Abstract
Chitin is a vital part of the insect exoskeleton and peritrophic membrane, synthesized by chitin synthase (CHS) enzymes. Chitin synthase 1 (CHS1) is a crucial enzyme in the final step of chitin biosynthetic pathway and consequently plays essential role towards insect growth and molting. RNA interference (RNAi) is an agent that could be used as an extremely target-specific and ecologically innocuous tactic to control different insect pests associated with economically important crops. The sole purpose of the current study is to use CHS1 as the key target gene against the cotton-melon aphid, Aphis gossypii, via oral feeding on artificial diets mixed with dsRNA-CHS1. Results revealed that the expression level of CHS1 gene significantly decreased after the oral delivery of dsRNA-CHS1. The knockdown of CHS1 gene caused up to 43%, 47%, and 59% mortality in third-instar nymph after feeding of dsCHS1 for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively, as compared to the control. Consistent with this, significantly lower longevity (approximately 38%) and fecundity (approximately 48%) were also found in adult stage of cotton-melon aphids that were fed with dsCHS1 for 72 h at nymphal stage. The qRT-PCR analysis of gene expression demonstrated that the increased mortality rates and lowered longevity and fecundity of A. gossypii were attributed to the downregulation of CHS1 gene via oral-delivery-mediated RNAi. The results of current study confirm that CHS1 could be an appropriate candidate target gene for the RNAi-based control of cotton-melon aphids.
1. Introduction
The cotton-melon aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) is a sucking and polyphagous insect pest infesting numerous species of plants worldwide, particularly Cucurbitaceae (melon, marrow, zucchini, watermelon) [1,2]. The direct damages of this pest are caused by curling and distorting the fresh leaves and twigs through direct feeding [3]. The indirect damages of A. gossypii are caused by transmitting more than 100 plant viruses, especially cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) [2], and by releasing a sugar-rich and sticky liquid material, i.e., honeydew, that also favors the development of fungus in the form of black sooty mold [4]. This pest act as a vector for transmitting 76 different viral diseases in more than 900 host plant species [5]. The application of chemical insecticides is considered crucial for the control of A. gossypii [6,7]. However, the frequent use of chemical insecticides leads towards resistance and hormesis effects resulting in significant control failures of insect pests [8,9,10], as well as potential multiple side effects on beneficial arthropods [11]. Resistance against synthetic chemical insecticides such as organophosphates, carbamates, pyrethroids, and neonicotinoids have been reported in A. gossypii throughout the world [12,13]. Aphis gossypii also showed resistance against imidacloprid, clothianidin, acetamiprid, thiacloprid, and thiamethoxam [13,14].
RNA interference (RNAi), a mechanism of post-transcriptional gene silencing that enables the downregulation of gene expression by artificial RNA molecules [15,16], was initially exposed in Caenorhabtidis elegans by Fire et al. [17]. In the last two decades, RNAi has been established as a molecular tool to silence key gene transcripts in many of insects from orders such as Coleoptera, Hemiptera, Diptera, Hymenoptera, and Lepidoptera [18,19,20,21,22]. Owing to its specificity, RNAi is also used as a new strategy for the control of a large number of pest species [23]. The selection of target gene and delivery method is crucial for the successful RNAi-based pest management [24]. The target gene for RNAi should be disastrous for the pest and harmless for the non-target insects and human beings [25]. The direct injection of dsRNA into insect body cavity and oral delivery techniques (such as droplet feeding and mixing with simulated diet) have been successfully used in several insect pests [21,26,27,28,29]. However, oral techniques minimize the side effects of microinjections and thus may be an efficacious method for RNAi-based control of A. gossypii [30,31].
Chitin is a major constituent of insect exoskeleton/cuticle and peritonea membranes, having a key part in the growth and molting process of insects [32,33]. The balance between the disintegration and formation of new chitin is essential for molting process and growth in insects, which are synchronized by different enzymes [34]. Chitin synthase (UDP-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine: chitin 4-β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase, EC 2.4.1.16) is a transmembrane protein, having major role in chitin synthesis [32,35]. Chitin synthase enzymes are encoded by two genes, i.e., Chitin synthase 1 (CHS1) and chitin synthase 2 (CHS2) [34]. CHS1 is expressed in the epidermal cells encoding enzymes that are essential for the catalysis of chitin production in cuticle [36,37], while CHS2 is expressed in the peritrophic membrane regulating enzymes for chitin production in insect midgut [38]. Several studies reported that CHS1 gene is crucial for chitin synthesis in aphid molting [39,40,41]. However, due to lacking peritrophic membrane, CHS2 was not existent in some insects [40,41,42]. Thus, for the suppression of chitin biosynthesis, CHS1 is the key candidate gene for RNAi-based insect control.
In the current study, we used an artificial diet for the delivery of dsRNA to knockdown CHS1 gene in cotton-melon aphid, A. gossypii. Moreover, the aphid mortality, longevity, and fecundity were investigated after feeding on dsRNA-CHS1. Results of the current study suggest that RNAi-mediated silencing of CHS1 gene could be a promising novel bio-pesticide for the long-term control strategy against cotton-melon aphid.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Culture
Developing cotton-melon aphid (A. gossypii) individuals were collected from Weifang District, Shandong Province, China. A colony of A. gossypii was established in the laboratory and was maintained on insecticide-free cucumber plants under standard laboratory conditions (25 ± 1 °C; 75% RH; 16:8 L:D) at China Agricultural University.
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
Total RNA was extracted from different instars (first, second, third, and fourth) of nymphs and adults of A. gossypii using TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), adopting the manufacturer’s instructions. Thirty surviving individuals from each group were pooled as one biological replicate. The RNA purity and concentrations were analyzed with a NAS-99 spectrophotometer (ACTGene). The cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg total RNA using the PrimeScript® RT Reagent Kit with the gDNA Eraser (Takara, Dalian, China), following the instructions given by the manufacturer.
2.3. Preparation of Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA)
CHS1 dsRNA (498 bp) was synthesized by Transcript Aid T7 High Yield Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using cDNA obtained from third-instar nymphs following the manufacturer’s recommended procedure. The T7 RNA polymerase promoter sequence 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG-3′ was added in front of the forward and reverse primers as required for subsequent dsRNA synthesis (Table 1). PCR was performed at 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 56 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s and an additional final polymerization step of 72 °C for 10 min. cDNA and single-stranded RNA were detached from the transcription reaction by DNase and RNase treatments. The dsRNA was purified by using phenol (pH 4.7) chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation method and eluted in diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC)-treated nuclease-free water. A 714 bp fragment of green fluorescent protein (GFP) dsRNA as control was amplified using same conditions as discussed above with primers shown in Table 1. The dsRNA was quantified using a NAS-99 spectrophotometer (ACTGene, Piscataway, NJ, USA), and the integrity was analyzed by gel electrophoresis (1% agarose). DEPC water was used as the negative control.

