Research on the Johnson–Cook Constitutive Model and Failure Behavior of TC4 Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
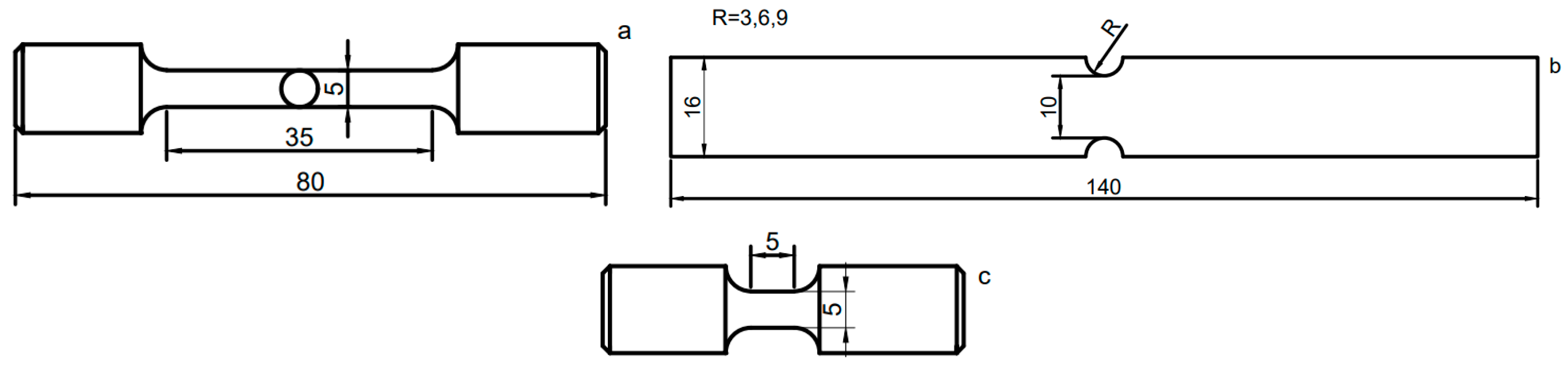
Material Tensile Test
3. Constitutive Model and Failure Criteria
