Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanism Analysis in an AlMg5 Aluminium Alloy Processed by ECAP and Subsequent Ageing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
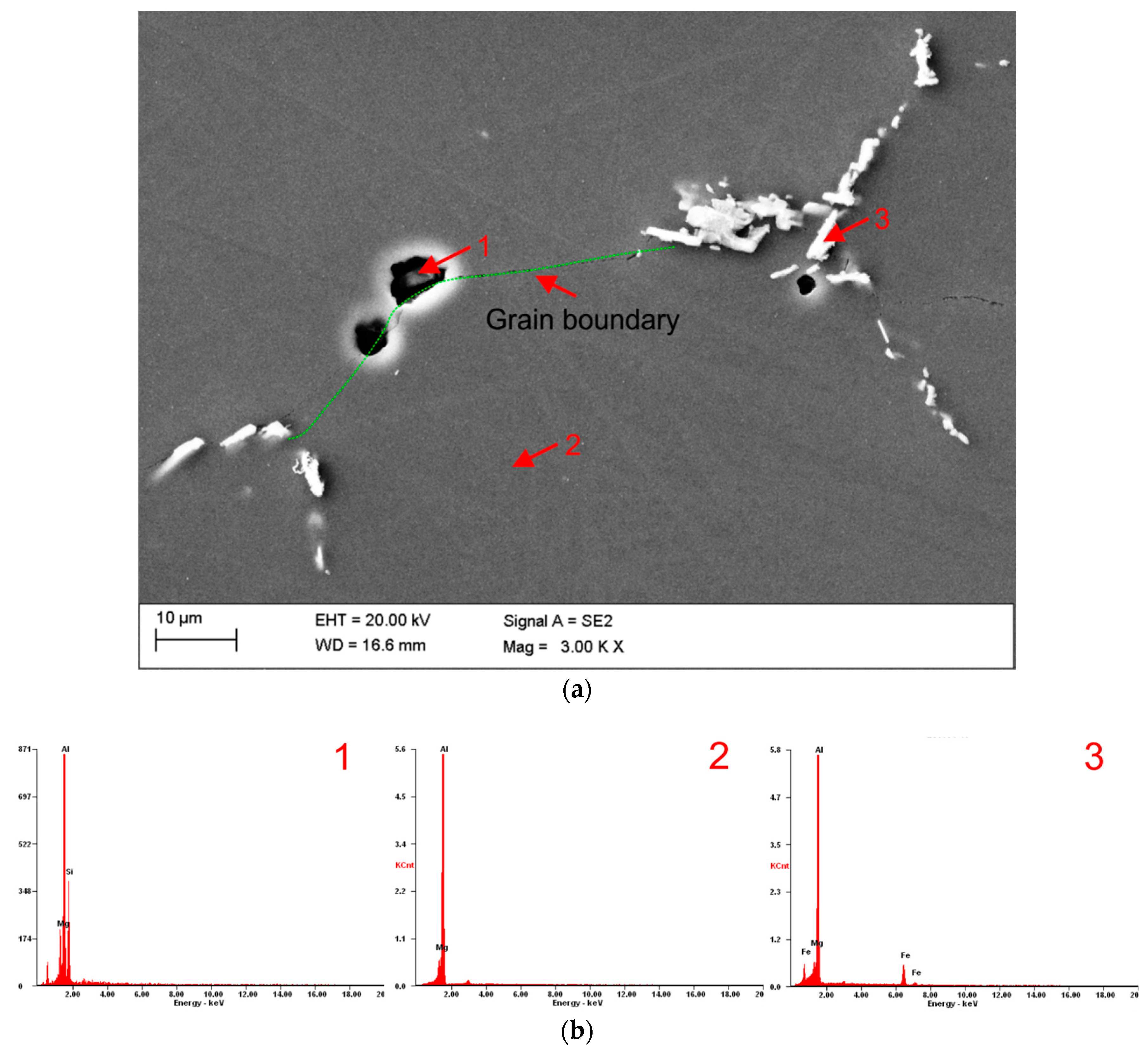
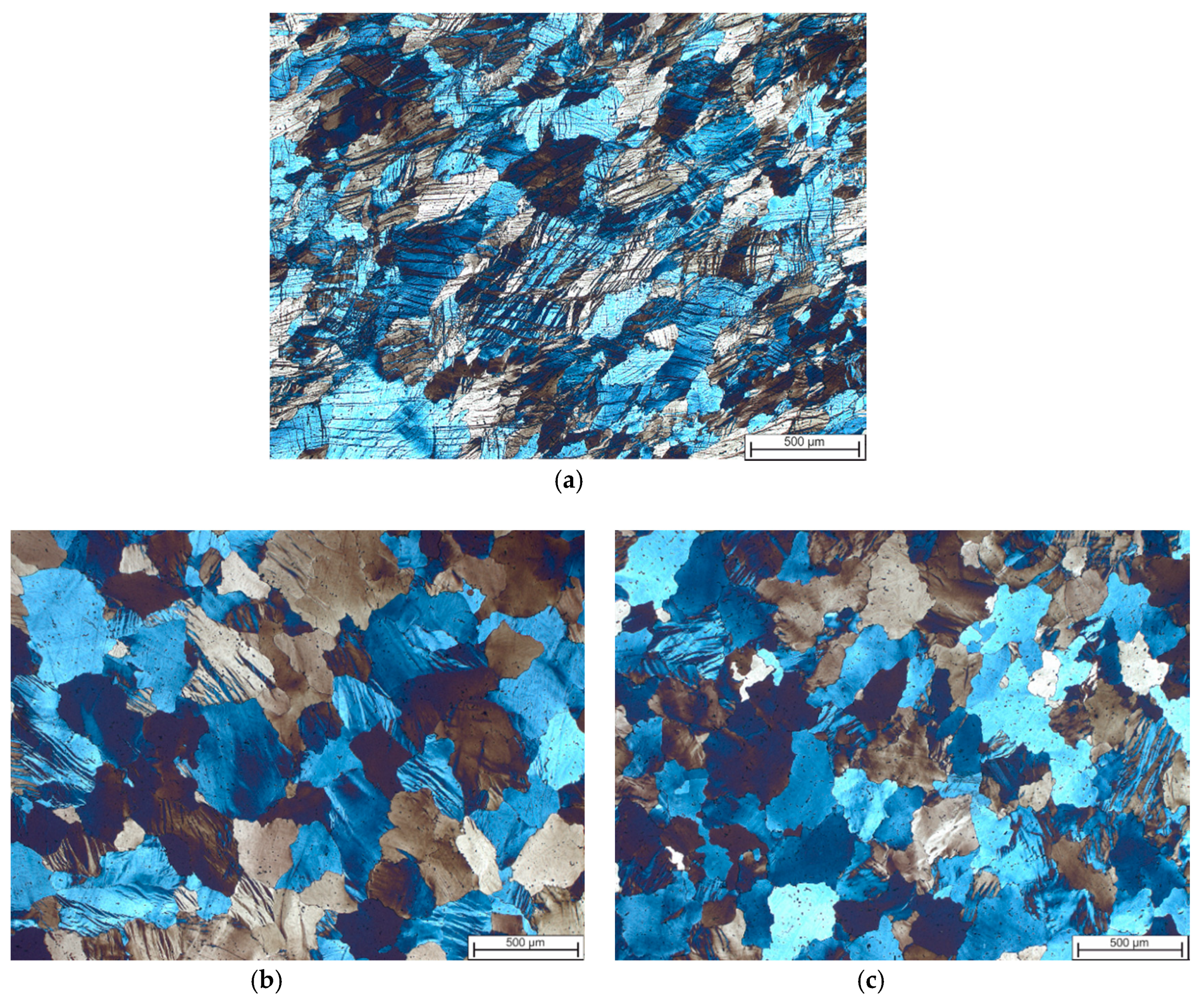
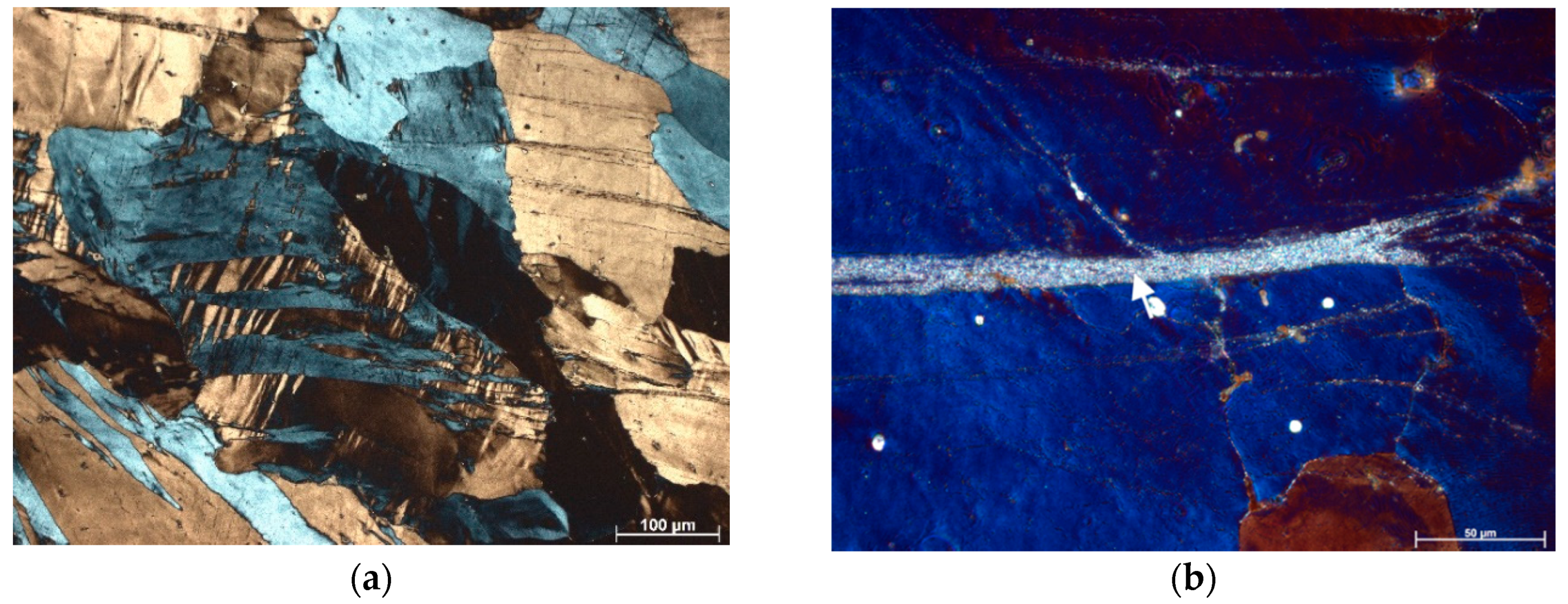
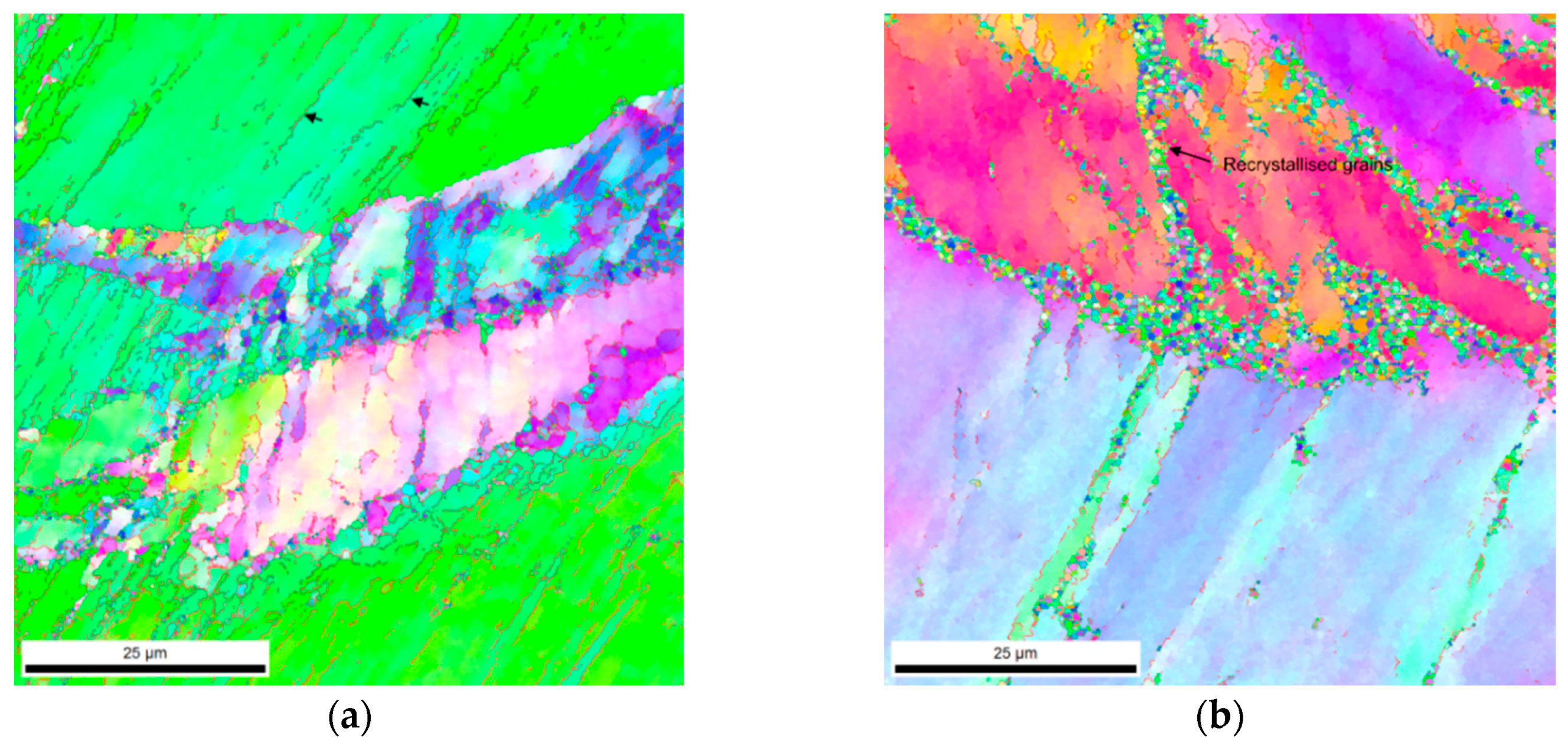
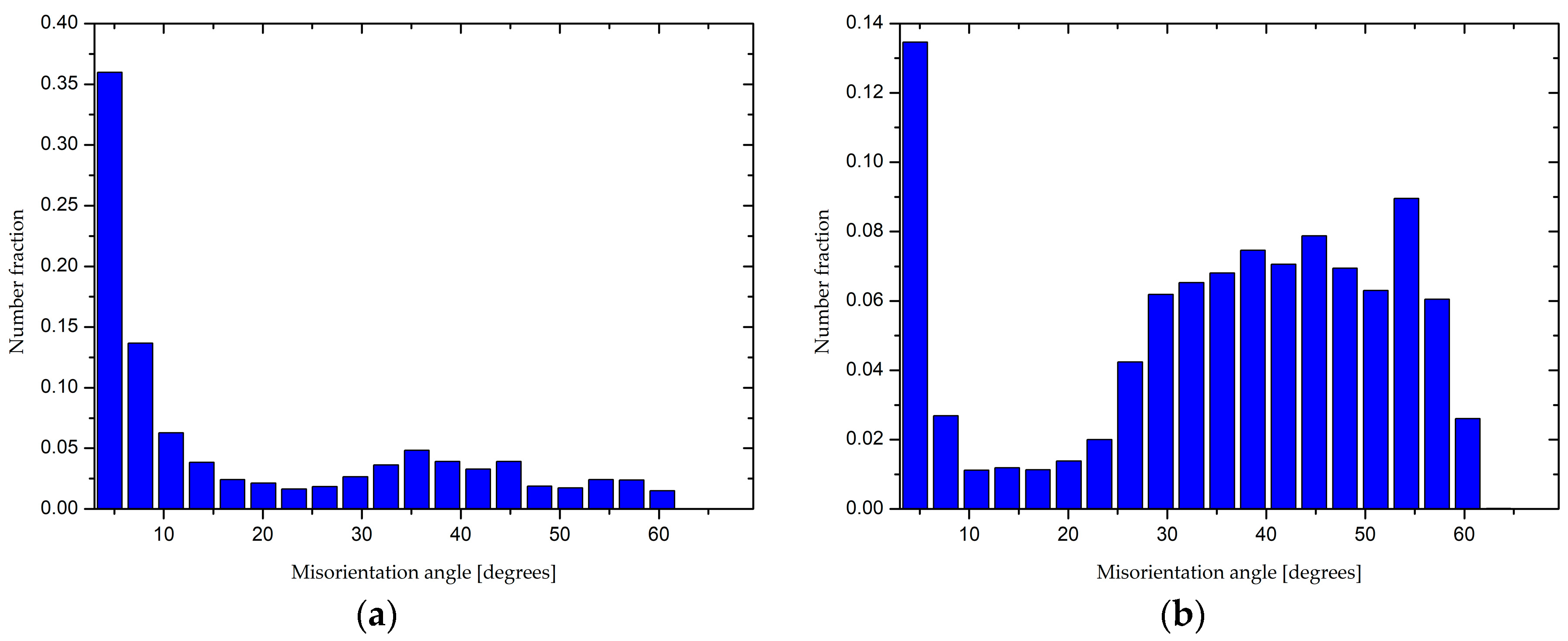
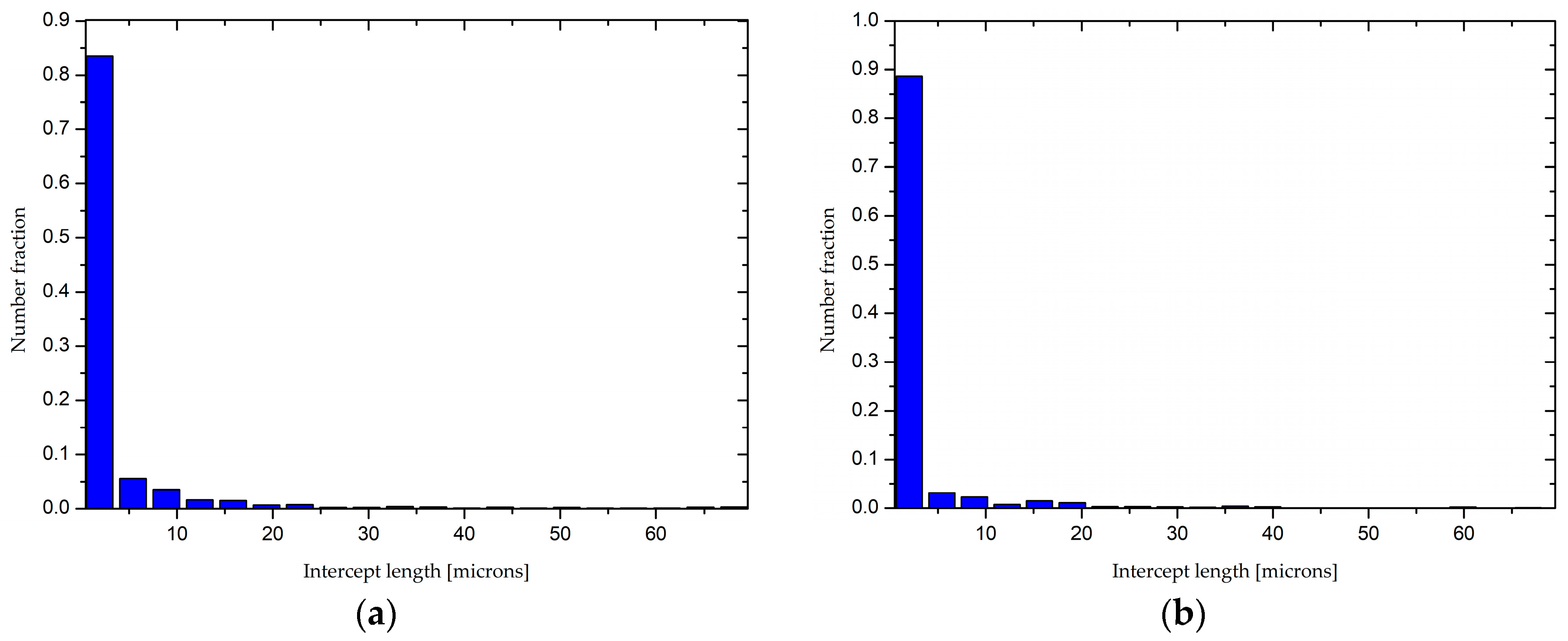
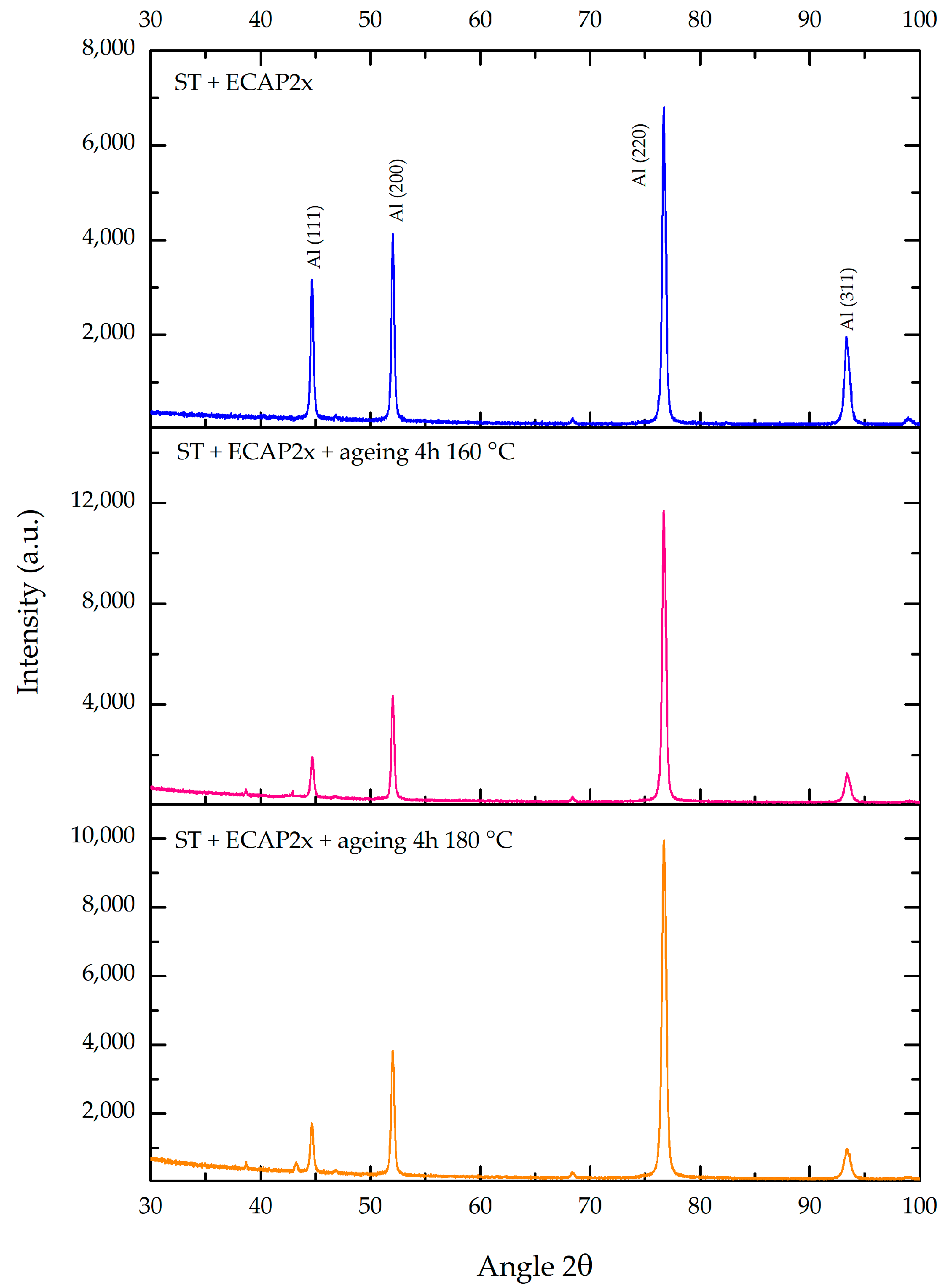
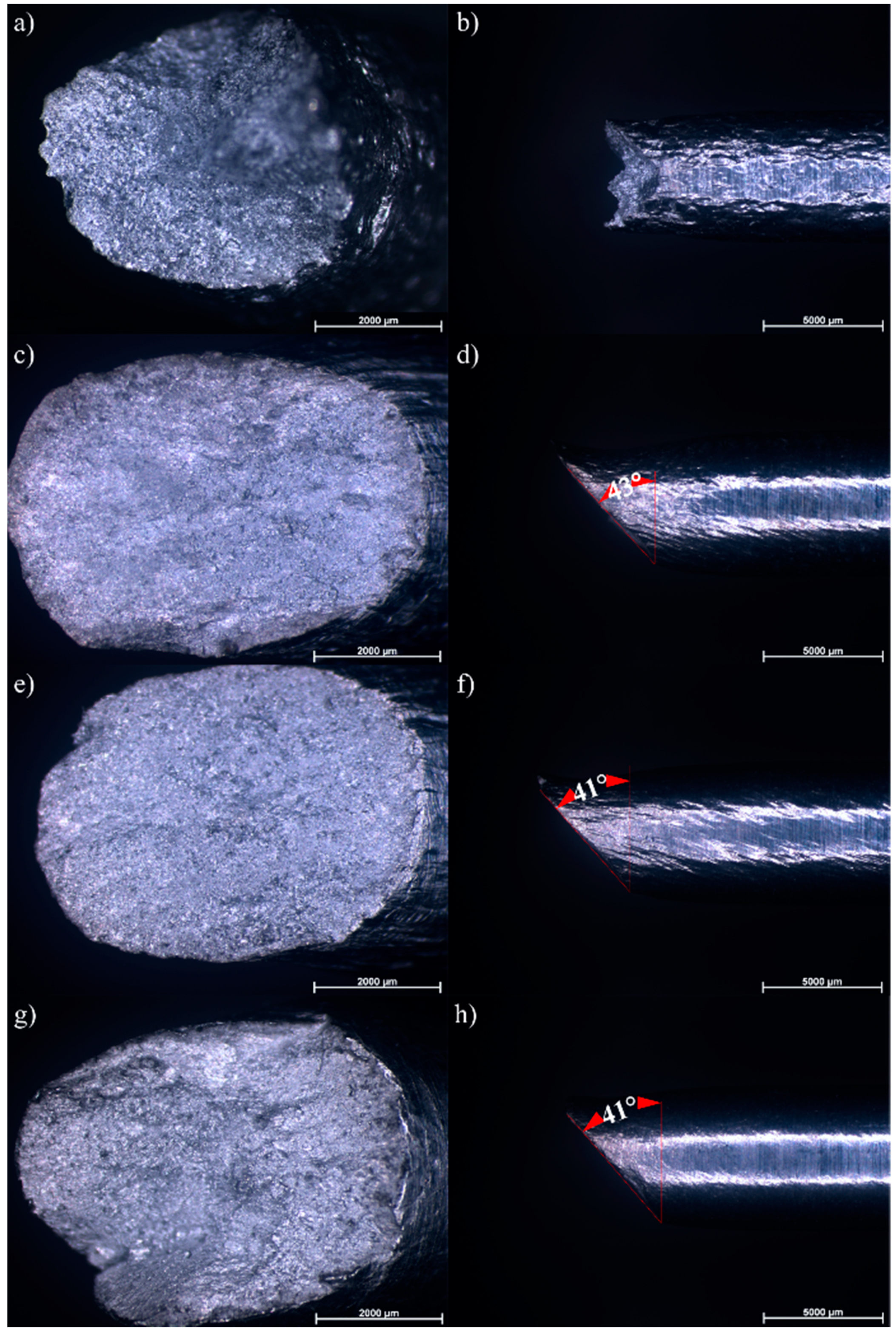
3.1. Microstructure
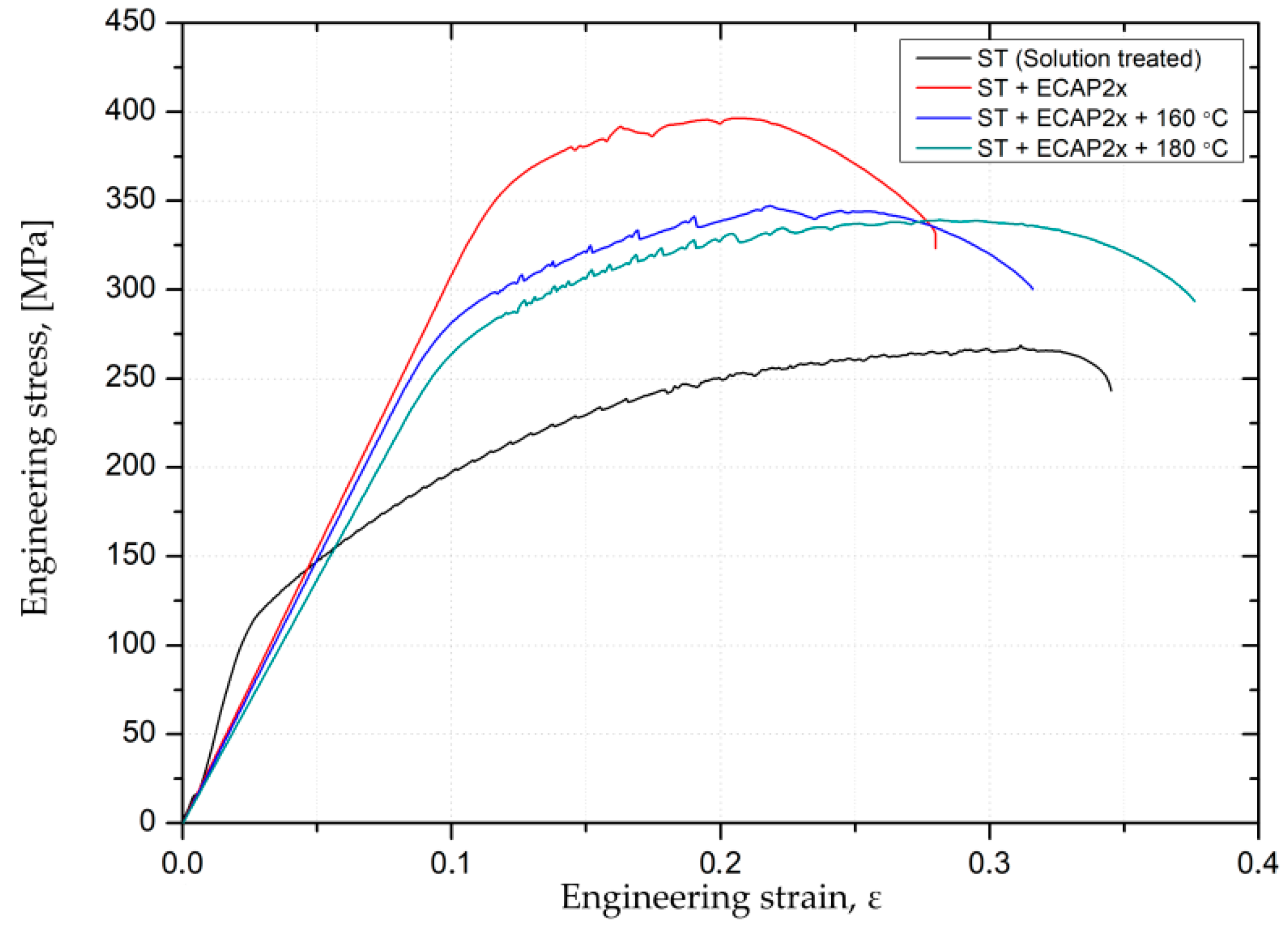
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Strengthening Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciemiorek, M.; Chrominski, W.; Olejnik, L.; Lewandowska, M. Evaluation of mechanical properties and anisotropy of ultrafine grained 1050 aluminum sheets produced by incremental ECAP. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenix, R.J.; Balasivanandha, P.S.; Padmanabhan, K.A. On the influence of repetitive corrugation and straightening on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AA 8090 Al-Li alloy. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; Roven, H.J.; Murashkin, M.; Valiev, R.Z.; Zhou, H. Effect of Mg on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Mg alloys produced by high pressure torsion. Scr. Mater. 