Constructal Design and Numerical Simulation Applied to Geometric Evaluation of Stiffened Steel Plates Subjected to Elasto-Plastic Buckling Under Biaxial Compressive Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
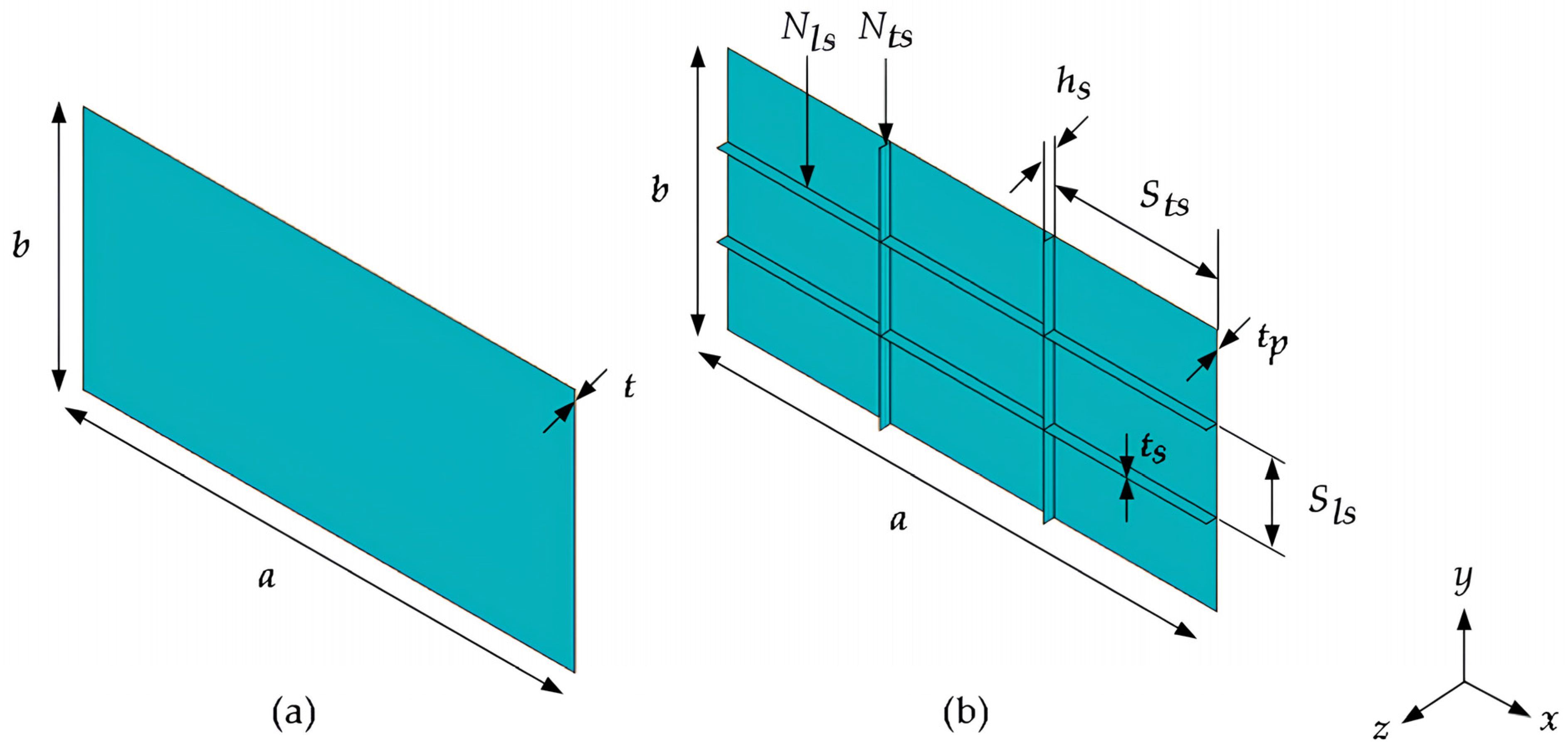
2.1. Computational Modeling of Unstiffened and Stiffened Plates
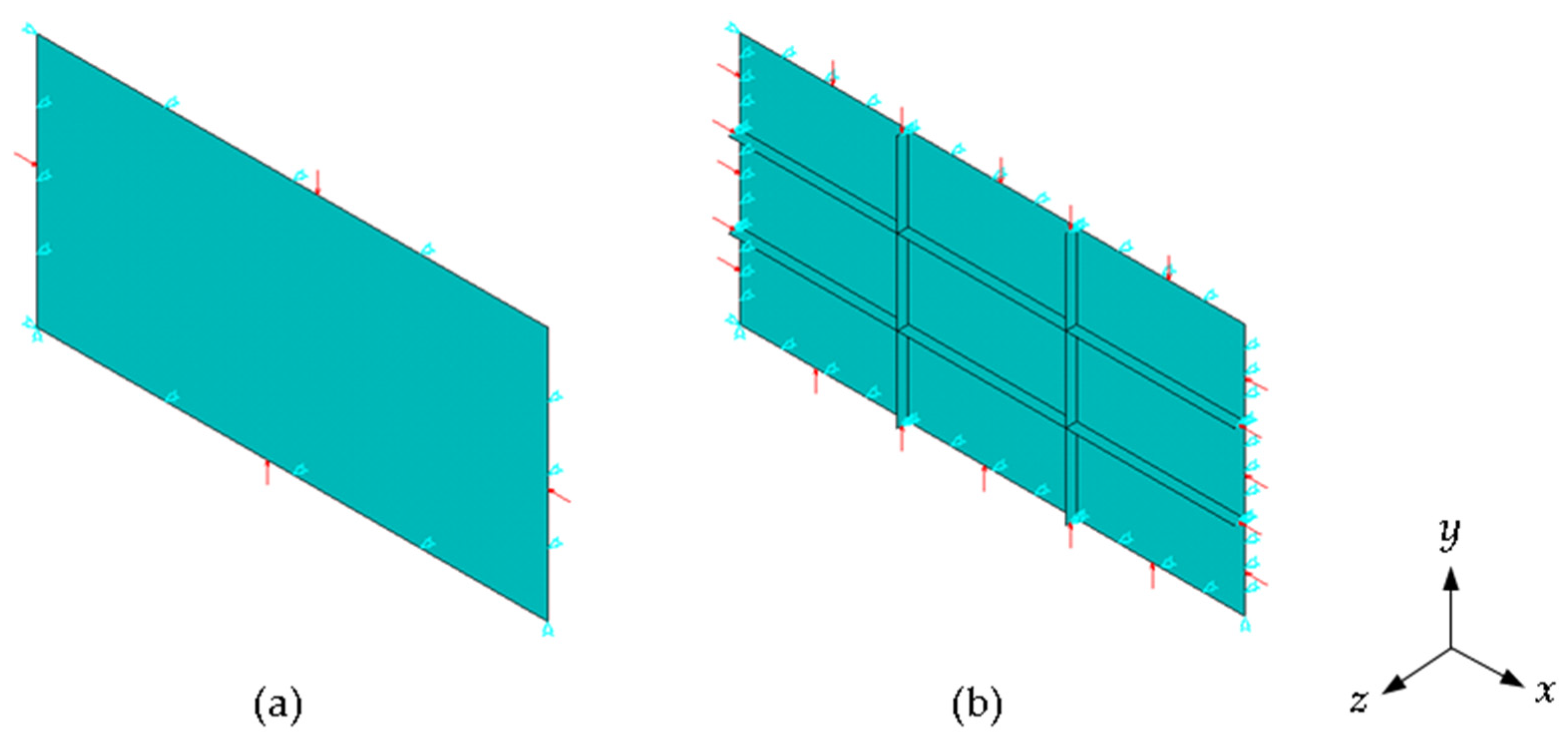
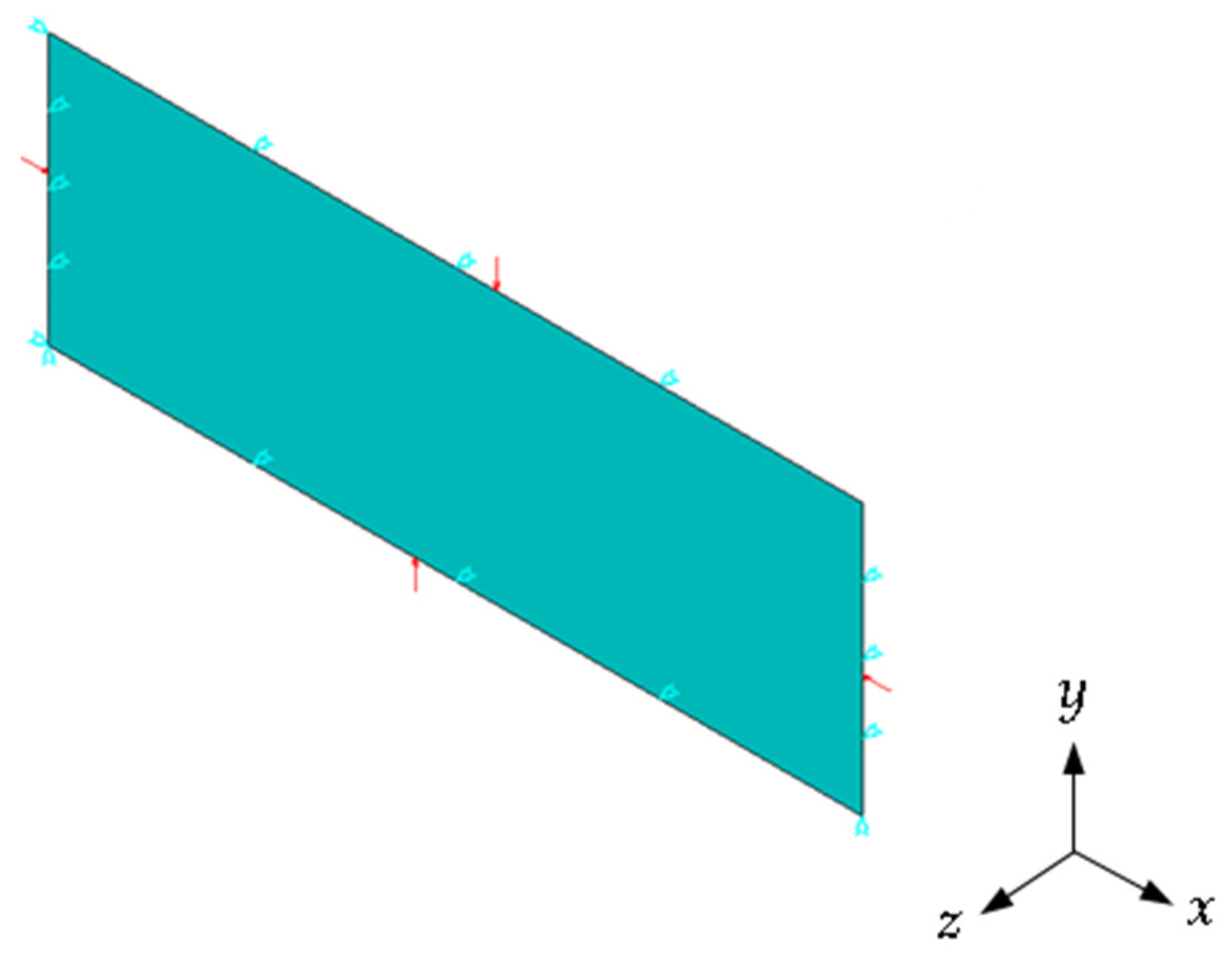
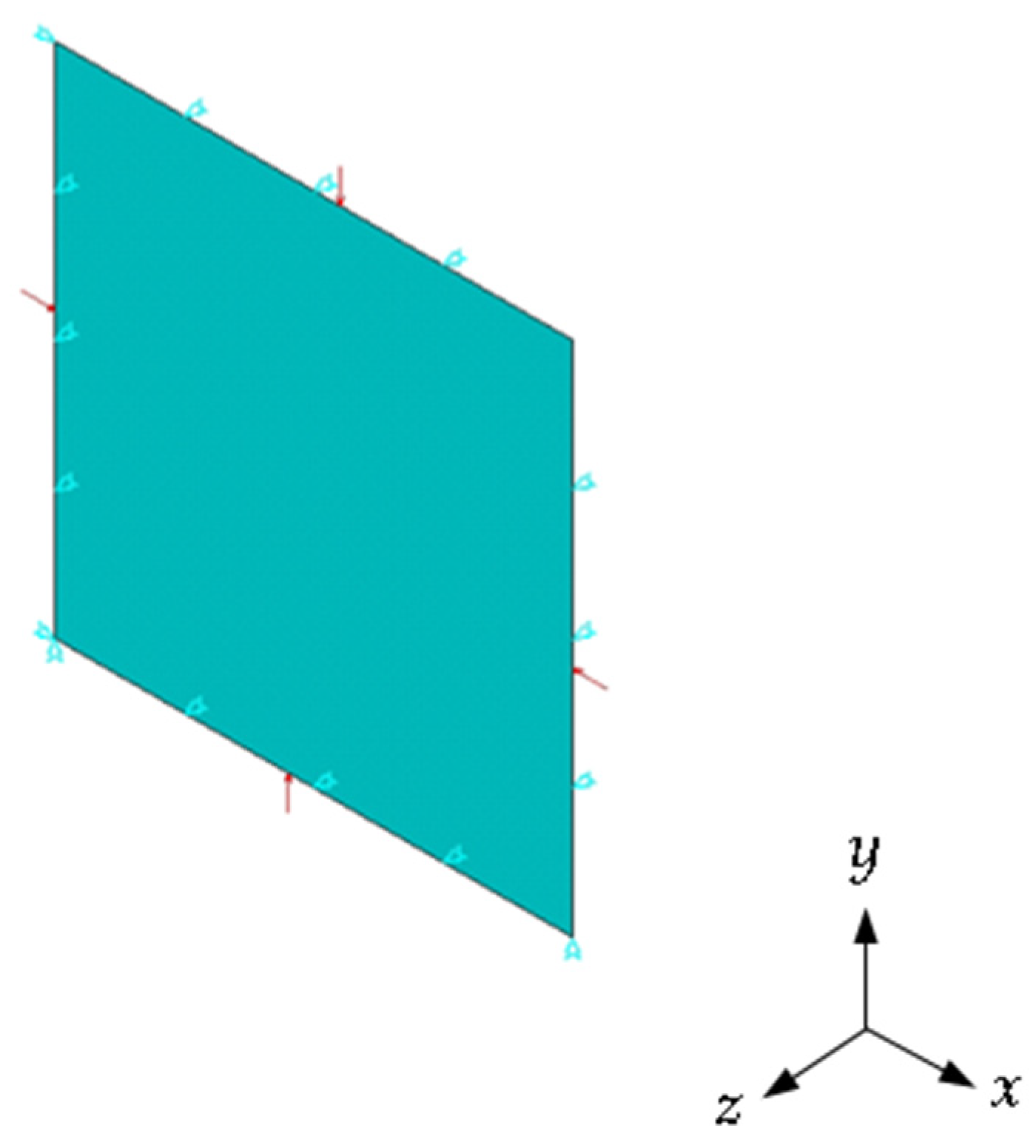
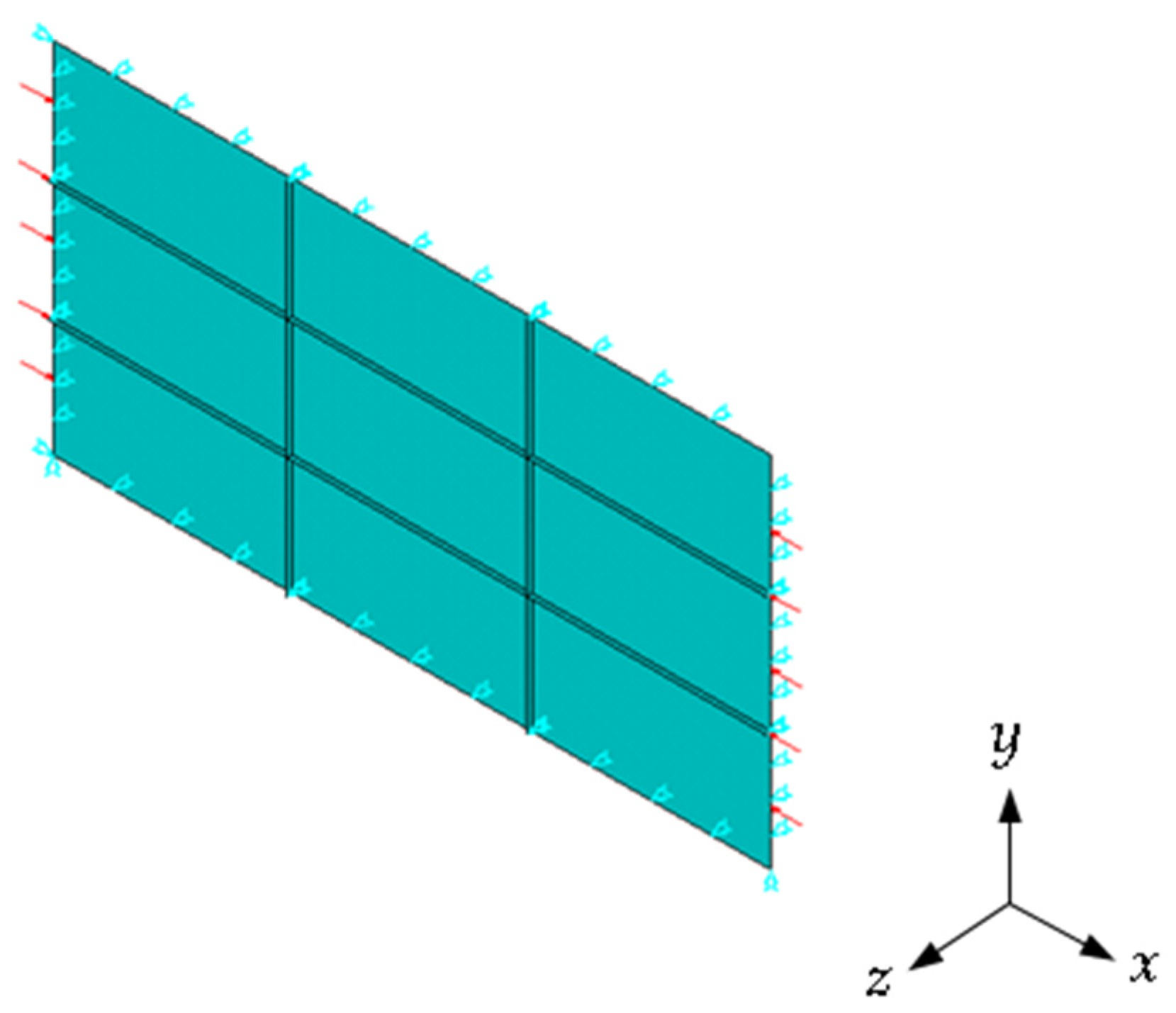
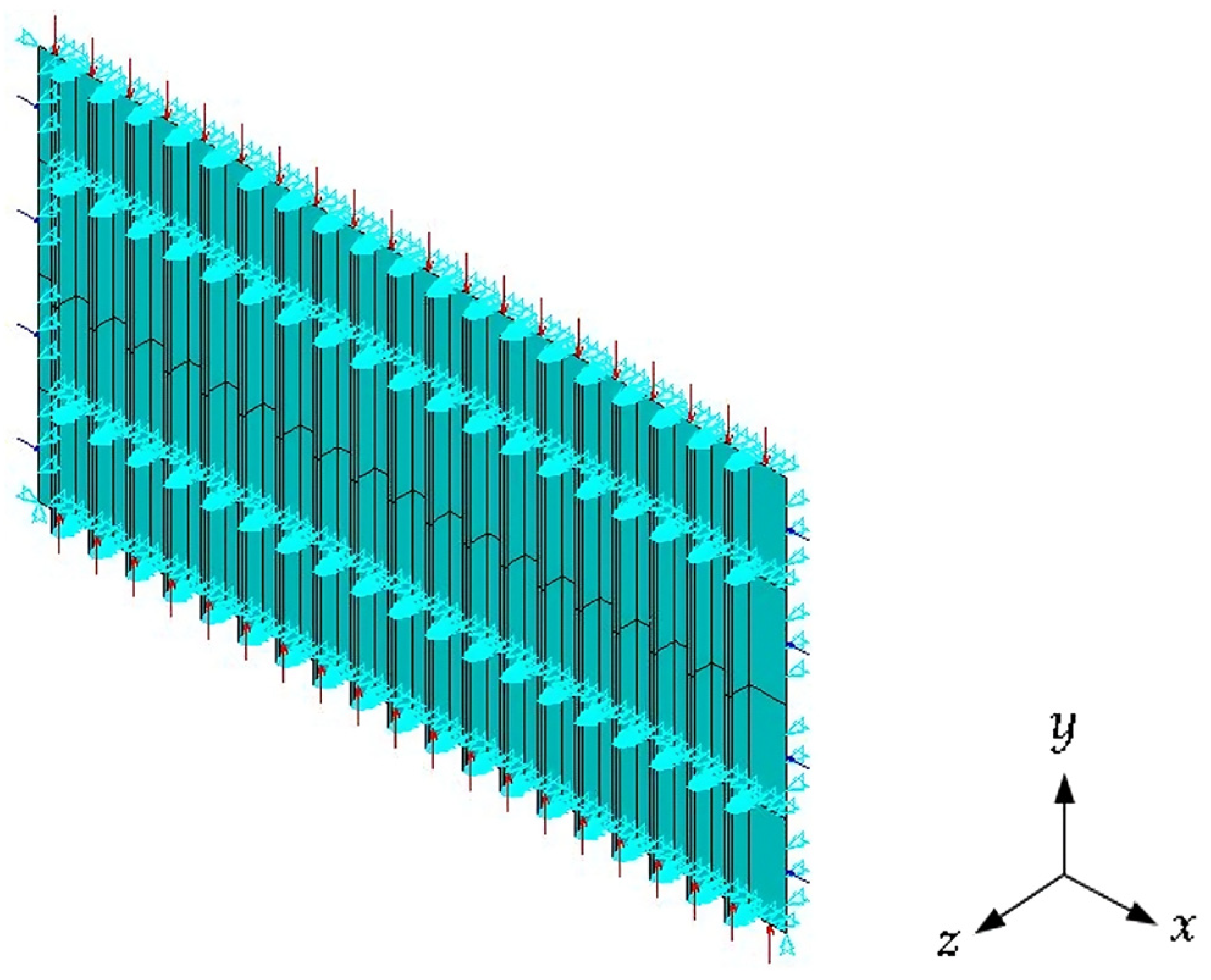
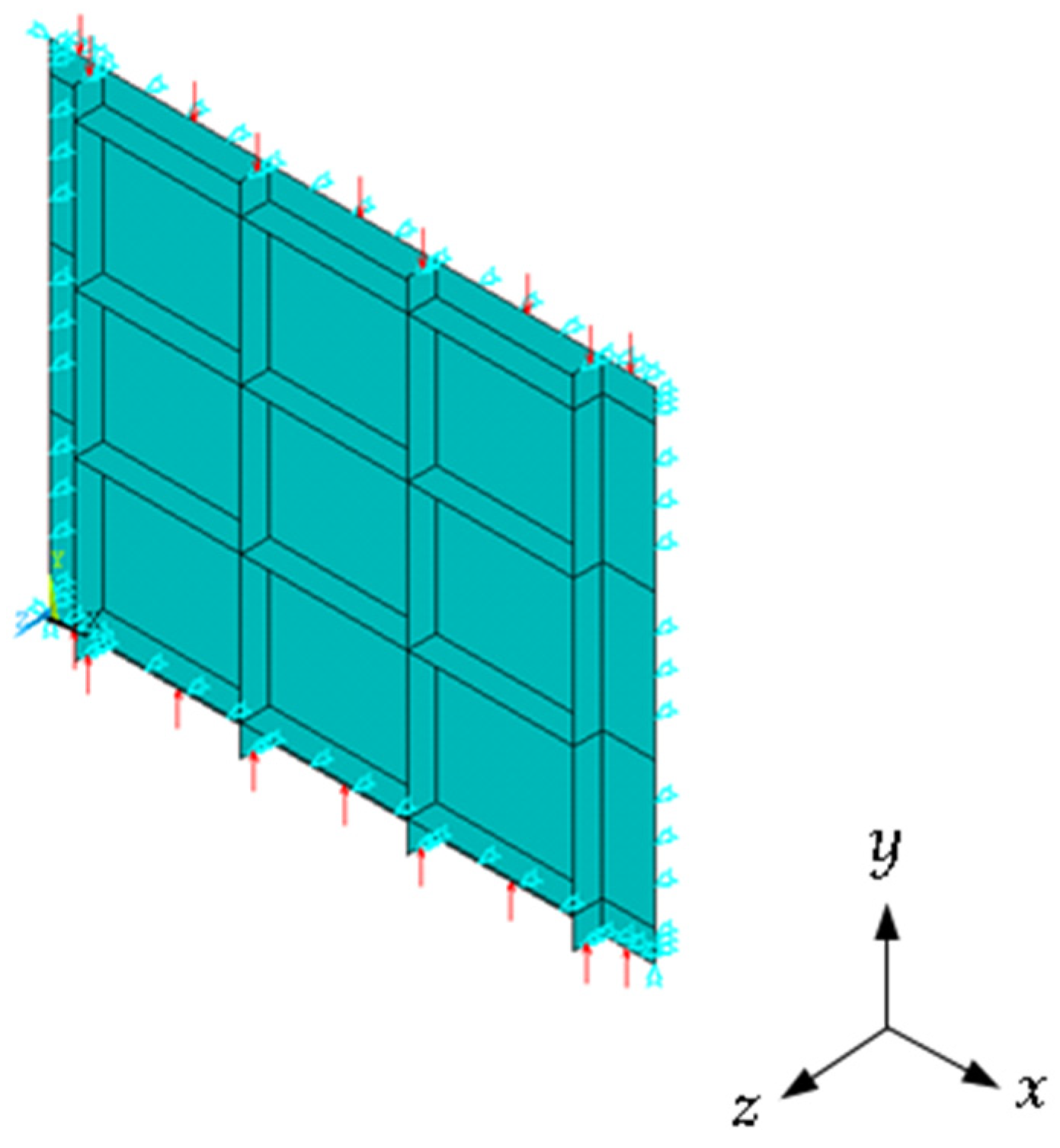
2.2. Boundary and Loading Conditions
2.3. Computational Modeling of Elastic Buckling
2.4. Computational Modeling of Elasto-Plastic Buckling
2.5. Finite Element
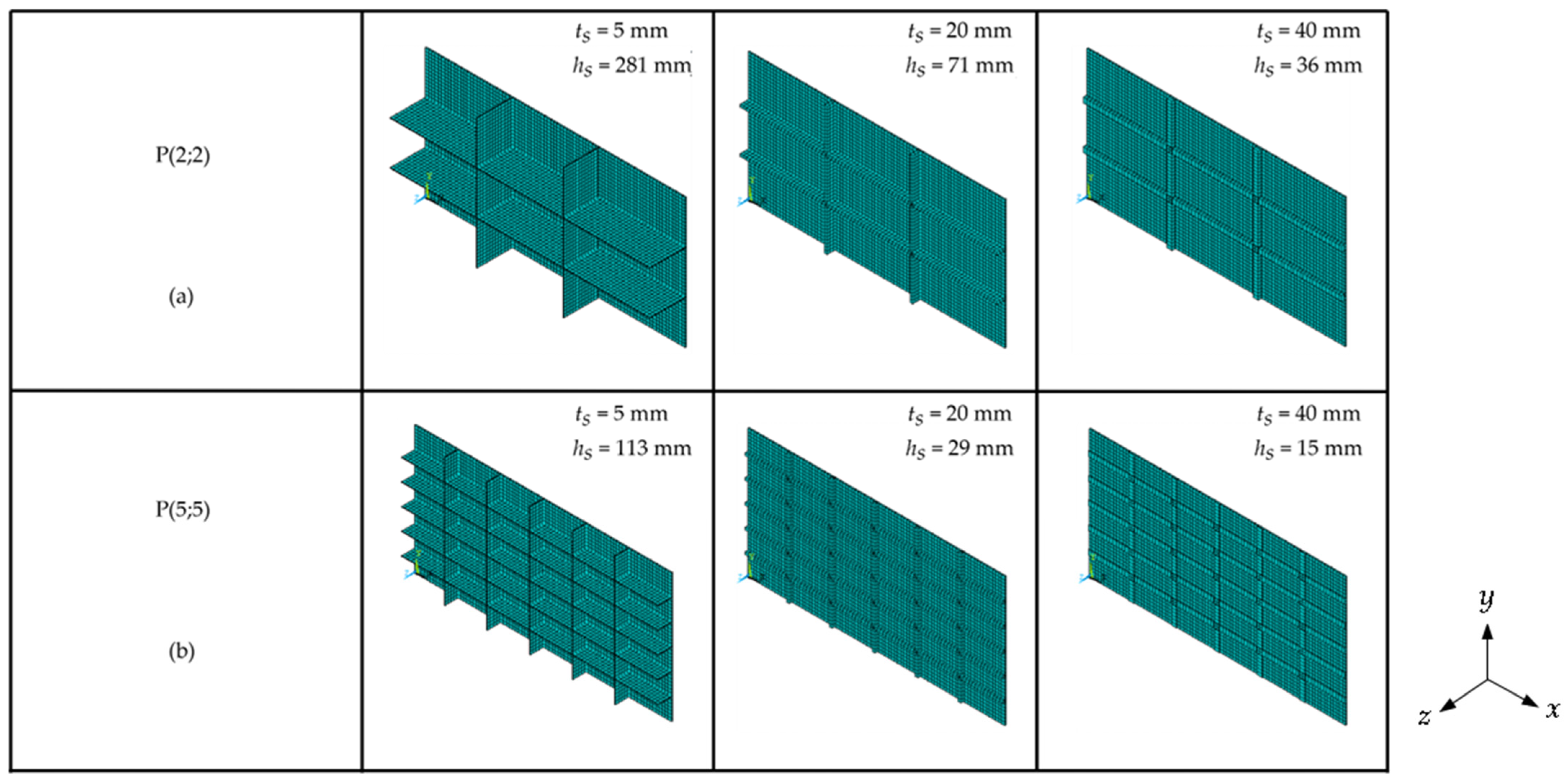
2.6. Constructal Design and Exhaustive Search
2.7. Mesh Convergence Test
2.8. Sub-Steps Load Convergence Test
2.9. Verification of Computational Model
3. Results and Discussion
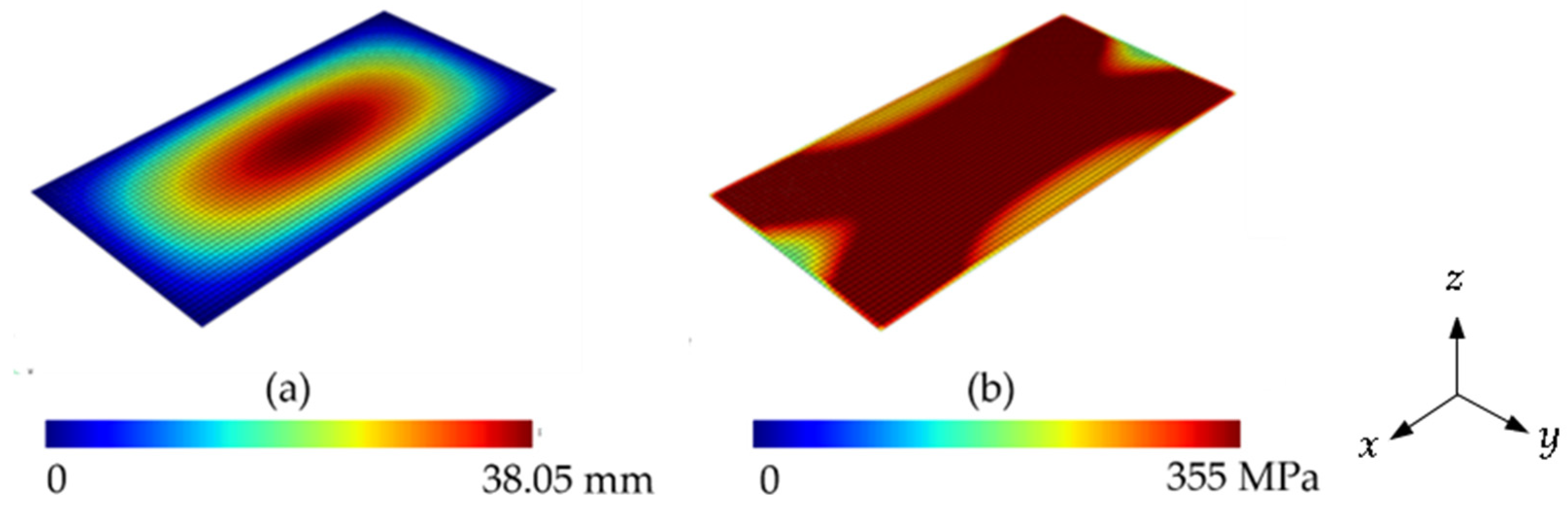
3.1. Computational Model Verification and Validation
3.1.1. Verification for Elasto-Plastic Buckling and Unstiffened Plates
3.1.2. Validation for Elasto-Plastic Buckling and Unstiffened Plates
3.1.3. Verification for Elasto-Plastic Buckling and Stiffened Plates
3.1.4. Validation for Elasto-Plastic Buckling and Stiffened Plates
3.2. Mesh Convergence Test—Case Study
3.3. Load-Steps Convergence Test—Case Study
3.4. Reference Plate
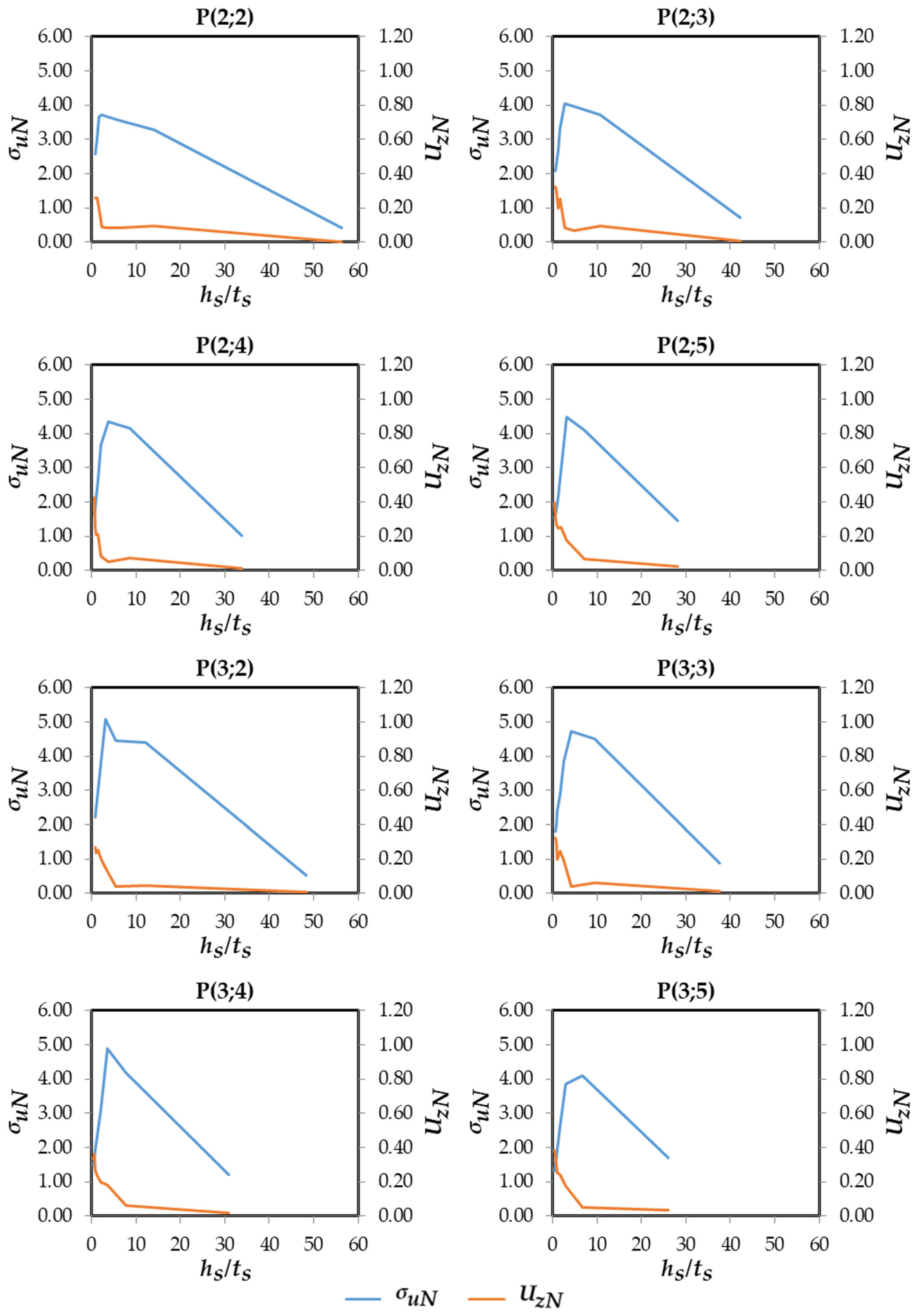
3.5. Influence of , and over
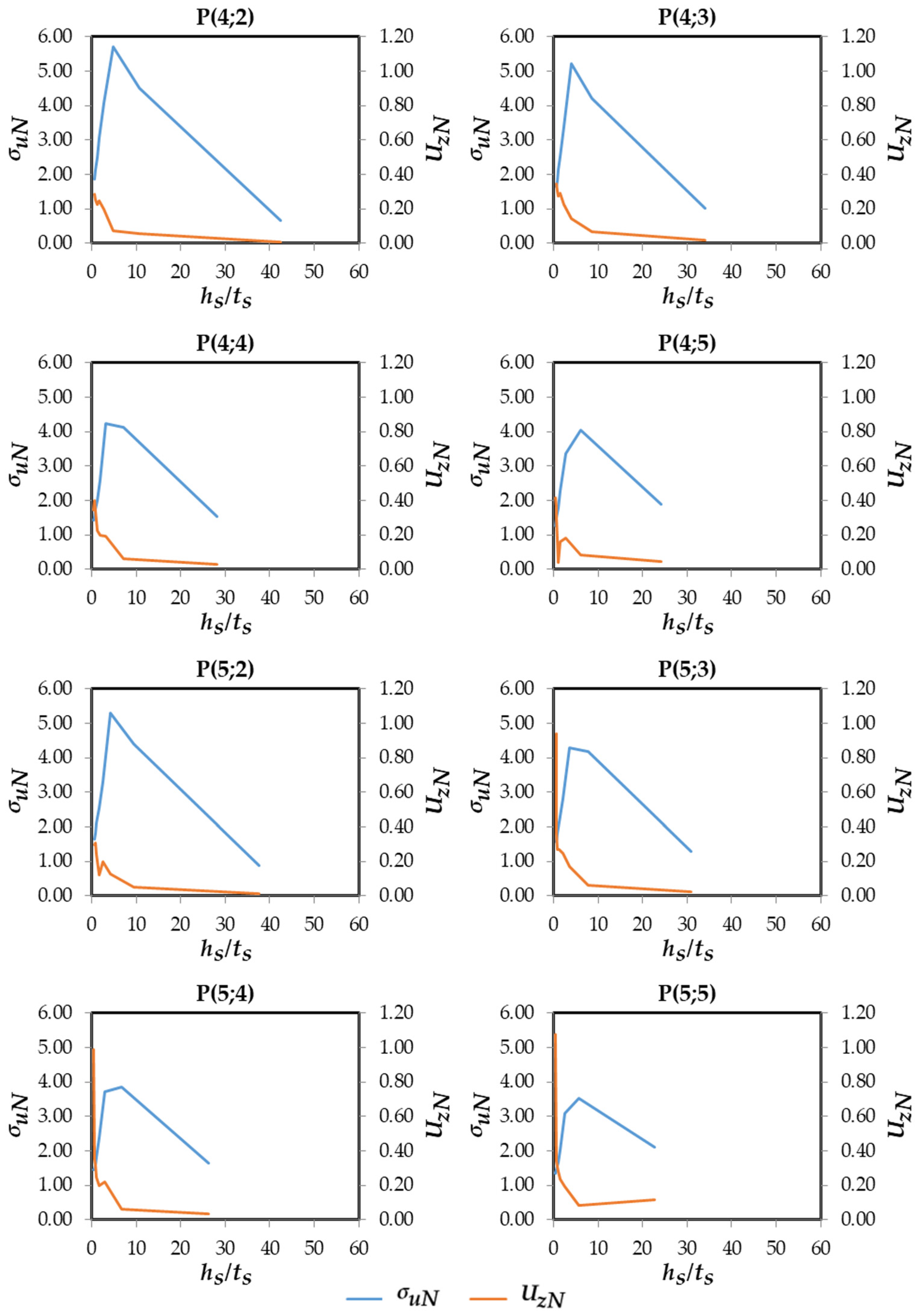
3.6. Influence of /, , and over and
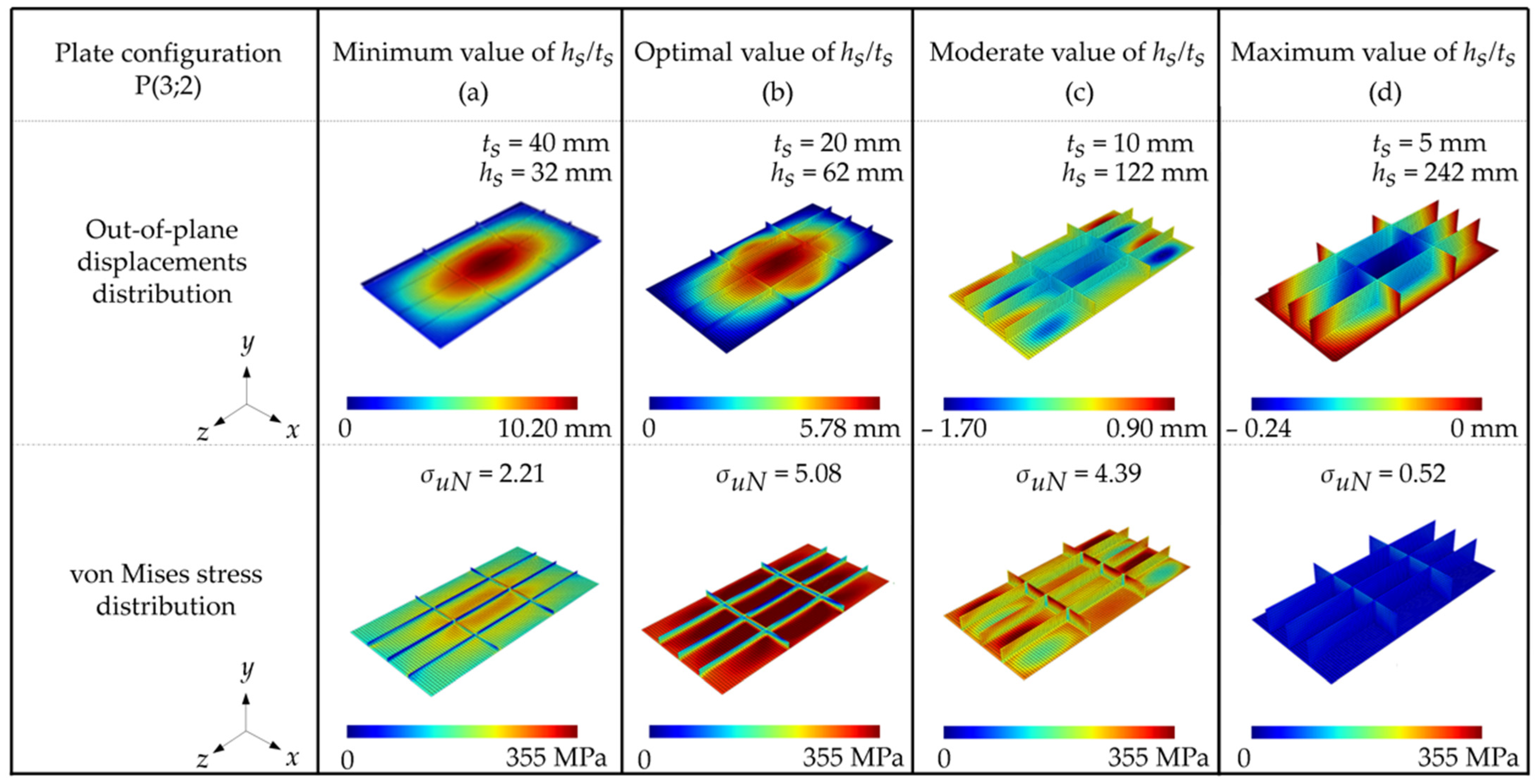
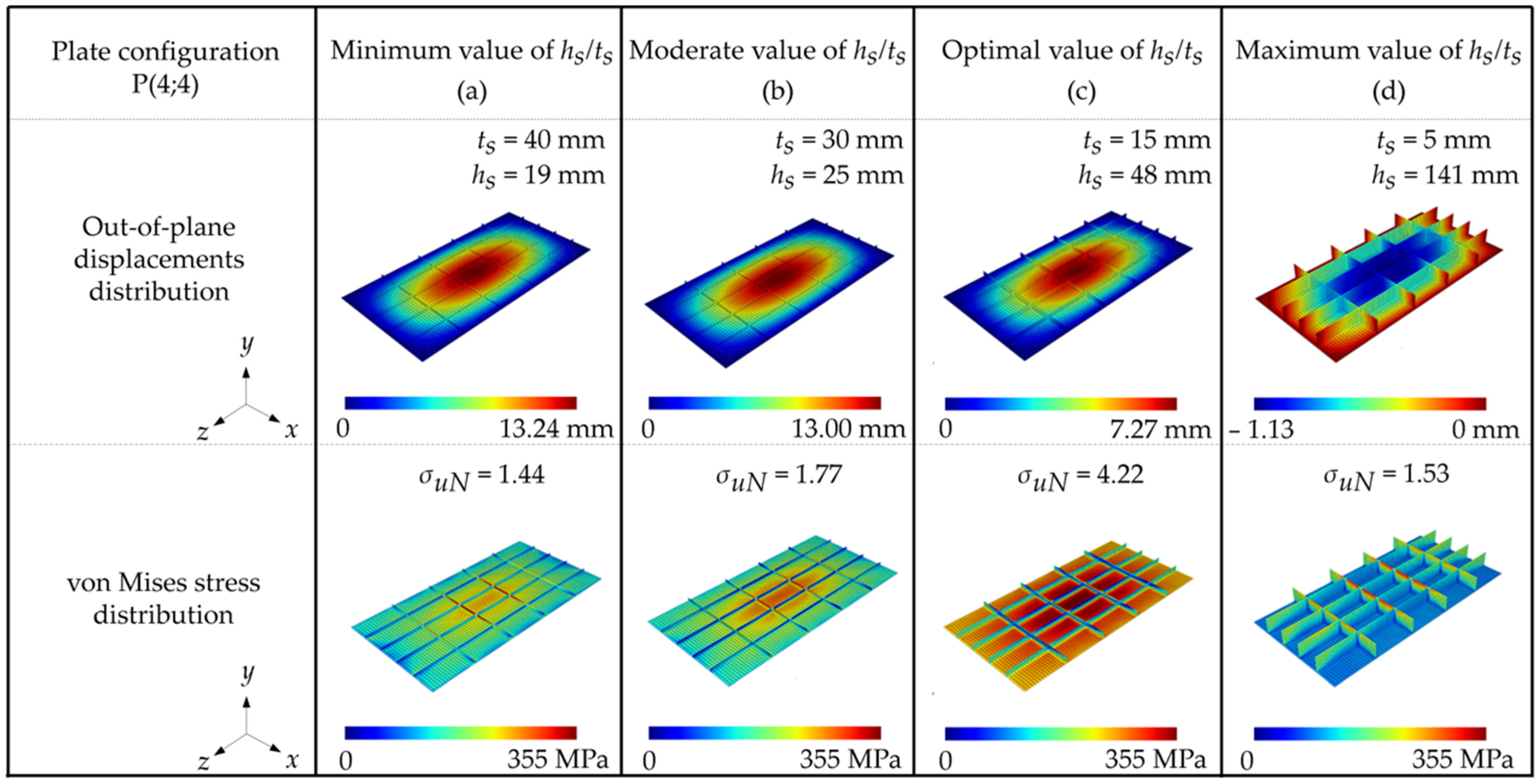
3.7. Highest and Lowest Values of /, , and over
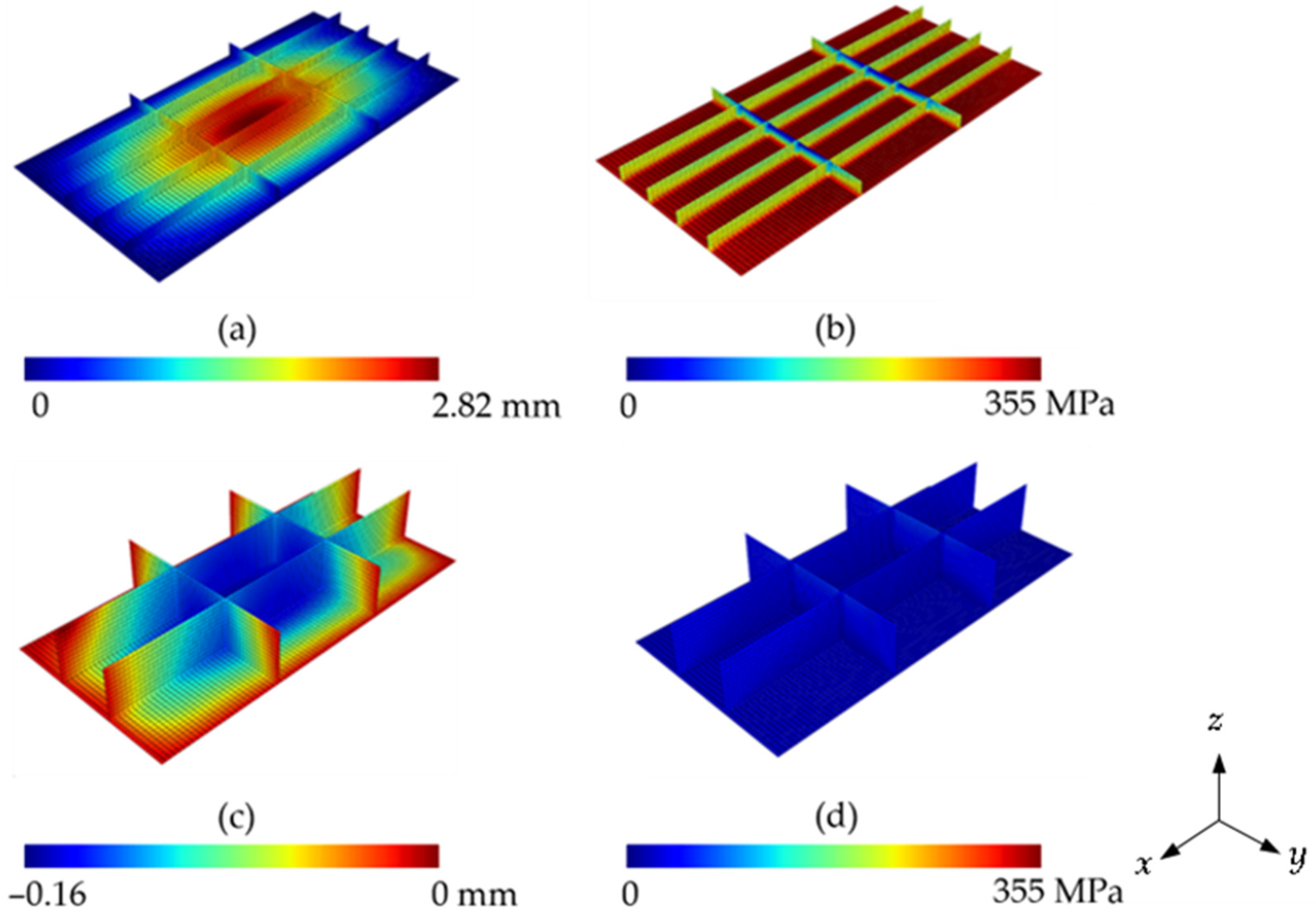
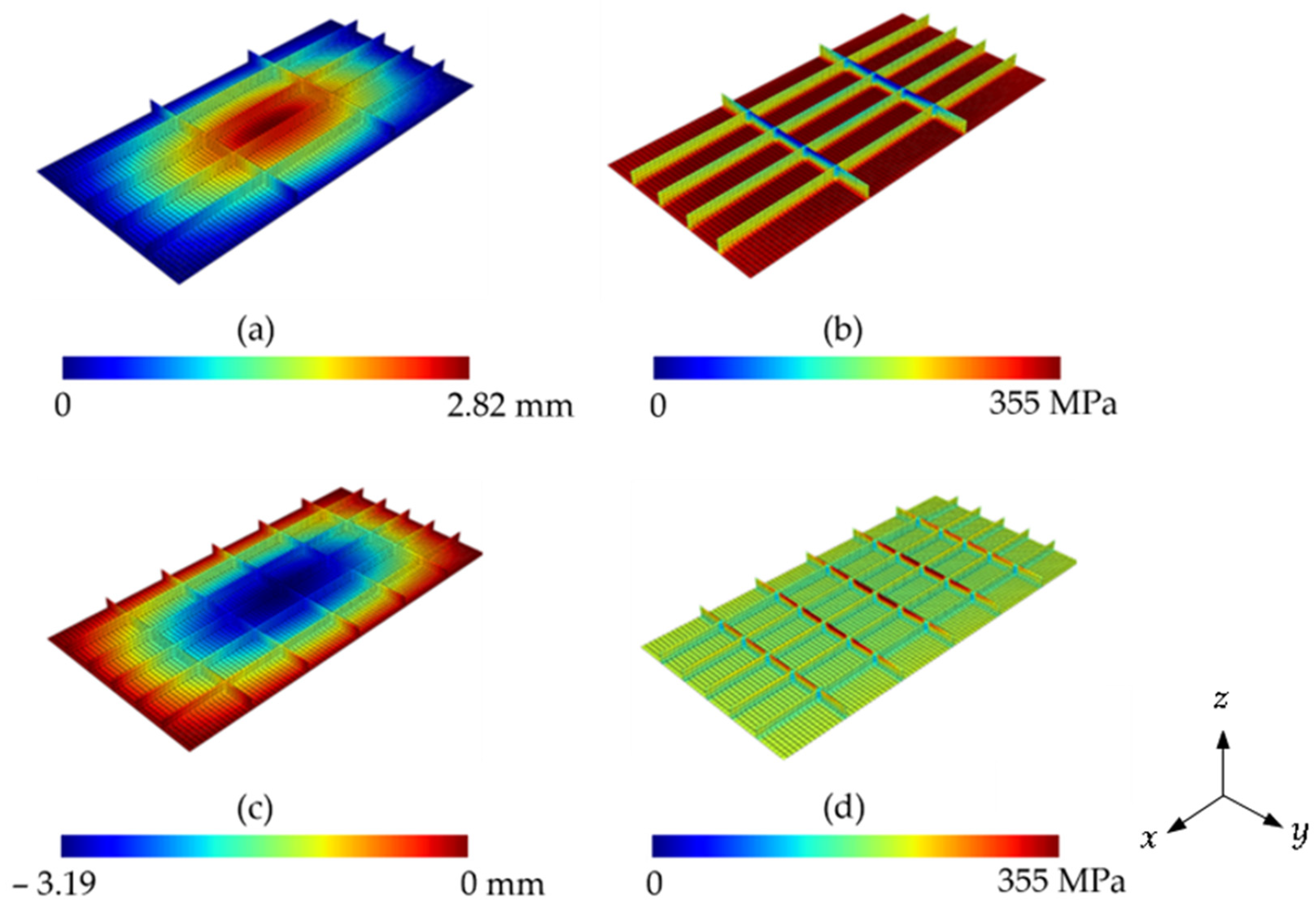
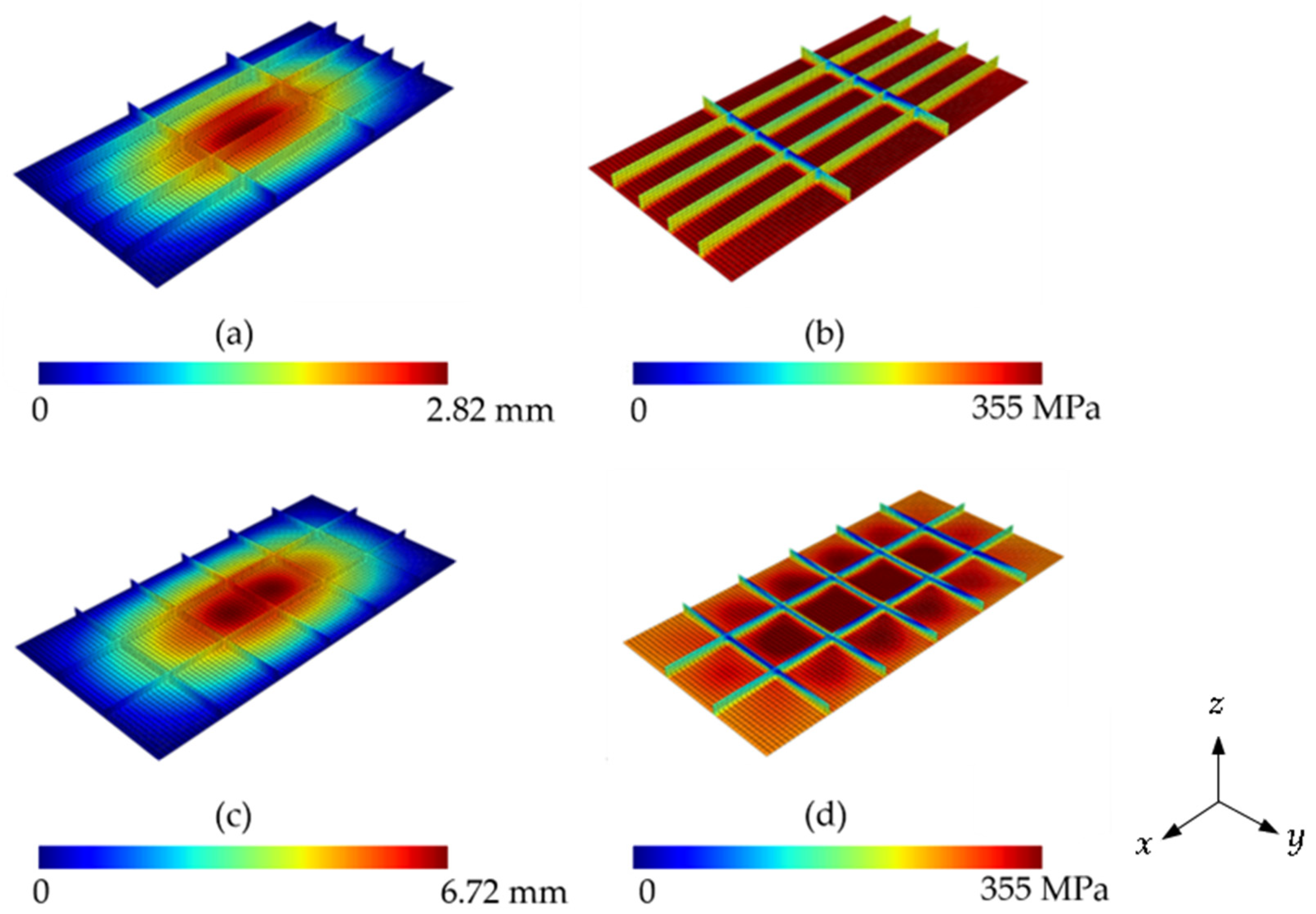
3.8. Influence of and over Once Optimized and Once Maximized
3.9. Influence of , , and on
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, R.M.R. Buckling of Bars, Plates and Shells; Bull Ridge Publishing: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Szilard, R. Theories and Applications of Plate Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Musmar, M.A. Structural Performance of Steel Plates. Front. Built Environ. 