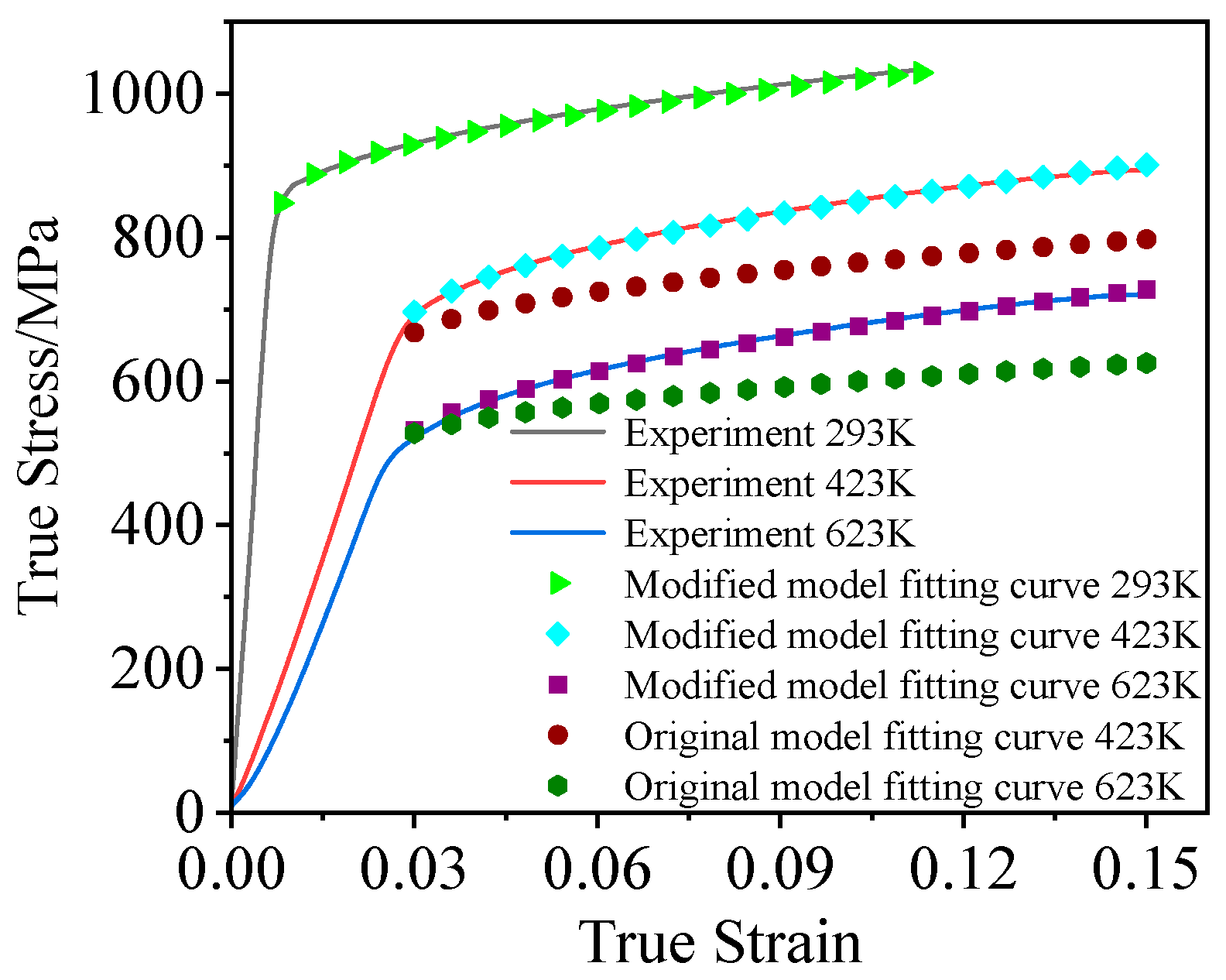
3.1. Modification and Development of the J–C Constitutive Model
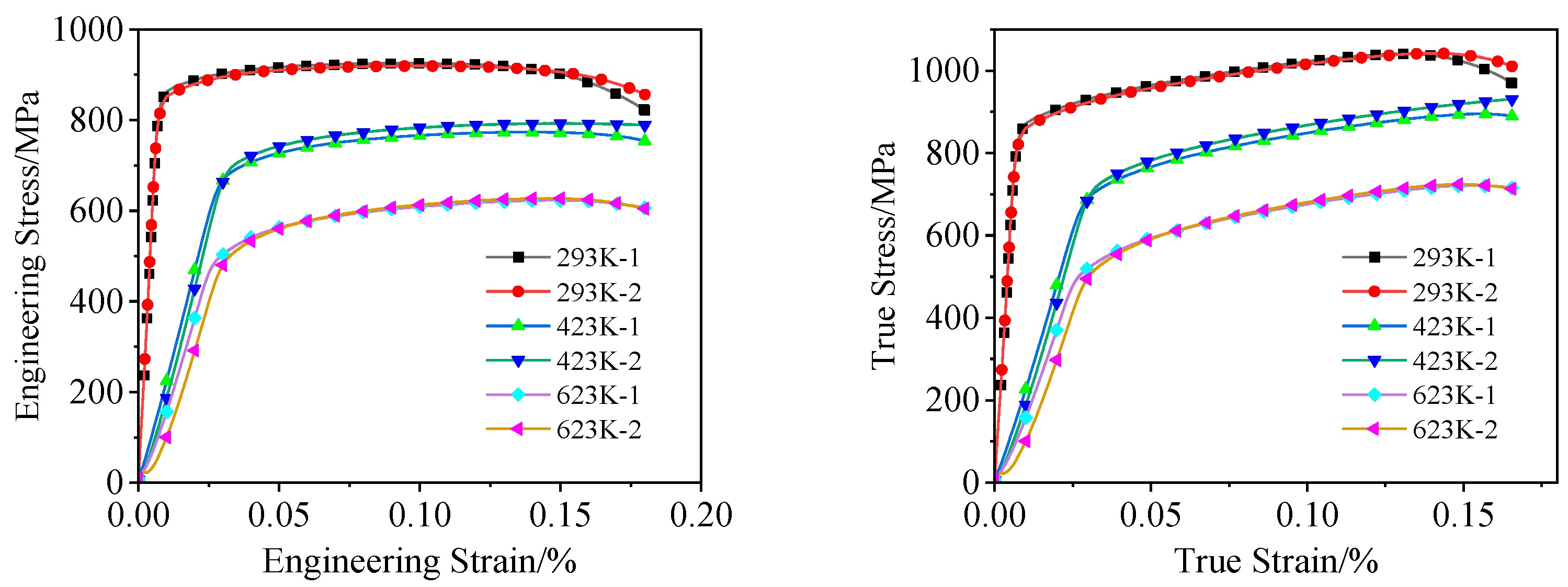
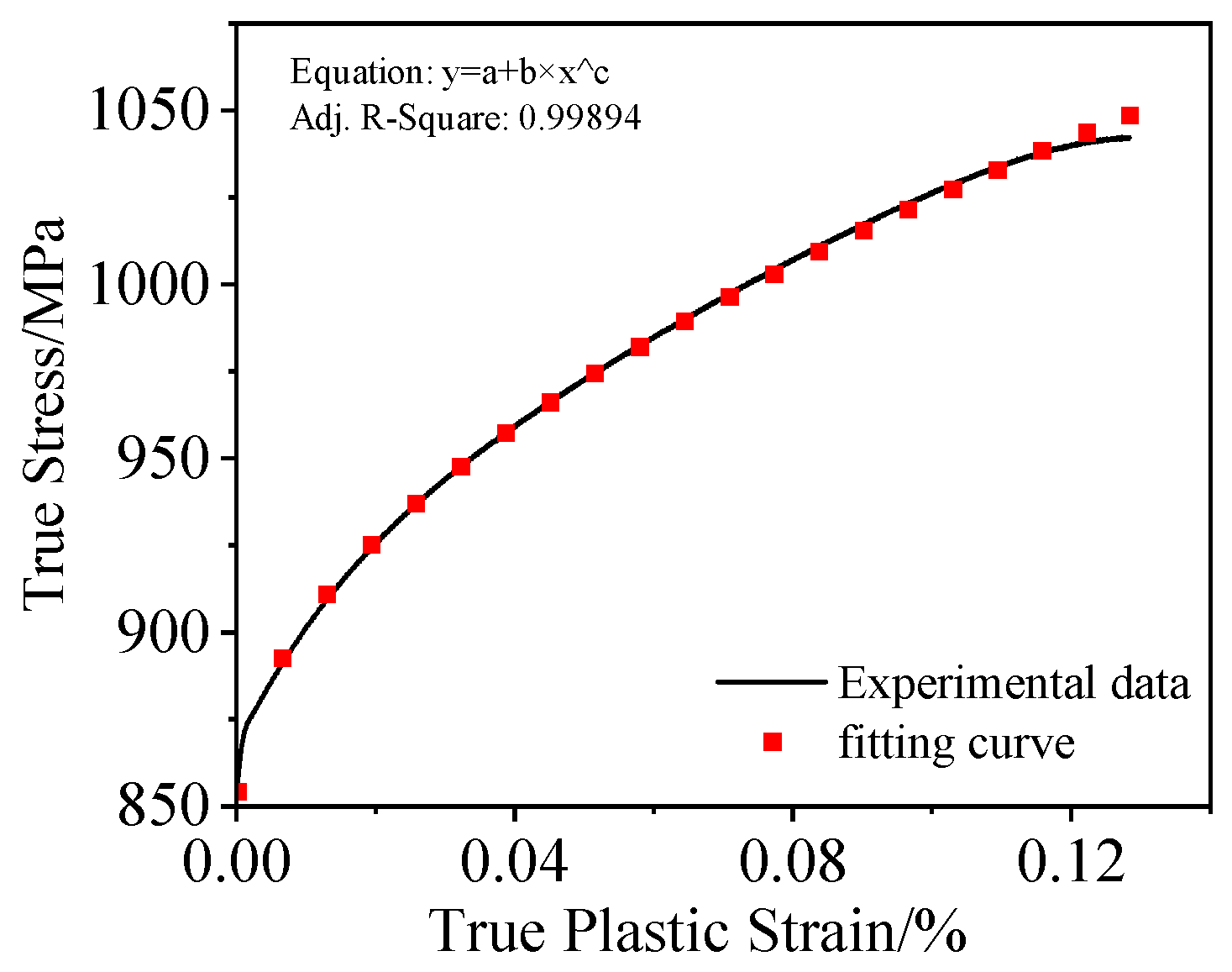