Table 1.
The specific primers used in dsRNA synthesis and qRT-PCR.
2.4. Dietary Delivery of the Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA)
The dsCHS1 (dsRNA of CHS1), dsGFP (dsRNA of GFP), or DEPC water was mixed in the synthetic feeding diet (0.5 mol/L sterile sucrose solution) at an ultimate concentration of 100 ng/μL and fed to the third-instar nymphs. For the in vitro feeding assays, sterilized glass tubes (3 cm in length and 2 cm in diameter) that open at both ends were used [43,44]. One end of each glass tube was wrapped with two coatings of parafilm membrane that contained a mixture of synthetic diet sandwiched between the two layers of parafilm. Fifty apterous adult aphids were placed into the tube with a fine brush. The tube was impenetrable with a piece of Chinese art paper (Xuan paper). The glass tubes were kept under standard laboratory conditions (25 ± 1 °C; 75% RH; 16:8 L:D). Mortality of cotton-melon aphids was recorded at 12, 24, 48, and 72 h post-feeding. All the experiments were repeated three times.
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was accomplished on the Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA) using SYBR® Premix Ex Taq™ (Tli RNaseH Plus) (Takara, Dalian, China) to analyze the expression level of CHS1 either from N1 to N4 and adults, as well as the nymphs after 12, 24, 48, and 72 h after treatment with RNAi. Primers for the CHS1 were designed based on the conserved sequence of soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura (Hemiptera: Aphididae) CH1 gene (GenBank Accession No. JQ246352.1). All primers were synthesized using PRIMER 3.0 (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3-0.4.0/) (Table 1). The reaction of qRT-PCR was performed in a 20 μL volume of a mixture, which contained 10 μL of SYBR® Premix Ex Taq, 7.8 μL ddH2O, 0.4 μL of ROX, 0.4 μL of each primer, and 1 μL of the cDNA. The qRT-PCR conditions were 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 34 s, and then one dissociation step cycle of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 1 min, 95 °C for 30 s, and 60 °C for 15 s. The qRT-PCR analysis was repeated in triplicate. The standard curve was established with serial dilutions of cDNA (1, 1/10, 1/100, 1/1000, 1/10,000, and 1/100,000) to check the amplification efficiencies and cycle threshold (Ct). Quantification of gene transcriptions was conducted using the 2−∆∆Ct method [45]. EF1α (GenBank Accession No. EU019874.1) and β-ACT (GenBank Accession No. KF018928.1) were used as the internal control [46].
2.6. Longevity and Fecundity Analysis
Newly emerged apterous adults were collected after constant feeding of dsRNA for 72 h at third instar nymphal stage. Each aphid was shifted to a fresh cucumber seedling. Thirty individuals per experimental group (DEPC-water, dsGFP, and dsCHS1) were used and each aphid was considered as a single replicate [6,8]. The longevity and fecundity (number of newly-born nymphs/individual aphid) were recorded daily until the aphids died. The neonate nymphs were detached from the seedlings after counting. Insecticide-free cucumber seedlings were replaced on a weekly basis throughout the experiment.
2.7. Data Analysis
The data related to longevity, fecundity, and gene expression of A. gossypii were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s post hoc test (IBM, SPSS Statistics, version 22). p < 0.05 was supposed to be significant for all tests.
3. Results
3.1. Expression of CHS1 Gene among Growth Stages of A. gossypii
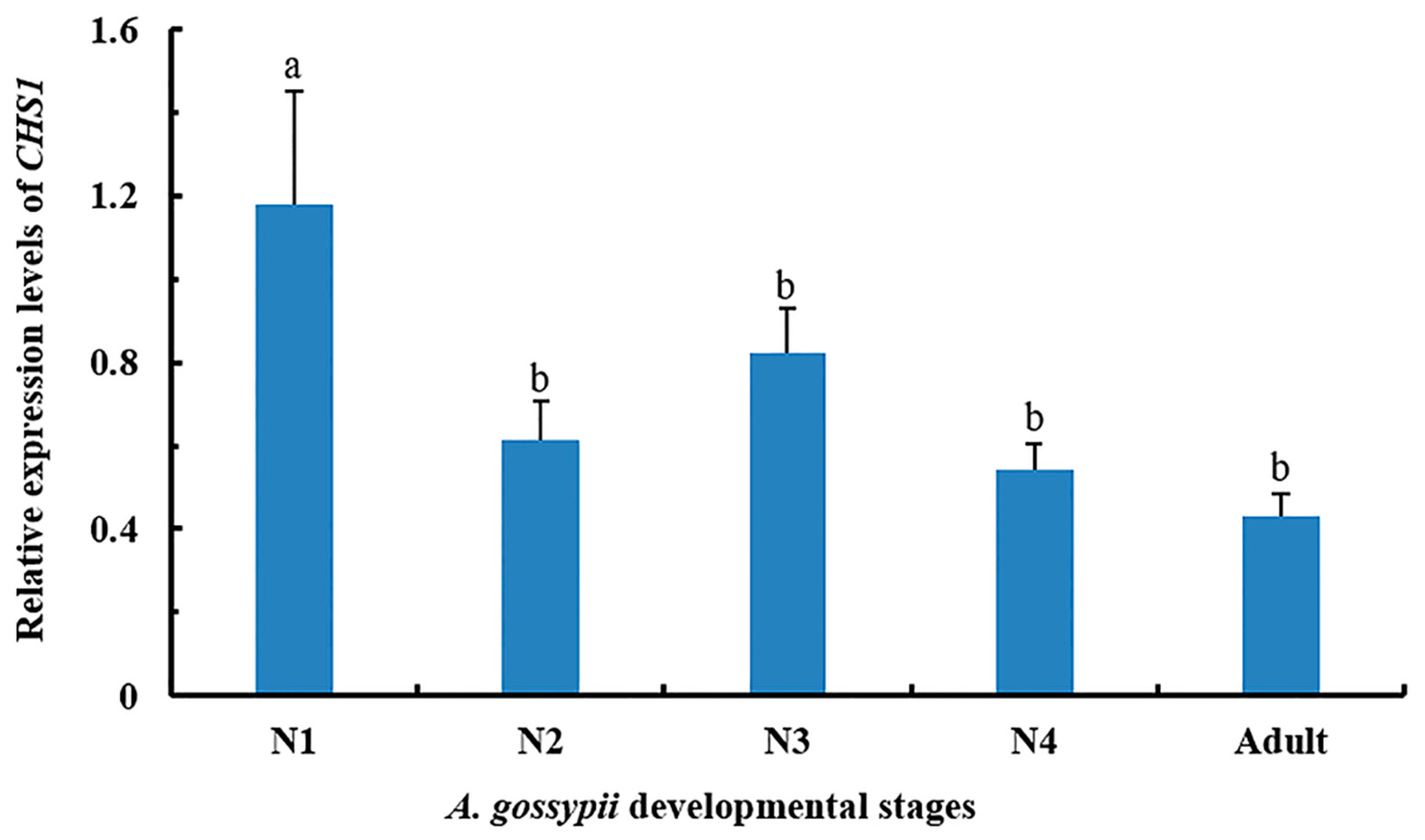
The relative expression level of CHS1 gene among different growing stages of A. gossypii was assessed by qRT-PCR. The mRNA transcriptions were detected in all life stages. However, the expression of CHS1 gene was highest during the first instar of nymphal stage compared to the second, third or fourth instar as well as adult growth stage (Figure 1). No significant differences were observed in the expression level of CHS1 gene in the second instar, third instar, fourth instar, and adult stage aphids.