2022, 8, 991061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sawy, K.M.; Nazmy, Y.A.S.; Martini, M.I. Elasto-Plastic Buckling of Perforated Plates under Uniaxial Compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2004, 42, 1083–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trahair, N.S.; Bradford, M.A.; Nethercot, D.A.; Gardner, L. The Behavior and Design of Steel Structures, 4th ed.; Taylor & Francis, CRC Press: Abingdon, UK, 2008; ISBN 9780415301565. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, Y.; Yao, T. Ultimate Strength of Compressed Stiffened Plates and Minimum Stiffness Ratio of Their Stiffeners. Eng. Struct. 1983, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Mahdi, M.A. Buckling Load Maximization of Stiffened Plates Using Level Set Topology Optimization and Inverse Isoparametric Mapping Algorithm. In Proceedings of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, San Diego, CA, USA, 8 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, R.L.; Baumgardt, G.R.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O.; da Silveira, T.; Lima, J.P.S.; Isoldi, L.A. Computational Model and Constructal Design Applied to Thin Stiffened Plates Subjected to Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loading Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troina, G.; Cunha, M.; Pinto, V.; Rocha, L.; Santos, E.D.; Fragassa, C.; Isoldi, L. Computational Modeling and Constructal Design Theory Applied to the Geometric Optimization of Thin Steel Plates with Stiffeners Subjected to Uniform Transverse Load. Metals 2020, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, J.P.T.P.; Cunha, M.L.; Pavlovic, A.; Rocha, L.A.O.; dos Santos, E.D.; Troina, G.d.S.; Isoldi, L.A. Geometric Evaluation of Stiffened Steel Plates Subjected to Transverse Loading for Naval and Offshore Applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, D.M.P.; Pinto, V.T.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Dos Santos, E.D.; Fragassa, C.; Isoldi, L.A. Geometric Analysis By Constructal Design Of Stiffened Steel Plates Under Bending with Transverse I-Shaped Or T-Shaped Stiffeners. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2022, 20, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.P.S.; Cunha, M.L.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Real, M.d.V.; Isoldi, L.A. Constructal Design for the Ultimate Buckling Stress Improvement of Stiffened Plates Submitted to Uniaxial Compressive Load. Eng. Struct. 