3.1.1. Parameters A, B, and n
3.1.2. Parameters C
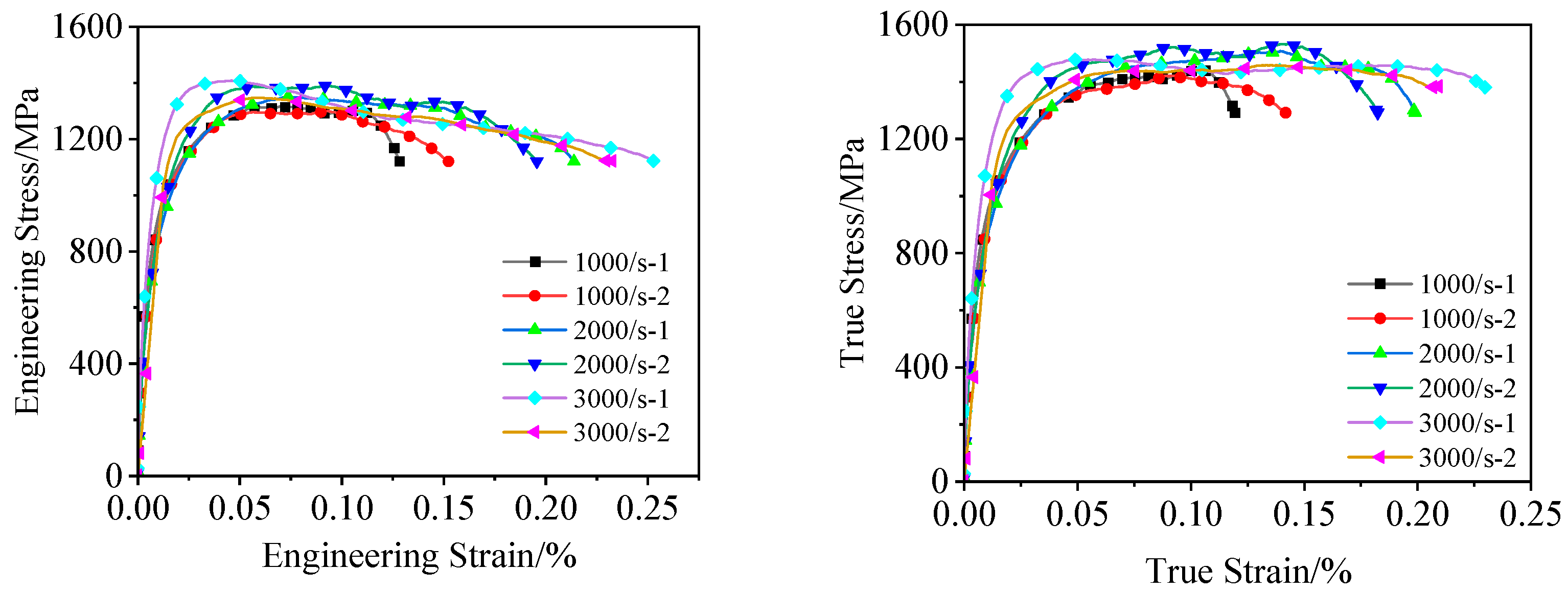
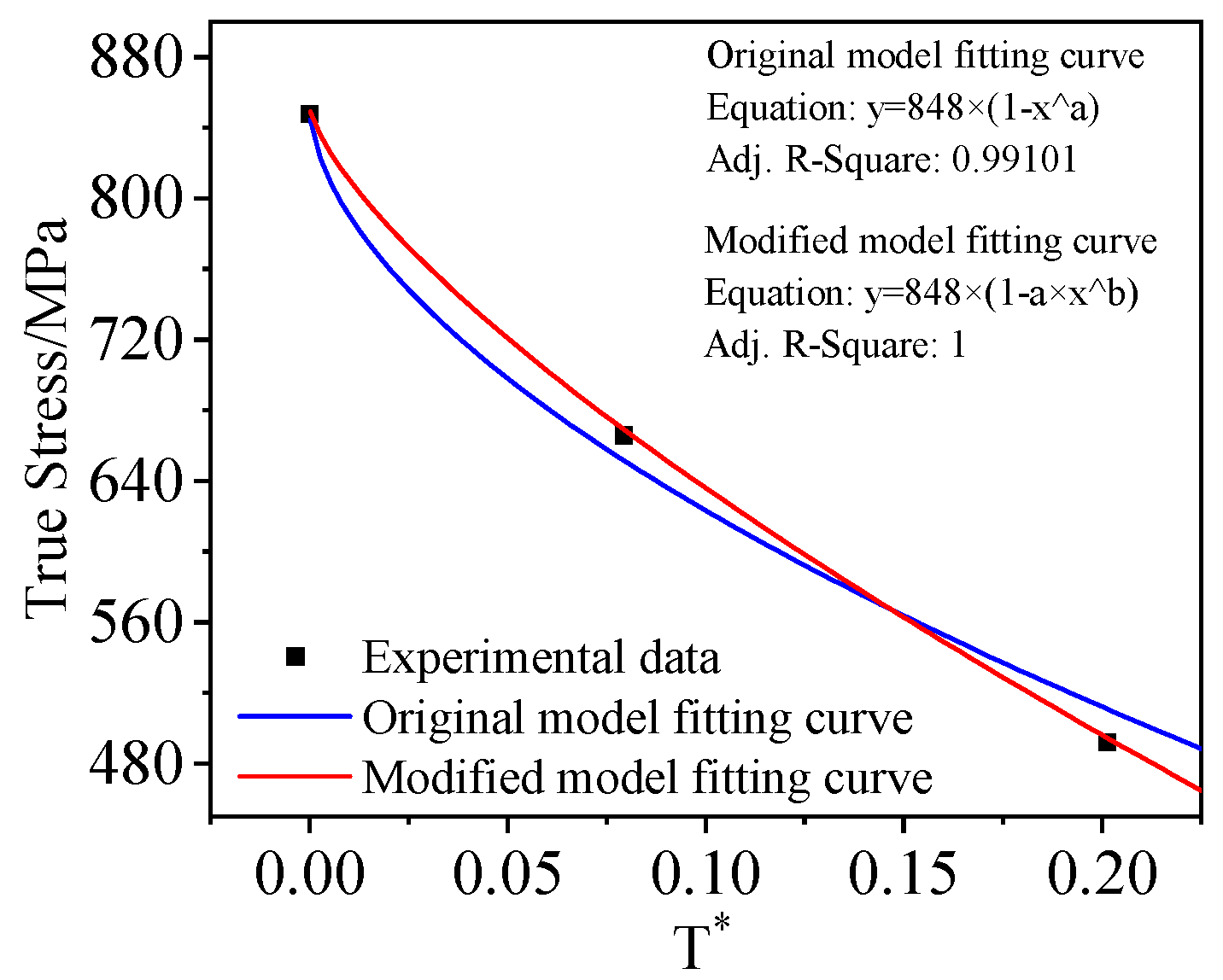
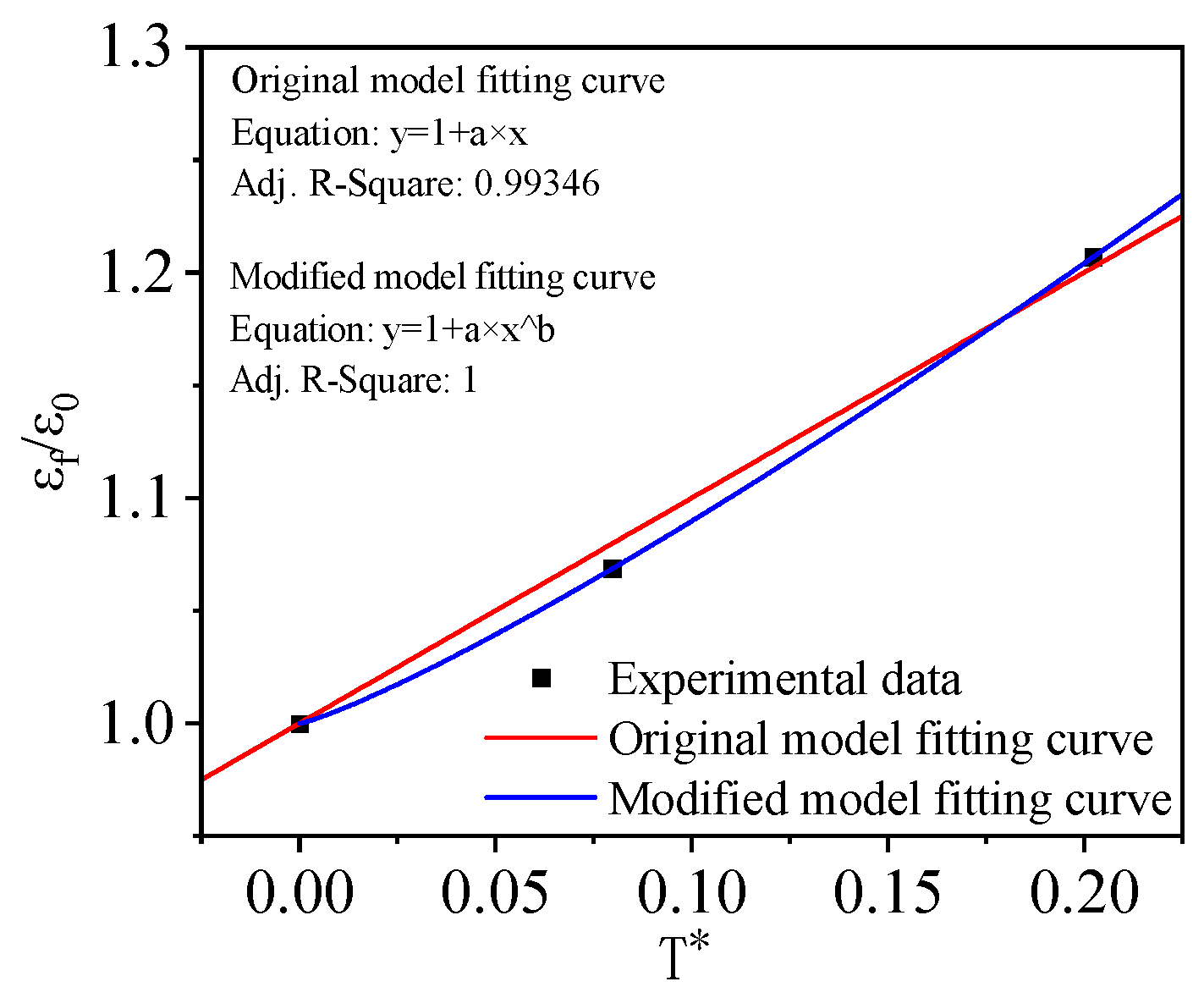
3.1.3. Parameters m
3.2. Calibration of J–C Failure Criterion Parameters