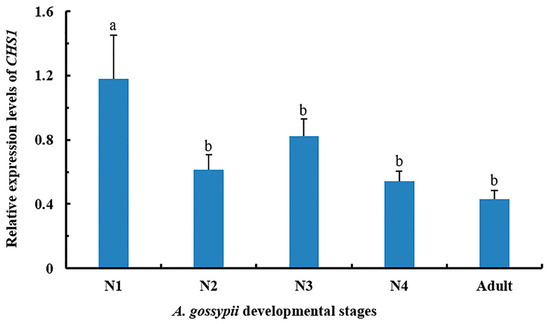
Figure 1.
Relative expression pattern of CHS1 gene at different developmental stages of A. gossypii analyzed by qRT-PCR. The expression level is expressed as the mean (±SE) of the three biological replicates, and thirty insects were used per pooled RNA sample. Letters above the bars represent significant differences at p < 0.05 level (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). EF1α and β-actin are used as the internal control. N1: first instar; N2: second instar; N3: third instar; N4: fourth instar.
3.2. Functional Analysis of CHS1 by RNAi
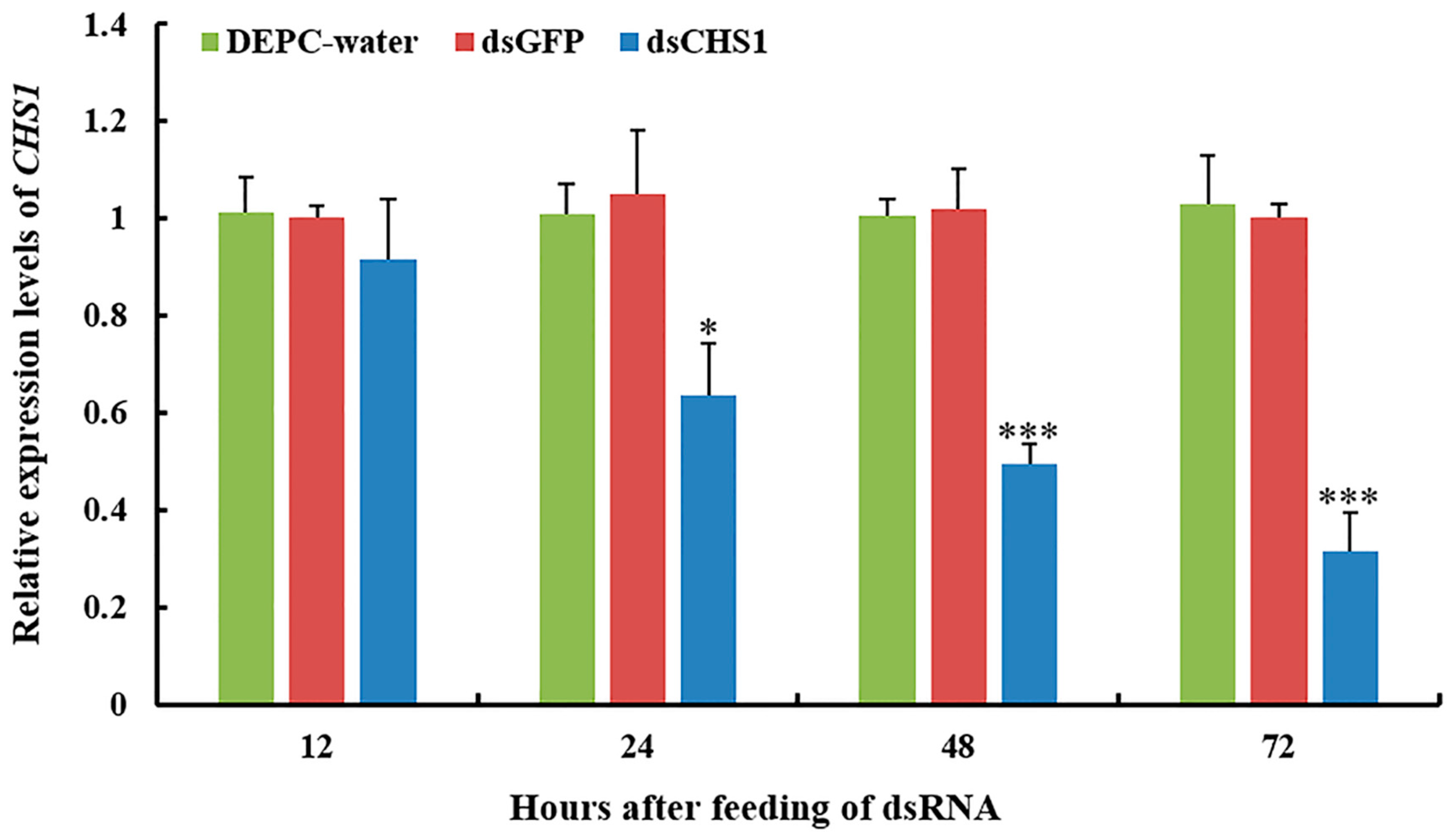
Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to scrutinize the silencing efficiency of dsCHS1 in aphids. We investigated the expression level of the CHS1 gene after continuous oral delivery of dsRNA to the third-instar nymph of A. gossypii for 12, 24, 48, and 72 h (Figure 2). RT-qPCR analysis indicated significantly (p < 0.05) reduced transcript level of CHS1 mRNA after the oral uptake of dsRNA-CHS1 for 24 h, as compared with the DEPC-water and dsGFP control treatments. After 48 and 72 h of ingestion, dsRNA-CHS1 caused very significant (p < 0.001) reduction in CHS1 mRNA abundance, indicating a substantial gene silencing (Figure 2). However, no significant differences were observed for CHS1 mRNA transcript level at 12 h post-feeding of dsRNA-CHS1, as compared with positive and negative control treatments.
