Exploring Transcriptional Regulation of Beta Cell SASP by Brd4-Associated Proteins and Cell Cycle Control Protein p21
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
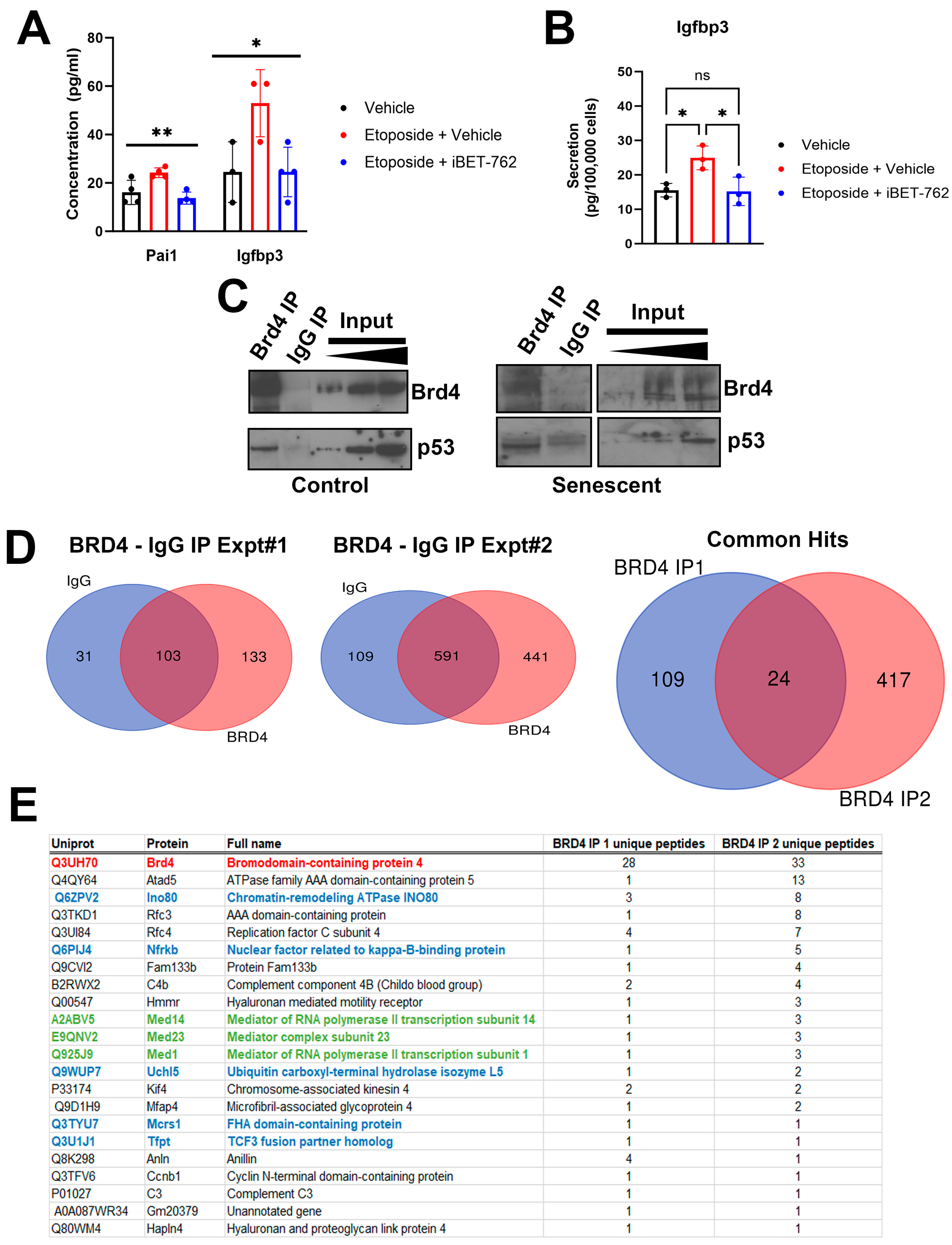
2.1. Identification of Brd4-Associated Proteins in the NIT-1 Beta Cell Line Senescence Model
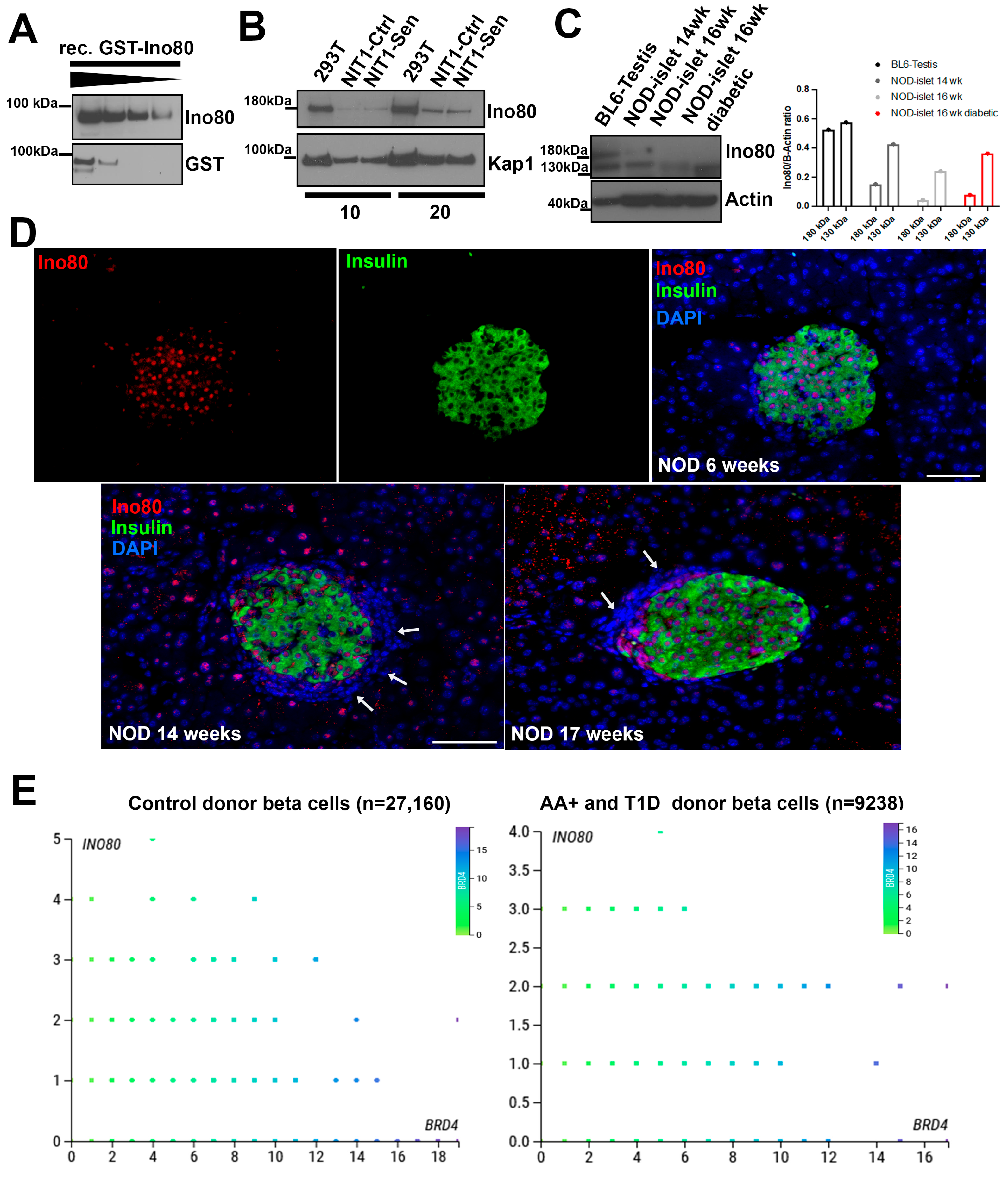
2.2. Characterization of Ino80 Expression in the Context of T1D
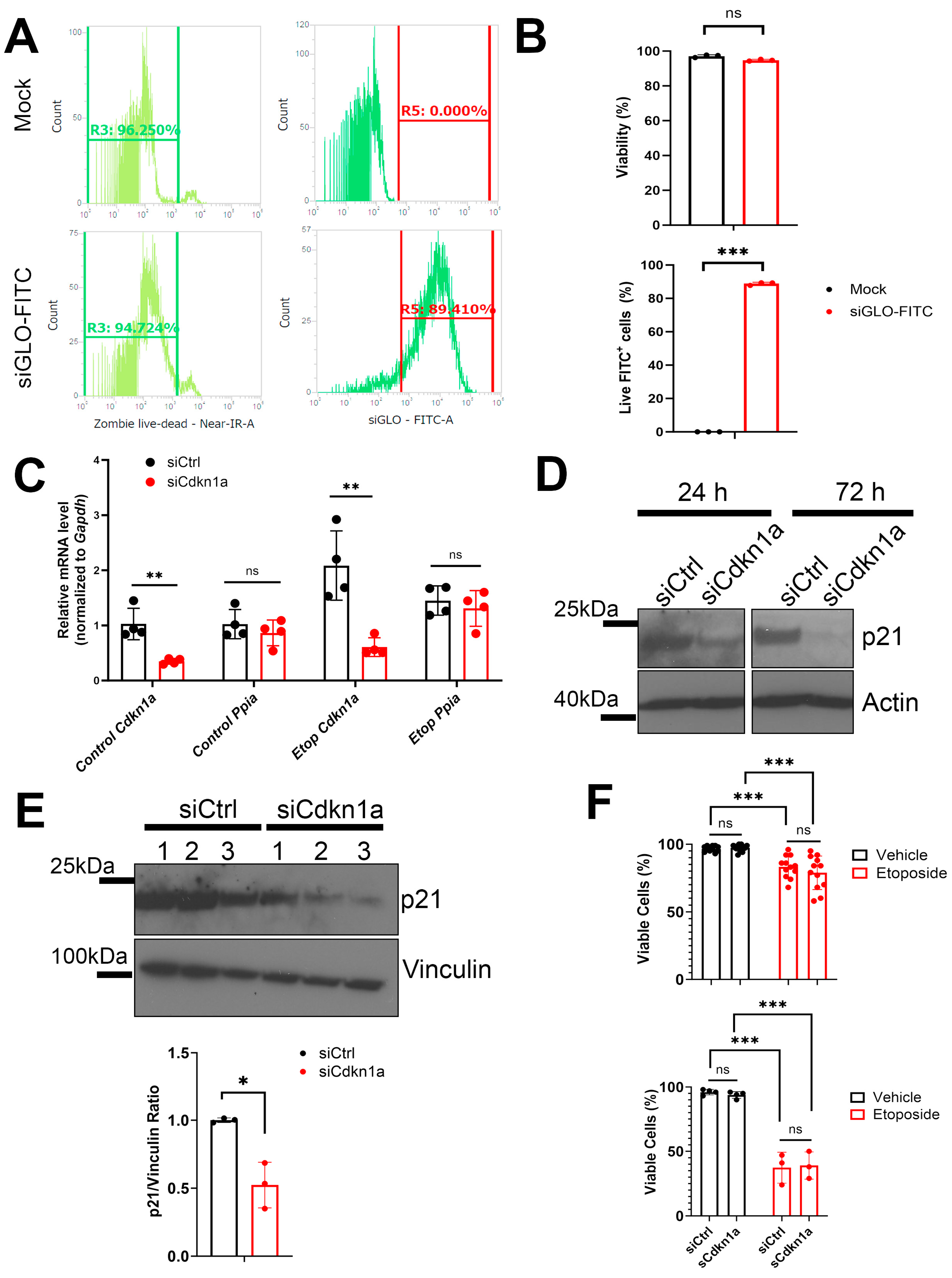
2.3. RNAi Knockdown to Investigate the Role of Ino80 and p21 during SASP in NIT-1 Cells
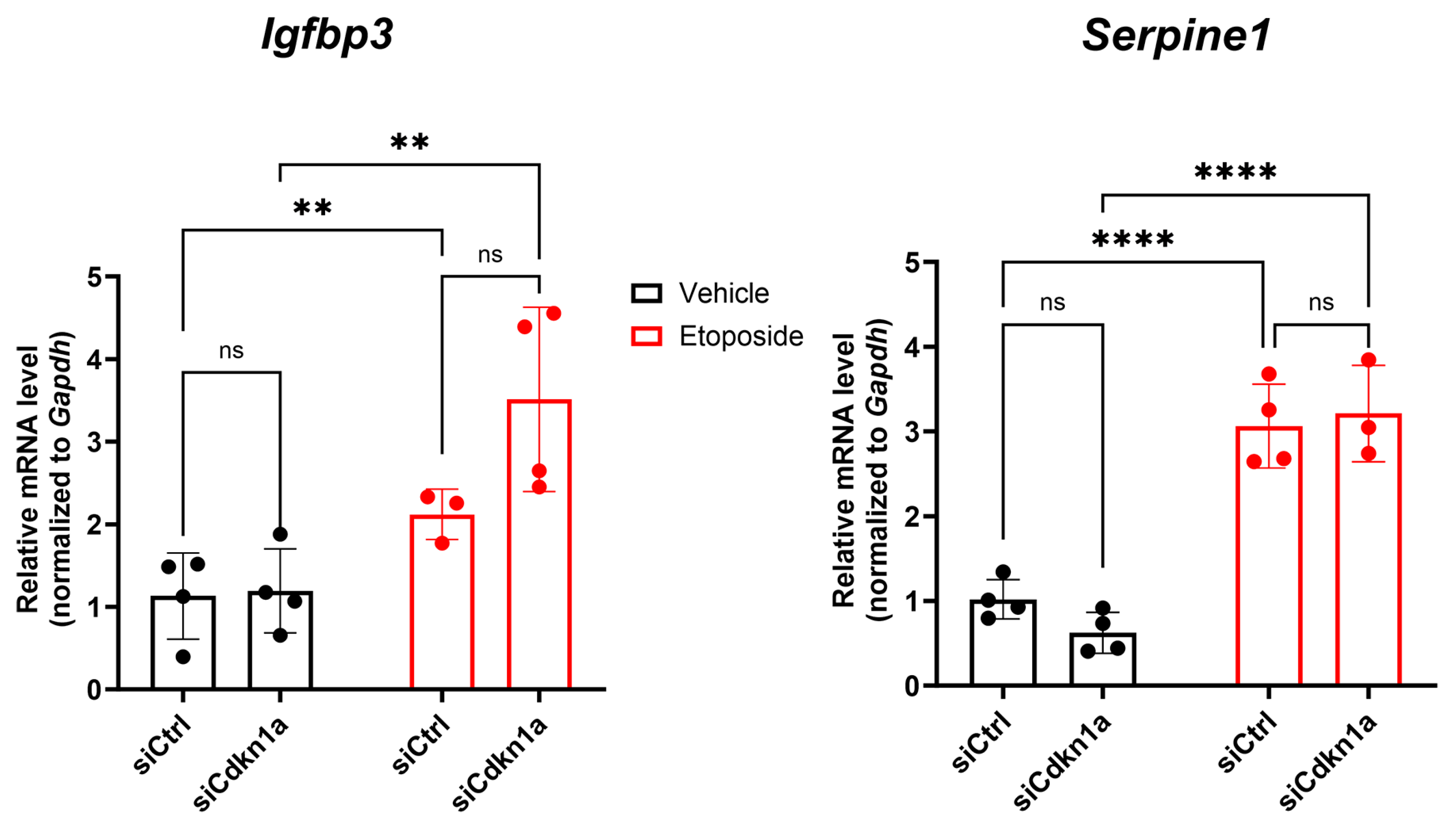
2.4. Effects of p21 Knockdown on SASP Gene Expression in NIT-1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture and RNAi
5.2. Immunopreciptation and Mass Spectrometry
5.3. Western Blotting
5.4. Immunohistochemistry
5.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR)
5.6. Single Cell RNA-Seq Data Analysis
5.7. Flow Cytometry
5.8. Luminex Assays
5.9. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lawrence, J.M.; Divers, J.; Isom, S.; Saydah, S.; Imperatore, G.; Pihoker, C.; Marcovina, S.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Hamman, R.F.; Dolan, L.; et al. Trends in Prevalence of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents in the US, 2001–2017. JAMA 2021, 326, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vived, C.; Lee-Papastavros, A.; Aparecida da Silva Pereira, J.; Yi, P.; MacDonald, T.L. Beta cell stress and endocrine function during T1D: What’s next to discover? Endocrinology 2023, 165, bqad162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, B.; Michie, S.A.; Rubins, K.H.; Schreriber, R.D.; McDevitt, H.O. Interferon-α initiates type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12439–12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, F.; Yermalovich, A.; Nguyen, T.; Hummasti, S.; Fu, W.; Eizirik, D.L.; Mathis, D.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Restoration of the unfolded protein response in pancreatic β cells protects mice against type 1. