Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloy Combinations: State-of-the-Art
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Progress in FSW of Dissimilar Al-Al Combinations
Summary of Published Works
3. Welding Parameters
3.1. Positioning of Alloy
3.2. Tool Rotation and Welding Speeds
3.3. Tool Geometry
4. Microstructure Evolution
5. Mechanical Properties
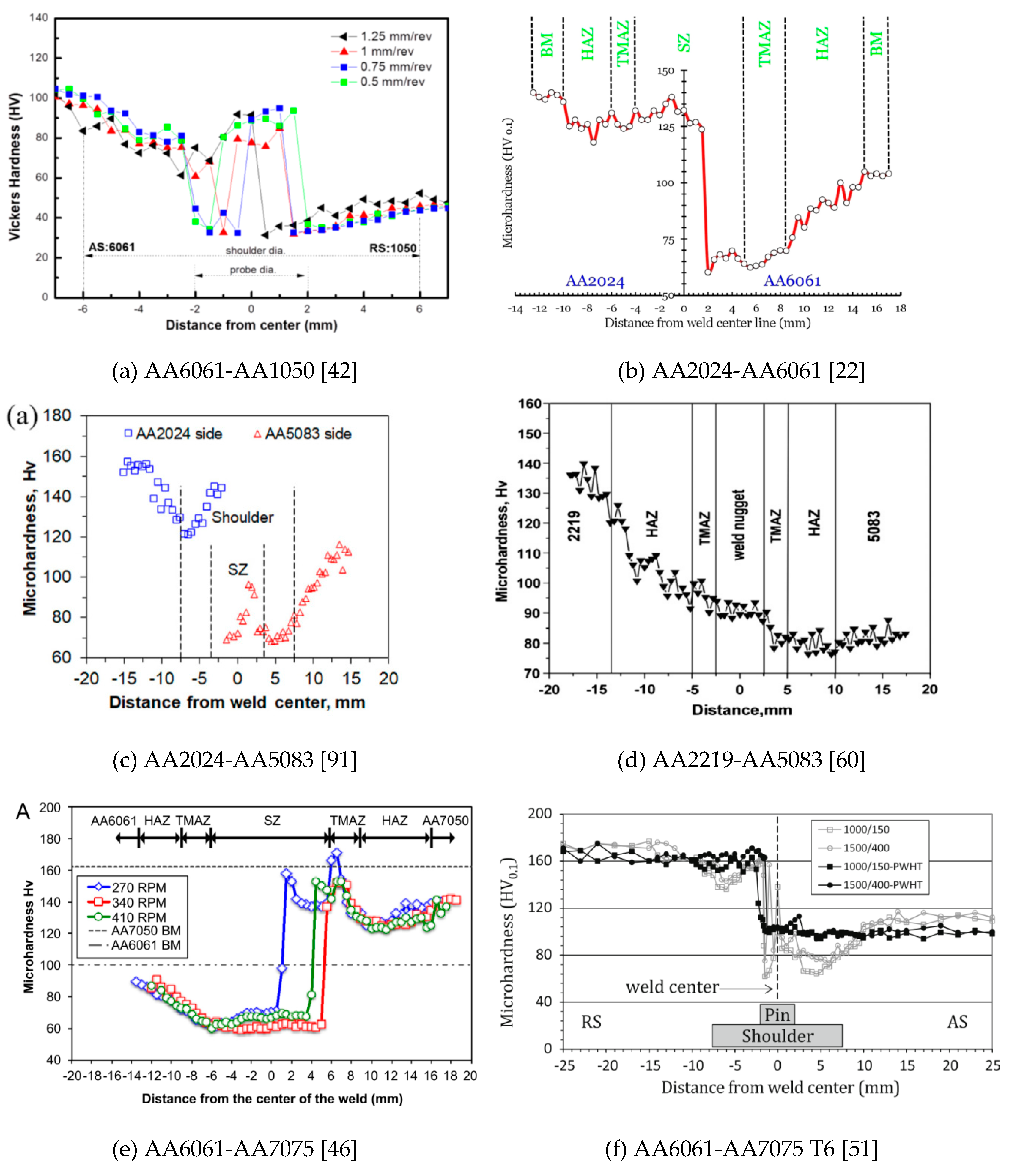
5.1. Hardness
5.2. Tensile Strength
6. Summary and Outlook
6.1. Al Alloy Combinations
6.2. Base Metal Placement
6.3. Tool Offset
6.4. Bobbing Tool and Stationary shoulder Tool
6.5. Corrosion and Fatigue Behavior
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, W.M.; Nicholas, E.D.; Needham, J.C.; Murch, M.G.; Temple-Smith, P.; Dawes, C.J. Friction Stir Butt Welding. International Patent Application No. PCT/GB92/02203; GB Patent Application No. 9125978.8; U.S. Patent Application No. 5,460,317, 6 December 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.; Ma, Z.; Mishra, R. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y.; Feng, A.H.; Chen, D.L.; Shen, J. Recent Advances in Friction Stir Welding/Processing of Aluminum Alloys: Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 43, 269–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.; Lammlein, D.; Prater, T.; Longhurst, W.; Cox, C.; Ballun, M.; Dharmaraj, K.; Cook, G.; Strauss, A.; Gibson, B. Friction stir welding: Process, automation, and control. J. Manuf. Processes 2014, 16, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Debroy, T.; Bhadeshia, H. Recent advances in friction-stir welding—Process, weldment structure and properties. Prog. Mater Sci. 2008, 53, 980–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhy, G.; Wu, C.; Gao, S. Friction stir based welding and processing technologies - processes, parameters, microstructures and applications: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.H.; Badheka, V.J. Friction stir welding of aluminium alloys: An overview of experimental findings—Process, variables, development and applications. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L: J. Mater. Des. Applic. 2017, 6, 1464420716689588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.A.; Khan, Z.A.; Siddiquee, A.N. Review on underwater friction stir welding: A variant of friction stir welding with great potential of improving joint properties. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherillo, F.; Curioni, M.; Aprea, P.; Impero, F.; Squillace, A.; Zhou, X. Study of the Linear Friction Welding Process of Dissimilar Ti-6Al-4V–Stainless Steel Joints AU - Astarita, Antonello. Materials and Manufacturing Processes 2016, 31, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, R.; Armentani, E.; di Lascio, P.; Citarella, R. Crack Growth Behavior of Welded Stiffened Panel. Procedia Engineering 2015, 109, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, A.; Prisco, U.; Squillace, A.; Villano, P.; Scherillo, F.; Coticelli, F. Theoretical analysis of a friction stir welded panel in comparison with the baseline version. Weld. Cutt. 2016, 15, 238–240. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, V.M.; Leitão, C.; Rodrigues, D.M. Friction stir welding industrialisation and research status. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 2017, 23, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Li, W.; Chen, D. Strain hardening behavior and mechanisms of friction stir welded dissimilar joints of aluminum alloys. Mater. Lett. 2018, 231, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Ishak, M.; Rejab, M.R.M. Effect of pin tool flute radius on the material flow and tensile properties of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2747–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Gao, S.; Ji, S.; Yan, D. Effect of pin length and welding speed on lap joint quality of friction stir welded dissimilar aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemba-Rec, I.; Kopyściański, M.; Miara, D.; Krasnowski, K. Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar 7075-T651 and 5083-H111 aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 2767–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarbali, B.; Shamanian, M.; Eslami, A. