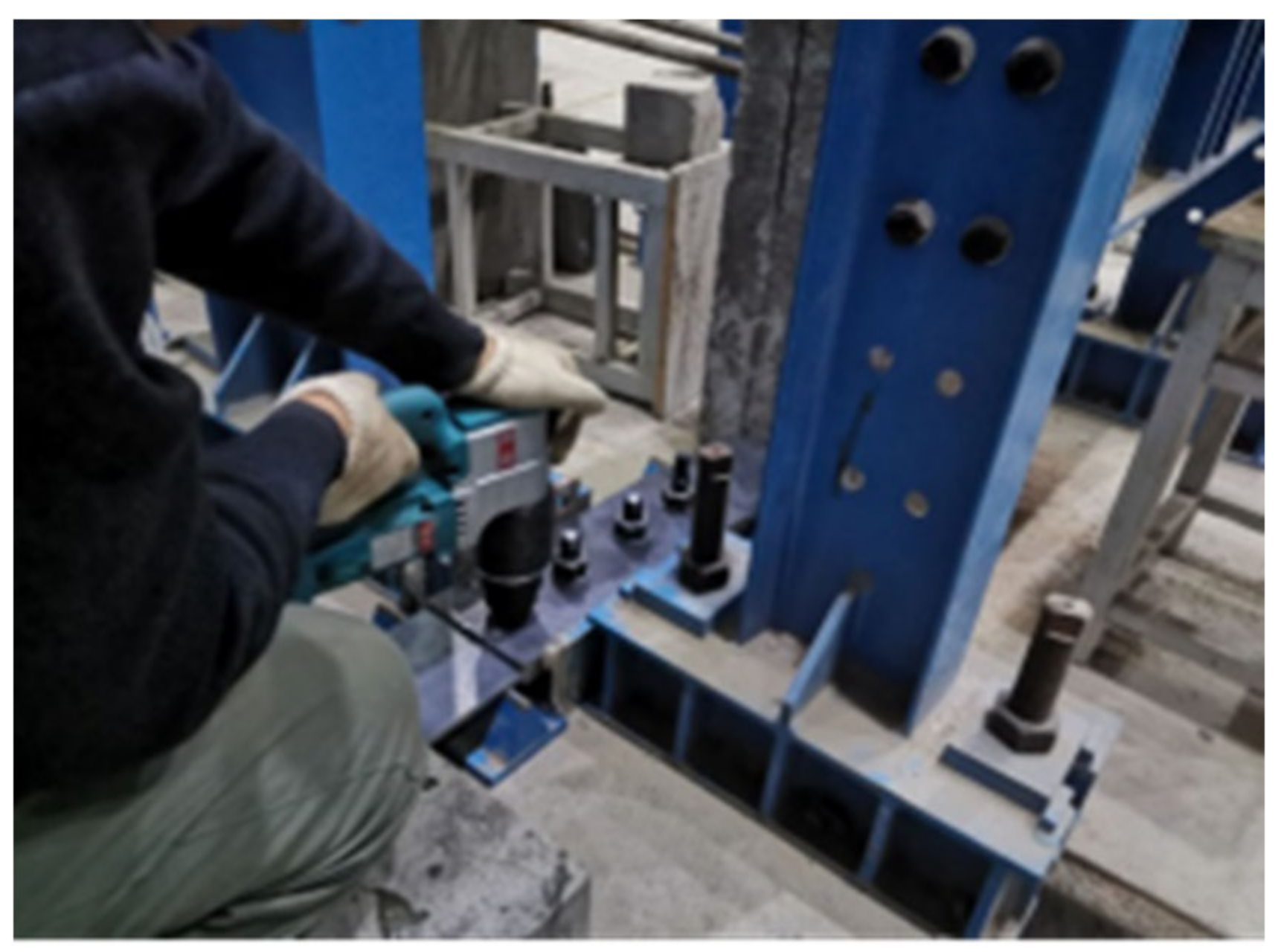
2.1. Assembly of High-Strength Bolted Connections
2.2. Monitoring of the Preload Force
2.3. Accelerated Corrosion Testing
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
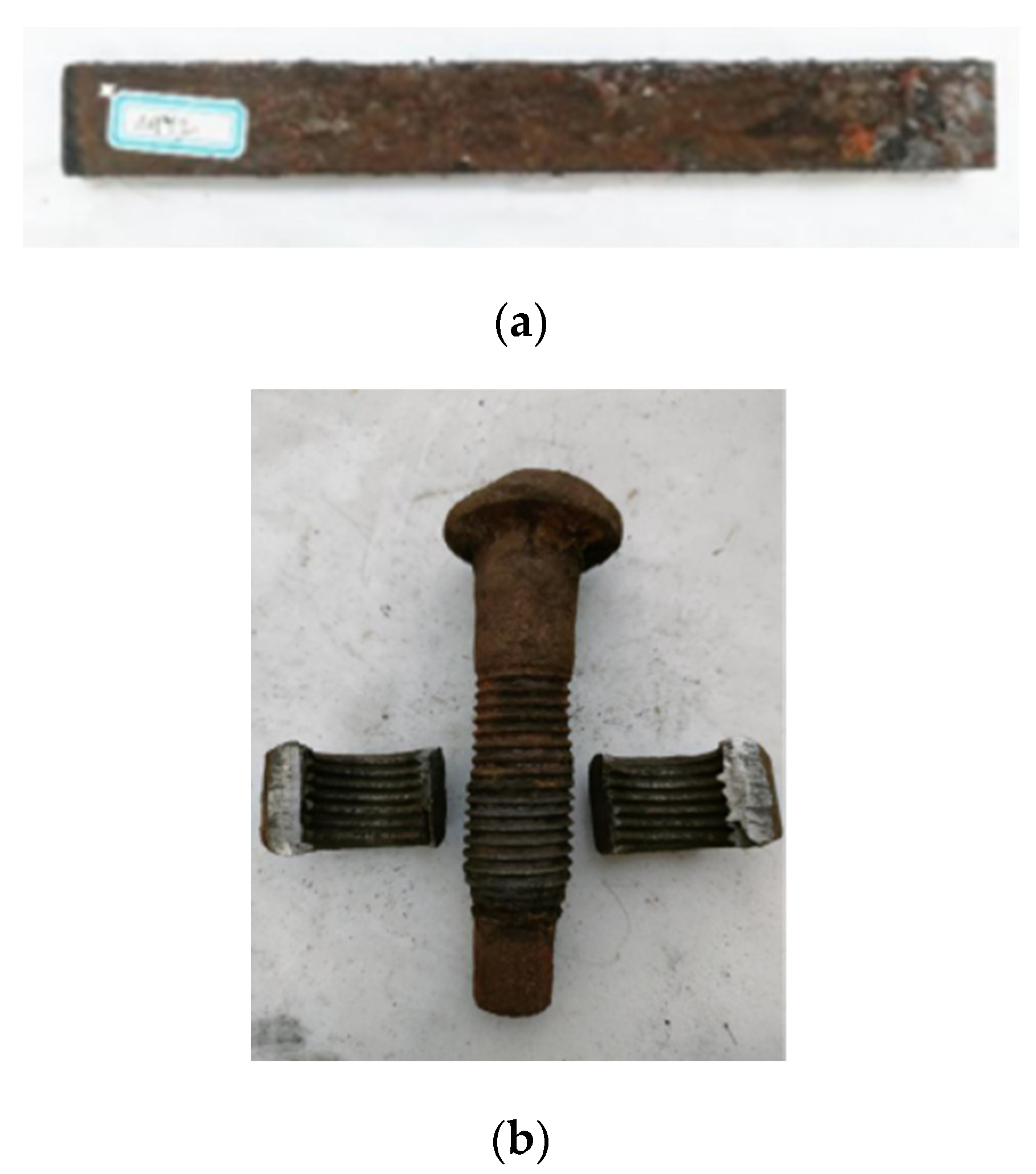
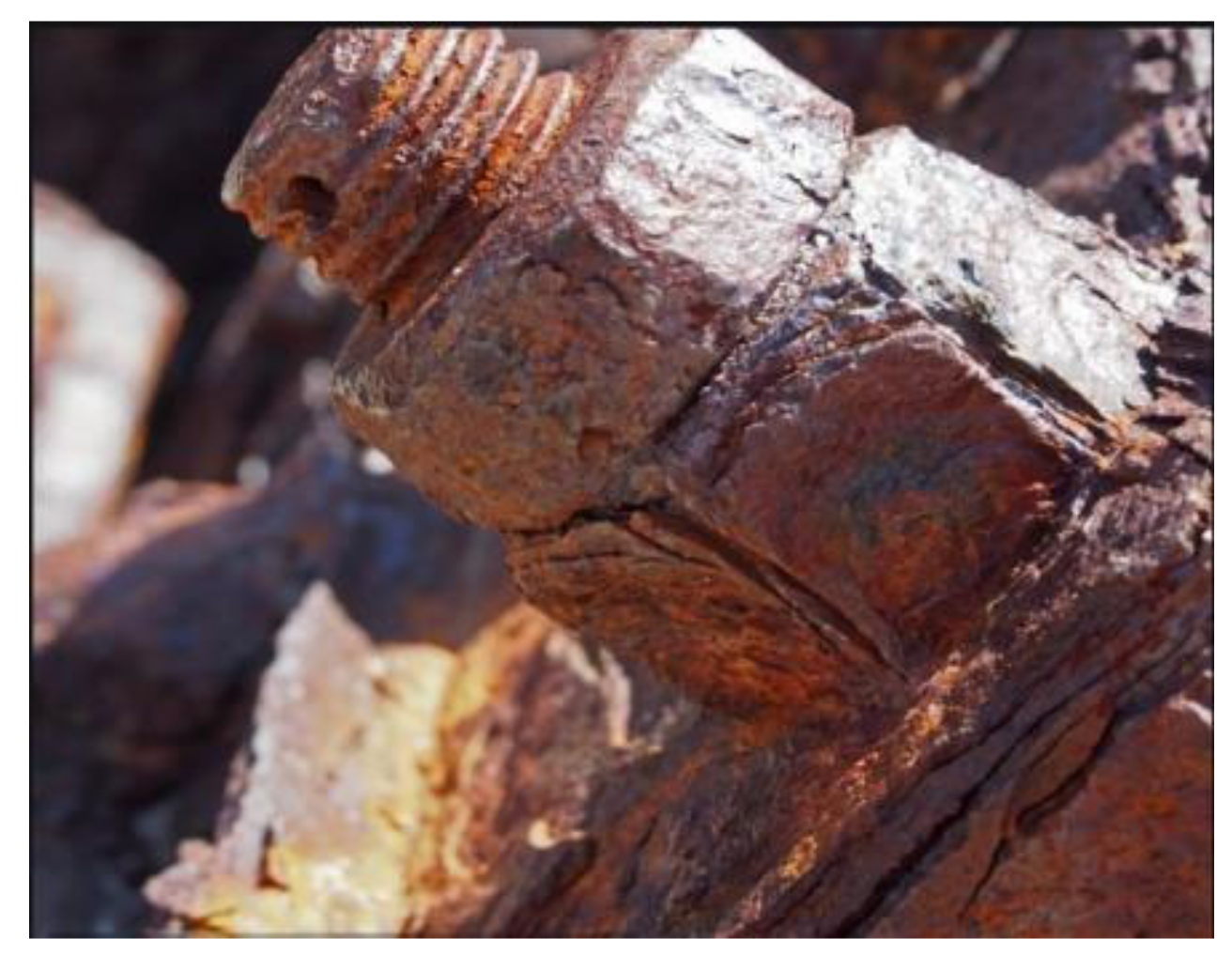
3.1. Corrosion Degree
