Ni-Driven Martensitic Packet Refinement to Improve the Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of Simulated CGHAZ in High-Strength Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
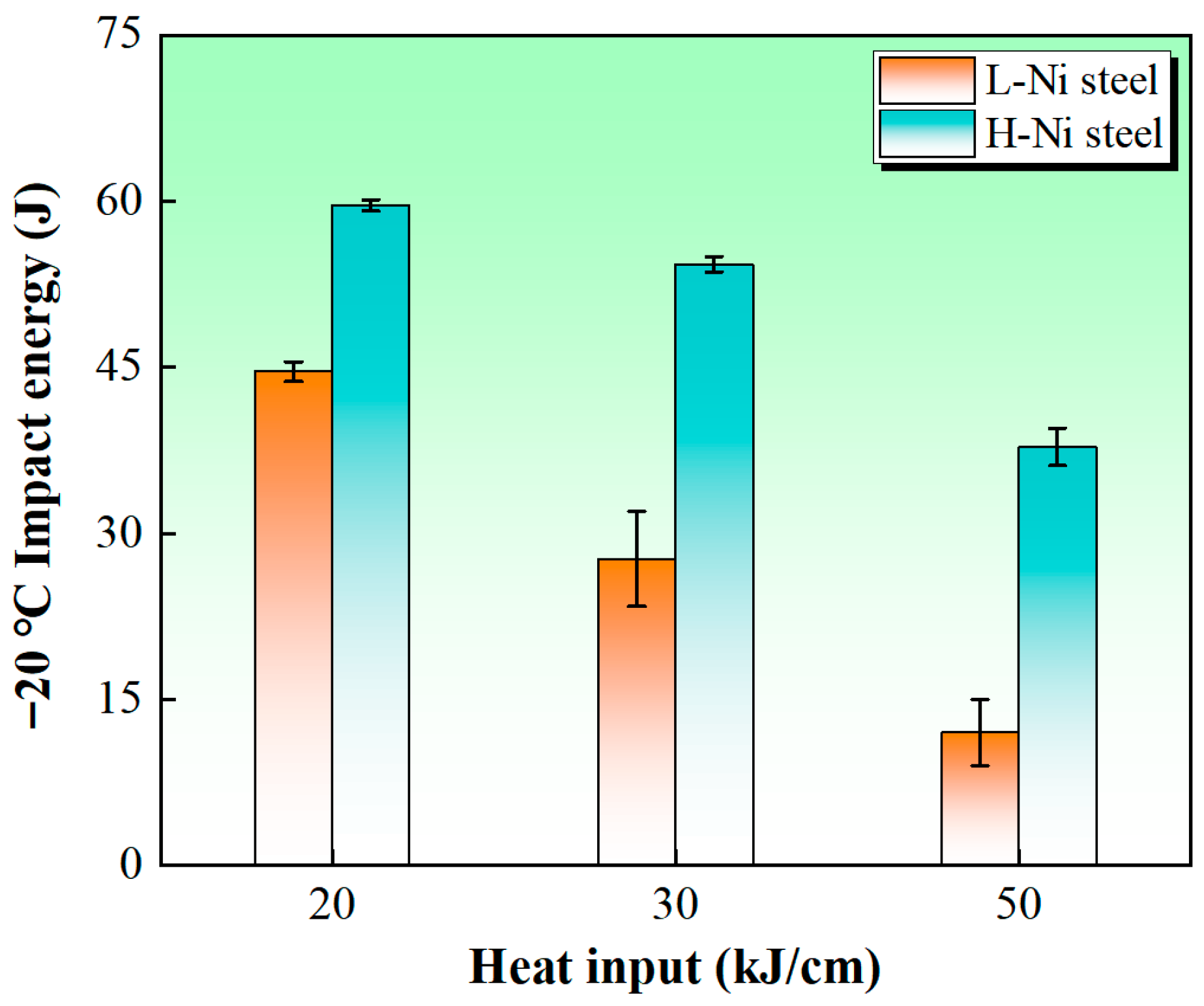
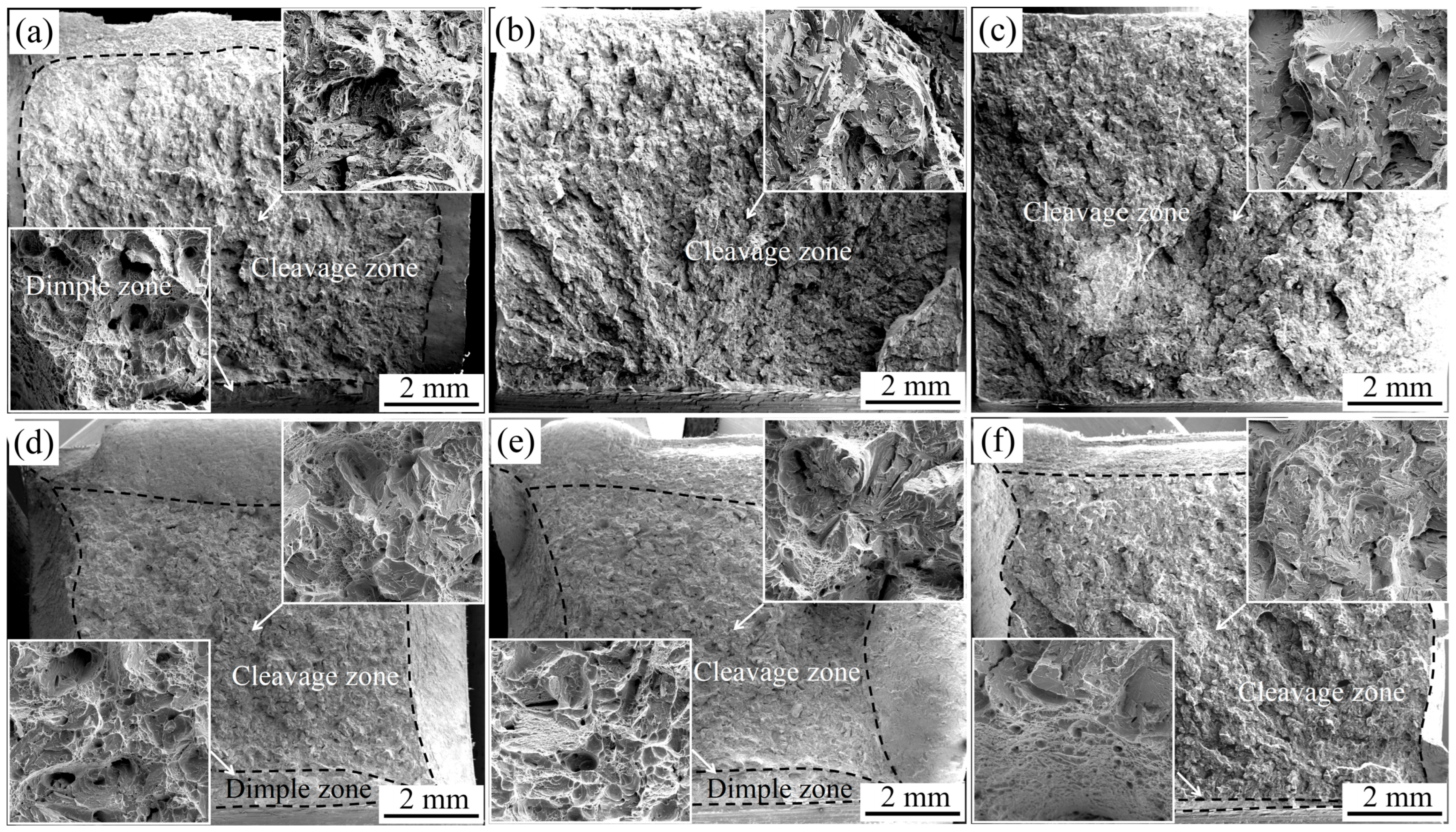
3.1. Impact Toughness and Fractographs of the Simulated Samples