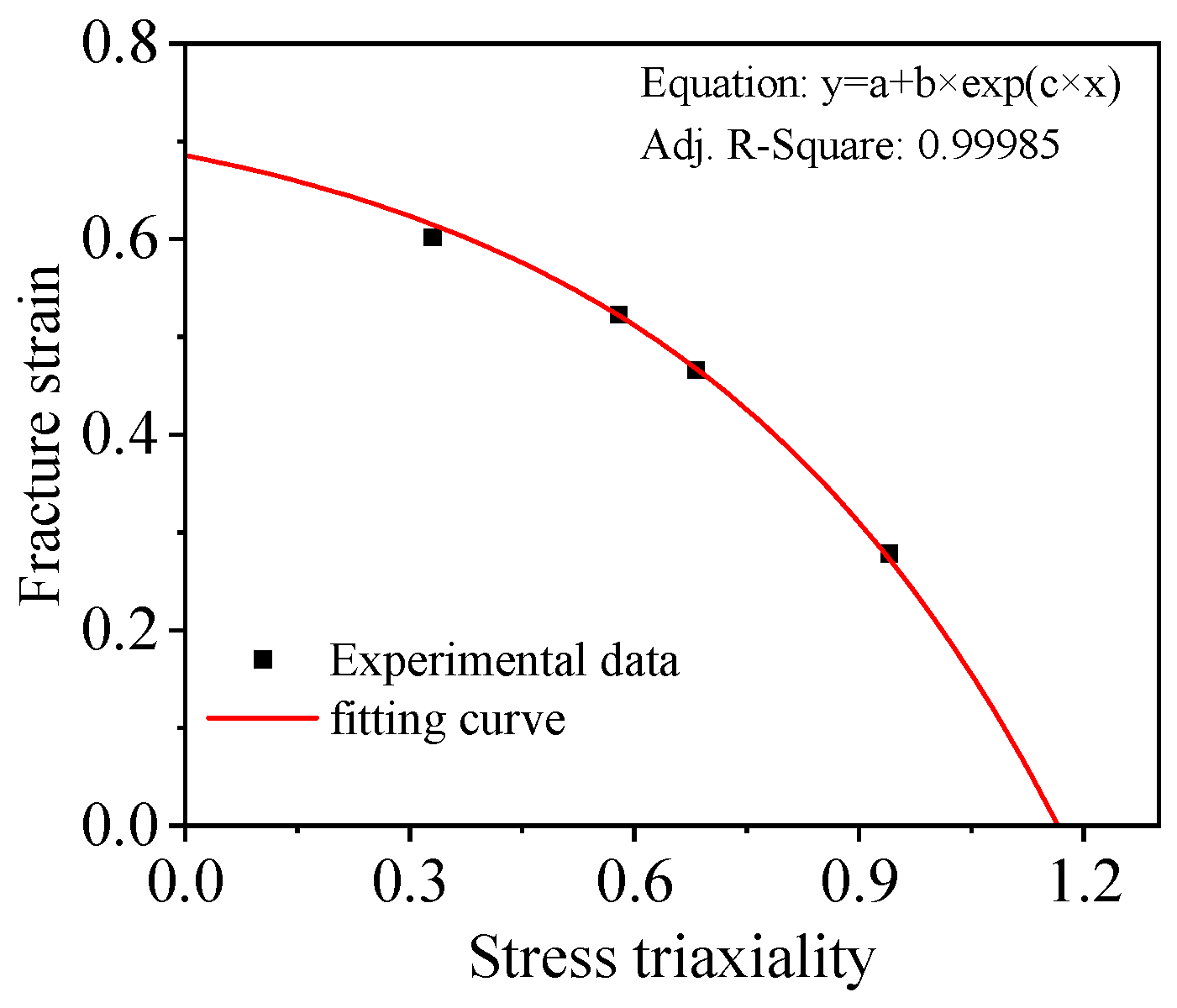
3.2.1. Parameters D1, D2, D3
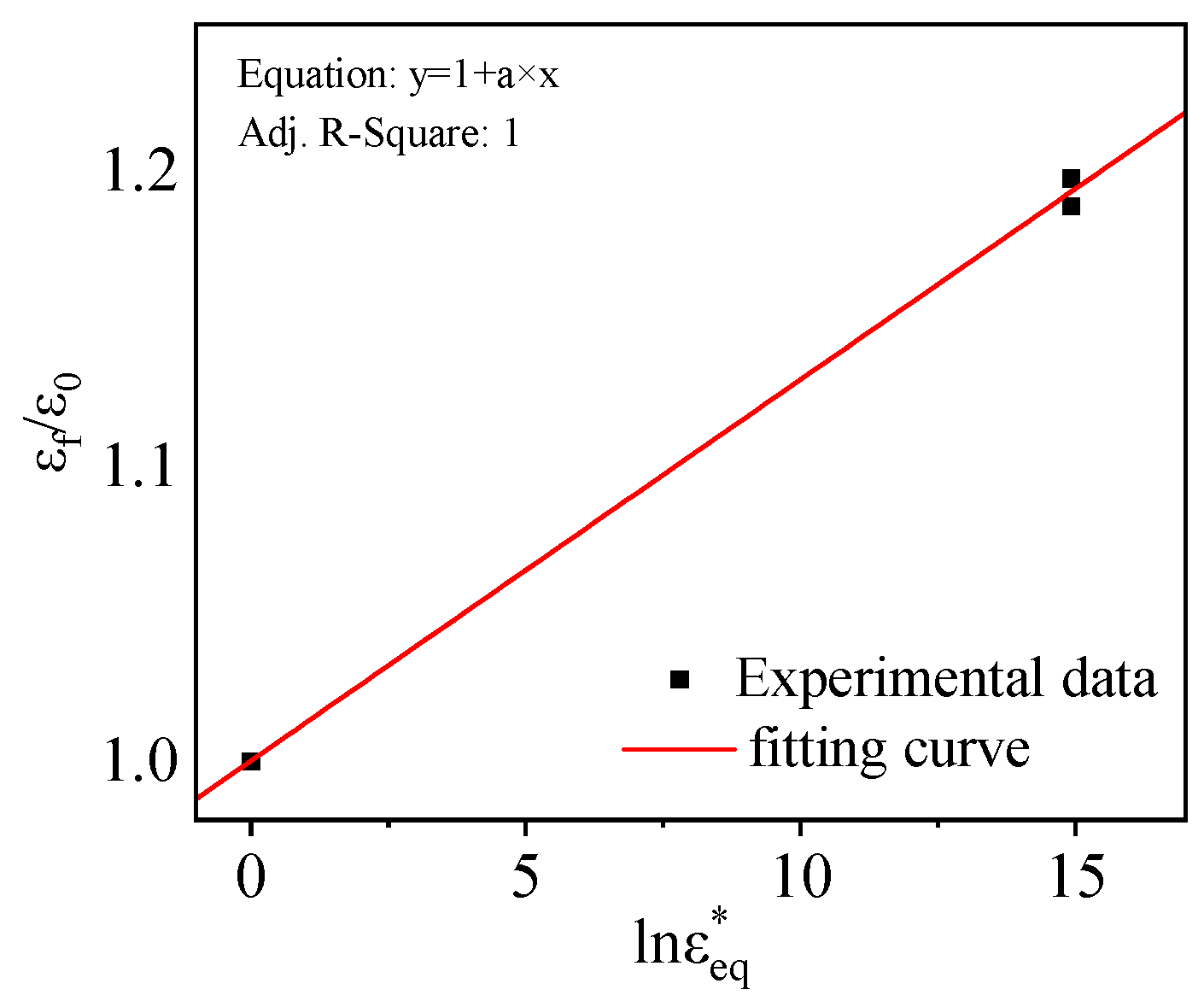
3.2.2. Parameters D4, D5, and D6
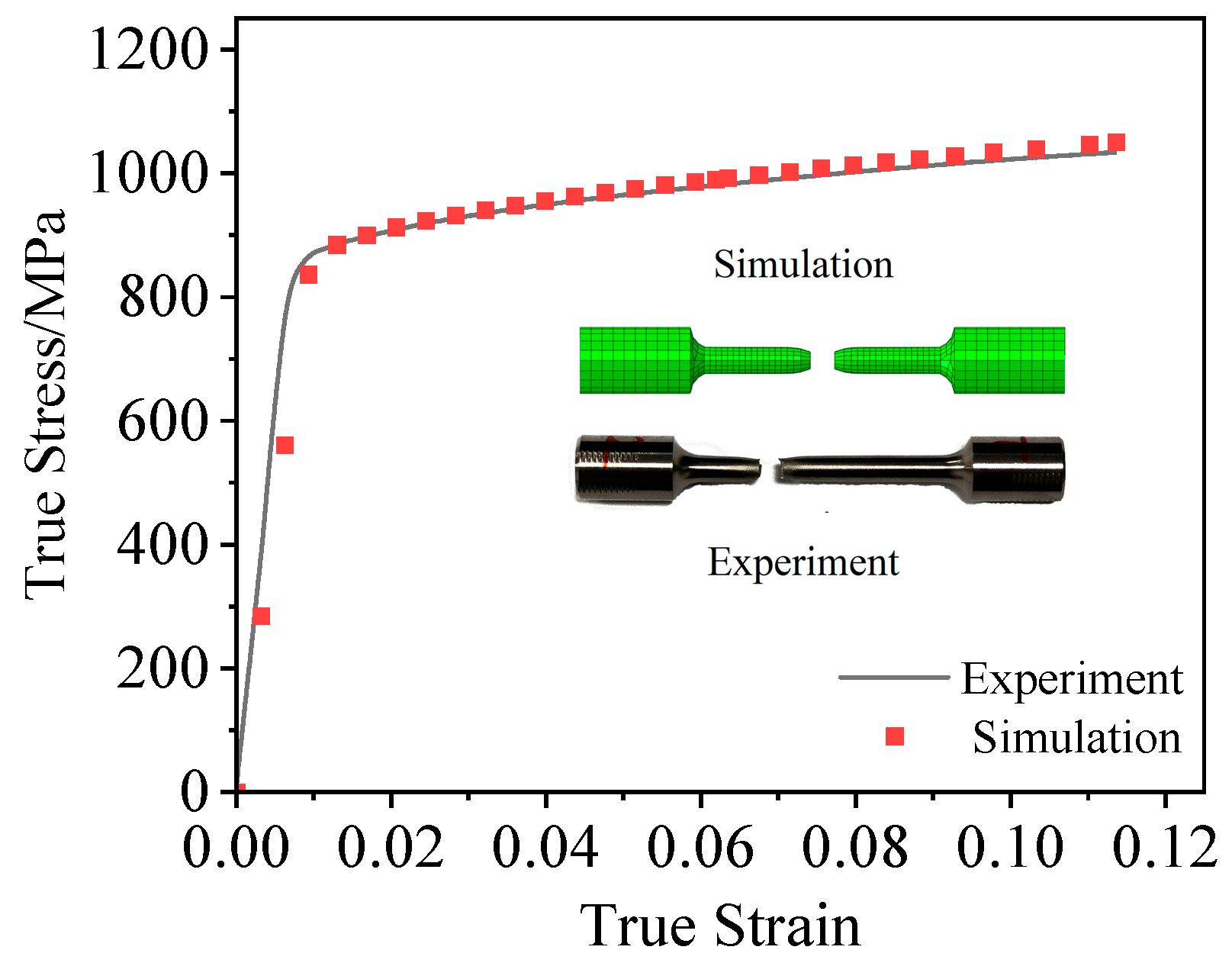