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on joint properties of dissimilar friction stir welded 2024-T4 and 7075-T6 aluminum alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Laubscher, R.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Dinaharan, I. Prediction and optimization of the mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welding of aluminum alloys using design of experiments. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 232, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.; Dymek, S.; Kopyściański, M.; Węglowska, A.; Pietras, A. Numerically Based Phase Transformation Maps for Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys Joined by Friction Stir-Welding. Metals 2018, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Pandey, K.; Kumar, R. Multi-objective optimization of friction stir welding process parameters for joining of dissimilar AA5083/AA6063 aluminum alloys using hybrid approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2016, 232, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.W.; Qin, Q.D.; Zhang, D.H.; Wu, Y.J.; Su, X.D. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Joints of Al-Mg2Si and 5052 Aluminum Alloy by Friction Stir Welding. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.M.; Aval, H.J.; Jamaati, R.; Amirkhanlou, S.; Ji, S. Microstructure and texture evolution of friction stir welded dissimilar aluminum alloys: AA2024 and AA6061. J. Manuf. Processes 2018, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, R.S.S.; Raj, K.H. Determination of Optimal Process Parameters of Friction Stir Welding to Join Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys Using Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 71, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, S.; Akinlabi, E. Effect of processing parameters on microhardness and microstructure of a double-sided dissimilar friction stir welded aa6082-t6 and aa7075-t6 aluminum alloy. Mater. Today: Proc. 2018, 5, 18315–18324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, S.; Akinlabi, E.; Kailas, S.; Brandi, S. Microstructural properties of a dissimilar friction stir welded thick aluminum aa6082-t6 and aa7075-t6 alloy. Mater. Today: Proc. 2018, 5, 18297–18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Jiang, W.; Huan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, T. Nanoindentation Hardness Distribution and Strain Field and Fracture Evolution in Dissimilar Friction Stir-Welded AA 6061-AA 5A06 Aluminum Alloy Joints. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Toppo, V. Effect of Tool Rotational Speed on Temperature and Impact Strength of Friction Stir Welded Joint of Two Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys. Mater. Today: Proc. 2018, 5, 6170–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsılmaz, F. Relationship between micro-structure and mechanical properties of dissimilar aluminum alloy plates by friction stir welding. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, K.; Yoo, J.-T.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, H.-S. Effect of Process Parameters on Friction Stir Welds on AA2219-AA2195 Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys. Korean J. Mater. Res. 2017, 27, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.; Dymek, S.; Dryzek, E.; Kopyściański, M.; Pietras, A.; Węglowska, A.; Wróbel, M. Application of positron lifetime annihilation spectroscopy for characterization of friction stir welded dissimilar aluminum alloys. Mater. Charact. 2017, 132, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopyściański, M.; Dymek, S.; Hamilton, C.; Weglowska, A.; Pietras, A.; Szczepanek, M.; Wojnarowska, M. Microstructure of Friction Stir Welded Dissimilar Wrought 2017A and Cast AlSi9Mg Aluminum Alloys. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpour, M.; Kazemi, M.; Sefat, M.J.M.; Aziz, A.; Dehghani, K. Evaluation of dissimilar joints properties of 5083-H12 and 6061-T6 aluminum alloys produced by tungsten inert gas and friction stir welding. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2015, 231, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijanrostami, K.; Barenji, R.V.; Hashemipour, M. Effect of Traverse and Rotational Speeds on the Tensile Behavior of the Underwater Dissimilar Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasman, S.; Kahraman, F.; Emiralioğlu, A. A Case Study for the Welding of Dissimilar EN AW 6082 and EN AW 5083 Aluminum Alloys by Friction Stir Welding. Metals 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Laubscher, R.F.; Dinaharan, I.; Murugan, N. Developing a Friction-Stir Welding Window for Joining the Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys AA6351 and AA5083. Mater. Technol. 2017, 51, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, J.K.; Kore, S.D. A Study on Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Thin Sheets of Aluminum Alloys AA 5052–AA 6061. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2016, 138, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, V.; Rajakumar, S.; Banerjee, N.; Amuthakkannan, R. Effect of shoulder diameter to pin diameter ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welded AA2024-T6 and AA7075-T6 aluminum alloy joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 3637–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Fang, H. Effect of Sheet Configuration on Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of Dissimilar Al–Mg–Si/Al–Zn–Mg Aluminum Alloys Friction Stir Welding Joints. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.-J.; Liu, X.-S.; Fang, H.-Y. Fatigue Behavior of Dissimilar Al–Mg–Si/Al–Zn–Mg Aluminum Alloys Friction Stir Welding Joints. Acta Metall. Sinica 2016, 29, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.; Kopyściański, M.; Węglowska, A.; Dymek, S.; Pietras, A. A Numerical Simulation for Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys Joined by Friction Stir Welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 4519–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, J.; Toro, M.; López, D. Residual stresses in friction stir dissimilar welding of aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 229, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tsuji, N.; Fujii, H. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Friction Stir Welding between Ultrafine Grained 1050 and 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloys. Metals 2016, 6, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texier, D.; Zedan, Y.; Amoros, T.; Feulvarch, E.; Stinville, J.; Bocher, P. Near-surface mechanical heterogeneities in a dissimilar aluminum alloys friction stir welded joint. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Jordon, J.; Allison, P.; Rushing, T.; Garcia, L. Low-cycle fatigue of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 654, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.-J.; Yun, J.-G.; Kang, C.-Y. Formation mechanism of typical onion ring structures and void defects in friction stir lap welded dissimilar aluminum alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Jordon, J.; Allison, P.; Rushing, T.; Garcia, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welding of 6061-to-7050 aluminum alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilangovan, M.; Boopathy, S.R.; Balasubramanian, V. Effect of tool pin profile on microstructure and tensile properties of friction stir welded dissimilar AA 6061–AA 5086 aluminium alloy joints. Defence Technol. 2015, 11, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza-E-Rabby, M.; Tang, W.; Reynolds, A.P. Effect of tool pin features on process response variables during friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 2015, 20, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatus, U.; Thompson, G.E.; Zhou, X. Anodizing Behavior of Friction Stir Welded Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, C657–C665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, A.; Mahmoud, T.S.; Zakaria, H.M.; Khalifa, T.A. Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar A319 and A413 Cast Aluminum Alloys. Arab J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 6363–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipekoğlu, G.; Çam, G. Effects of Initial Temper Condition and Postweld Heat Treatment on the Properties of Dissimilar Friction-Stir-Welded Joints between AA7075 and AA6061 Aluminum Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 3074–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, E.G.; Fehrenbacher, A.; Duffie, N.A.; Zinn, M.R.; Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Ferrier, N.J. Weld temperature effects during friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys 6061-t6 and 7075-t6. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 71, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, X.; Cui, L.; Hou, X.; Shen, Z.; Xu, Y. Defect features and mechanical properties of friction stir lap welded dissimilar AA2024–AA7075 aluminum alloy sheets. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannet, S.; Mathews, P.K. Effect of Welding Parameters on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloy Joints Produced by Friction Stir Welding. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 592, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Mathews, P.K.; Dinaharan, I.; Murugan, N. Mechanical and metallurgical properties of dissimilar friction stir welded AA5083-H111 and AA6351-T6 aluminum alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonckheere, C.; De Meester, B.; Denquin, A.; Simar, A. Torque, temperature and hardening precipitation evolution in dissimilar friction stir welds between 6061-T6 and 2014-T6 aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Mathews, P.K.; Murugan, N. Optimization of process parameters to maximize ultimate tensile strength of friction stir welded dissimilar aluminum alloys using response surface methodology. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Husain, M.M.; Kumar, K.; Kailas, S.V. Friction Stir-Welded Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Physical State. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 3890–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velotti, C.; Squillace, A.; Villano, M.G.; Prisco, U.; Montuori, M.; Giorleo, G.; Astarita, A.; Ciliberto, S.; Giuliani, M.; Bellucci, F. On the critical technological issues of friction stir welding lap joints of dissimilar aluminum alloys. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koilraj, M.; Sundareswaran, V.; Vijayan, S.; Rao, S.K. Friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys AA2219 to AA5083 – Optimization of process parameters using Taguchi technique. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinaharan, I.; Kalaiselvan, K.; Vijay, S.; Raja, P.; J, V.S. Effect of material location and tool rotational speed on microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2012, 12, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Mathews, P.K.; Murugan, N.; Dinaharan, I. Effect of tool rotational speed and pin profile on microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar friction stir welded AA5083-H111 and AA6351-T6 aluminum alloys. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, B.-C.; Yoon, T.-J.; Kim, N.-K.; Kim, I.-B.; Kang, C.-Y. Liquation Cracking of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys during Friction Stir Welding. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Kumar, K.; Kailas, S.; Ray, A. Optimization of friction stir welding parameters for dissimilar aluminum alloys. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3033–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-K.; Kim, B.-C.; An, Y.-G.; Jung, B.-H.; Song, S.-W.; Kang, C.-Y. The effect of material arrangement on mechanical properties in Friction Stir Welded dissimilar A5052/A5J32 aluminum alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2009, 15, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime, M.; Gnaupel-Herold, T.; Baumann, J.; Lederich, R.; Bowden, D.; Sebring, R. Residual stress measurements in a thick, dissimilar aluminum alloy friction stir weld. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 4013–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.P.; Nelson, T.W.; Melton, D.W. Formability of friction-stir-welded dissimilar-aluminum-alloy sheets. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 3335–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.H.; Kovacevic, R. Material flow and microstructure in the friction stir butt welds of the same and dissimilar aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2002, 11, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbini, A.; Carstensen, J.; Dos Santos, J. Influence of Alloys Position, Rolling and Welding Directions on Properties of AA2024/AA7050 Dissimilar Butt Weld Obtained by Friction Stir Welding. Metals 2018, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; De Santis, A.; Panella, F.; Squillace, A. Effect of welding parameters on mechanical and microstructural properties of dissimilar AA6082-AA2024 joints produced by friction stir welding. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Xu, Y.; Chen, D. Exfoliation corrosion of friction stir welded dissimilar 2024-to-7075 aluminum alloys. Mater. Charact. 2019, 147, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Badheka, V.J. Process parameters/material location affecting hooking in friction stir lap welding: Dissimilar aluminum alloys. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Badheka, V.J. Effect of friction stir lap weld and post weld heat treatment on corrosion behavior of dissimilar aluminum alloys. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2017, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Badheka, V. Influence of Heat Input/Multiple Passes and Post Weld Heat Treatment on Strength/Electrochemical Characteristics of Friction Stir Weld Joint. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 33, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastanaiah, P.; Sharma, A.; Reddy, G.M. Dissimilar Friction Stir Welds in AA2219-AA5083 Aluminium Alloys: Effect of Process Parameters on Material Inter-Mixing, Defect Formation, and Mechanical Properties. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 69, 1397–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasman, Ş.; Yenier, Z. Analyzing dissimilar friction stir welding of AA5754/AA7075. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 70, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcellese, A.; Simoncini, M.; Casalino, G. Influence of Process Parameters on the Vertical Forces Generated during Friction Stir Welding of AA6082-T6 and on the Mechanical Properties of the Joints. Metals 2017, 7, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, M.; Manafi, B.; Givi, M.B.; Faraji, G. Mathematical modeling and optimization of friction stir welding process parameters in AA5083 and AA7075 aluminum alloy joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 230, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yu, T.; Wu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. A Finite Element Model to Simulate Defect Formation during Friction Stir Welding. Metals 2017, 7, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godhani, P.S.; Patel, V.V.; Vora, J.J.; Chaudhary, N.D.; Banka, R. Effect of Friction Stir Welding of Aluminum Alloys AA6061/AA7075: Temperature Measurement, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. In Innovations in Infrastructure; Springer: Singapore, Singapore, 2019; pp. 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Xia, J. Influences of Pin Shape on a High Rotation Speed Friction Stir Welding Joint of a 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy Sheet. Metals 2018, 8, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, P.; Siddiquee, A.; Khan, N.; Hussain, M.; Khan, Z.; Abidi, M.; Al-Ahmari, A. Investigation on the Effect of Tool Pin Profiles on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Friction Stir Butt and Scarf Welded Aluminium Alloy 6063. Metals 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.V.; Badheka, V.; Kumar, A. Friction Stir Processing as a Novel Technique to Achieve Superplasticity in Aluminum Alloys: Process Variables, Variants, and Applications. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2016, 5, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.V.; Badheka, V.; Kumar, A. Effect of polygonal pin profiles on friction stir processed superplasticity of AA7075 alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 240, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.V.; Badheka, V.J.; Kumar, A. Influence of Pin Profile on the Tool Plunge Stage in Friction Stir Processing of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu Alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2016, 70, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.V.; Li, W.Y.; Vairis, A.; Badheka, V.J. Recent Development in Friction Stir Processing as a Solid-State Grain Refinement Technique: Microstructural Evolution and Property Enhancement. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialami, N.; Cervera, M.; Chiumenti, M. Numerical Modelling of Microstructure Evolution in Friction Stir Welding (FSW). Metals 2018, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Obikawa, T.; Nishizaki, I.; Enomoto, M.; Fang, Z. Friction Stir Welding of Non-Heat-Treatable High-Strength Alloy 5083-O. Metals 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.A.; Zolkarnain, L.; Rahim, M.A.Z.B.A.; Fadaeifard, F.; Matori, K.A. Effect of the Welding Speed on the Macrostructure, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA6061-T6 Friction Stir Butt Welds. Metals 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.V.; Badheka, V.; Kumar, A. Influence of Friction Stir Processed Parameters on Superplasticity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Li, W.; Vairis, A.; Chen, D. Cyclic deformation behavior of friction-stir-welded dissimilar AA5083-to-AA2024 joints: Effect of microstructure and loading history. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 744, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamadon, A.; Pons, D.J.; Sued, K.; Clucas, D. Thermomechanical Grain Refinement in AA6082-T6 Thin Plates under Bobbin Friction Stir Welding. Metals 2018, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Patel, V. Experimental and numerical investigations of bonding interface behavior in stationary shoulder friction stir lap welding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Li, W.; Xu, Y. Stationary shoulder tool in friction stir processing: a novel low heat input tooling system for magnesium alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 34, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Niu, P.; Yan, S.; Patel, V.; Wen, Q. Improving microstructural and tensile properties of AZ31B magnesium alloy joints by stationary shoulder friction stir welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbini, A.; Carstensen, J.; Dos Santos, J.F. Influence of a non-rotating shoulder on heat generation, microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar AA2024/AA7050 FSW joints. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
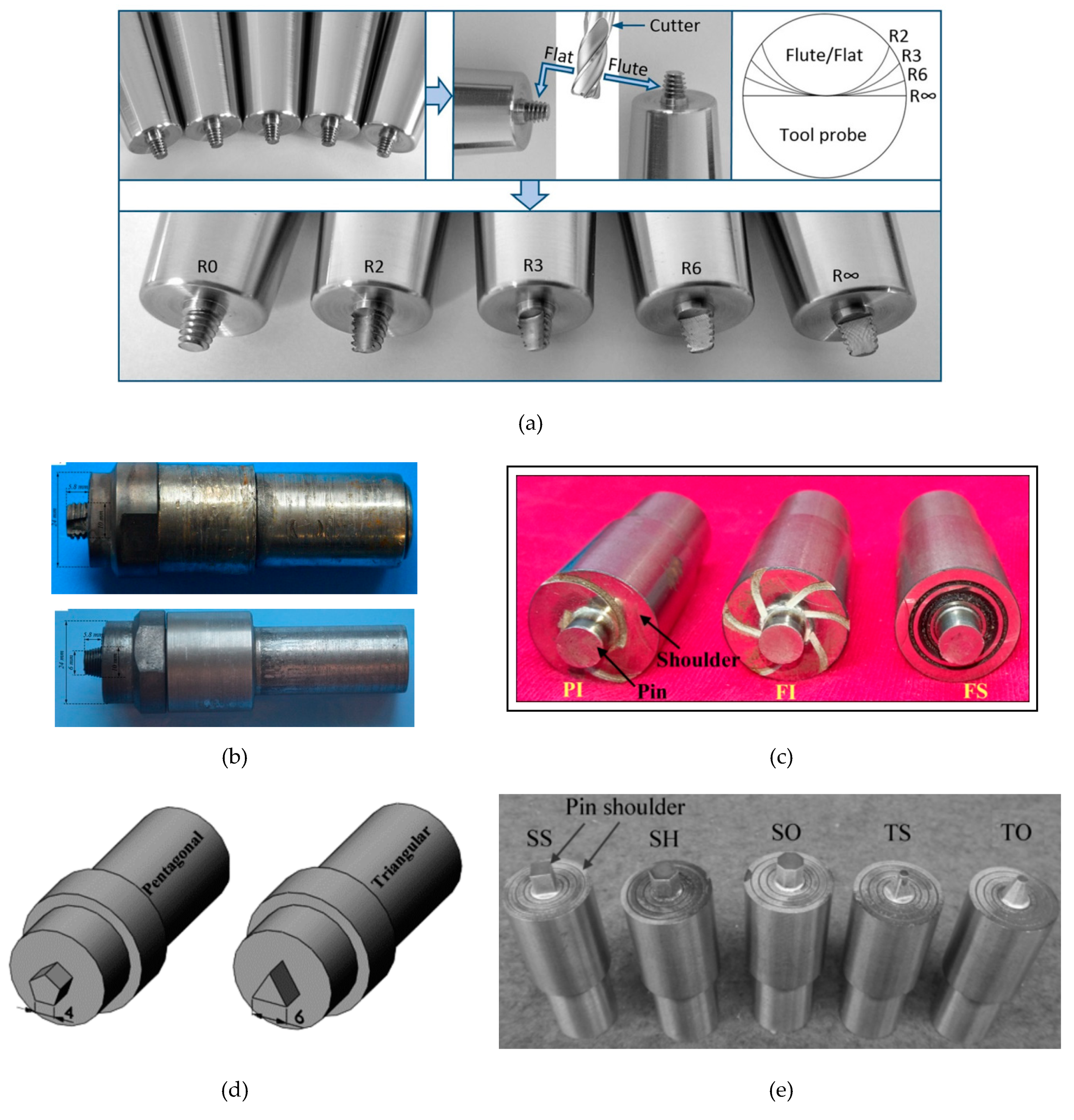
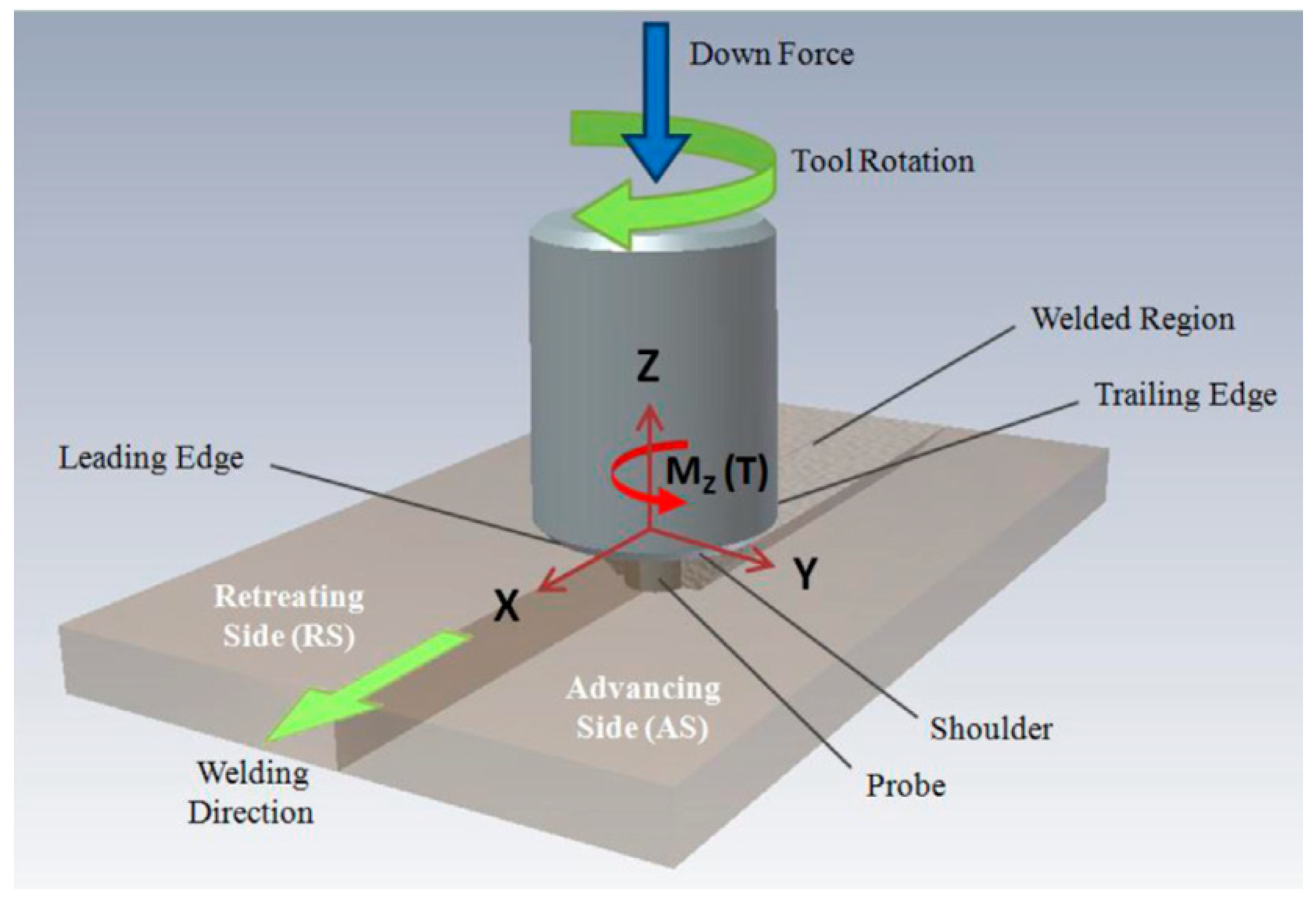
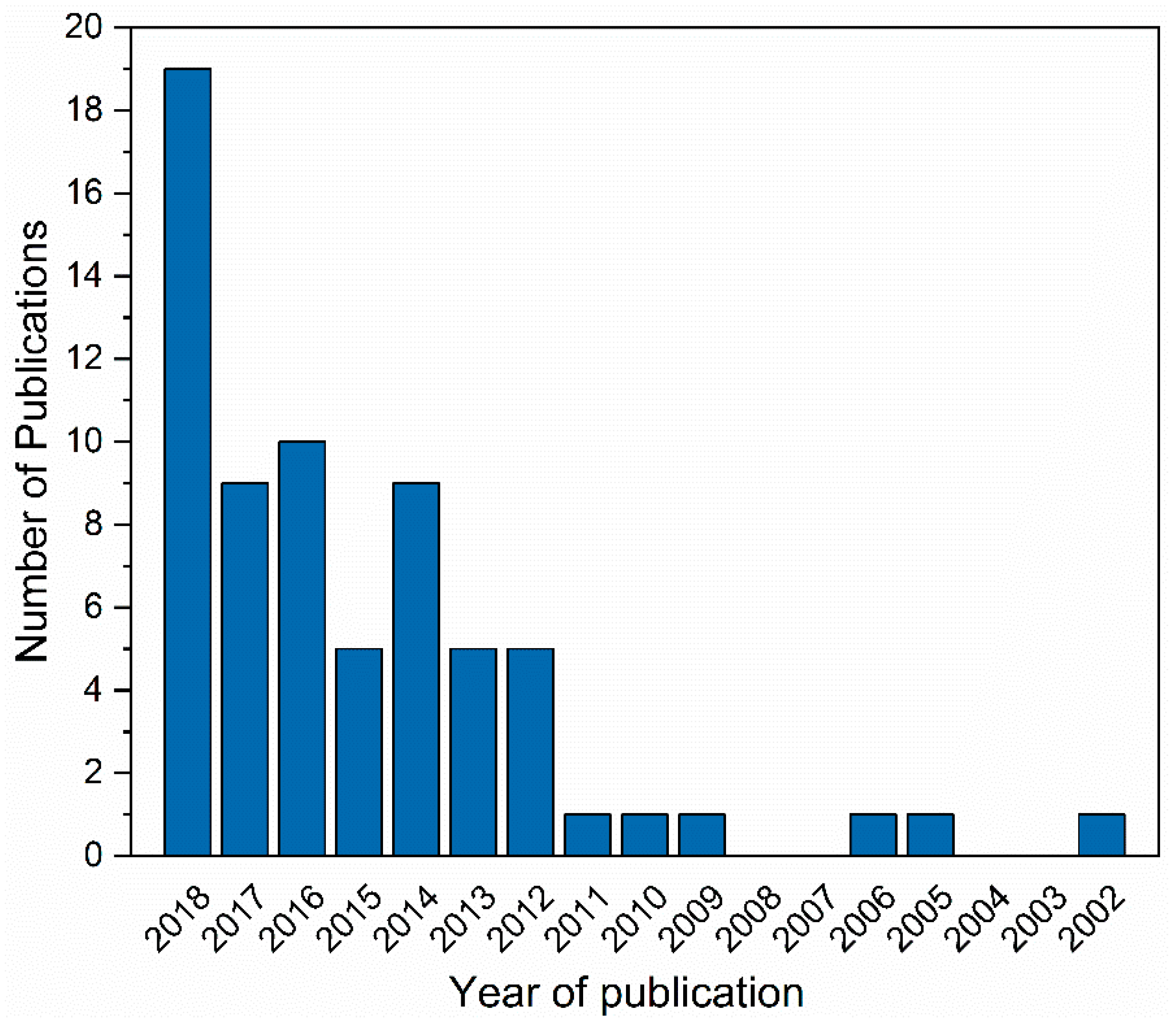
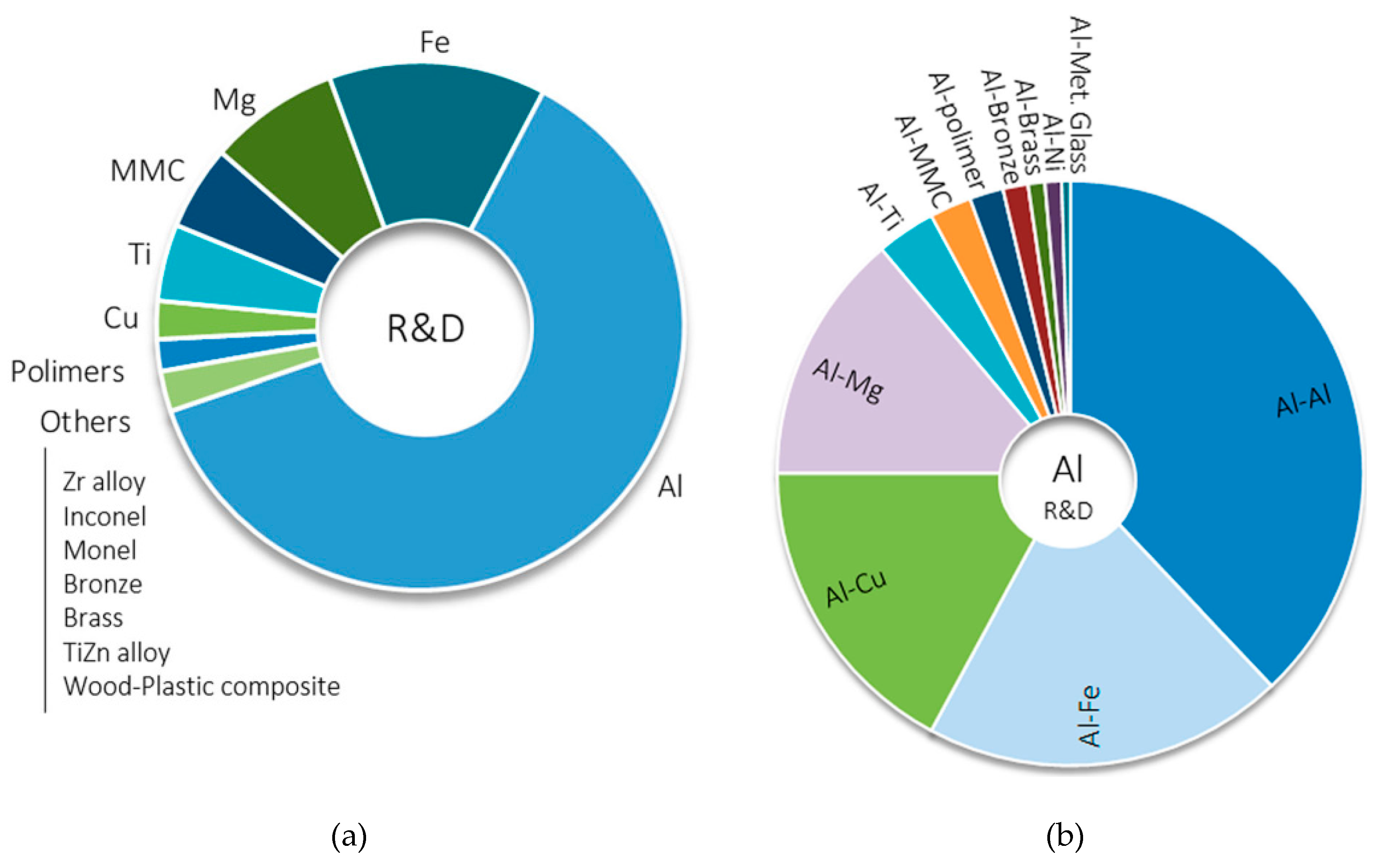
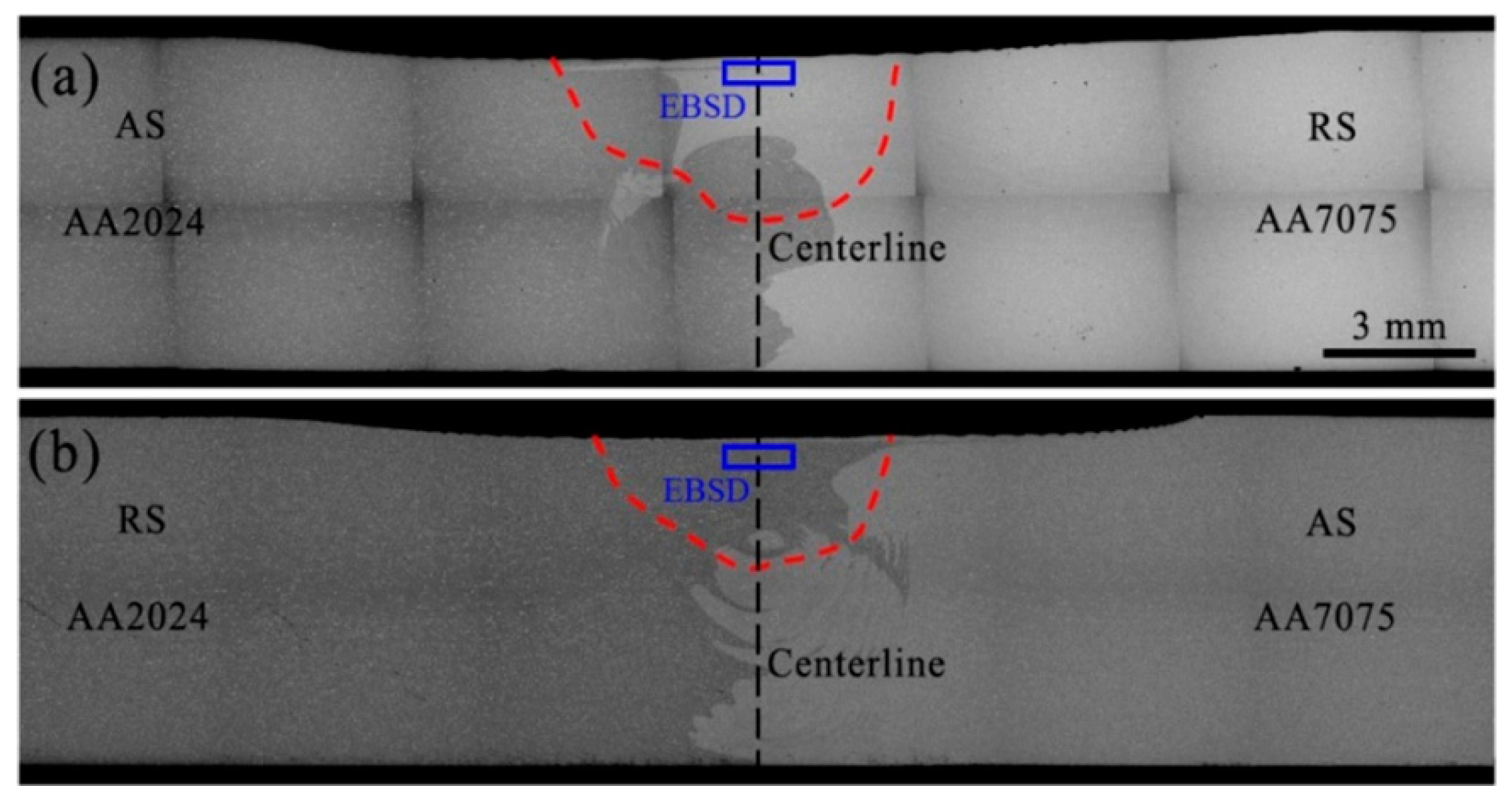
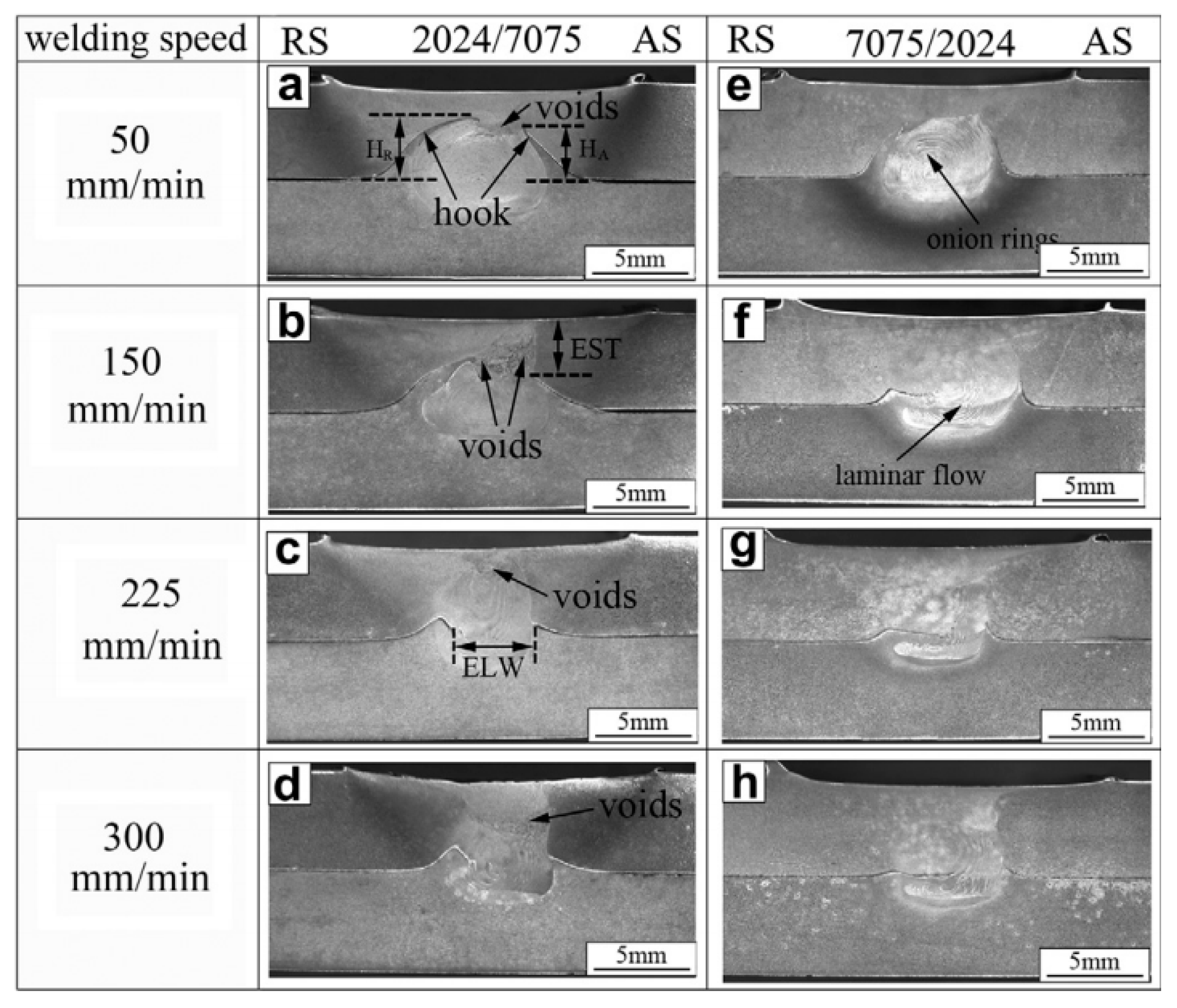
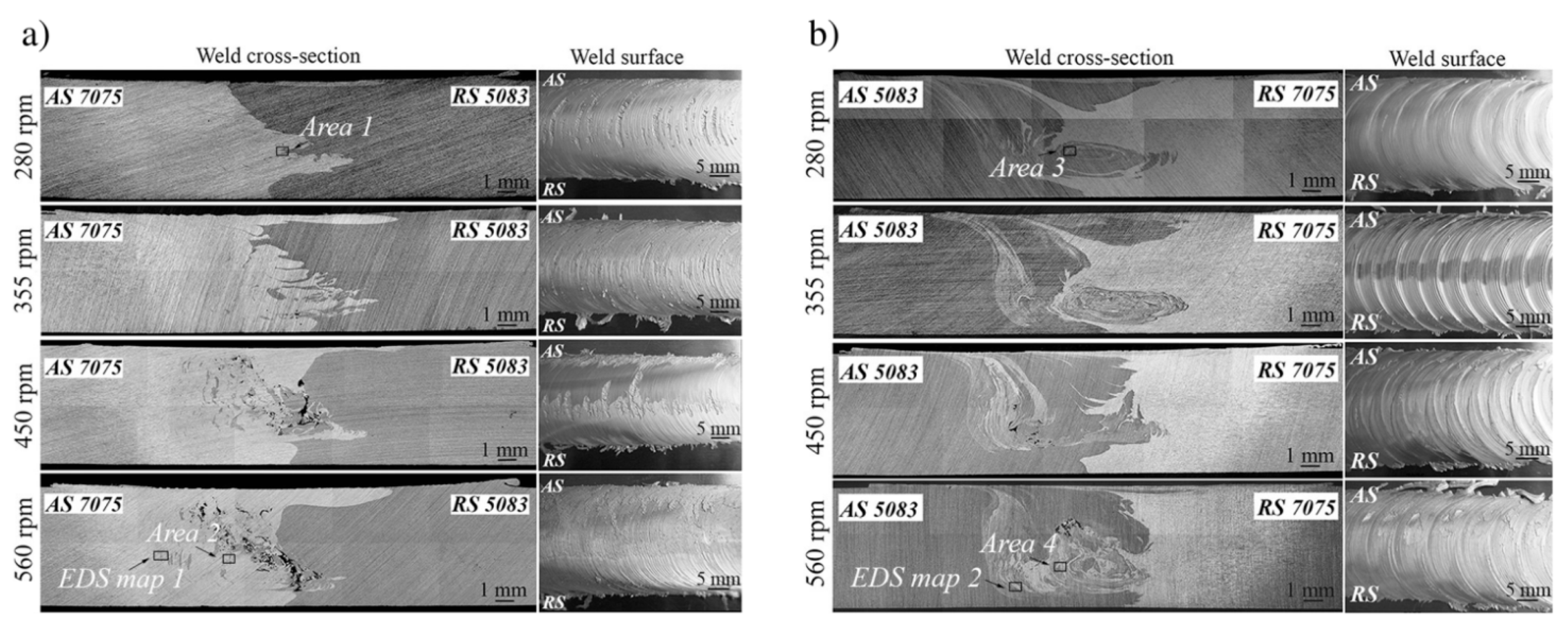

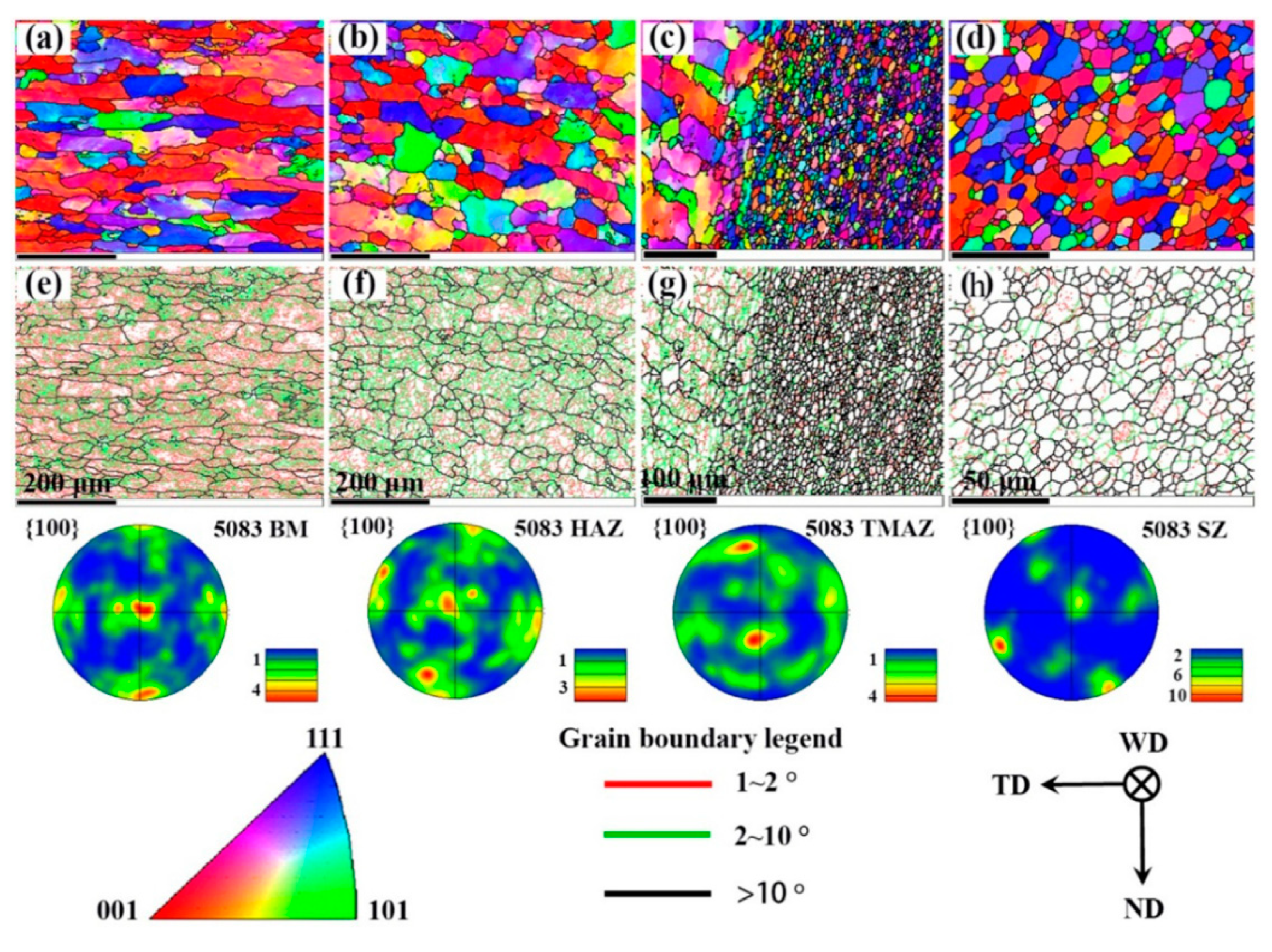

| No. | Author (s) | Alloy Combinations | Thick (mm) | Welding Parameters | Objective of Study | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Positioning | Rotation Speed (rpm) | Welding Speed (mm/min) | ||||||
| AS | RS | |||||||
| 1 | Niu, et al. [13] | 2024-T351 & 5083-H112 | 6.35 | 2024 | 5083 | 600 | 150 | Strain hardening behavior and mechanism |
| 2 | Niu, et al. [13] | 7075-T651 & 2024-T351 | 6.35 | 7075 | 2024 | 600 | 150 | Strain hardening behavior and mechanism |
| 3 | Hasan, et al. [14] | 7075-T651 & 2024-T351 | 6 | Both | both | 900 | 150 | Effect of pin flute radius and alloy positioning |
| 4 | Ge, et al. [15] | 7075-T6 & 2024-T3 Lap joint: 7075-upper; 2024-lower | 3 | NA | NA | 600 | 30, 60, 90, 120 | Effect of pin length and welding speed |
| 5 | Kalemba–Rec, et al. [16] | 7075-T651 & 5083-H111 | 6 | Both | Both | 280, 355, 450, 560 | 140 | Influence of tool rotation speed, pin geometry and alloy positioning |