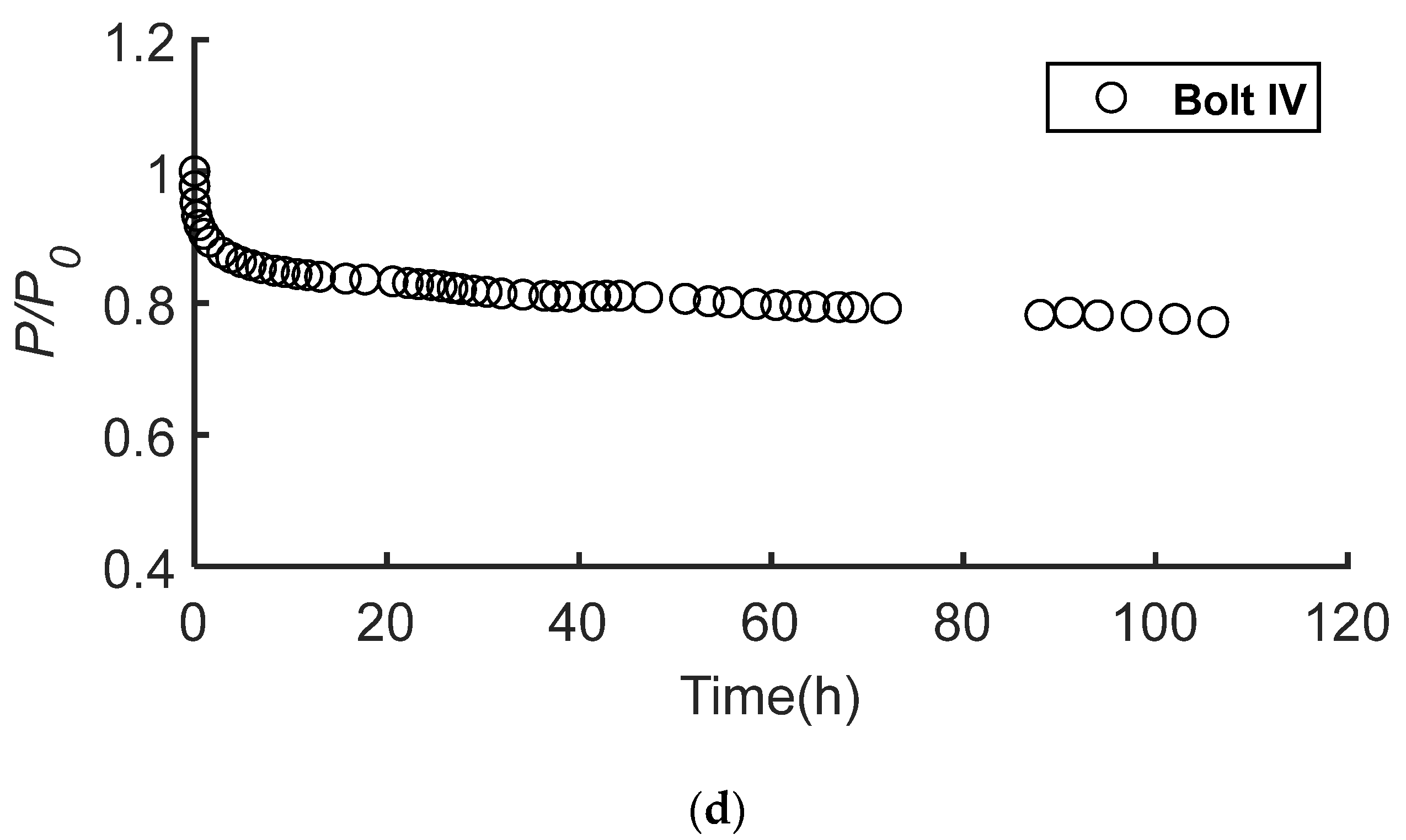
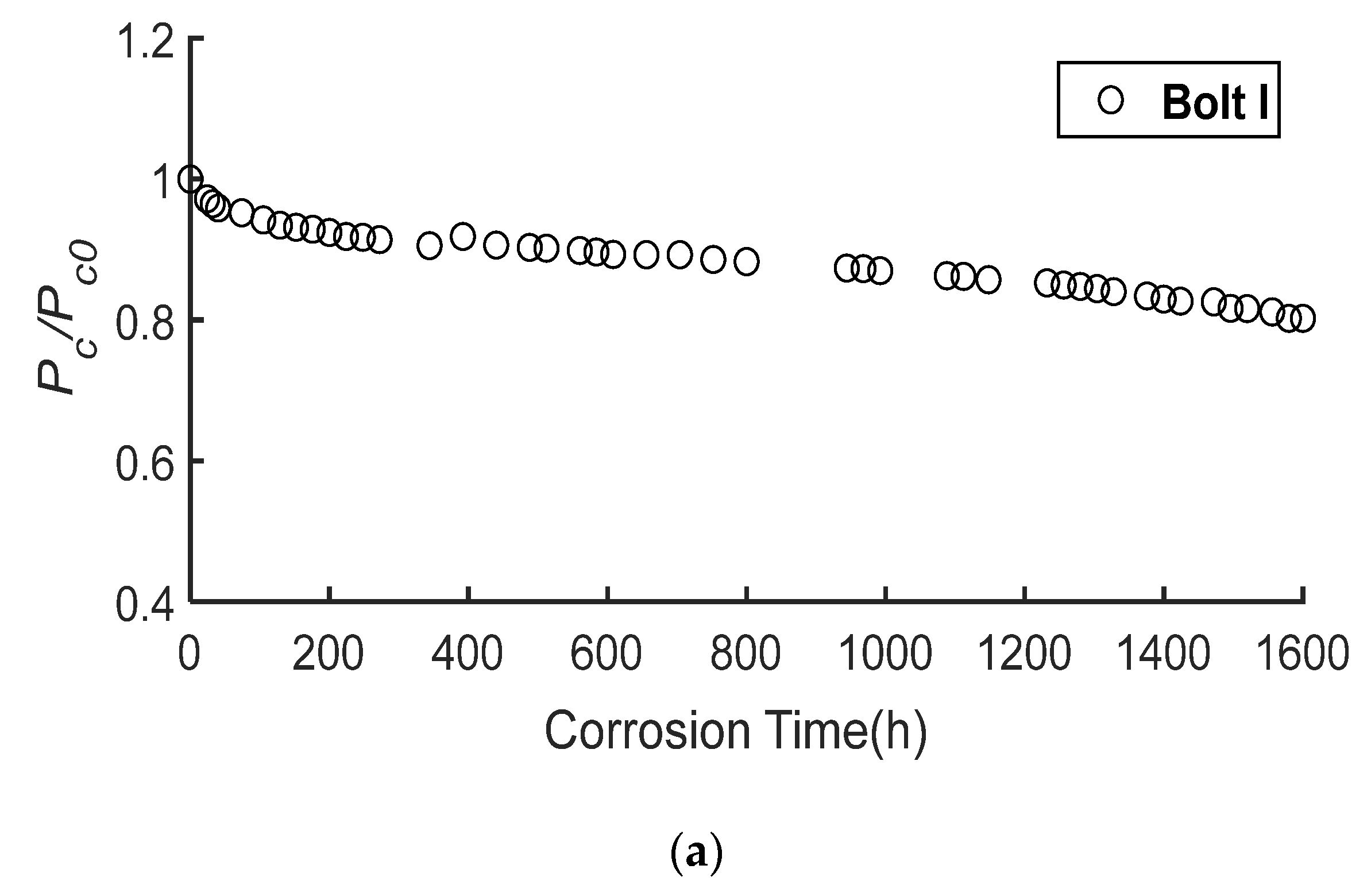
3.2. Degradation of the Preload Force
3.2.1. Stress Relaxation
3.2.2. Effect of Corrosion on the Preload Force
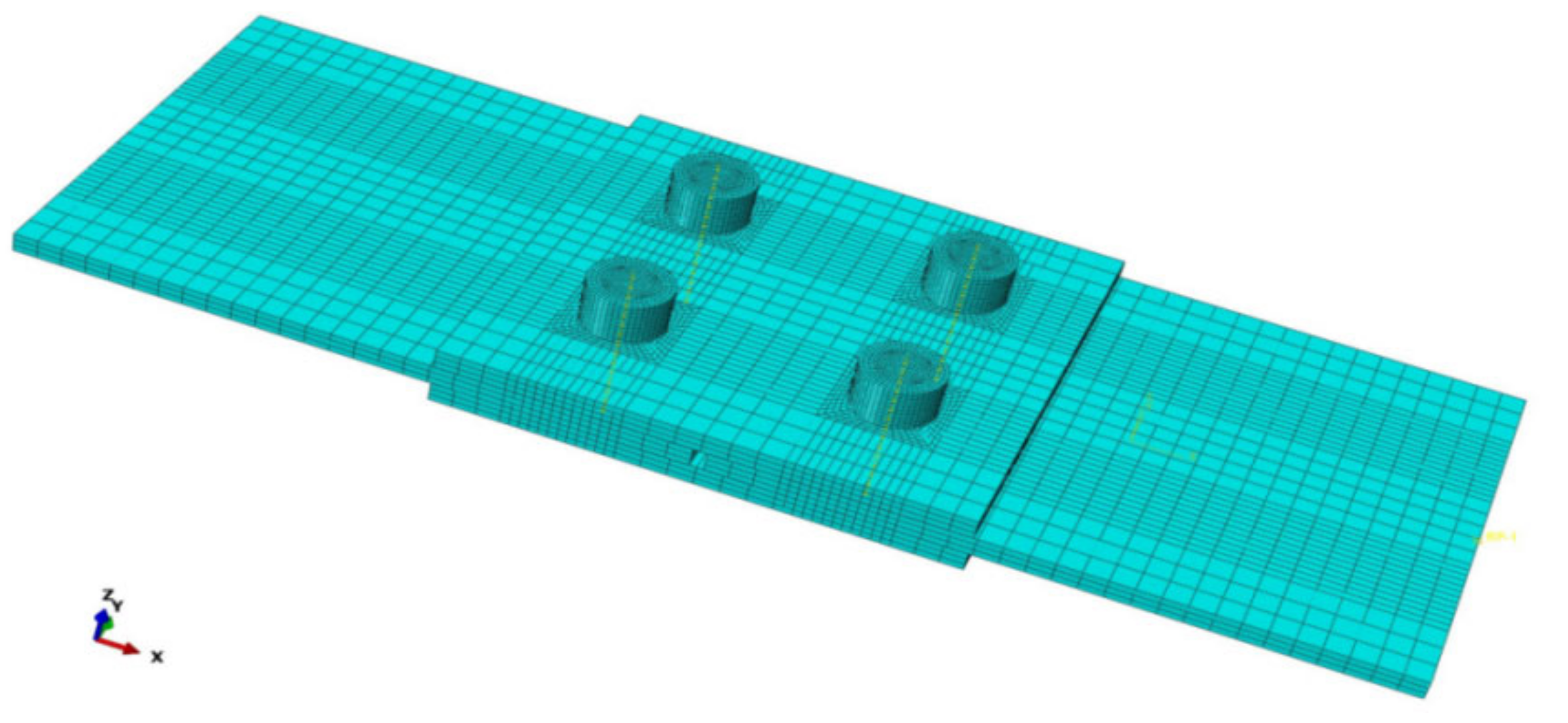
4. Finite Element Analysis
4.1. Finite Element Method
