Influence of Material Property Variation on Computationally Calculated Melt Pool Temperature during Laser Melting Process
Abstract
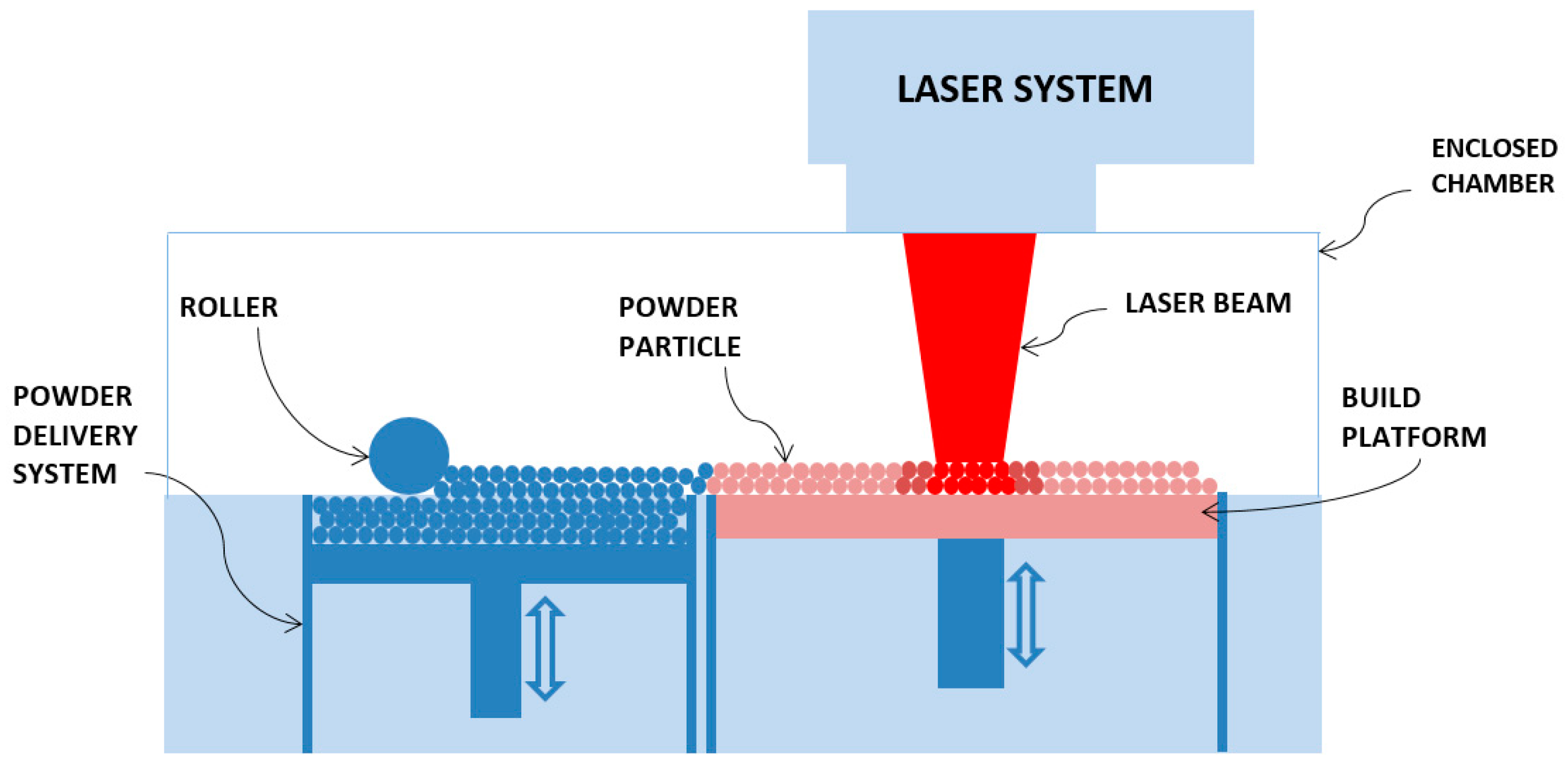
1. Introduction
2. Finite Element Modeling
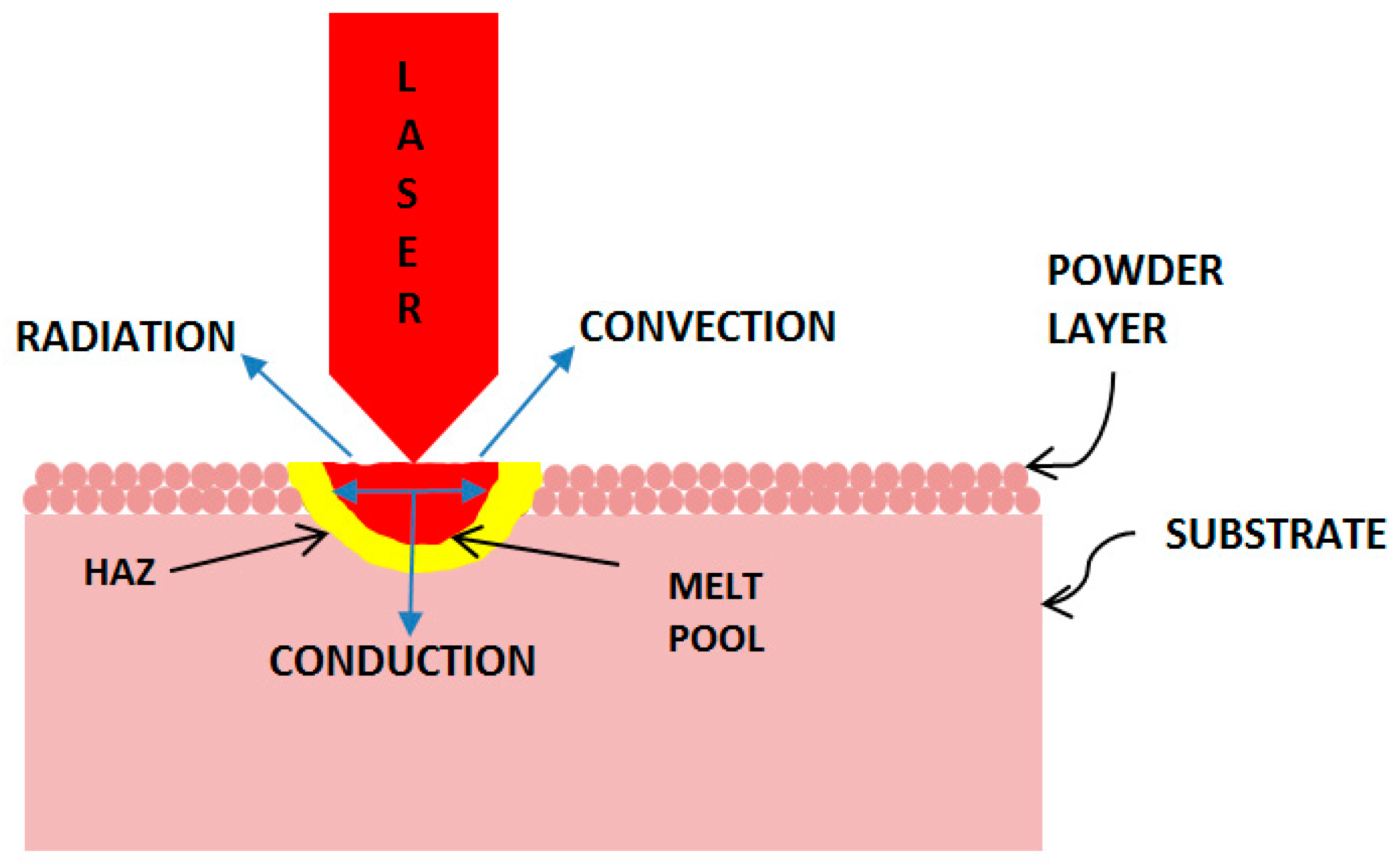
2.1. Governing Equations
- (x,y,z) = coordinate system attached to the heat source
- Q = power generation per unit volume in the domain D (W m−3)
- kx, ky, kz = thermal conductivity in the x, y and z directions (W m−1 K−1)
- c = specific heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
- ρ = density (kg m−3)
- t = time (s)
- v = velocity of laser (m s−1)
- kn = thermal conductivity normal to S (W/m-K)
- h = heat transfer coefficient for convection (W/m2-K)
- σ = Stefan–Boltzmann constant for radiation (5.67 × 10−8 W/m2-K4)
- ε = emissivity
- To = ambient temperature (K)
- q = heat flux normal to S (W/m2)
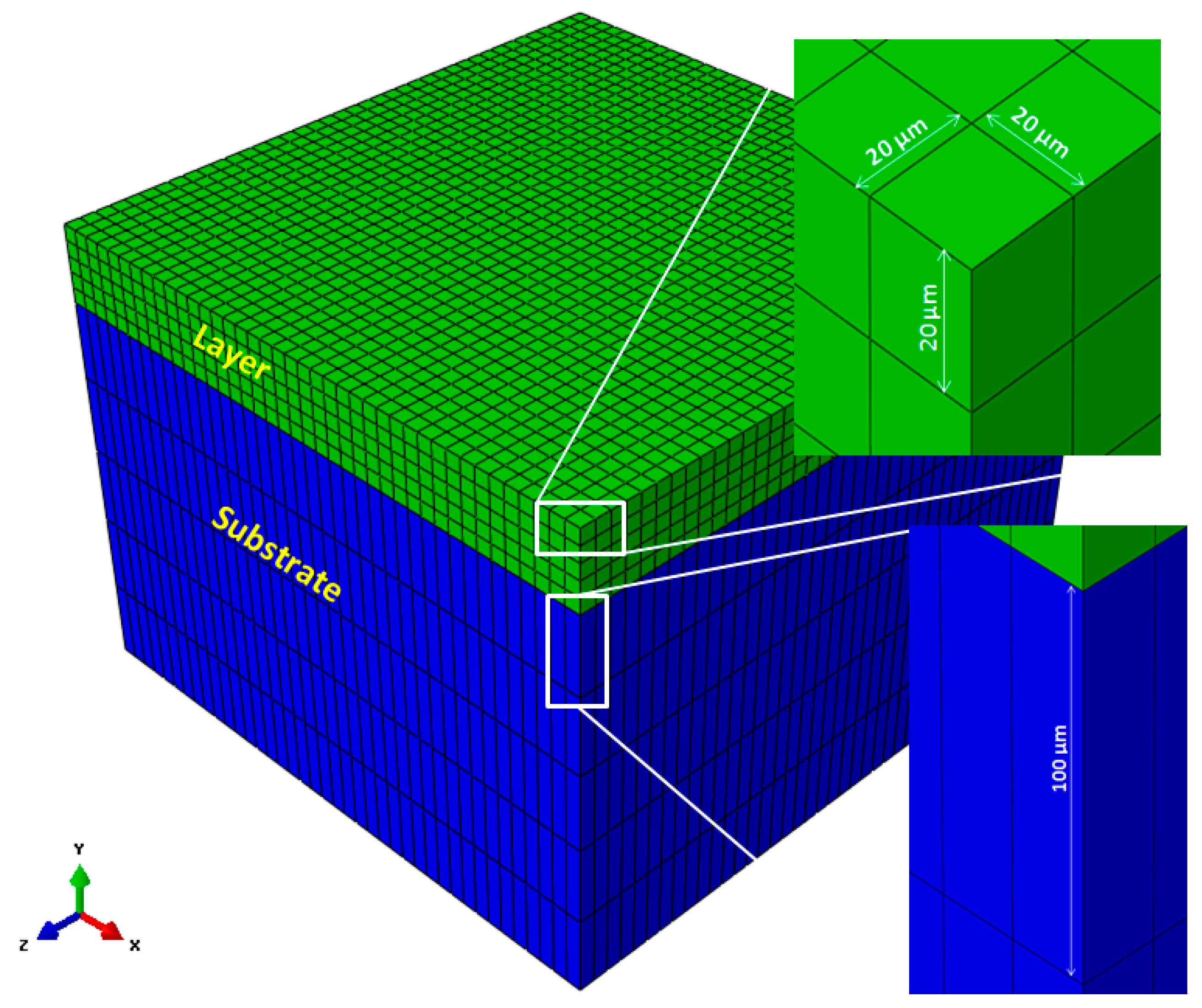
2.2. Description of the Model
2.3. Material Properties
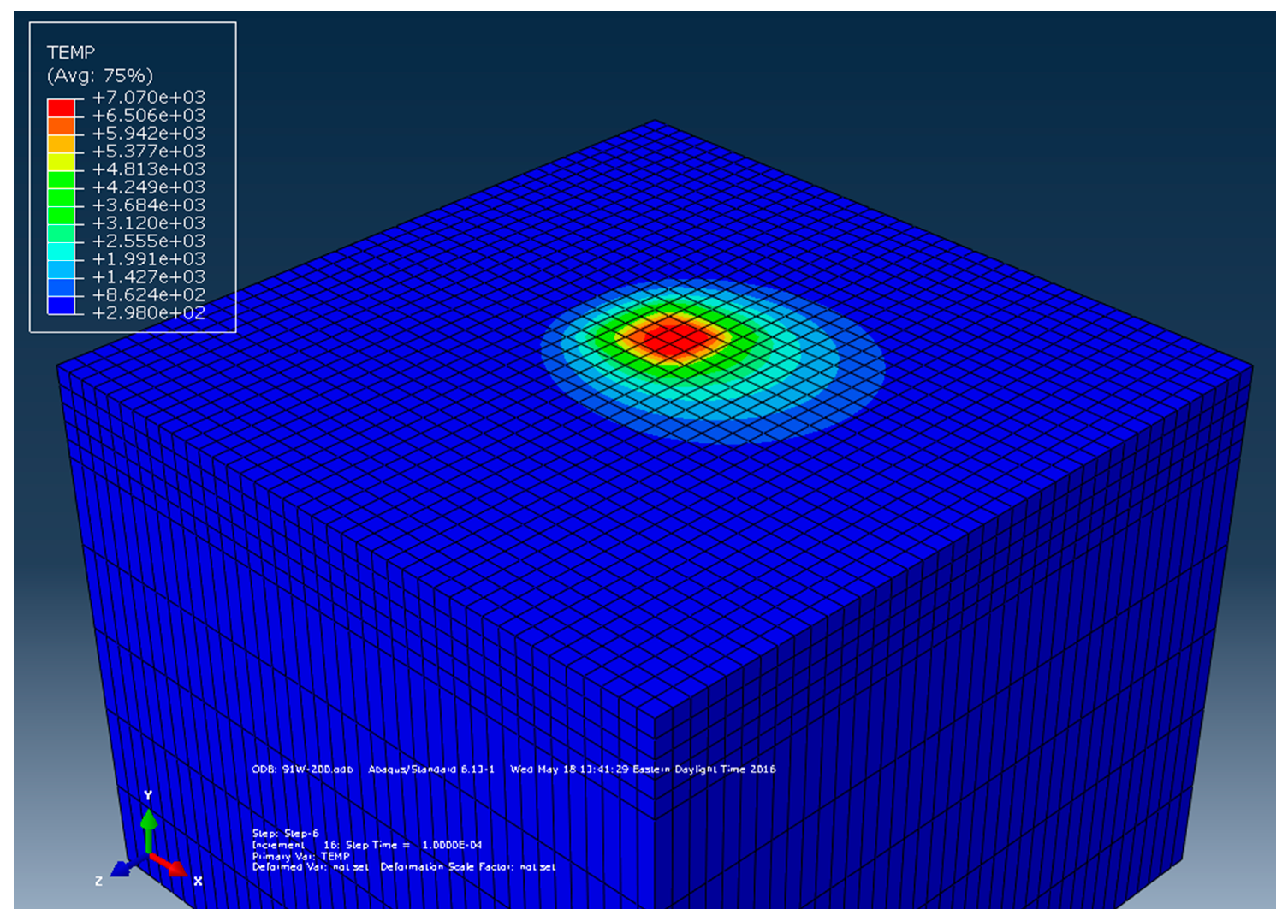
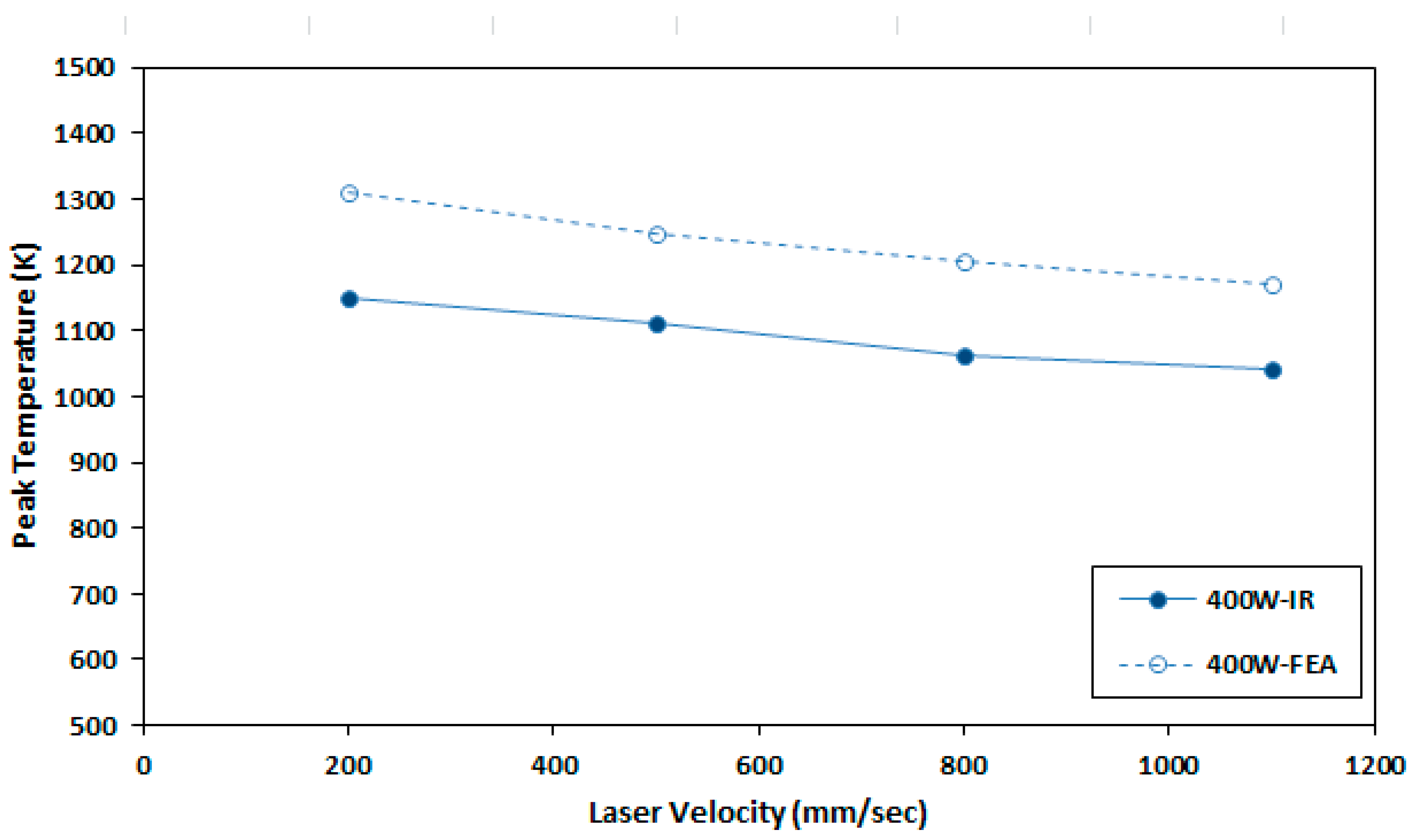
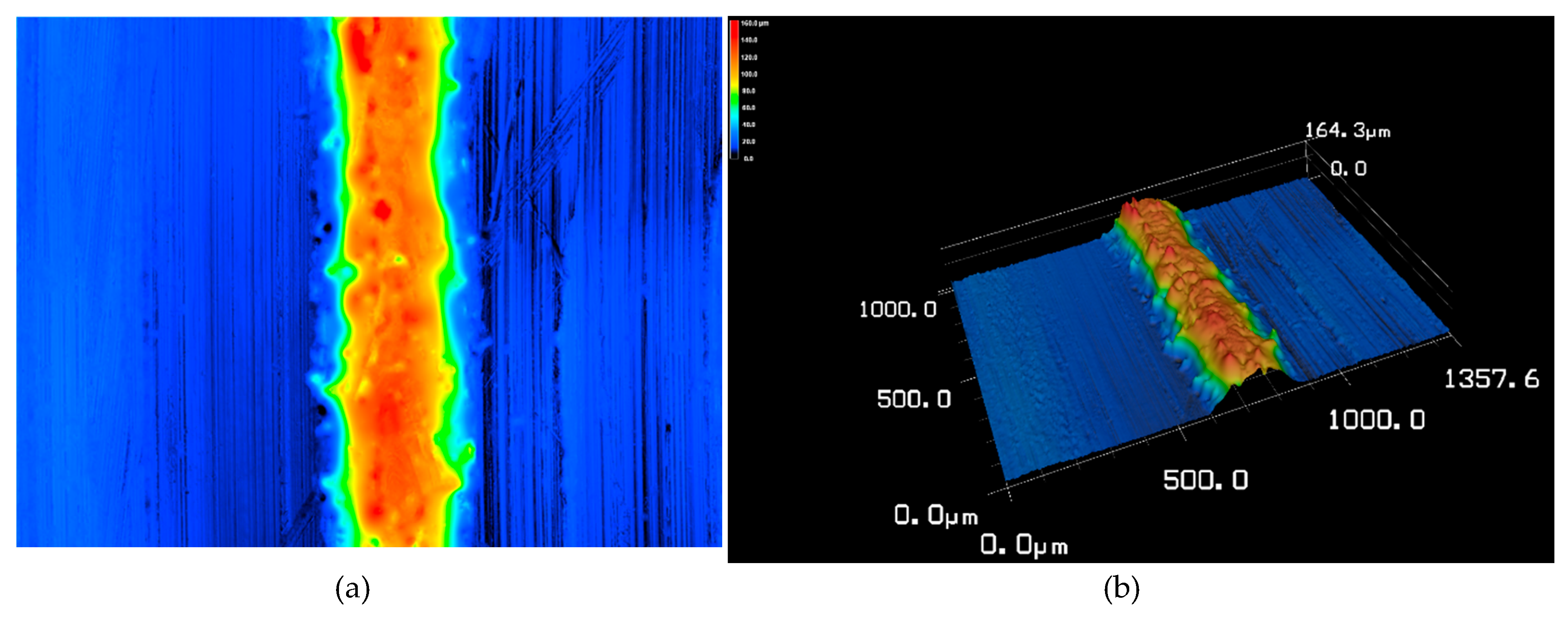
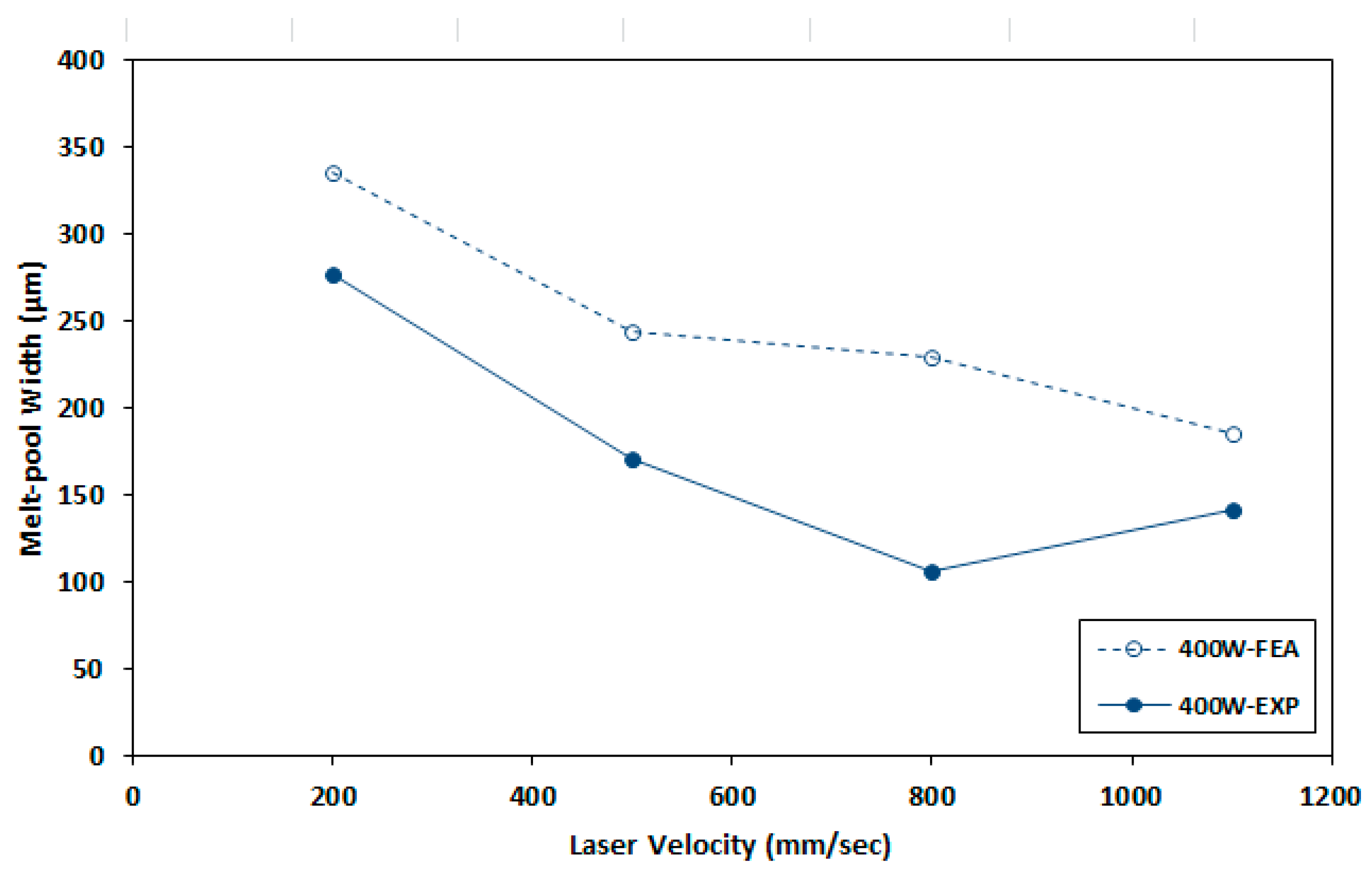
2.4. Experimental Data to Verify Reference FEA Model