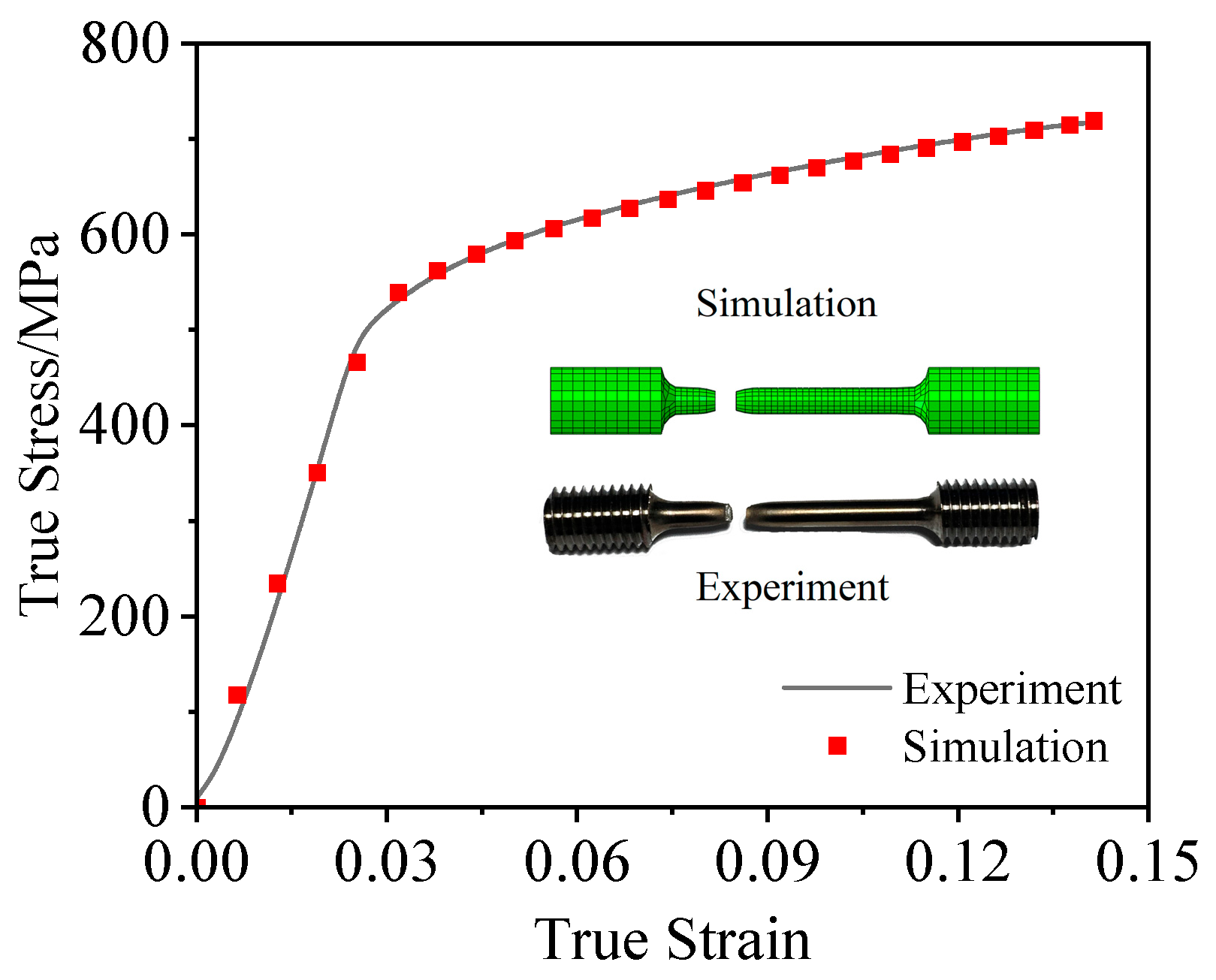
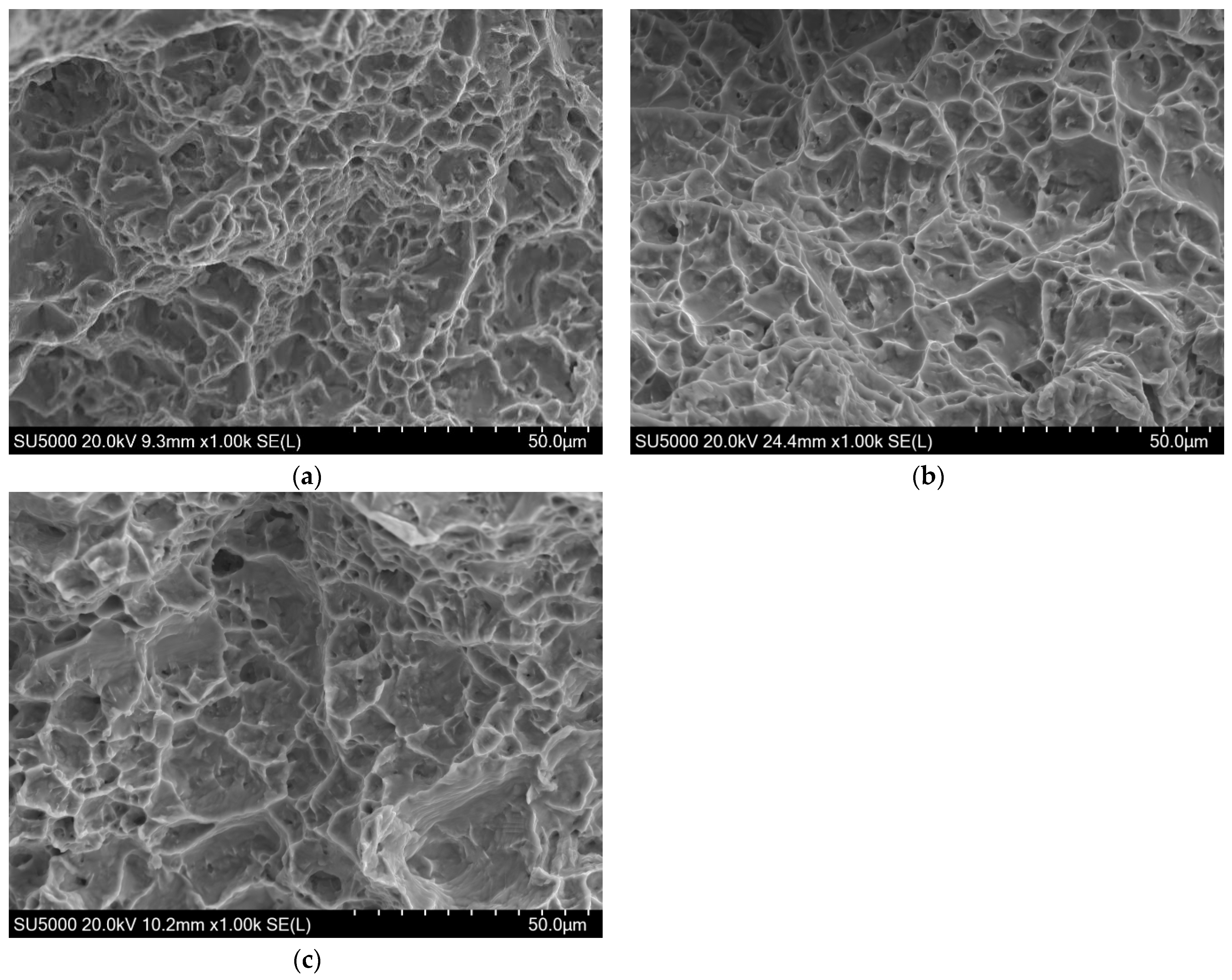
4. Model Reliability Validation and Microscopic Fractography Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The flow stress of TC4 alloy decreases with increasing temperature, while its fracture strain increases with temperature elevation, exhibiting a significant temperature-softening effect. The notch radius notably influences the alloy’s load-bearing capacity and post-fracture elongation, with larger notch radii resulting in better plasticity. Furthermore, within the strain rate range of 1000 s−1 to 3000 s−1, the strain-hardening effect of TC4 alloy appears relatively weak.