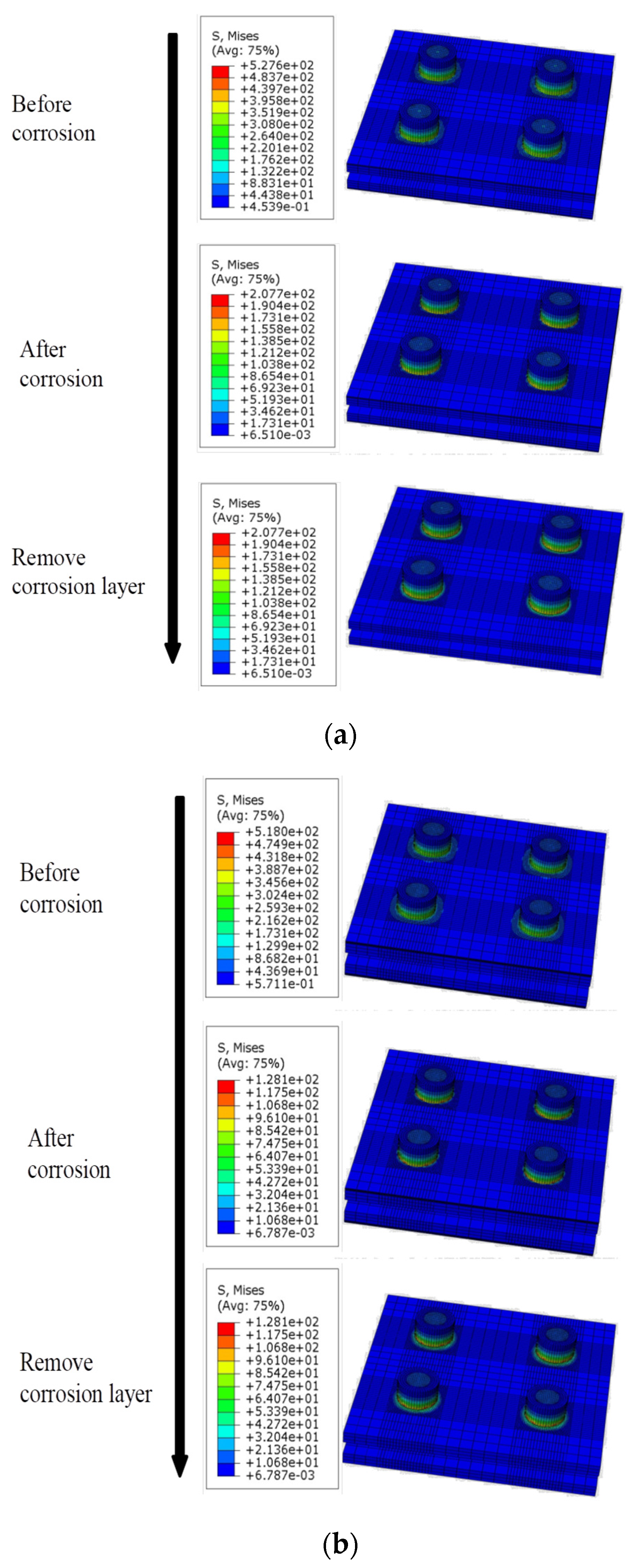
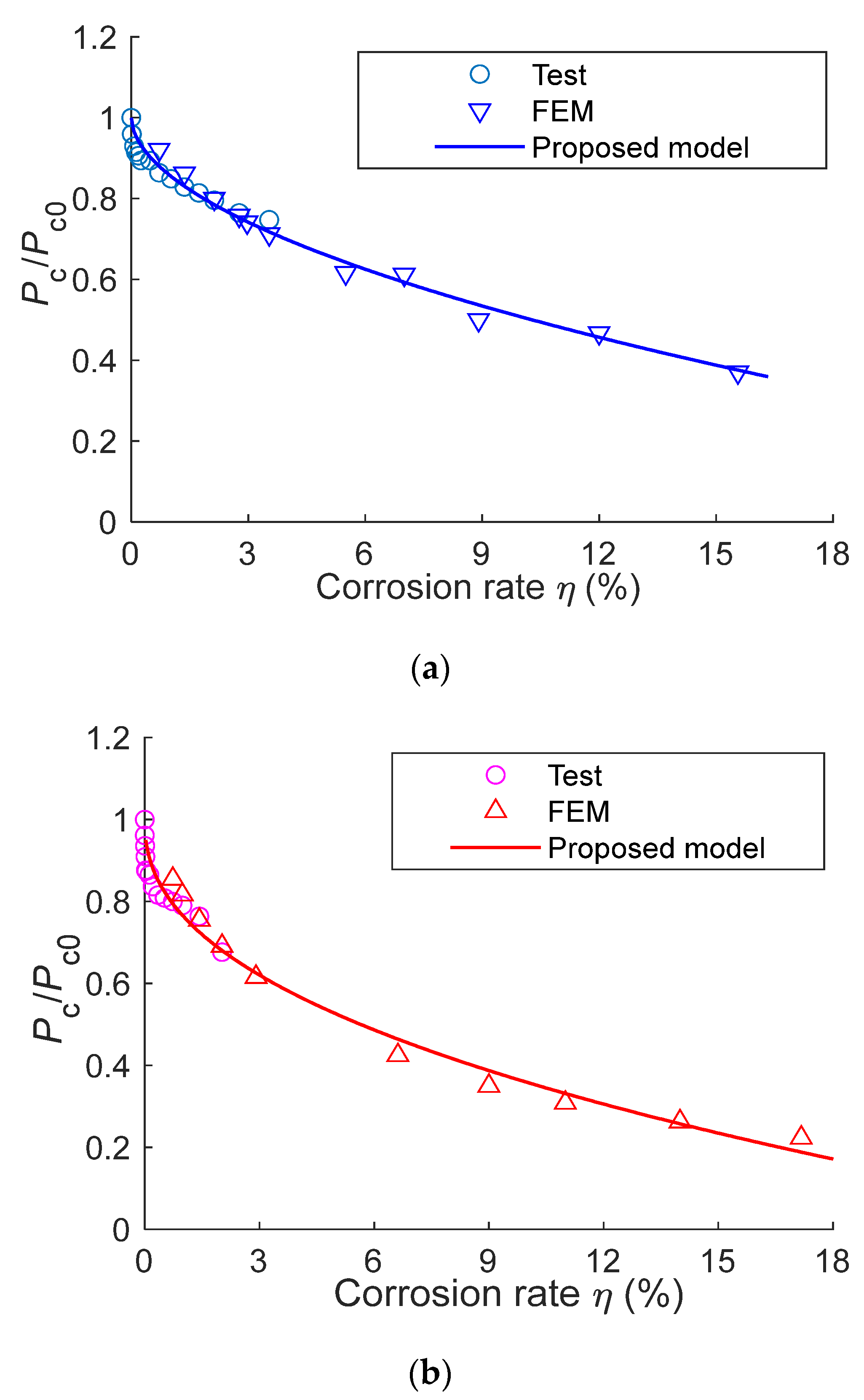
4.2. Validation of Finite Element Analysis
4.3. Parametric Study
5. Model for the PF-HSB
5.1. Stress Relaxation of High-Strength Bolts
5.2. Degradation Model for the Preload Force of Corroded High-Strength Bolts
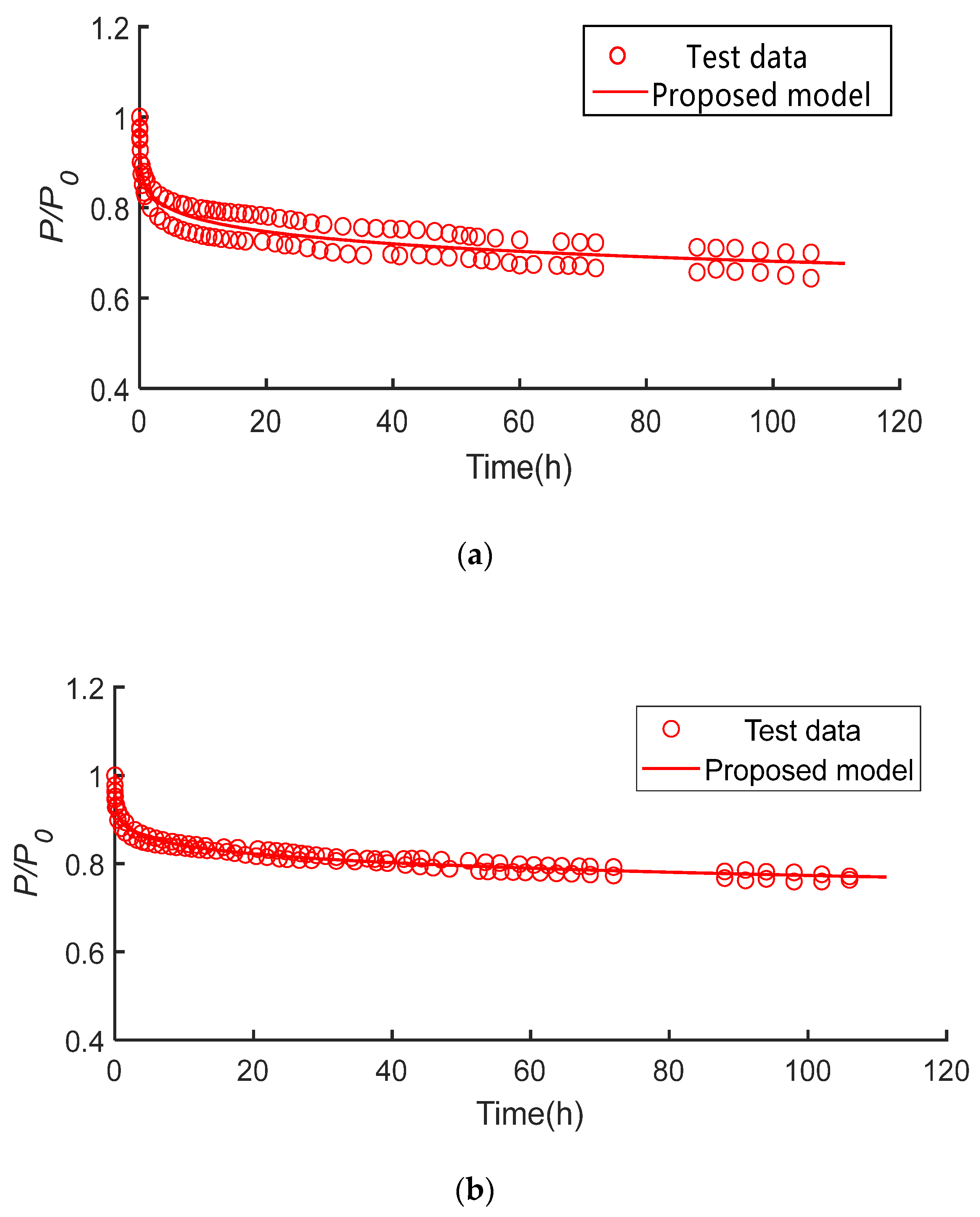
5.3. Evaluation of the Proposed Model
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The PF-HSB decreases rapidly in the first five hours after the final screwing, and it tends to be stable after 45 h. A model that can predicts the stress relaxation of high-strength bolts after final screwing is suggested.