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 211ra156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalle, F.; Grimes, T.; Xu, G.; Patel, A.J.; Grayson, T.B.; Thielen, L.A.; Li, P.; Shalev, A. Verapamil and beta cell function in adults with recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forlenza, G.P.; McVean, J.; Beck, R.W.; Bauza, C.; Bailey, R.; Buckingham, B.; Dimeglio, L.A.; Sherr, J.L.; Clements, M.; Neyman, A.; et al. Effect of Verapamil on Pancreatic Beta Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waibel, M.; Wentworth, J.M.; So, M.; Couper, J.J.; Cameron, F.J.; MacIsaac, R.J.; Gorelik, A.; Litwak, S.; Sanz-Villanueva, L.; Trivedi, P.; et al. Baricitinib and β-Cell Function in Patients with New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.J.; Shah, A.; Ntranos, V.; Van Gool, F.; Atkinson, M.; Bhushan, A. Targeted Elimination of Senescent Beta Cells Prevents Type 1 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, R.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Baker, D.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence in ageing: From mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Sharma, A.; Stolzing, A.; Stolzing, A.; Desprez, P.Y.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J.; Campisi, J. Role of immune cells in the removal of deleterious senescent cells. Immun. Ageing 2020, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.J.; Shah, A.; Apostolopolou, H.; Bhushan, A. BET proteins are required for transcriptional activation of the senescent islet cell secretome in type 1 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, E.; Petosa, C.; McKenna, C.E. Bromodomains: Structure, function and pharmacology of inhibition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 106, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, N.; Banito, A.; Roe, J.-S.; Alonso-Curbelo, D.; Camiolo, M.; Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Huang, C.