2020, 203, 109883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.P.S.; Rocha, L.A.O.; dos Santos, E.D.; Real, M.d.V.; Isoldi, L.A. Constructal Design And Numerical Modeling Applied To Stiffened Steel Plates Submitted To Elasto-Plastic Buckling. Proc. Rom. Acad. Ser. A—Math. Phys. Tech. Sci. Inf. Sci. 2018, 19, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ringsberg, J.W.; Darie, I.; Nahshon, K.; Shilling, G.; Vaz, M.A.; Benson, S.; Brubak, L.; Feng, G.; Fujikubo, M.; Gaiotti, M.; et al. The ISSC 2022 Committee III.1-Ultimate Strength Benchmark Study on the Ultimate Limit State Analysis of a Stiffened Plate Structure Subjected to Uniaxial Compressive Loads. Mar. Struct. 2021, 79, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tian, K.; Hao, P.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Hybrid Analysis and Optimization of Hierarchical Stiffened Plates Based on Asymptotic Homogenization Method. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, K.; Khedmati, M.R. Numerical and Experimental Investigations on the Compression Behaviour of Stiffened Plates. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2006, 62, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Kurgan, N. Modeling and Buckling Analysis of Rectangular Plates in ANSYS. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 11, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, N.E.; Narayanan, R. Ultimate Strength of Biaxially Loaded Plates. In Stability and Ductility of Steel Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Piscopo, V. Refined Buckling Analysis of Rectangular Plates Under Uniaxial and Biaxial Compression. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2010, 4, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Kim, B.J.; Seo, J.K. Methods for Ultimate Limit State Assessment of Ships and Ship-Shaped Offshore Structures: Part I-Unstiffened Plates. Ocean. Eng. 2008, 35, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Seo, J.K. Nonlinear Finite Element Method Models for Ultimate Strength Analysis of Steel Stiffened-Plate Structures under Combined Biaxial Compression and Lateral Pressure Actions—Part I: Plate Elements. Thin-Walled Struct. 2009, 47, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Yanagihara, D.; Yasuoka, A.; Harada, M.; Okazawa, S.; Fujikubo, M.; Yao, T. Evaluation of Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Panels under Longitudinal Thrust. Mar. Struct. 