- (2)
- Corrosion has significant influences on the PF-HSB. The PF-HSB decreases by 30.0% when the corrosion degree of steel plates reaches 3.5%.
- (3)
- A finite element method is developed to predict the loss of PF-HSB after corrosion.
- (4)
- Accurate models for predicting the loss of PF-HSB after corrosion are proposed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gresnigt, A.M.; Steenhuis, C.M. Stiffness of Lap Joints with Preloaded Bolts; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Yang, D.; Hassanein, M.F.; Zhang, J.; Lin, A. Failure analysis of high-strength bolts in steel truss bridges. Civ. Eng. 2017, 170, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gao, X.; An, Y. The Influence of Thickness of Steel Plate on Bearing Capacity of Friction-Type High-Strength Bolts. Technol. Highw. Transp. 2018, 34, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulak, G.L.; Fisher, J.W.; Struik, J.H.A. Guide to Design Criteria for Bolted and Riveted Joints, 2nd ed.; AISC: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Society of Steel construction (KSSC). Design of Steel Structures, 3rd ed.; Gumiseogwan: Seoul, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Road and Transportation Association (KRTA). Korean Bridge Design Specification; Korea Road and Transportation Association (KRTA): Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.T.; Lee, J.M.; Huh, J.; Ahn, J.H. Tensile behaviors of friction bolt connection with bolt head corrosion damage: Experimental research B. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 59, 526–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AISC 360-16; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 2016.
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN). Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1–8: Design of Joints; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- GB50017-2017; Design Standard for Steel Structures. China Building Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Braithwaite, J.; Goenaga, I.G.; Tafazzolimoghaddam, B.; Mehmanparast, A. Sensitivity analysis of friction and creep deformation effects on preload relaxation in offshore wind turbine bolted connections. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2020, 101, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, H. Experimental Research On Strain Relaxation Of High-Strength Bolts In End-Plate Connections. Constr. Technol. 2003, 11, 15–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Long-time Monitoring on Strain Relaxation of High Strength Bolts in End-plate Connections. Constr. Technol. 2004, 11, 11–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, G.F.; Latour, M.; Francavilla, A.B.; Piluso, V.; Rizzano, G. Standardised friction damper bolt assemblies time-related relaxation and installed tension variability. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 141, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Valve Ring Bolt Group Assembly Process Optimization and Experimental Research; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M. Research of Bolt Group Assembly Process on the Body-in-White Door; Tianjin University of Technology: Tianjin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cai, L.; Xu, W. Research on preload of bolted joints tightening sequence-related relaxation considering elastic interaction between bolts. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 160, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. Experimental Study on Pre-tension Relaxation of High-Strength Bolts of Joint Plate. Steel Struct. 2019, 11, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccese, V.; Berube, K.A.; Fernandez, M.; Melo, J.D.; Kabche, J.P. Influence of stress relaxation on clamp-up force in hybrid composite-to-metal bolted joints. Compos. Struct. 