| 6 | Safarbali, et al. [17] | 2024-T4 & 7075-T6 | 4 | 2024 | 7075 | 1140 | 32 | Effect of post-weld treatment |
| 7 | Palanivel, et al. [18] | 6351-T6 & 5083-H111 | 6 | 6351 | 5083 | 800, 1000, 1200 | 45, 60, 75 | Optimization of shoulder profile, rotational speed and welding speed |
| 8 | Hamilton, et al. [19] | 2017A-T451 & 7075-T651 | 6 | Both | Both | 355 | 112 | Phase transformation maps |
| 9 | Gupta, et al. [20] | 5083-O & AA6063- T6 | 6 | NR | NR | 700, 900, 1100 | 40, 60, 80 | Optimization of tool geometry, rotational speed and welding speed |
| 10 | Huang, et al. [21] | 5052&AlMg2Si | 8 | Al-Mg2Si | 5052 | 1000 | 80 | Microstructure and mechanical properties |
| 11 | Moradi, et al. [22] | 2024-T351& 6061-T6 | 6 | 2024 | 6061 | 800 | 31.5 | Texture evolution |
| 12 | Prasanth and Raj [23] | 6061-T6 & 6351-T6 | 6.35 | NR | NR | 600, 900, 1200 | 30, 60, 90 | Optimization of rotational speed, welding speed and axial force |
| 13 | Azeez and Akinlabi [24] | 6082-T6 & 7075-T6 | 10 | 7075 | 6082 | 950, 1000 | 80, 100 | Double-sided weld |
| 14 | Azeez, et al. [25] | 6082-T6 & 7075-T6 | 10 | 7075 | 6082 | 950, 1000 | 80, 100 | Single-sided weld |
| 15 | Peng, et al. [26] | 6061-T651 & 5A06-H112 | 5 | 6061 | 5A06 | 600, 900, 1200 | 100, 150 | Nanoindentation hardness and fracture behavior |
| 16 | Das and Toppo [27] | 6101-T6 & 6351-T6 | 12 | 6101 | 6351 | 900, 1100, 1300 | 16 | Influence of rotational speed on temperature and impact strength |
| 17 | Sarsilmaz [28] | 2024-T3 & 6063-T6 | 8 | 2024 | 6063 | 900, 1120, 1400 | 125, 160, 200 | Microstructure, tensile and fatigue behavior |
| 18 | Kookil, et al. [29] | 2219-T87 & 2195-T8 | 7.2 | Both | Both | 400, 600, 800 | 120, 180, 240, 300 | Effect of rotational speed and welding speed |
| 19 | Hamilton, et al. [30] | 2017A-T451 & 7075-T651 | 6 | Both | Both | 355 | 112 | Positron lifetime annihilation spectroscopy |
| 20 | Kopyscianski, et al. [31] | 2017A-T451 & Cast AlSi9Mg | 6 | 2017A | AlSi9Mg | 355 | 112 | Microstructural study |
| 21 | Ghaffarpour, et al. [32] | 5083-H12 & 6061-T6 | 1.5 | 6061 | 5083 | 700, 1800, 2500 | 25, 30, 212.5, 400 | Optimization of rotational speed, welding speed and tool dimensions |
| 22 | Bijanrostami, et al. [33] | 6061-T6 & 7075-T6 | 5 | 6061 | 7075 | 1000, 1375, 1750, 2125, 2500 | 50, 125, 200, 275, 350 | Underwater FSW: optimizations of rotational and welding speeds on tensile properties |
| 23 | Kasman, et al. [34] | 5083-H111& 6082-T6 | 5 | NR | NR | 400, 500, 630, 800 | 40, 50, 63, 80 | Effect of probe shape, rotational speed, welding speed. |
| 24 | Palanivel, et al. [35] | 5083-H111 & 6351-T6 | 6 | 6351 | 5083 | 800-1200 | 45-85 | Macrostructure examination at different rotational and welding speeds |
| 25 | Doley and Kore [36] | 5052 & 6061 | 1, 1.5 | 6061 | 5052 | 1500 | 63, 98 | Study of welding speed |
| 26 | Saravanan, et al. [37] | 2024-T6 & 7075-T6 | 5 | 2024 | 7075 | 1200 | 12 | Effect of shoulder diameter to probe diameter |
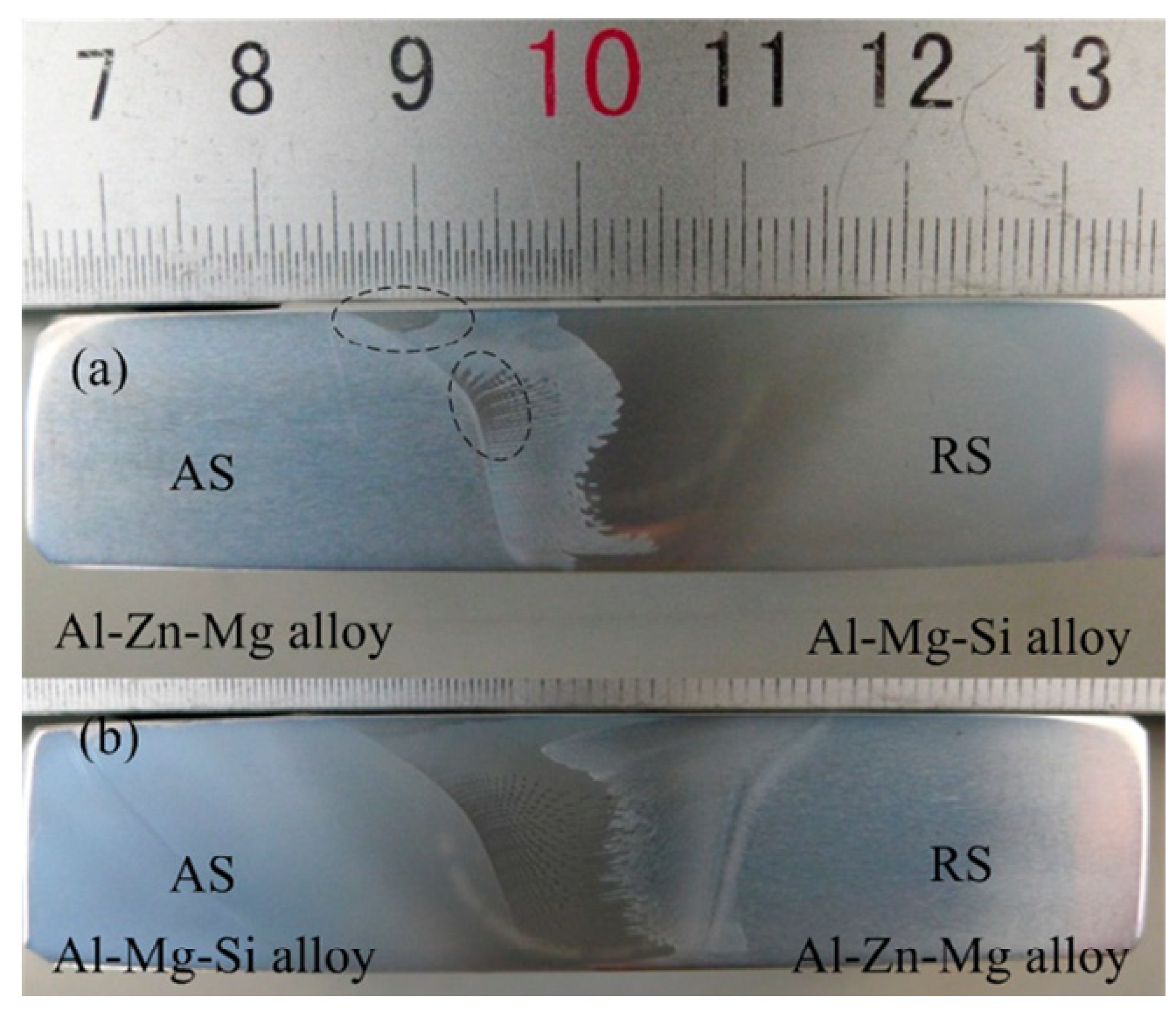
| 27 | Yan, et al. [38] | Al-Mg-Si & Al-Zn-Mg | 15 | Both | Both | 800 | 180 | Effect of alloy positioning on fatigue property |
| 28 | Yan, et al. [39] | Al-Mg-Si & Al-Zn-Mg | 15 | Both | Both | 800 | 180 | Study of Fatigue behavior |
| 29 | Hamilton, et al. [40] | 2017A-T451 & 7075-T651 | 6 | Both | Both | 355 | 112 | Numerical simulation |
| 30 | Zapata, et al. [41] | 2024-T3 & 6061-T6 | 4.8 | 2024 | 6061 | 500, 650, 840 | 45, 65 | Effect of rotational and welding speeds on residual stress |
| 31 | Sun, et al. [42] | UFG 1050 & 6061-T6 | 2 | Both | Both | 800 | 400, 600, 800, 1000 | Microstructure and mechanical properties at different welding speeds |
| 32 | Texier, et al. [43] | 2024-T3 & 2198-T3 | 3.18 | 2198 | 2024 | NR | NR | Heterogeneities in microstructure and tensile properties at the shoulder-affected regions |
| 33 | Rodriguez, et al. [44] | 6061-T6 & 7050-T7451 | 5 | 7050 | 6061 | 270, 340, 310 | 114 | Fatigue behavior |
| 34 | Yoon, et al. [45] | 6111-T4 & 5023-T4 Lap joint | 1 | NA | NA | 1500 1000 | 100 700 | Mechanism of onion ring formation |