2014, 36, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfantis, K.N.; Pantazopoulou, S.; Papanikolaou, N. Generalized Probabilistic Response Surfaces for the Buckling Strength Assessment of Stiffened Panels. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 189, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneel Kumar, M.; Lavana Kumar, C.; Alagusundaramoorthy, P.; Sundaravadivelu, R. Ultimate Strength of Orthogonal Stiffened Plates Subjected to Axial and Lateral Loads. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 14, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xing, Y. A Semi-Analytical Solution for Critical Buckling Loads of Orthotropic Stiffened Rectangular Thin Plates. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 205, 112449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.; Ergin, A.; Yanagihara, D.; Tanaka, S.; Yao, T. A New Method to Estimate Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Panels under Longitudinal Thrust Based on Analytical Formulas. Mar. Struct. 2018, 59, 510–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Cui, J.; Wang, D. An Experimental Investigation on the Collapse Modes of Stiffened Plates Subjected to Combined Axial and Lateral Loads. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 299, 117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Mei, H.; Wang, D. Scale Model Design for the Stiffened Plate Subjected to Combined Longitudinal Compression and Lateral Pressure Considering Collapse Modes. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 243, 110289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.C.; Song, Z.J.; Zhang, B.W.; Pan, J. Empirical Formula for Predicting Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Panel of Ship Structure under Combined Longitudinal Compression and Lateral Loads. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 162, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Kong, X.; Wu, W. A Universal Similarity Method and Design Procedure for Buckling Assessment of Stiffened Plates under Compression Load on Real Ships. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 181, 110025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, D. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Plates Subjected to Combined Biaxial Compression and Lateral Loads. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 228, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikubo, M.; Harada, M.; Yao, T.; Khedmati, M.R.; Yanagihara, D. Estimation of Ultimate Strength of Continuous Stiffened Panel under Combined Transverse Thrust and Lateral Pressure Part 2: Continuous Stiffened Panel. Mar. Struct. 2005, 18, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.-J.; Xiong, Y.-F.; Cai, S.-J.; Wang, D.-Y. Experiment Study of Dynamic Buckling for Stiffened Panels under Longitudinal Impact. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 284, 115243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfantis, K.N. Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Panels Subjected to Non-Uniform Thrust. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 12, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad-Eldeen, S.; Garbatov, Y. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Structural Capacity of Perforated Stiffened Plates. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, N.E.; Dongqi, Z.; Choo, Y.S.; Arockiaswamy, M. Experimental Studies on Stiffened Plates under In-Plane Load and Lateral Pressure. Thin-Walled Struct. 2014, 80, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.K.; Song, C.H.; Park, J.S.; Paik, J.K. Nonlinear Structural Behaviour and Design Formulae for Calculating the Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Curved Plates under Axial Compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 107, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Kim, B.J.; Seo, J.K. Methods for Ultimate Limit State Assessment of Ships and Ship-Shaped Offshore Structures: Part II-Stiffened Plates. Ocean. Eng. 2008, 35, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Kim, B.J. Ultimate Strength Formulations for Stiffened Panels under Combined Axial Load, in-Plane Bending and Lateral Pressure: A Benchmark Study. Thin-Walled Struct. 2002, 40, 45–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Wang, D. Ultimate Strength Characteristics and Assessment of Laser-Welded Web-Core Sandwich Plates under Combined Biaxial Compression and Lateral Pressure. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 263, 112324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, M.I.; Adiputra, R.; Prabowo, A.R.; Yamada, Y.; Firdaus, N. Assessment of the Ultimate Strength of Stiffened Panels of Ships Considering Uncertainties in Geometrical Aspects: Finite Element Approach and Simplified Formula. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 286, 115522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Yan, B.; Tong, M.; Wang, F. Buckling and Post-Buckling Analysis of Composite Stiffened Panels: A Ten-Year Review (2014–2023). Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 205, 112525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, X.; Wu, W.; Kim, D.K. An Advanced Design Diagram of Stiffened Plate Subjected to Combined In-Plane and Lateral Loads Considering Initial Deflection Effects. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 203, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgardt, G.R.; Fragassa, C.; Rocha, L.A.O.; dos Santos, E.D.; da Silveira, T.; Isoldi, L.A. Computational Model Verification and Validation of Elastoplastic Buckling Due to Combined Loads of Thin Plates. Metals 2023, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przemieniecki, J.S. Theory of Matrix Structural Analysis; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1985; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Grimesf, R.G.; Lewisf, J.G.; Simon, H.D. A Shifted Block Lanczos Algorithm for Solving Sparse Symmetric Generalized Eigenproblems. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 1994, 15, 228–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellobody, E.; Feng, R.; Young, B. Finite Element Analysis and Design of Metal Structures, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, E.M.M. Steel Columns under Compression with Different Sizes of Square Hollow Cross-Sections, Lengths, and End Constraints. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, D.; Da Silva, C.C.C.; Real, M.d.V.; dos Santos, E.D.; Isoldi, L.A.; Rocha, L.A.O. Study about Buckling Phenomenon in Perforated Thin Steel Plates Employing Computational Modeling and Constructal Design Method. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 13, 1912–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc. Mechanical APDL 2024 R2—Element Reference. In Ansys Mechanical APDL Element Reference; ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2024; pp. 254–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bathe, K.J. Finite Element Procedures, 2nd ed.; Bathe, K.