2019, 159, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Mu, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, L.; Roven, H.J. Strengthening and toughening mechanisms of an ultrafine grained Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy processed by cyclic extrusion and compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 699, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morovvati, M.R.; Dariani, B.M. The effect of annealing on the formability of aluminum 1200 after accumulative roll bonding. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totten, G.E.; MacKenzie, D.S. Handbook of Aluminum: Physical Metallurgy and Processes; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Snopiński, P.; Król, M.; Tański, T.; Krupińska, B. Effect of cooling rate on microstructural development in alloy ALMG9. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumal, B.B.; Baretzky, B.; Mazilkin, A.A.; Phillipp, F.; Kogtenkova, O.A.; Volkov, M.N.; Valiev, R.Z. Formation of nanograined structure and decomposition of supersaturated solid solution during high pressure torsion of Al–Zn and Al–Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4469–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.C.; Chinh, N.Q.; Xu, C.; Langdon, T.G. Developing processing routes for the equal-channel angular pressing of age-hardenable aluminum alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkin, D.; Lee, Z.; Rodriguez, R.; Nutt, S.; Lavernia, E. Al–Mg alloy engineered with bimodal grain size for high strength and increased ductility. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.S.; Zhang, F.C.; Zhang, M.; Lv, B. A novel process to obtain ultrafine-grained low carbon steel with bimodal grain size distribution for potentially improving ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaeri, M.H.; Salehi, M.T.; Seyyedein, S.H.; Abutalebi, M.R.; Park, J.K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-7075 alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing combined with aging treatment. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tański, T.; Snopiński, P.; Prusik, K.; Sroka, M. The effects of room temperature ECAP and subsequent aging on the structure and properties of the Al-3%Mg aluminium alloy. Mater. Charact. 2017, 133, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tański, T.; Snopiński, P.; Borek, W. Strength and structure of AlMg3 alloy after ECAP and post-ECAP processing. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2017, 32, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tański, T.; Snopiński, P.; Hilser, O. Microstructure and mechanical properties of two binary Al–Mg alloys deformed using equal channel angular pressing. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech. 2017, 48, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, M.; Zieliński, A.; Hernas, A.; Kania, Z.; Rozmus, R.; Tański, T.; Śliwa, A. The effect of long-term impact of elevated temperature on changes in the microstructure of Inconel 740H alloy. Metalurgija 2017, 56, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.J.; Choo, H.; Liaw, P.K.; Lavernia, E.J. Plastic deformation and fracture of ultrafine-grained Al–Mg alloys with a bimodal grain size distribution. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Chung, C.S.; Ma, D.S.; Hong, S.I.; Kim, H.K. Optimization of strength and ductility of 2024 Al by equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) and post-ECAP aging. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Ni, S.; Du, Y.; Song, M. A coupled EBSD/TEM study of the microstructural evolution of multi-axial compressed pure Al and Al–Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.; Li, Y.; Mathiesen, R.H.; Bjørge, R.; Roven, H.J. High ductility bulk nanostructured Al–Mg binary alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing and inter-pass annealing. Scr. Mater. 2015, 105, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chai, Y.C.; Roven, H.J.; Gireesh, S.S.; Yu, Y.D.; Hjelen, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–xMg alloys processed by room temperature ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 545, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumbach, M.; Goerdeler, M.; Gottstein, G. Modelling of recrystallisation textures in aluminium alloys: I. Model set-up and integration. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 3275–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckham, A.; Engler, O.; Knutsen, R.D. Moderation of the recrystallization texture by nucleation at copper-type shear bands in Al-1Mg. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2881–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Ma, M.; Liu, W.C. Effect of initial grain size on the recrystallization and recrystallization texture of cold-rolled AA 5182 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 690, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.; Li, Y.; Mathiesen, R.H.; Bjørge, B.; Roven, H.J. Annealing response of binary Al–7Mg alloy