2009, 89, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Nie, B. Fatigue behavior of corroded steel plates strengthened with CFRP plates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Kong, D.; Xu, S. Stochastic constitutive model of structural steel based on random field of corrosion depth. Case. Stud.Constr. Mat. 2022, 16, e00972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Experimental Study on Performance Degradation of Friction Type Joints of Corroded Steel Structure with High-Strength Bolts; Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Cheung, J.H.; Kim, I.T. Clamping force loss of high-strength bolts as a result of bolt head corrosion damage: Experimental research A. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 59, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, F.; Qin, S.; Tu, K.; Guo, J. Corrosion-Induced Mechanical Degradation of High-Strength Bolted Steel Connection. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xiong, W.; Cai, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. Preload force loss of high-strength bolts in friction connections considering corrosion damage and fatigue loading. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 137, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JGJ 82-2011; Technical Specification for High Strength Bolt Connection of Steel Structure. China Building Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T 10125-2012; Corrosion Test of Artificial Atmosphere Salt Spray Test. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Kong, Z.; Jin, Y.; Hossen, G.M.S.; Hong, S.; Wang, Y.; Vu, Q.; Truong, V.; Tao, Q.; Kim, S.E. Experimental and theoretical study on mechanical properties of mild steel after corrosion. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 246, 110652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xing, L.; Song, H.; Tong, H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, M. Corrosion Resistance of Weathering Steels in Simulated South China Sea Atmospheric Environment. Equip. Environ. Eng. 2018, 15, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS. ABAQUS Analysis User’s Manual; Version 2016; Dassault Systems Simulia Corp: Providence, RI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Z.; Jin, Y.; Yang, F.; Vu, Q.; Truong, V.; Yu, B.; Kim, S.E. Numerical simulation for structural behaviour of stainless steel web cleat connections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 183, 106706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Kuwamura, H. Numerical investigation on strength design and curling effect of mechanically fastened joints in cold-formed austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3942–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhao, O.; Tan, K. Experimental and numerical study of S700 high strength steel double shear bolted connections in tension. Eng. Struct. 2020, 225, 111175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S. Research on Carrying Capacity of Corroded High-Strength Bolt Shear Connections; Anhui University of Technology: Anhui, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Z.; Hong, S.; Vu, Q.-V.; Cao, X.; Kim, S.-E.; Yu, B. New equations predicting initial stiffness and ultimate moment of flush end-plate connections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 175, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Kim, S.-E. Numerical estimation for initial stiffness and ultimate moment of T-stub connections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 141, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Bijlaard, F.S.; Kolstein, H.; Jiang, X. Behaviour of beam-to-column high strength steel endplate connections under fire conditions—Part 2: Numerical study. Eng. Struct. 2014, 64, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, Y. Explain of Finite Element Analysis with Examples Using Abaqus; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, D.; Xing, K.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, J. Study on material mechanical performance of corroded cold-formed 2 millimetre thin-walled steel. Ind. Constr. 2016, 46, 114–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
