Effect of High Ti Contents on Austenite Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation in Low Carbon Nb Microalloyed Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
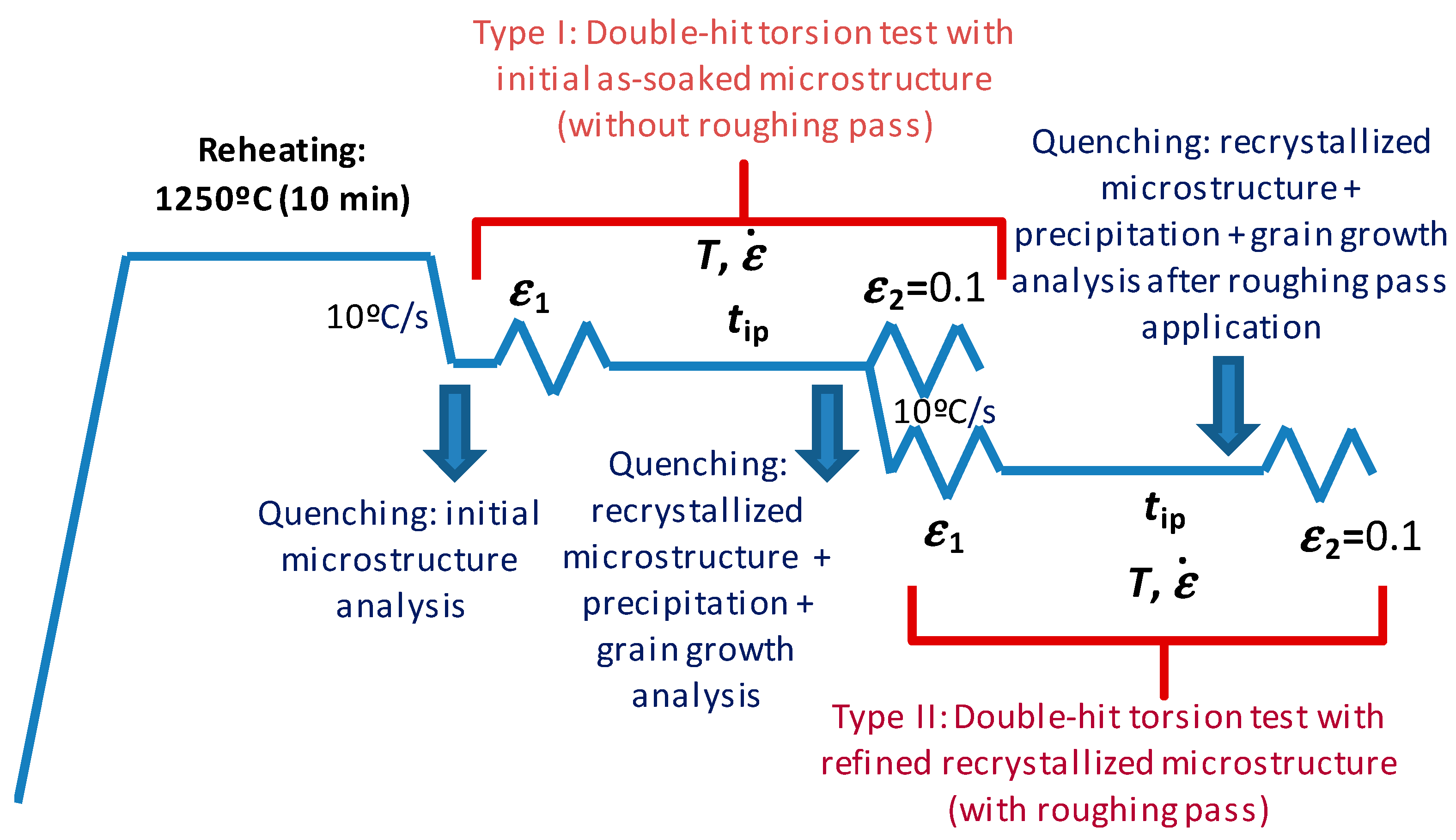
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
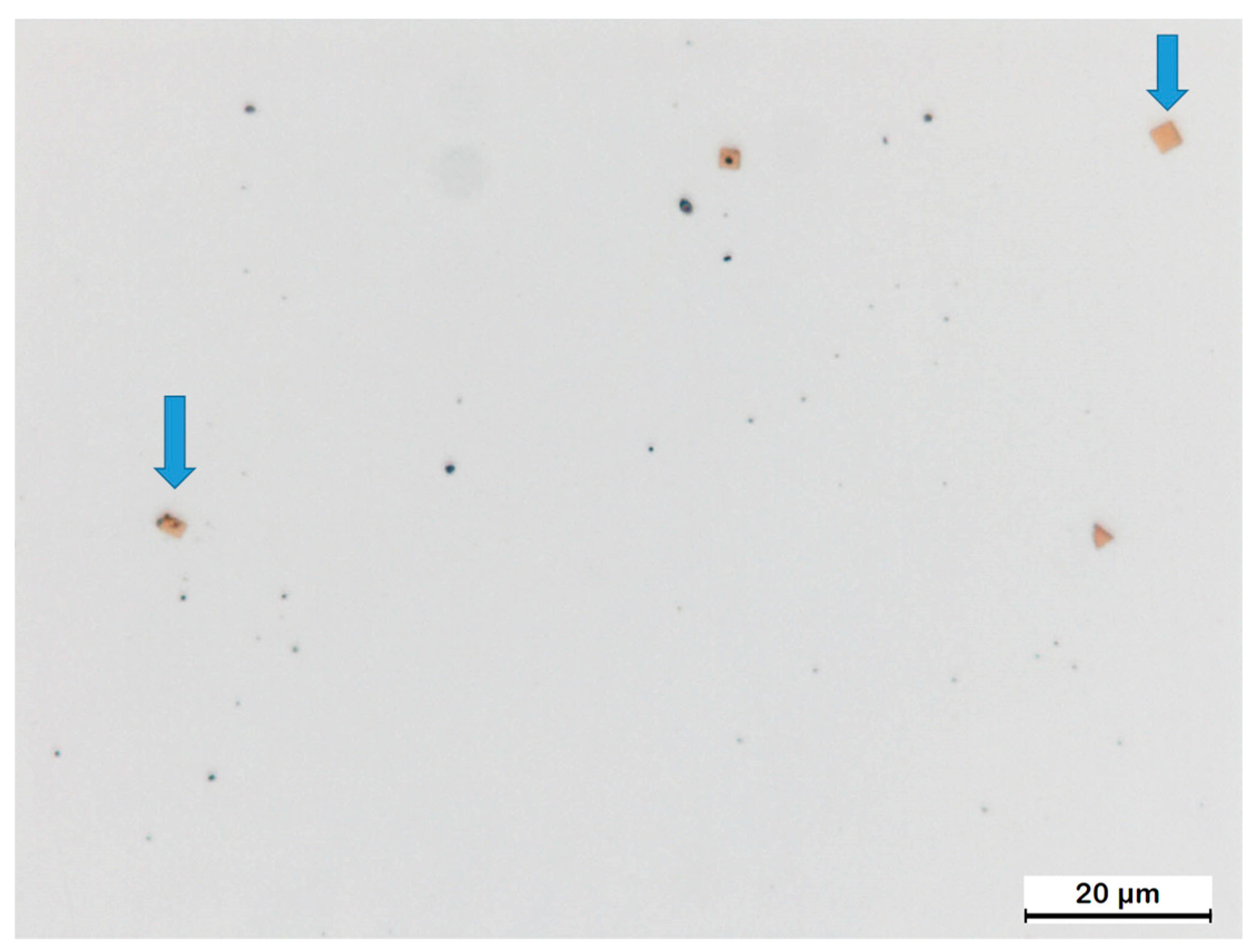
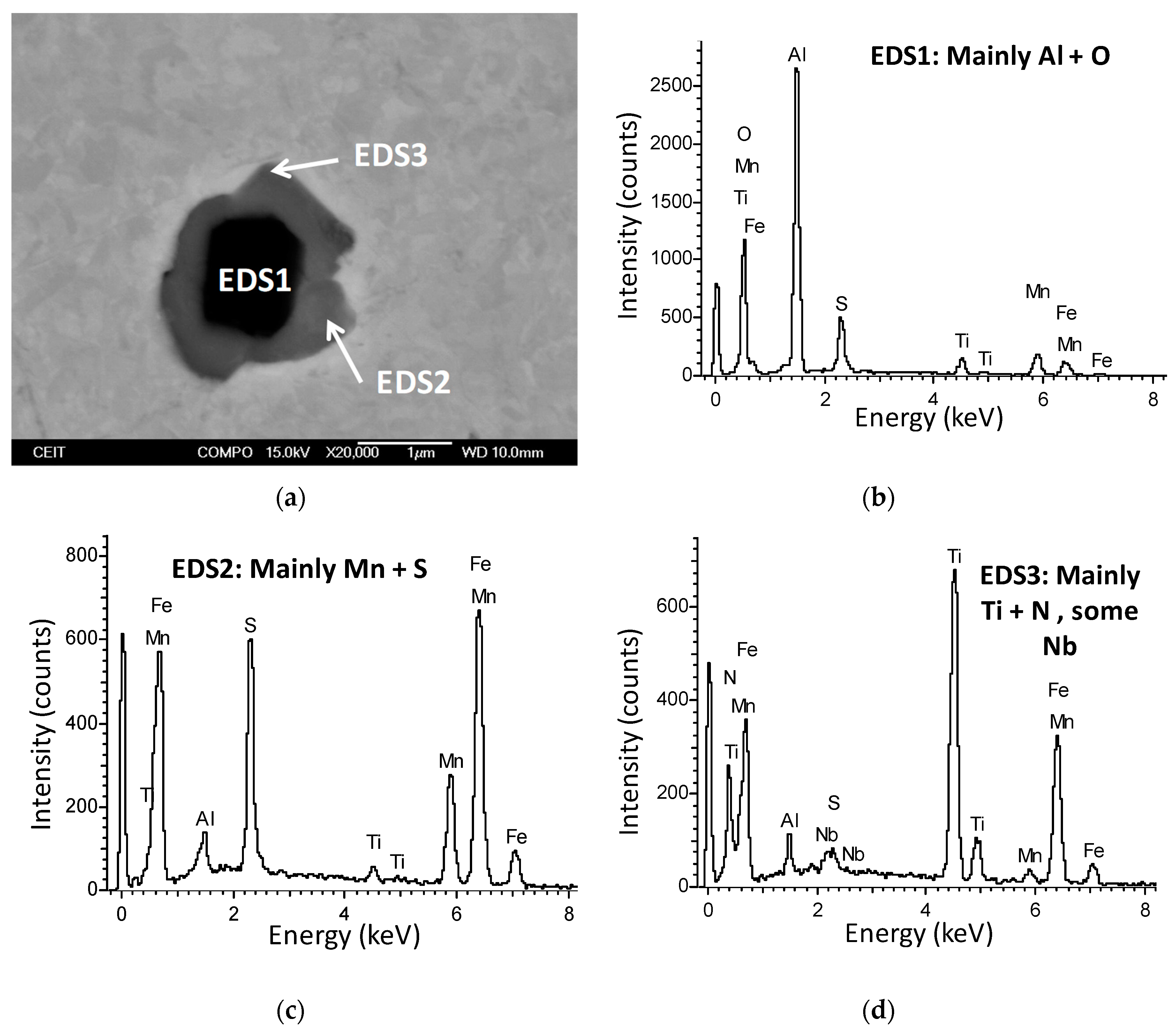
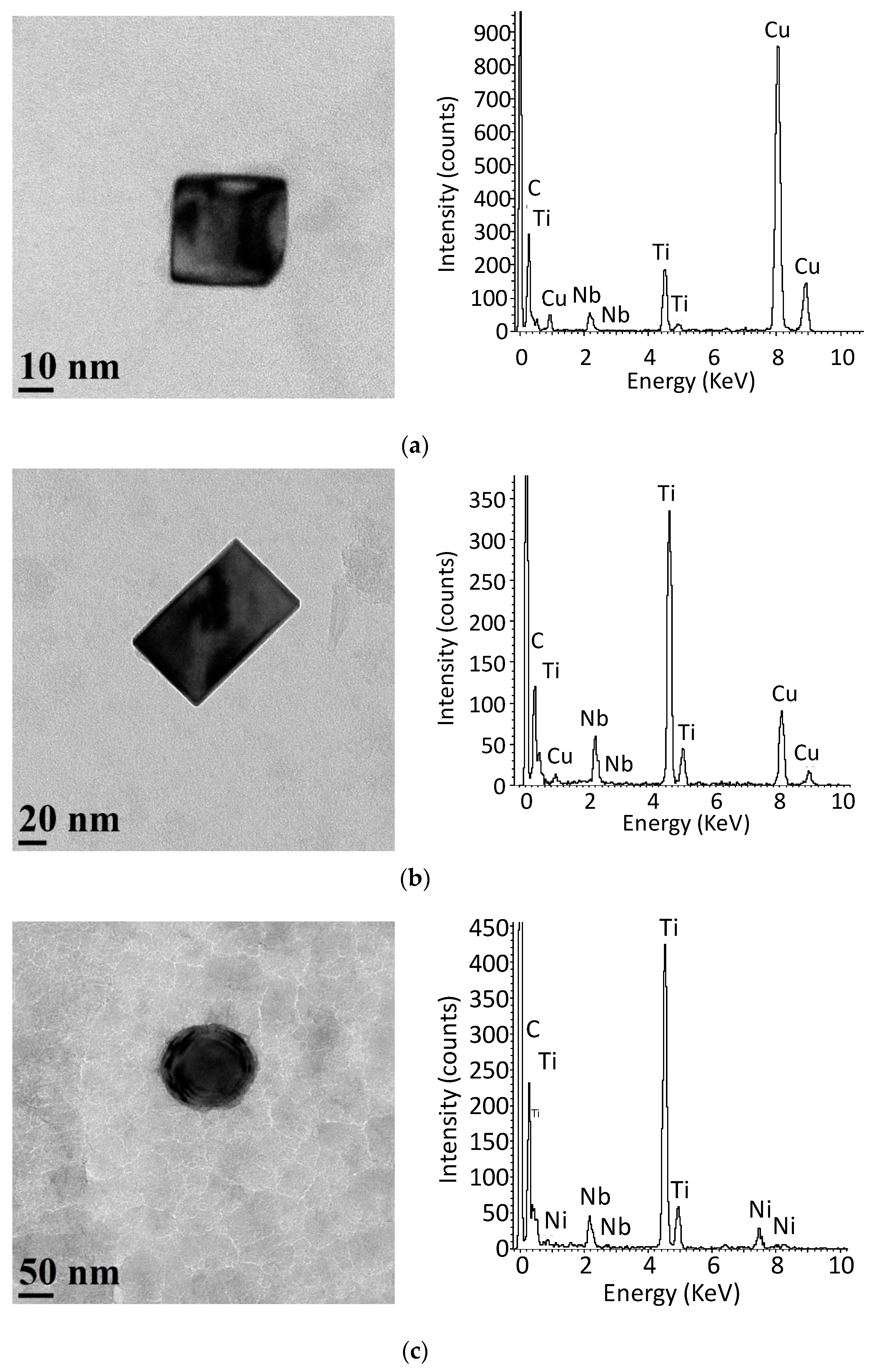
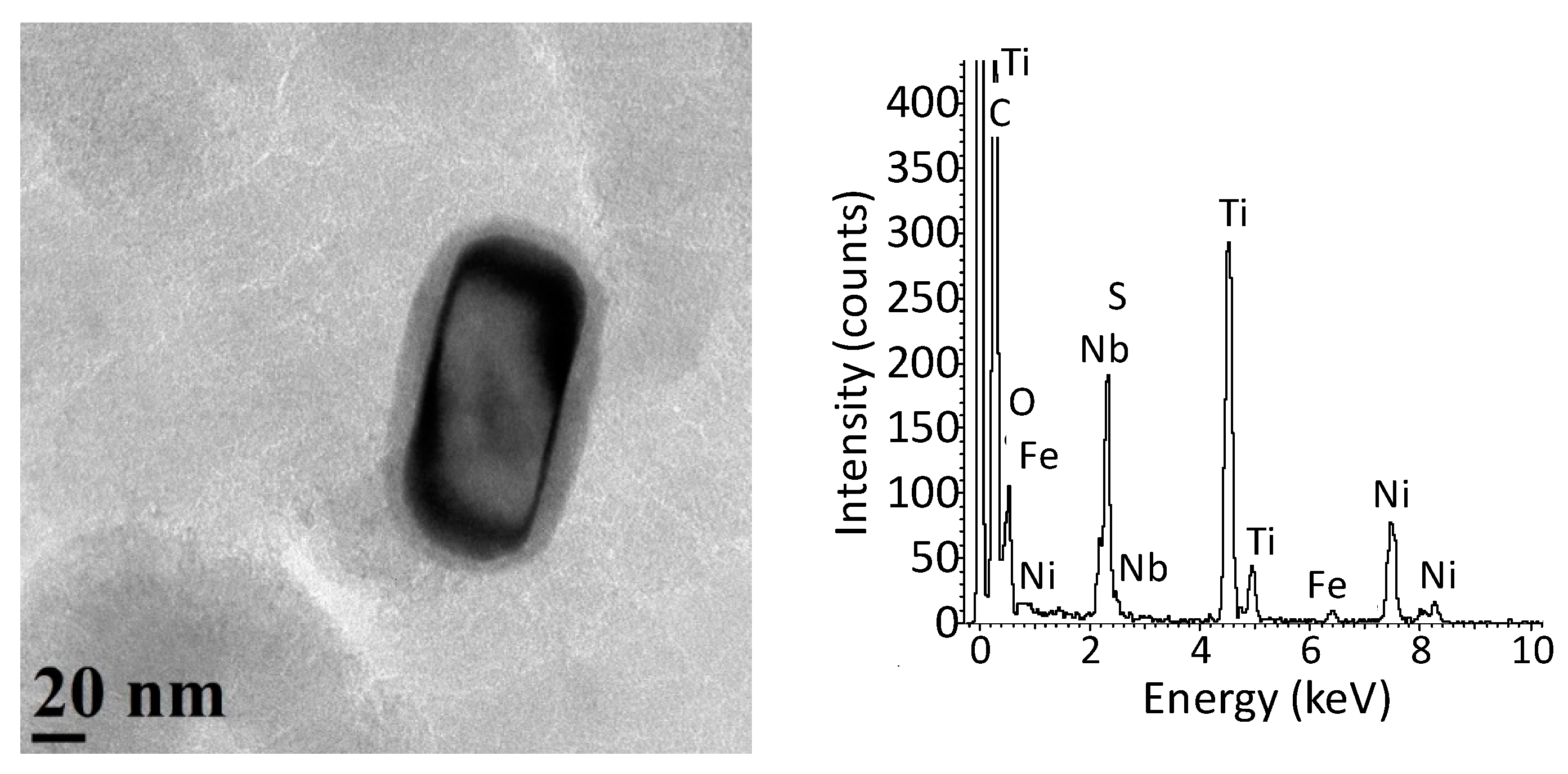
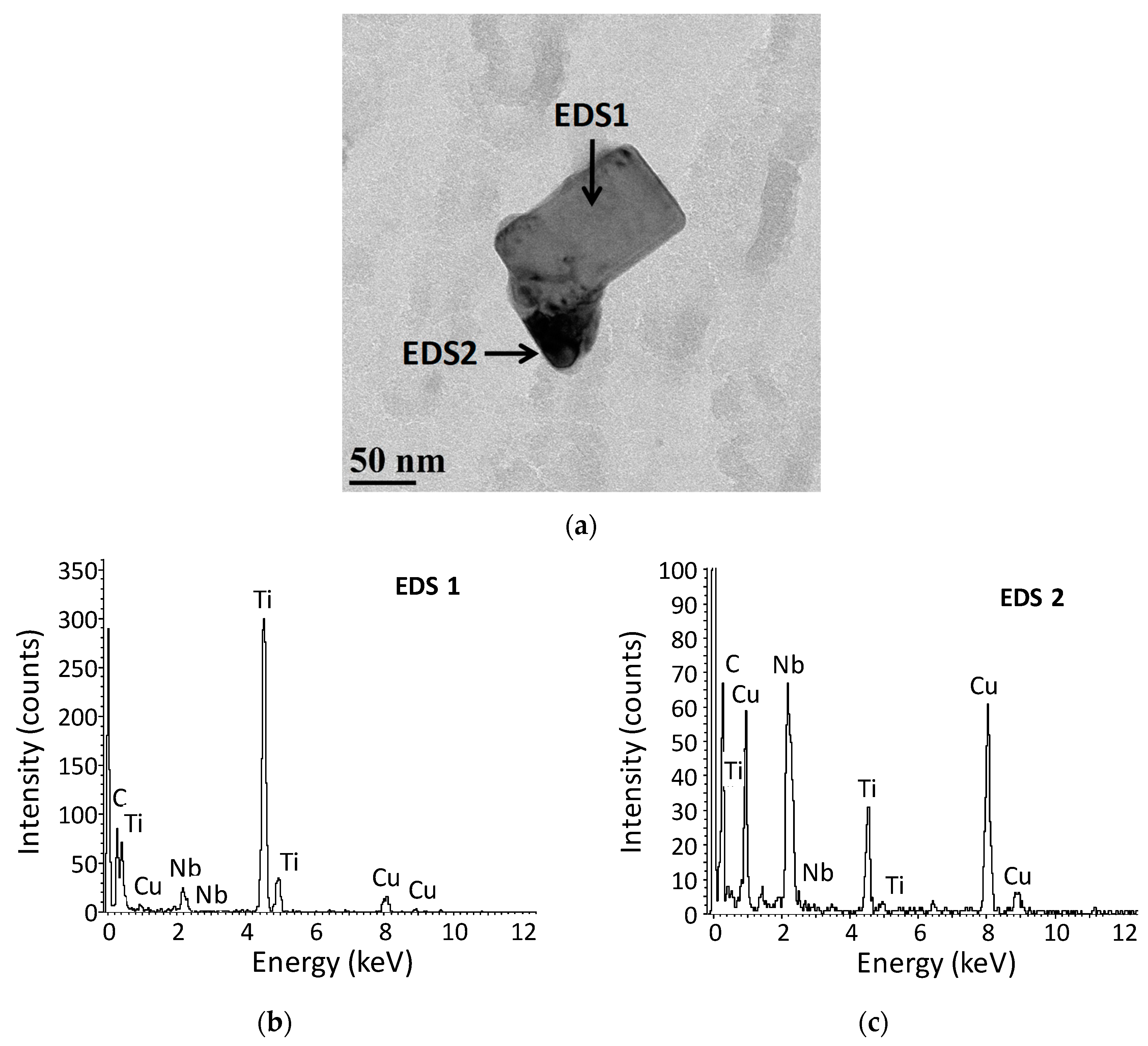
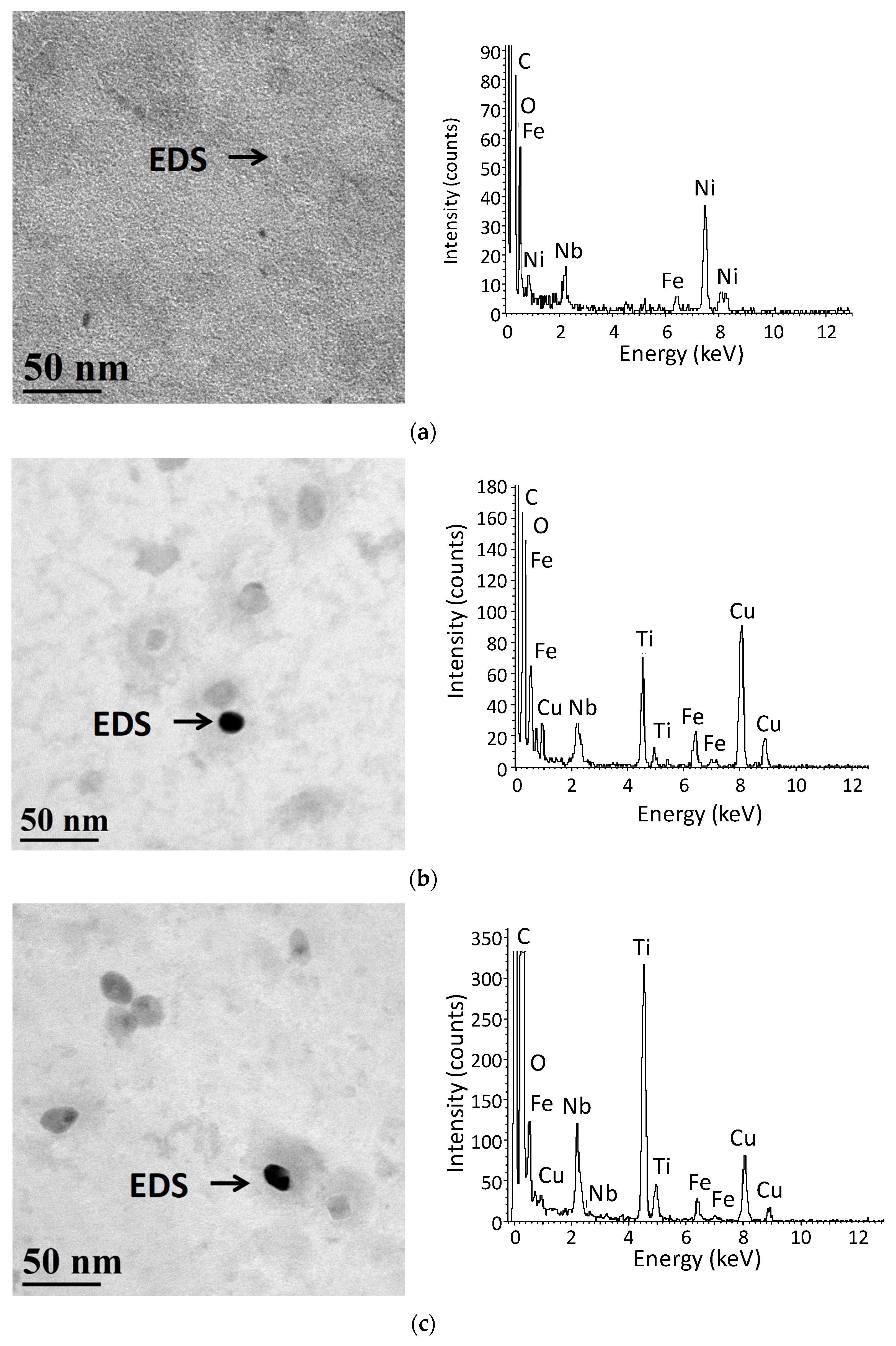
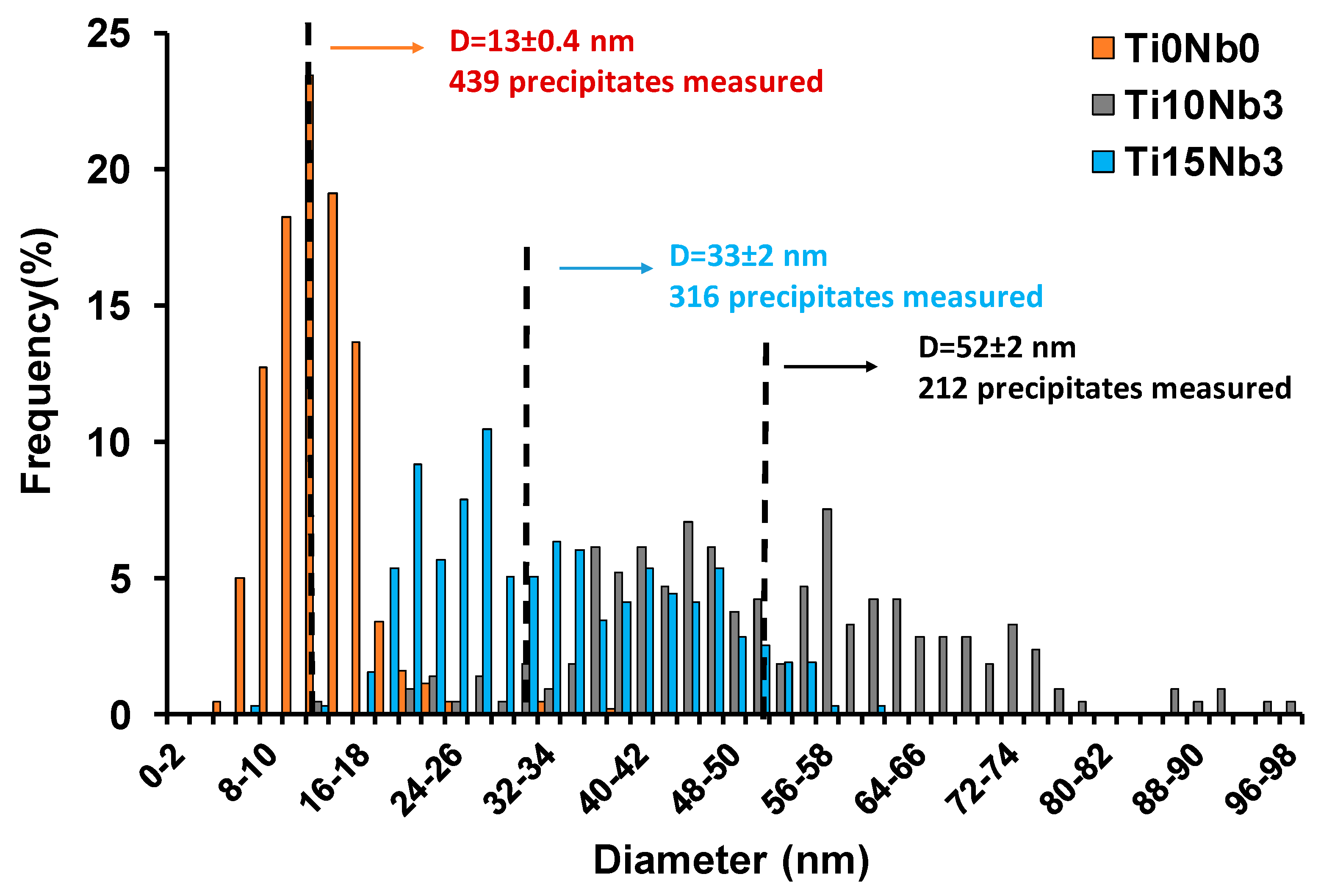
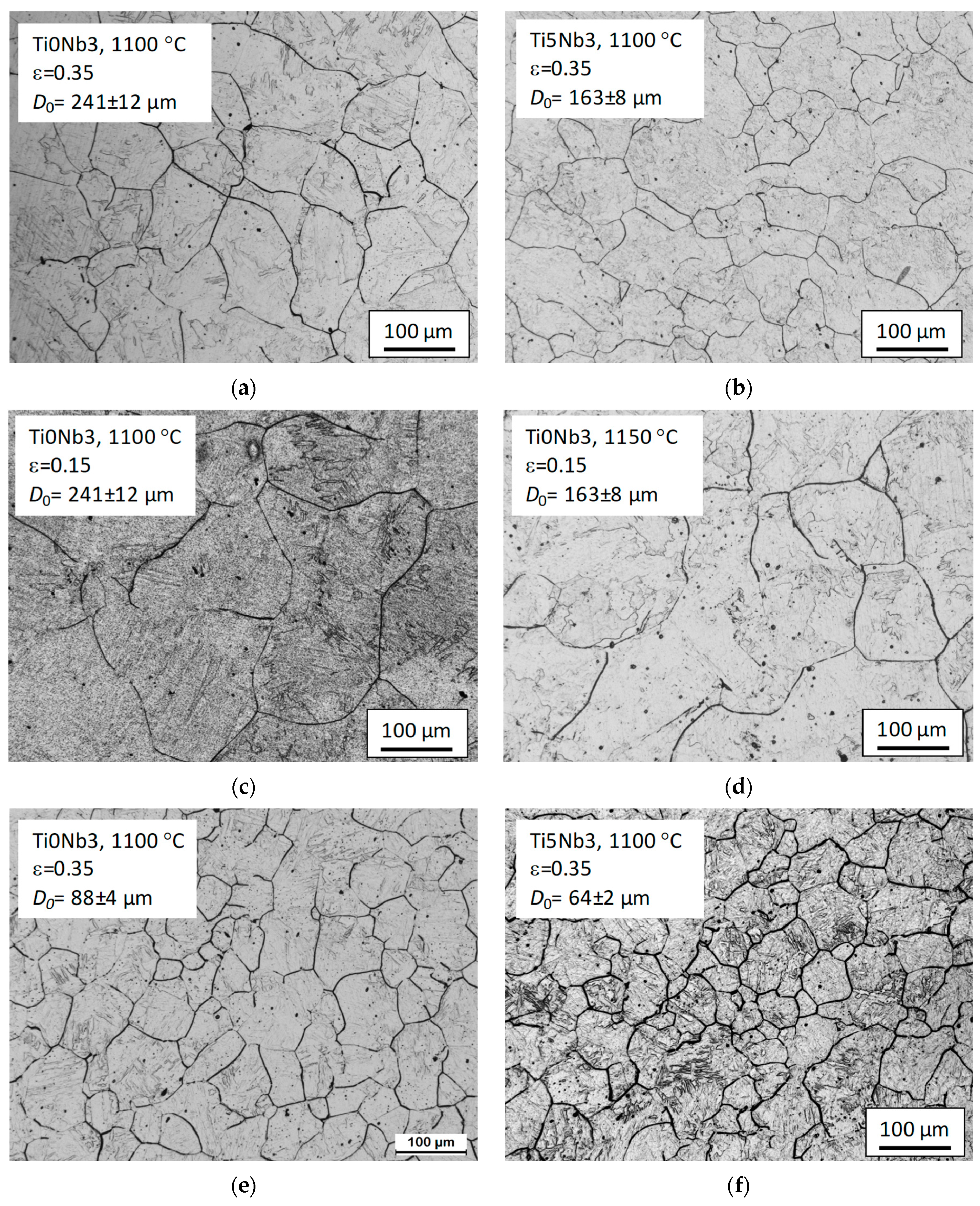
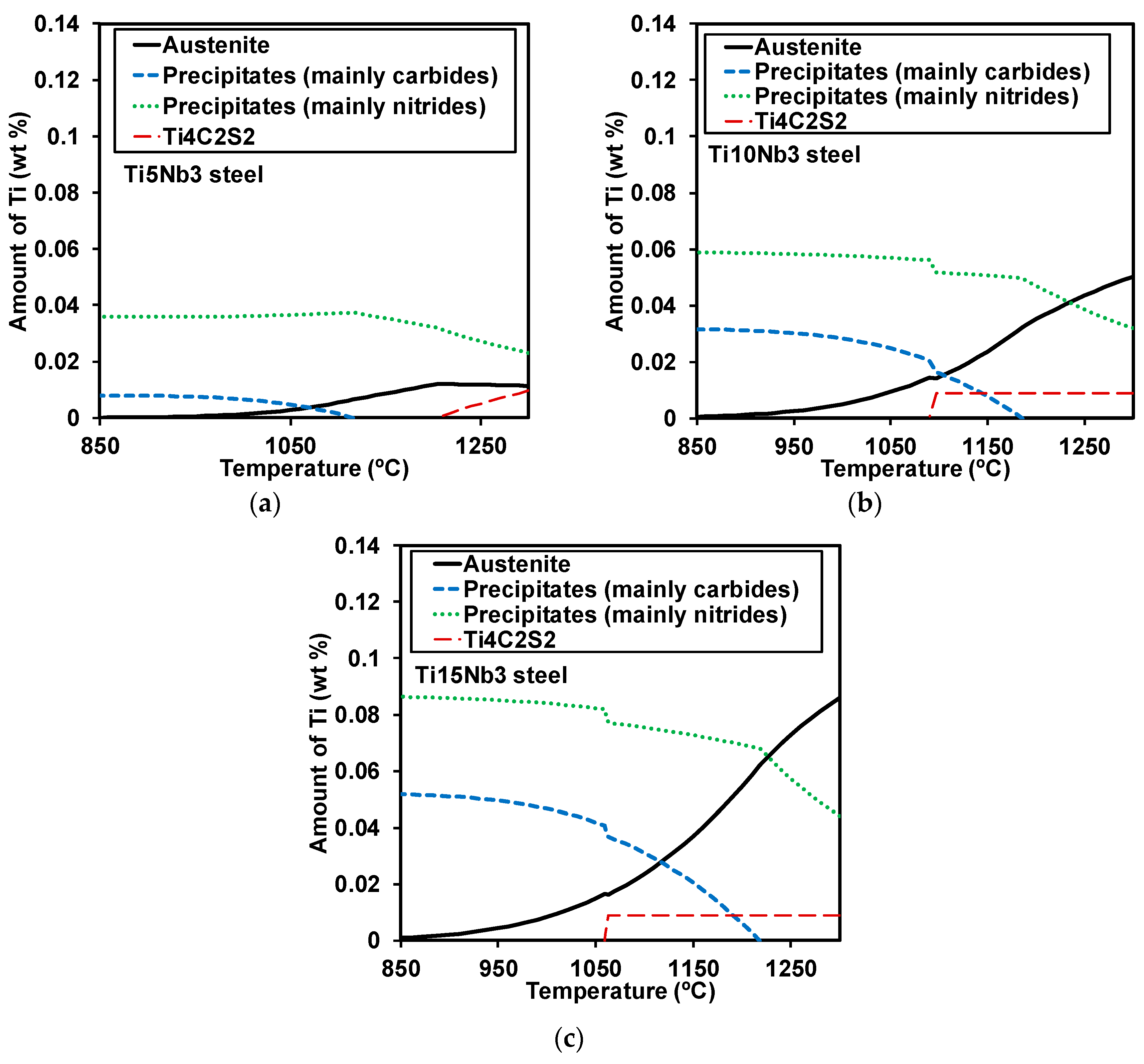
3.1. Initial Precipitation and Microstructural State
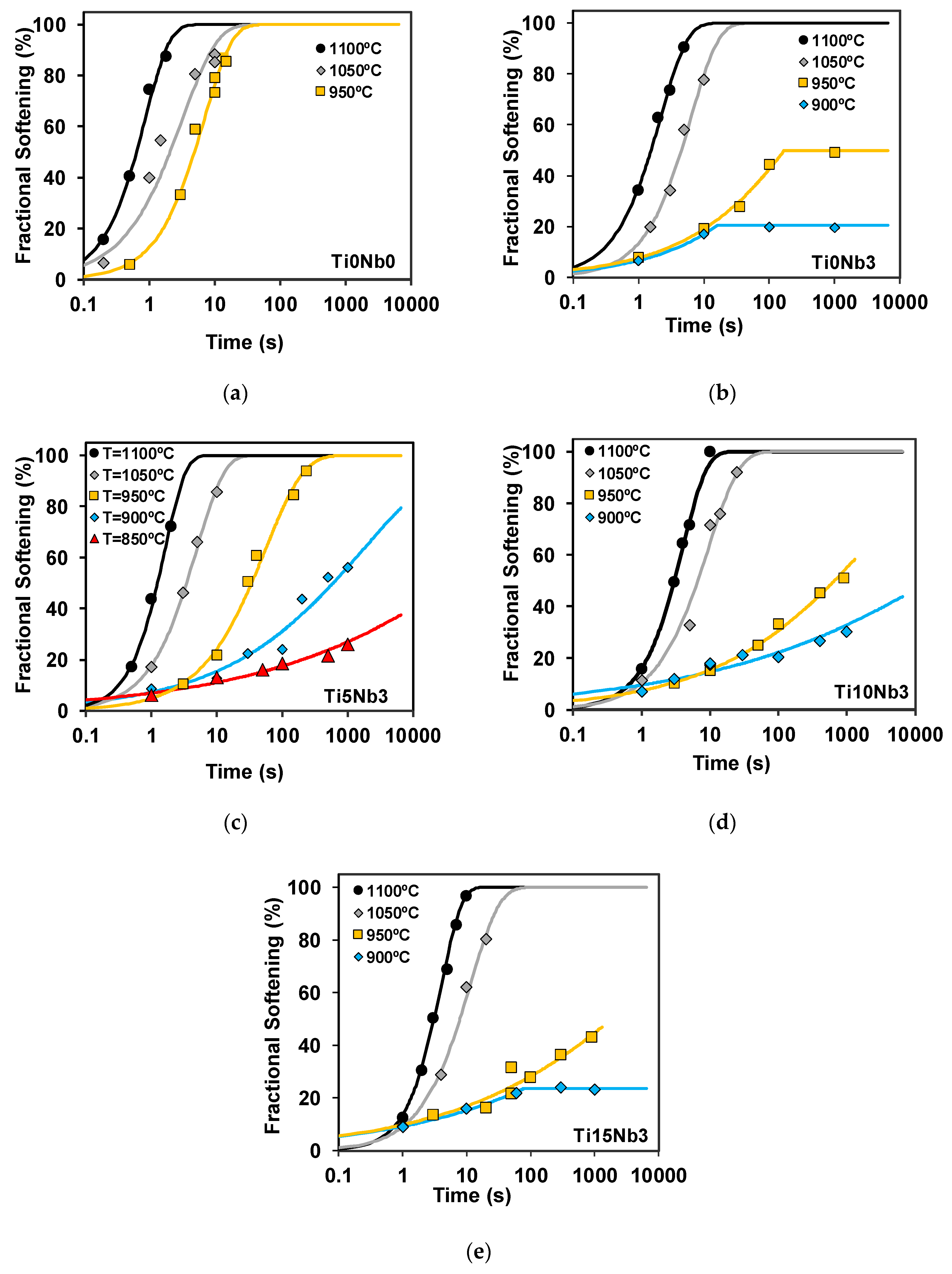
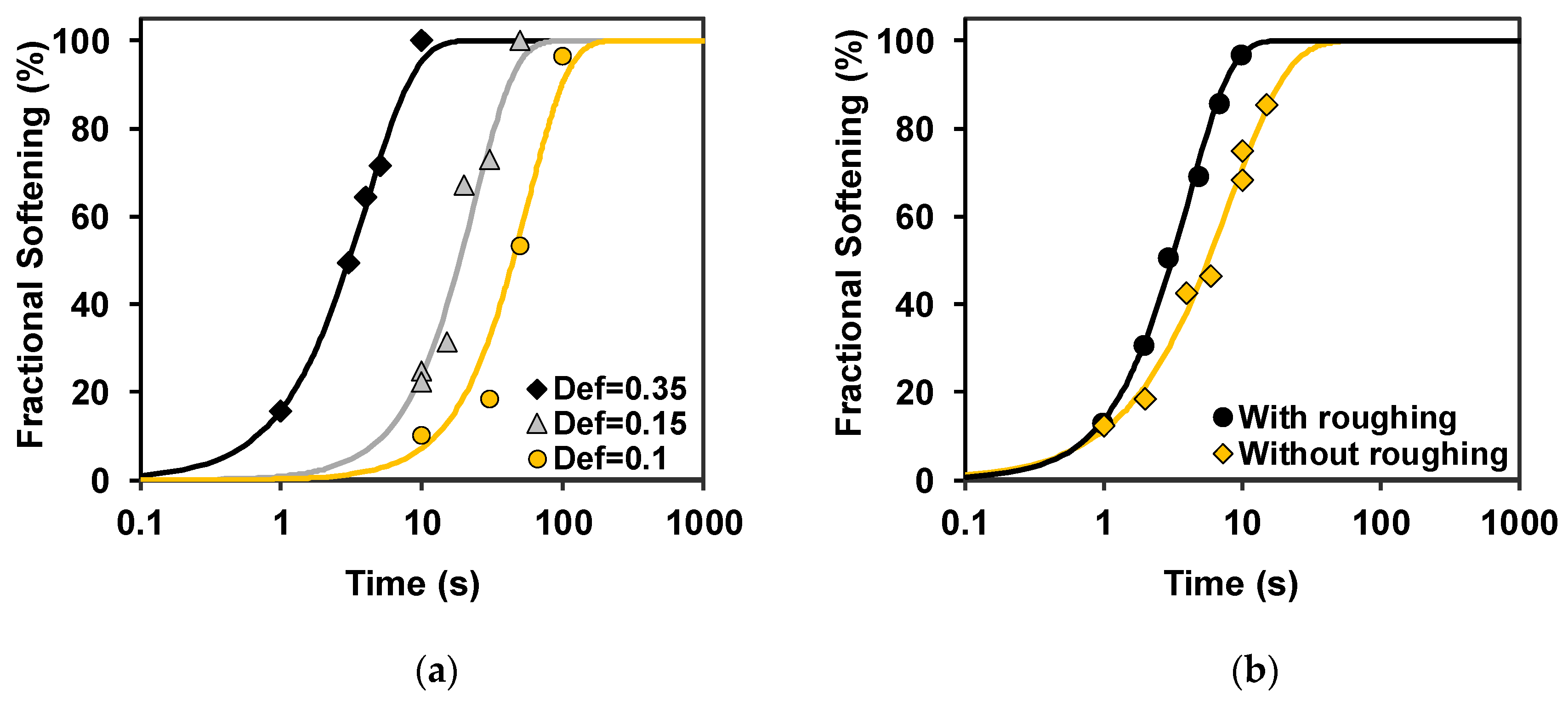
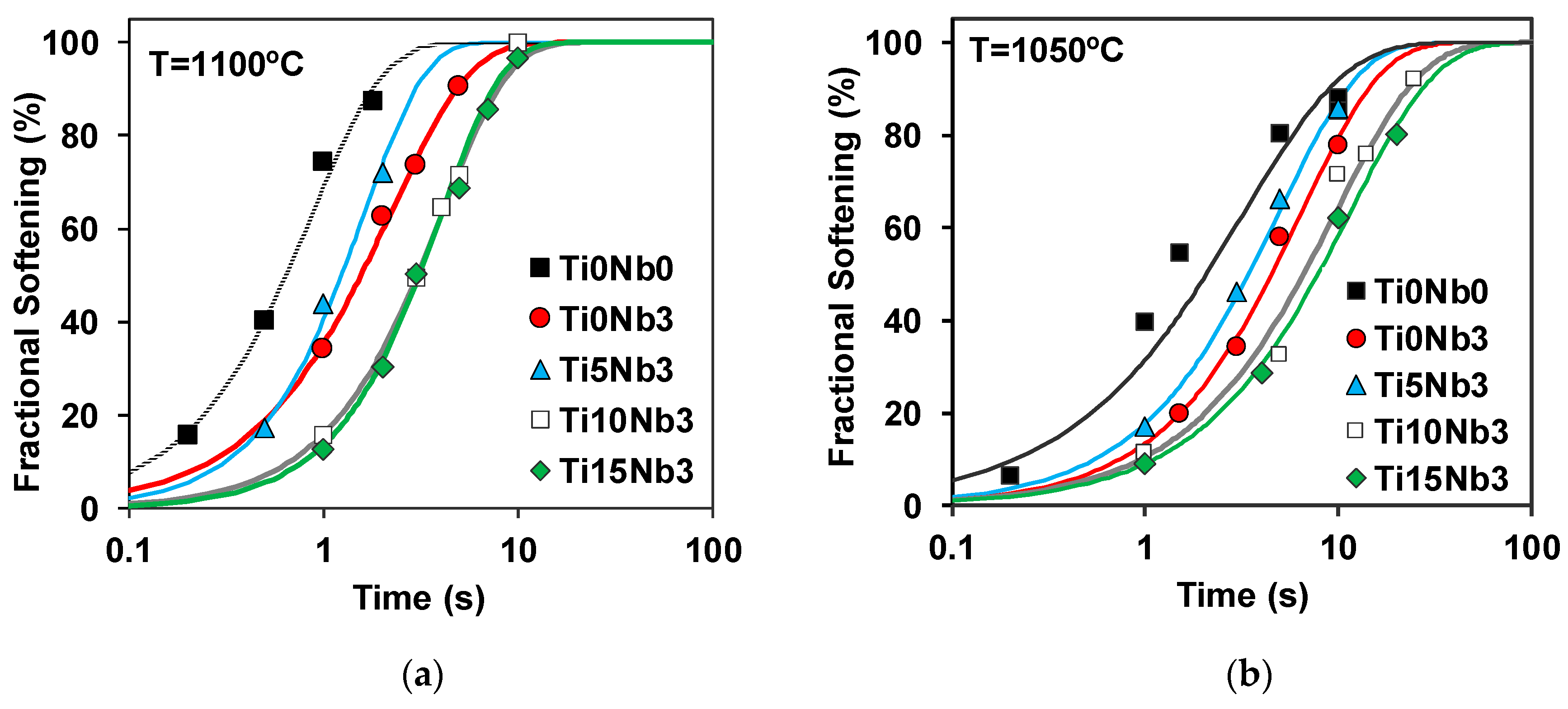
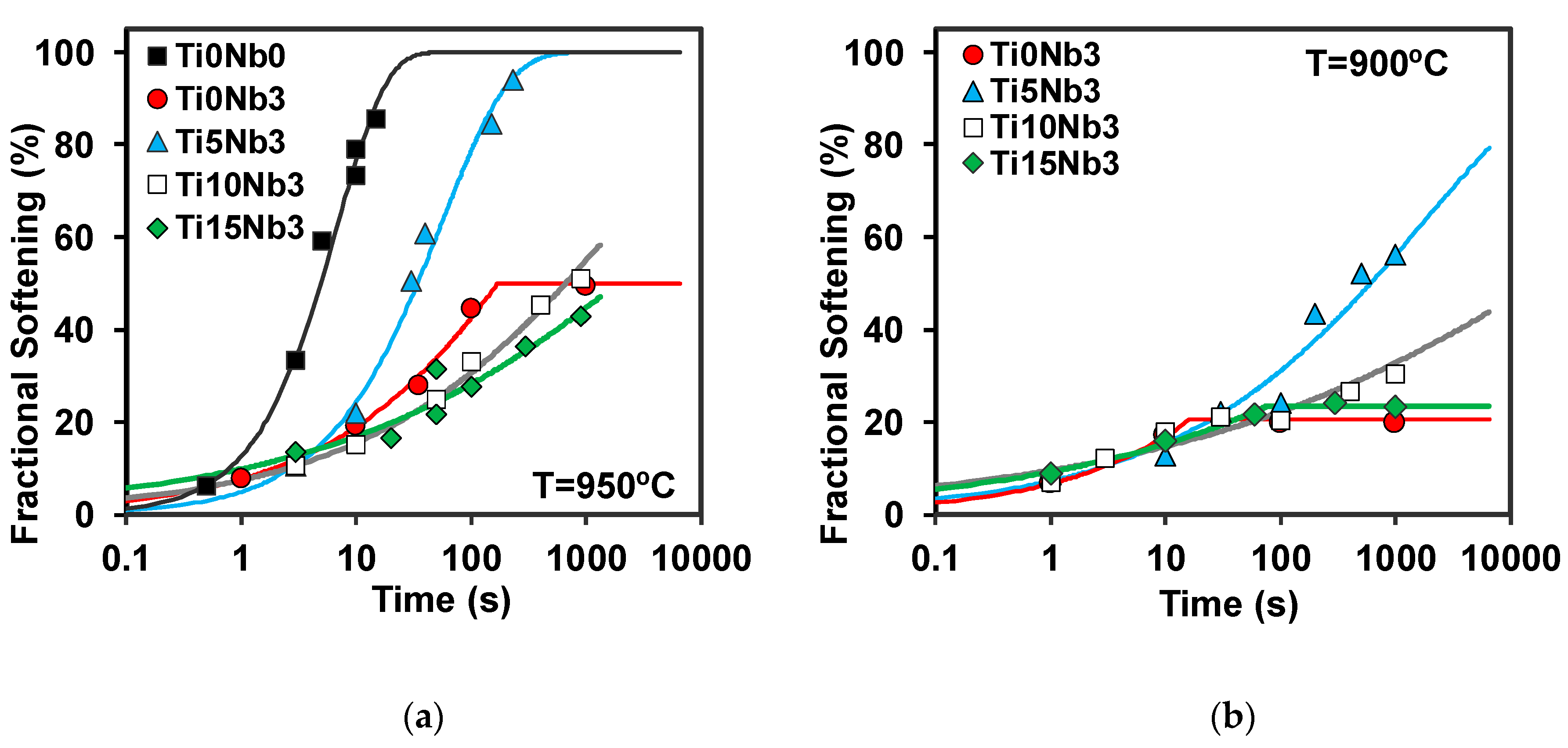
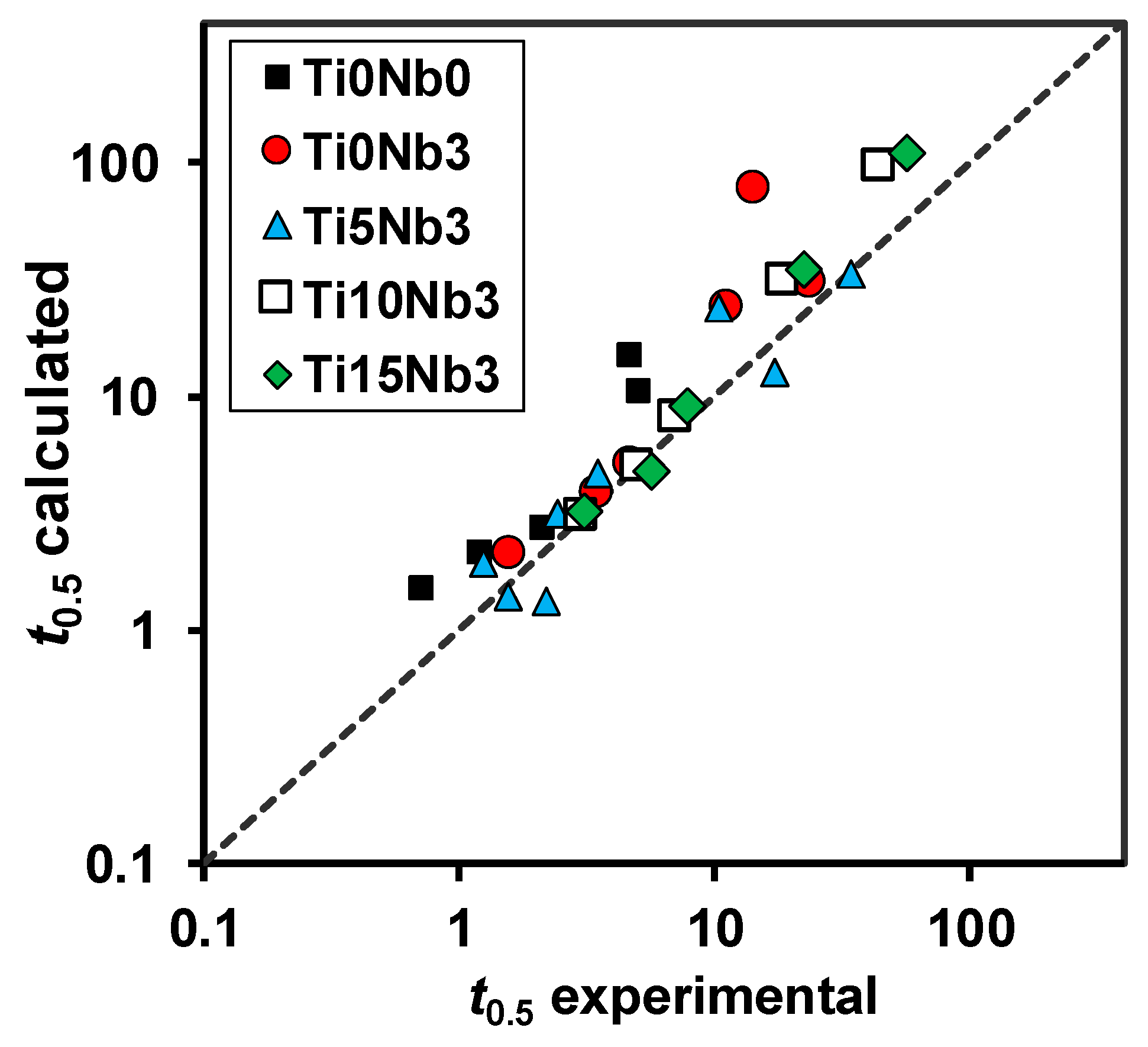
3.2. Softening Kinetics
3.3. Strain-Induced Precipitation Behavior
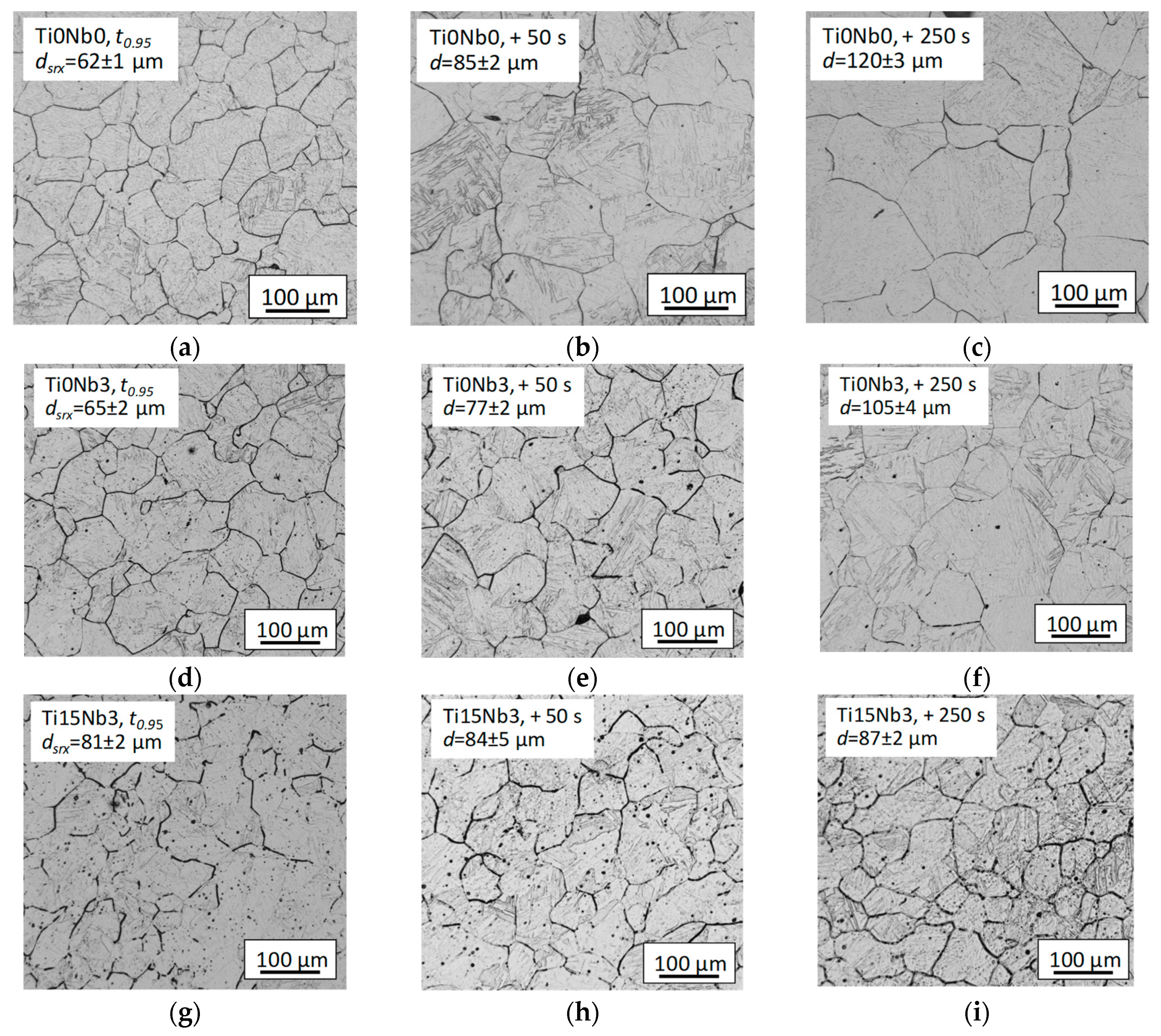
3.4. Recrystallized Grain Size
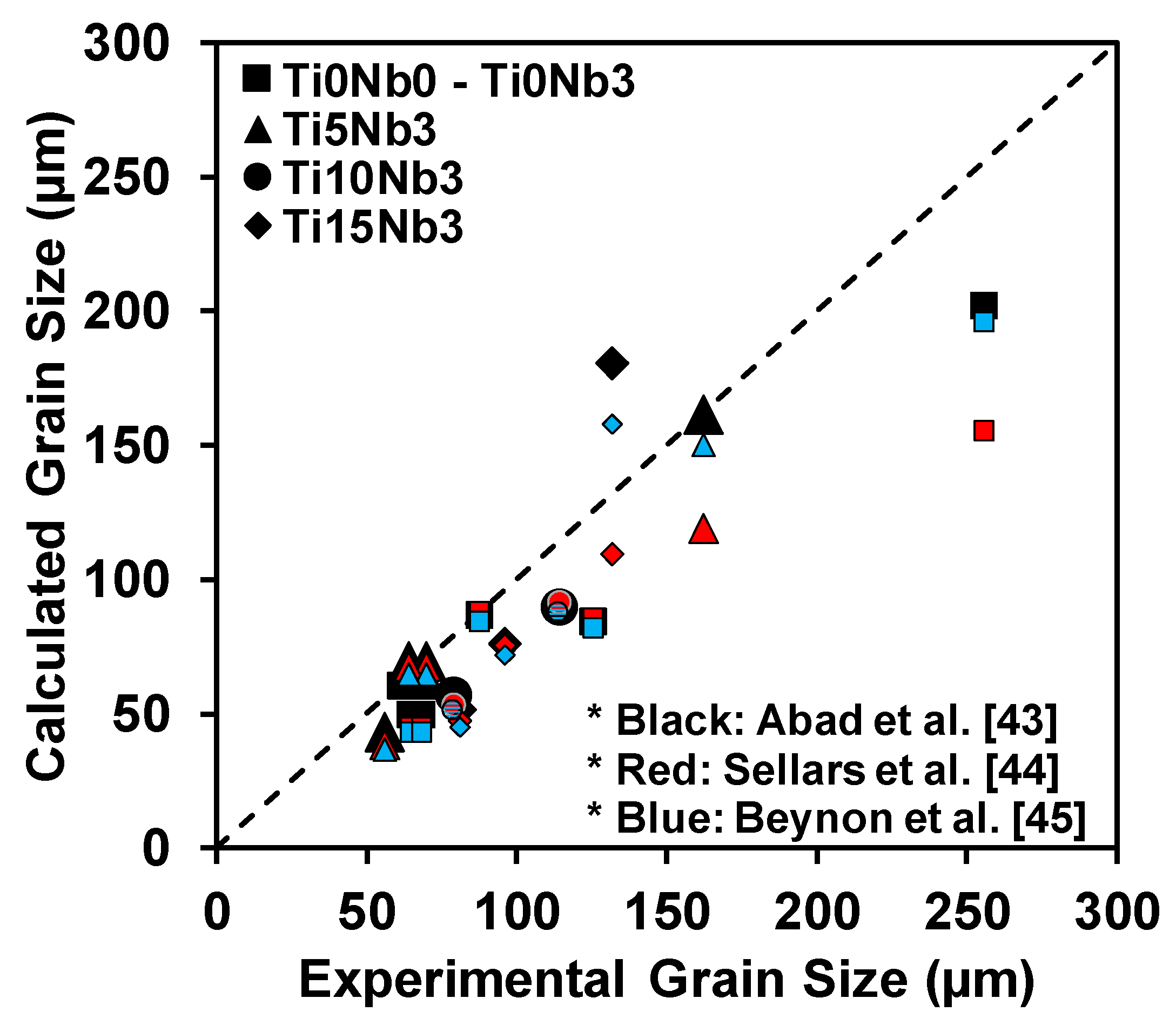
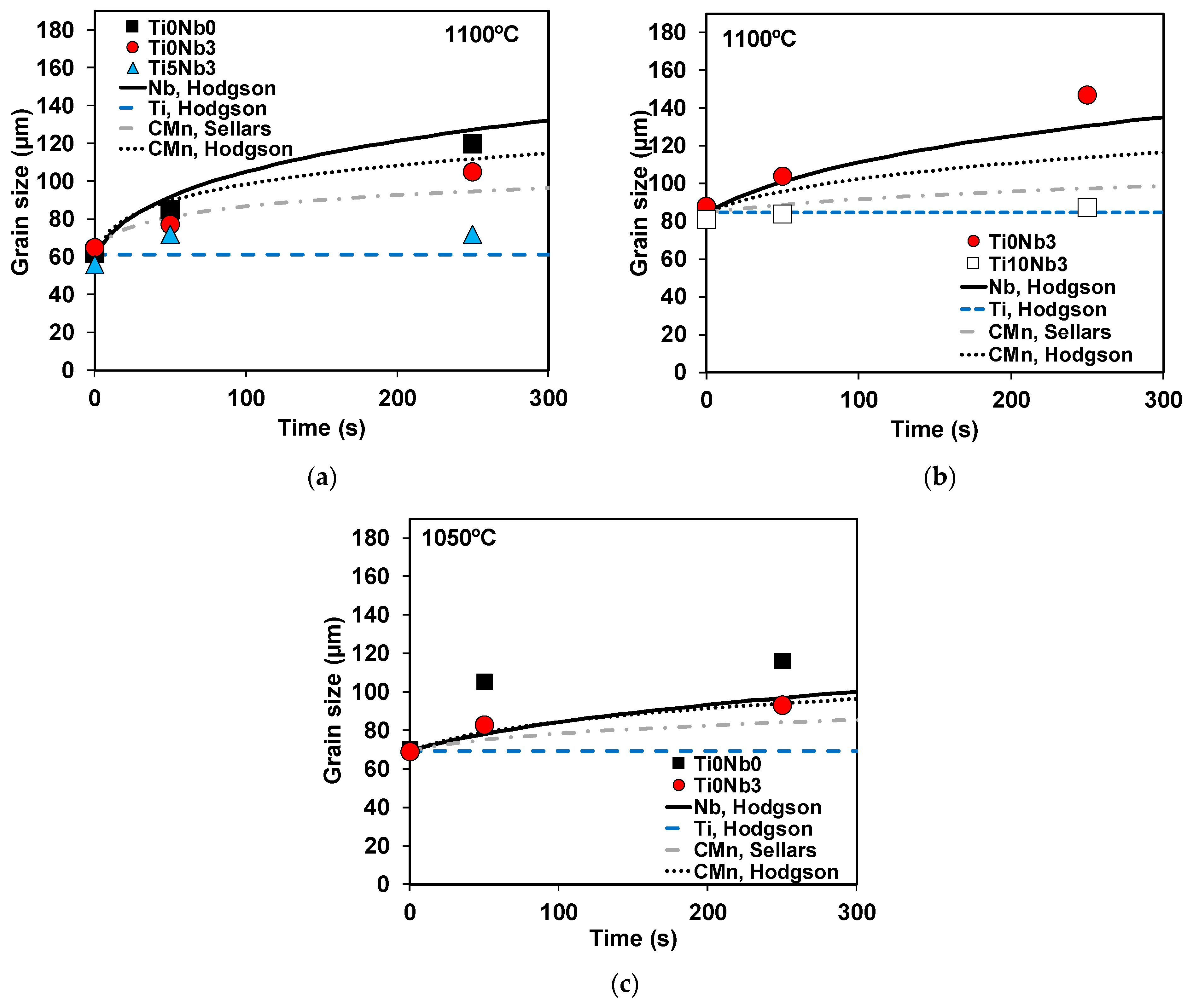
3.5. Grain Growth Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Initial Microstructural and Precipitation State
4.2. Static Softening and Strain-Iduced Precipitation Behavior