-H.; Aksoy, O.; Bolden, J.E.; Chen, C.-C.; et al. BRD4 Connects Enhancer Remodeling to Senescence Immune Surveillance. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirguet, O.; Gosmini, R.; Toum, J.J.; Clement, C.A.; Barnathan, M.M.; Brusq, J.-M.M.; Mordaunt, J.E.; Grimes, R.M.; Crowe, M.; Pineau, O.; et al. Discovery of epigenetic regulator i-bet762: Lead optimization to afford a clinical candidate inhibitor of the bet bromodomains. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7501–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Farache, J.; Clardy, S.M.; Hattori, K.; Mander, P.; Lee, K.; Rioja, I.; Weissleder, R.; Prinjha, R.K.; Benoist, C.; et al. Epigenetic modulation of type-1 diabetes via a dual effect on pancreatic macrophages and Beta cells. Elife 2014, 3, e04631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brawerman, G.; Pipella, J.; Thompson, P.J. DNA damage to β cells in culture recapitulates features of senescent β cells that accumulate in Type 1 Diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2022, 62, 101524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, K.; Gaskins, H.R.; Leiter, E.H. NIT-1, a pancreatic β-cell line established from a transgenic NOD/Lt mouse. Diabetes 1991, 40, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawerman, G.; Ntranos, V.; Thompson, P.J. Alpha cell dysfunction in type 1 diabetes is independent of a senescence program. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 932516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Lee, A.Y.; Lai, H.T.; Zhang, H.; Chiang, C.M. Phospho switch triggers brd4 chromatin binding and activator recruitment for gene-specific targeting. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, S.R.; Mohni, K.N.; Luzwick, J.W.; Dungrawala, H.; Cortez, D. Functional Analysis of the Replication Fork Proteome Identifies BET Proteins as PCNA Regulators. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3497–3509.