Increasing Hardness and Wear Resistance of Austenitic Stainless Steel Surface by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Processing
2.2. Study of the Surface Morphology and Microstructure
2.3. The Microhardness Measurement
2.4. Surface Roughness and Weight of Samples Measurement
2.5. Study of Phase Composition
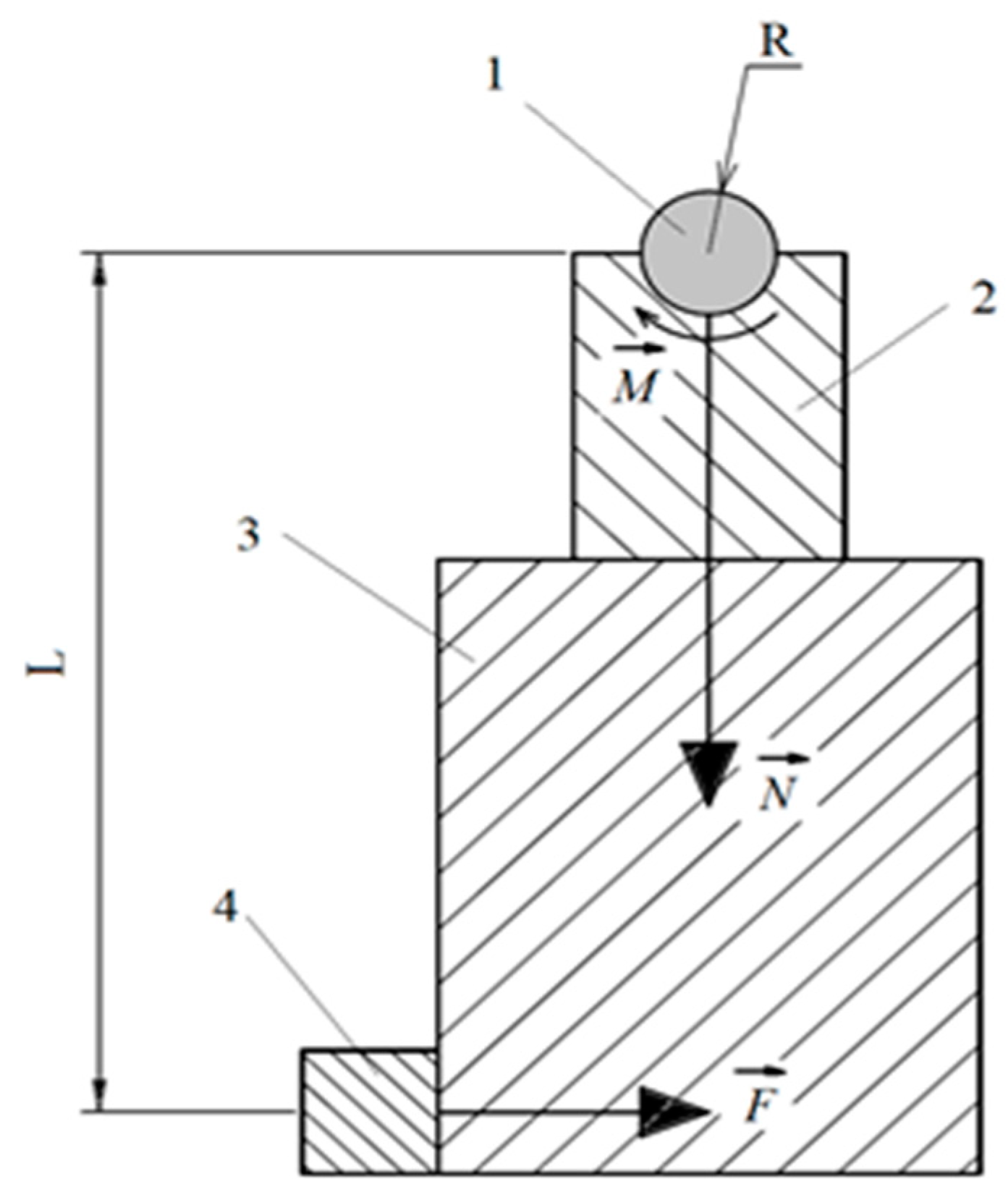
2.6. Study of Tribological Properties
2.7. Wear Mechanism Calculation
3. Results
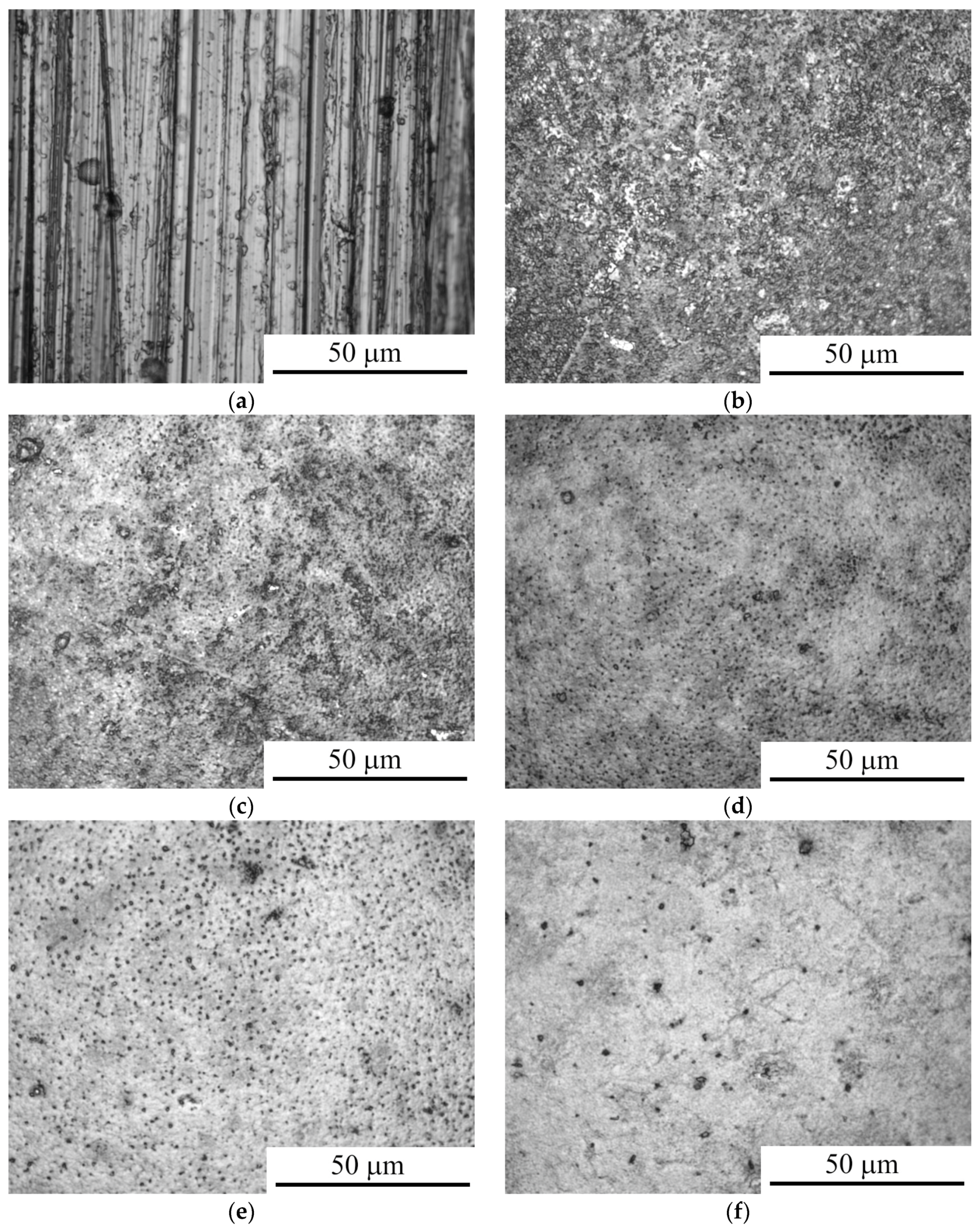
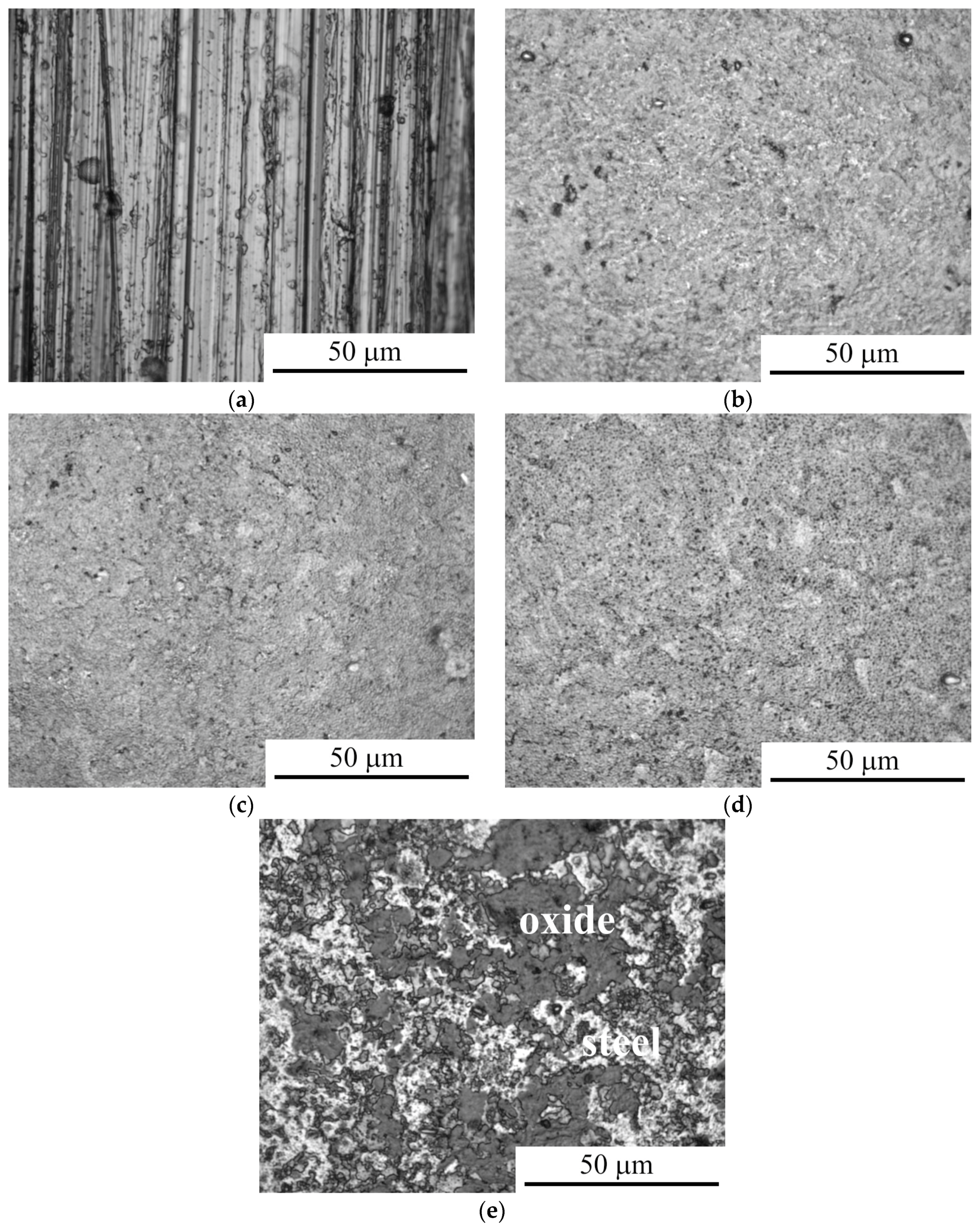
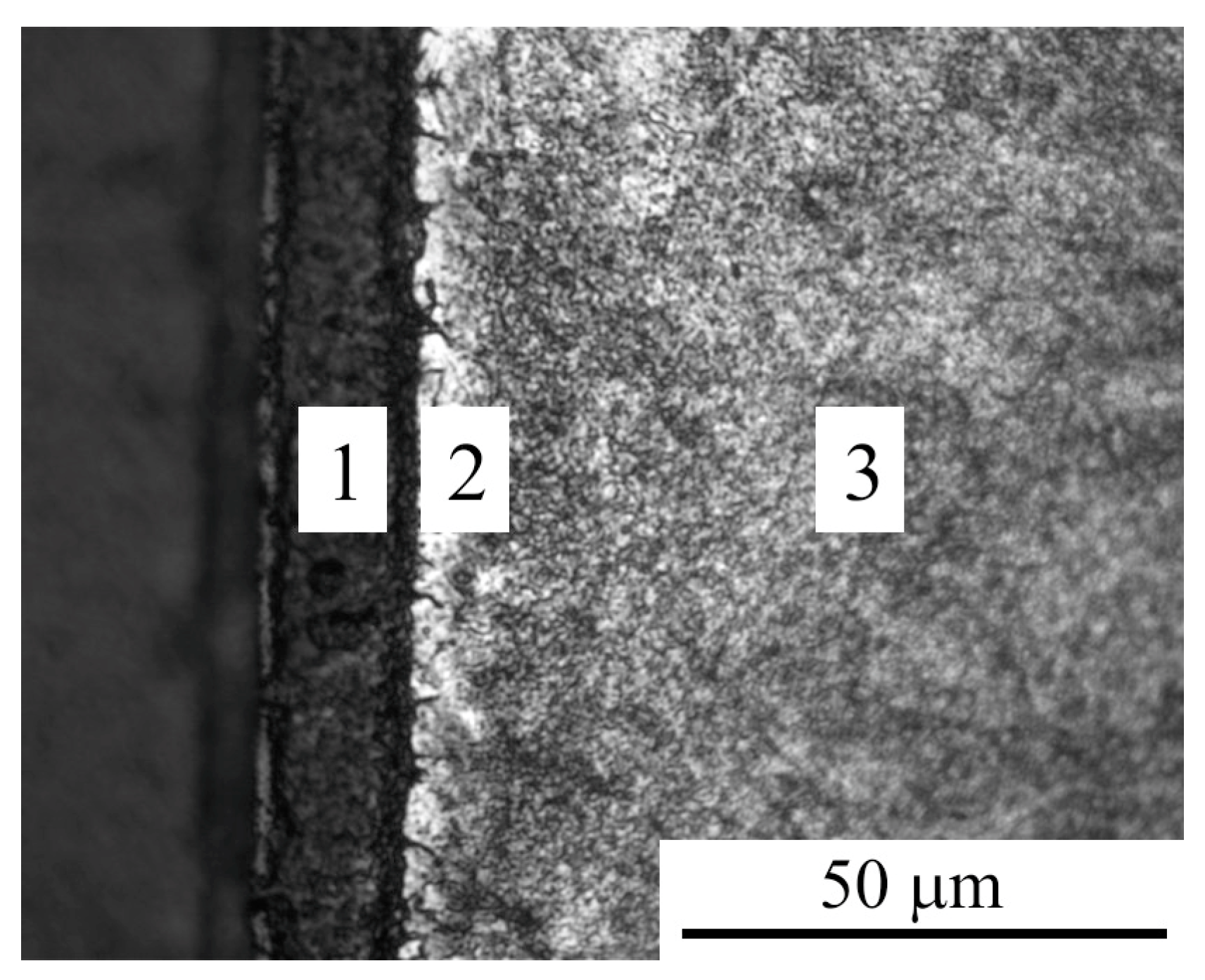
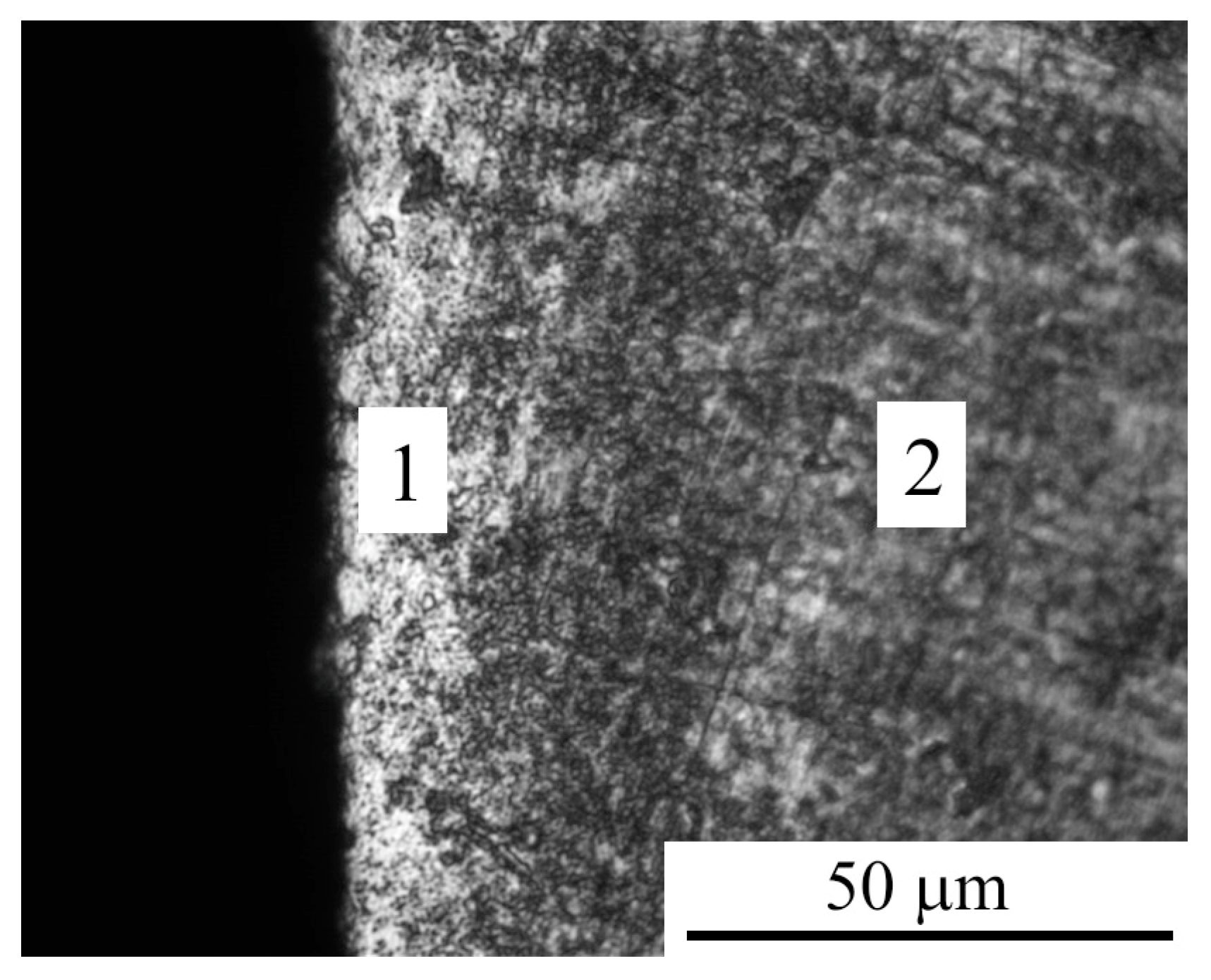
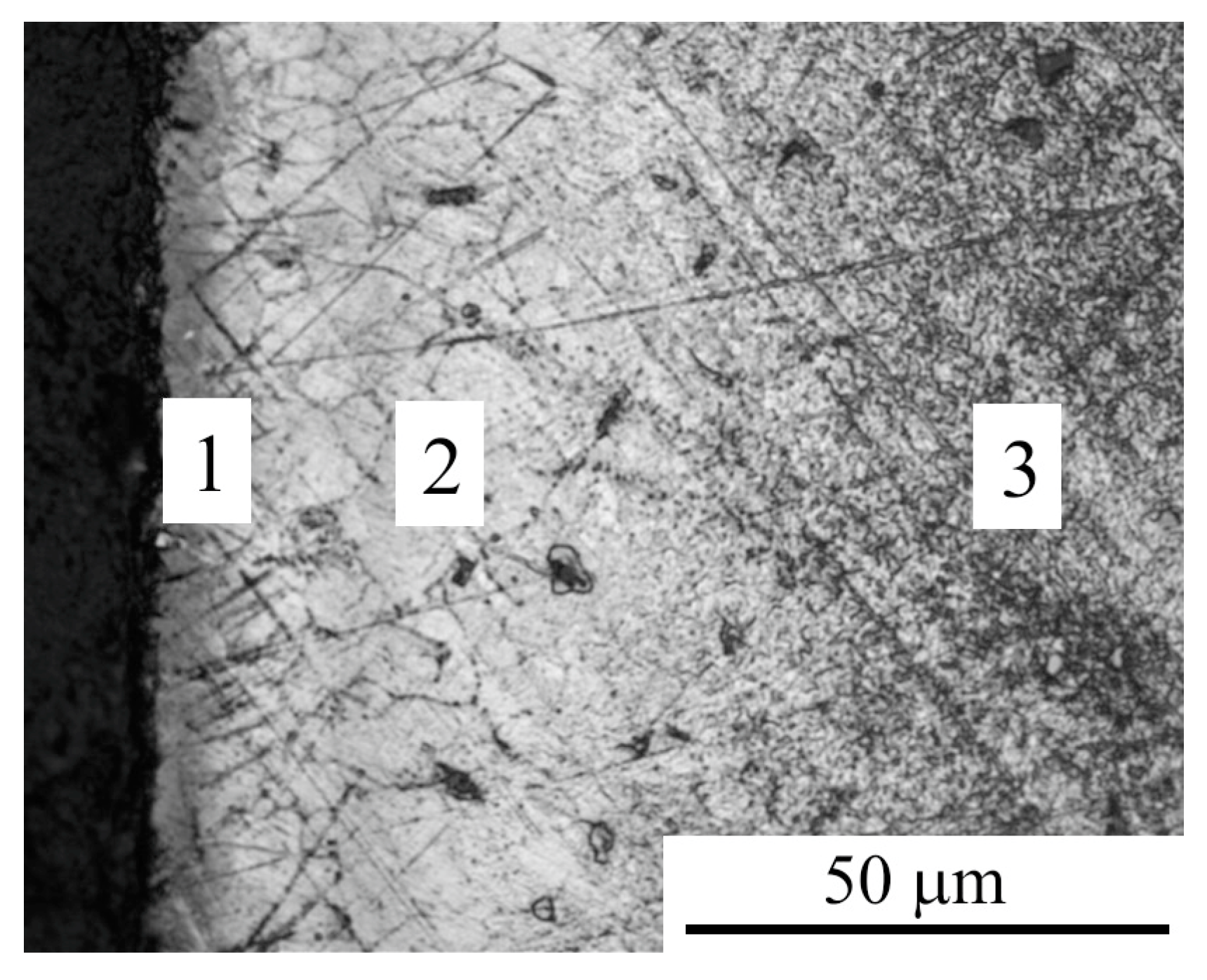
3.1. Morphology and Roughness of the Surface
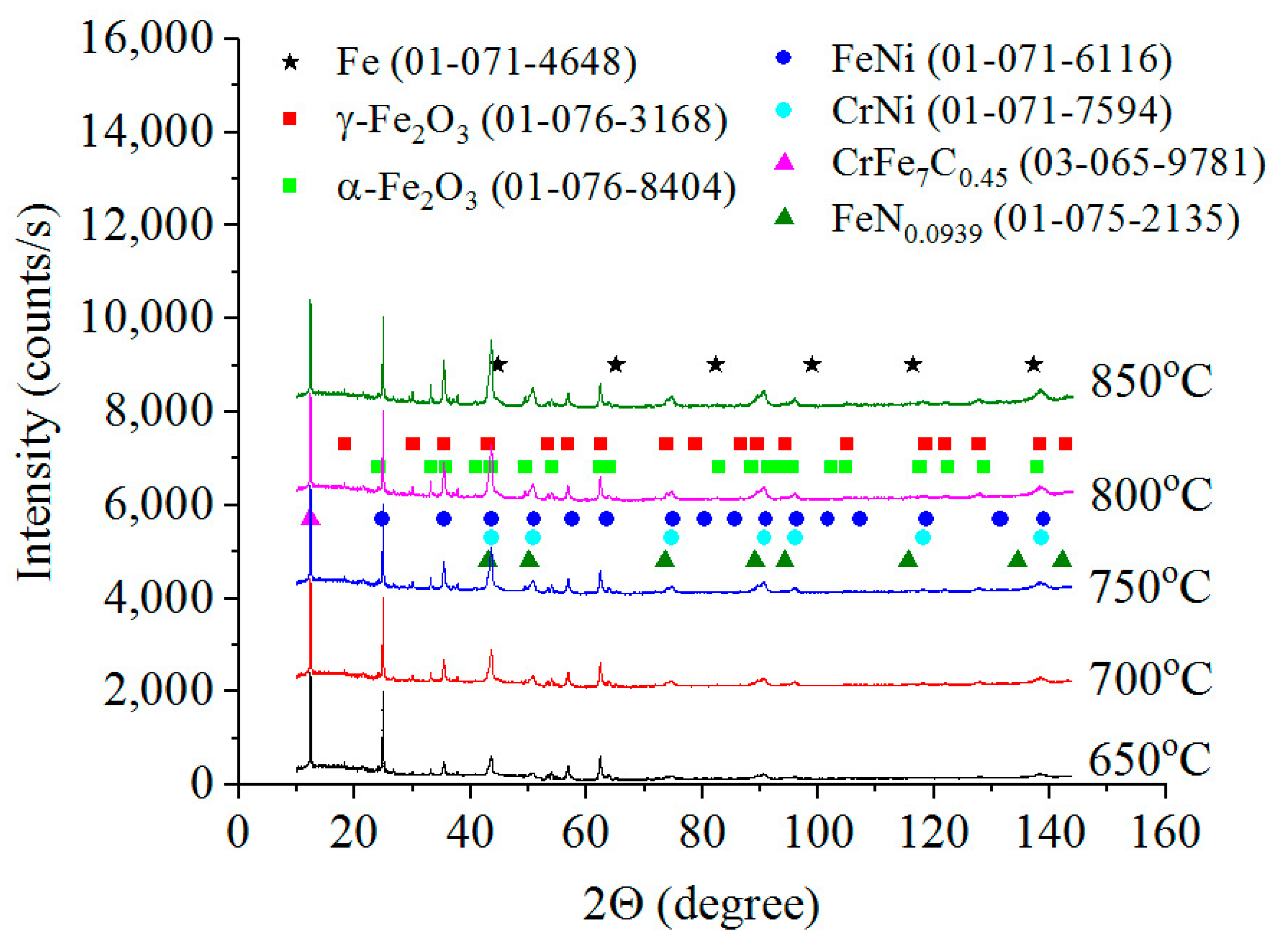
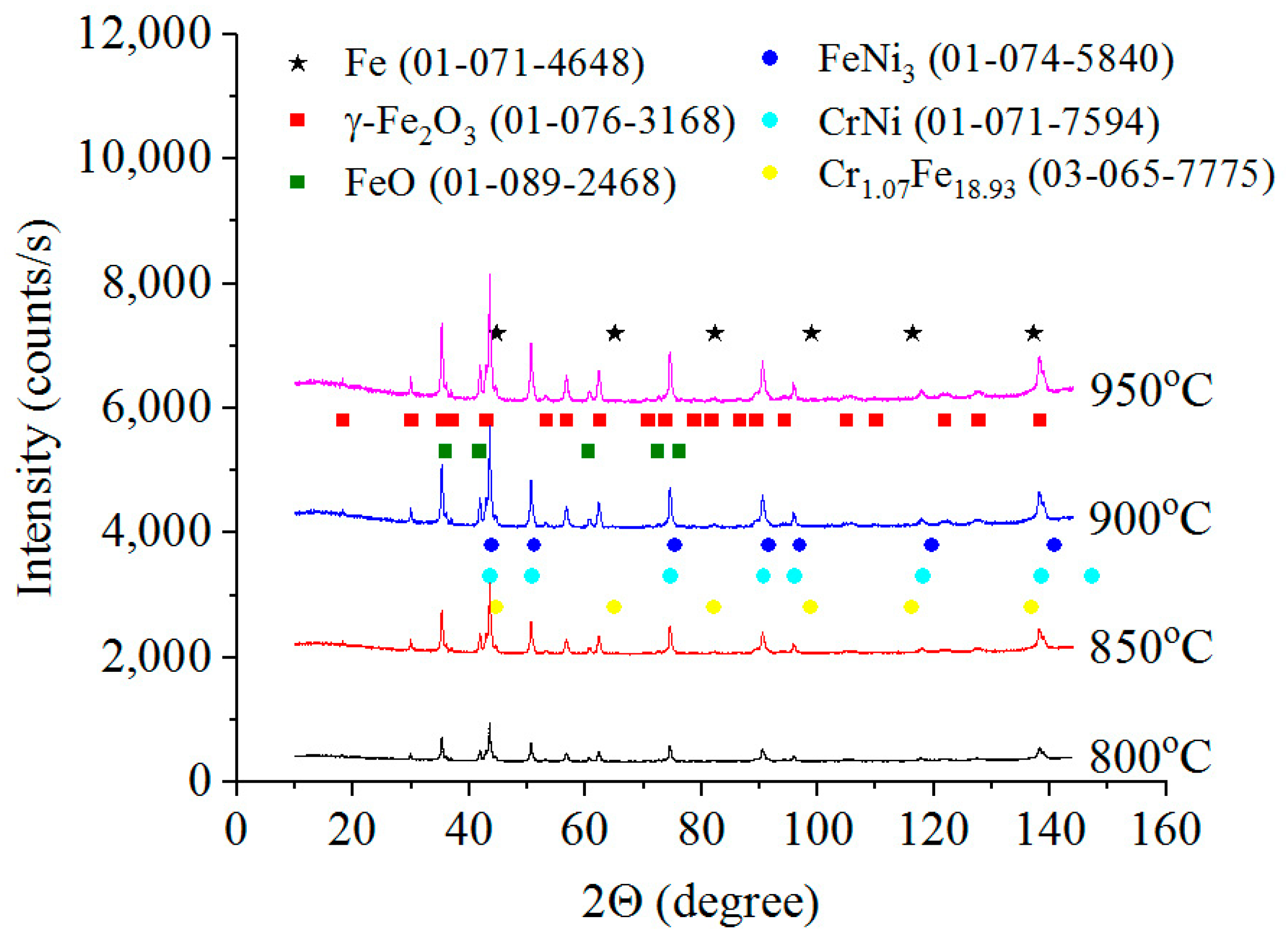
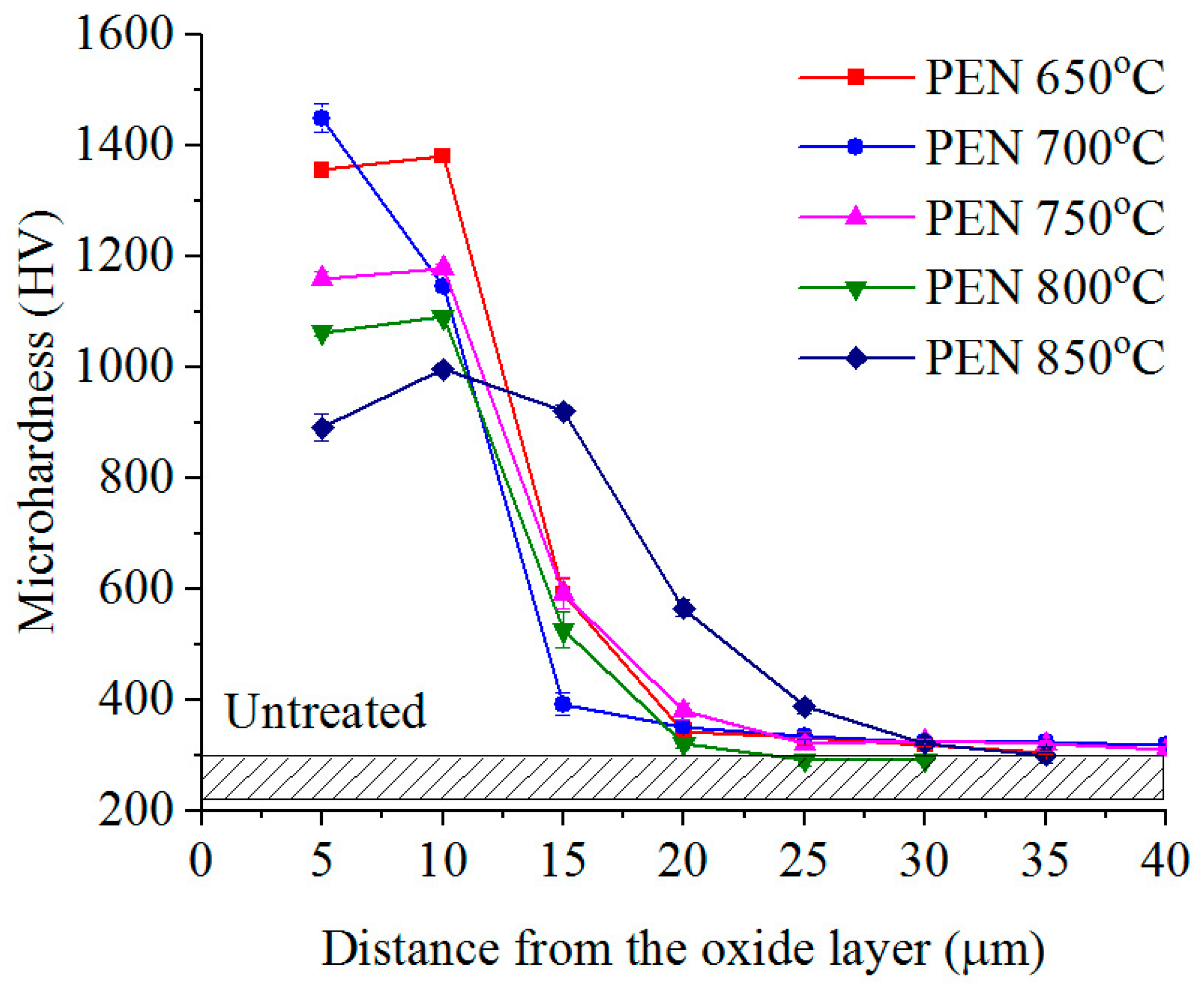
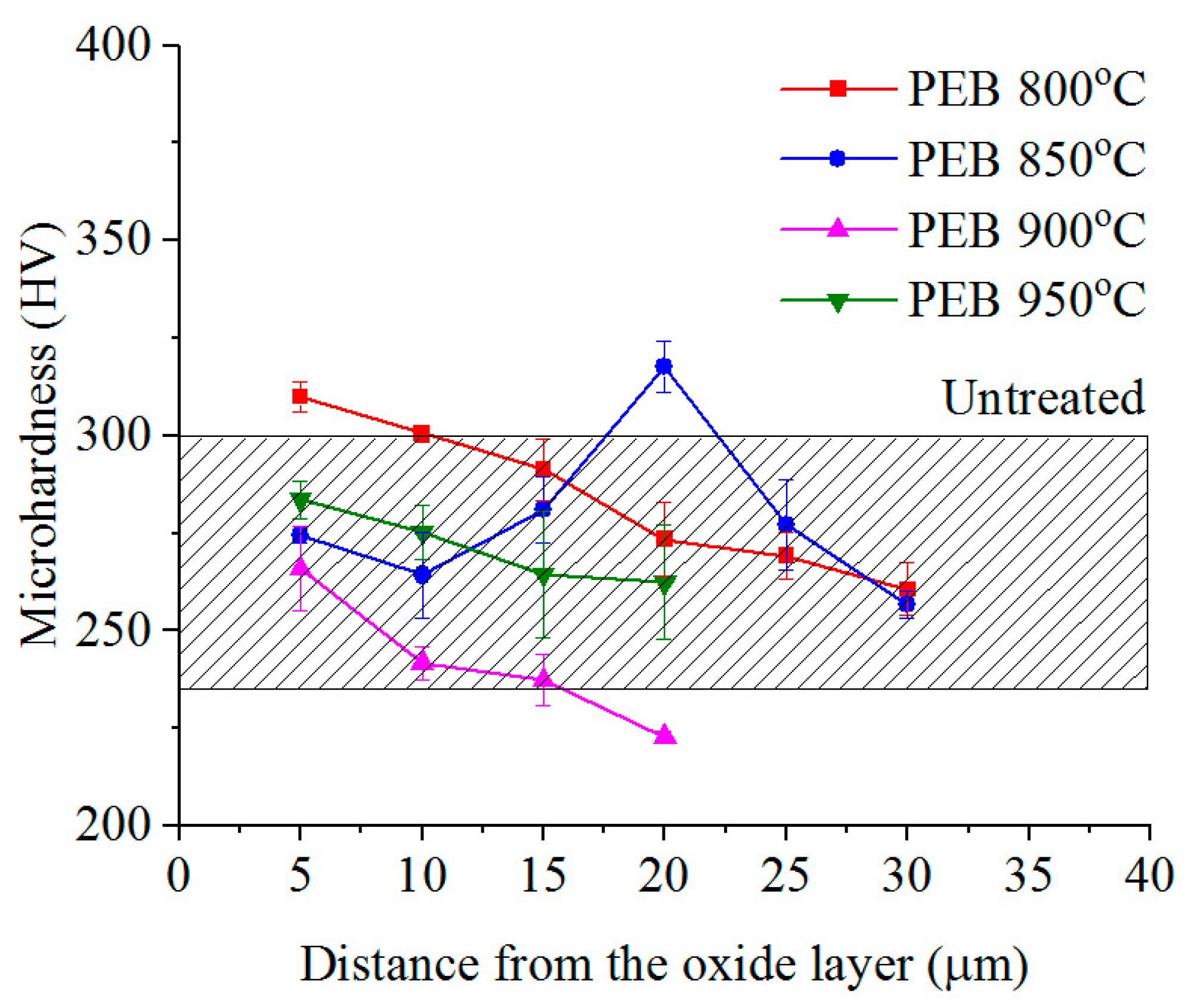
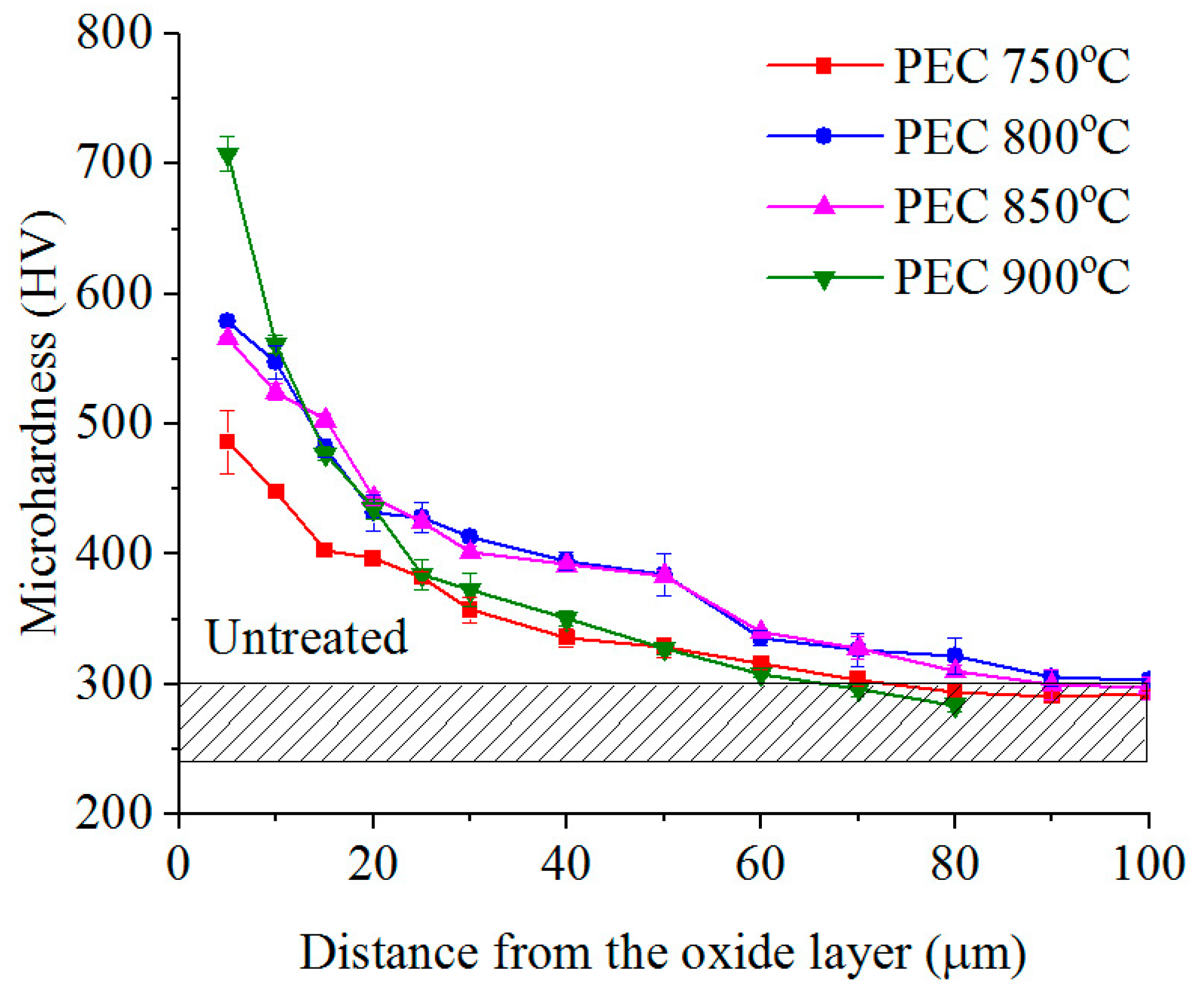
3.2. Phase Composition, Structure and Microhardness of the Surface Layer
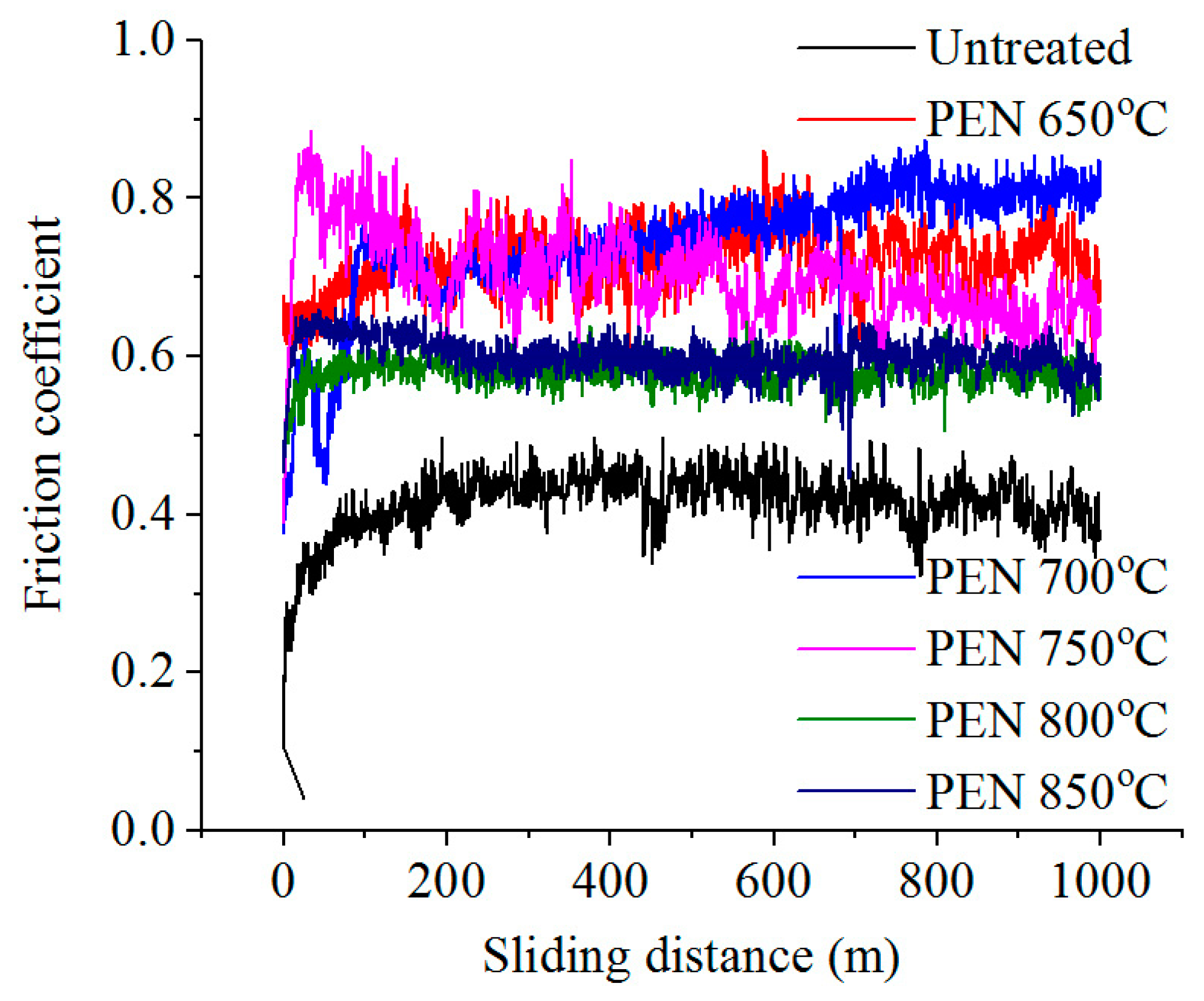
3.3. Tribological Properties of Treated Surface
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, F.; Hu, S.; Xu, R.; Han, X.; Qian, D.; Wei, W.; Hua, L.; Zhao, K. Strain rate sensitivity of the ultrastrong gradient nanocrystalline 316L stainless steel and its rate-dependent modeling at nanoscale. Int. J. Plast. 2020, 129, 102696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hu, S.; Liu, Y.; Hua, L.; Yin, F. Surface Nanocrystallization and Numerical Modeling of 316L Stainless Steel during Ultrasonic Shot Peening Process. Metals 2022, 12, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhu, C.; Hu, K.; Yin, F. The effect of ultrasonic shot peening on the fatigue life of alloy materials: A review. Int. J. Comput. Mater. Sci. Surf. Eng. 2021, 10, 209–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kim, Y.; Jung, J.; Bae, S.; Jeong, S.; Shin, K. Effect of Ultrasonic Shot Peening and Laser Shock Peening on the Microstructure and Microhardness of IN738LC Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Feng, X.; Teng, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, L. Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and fatigue properties of thin-wall welded Ti-6A1-4V alloy. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, Q.; Liu, S.; Peng, Q. Surface strengthening of stainless steels by nondestructive laser peening. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Sanchez, H.; Pixner, F.; Buzolin, R.; Mohedano, M.; Arrabal, R.; Warchomicka, F.; Matykina, E. Combination of Electron Beam Surface Structuring and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation for Advanced Surface Modification of Ti6Al4V Alloy. Coatings 2022, 12, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, H.; Vargas, G.; Magdaleno, C.; Silva, R. Article: Oxy-Nitriding AISI 304 Stainless Steel by Plasma Electrolytic Surface Saturation to Increase Wear Resistance. Metals 2023, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuz, N.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Rangel, E.C.; Cristino da Cruz, N.; Correa, D.R.N. The Effect of PEO Treatment in a Ta-Rich Electrolyte on the Surface and Corrosion Properties of Low-Carbon Steel for Potential Use as a Biomedical Material. Metals 2023, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumruoglu, L.C.; Ozel, A. Plasma electrolytic saturation of 316L stainless steel in an aqueous electrolyte containing urea and ammonium nitrate. Mater. Technol. 2013, 47, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Tewari, R.K.; Sharma, R.C.; Sherhar, R. Feasibility study of aqueous electrolyte plasma nitriding. Surf. Eng. 2007, 23, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, M.K.; Sabour, A.; Taheri, P. Study of corrosion protection of different stainless steels by nanocrystalline plasma electrolysis. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2008, 44, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skakov, M.; Kurbanbekov, S.; Scheffler, M. Influence of Regimes Electrolytic Plasma Cementation on the Mechanical Properties of Steel 12Cr18Ni10Ti. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 531–532, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliofkhazraei, M.; Sabour Rouhaghdam, A. Relationship Study among Nanocrystallite Distribution and Roughness of a Nanostructured Hard Layer. Defect Diffus. Forum 2009, 293, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, A.; Lungu, C.; Oncioiu, G.; Diaconu, C. Plasma processing for improvements of structural materials properties. In