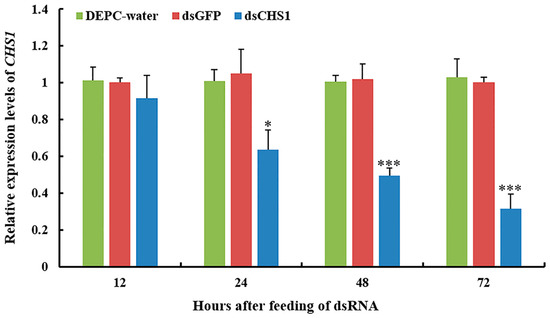
Figure 2.
Gene silencing of CHS1 in A. gossypii fed an artificial diet with or without dsRNA-CHS1. Relative abundance of CHS1 gene transcripts were determined as mean (±SE) of the three biological replicates, and thirty insects were used per pooled RNA sample with control as the calibrator, i.e., cDNA from non-RNAi aphids (only fed on artificial diet with DEPC-water and dsGFP). EF1α and β-actin are used as the internal control. Treatments were compared using one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s HSD test, p < 0.05). * and *** represent p < 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively.
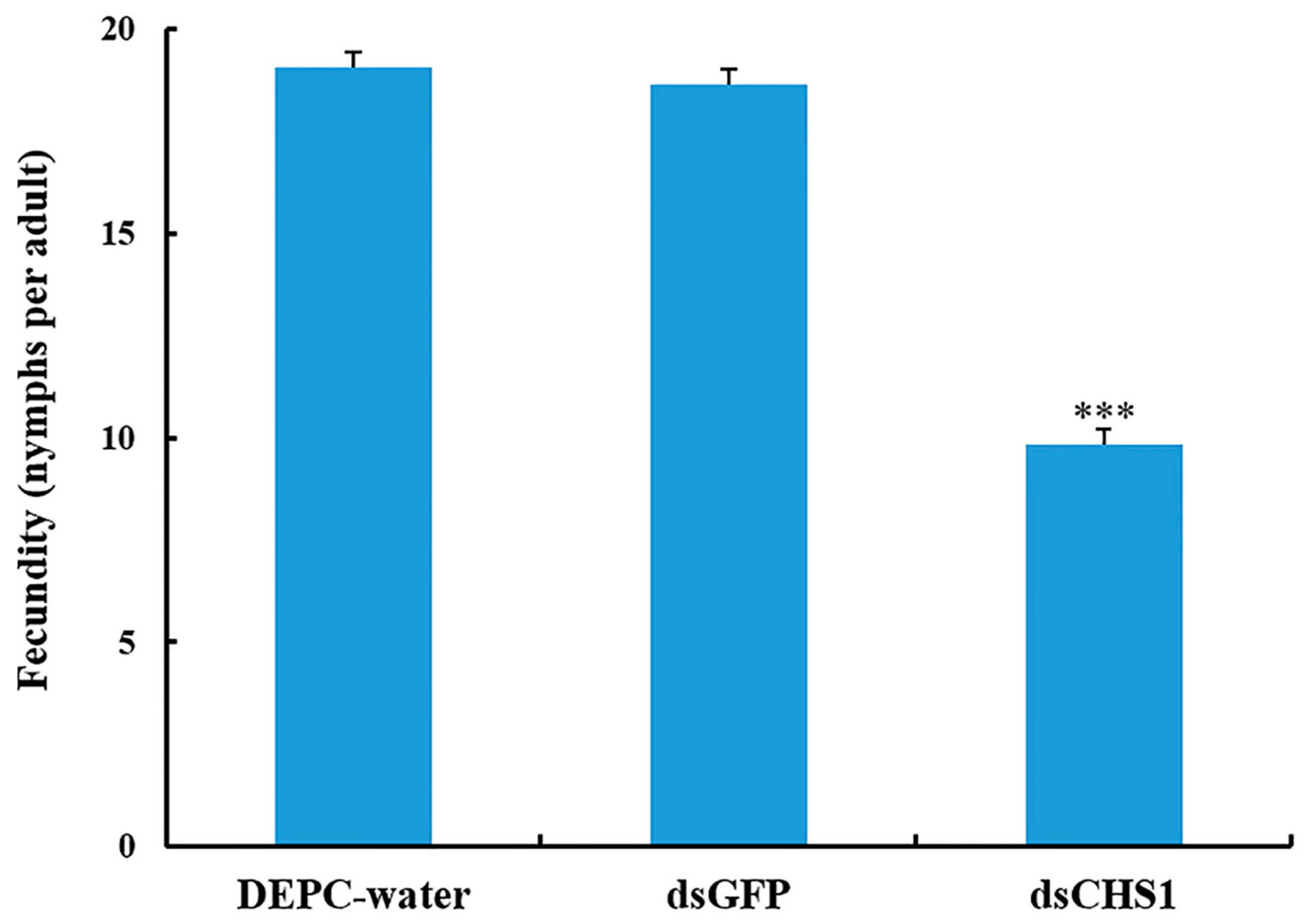
3.3. Effects of dsRNA-CHS1 on Aphid Mortality, Longevity, and Fecundity
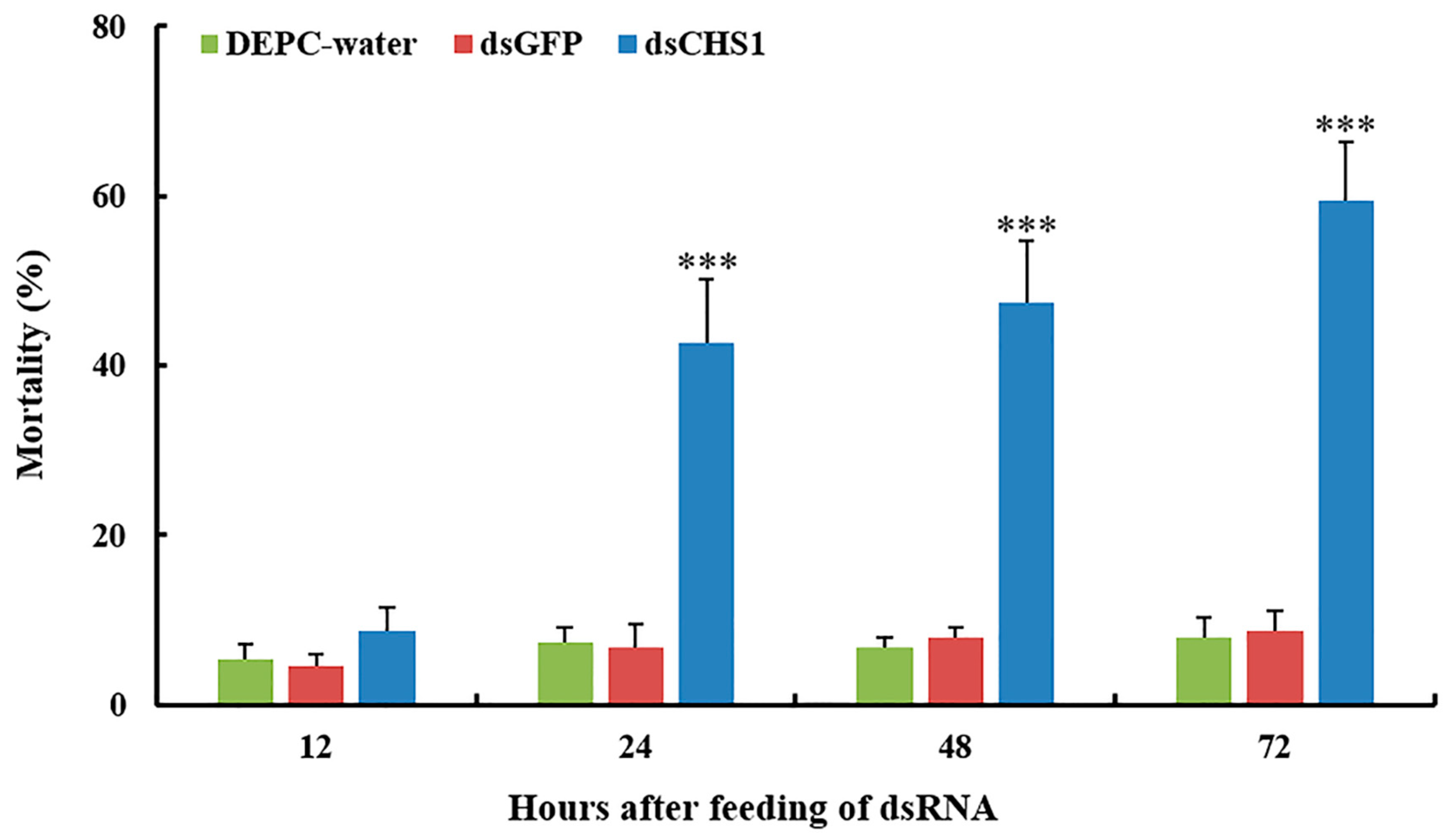
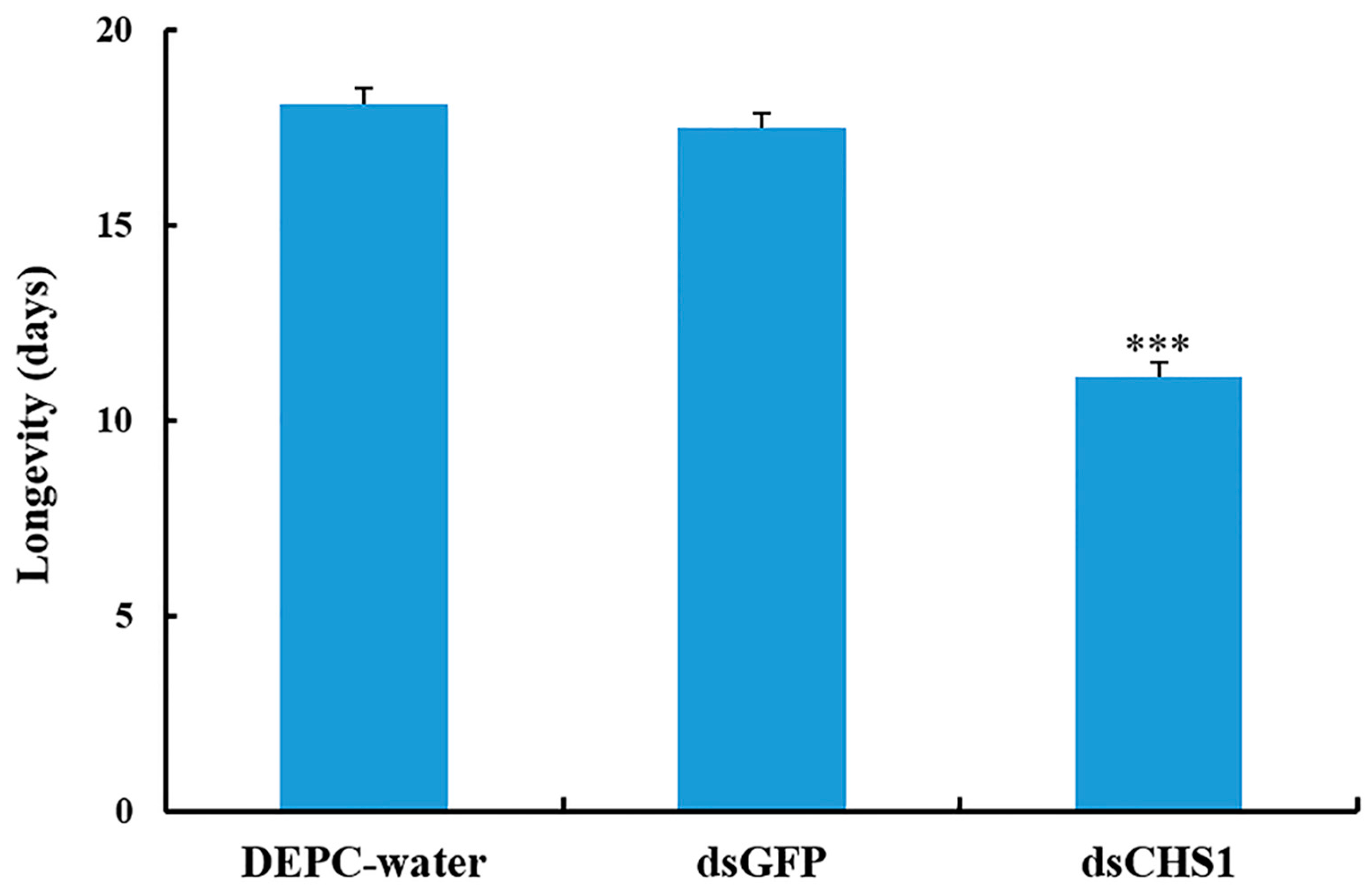
No considerable aphid mortality was seen after feeding of dsCHS1, dsGFP, and DEPC-water for 12 h. However, a significantly increased mortality (p < 0.005) of A. gossypii was observed at 24, 48, and 72 h post-feeding of dsRNA-CHS1, as compared with the positive and negative control treatments (Figure 3). The average mortality of A. gossypii reached 43%, 47%, and 59% after continuous feeding of dsCHS1 for 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. The mortality of aphids treated with DEPC-water at 24, 48, and 72 h was 7%, 7%, and 8%, respectively, while the mortality for aphids fed on dsGFP was 7%, 8%, and 9% at 24, 48, and 72 h post-feeding, respectively (Figure 3). The continuous feeding of dsCHS1 for 72 h significantly (p < 0.005) reduced the longevity of A. gossypii (approximately 38%), compared with the dsGFP and DEPC-water treated groups (Figure 4). Similarly, a significant (p < 0.005) decline was noticed in the fecundity of surviving A. gossypii (approximately 48%) prior to dietary delivery of dsCHS1 for 72 h, as compared to control treatments (Figure 5).
