Abstract
Structural lubricity is an intriguing tribological concept, where extremely low friction is anticipated, if two surfaces in relative motion do not share the same lattice structure and consequently instabilities originating from interlocking surface potentials are strongly reduced. Currently, the challenges related to the phenomenon of structural lubricity are considered to be twofold. On one hand, experimental systems suitable for showing structural lubricity must be identified, while at the same time, it is also crucial to understand the intricate details of interface interaction. Here, we introduce a new material combination, namely NaCl-particles on highly oriented pyrolithic graphite (HOPG), where the nanoparticles coalesce under the influence of ambient humidity. Our experiments reveal that the interfacial friction can be described by the concept of structural lubricity despite the seemingly unavoidable contamination of the interface. By systematically analyzing the friction versus area scaling, this unlikely candidate for structural lubricity then shows two separate friction branches, with distinct differences of the friction versus area scaling. The exact tribological behavior of the nanoparticles can ultimately be understood by a model that considers the influence of nanoparticle preparation on the interface conditions. By taking into account an inevitable water layer at the interface between particle and substrate that can exist in different crystalline configurations all friction phenomena observed in the experiments can be understood.
1. Introduction
In principle, strucural lubricity is a fundamental concept, where strongly reduced or even vanishing friction is anticipated, if two surfaces in relative motion do not share the same lattice structure and consequently, energy dissipation (i.e., friction) related to instabilities from interlocking surface potentials is strongly reduced. But despite this intriguingly simple mechanism, the analysis of structural lubricity still remains a demanding problem of vibrant research [1,2,3], which usually consists of two main challenges that have received particular attention during recent years:
First, it is required to find or prepare experimental systems where the interfaces are compatible with the concept of structural lubricity. In this context, it is usually assumed that the collective force cancellation effects, which are characteristic for structural lubricity, can be eliminated by either interface contamination [4,5] or insufficient quality of the surfaces, with for example, defects or asperities acting as individual dissipation centers—contrary to the collective effects required for structural lubricity. Consequently, one strategy to achieve structural lubricity is to prepare and analyze well defined model systems under ultra high vacuum (UHV) conditions, which are more tractable theoretically. Here, especially metallic nanoparticles prepared by thermal evaporation on layered materials with van der Waals interaction between layers, like for example, highly oriented pyrolithic graphite (HOPG) or MoS, have proven to be suitable [5,6,7,8,9,10]. At the same time, researchers strove to establish structural lubricity also under ambient conditions. It was found that metallic nanoparticles, namely Au- and Pt-particles, on HOPG prepared under UHV conditions can show superlubricity even under ambient conditions [11,12], a result which was related to the general inability of contamination to enter the interface for these particular material combinations [11]. Additionally, structural lubricity was also found under ambient conditions for graphene stacks sliding on HOPG [13,14,15,16]. Here, a recently described self cleaning effect of the graphene interfaces under relative motion is considered to be the reason that even interfaces formed by pushing partial graphene stacks onto HBn or HOPG under ambient conditions [17,18,19] do show typical behavior of structural lubricity, despite the potential influence of initial contamination. However, the overall number of material combinations showing structural lubricity is still very limited and it remains a particular challenge to produce tribological systems compatible with the influence of ambient conditions.
Besides the general efforts to create superlubric systems, a second research focus is directed towards understanding the underlying physical principles governing friction for the case of incommensurate interfaces. By employing both theoretical and experimental approaches, a number of key characteristics of superlubricity could be unveiled. First, it was found that superlubric friction can be characterized by a sublinear friction versus area scaling, which is related to the increasing effectiveness of force cancellation with increasing slider size [4,20,21]. At the same time, also the relative orientation between slider and substrate needs to be taken into account. This was first demonstrated for the case of grahene flakes sliding on HOPG [22] and recent theoretical and experimental studies have pointed out how especially interfaces formed by different surfaces can show extremely intricate dependencies of friction on relative orientation, where also the friction versus area scaling depends sensitively on the relative orientation [9,23,24]. Additionally, a number of studies have emphasized that additional effects can become relevant, if the interfaces cannot be assumed to be completely rigid. In this case, contact aging or enhanced static friction can occur [7,8,25,26]. Depending on the elastic properties of the materials additionally pseudo-commensurate states can appear [23] and superlubricity can even break down completely once a critical system size is reached and dislocations can be accommodated within the interface [10,21,27].