Proceedings of the 35th EPS Conference on Plasma Physics, Hersonissos, Greece, 9–13 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Andrei, V.; Vlaicu, G.; Fulger, M.; Ducu, C.; Diaconu, C.; Oncioiu, G.; Andrei, E.; Bahrim, M.; Gheboianu, A. Chemical and structural modifications induced in structural materials by electrolchemical process. Roman. Report. Phys. 2009, 61, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, H. Research on liquid plasma surface strengthening of stainless steel. Hot Work. Technol. 2007, 12, 58–59. Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFD2007&filename=SJGY200712019&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=UmKJpFeqc4eDOKZqgJD0JOIw42o5SJBWWBr09sbbr-MvLaU0wx3gItmBOAIoBDNU (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Xue, W.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, X. Characterization of Plasma Electrolytic Carburized Stainless Steel in Glycerin Aqueous Solution. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2010, 30, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Leyland, A.; Tsotsos, C.; Wilson, A.D.; Nie, X.; Matthews, A. Duplex surface treatments combining plasma electrolytic nitrocarburising and plasma-immersion ion-assisted deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 142–144, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Dehghanian, C. A phenomenological model of nanocrystalline coating production using plasma electrolytic saturation (PES) technique. Sci. Iran. 2009, 16, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kazerooniy, N.A.; Bahrololoom, M.E.; Shariat, M.H.; Mahzoon, F.; Jozaghi, T. Effect of Ringer’s solution on wear and friction of stainless steel 316L after plasma electrolytic nitrocarburising at low voltages. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Tsotsos, C.; Wilson, A.; Yerokhin, A.L.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A. Characteristics of a plasma electrolytic nitrocarburising treatment for stainless steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 139, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Dehghanian, C. Wear and corrosion properties of nanocrystalline coatings on stainless steel produced by plasma electrolytic nitrocarburising. Int. J. Mat. Res. 2008, 99, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, P.N.; Kusmanov, S.A.; Zhirov, A.V.; Belkin, V.S.; Parfenyuk, V.I. Anode Plasma Electrolytic Saturation of Titanium Alloys with Nitrogen and Oxygen. J. Mat. Sci. Tech. 2016, 32, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Dyakov, I.G.; Belkin, P.N.; Gracheva, I.A.; Belkin, V.S. Plasma electrolytic modification of the VT1-0 titanium alloy surface. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2015, 9, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, P.N.; Borisov, A.M.; Kusmanov, S.A. Plasma Electrolytic Saturation of Titanium and Its Alloys with Light Elements. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2016, 10, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, P.N.; Kusmanov, S.A. Plasma electrolytic nitriding of steels. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2017, 11, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.; Tambovskiy, I.; Silkin, S.; Nikiforov, R.; Belov, R. Increasing the Hardness and Corrosion Resistance of the Surface of CP-Ti by Plasma Electrolytic Nitrocarburising and Polishing. Materials 2023, 16, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelekhov, E.V.; Sviridova, T.A. Programs for X-ray analysis of polycrystals. Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 2000, 42, 309–313 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazulis, S.; Chateigner, D.; Downs, R.T.; Yokochi, A.T.; Le Bail, A. Crystallography open database—An open-access collection of crystal structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambovskiy, I.; Mukhacheva, T.; Gorokhov, I.; Suminov, I.; Silkin, S.; Dyakov, I.; Kusmanov, S.; Grigoriev, S. Features of Cathodic Plasma Electrolytic Nitrocarburizing of Low-Carbon Steel in an Aqueous Electrolyte of Ammonium Nitrate and Glycerin. Metals 2022, 12, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhacheva, T.; Kusmanov, S.; Suminov, I.; Podrabinnik, P.; Khmyrov, R.; Grigoriev, S. Increasing Wear Resistance of Low-Carbon Steel by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Sulfiding. Metals 2022, 12, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhacheva, T.L.; Belkin, P.N.; Dyakov, I.G.; Kusmanov, S.A. Wear mechanism of medium carbon steel after its plasma