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.P.; Picaud, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Hou, H.; Savitsky, P.; Uusküla-Reimand, L.; Gupta, G.D.; Abdouni, H.; Lin, Z.Y.; Tucholska, M.; et al. Interactome Rewiring Following Pharmacological Targeting of BET Bromodomains. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 621–638.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, J.; Gasser, S.M.; Papamichos-Chronakis, M. The INO80 remodeller in transcription, replication and repair. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Wan, D.; Zhou, R.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, L.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; et al. The biological function of metazoan-specific subunit nuclear factor related to kappaB binding protein of INO80 complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, S.; Wu, H.-J.; Ge, J.Y.; Zeid, R.; Harris, I.S.; Jovanović, B.; Murphy, K.; Wang, B.; Qiu, X.; Endress, J.E.; et al. Synthetic Lethal and Resistance Interactions with BET Bromodomain Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1096–1113.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Bennett, B.D.; He, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, C.; Han, L.; Diao, L.; Li, P.; et al. INO80 governs superenhancer-mediated oncogenic transcription and tumor growth in melanoma. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serber, D.W.; Runge, J.S.; Menon, D.U.; Magnuson, T. The mouse INO80 chromatin-remodeling complex is an essential meiotic factor for spermatogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, K.H.; Powers, A.C.; Naji, A.; Atkinson, M.A. NIH Initiative to Improve Understanding of the Pancreas, Islet, and Autoimmunity in Type 1 Diabetes: The Human Pancreas Analysis Program (HPAP). Diabetes 2019, 68, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturmlechner, I.; Zhang, C.; Sine, C.C.; van Deursen, E.