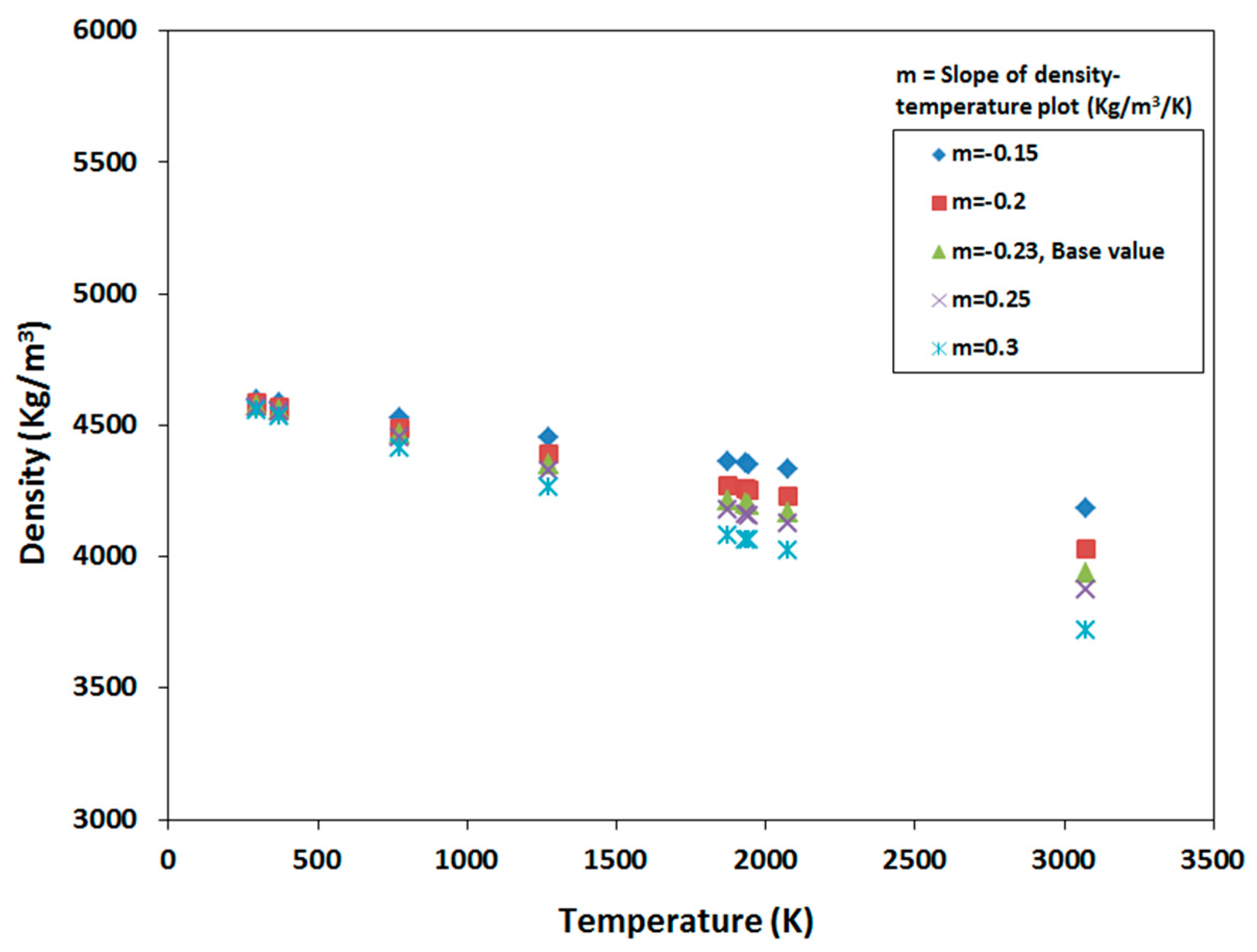
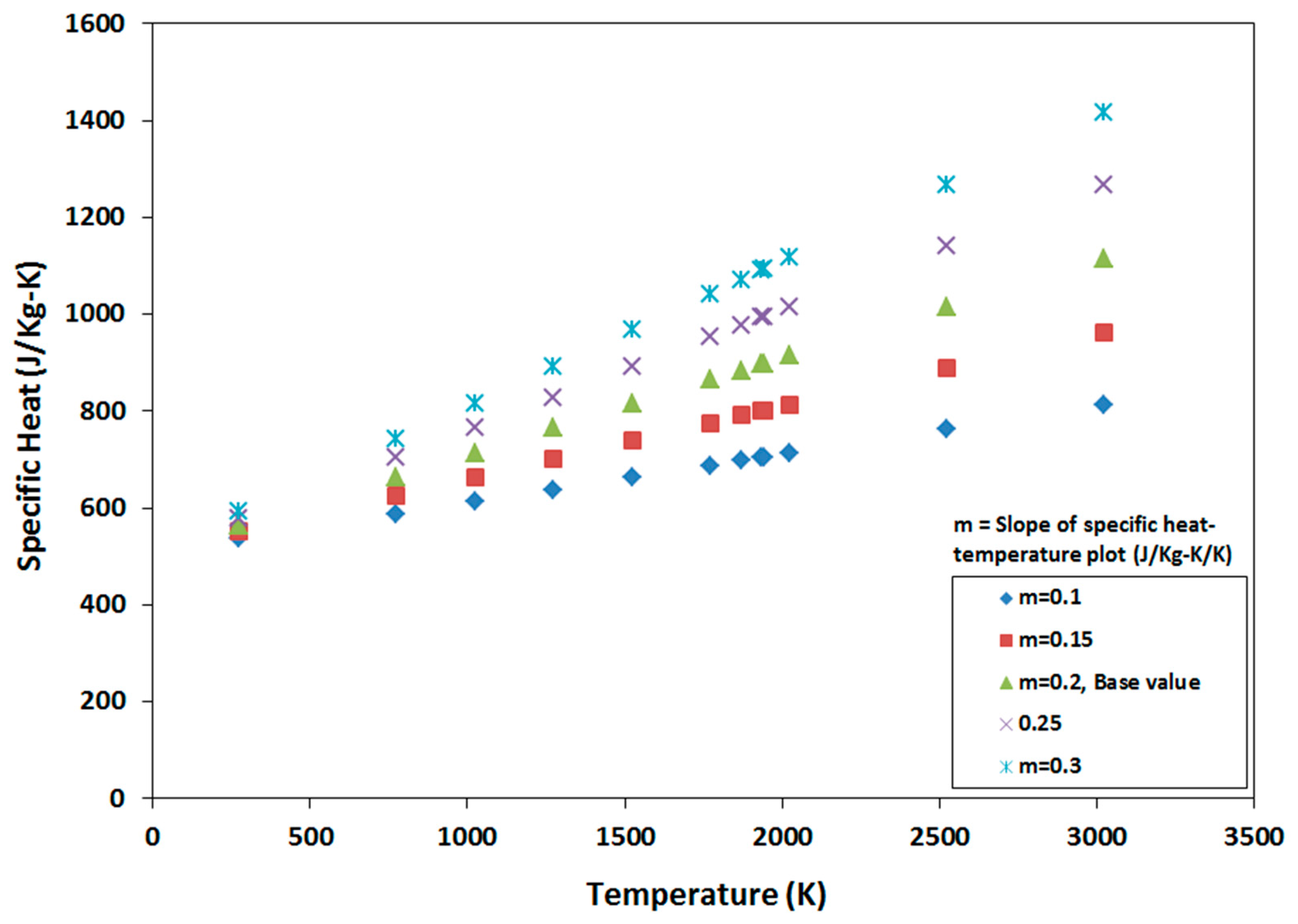
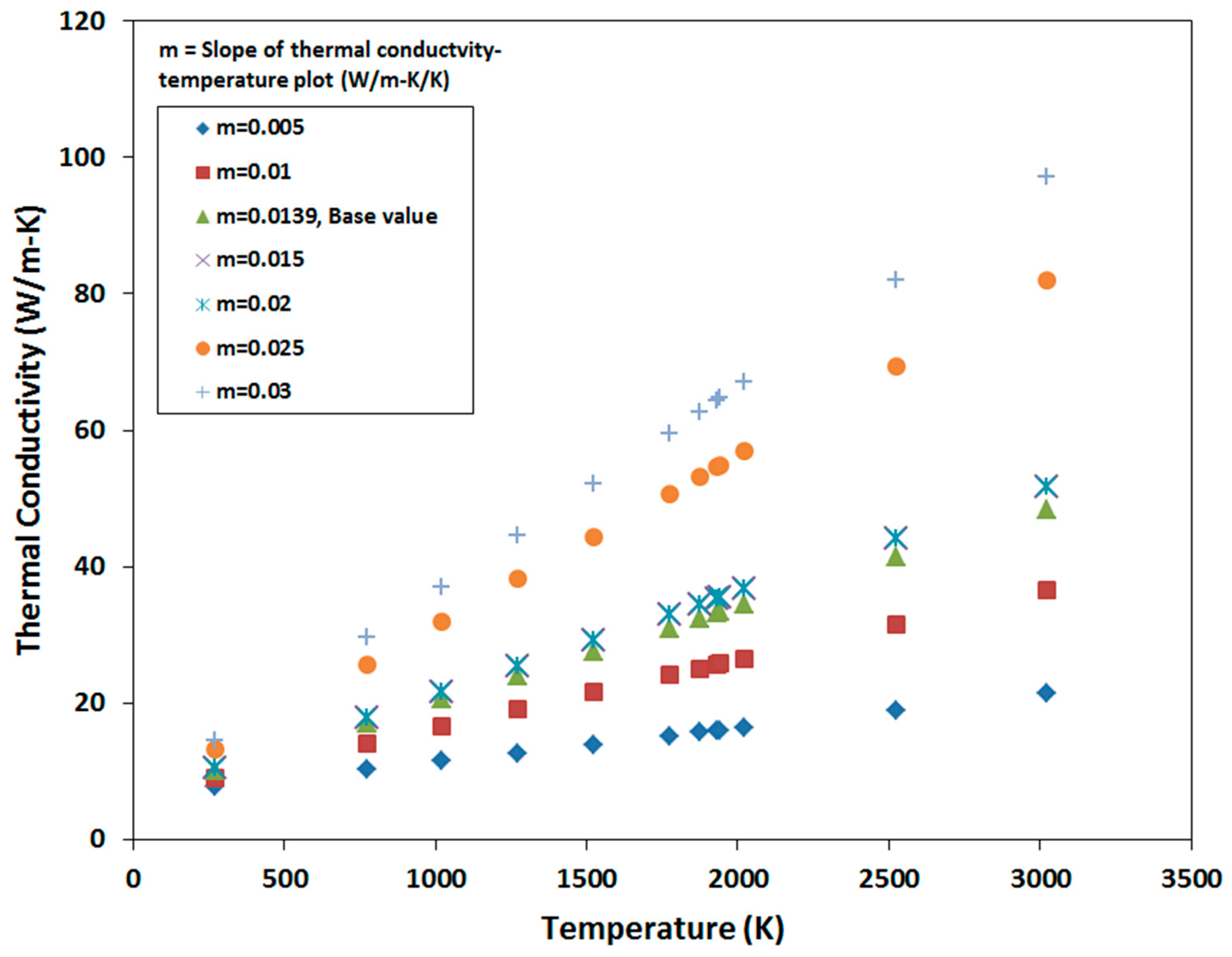
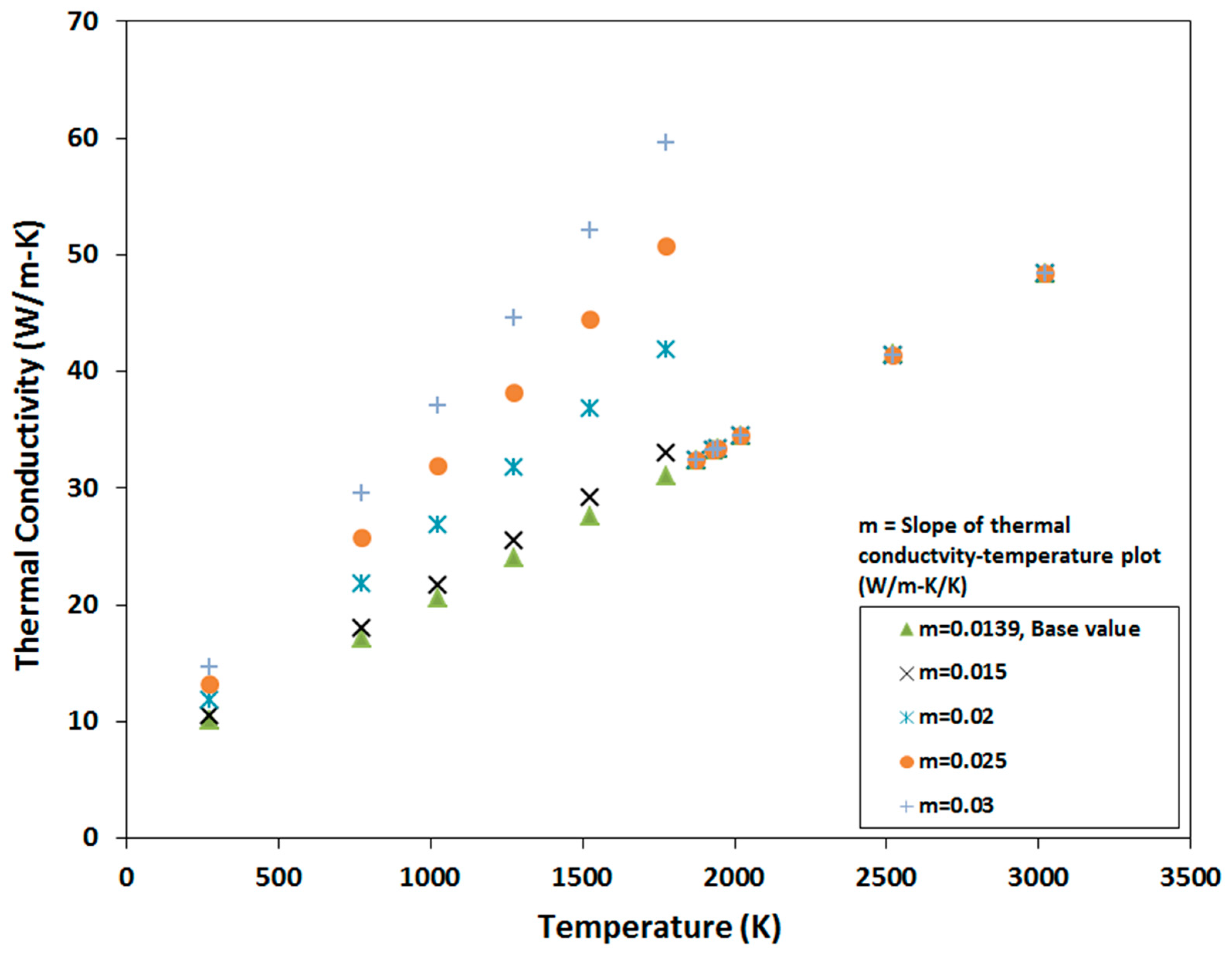
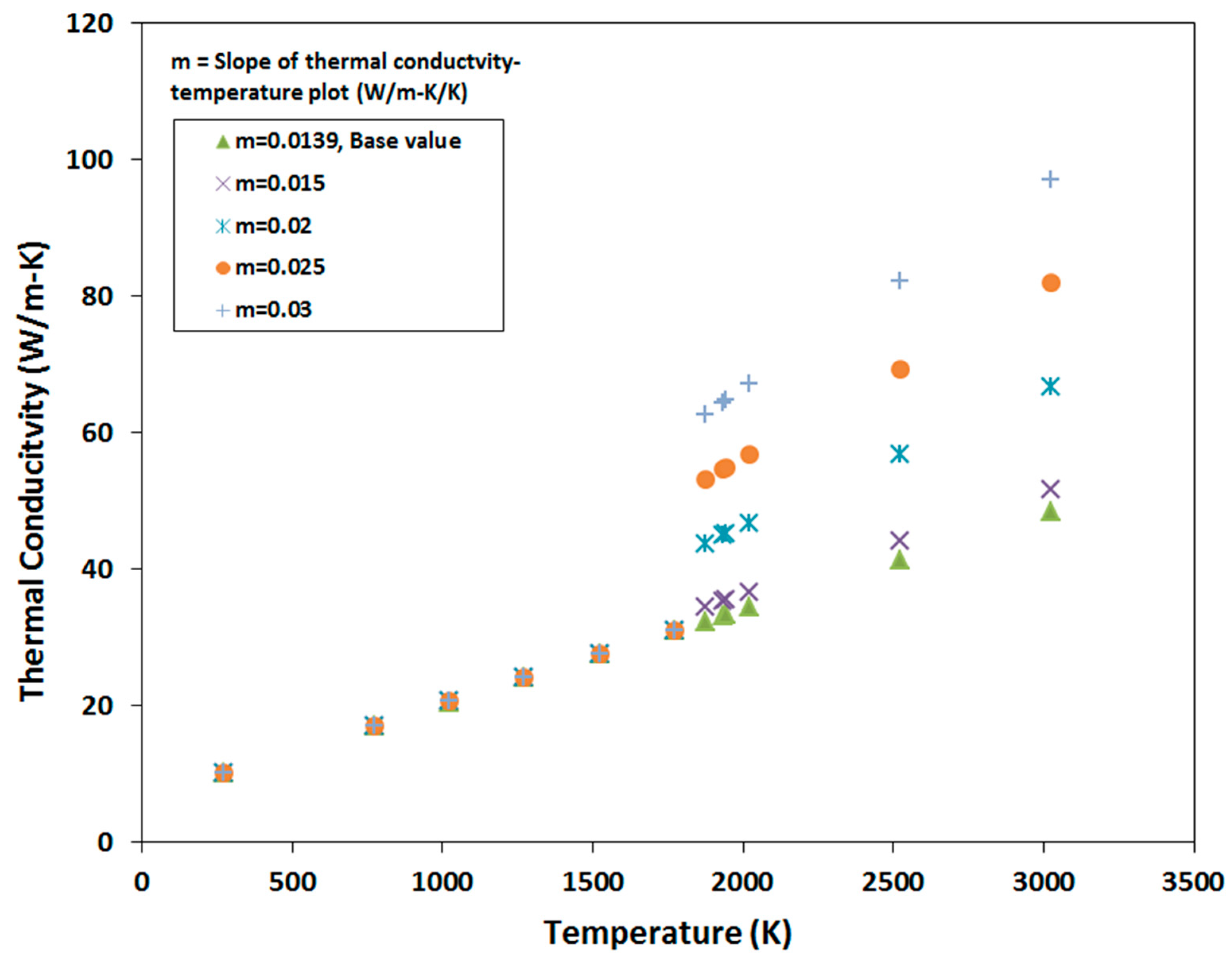
3. Variation in Material Properties
4. Results and Discussion
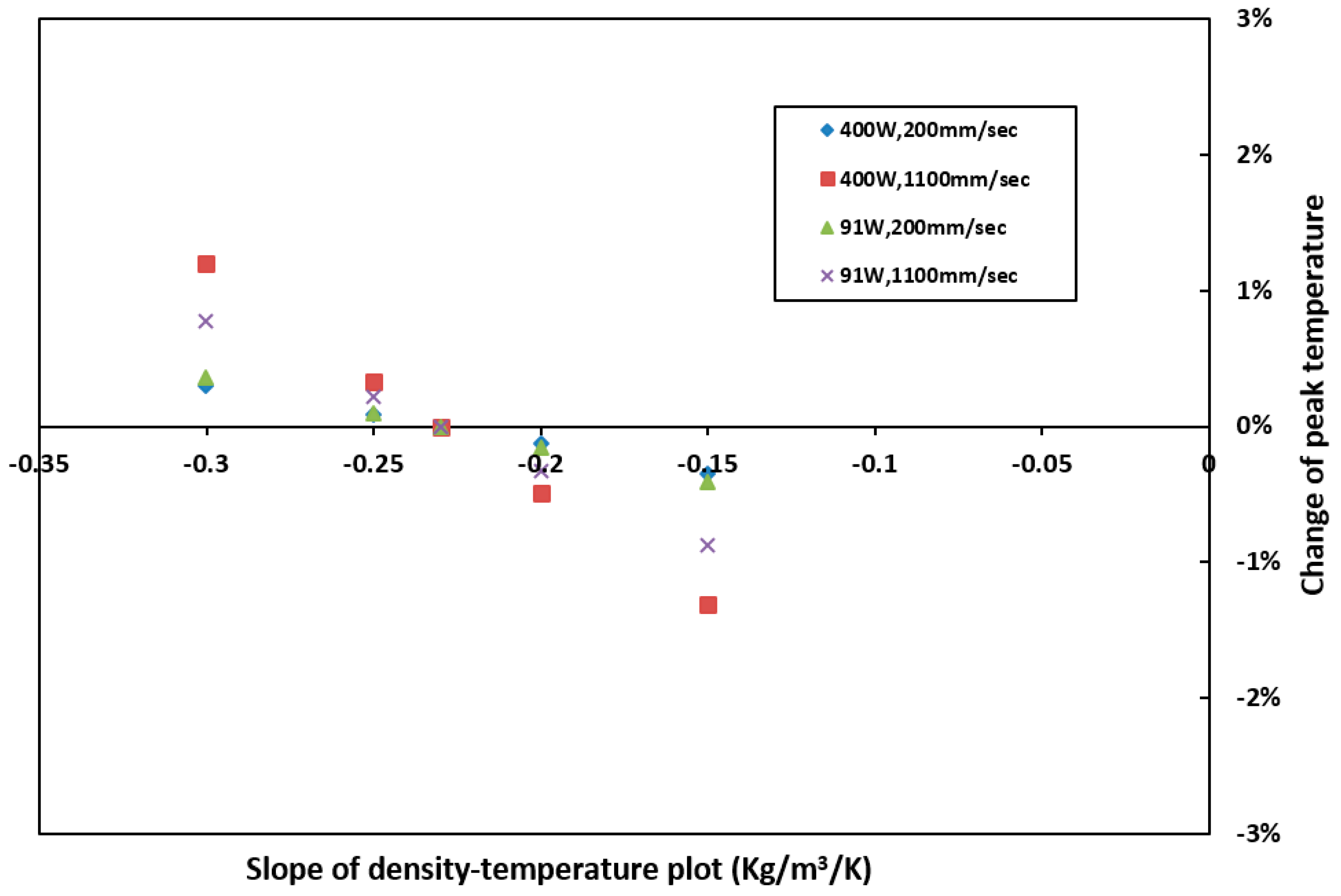
4.1. Sensitivity to Density
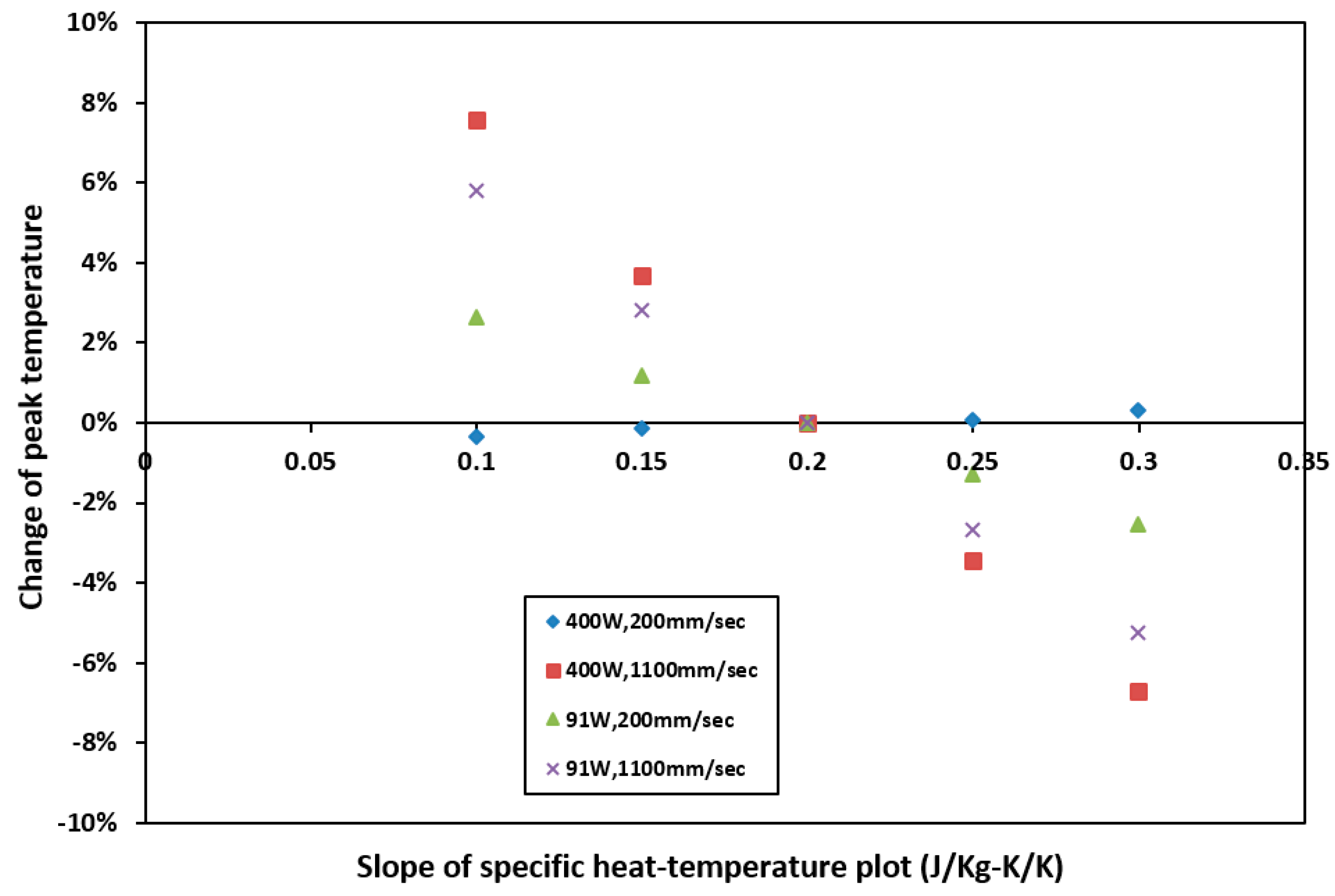
4.2. Sensitivity to Specific Heat
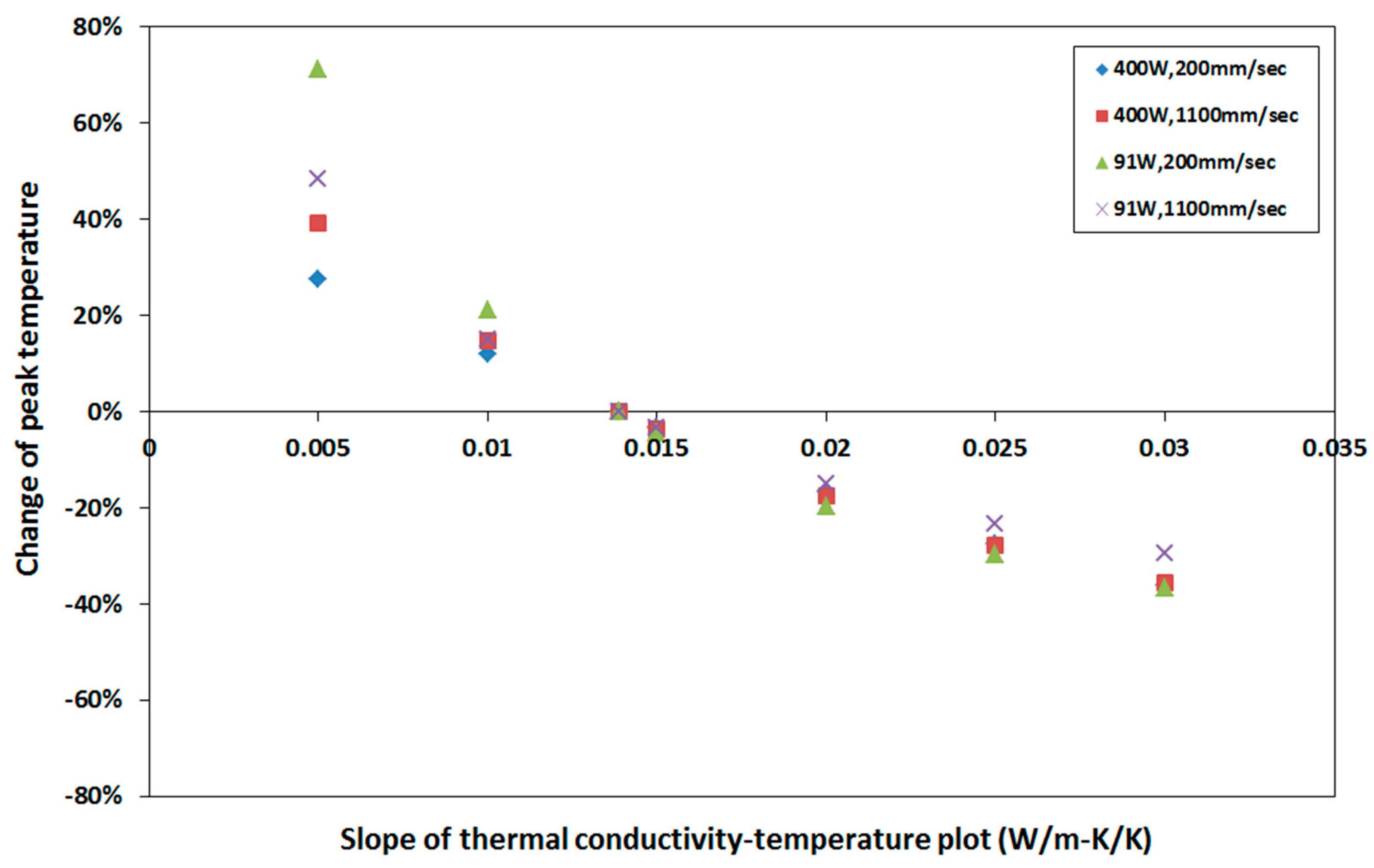
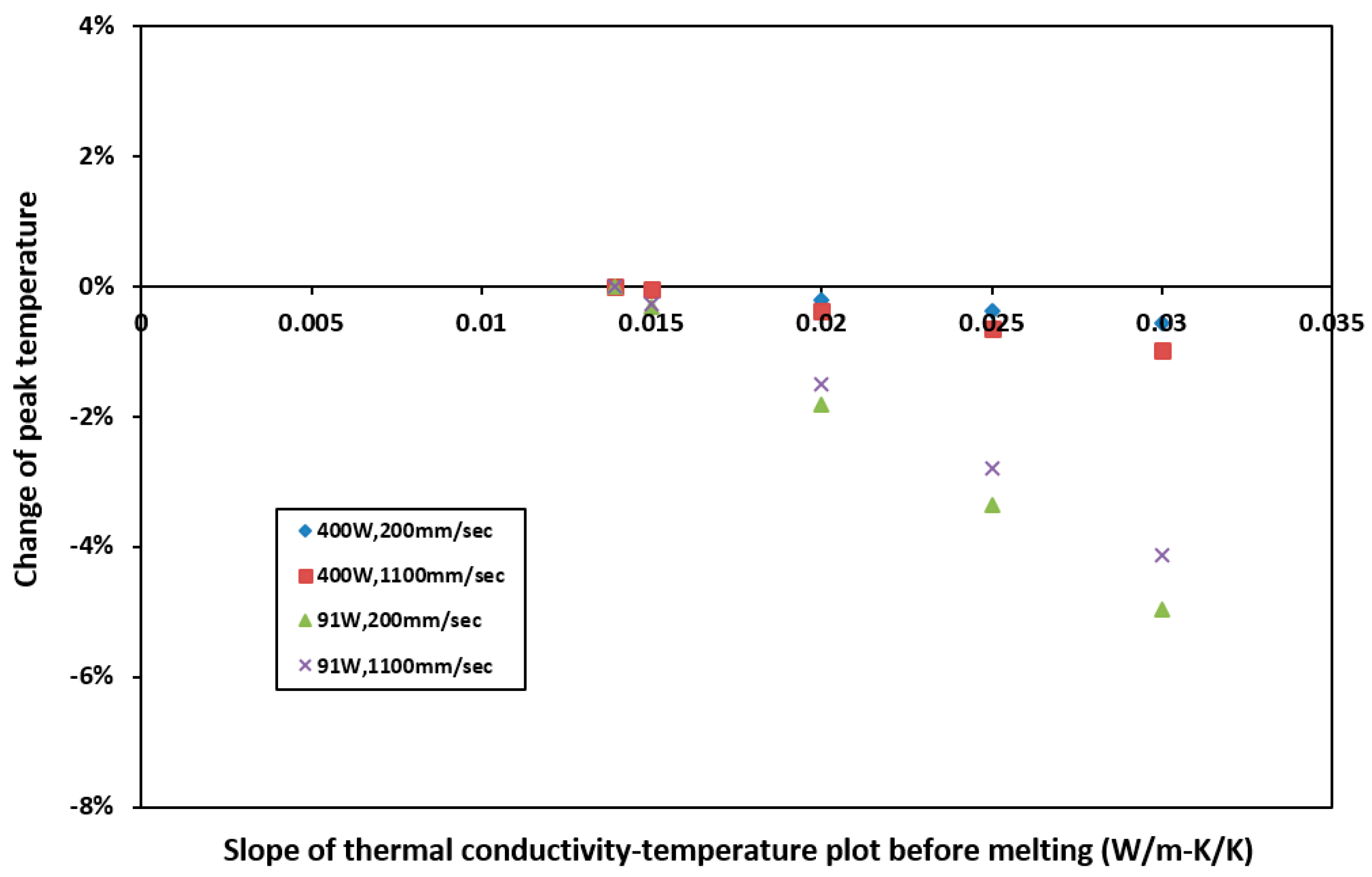
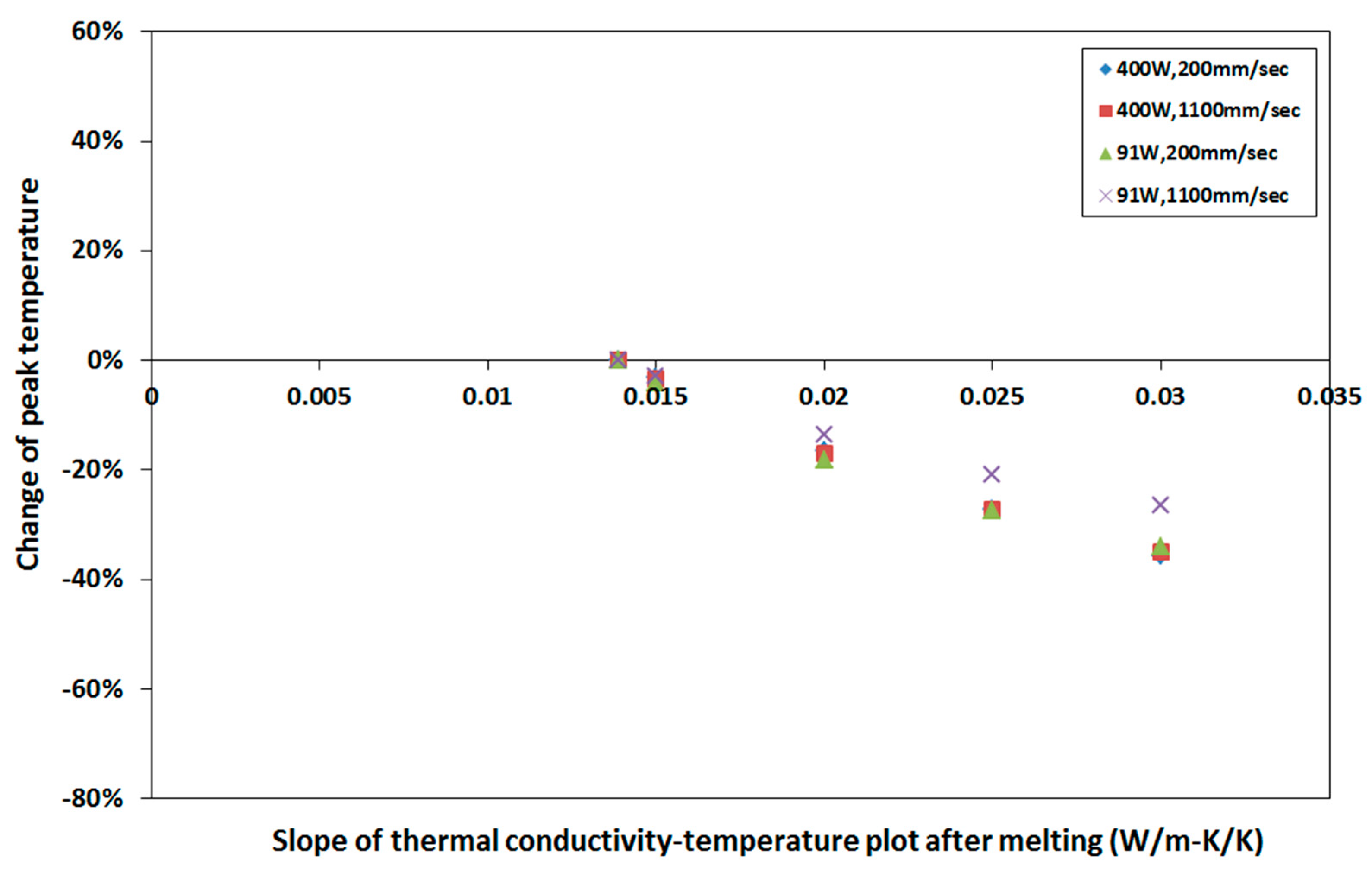
4.3. Sensitivity to Thermal Conductivity
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nickels, L. 3D printing the world’s first metal bicycle frame. Met. Powder Rep. 2014, 69, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, B.P.; Manogharan, G.P.; Martof, A.N.; Rodomsky, L.M.; Rodomsky, C.M.; Jordan, D.C.; Limperos, J.W. Making sense of 3-D printing: Creating a map of additive manufacturing products and services. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 1–4, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Krakhmalev, P.; Yadroitsava, I. Selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V alloy for biomedical applications: Temperature monitoring and microstructural evolution. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertol, L.S.; Júnior, W.K.; da Silva, F.P.; Aumund-Kopp, C. Medical design: Direct metal laser sintering of Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3982–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewellery and Watches—DMLS for Individual Specimens and Serial Production. EOS. Available online: http://www.eos.info/industries_markets/lifestyle_products/jewellery_watches (accessed on 9 September 2016).
- Galba, M.; Reischle, T. Additive manufacturing of metals using powder-based technology. In Additive Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 97–142. [Google Scholar]
- Srivatsan, T.S.; Sudarshan, T.S. (Eds.) Additive Manufacturing: Innovations, Advances, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bontha, S.; Klingbeil, N.W.; Kobryn, P.A.; Fraser, H.L. Effects of process variables and size-scale on solidification microstructure in beam-based fabrication of bulky 3D structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 513–514, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontha, S.; Klingbeil, N.W.; Kobryn, P.A.; Fraser, H.L. Thermal process maps for predicting solidification microstructure in laser fabrication of thin-wall structures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 178, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Gu, D.; Xia, M.; Cao, S.; Rong, T. Effects of laser processing parameters on thermal behavior and melting/solidification mechanism during selective laser melting of TiC/Inconel 718 composites. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 84, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.E.; Anderson, A.T.; Ferencz, R.M.; Hodge, N.E.; Kamath, C.; Khairallah, S.A.; Rubenchik, A.M. Laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing of metals; physics, computational, and materials challenges. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.H.; Guo, Y.B. Three-Dimensional temperature gradient mechanism in selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 061004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaeghe, F.; Craeghs, T.; Heulens, J.; Pandelaers, L. A pragmatic model for selective laser melting with evaporation. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 6006–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; Mortello, M.; Peyre, P. FEM analysis of fiber laser welding of titanium and aluminum. Procedia CIRP 2016, 41, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, X.; Shu, L.; Li, X. Optimization of laser welding process parameters of stainless steel 316L using FEM, Kriging and NSGA-II. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 99, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanth, K.G.; Damodaram, R.; Scudino, S.; Wang, Z.; Prasad Rao, K.; Eckert, J. Friction welding of Al–12Si parts produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wits, W.W.; Becker, J.M.J. Laser beam welding of titanium additive manufactured parts. Procedia CIRP 2015, 28, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolossov, S.; Boillat, E.; Glardon, R.; Fischer, P.; Locher, M. 3D FE simulation for temperature evolution in the selective laser sintering process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Hao, L.; Yan, C.; Everson, R. Finite element simulation of the temperature and stress fields in single layers built without-support in selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Makradi, A.; Ahzi, S.; Remond, Y. Three-dimensional transient finite element analysis of the selective laser sintering process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Mian, A.; Amin, M.; Auner, G.; Witte, R.; Herfurth, H.; Newaz, G. Finite Element Modeling of Transmission Laser Microjoining Process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 186, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C.; Feshbach, H. Conduction of heat in solids. Phys. Today 1962, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS/CAE. 2017. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/simulia/ (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- Shi, Y.; Shen, H.; Yao, Z.; Hu, J. Temperature gradient mechanism in laser forming of thin plates. Opt. Laser Technol. 2007, 39, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, J.; Ladani, L.; Razmi, J.; Sadowski, M. Temperature distribution and melt geometry in laser and electron-beam melting processes—A comparison among common materials. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E. Rules of Thumb for Mechanical Engineers: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Mechanical Engineering Problems; Gulf Pub.: Houston, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.C. Recommended Values of Thermophysical Properties for Selected Commercial Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA; Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Boivineau, M.; Cagran, C.; Doytier, D.; Eyraud, V.; Nadal, M.; Wilthan, B.; Pottlacher, G. Thermophysical properties of solid and liquid Ti-6Al-4V (TA6V) alloy. Int. J. Thermophys. 2006, 27, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, C.; Ahmed, S.; Mian, A.; Srinivasan, R. Effect of Laser Power and Scan Speed on Melt Pool Characteristics of Commercially Pure Titanium (CP-Ti). J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 3560–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Initial Temperature | 298 K |
|---|---|
| Convection | - |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient | 20 W/m2-K |
| Ambient temperature | 298 K |
| Radiation | - |
| Emissivity | 0.35 |
| Element | C | O | N | H | Fe | Al | V | Cu | Sn | Y | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % wt | 0.02 | 0.14–0.17 | 0.02 | 0.013 | 0.05–0.25 | 5.50–6.75 | 3.5–4.5 | <0.10 | <0.10 | <0.005 | Balance |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.H.; Mian, A. Influence of Material Property Variation on Computationally Calculated Melt Pool Temperature during Laser Melting Process. Metals 2019, 9, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040456
Ahmed SH, Mian A. Influence of Material Property Variation on Computationally Calculated Melt Pool Temperature during Laser Melting Process. Metals. 2019; 9(4):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040456
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Sazzad H., and Ahsan Mian. 2019. "Influence of Material Property Variation on Computationally Calculated Melt Pool Temperature during Laser Melting Process" Metals 9, no. 4: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040456
APA StyleAhmed, S. H., & Mian, A. (2019). Influence of Material Property Variation on Computationally Calculated Melt Pool Temperature during Laser Melting Process. Metals, 9(4), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9040456