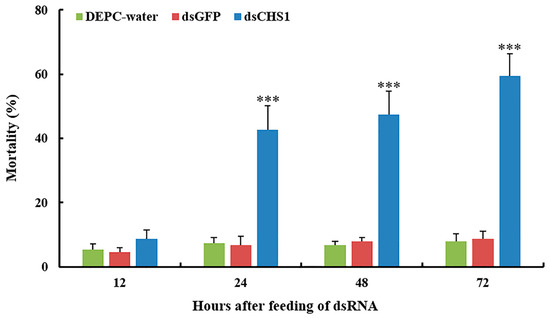
Figure 3.
Mortality rates (%) of A. gossypii fed with artificial diet containing DEPC-water, dsGFP, and dsCHS1 at third instar nymphal stage over time. The values are presented as the mean (±SE) of three replications (50 insects were used per replicate). Treatments were compared using one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s HSD test, p < 0.05). *** represents p < 0.001.
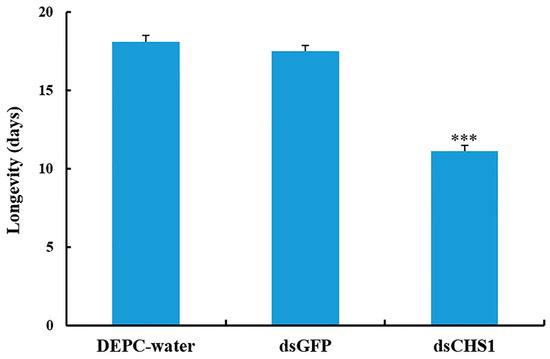
Figure 4.
Impact of CHS1 gene silencing on adult longevity of A. gossypii, previously fed artificial diets containing DEPC-water, dsGFP, and dsCHS1 at their nymphal stage (third instar). The values are presented as the mean (±SE). Thirty individuals per experimental group (DEPC-water, dsGFP, and dsCHS1) were used, and each aphid was considered as a single replicate. Treatments were compared using one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s HSD test, p < 0.05). *** represents p < 0.001.
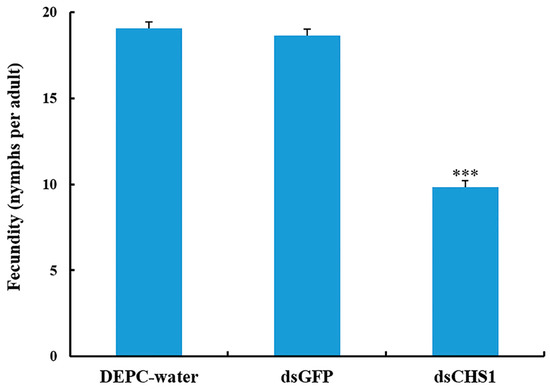
Figure 5.
Effect of CHS1 gene silencing on fecundity of A. gossypii, previously fed artificial diets containing DEPC-water, dsGFP, and dsCHS1 at their nymphal stage (third instar). The values are presented as the mean (±SE). Thirty individuals per experimental group (DEPC-water, dsGFP, and dsCHS1) were used and each aphid was considered as a single replicate. Treatments were compared using one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s HSD test, p < 0.05). *** represents p < 0.001.
4. Discussion
Chitin synthase 1 (CHS1) contributes significantly towards the formation of chitin in insects [32] and is extremely critical for insect molting [34,47,48,49]. Chitin synthase genes have been deliberated in a number of insect pest species, such as A. gossypii, soybean aphid (A. glycines), and brown citrus aphid (Toxoptera citricida) [7,40,41]. As chitin is absent in plants and mammals [47,48,50], RNAi-mediated silencing of genes related to the chitin synthesis pathways is a striking target for insect pest control. The abundance of CHS1 mRNA transcript in migratory locust (L. migratoria) was at maximum in the adult stage and was lowest in the developmental stages [51]. However, in soybean aphid (A. glycines Matsumura), the mRNA transcription of CHS1 gene was highest in the nymphal stage (second instar) [41]. Similarly, the peak expression level of CHS1 was also detected during developmental stages of grain aphid (Sitobion avenae) [39]. In the present study, transcripts of CHS1 gene were perceived in all life stages of A. gossypii; however, the highest expression was observed in the first-instar nymph. These results suggested that expression patterns of CHS1 gene are different among different insect pests.
RNA interference is a gene-silencing technique that has been efficiently used for the last two decades in order to study the resistance mechanisms, functional analysis of detoxification genes, and control of insect pests through oral dietary delivery or artificial injection [26,52,53,54,55,56,57]. For the effective silencing of target genes, it is necessary to introduce the dsRNA molecule into the body of insect to disrupt the expression of target genes at the transcription level. RNAi-mediated gene knockdown has largely been adopted through oral dietary delivery, droplet-feeding, or injection of dsRNA [52,53,57,58,59]. RNAi-mediated insect control was initially studied by Mao et al. and Baum et al. [18,60]. They developed transgenic plants that express dsRNA for the control of cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera), and Western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera (Coleoptera). Afterward, many studies were conducted to target different insect genes through various methods, e.g., feeding, injection, soaking, and transgenic plants, which are summarized in certain previous works, such as those of Kola et al. and Kim et al. [25,61]. The difficulties and endorsements for the RNAi-mediated positive insect control were discussed in detail by Scott et al. and Burand and Hunter in their review papers [22,24].