| 35 | Rodriguez, et al. [46] | 6061-T6 & 7050-T7451 | 5 | 7050 | 6061 | 270, 340, 310 | 114 | Microstructure and mechanical properties |
| 36 | Ilangovan, et al. [47] | 5086-O & 6061-T6 | 6 | 6061 | 5086 | 1100 | 22 | Effect of probe profiles |
| 37 | Reza–E–Rabby, et al. [48] | 2050-T4 & 6061-T651 | 20 | Both | Both | 150 300 300 | 101 203 406 | Effect of probe features |
| 38 | Donatus, et al. [49] | 5083-O & 6082-T6 | NR | 5083 | 6082 | 400 | 400 | Anodizing behavior |
| 39 | Karam, et al. [50] | A319 & A413 cast | 10 | A413 | A319 | 630, 800, 1000 | 20, 40, 63 | Influence of rotational and welding speed |
| 40 | Ipekoglu and Cam [51] | 7075-O & 6061-O 7075-T6 & 6061-T6 | 3.17 | 6061 | 7075 | 1000 1500 | 150 400 | Effect of initial temper conditions and postweld heat treatment |
| 41 | Cole, et al. [52] | 6061-T6 & 7075-T6 | 4.6 | Both | Both | 700-1450 | 100 | Effect of temperature |
| 42 | Song, et al. [53] | 2024-T3 & AA7075-T6 Lap joint | 5 | NA | NA | 1500 | 50, 150, 225, 300 | Effect of alloy positioning and welding speed on defects and mechanical properties |
| 43 | Jannet and Mathews [54] | 5083-O & 6061-T6 | 6 | 6061 | 5083 | 600, 750, 900 | 60 | Effect of rotational speed |
| 44 | Palanivel, et al. [55] | 6351-T6 & 5083-H111 | 6 | 6351 | 5083 | 950 | 36, 63, 90 | Effect of welding speed |
| 45 | Jonckheere, et al. [56] | 2014-T6 & 6061-T6 | 4.7 | Both | Both | 500, 1500 | 90 | Effect of alloy positioning and tool offset on temperature and hardness |
| 46 | Palanivel, et al. [57] | 6351-T6 & 5083-H111 | 6 | 6351 | 5083 | 600-1300 | 36-90 | Optimization of process parameters (probe shapes, rotational and welding speeds, axial force) for UTS |
| 47 | Ghosh, et al. [58] | A356 & 6061-T6 | 3 | 6061 | A356 | 1000 | 70-240 | Effect of welding speed |
| 48 | Velotti, et al. [59] | 2198-T351 & 7075-T6 Lap joint | 3 & 1.9 | NA | NA | 830 | 40 | Stress corrosion cracking investigation |
| 49 | Koilraj, et al. [60] | 2219-T87 & 5083-H321 | 6 | 2219 | 5083 | 400-800 | 15-60 | Optimization of process parameters (probe shapes, rotational and welding speeds, shoulder to probe diameter ratio) for UTS |
| 50 | Dinaharan, et al. [61] | 6061 cast &6061 rolled | 6 | Both | Both | 800, 1000, 1200, 1400 | 50 | Effect of rotational speed and alloy positioning |
| 51 | Palanivel, et al. [62] | 6351-T6 & 5083-H111 | 6 | 6351 | 5083 | 600, 950, 1300 | 60 | Effect of rotational speed and probe profile |
| 52 | Song, et al. [63] | 5052-H34 & 5023-T4 | ~1.5 | 5052 | 5023 | 1500 | 100-700 | Liquation cracking study |
| 53 | Ghosh, et al. [64] | A356 & 6061-T6 | 3 | 6061 | A356 | 1000, 1400 | 80, 240 | Effect of rotational and welding speed |
| 54 | Kim, et al. [65] | 5052-H34 & 5023-T4 | 1.5 & 1.6 | Both | Both | 1000, 1500 | 100, 200, 300, 400 | Effect of alloy positioning |
| 55 | Prime, et al. [66] | 7050-T7451 & 2024-T351 | 25.4 | 2024 | 7050 | NR | 50.8 | Residual stress study |
| 56 | Miles, et al. [67] | 5182-O & 5754-O 5182-O & 6022-T4 5754-O & 6022-T4 | ~2 | NR | NR | 500, 1000, 1500 | 130, 240, 400 | Formability study |
| 57 | Ouyang and Kovacevic [68] | 6061-T6 & 2024-T3 | 12.7 | NR | NR | 637 | 133 | Material flow study |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, V.; Li, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Vairis, A.; Niu, P. Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloy Combinations: State-of-the-Art. Metals 2019, 9, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030270
Patel V, Li W, Wang G, Wang F, Vairis A, Niu P. Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloy Combinations: State-of-the-Art. Metals. 2019; 9(3):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030270
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Vivek, Wenya Li, Guoqing Wang, Feifan Wang, Achilles Vairis, and Pengliang Niu. 2019. "Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloy Combinations: State-of-the-Art" Metals 9, no. 3: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030270
APA StylePatel, V., Li, W., Wang, G., Wang, F., Vairis, A., & Niu, P. (2019). Friction Stir Welding of Dissimilar Aluminum Alloy Combinations: State-of-the-Art. Metals, 9(3), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9030270