-J., Ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Oñate, E. Structural Analysis with the Finite Element Method—Linear Statics, 2nd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.D. American Society for Quality Factorial Sampling Plans for Preliminary Computational Experiments. Technometrics 1991, 33, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A.; Lorente, S. Design with Constructal Theory; Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A. Shape and Structure: From Engineering to Nature; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]





| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 186.45 |
| 75 | 378 | 184.13 |
| 50 | 800 | 184.13 |
| 25 | 3200 | 186.45 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 24 | 55.28 |
| 75 | 40 | 55.28 |
| 50 | 75 | 55.28 |
| 25 | 290 | 55.28 |
| 10 | 1728 | 55.28 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (kN) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 81 | 33.05 |
| 7.5 | 144 | 33.05 |
| 5 | 324 | 33.05 |
| 2.5 | 1225 | 33.05 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 318 | 284.42 |
| 75 | 489 | 284.10 |
| 50 | 1008 | 281.77 |
| 25 | 3648 | 281.22 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 924 | 99.54 | 149.31 |
| 750 | 1164 | 71.19 | 106.79 |
| 500 | 1940 | 69.93 | 104.90 |
| 250 | 5616 | 69.30 | 103.95 |
| 100 | 27,544 | 69.30 | 103.95 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (kN) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 246 | 1169.57 |
| 75 | 382 | 1131.64 |
| 50 | 894 | 1118.99 |
| 25 | 2946 | 1118.99 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 60.57 |
| 75 | 378 | 59.68 |
| 50 | 800 | 59.68 |
| 25 | 3200 | 59.68 |
| Element Length (mm) | Number of Elements | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 468 | 122.70 |
| 75 | 780 | 122.70 |
| 50 | 1338 | 122.70 |
| 25 | 4788 | 122.70 |
| Number of Sub-Steps | Maximum Number of Sub-Steps | Minimum Number of Sub-Steps | Processing Time (s) | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 10 | 91 | 116.26 |
| 100 | 200 | 25 | 94 | 117.59 |
| 200 | 400 | 50 | 153 | 122.70 |
| 300 | 600 | 100 | 195 | 120.64 |
| Plate Configuration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(2;2) | 2 | 2 | 2.28 | 3.71 |
| P(2;3) | 2 | 3 | 2.70 | 4.04 |