-J.J.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Hamada, N.; Grasic, J.; Friedman, D.; Stutchman, J.T.; Can, I.; et al. p21 produces a bioactive secretome that places stressed cells under immunosurveillance. Science 2021, 374, eabb3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zio, D.; Cianfanelli, V.; Cecconi, F. New insights into the link between DNA damage and apoptosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticli, G.; Cazzalini, O.; Stivala, L.A.; Prosperi, E. Revisiting the Function of p21CDKN1A in DNA Repair: The Influence of Protein Interactions and Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Sahin, G.S.; Chen, C.; Hatzoglou, M.; Eizirik, D.L.; Engin, F. Stress-induced b cell early senescence confers protection against type 1 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 2200–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppe, J.P.; Rodier, F.; Patil, C.K.; Freund, A.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Tumor suppressor and aging biomarker p16 INK4a induces cellular senescence without the associated inflammatory secretory phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36396–36403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ruiz, P.D.; McKimpson, W.M.; Novikov, L.; Kitsis, R.N.; Gamble, M.J. MacroH2A1 and ATM Play Opposing Roles in Paracrine Senescence and the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, F.; Coppé, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Hoeijmakers, W.A.M.; Muñoz, D.P.; Raza, S.R.; Freund, A.; Campeau, E.; Davalos, A.R.; Campisi, J. Persistent DNA damage signalling triggers senescence-associated inflammatory cytokine secretion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Gower, A.C.; Ding, H.; Giorgadze, N.; Palmer, A.K.