4.3. Recrystallized Grain Size
4.4. Grain Growth Behavior
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrade, H.L.; Akben, M.G.; Jonas, J.J. Effect of Molybdenum, Niobium, and Vanadium on Static Recovery and Recrystallization and on Solute Strengthening in Microalloyed Steels. Metall. Trans. A 1983, 14, 1967–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.F.; Quispe, A. Improved Model for Static Recrysallization Kinetics of Hot Deformed Austenite in Low Alloy and Nb/V Microalloyed Steels. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.I.; Uranga, P.; López, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Static Recrystallization Behaviour of a Wide Range of Austenite Grain Sizes in Microalloyed Steels. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretxabaleta, Z.; Pereda, B.; Lopez, B. Multipass Hot Deformation Behaviour of High Al and Al-Nb Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 600, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengochea, R.; Lopez, B.; Gutierrez, I. Influence of the Prior Austenite Microstructure on the Transformation Products obtained for C-Mn-Nb Steels after Continuous Cooling. ISIJ Int. 1999, 39, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeArdo, A.J. Niobium in Modern Steels. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 48, 371–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolczynski, W. Back-Diffusion in Crystal Growth. Eutectics. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolczynski, W. Back-Diffusion in Crystal Growth. Peritectics. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 2409–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himemiya, T.; Wolczynski, W. Solidification Path and Solute Redistribution of an Iron-Based MultiComponent Allow with Solute Diffusion in the Solid. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 2409–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Medina, S.F.; Chapa, P.; Valles, A.; Quispe, M.I.; Vega, M.I. Influence of Ti and N Contents on Austenite Grain Control and Precipitate Size in Structural Steels. ISIJ Int. 1999, 39, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagneborg, R.; Siwecki, T.; Zajac, S. Role of Vanadium in Microalloyed Steels. Scand. J. Metall. 1999, 28, 186–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, L.; Pereda, B.; Lopez, B. Effect of Thermomechanical Treatment and Coiling Temperature on the Strengthening Mechanisms of Low Carbon Steels Microalloyed with Nb. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 685, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iza-Mendia, A.; Altuna, M.A.; Pereda, B.; Gutierrez, I. Precipitation of Nb in Ferrite after Austenite Conditioning. Part I: Microstructural Characterization. Metall. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4553–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuna, M.A.; Iza-Mendia, A.; Gutierrez, I. Precipitation of Nb in Ferrite after Austenite Conditioning. Part II: Strengthening Contribution in High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 4571–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.; Honeycombe, R.W.K. Strengthening of Titanium Steels by Carbide Precipitation. Met. Sci. 1977, 11, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakawa, Y.; Shiozaki, T.; Tomita, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Maeda, E. Development of High Strength Hot-Rolled Sheet Steel consisting of Ferrite and Nanometer-Sized Carbides. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.Z.; Wang, X.M.; Yang, S.W.; Shang, C.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Contribution of Interphase Precipitation on Yield Strength in Thermomechanically Simulated Ti-Nb and Ti-Nb-Mo Microalloyed Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 620, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Yen, H.W.; Kao, F.H.; Li, W.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, J.R.; Wang, S.H. Precipitation Hardening of High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels by Nanometer-Sized Carbides. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 449, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.D. Precipitation Characteristics in a Low-Carbon Vanadium-Titanium-Bearing Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2015, 86, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sesma, L.; Lopez, B.; Lopez, B.; Pereda, B. Effect of Coiling Conditions on the Strengthening Mechanisms of Nb Microalloyed Steels with High Ti Addition Levels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 748, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, P.K.; Sam, S.; Singhai, M.; Hazra, S.S.; Ram, G.D.J.; Bakshi, S.R. Effect of Coiling Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hot-Rolled Ti-Nb Microalloyed Ultra High Strength Steel. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, P.D.; Gibbs, R.K. A Mathematical Model to Predict the Mechanical Properties of Hot Rolled C-Mn and Microalloyed Steels. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M.; Lopez, B. I Improved Model of Kinetics of Strain Induced Precipitation and Microstructure Evolution of Nb Microalloyed Steels during Multipass Rolling. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akben, M.G.; Chandra, T.; Plassiard, P.; Jonas, J.J. Dynamic Precipitation and Solute Hardening in a Titanium Microalloyed Steel Containing Three Levels of Manganese. Acta Metall. 1984, 32, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Jonas, J.J. A Stress Relaxation Method for Following Carbonitride Precipitation in Austenite at Hot Working Temperatures. Metall. Trans. A 1988, 19, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Jonas, J.J. Ti(CN) Precipitation in Microalloyed Austenite during Stress Relaxation. Metall. Trans. A 1988, 19, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, X.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X.; Yong, Q.; Li, Z.; Wen, Y. Strain-induced Precipitation in a Ti Micro-Alloyed HSLA Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 529, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Yang, Z.; Yong, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Weng, Y. Effect of Mn Concentration on the Kinetics of Strain Induced Precipitation in Ti Microalloyed Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 561, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.G.; Kang, K.B.; Park, C.G. Strain-induced Precipitation of NbC in Nb and Nb-Ti Microalloyed HSLA Steels. Scripta Mater. 2002, 46, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaguchi, S.; Hashimoto, T. Computer Model for Prediction of Carbonitride Precipitation during Hot Working in Nb-Ti Bearing HSLA Steels. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.I.; Lopez, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Relationship Between the Austenite Recrystallized Fraction and the Softening Measured from the Interrupted Torsion Test Technique. Scripta Mater. 1999, 40, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, L.; Pereda, B.; Lopez, B. Interaction Between Recovery, Recrystallization and NbC Strain-Induced Precipitation in High-Mn Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 5248–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechet, S.; Beaujard, L. New Reagent for the micrographical demonstration of the austenite grain of hardened or hardened-tempered steels. Rev. Met. 1955, 52, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.O.; Helander, T.; Höglund, L.; Shi, P.F.; Sundman, B. Thermo-Calc and DICTRA, Computational Tools for Materials Science. Calphad 2002, 26, 273–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo-Calc Software. TCFE9 Steels/Fe-Alloys Database; Thermo-Calc Software: Solna, Sweden.