| P(2;4) | 2 | 4 | 3.80 | 4.34 |
| P(2;5) | 2 | 5 | 3.20 | 4.48 |
| P(3;2) | 3 | 2 | 3.10 | 5.08 |
| P(3;3) | 3 | 3 | 4.27 | 4.74 |
| P(3;4) | 3 | 4 | 3.47 | 4.88 |
| P(3;5) | 3 | 5 | 6.60 | 4.11 |
| P(4;2) | 4 | 2 | 4.80 | 5.72 |
| P(4;3) | 4 | 3 | 3.87 | 5.20 |
| P(4;4) | 4 | 4 | 3.20 | 4.22 |
| P(4;5) | 4 | 5 | 6.10 | 4.05 |
| P(5;2) | 5 | 2 | 4.27 | 5.31 |
| P(5;3) | 5 | 3 | 3.47 | 4.29 |
| P(5;4) | 5 | 4 | 6.60 | 3.86 |
| P(5;5) | 5 | 5 | 5.70 | 3.51 |
| Plate Configuration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(2;5) | 2 | 5 | 3.20 | 4.48 |
| P(3;2) | 3 | 2 | 3.10 | 5.08 |
| P(4;2) | 4 | 2 | 4.80 | 5.72 |
| P(5;2) | 5 | 2 | 4.27 | 5.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lançanova, A.F.; Vieira, R.L.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O.; da Silveira, T.; Lima, J.P.S.; Estrada, E.d.S.D.; Isoldi, L.A. Constructal Design and Numerical Simulation Applied to Geometric Evaluation of Stiffened Steel Plates Subjected to Elasto-Plastic Buckling Under Biaxial Compressive Loading. Metals 2025, 15, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080879
Lançanova AF, Vieira RL, dos Santos ED, Rocha LAO, da Silveira T, Lima JPS, Estrada EdSD, Isoldi LA. Constructal Design and Numerical Simulation Applied to Geometric Evaluation of Stiffened Steel Plates Subjected to Elasto-Plastic Buckling Under Biaxial Compressive Loading. Metals. 2025; 15(8):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080879
Chicago/Turabian StyleLançanova, Andrei Ferreira, Raí Lima Vieira, Elizaldo Domingues dos Santos, Luiz Alberto Oliveira Rocha, Thiago da Silveira, João Paulo Silva Lima, Emanuel da Silva Diaz Estrada, and Liércio André Isoldi. 2025. "Constructal Design and Numerical Simulation Applied to Geometric Evaluation of Stiffened Steel Plates Subjected to Elasto-Plastic Buckling Under Biaxial Compressive Loading" Metals 15, no. 8: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080879
APA StyleLançanova, A. F., Vieira, R. L., dos Santos, E. D., Rocha, L. A. O., da Silveira, T., Lima, J. P. S., Estrada, E. d. S. D., & Isoldi, L. A. (2025). Constructal Design and Numerical Simulation Applied to Geometric Evaluation of Stiffened Steel Plates Subjected to Elasto-Plastic Buckling Under Biaxial Compressive Loading. Metals, 15(8), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15080879