In the context of these current problems and topics related to the analysis of structural lubrictity, we are now introducing a new material system, namely NaCl-nanoparticles on HOPG. As we will show, structural lubricity can be found for this disparate interface despite major steps of nanoparticle preparation performed under ambient conditions. By anaylzing the contact area dependence of friction for the NaCl-nanoparticles sliding on HOPG using atomic force microscopy (AFM) assisted nanomanipulation, we not only verify the main characteristics of structural lubricity but at the same time provide further insight into the complex interface processes related to effects of crystalline structure and relative orientation between slider and substrate [9,19,22,23,24]. In particular we will show that the friction versus area scaling of the NaCl-nanoparticles shows distinct branches, a behavior that will be linked to irreversible changes of the interface conditions, namely a transition from amorphous to polycrystalline that is related to an interfacial water layer, which exists as a residual effect of the preparation process. An important aspect to describe this tribological scenario is to understand the fundamental mechanisms of superlubricity for the case of polycrystalline interfaces, as it is done by our theoretical calculations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticle Preparation
To prepare our NaCl nanoparticles on HOPG, we used an evaporation approach, similar to a method described in Reference [28]. More specifically, a small amount of NaCl was placed inside a metal tube of approximately 10 mm length and 1 mm diameter that was welded to a conventional AFM sample holder. This holder was placed onto a heatable manipulator inside the preparation chamber of our Omicron UHV-VT-AFM system. A small resistive heater within the manipulator allowed to heat up the sample holder to a temperature of about 500 °C, while at the same time a freshly cleaved HOPG sample was placed in front of the open tube end for an evaporation time of 60 s at a distance of approximately 5 mm. After evaporation, the sample was transferred from the preparation chamber to the UHV-AFM without breaking the vacuum. Figure 1a shows an image of the resulting sample surface obtained in contact AFM-mode. From this image, it becomes obvious that our evaporation procedure did not produce compact and well defined NaCl-particles but instead the only traces of deposited NaCl stem from lines in the image, where NaCl has probably been dragged along by the AFM-tip. Varying both the evaporation temperature and the exposure time of the substrate did not significantly change the general structure of the NaCl.
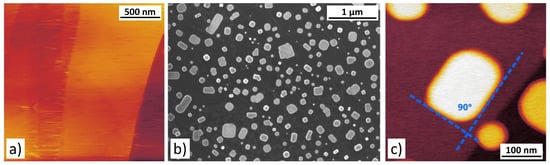
Figure 1.
Overview over the different steps of particle preparation as described in the main text. (a) Contact mode atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis of the sample surface directly after evaporation of NaCl without breaking the vacuum. (b) Scanning electron microscopy image of the sample surface showing a relatively dense coverage of the surface with NaCl-nanoparticles after exposure to ambient conditions. (c) AFM-image of the sample surface after SEM analysis, showing well defined nanoparticles. All images (a–c) have been taken at room temperature under vacuum conditions
In addition to the AFM measurements, we transferred the samples to a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in order to gain a more comprehensive overview over the samples. In the process, the samples were exposed to ambient conditions. Surprisingly, the SEM images (Figure 1b) revealed compact nanoparticles of mostly rectangular shape with rounded edges across the whole sample surface, although previous AFM measurements on the exact same sample showed no particles. Since the experimental conditions within the UHV-AFM and the scanning electron microscope are comparable, it appears likely that the unexpected transformation of the NaCl-coverage must be related to the exposure to ambient conditions between the measurements, which were performed in two different set-ups.
After SEM-imaging the sample was re-inserted into the UHV-AFM and NaCl-nanoparticles suitable for nanomanipulation experiments were readily found (cf. Figure 1c). Additionally, it can be confirmed that typical particle shapes as shown in Figure 1c are in good agreement with the square lattice structure of NaCl, while particle heights are usually found to be around 10–12 nm.
Since exposure to ambient condition was identified as a likely candidate to induce the structural transformation of the NaCl, we used an additional test protocol to verify this assumption. Here, we started with the previously described evaporation process, after which the sample was immediately analyzed by AFM and revealed the previously found lack of particles. Then, the sample was transferred to the load-lock of the UHV-system, where it was kept under pressurized (i.e., ambient) conditions for 2 h with a relative humidity of about 35–40%. After that, the sample was again analyzed by atomic force microscopy under UHV conditions and defined nanoparticles could be identified.