electrolytic nitrocarburising. Wear 2020, 462–463, 203516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demkin, N.B.; Izmailov, V.V. Surface topography and properties frictional contacts. Trib. Int. 1991, 24, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragelsky, I.V.; Dobychin, M.N.; Kombalov, V.S. Friction and Wear Calculation Methods; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1982; Available online: https://books.google.ru/books?id=QLcgBQAAQBAJ&hl=ru (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Belkin, P.N.; Kusmanov, S.A. Plasma Electrolytic Carburising of Metals and Alloys. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2021, 57, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrin, S.Y.; Belkin, P.N.; Tambovskiy, I.V.; Kusmanov, S.A. Physical Features of Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Carburising of Low-Carbon Steels. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2020, 40, 549–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Silkin, S.A.; Smirnov, A.A.; Belkin, P.N. Possibilities of increasing wear resistance of steel surface by plasma electrolytic treatment. Wear 2017, 386–387, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Dyakov, I.G.; Kusmanova, Y.V.; Belkin, P.N. Surface Modification of Low-Carbon Steels by Plasma Electrolytic Nitrocarburising. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2016, 36, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Kusmanova, Y.V.; Naumov, A.R.; Belkin, P.N. Formation of diffusion layers by anode plasma electrolytic nitrocarburising of low carbon steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Smirnov, A.A.; Silkin, S.A.; Belkin, P.N. Increasing wear and corrosion resistance of low-alloy steel by anode plasma electrolytic nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Tambovskiy, I.V.; Sevostyanova, V.S.; Savushkina, S.V.; Belkin, P.N. Anode plasma electrolytic boriding of medium carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 291, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, P.N.; Kusmanov, S.A. Plasma Electrolytic Boriding of Steels and Titanium Alloys. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2019, 55, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Kusmanova, Y.V.; Smirnov, A.A.; Belkin, P.N. Modification of steel surface by plasma electrolytic saturation with nitrogen and carbon. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 175, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, X.; Gong, H.; Zheng, S.; Cao, B.; Wang, H.; Möhwald, H.; Shchukin, D. Submicron-Lubricant Based on Crystallized Fe3O4 Spheres for Enhanced Tribology Performance. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5113–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



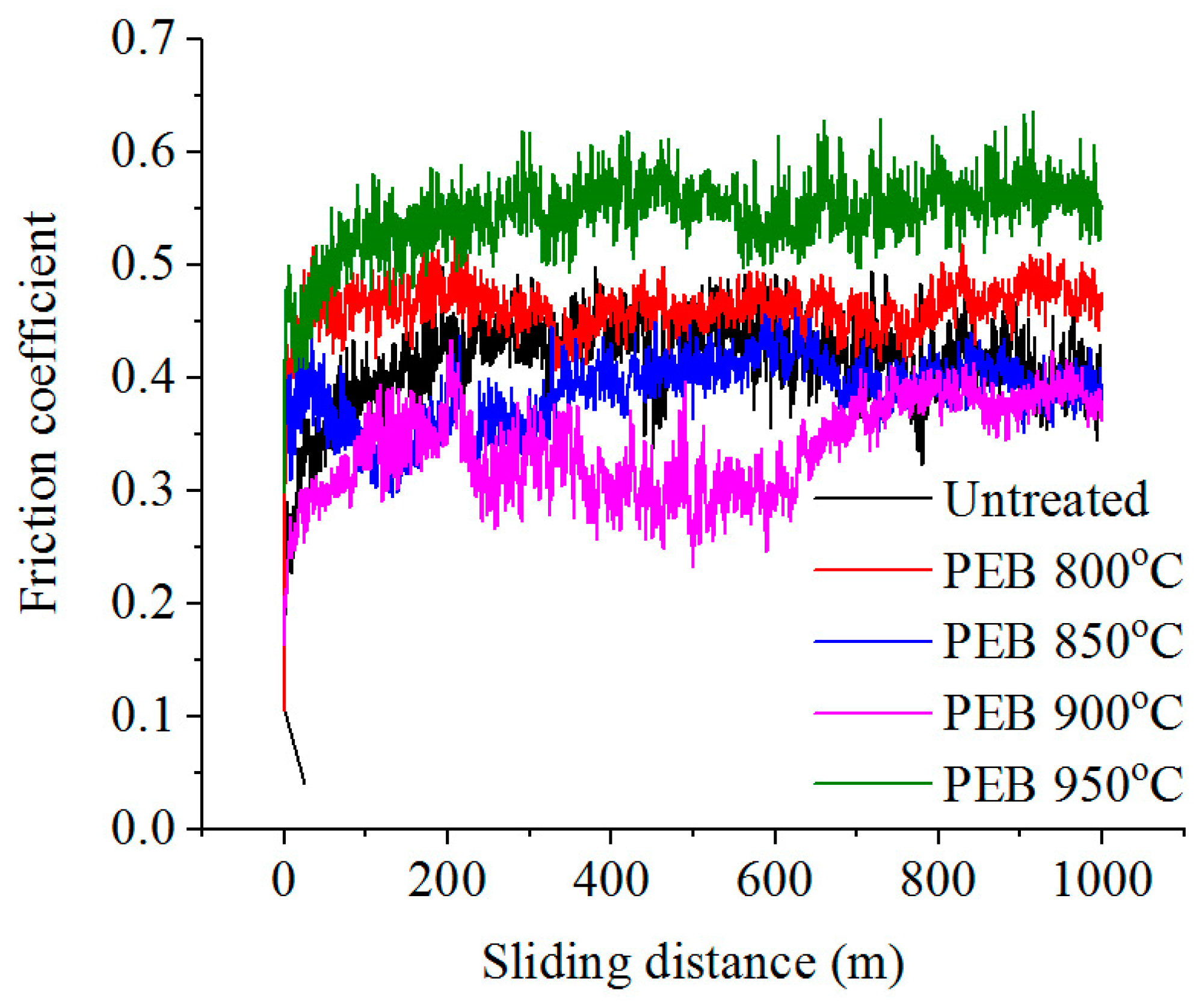
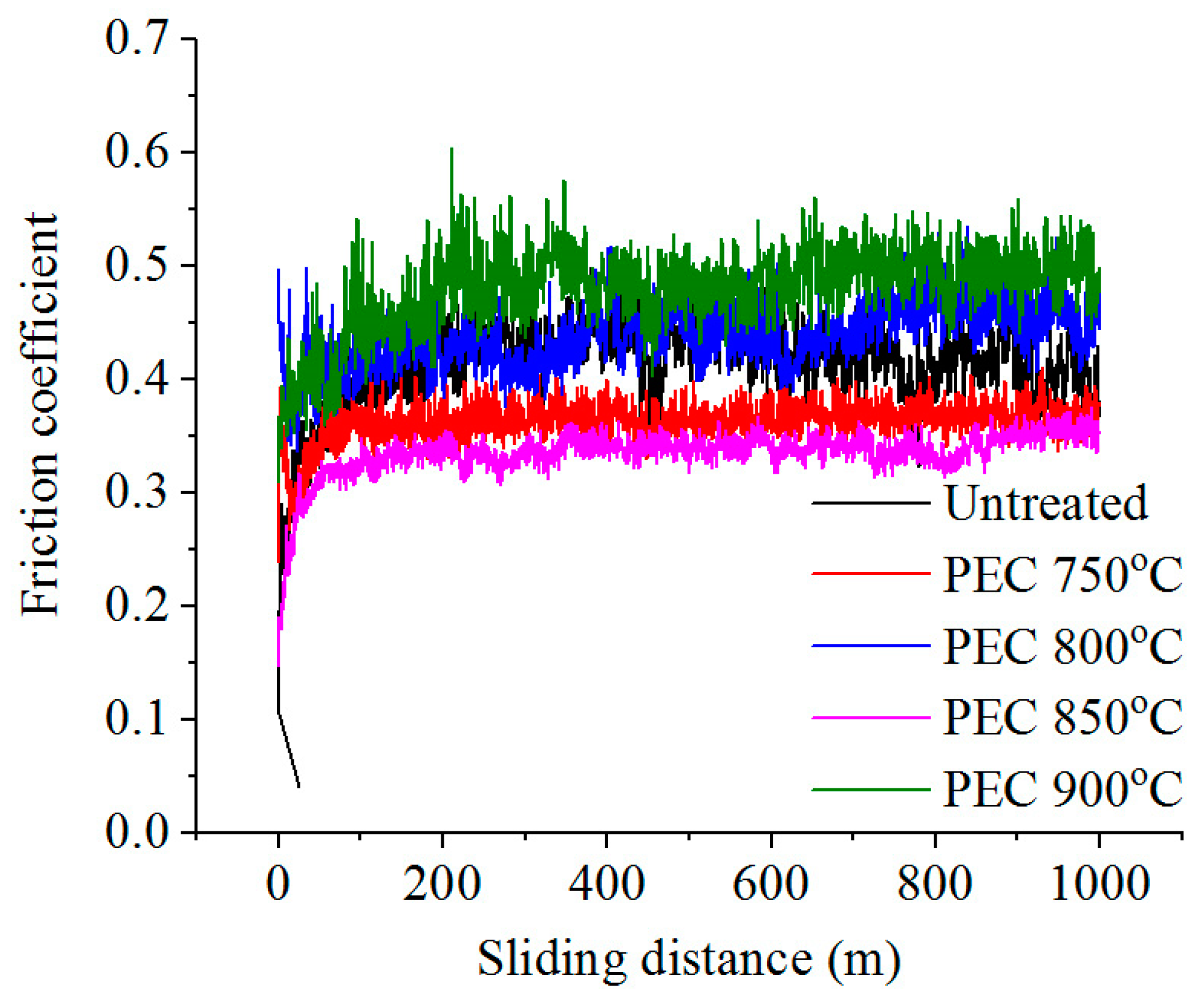
| Temperature (°C) | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Weight Loss of Samples during PEN (mg) | Surface Roughness Ra 1 (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 650 | 160 | 7.2 | 51.0 ± 0.3 | 0.24 ± 0.03 |
| 700 | 166 | 7.5 | 53.5 ± 0.4 | 0.28 ± 0.03 |
| 750 | 182 | 7.1 | 53.1 ± 0.1 | 0.22 ± 0.03 |
| 800 | 188 | 7.3 | 61.1 ± 0.3 | 0.20 ± 0.02 |
| 850 | 191 | 7.7 | 76.1 ± 0.2 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Temperature (°C) | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Weight Loss of Samples during PEB (mg) | Surface Roughness Ra 1 (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | 149 | 11.7 | 50.1 ± 0.3 | 0.33 ± 0.04 |
| 850 | 155 | 11.3 | 38.0 ± 0.2 | 0.38 ± 0.04 |
| 900 | 170 | 11.5 | 45.5 ± 0.2 | 0.49 ± 0.03 |
| 950 | 194 | 10.5 | 50.8 ± 0.3 | 0.62 ± 0.06 |
| Temperature (°C) | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Weight Loss of Samples during PEC (mg) | Surface Roughness Ra 1 (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 | 138 | 10.2 | 90.9 ± 0.5 | 0.33 ± 0.04 |
| 800 | 157 | 8.8 | 64.1 ± 0.4 | 0.17 ± 0.04 |
| 850 | 175 | 8.2 | 52.5 ± 0.3 | 0.23 ± 0.03 |
| 900 | 195 | 6.9 | 41.6 ± 0.2 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| T (°C) | Δ | h (MCM) | r (MCM) | h/r | Kp | Ar (MCM2) | Ar/Aa | nc/nr | Tfr (°C) | μ | Δmfr (Mг) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| untreated | 0.989 ± 0.017 | 1.44 ± 0.02 | 14.38 ± 0.24 | 0.100 ± 0.002 | 22.5 ± 0.4 | 8.22 ± 0.14 | 0.24 | 202 ± 5 | 68 | 0.401 ± 0.004 | 23.2 ± 0.3 |