- Hua, M.; Garcia, C.I.; DeArdo, A.J. Multi-phase Precipitates in Interstitial-Free Steels. Scripta Metall. Mater. 1993, 28, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, B.; Lopez, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Increasing the Non-Recrystallization Temperature of Nb Microalloyed Steels by Mo Addition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microalloyed Steels: Processing, Microstructure, Properties and Performance Proceedings, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 16–19 July 2007; pp. 151–159. [Google Scholar]
- Pereda, B.; Aretxabaleta, Z.; Lopez, B. Softening Kinetics in High Al and High Al-Nb-Microalloyed Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañaga-Otegui, A.; Pereda, B.; Jorge-Badiola, D.; Gutierrez, I. Austenite Static Recrystallization Kinetics in Microalloyed, B. Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3150–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llanos, L.; Pereda, B.; Lopez, B.; Rodriguez-Ibabe, J.M. Modelling of Static Recrystallization Behavior of High Manganese Austenitic Steels with Different Alloying Contents. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Palmiere, E.J.; Sellars, C.M. Modelling the Kinetics of Strain Induced Precipitation in Nb Microalloyed Steels. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.T.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Titanium Nitride Precipitation Behaviour in Thin-Slab Cast High-Strength Low-Allow Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 3099–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, R.; Fernandez, A.I.; Lopez, B. Interaction Between Recrystallization and Precipitation during Multipass Rolling in a Low Carbon Niobium Microalloyed Steel. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, C.M. Hot Working and Forming Processes. In Proceedings of the International Conference, Sheffield, UK, 17–20 July 1979; Sellars, C.M., Davies, G.J., Eds.; Metals Society: London, UK, 1980; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Beynon, J.H.; Sellars, C.M. Modelling Microstructure and Its Effects during Multipass Hot Rolling. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, C.M.; Whiteman, J.A. Recrystallization and Grain Growth in Hot Working. Met. Sci. 1979, 13, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Steel | C | Mn | Nb | Ti | P | S | Al | Si | Cr | Ni | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti0Nb0 | 0.058 | 1.82 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.0064 |
| Ti0Nb3 | 0.059 | 1.79 | 0.033 | 0.003 | 0.020 | 0.003 | 0.036 | 0.026 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.0036 |
| Ti5Nb3 | 0.058 | 1.81 | 0.033 | 0.044 | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.012 | 0.019 | 0.006 | 0.0064 |
| Ti10Nb3 | 0.059 | 1.80 | 0.034 | 0.091 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.036 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.006 | 0.0054 |
| Ti15Nb3 | 0.059 | 1.82 | 0.033 | 0.139 | 0.021 | 0.003 | 0.040 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0.0054 |
| Condition | Ti0Nb0 | Ti0Nb3 | Ti5Nb3 | Ti10Nb3 | Ti15Nb3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain size after Reheating (µm) | 230 ± 15 | 241 ± 12 | 163 ± 8 | 258 ± 4 | 193 ± 10 |
| Grain size with Roughing (µm) | 126 ± 4 | 88 ± 4 | 70 ± 2 | 114 ± 4 | 96 ± 3 |
| Steel | (μm) | Tdef (°C) | (s−1) | (μm) | Steel | (μm) | Tdef (°C) | (s−1) | (μm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti0Nb0 | 0.35 | 230 ± 15 | 1100 | 1 | 126 ± 4 | Ti5Nb3 | 0.35 | 163 ± 8 | 1100 | 1 | 70 ± 2 |
| 0.35/0.35 | 126 ± 4 | 1100 | 1 | 62 ± 1 | 0.35 | 163 ± 8 | 1100 | 5 | 64 ± 2 | ||
| 0.35/0.35 | 126 ± 4 | 1050 | 1 | 70 ± 2 | 0.15 | 163 ± 8 | 1150 | 1 | 162 ± 9 | ||
| Ti0Nb3 | 0.35 | 241 ± 12 | 1100 | 1 | 88 ± 4 | 0.35/0.35 | 70 ± 2 | 1100 | 1 | 56 ± 1 | |
| 0.15 | 241 ± 12 | 1100 | 1 | 256 ± 14 | Ti10Nb3 | 0.35 | 258 ± 4 | 1100 | 1 | 114 ± 4 | |
| 0.35/0.35 | 88 ± 4 | 1100 | 1 | 65 ± 2 | 0.35/0.35 | 114 ± 4 | 1100 | 1 | 79 ± 2 | ||
| 0.35/0.35 | 88 ± 4 | 1050 | 1 | 69 ± 2 | Ti15Nb3 | 0.35 | 193 ± 10 | 1100 | 1 | 96 ± 3 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.35/0.35 | 96 ± 3 | 1100 | 1 | 81 ± 2 | |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.35/0.15 | 96 ± 3 | 1100 | 1 | 131 ± 7 |
| Microalloying Element | Ti0Nb3 | Ti5Nb3 | Ti10Nb3 | Ti15Nb3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb(%) | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.034 | 0.032 |
| Ti (%) | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.044 | 0.073 |
| Steel | (μm) | Tdef (°C) | (s−1) | (s) | Steel | (μm) | Tdef (°C) | (s−1) | (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti0Nb0 | 230 ± 15 | 0.35 | 1100 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.0 | Ti10Nb3 | 258 ± 4 | 0.35 | 1100 | 1 | 4.9 | 1.1 |
| 126 ± 4 | 0.35 | 1100 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 114 ± 4 | 0.35 | 1050 | 6.7 | 1.0 | ||||
| 0.15 | 1100 | 4.6 | 2.0 | 0.35 | 1100 | 3.0 | 1.3 | ||||||
| 0.35 | 1050 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 1100 | 18.6 | 1.5 | ||||||
| 0.35 | 950 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1100 | 44.3 | 1.5 | ||||||
| Ti0Nb3 | 241 ± 12 | 0.35 | 1100 | 1 | 3.4 | 1.1 | Ti15Nb3 | 193 ± 10 | 0.35 | 1100 | 1 | 5.7 | 1.0 |
| 0.15 | 1100 | 23.1 | 0.9 | 96 ± 3 | 0.35 | 1050 | 7.9 | 1.0 | |||||
| 88 ± 4 | 0.35 | 1050 | 4.5 | 1.0 | 0.35 | 1100 | 3.1 | 1.4 | |||||
| 0.35 | 1100 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 0.15 | 1100 | 22.5 | 1.5 | ||||||
| 0.15 | 1100 | 11 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 1100 | 57.3 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 0.1 | 1100 | 14 | 2.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Ti5Nb3 | 163 ± 8 | 0.35 | 1100 | 1 | 2.4 | 1.2 | - | - | - | - | - | -- | |
| 0.35 | 1100 | 5 | 2.2 | 0.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 0.35 | 1150 | 1 | 1.6 | 1.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 0.15 | 1150 | 17.1 | 1.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| 70 ± 2 | 0.35 | 950 | 34.1 | 0.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 0.35 | 1050 | 3.5 | 1.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| 0.35 | 1100 | 1.2 | 1.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| 0.15 | 1100 | 10.3 | 1.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Sesma, L.; López, B.; Pereda, B. Effect of High Ti Contents on Austenite Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation in Low Carbon Nb Microalloyed Steels. Metals 2020, 10, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020165
García-Sesma L, López B, Pereda B. Effect of High Ti Contents on Austenite Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation in Low Carbon Nb Microalloyed Steels. Metals. 2020; 10(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Sesma, Leire, Beatriz López, and Beatriz Pereda. 2020. "Effect of High Ti Contents on Austenite Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation in Low Carbon Nb Microalloyed Steels" Metals 10, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020165
APA StyleGarcía-Sesma, L., López, B., & Pereda, B. (2020). Effect of High Ti Contents on Austenite Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation in Low Carbon Nb Microalloyed Steels. Metals, 10(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020165