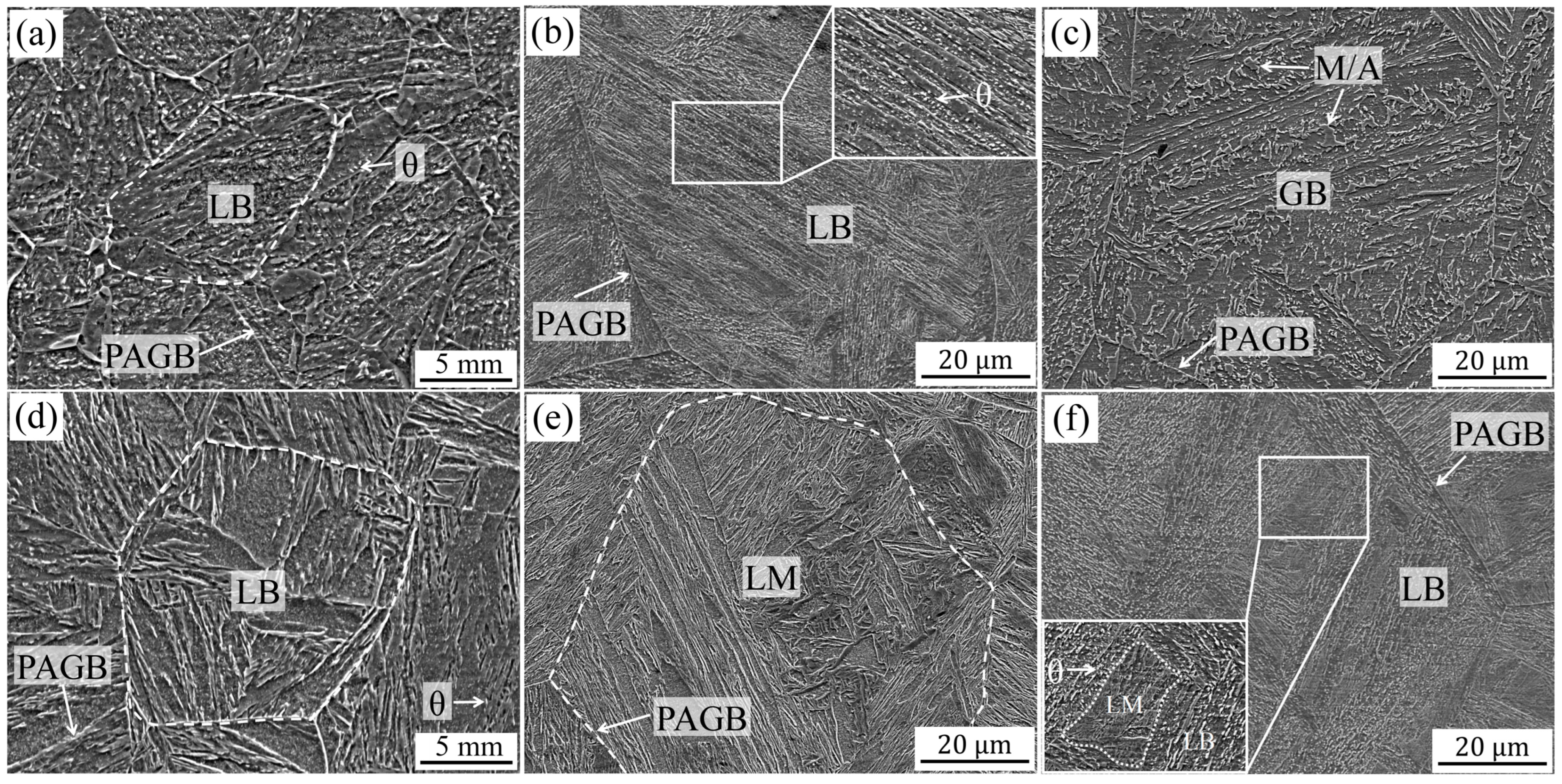
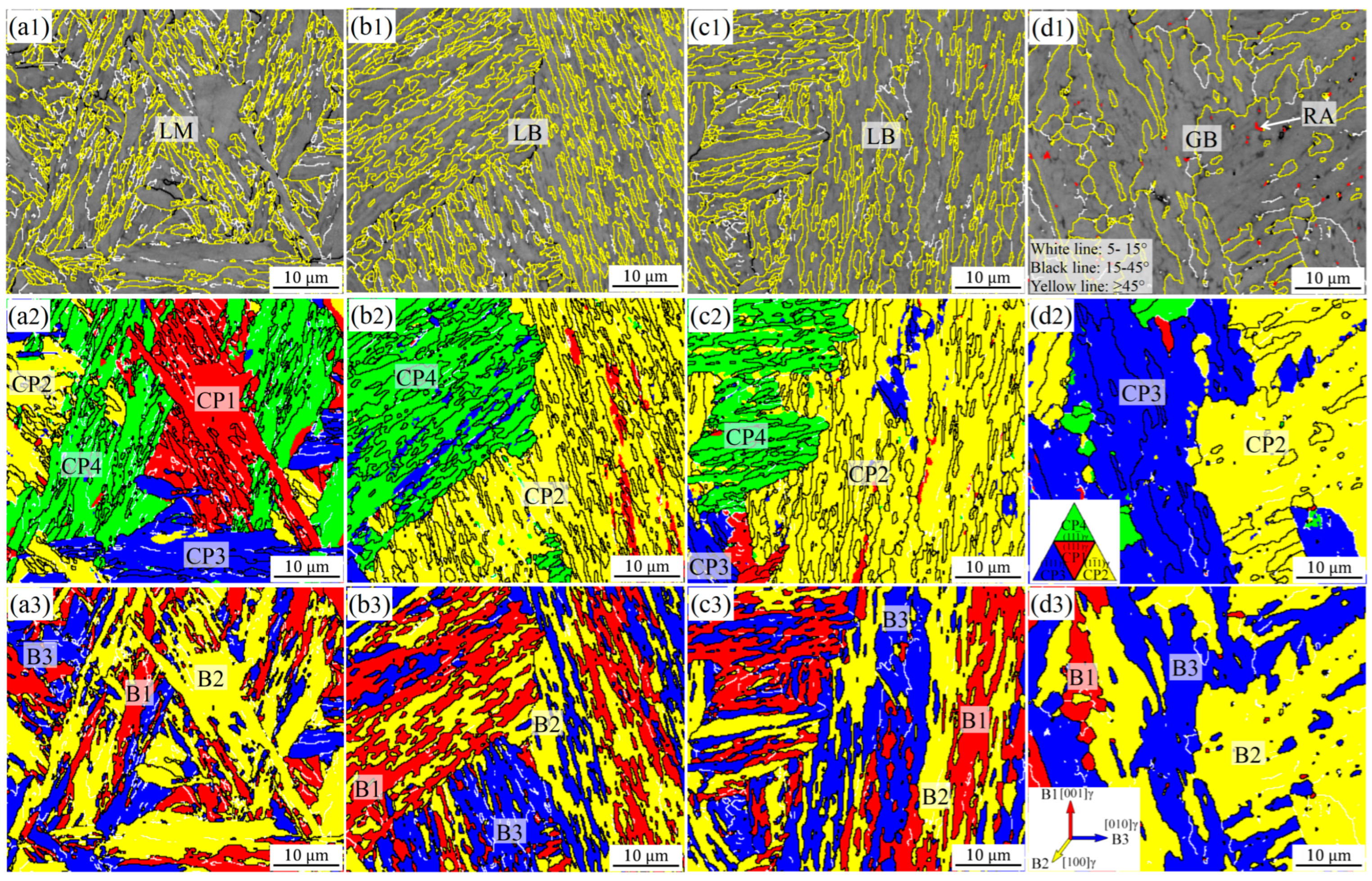
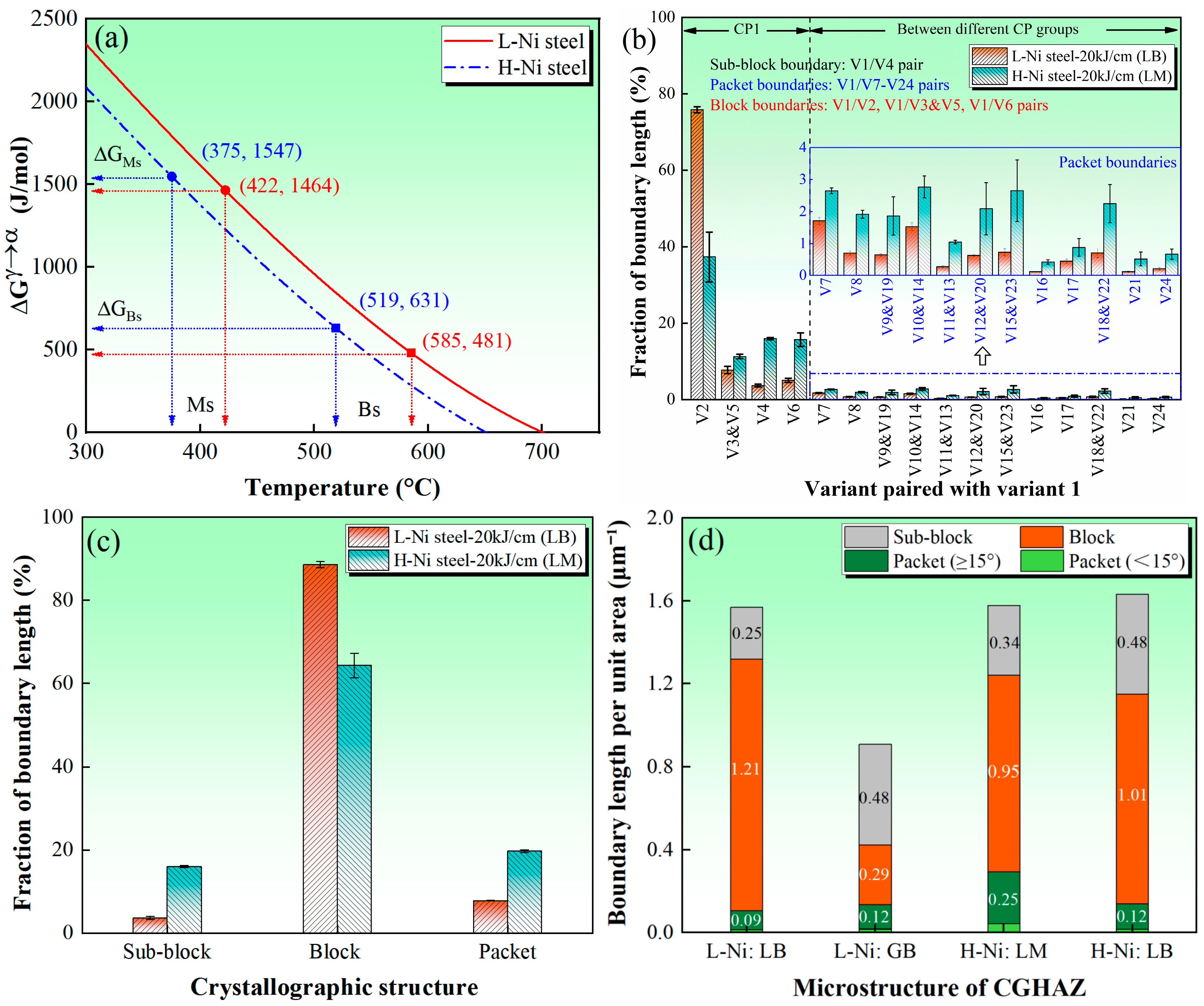
3.2. Microstructure Evolution in Base Metal and Simulated Samples and Phase Transformation Mechanisms
3.3. Crack Propagation Mechanisms in Simulated Samples
3.4. Overall Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Increasing Ni content (from 1.15 wt.% to 3.2 wt.%) significantly enhances the low-temperature (−20 °C) impact toughness of the simulated welded CGHAZ of low-alloy high-strength steels, enabling the CGHAZ to maintain excellent toughness even under relatively high heat input conditions. For the H-Ni steel, the simulated CGHAZ achieved average impact energy values of 59.6, 54.3 and 37.8 J under the heat input conditions of 20, 30 and 50 kJ/cm, respectively. In contrast, the average impact energy values of the L-Ni steel under the same heat input conditions were 44.6, 27.7 and 12 J, respectively.
- (2)
- Ni regulates the phase transformation and crystallographic structure of the CGHAZ: it weakens martensite variant selection, leading to refined and staggered packet arrangements in the LM structure, and promotes low-temperature bainite transformation to form LB structure at lower cooling rates, both improving brittle crack propagation resistance.