| 650 | 0.379 ± 0.006 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 6.09 ± 0.11 | 0.079 ± 0.001 | 17.2 ± 0.4 | 2.07 ± 0.04 | 0.06 | 71 ± 1 | 79 | 0.698 ± 0.008 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| 700 | 0.408 ± 0.007 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 5.54 ± 0.09 | 0.083 ± 0.001 | 21.3 ± 0.5 | 1.95 ± 0.03 | 0.06 | 78 ± 2 | 81 | 0.773 ± 0.009 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| 750 | 0.402 ± 0.007 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 5.98 ± 0.10 | 0.080 ± 0.001 | 19.2 ± 0.4 | 2.62 ± 0.04 | 0.08 | 70 ± 1 | 86 | 0.615 ± 0.007 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| 800 | 0.398 ± 0.007 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 5.95 ± 0.11 | 0.079 ± 0.001 | 18.8 ± 0.4 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 69 ± 1 | 78 | 0.586 ± 0.007 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| 850 | 0.387 ± 0.007 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 6.03 ± 0.10 | 0.074 ± 0.001 | 20.0 ± 0.5 | 2.87 ± 0.05 | 0.08 | 73 ± 1 | 81 | 0.606 ± 0.007 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| T (°C) | Δ | h (MCM) | r (MCM) | h/r | Kp | Ar (MCM2) | Ar/Aa | nc/nr | Tfr (°C) | μ | Δmfr (Mг) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| untreated | 0.989 ± 0.017 | 1.44 ± 0.02 | 14.38 ± 0.24 | 0.100 ± 0.002 | 22.5 ± 0.4 | 8.22 ± 0.14 | 0.24 | 202 ± 5 | 68 | 0.401 ± 0.004 | 23.2 ± 0.3 |
| 800 | 0.451 ± 0.008 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 5.33 ± 0.09 | 0.084 ± 0.001 | 22.6 ± 0.4 | 6.82 ± 0.12 | 0.20 | 115 ± 3 | 62 | 0.478 ± 0.005 | 24.7 ± 0.2 |
| 850 | 0.415 ± 0.007 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 6.73 ± 0.11 | 0.080 ± 0.001 | 16.3 ± 0.3 | 6.51 ± 0.11 | 0.19 | 112 ± 3 | 74 | 0.388 ± 0.004 | 3.3 ± 0.1 |
| 900 | 0.430 ± 0.007 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 6.54 ± 0.11 | 0.079 ± 0.001 | 17.2 ± 0.3 | 6.43 ± 0.11 | 0.19 | 118 ± 3 | 83 | 0.386 ± 0.004 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| 950 | 0.462 ± 0.008 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 5.98 ± 0.10 | 0.089 ± 0.002 | 24.4 ± 0.4 | 6.72 ± 0.11 | 0.19 | 120 ± 3 | 76 | 0.564 ± 0.006 | 26.2 ± 0.1 |
| T (°C) | Δ | h (MCM) | r (MCM) | h/r | Kp | Ar (MCM2) | Ar/Aa | nc/nr | Tfr (°C) | μ | Δmfr (Mг) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| untreated | 0.989 ± 0.017 | 1.44 ± 0.02 | 14.38 ± 0.24 | 0.100 ± 0.002 | 22.5 ± 0.4 | 8.22 ± 0.14 | 0.24 | 202 ± 5 | 68 | 0.401 ± 0.004 | 23.2 ± 0.3 |