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lenburg, M.; et al. The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: From transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, V.S.Y.; Devaraj, S.; Koh, T.; Ke, G.; Crasta, K.C.; Ali, Y. Increased double strand breaks in diabetic β-cells with a p21 response that limits apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettersten, H.I.; Hwang, S.H.; Li, C.; Shiu, E.Y.; Wecksler, A.T.; Hammock, B.D.; Weiss, R.H. A novel p21 attenuator which is structurally related to sorafenib. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.J.; Dulberg, V.; Moon, K.; Foster, L.J.; Chen, C.; Karimi, M.M.; Lorincz, M.C. hnRNP K Coordinates Transcriptional Silencing by SETDB1 in Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, S.N.; Naji, A.; Atkinson, M.A.; Powers, A.C.; Kaestner, K.H. Understanding islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes through multidimensional pancreatic phenotyping: The Human Pancreas Analysis Program. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manji, J.; Pipella, J.; Brawerman, G.; Thompson, P.J. Exploring Transcriptional Regulation of Beta Cell SASP by Brd4-Associated Proteins and Cell Cycle Control Protein p21. Epigenomes 2024, 8, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes8010010
Manji J, Pipella J, Brawerman G, Thompson PJ. Exploring Transcriptional Regulation of Beta Cell SASP by Brd4-Associated Proteins and Cell Cycle Control Protein p21. Epigenomes. 2024; 8(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes8010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleManji, Jasmine, Jasmine Pipella, Gabriel Brawerman, and Peter J. Thompson. 2024. "Exploring Transcriptional Regulation of Beta Cell SASP by Brd4-Associated Proteins and Cell Cycle Control Protein p21" Epigenomes 8, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes8010010
APA StyleManji, J., Pipella, J., Brawerman, G., & Thompson, P. J. (2024). Exploring Transcriptional Regulation of Beta Cell SASP by Brd4-Associated Proteins and Cell Cycle Control Protein p21. Epigenomes, 8(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes8010010