- (3)
- The superior low-temperature impact toughness of the H-Ni steel’s CGHAZ is attributed to the higher density of packet boundaries in its microstructure, as well as the irregular interlaced distribution of crystallographic units, rather than just grain boundary density, providing a reasonable compositional design for high-strength steels in high-efficiency (high heat input) welding of thick/extra-thick plates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, J.W., Jr.; Guo, Z.; Krenn, C.R.; Kim, Y.-H. The limits of strength and toughness in steel. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Far, A.H.; Anijdan, S.M.; Abbasi, S. The effect of increasing Cu and Ni on a significant enhancement of mechanical properties of high strength low alloy, low carbon steels of HSLA-100 type. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 746, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Y.; Hu, C.Y.; Wu, G.H.; Wu, K.M.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of nickel on hardening behavior and mechanical properties of nanostructured bainite-austenite steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 817, 141410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norström, L.Å.; Vingsbo, O. Influence of nickel on toughness and ductile-brittle transition in low-carbon martensite steels. Met. Sci. 1979, 13, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.Q.; Zhao, J.X.; Wang, X.L.; Shang, C.J.; Zhou, W.H. New insights from crystallography into the effect of Ni content on ductile-brittle transition temperature of 1000 MPa grade high-strength low-alloy steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.C.; Chai, F.; Luo, X.B.; Ma, S.; Shi, Z.R.; Chai, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M. Effect of the Ni content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-bearing high-strength steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 943, 148762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Han, P.; Yang, S.W.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y.H.; Shang, C.J. Crystallographic understanding of the effect of Ni content on the hardenability of high-strength low-alloy steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2024, 60, 789–801. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Geng, R.M.; Cao, Y.X.; Han, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Zheng, L.J. Microstructures and mechanical properties of novel 2.3 GPa secondary hardening steels with different Ni contents. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.L.; Ji, Y.F.; Wang, P.J.; Wu, S.W.; Cao, G.M.; Liu, Z.Y. Cryogenic impact toughness of 5.5% Ni steel at 196 °C: Synergy of a dual-phase heterogeneous lamellar structure and the stability of reversed austenite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 943, 148740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Xu, T.F.; Xu, J.K.; Li, W.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Hou, J.P. Effect of microstructural homogeneity on ultra-low temperature impact fracture mechanism of high-strength 9%Ni steel. Mater. Des. 2025, 256, 114318. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Dong, L.M.; Yang, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Shang, C.J. Effect of Mn, Ni, Mo proportion on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal of K65 pipeline steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2016, 52, 649–660. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Shang, C.J.; Subramanian, S. Effect of Ni addition on toughness and microstructure evolution in coarse grain heat affected zone. Met. Mater. Int. 2014, 20, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Lee, D.H.; Sohn, S.S.; Kim, W.G.; Um, K.K.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S. Effects of Ni and Mn addition on critical crack tip opening displacement (CTOD) of weld-simulated heat-affected zones of three high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 697, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.L.; Jia, S.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Shang, C.J. Effects of Cr and Ni addition on critical crack tip opening displacement (CTOD) and supercritical CO2 low-alloy steel (HSLAs). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 908, 146772. [Google Scholar]
- Mohrbacher, H.; Kern, A. Nickel alloying in carbon steel: Fundamentals and applications. Alloys 2023, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Xie, Z.J.; Li, X.C.; Shang, C.J. Recent progress in visualization and digitization of coherent transformation structures and application in high-strength steel. Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 2024, 31, 1298–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Dong, L.L.; Shang, C.J.; Ma, X.P.; Subramanian, S.V. New insights into the mechanism of cooling rate on the impact toughness of coarse grained heat affected zone from the aspect of variant selection. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 704, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E2298-18; Standard Test Method for Instrumented Impact Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Yang, X.C.; Di, X.J.; Liu, X.G.; Wang, D.P.; Li, C.N. Effects of heat input on microstructure and fracture toughness of simulated coarse-grained heat affected zone for HSLA steels. Mater. Charact. 