| 750 | 0.362 ± 0.006 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 7.22 ± 0.12 | 0.059 ± 0.001 | 16.8 ± 0.3 | 4.43 ± 0.08 | 0.13 | 87 ± 2 | 45 | 0.313 ± 0.003 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 800 | 0.412 ± 0.007 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 6.54 ± 0.11 | 0.071 ± 0.001 | 23.5 ± 0.4 | 3.76 ± 0.06 | 0.11 | 120 ± 3 | 51 | 0.452 ± 0.005 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| 850 | 0.387 ± 0.007 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 7.06 ± 0.12 | 0.061 ± 0.001 | 17.3 ± 0.3 | 3.81 ± 0.06 | 0.11 | 94 ± 2 | 79 | 0.354 ± 0.004 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 900 | 0.423 ± 0.007 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 6.32 ± 0.11 | 0.078 ± 0.001 | 24.1 ± 0.4 | 3.27 ± 0.06 | 0.09 | 125 ± 3 | 76 | 0.497 ± 0.005 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kusmanov, S.; Mukhacheva, T.; Tambovskiy, I.; Naumov, A.; Belov, R.; Sokova, E.; Kusmanova, I. Increasing Hardness and Wear Resistance of Austenitic Stainless Steel Surface by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Treatment. Metals 2023, 13, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050872
Kusmanov S, Mukhacheva T, Tambovskiy I, Naumov A, Belov R, Sokova E, Kusmanova I. Increasing Hardness and Wear Resistance of Austenitic Stainless Steel Surface by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Treatment. Metals. 2023; 13(5):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050872
Chicago/Turabian StyleKusmanov, Sergei, Tatiana Mukhacheva, Ivan Tambovskiy, Alexander Naumov, Roman Belov, Ekaterina Sokova, and Irina Kusmanova. 2023. "Increasing Hardness and Wear Resistance of Austenitic Stainless Steel Surface by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Treatment" Metals 13, no. 5: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050872
APA StyleKusmanov, S., Mukhacheva, T., Tambovskiy, I., Naumov, A., Belov, R., Sokova, E., & Kusmanova, I. (2023). Increasing Hardness and Wear Resistance of Austenitic Stainless Steel Surface by Anodic Plasma Electrolytic Treatment. Metals, 13(5), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050872