deformed by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 586, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Rao, P.N.; Jayaganthan, R. Effect of deformation temperature on mechanical properties of ultrafine grained Al–Mg alloys processed by rolling. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotorevskiy, V.S.; Dobrojinskaja, R.I.; Cheverikin, V.V.; Khamnagdaeva, E.A.; Pozdniakov, A.V.; Levchenko, V.S.; Besogonova, E.S. Evolution of the structure and mechanical properties of sheets of the Al–4.7Mg–0.32Mn–0.21Sc–0.09Zr alloy due to deformation accumulated upon rolling. Phys. Met. Metall. 2016, 117, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Meng, C.; Mao, F.; Hu, W.; Gottstein, G. Influence of severe plastic deformation on dynamic strain aging of ultrafine grained Al–Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 76, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.; Nagasaki, S.; Patlan, V.; Kitagawa, K.; Kawazoe, M. Fatigue properties of 5056 Al–Mg alloy produced by equal-channel angular pressing. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 11, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Al | Mg | Si | Fe | Mn | Ti | Zn | Cu | Residuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 94.26 | 5.54 | 0.037 | 0.079 | 0.0055 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.0665 |
| Element/Line | The Average Concentration of Elements | |
|---|---|---|
| Weight (%) | Atomic (%) | |
| Point 1 | ||
| MgK | 4.7 | 5.3 |
| AlK | 57.6 | 58.1 |
| SiK | 37.7 | 36.6 |
| Point 2 | ||
| MgK | 6.9 | 7.6 |
| AlK | 93.1 | 92.4 |
| Point 3 | ||
| MgK | 4.5 | 5.4 |
| AlK | 78.4 | 85.5 |
| FeK | 17.1 | 9.1 |
| Condition | Lattice Strain, e | Crystallite Size, d (nm) | Dislocation Density ρ |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST + ECAP 2× | 1.25 × 10−3 | 60 | 0.224 × 1014 m−2 |
| ST + ECAP 2× + ageing 160 °C for 4 h | 1.16 × 10−3 | 67 | 0.209 × 1014 m−2 |
| ST + ECAP 2× + ageing 180 °C for 4 h | 9.21 × 10−4 | 83 | 0.134 × 1014 m−2 |
| The Property | ST | ST + ECAP 2× | ST + ECAP 2× + 160 °C 4 h | ST + ECAP 2× + 180 °C 4 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | 269 ± 1 | 395 ± 2 | 345 ± 2 | 340 ± 1 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 110 ± 1 | 326 ± 2 | 271 ± 2 | 255 ± 1 |
| Elongation, % | 28 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 21 ± 1 | 23 ± 2 |
| Hardness, HV0.3 | 73 ± 1 | 136 ± 1 | 123 ± 1 | 120 ± 1 |
| Condition | σ0 (MPa) | ΔσMg (MPa) | ΔσGB (MPa) | ΔσD (MPa) | Calculated Yield Strength (MPa) | Measured Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST + ECAP 2× + ageing 160 °C for 4 h | 10 | 102 | 84 | 69 | 265 | 271 |
| ST + ECAP 2× + ageing 180 °C for 4 h | 85 | 62 | 259 | 255 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snopiński, P.; Król, M. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanism Analysis in an AlMg5 Aluminium Alloy Processed by ECAP and Subsequent Ageing. Metals 2018, 8, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110969
Snopiński P, Król M. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanism Analysis in an AlMg5 Aluminium Alloy Processed by ECAP and Subsequent Ageing. Metals. 2018; 8(11):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110969
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnopiński, Przemysław, and Mariusz Król. 2018. "Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanism Analysis in an AlMg5 Aluminium Alloy Processed by ECAP and Subsequent Ageing" Metals 8, no. 11: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110969
APA StyleSnopiński, P., & Król, M. (2018). Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanism Analysis in an AlMg5 Aluminium Alloy Processed by ECAP and Subsequent Ageing. Metals, 8(11), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8110969