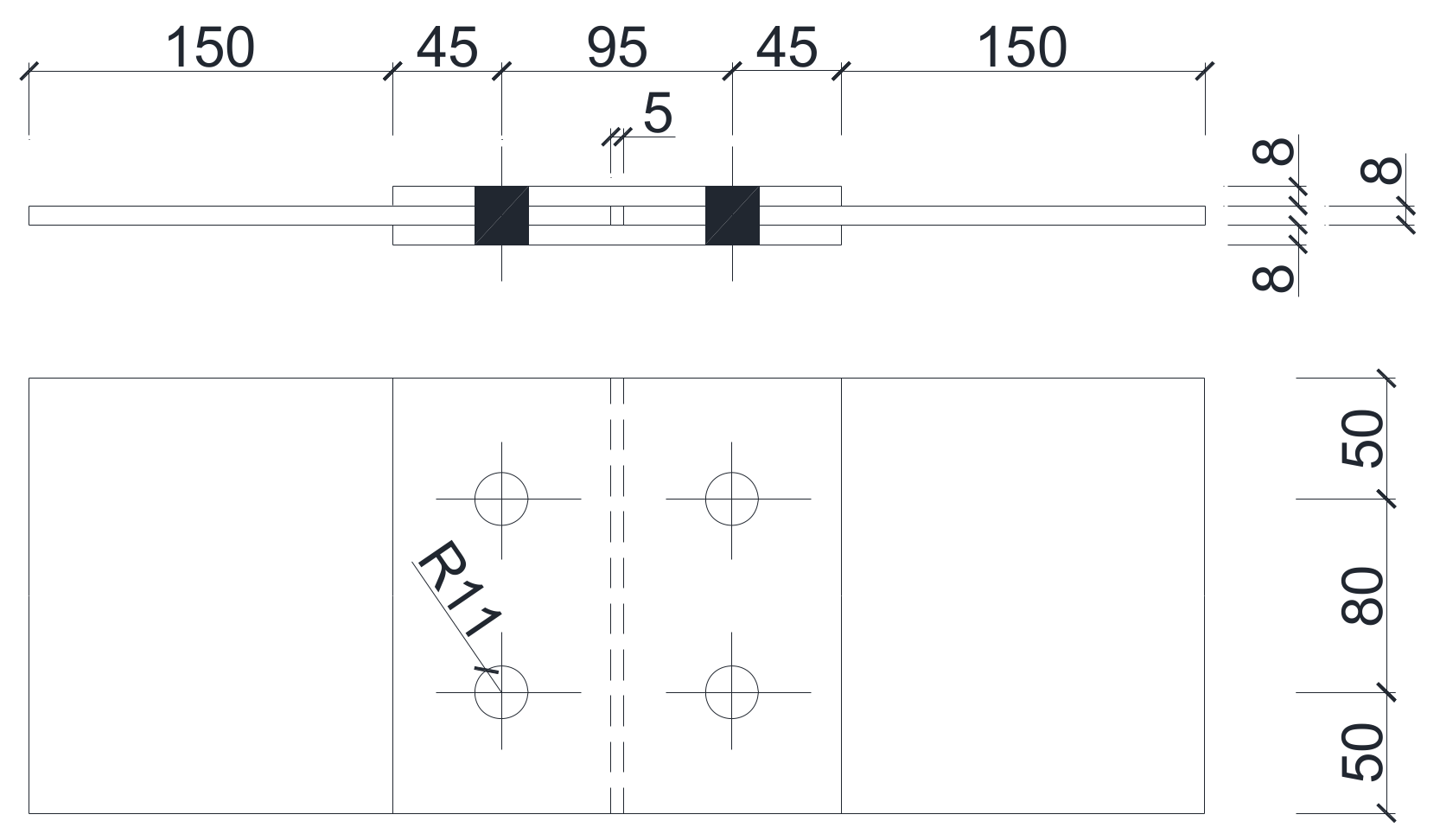
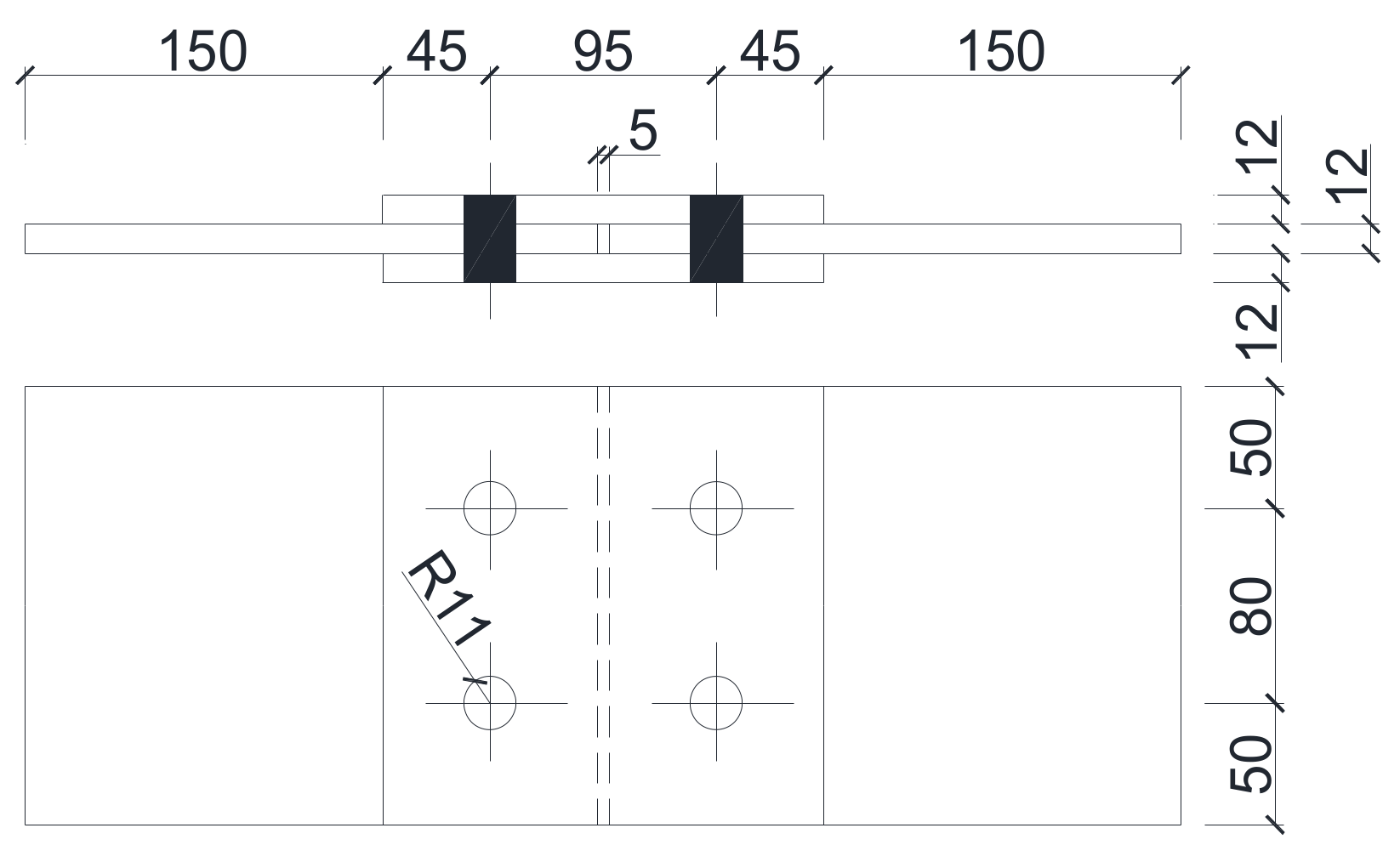
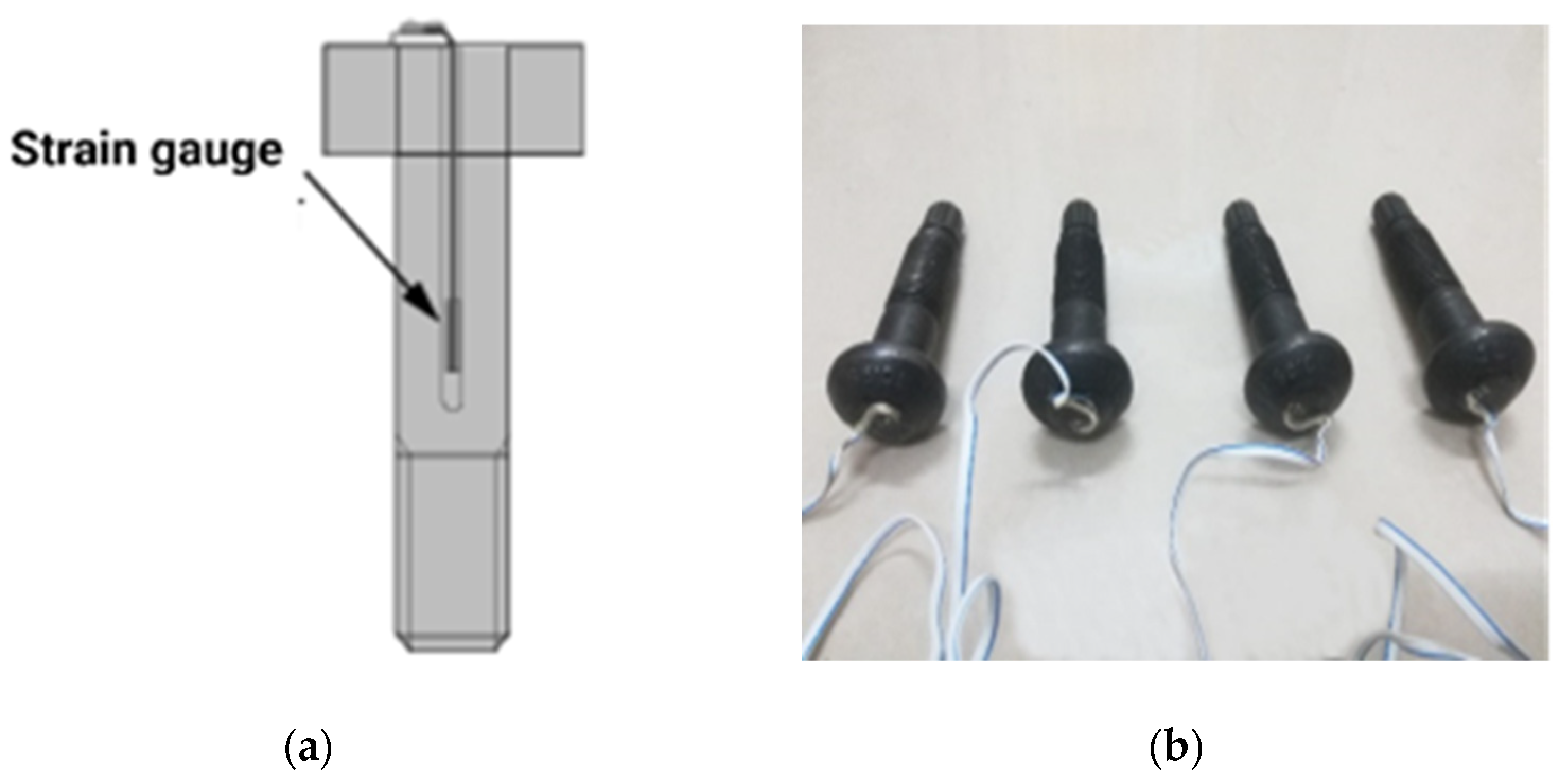
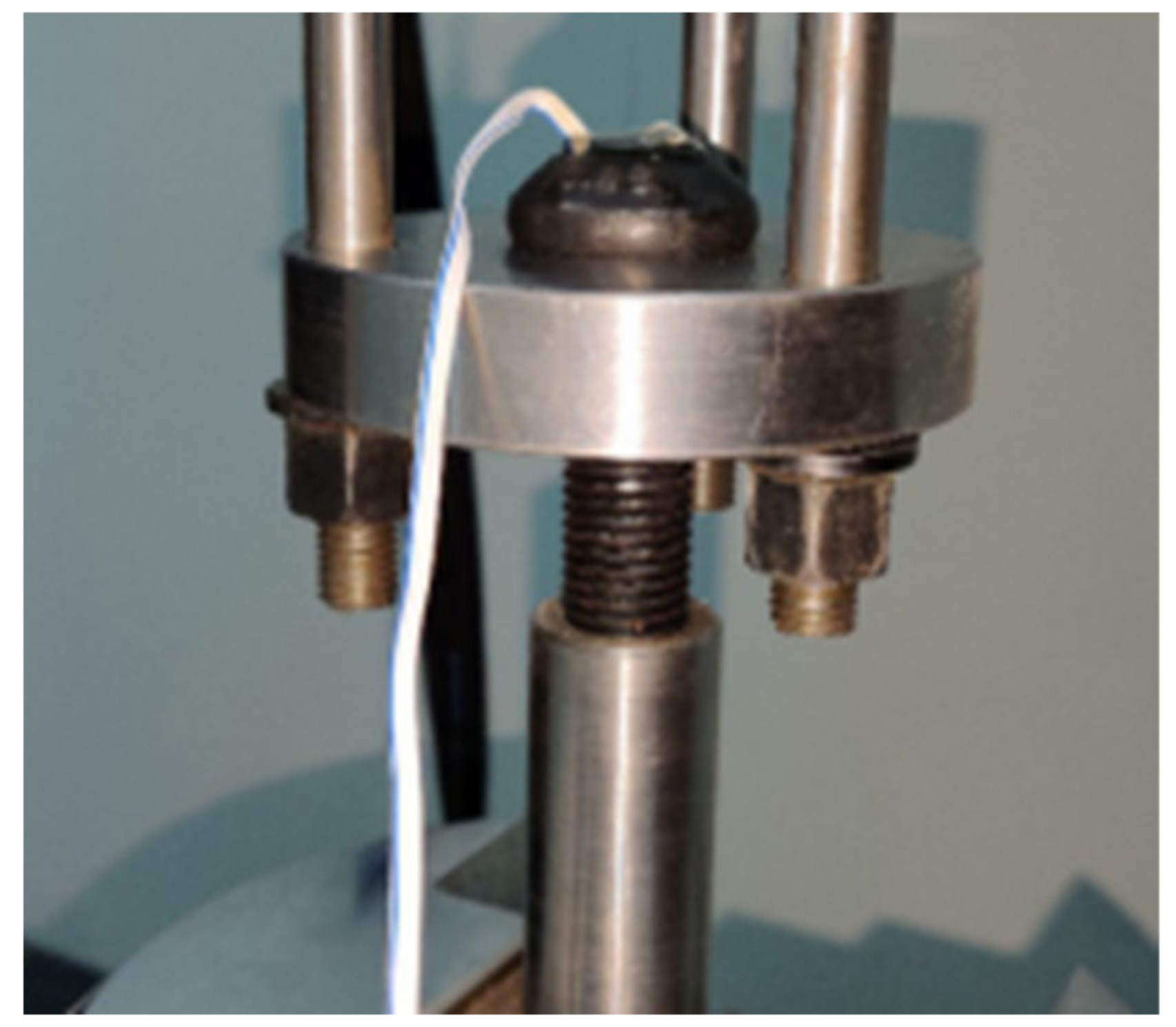












| Applied Force (kN) | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | Calibration Coefficient (kN/μ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolt I | 0 | 25 | 48 | 76 | 118 | 154 | 0.098 |
| Bolt II | 0 | 32 | 68 | 106 | 142 | 176 | 0.084 |
| Bolt III | 0 | 32 | 68 | 102 | 142 | 180 | 0.081 |
| Bolt IV | 0 | 50 | 94 | 142 | 186 | 236 | 0.065 |
| Specimen Number | Bolt Grade | Diameter of Bolt (mm) | Steel Plate | Numbers of Bolts in Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S235-1 | 10.9S | 20 | Q235 | 2 (Bolt I and Bolt II) |
| S355-1 | 10.9S | 20 | Q355 | 2 (Bolt III and Bolt IV) |
| Bolts Number | Corrosion Time (h) | Mass before Corrosion(g) | Mass after Corrosion(g) | Corrosion Rate (%) | Average Corrosion Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ11 | 1440 | 263.50 | 254.50 | 3.42 | 3.55 |
| MZ12 | 263.50 | 254.00 | 3.61 | ||
| MZ13 | 263.50 | 254.00 | 3.61 | ||
| MZ21 | 2880 | 263.50 | 245.00 | 7.02 | 6.78 |
| MZ22 | 262.00 | 246.00 | 6.11 | ||
| MZ23 | 263.00 | 244.00 | 7.22 | ||
| MZ31 | 4320 | 262.00 | 224.50 | 14.31 | 17.05 |
| MZ32 | 263.50 | 217.50 | 17.46 | ||
| MZ33 | 263.00 | 212.00 | 19.39 |
| Specimen Number | Corrosion Time (h) | Mass before Corrosion (g) | Mass after Corrosion (g) | Corrosion Rate (%) | Average Corrosion Rate (%) | Average Thickness Loss of Steel Plate (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MX11 | 1440 | 441.50 | 428.50 | 2.94 | 2.97 | 0.22 |
| MX12 | 444.00 | 430.50 | 3.04 | |||
| MX13 | 442.50 | 429.50 | 2.94 | |||
| MY11 | 706.50 | 686.00 | 2.90 | 2.91 | 0.35 | |
| MY12 | 697.50 | 676.50 | 3.01 | |||
| MY13 | 711.00 | 691.00 | 2.81 | |||
| MX21 | 2880 | 440.00 | 401.00 | 8.86 | 8.91 | 0.67 |
| MX22 | 443.00 | 404.50 | 8.69 | |||
| MX23 | 442.00 | 401.50 | 9.16 | |||
| MY21 | 712.00 | 665.00 | 6.60 | 6.62 | 0.80 | |
| MY22 | 706.50 | 659.50 | 6.65 | |||
| MY23 | 704.50 | 658.00 | 6.60 | |||
| MX31 | 4320 | 444.00 | 375.00 | 15.54 | 15.56 | 1.17 |
| MX32 | 441.00 | 373.00 | 15.42 | |||
| MX33 | 445.50 | 375.50 | 15.71 | |||
| MY31 | 706.00 | 588.00 | 16.71 | 17.17 | 2.07 | |
| MY32 | 716.00 | 590.00 | 17.60 | |||
| MY33 | 706.50 | 585.00 | 17.20 |
| Time | Bolt I | Bolt II | Bolt III | Bolt IV | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| 5 h | 81.41% | 75.89% | 84.56% | 86.16% | 82.01% |
| 10 h | 79.66% | 73.53% | 83.55% | 84.42% | 80.29% |
| 15 h | 78.79% | 72.69% | 82.82% | 83.76% | 79.52% |
| 20 h | 78.05% | 72.33% | 81.74% | 83.41% | 78.88% |
| 25 h | 77.02% | 71.37% | 80.98% | 82.66% | 78.01% |
| 30 h | 76.04% | 70.12% | 80.71% | 81.71% | 77.15% |
| 35 h | 75.52% | 69.38% | 80.48% | 81.21% | 76.65% |
| 40 h | 75.23% | 69.24% | 80.06% | 80.99% | 76.38% |
| 45 h | 74.93% | 69.47% | 79.22% | 81.11% | 76.18% |
| 50 h | 74.03% | 68.60% | 78.80% | 80.45% | 75.47% |
| 60 h | 72.92% | 67.18% | 78.34% | 79.38% | 74.46% |
| 70 h | 72.34% | 66.66% | 77.81% | 78.96% | 73.94% |
| 88 h | 71.17% | 65.68% | 76.74% | 78.18% | 72.94% |
| 90 h | 71.34% | 66.06% | 76.74% | 78.36% | 73.13% |
| 100 h | 70.45% | 65.17% | 76.32% | 77.68% | 72.41% |
| Specimens | Material of Plates | Corrosion Rate η (%) | Test Data Pc/Pc0 | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX Series | Q235 | 0.075 | 0.930 | Predicting group |
| Q235 | 0.123 | 0.915 | ||
| Q235 | 0.183 | 0.906 | ||
| Q235 | 0.250 | 0.894 | ||
| Q235 | 0.485 | 0.894 | ||
| Q235 | 1.733 | 0.814 | ||
| Q235 | 0.714 | 0.864 | Verifying group | |
| Q235 | 1.363 | 0.829 | ||
| Q235 | 2.129 | 0.796 | ||
| Q235 | 2.768 | 0.765 | ||
| Q235 | 3.537 | 0.747 | ||
| TY Series | Q355 | 0.047 | 0.874 | Predicting group |