2019, 155, 109818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; An, T.B.; Cao, Z.L.; Zuo, Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Kang, J. Effect of heat input on microstructure, variant pairing, and impact toughness of CGHAZ in 1000 MPa-grade marine engineering steel. Structures 2025, 77, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.N.; Huan, P.C.; Wang, X.N.; Di, H.S.; Shen, X.J.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Z.G.; He, J.R. Study on the mechanism of heat input on the grain boundary distribution and impact toughness in CGHAZ of X100 pipeline steel from the aspect of variant. Mater. Charact. 2021, 179, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nie, P.L.; Qu, Z.X.; Ojo, O.A.; Xia, L.Q.; Li, Z.G.; Huang, J. Influence of heat input on the changes in the microstructure and fracture behavior of laser welded 800MPa grade high-strength low-alloy steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 50, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, S.Z.; Yu, H.; Mao, X.P. Achieving enhanced cryogenic toughness in a 1 GPa grade HSLA steel through reverse transformation of martensite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 6696–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.Y.; Yang, R.X.; Sun, D.Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.C.; Yang, Z.N.; Li, Y.G. Roles of cooling rate of undercooled austenite on isothermal transformation kinetics, microstructure, and impact toughness of bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 870, 144821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morito, S.; Yoshida, H.; Maki, T.; Huang, X. Effect of block size on the strength of lath martensite in low carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgues, A.-F.; Flower, H.M.; Lindley, T.C. Electron backscattering diffraction study of acicular ferrite, bainite, and martensite steel microstructures. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Argon, A.S. Cleavage cracking resistance of high angle grain boundaries in Fe-3%Si alloy. Mech. Mater. 2003, 35, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Ma, X.P.; Subramanian, S.V.; Xie, Z.J.; Shang, C.J.; Li, X.C. Analysis of impact toughness scatter in simulated coarse-grained HAZ of E550 grade offshore engineering steel from the aspect of crystallographic structure. Mater. Charact. 2018, 140, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Xu, G.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Hu, H.J.; Zhou, M.M. Effect of Ni addition on bainite transformation and properties in a 2000 MPa grade ultrahigh strength bainitic steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Van Der Wolk, P.J.; Van Der Zwaag, S. On the influence of alloying elements on the bainite reaction in low alloy steels during continuous cooling. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 4393–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancel, L.; Gómez, M.; Medina, S.F.; Gutierrez, I. Measurement of bainite packet size and its influence on cleavage fracture in a medium carbon bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 530, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.T.; Liu, W.S.; Ma, Y.Z.; Cai, Q.S.; Zhu, W.T.; Li, J. Effect of Ni addition upon microstructure and mechanical properties of hot isostatic pressed 30CrMnSiNi2A ultrahigh strength steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 850, 143599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Cai, Y.; Wang, B.S.; Mu, W.D.; Xin, D.Q. Effect of microstructure synergism on cryogenic toughness for CGHAZ of low-carbon martensitic steel containing nickel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 830, 142240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr + Mo + V | Ti | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Ni steel | 0.16 | 0.23 | 1.02 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 1.15 | 1.30 | 0.016 | 0.0015 |
| H-Ni steel | 0.16 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 3.20 | 1.31 | 0.016 | 0.0014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Ni-Driven Martensitic Packet Refinement to Improve the Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of Simulated CGHAZ in High-Strength Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121382
Zhang G, Liu Z, Wang X, Li L, Li Y, Yang Y. Ni-Driven Martensitic Packet Refinement to Improve the Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of Simulated CGHAZ in High-Strength Steel. Metals. 2025; 15(12):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121382
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guodong, Zhongzhu Liu, Xuelin Wang, Lixia Li, Yuanyuan Li, and Yanli Yang. 2025. "Ni-Driven Martensitic Packet Refinement to Improve the Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of Simulated CGHAZ in High-Strength Steel" Metals 15, no. 12: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121382
APA StyleZhang, G., Liu, Z., Wang, X., Li, L., Li, Y., & Yang, Y. (2025). Ni-Driven Martensitic Packet Refinement to Improve the Low-Temperature Impact Toughness of Simulated CGHAZ in High-Strength Steel. Metals, 15(12), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15121382