- (2)
- The J–C constitutive parameters and failure parameters were calibrated based on experimental data and validated through numerical simulations. The results demonstrate that the fitted J–C constitutive parameters and failure parameters can accurately describe the material’s mechanical properties as well as its deformation and failure behavior.
- (3)
- The fractographic analysis of TC4 alloy under varying temperatures and strain rates reveals a ductile fracture mechanism dominated by microvoid nucleation, growth, and coalescence. At low strain rate (0.001 s−1), the fracture surfaces exhibit uniformly distributed equiaxed dimples (5–8 μm) with secondary-phase particle debonding-induced microvoids, consistent with the plastic deformation behavior of α + β dual-phase Ti alloys. At high strain rate (3000 s−1), localized shear deformation is evidenced by tear ridges (1–2 μm height) aligned at 45° to the crack propagation path.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, Z.Y.; Dunstan, M.K.; McWilliams, B.; Robertson, S.; Hague, R.; Simonelli, M. Development of low-cost Ti alloys with a balanced strength and ductility with generation of ultra-fine microstructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1030, 180786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.W.; Ma, C.H.; Liu, J.L.; Zhao, H.J.; He, J.J. Improved dynamic impact behavior of TC4 alloy coated with Ti-SiC. Mater. Lett. 2025, 395, 138727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, H.X.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liang, Y.Y.; Hao, Y. Experimental Study of Performance of Ti-6Al-4V Femoral Implants Using Selective Laser Melting (SLM) Methodology. Metals 2024, 14, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.X.; Barella, S.B.; You, B.J.; Xiao, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, C.Y.; Gruttadauria, A.; Mapelli, C. Study on the mechanism of synergistic improvement of bonding strength and elongation of Ti/Al composite plates by annealing treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 941, 148603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.P.; Lei, M.; Li, X.W.; Li, Y.L. Phase formation, microstructure evolution, corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of porous Ti prepared by heat-treating Ag-coated Ti plate. Mater. Charact. 2025, 224, 115067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, S.H.; Deng, L.R.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, H. Investigation on dynamic deformation behavior of 7A75 aluminum alloy over wide strain rates and constitutive model establishment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 5963–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoria, S.R.; Gulhane, S.; Khan MD, F.; Sahoo, B.N. Hot deformation behavior study of coarse grained and ultrafine grained QE22 magnesium alloy through development of constitutive analysis and Johnson–Cook model. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1013, 178530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.T.; Zhang, C.T.; Zhu, H.J.; An, R.B. Modified Johnson-Cook constitutive model for butt-welded Q345 structural steel after high temperature cooling. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2025, 235, 109801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.J.; Fan, X.G.; Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Li, H. A modified Johnson–Cook model for NC warm bending of large diameter thin-walled Ti–6Al–4V tube in wide ranges of strain rates and temperatures. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.T.; Zhou, C.W.; Shi, Y.S.; Hu, A.; Xiao, X.K. Plasticity, ductile fracture and ballistic impact behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Impact. Eng. 2023, 174, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbrello, D.; M’Saoubi, R.; Outeiro, J.C. The influence of Johnson-Cook material constants on finite element simulation of machining of AISI 316L steel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manu. 2007, 47, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, K.X.; Chu, X.R.; Zhao, B.; Gao, J. Constitutive modelling and microscopic analysis of TC4 alloy sheet at elevated temperature. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; An, J.D.; Zhang, T.C.; Zhou, C.P. Mechanical properties and constitutive relationship of TC4 titanium alloy. J. Vib. Shock. 2020, 39, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.Z.; Xu, Z.J.; Dou, W.; Huang, F.L. Effects of strain rate and stress state on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 145, 103689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Huang, C.Z.; Zou, B.; Liu, H.L.; Zhu, H.T.; Wang, J. Dynamic behavior and a modified Johnson-Cook constitutive model of Inconel 718 at high strain rate and elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgman, P.W. Studies in Large Plastic Flow and Fracture with Special Emphasis on the Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshan, H.; Oñate, E.; Carbonell, J.M. Microstructure evolution modeling of Ti6Al4V alloy during cutting using the Particle Finite Element Method and homogeneous field distributions. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 131, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Al | V | Fe | O | C | N | H | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.38 | 4.17 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.013 | Bal. |
| Density/(g × cm−3) | Elastic Modulus/GPa | Poisson’s Ratio | Melting Point range/°C | Tensile Yield Strength/MPa | Ultimate Tensile Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.51 | 130 | 0.34 | 1600–1650 | 848 | 1042 |
| A/MPa | B/MPa | n | C | Maximum Strain Rate/s−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [10] | 895.2 | 910.1 | 0.749 | 0.033 | 4219 |
| Ref. [13] | 1040 | 1030 | 0.757 | 0.030 | 1137 |
| Ref. [14] | 797.5 | 305.7 | 0.285 | 0.020 | 6500 |
| This study | 848 | 566 | 0.505 | 0.034 | 3000 |
| R | ||
|---|---|---|
| 0 (smooth) | 0.333 | 0.6022 |
| 3 | 0.939 | 0.2785 |
| 6 | 0.682 | 0.4663 |
| 9 | 0.578 | 0.5227 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Zhi, H.; Huang, T.; Ding, N.; Yan, Z. Research on the Johnson–Cook Constitutive Model and Failure Behavior of TC4 Alloy. Metals 2025, 15, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15090951
Zhu J, Zhi H, Huang T, Ding N, Yan Z. Research on the Johnson–Cook Constitutive Model and Failure Behavior of TC4 Alloy. Metals. 2025; 15(9):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15090951
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiaxuan, Huidong Zhi, Tong Huang, Ning Ding, and Zhaoming Yan. 2025. "Research on the Johnson–Cook Constitutive Model and Failure Behavior of TC4 Alloy" Metals 15, no. 9: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15090951
APA StyleZhu, J., Zhi, H., Huang, T., Ding, N., & Yan, Z. (2025). Research on the Johnson–Cook Constitutive Model and Failure Behavior of TC4 Alloy. Metals, 15(9), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15090951