| Q355 | 0.120 | 0.865 | ||
| Q355 | 0.208 | 0.836 | ||
| Q355 | 0.347 | 0.816 | ||
| Q355 | 0.522 | 0.809 | ||
| Q355 | 0.734 | 0.800 | Verifying group | |
| Q355 | 0.983 | 0.790 | ||
| Q355 | 1.428 | 0.764 | ||
| Q355 | 2.022 | 0.676 |
| Specimens | (%) | Test Results | FEM Results | Error (%) | Average Error (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preload Force (kN) | Pc/Pc0 | Preload Force (kN) | Pc/Pc0 | ||||
| TX1 | 0.7137 | 107.11 | 0.864 | 114.20 | 0.921 | 6.60% | 3.36% |
| TX2 | 1.363 | 102.73 | 0.828 | 106.91 | 0.862 | 4.10% | |
| TX3 | 2.129 | 98.64 | 0.796 | 99.18 | 0.800 | 0.50% | |
| TX4 | 2.768 | 94.80 | 0.765 | 93.99 | 0.758 | 0.92% | |
| TX5 | 3.537 | 92.68 | 0.747 | 83.31 | 0.712 | 4.69% | |
| TY1 | 0.734 | 96.76 | 0.800 | 103.46 | 0.855 | 6.92% | 3.45% |
| TY2 | 0.983 | 95.62 | 0.790 | 98.81 | 0.817 | 3.33% | |
| TY3 | 1.428 | 92.41 | 0.764 | 91.33 | 0.755 | 1.17% | |
| TY4 | 2.022 | 81.83 | 0.676 | 83.71 | 0.692 | 2.37% | |
| Specimens | Material of Plates | Plate Thickness (mm) | (%) | Corrosion Depth (mm) | Young’s Modulus (Gpa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX0 | Q235 | 8 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 206 | 0.3 |
| TX1 | Q235 | 8 | 0.714 | 0.053 | 204.7 | 0.3 |
| TX2 | Q235 | 8 | 1.363 | 0.101 | 203.54 | 0.3 |
| TX3 | Q235 | 8 | 2.129 | 0.158 | 202.16 | 0.3 |
| TX4 | Q235 | 8 | 2.768 | 0.206 | 201.01 | 0.3 |
| TX5 | Q235 | 8 | 3.537 | 0.263 | 200.65 | 0.3 |
| TX 6 | Q235 | 8 | 2.97 | 0.220 | 199.62 | 0.3 |
| TX 7 | Q235 | 8 | 5.500 | 0.408 | 196.08 | 0.3 |
| TX 8 | Q235 | 8 | 7.000 | 0.520 | 193.38 | 0.3 |
| TX 9 | Q235 | 8 | 8.910 | 0.670 | 189.94 | 0.3 |
| TX 10 | Q235 | 8 | 12.000 | 0.891 | 184.37 | 0.3 |
| TX 11 | Q235 | 8 | 15.560 | 1.175 | 177.95 | 0.3 |
| TY0 | Q355 | 12 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 206 | 0.3 |
| TY1 | Q355 | 12 | 0.734 | 0.090 | 204.21 | 0.3 |
| TY2 | Q355 | 12 | 0.983 | 0.120 | 203.02 | 0.3 |
| TY3 | Q355 | 12 | 1.428 | 0.175 | 201.02 | 0.3 |
| TY4 | Q355 | 12 | 2.022 | 0.247 | 198.59 | 0.3 |
| TY 5 | Q355 | 12 | 2.910 | 0.350 | 195.40 | 0.3 |
| TY 6 | Q355 | 12 | 6.620 | 0.800 | 186.48 | 0.3 |
| TY 7 | Q355 | 12 | 9.000 | 1.101 | 183.21 | 0.3 |
| TY 8 | Q355 | 12 | 11.000 | 1.346 | 181.38 | 0.3 |
| TY 9 | Q355 | 12 | 14.000 | 1.713 | 179.61 | 0.3 |
| TY 10 | Q355 | 12 | 17.170 | 2.070 | 178.54 | 0.3 |
| Specimens | (%) | Test Data Pc/Pc0 | Proposed Model Pc/Pc0 | Error (%) | Average Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX1 | 0.714 | 0.864 | 0.880 | 1.85% | 1.12% |
| TX2 | 1.363 | 0.828 | 0.831 | 0.36% | |
| TX3 | 2.129 | 0.796 | 0.7857 | 1.29% | |
| TX4 | 2.768 | 0.764 | 0.752 | 1.57% | |
| TX5 | 3.537 | 0.747 | 0.743 | 0.54% | |
| TY1 | 0.734 | 0.800 | 0.794 | 0.75% | 2.34% |
| TY2 | 0.983 | 0.790 | 0.767 | 2.91% | |
| TY3 | 1.428 | 0.764 | 0.725 | 5.10% | |
| TY4 | 2.022 | 0.676 | 0.680 | 0.59% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Z.; Jin, Y.; Hong, S.; Liu, Q.; Vu, Q.-V.; Kim, S.-E. Degradation Behavior of the Preload Force of High-Strength Bolts after Corrosion. Buildings 2022, 12, 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122122
Kong Z, Jin Y, Hong S, Liu Q, Vu Q-V, Kim S-E. Degradation Behavior of the Preload Force of High-Strength Bolts after Corrosion. Buildings. 2022; 12(12):2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122122
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Zhengyi, Ya Jin, Shaozheng Hong, Quanwei Liu, Quang-Viet Vu, and Seung-Eock Kim. 2022. "Degradation Behavior of the Preload Force of High-Strength Bolts after Corrosion" Buildings 12, no. 12: 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122122
APA StyleKong, Z., Jin, Y., Hong, S., Liu, Q., Vu, Q.-V., & Kim, S.-E. (2022). Degradation Behavior of the Preload Force of High-Strength Bolts after Corrosion. Buildings, 12(12), 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12122122