Zhang et al. demonstrated that RNAi-mediated silencing of CHS1 through injection with 1 μg μL−1 LmCHS1, LmCHS1A, and LmCHS1B dsRNA causes 95%, 88%, and 51% mortalities in the oriental migratory locust, respectively [51]. Mohammed et al. reported approximately 30%, 55%, and 75% larval mortalities in the potato tuber moth (Phthorimaea operculella) after injection with 50, 100, and 200 ng 5′-dsRNA-CHS1, respectively [27]. Souza-Ferreira et al. showed a 25% decrease in transcripts of CHS after injection of dsRNA-CHSe in Rhodnius prolixus [37]. Moreover, the chitin deposition and eclosion were also affected in the first-instar nymph fed with dsRNA. Zhao et al. reported that plant-mediated RNAi of Sitobion avenae CHS1 gene causes ~50% decreased transcription, whereas ~20% reduction was observed in number of grain aphid and ecdysis [39]. Our results showed that RNA-interference-mediated knockdown of the CHS1 gene causes a significant (p < 0.001) reduction in the mRNA transcription after oral delivery of dsRNA-CHS1 for 48 and 72 h. Moreover, 59% mortality of cotton-melon aphid was observed at 72 h post-feeding of dsCHS1. The mortalities of aphids treated with DEPC-water and dsGFP were 8% and 9% at 72 h post-feeding, respectively, which could be due to the side effects of controls, as reported previously [31,62]. In the present study, knockdown of CHS1 gene also significantly (p < 0.005) reduced the longevity (approximately 38%) and the fecundity (approximately 48%) of the surviving cotton-melon aphids after oral uptake of dsRNA-CHS1 for 72 h. These results demonstrated that the oral dietary delivery dsRNA-CHS1 could lead to the decreased transcription level of CHS1 and subsequently affect aphid development.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study revealed that knockdown of the chitin synthase 1 (CHS1) gene via oral delivery of dsRNA-CHS1 in A. gossypii caused mortality. Moreover, oral-delivery-mediated RNAi of CHS1 also disrupted the adult longevity and fecundity of the cotton-melon aphid. Furthermore, the current study proposes that CHS1 might be a possible candidate gene to target with RNA interference technology. For the long-term control tactics of pests, this strategy might be more suitable for innovative management of A. gossypii in field conditions.
Author Contributions
F.U. and D.S. designed the experiment; F.U. and H.G. reared the insects; F.U. and H.G. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; F.U., H.G., X.W., Q.D., F.S., N.D., and D.S. wrote and reviewed the manuscript; D.S. and X.G. contributed to the reagents/materials. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding was provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0200500) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272077) to F.U., H.G., X.W., Q.D., X.G. and D.S.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Hullé, M.; Chaubet, B.; Turpeau, E.; Simon, J. Encyclop’Aphid: A website on aphids and their natural enemies. Entomol. Gen. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Emden, H.F.; Harrington, R. Aphids as Crop Pests; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, M.; Callaghan, A.; Field, L.; Williamson, M.; Moores, G. Identification of mutations conferring insecticide-insensitive AChE in the cotton-melon aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover. Insect Mol. Biol. 2004, 13, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, R.; Croft, P. Strategies for the control of Aphis gossypii Glover (Hom.: Aphididae) with Aphidius colemani Viereck (Hym.: Braconidae) in protected cucumbers. Biocontrol. Sci. Technol. 1998, 8, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Tariq, K.; Ali, A.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Clothianidin-induced sublethal effects and expression changes of vitellogenin and ecdysone receptors genes in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Yousaf, H.K.; Xiu, W.; Qian, D.; Gao, X.; Tariq, K.; Han, P.; Desneux, N.; Song, D. Impact of low lethal concentrations of buprofezin on biological traits and expression profile of chitin synthase 1 gene (CHS1) in melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Imidacloprid-induced hormetic effects on demographic traits of the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Khattak, A.M.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Acetamiprid-induced hormetic effects and vitellogenin gene (Vg) expression in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, H.; Ullah, F.; Biondi, A.; Desneux, N.; Qian, D.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Resistance against clothianidin and associated fitness costs in the chive maggot, Bradysia odoriphaga. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.; Graves, J. Insecticide resistance and reproductive biology of Aphis gossypii Glover. Southwest. Entomol. (USA) 1992, 17, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, H.-N.; An, J.-J.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, G.-H. Regional susceptibilities to 12 insecticides of melon and cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and a point mutation associated with imidacloprid resistance. Crop Prot. 2014, 55, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Qi, H.; Yang, D.; Yuan, H.; Rui, C. Cycloxaprid: A novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide to control imidacloprid-resistant cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 132, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinek, M.; Doudna, J.A. A three-dimensional view of the molecular machinery of RNA interference. Nature 2009, 457, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whangbo, J.S.; Hunter, C.P. Environmental RNA interference. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang-Pruski, G.; You, M. Phyllotreta striolata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): Arginine kinase cloning and RNAi-based pest control. Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walshe, D.; Lehane, S.; Lehane, M.; Haines, L. Prolonged gene knockdown in the tsetse fly Glossina by feeding double stranded RNA. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 18, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.K.; Chandrashekar, K.; Thakur, N.; Verma, P.C.; Borgio, J.F.; Singh, P.K.; Tuli, R. RNA interference for the control of whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci) by oral route. J. Biosci. 2011, 36, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burand, J.P.; Hunter, W.B. RNAi: Future in insect management. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 112, S68–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Knipple, D.C. Recent advances in RNA interference research in insects: Implications for future insect pest management strategies. Crop Prot. 2013, 45, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Michel, K.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Siegfried, B.D.; Hunter, W.B.; Smagghe, G.; Zhu, K.Y.; Douglas, A.E. Towards the elements of successful insect RNAi. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kola, V.S.R.; Renuka, P.; Madhav, M.S.; Mangrauthia, S.K. Key enzymes and proteins of crop insects as candidate for RNAi based gene silencing. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, K.; Ali, A.; Davies, T.E.; Naz, E.; Naz, L.; Sohail, S.; Hou, M.; Ullah, F. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of voltage-gated sodium channel (MpNa v) gene causes mortality in peach-potato aphid, Myzus persicae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Diab, M.R.; Abdelsattar, M.; Sayed, M. Characterization and RNAi-mediated knockdown of Chitin Synthase A in the potato tuber moth, Phthorimaea operculella. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Merzendorfer, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Muthukrishnan, S. Biosynthesis, turnover, and functions of chitin in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C.; Davy, M.; MacDiarmid, R.; Plummer, K.; Birch, N.; Newcomb, R. RNA interference in the light brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana (Walker) induced by double-stranded RNA feeding. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Le Trionnaire, G.; Bonhomme, J.; Christophides, G.K.; Rispe, C.; Tagu, D. Gene knockdown by RNAi in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. BMC Biotechnol. 2007, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.M.F.; Simões, Z.L.P. A non-invasive method for silencing gene transcription in honeybees maintained under natural conditions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H.; Zimoch, L. Chitin metabolism in insects: Structure, function and regulation of chitin synthases and chitinases. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 4393–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, K.J.; Hopkins, T.L.; Schaefer, J. Applications of solids NMR to the analysis of insect sclerotized structures. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 25, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.S.; Tang, B.; Chen, X.; Tian, H.; Zhang, W. Molecular cloning, expression pattern and comparative analysis of chitin synthase gene B in Spodoptera exigua. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 149, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellam, R.L.; Eisemann, C. Chitin is only a minor component of the peritrophic matrix from larvae of Lucilia cuprina. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, J.F.; Alvarenga, E.S.; Figueira-Mansur, J.; Franco, T.A.; Ramos, I.B.; Masuda, H.; Melo, A.C.; Moreira, M.F. Effects of chitin synthase double-stranded RNA on molting and oogenesis in the Chagas disease vector Rhodnius prolixus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza-Ferreira, P.S.; Mansur, J.F.; Berni, M.; Moreira, M.F.; dos Santos, R.E.; Araújo, H.M.M.; de Souza, W.; Ramos, I.B.; Masuda, H. Chitin deposition on the embryonic cuticle of Rhodnius prolixus: The reduction of CHS transcripts by CHS–dsRNA injection in females affects chitin deposition and eclosion of the first instar nymph. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimoch, L.; Merzendorfer, H. Immunolocalization of chitin synthase in the tobacco hornworm. Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 308, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sui, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Lu, L.; You, M.; Xie, C.; Li, B.; Ni, Z.; Liang, R. Plant-mediated RNAi of grain aphid CHS1 gene confers common wheat resistance against aphids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 747, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Xia, W.K.; Wei, D.D.; Wei, D.; Wang, J.J. Identification, characterization and functional analysis of a chitin synthase gene in the brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida (Hemiptera, Aphididae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Mian, M.R.; Mittapalli, O.; Michel, A.P. Characterization of a chitin synthase encoding gene and effect of diflubenzuron in soybean aphid, Aphis. glycines. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, H.-W.; Huang, H.-J.; Xue, J.; Wu, W.-J.; Bao, Y.-Y.; Xu, H.-J.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Cheng, J.-A.; Zhang, C.-X. Chitin synthase 1 gene and its two alternative splicing variants from two sap-sucking insects, Nilaparvata lugens and Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liang, P.; Wang, B.; Gao, X. Overexpression of multiple cytochrome P450 genes associated with sulfoxaflor resistance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 157, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Li, F.; Tang, Q.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X. CYP4CJ1-mediated gossypol and tannic acid tolerance in Aphis gossypii Glover. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.-S.; Li, F.; Liang, P.-Z.; Chen, X.-W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.-W. Identification and validation of reference genes for the normalization of gene expression data in qRT-PCR analysis in Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Insect Sci. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.P. The cell wall: A carbohydrate armour for the fungal cell. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenardon, M.D.; Munro, C.A.; Gow, N.A. Chitin synthesis and fungal pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Kumar, N.S.; Tang, B.; Sun, X.; Qiu, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W. The class A chitin synthase gene of Spodoptera exigua: Molecular cloning and expression patterns. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. Chitin synthesis and inhibition: A revisit. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ma, E.; Zhu, K.Y. Silencing of two alternative splicing-derived mRNA variants of chitin synthase 1 gene by RNAi is lethal to the oriental migratory locust, Locusta migratoria manilensis (Meyen). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.Y.; Xue, X.Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Chen, X.Y.; Mao, Y.B. Gossypol-enhanced P450 gene pool contributes to cotton bollworm tolerance to a pyrethroid insecticide. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 4371–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Gong, C.; Yao, X.; Jiang, C.; Yang, Q. Molecular identification of four novel cytochrome P450 genes related to the development of resistance of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to chlorantraniliprole. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-L.; Staehelin, C.; Xia, Q.-Q.; Su, Y.-J.; Zeng, R.-S. Identification and characterization of CYP9A40 from the tobacco cutworm moth (Spodoptera litura), a cytochrome P450 gene induced by plant allelochemicals and insecticides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 22606–22620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-L.; He, Y.-N.; Staehelin, C.; Liu, S.-W.; Su, Y.-J.; Zhang, J.-E. Identification of Two Cytochrome Monooxygenase P450 Genes, CYP321A7 and CYP321A9, from the Tobacco Cutworm Moth (Spodoptera Litura) and Their Expression in Response to Plant Allelochemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Shen, G.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q.; He, L. Collaborative contribution of six cytochrome P450 monooxygenase genes to fenpropathrin resistance in Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Boisduval). Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, M.; Liu, S.; Jan, S.; Shi, L.; Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Gulzar, A.; Ali, B.; Rehman, M.; Wang, M. Knock-down of gossypol-inducing cytochrome P450 genes reduced deltamethrin sensitivity in Spodoptera exigua (Hübner). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-L.; Liu, S.-W.; Baerson, S.; Qin, Z.; Ma, Z.-H.; Su, Y.-J.; Zhang, J.-E. Identification and functional analysis of a novel cytochrome P450 gene CYP9A105 associated with pyrethroid detoxification in Spodoptera exigua hübner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hafeez, M.; Zhang, X.; Dawar, F.U.; Guo, J.; Gao, C.; Wang, M. Isolation and functional identification of three cuticle protein genes during metamorphosis of the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16061. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.-B.; Cai, W.-J.; Wang, J.-W.; Hong, G.-J.; Tao, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Huang, Y.-P.; Chen, X.-Y. Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Issa, M.S.; Cooper, A.M.; Zhu, K.Y. RNA interference: Applications and advances in insect toxicology and insect pest management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.; Aleixo, A.; Barchuk, A.; Bomtorin, A.; Grozinger, C.; Simões, Z. Non-target effects of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-derived double-stranded RNA (dsRNA-GFP) used in honey bee RNA interference (RNAi) assays. Insects 2013, 4, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).