Based on these observations, humidity must be considered as a likely candidate to drive the nanoparticle formation process. It is known that both NaCl and HOPG can be covered by roughly a monolayer of water under ambient conditions with relative humidity of about 40% [29,30]. Such an amount of water molecules is already sufficient to enable ionic mobility and reconstruction of NaCl [30,31]. However, in our case the particle formation process must also involve material flow on the HOPG substrate. The fact that nanoparticles have indeed been observed upon restoring UHV conditions, suggests that this level of humidity was also sufficient to allow for at least partial dissolution of the NaCl and restructuring on HOPG under these conditions. Still, further insight into the nanoparticle formation process beyond this basic concept would now require more dedicated research.
2.2. Nanoparticle Manipulation
The nanoparticles prepared according to Section 2.1 provide excellent samples for nanomanipulation experiments. In particular, a grazing incidence of evaporation leads to significant variations in particle coverage across the sample surfaces. This allows to identify areas with a sufficient number of particles as well as enough free space for the manipulation experiments.
Figure 2a,b illustrate the general nanomanipulation technique, based on conventional friction force microscopy [32], where the tip is used to push the nanoparticles from the side, while simultaneously measuring friction based on the increased cantilever torsion during manipulation. All nanomanipulations have been carried out using standard Si-cantilevers (Masch CSC37) at typical scanning velocities of 300–1000 nm/s and normal force of 2.5–4 nN. By subtracting the friction signals recorded during the manipulation stages of Figure 2a,b, the tip/substrate friction is eliminated and the resulting difference only reflects the friction between particle and substrate. In general, friction of the nanoparticles was found to be very low, with absolute friction values of a few 10 nN as maximum. Facilitating both imaging of the nanoparticles and their subsequent manipulation therefore requires a specific experimental approach as outlined in previous publications [3,6]. Based on this approach, Figure 2c shows a typical nanomanipulation experiment, where the NaCl-particle was first imaged using non-contact AFM (NC-AFM) operation (see Figure 2c, inset). After that, the AFM-tip was positioned beside the particle and the system was switched to contact mode operation. Now the lateral manipulation of the particle was carried out by moving the AFM-tip along a straight vector perpendicular to the long cantilever axis, while simultaneously recording the lateral force signal . Before the AFM-tip reaches the nanoparticle ( nm in Figure 2c), the lateral force signal only reflects the friction between the AFM-tip and the substrate and can thus be subtracted as a reference level. Then, the second part of the curve ( nm) only reflects the interfacial friction between the nanoparticle and the substrate. Once the manipulation procedure is finished, the AFM can be switched back to NC-AFM mode in order to record a control image to verify the change in nanoparticle position (Figure 2c, inset). Finally, all lateral force values have been calibrated using the wedge calibration method as suggested by Varenberg et al. [33].
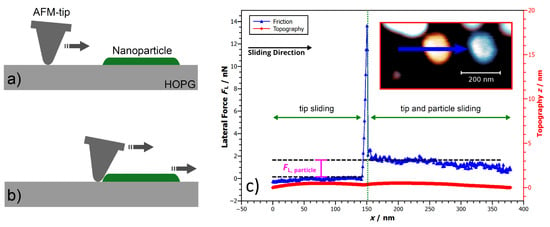
Figure 2.
Concept of Nanoparticle Manipulation by pushing the nanoparticle from the side. During the manipulation, two stages can be distinguished: (a) the AFM tip approaches the particle and the lateral force signal originates solely from the tip/substrate interface. (b) Once the tip reaches the nanoparticle and starts pushing it, the lateral force signal increases and can be attributed to both tip/substrate and particle/substrate friction. Subtracting the two lateral force levels then gives access to only the friction of the nanoparticle. (c) Example of a nanoparticle manipulation. The overlay image of the inset shows the nanoparticle, before and after it has been manipuated by the AFM tip along the direction indicated by the arrow. The main part of the figure shows the lateral force trace. The lateral force signal before the tip reaches the particle (tip sliding) can be used as reference to extract the absolute friction of the sliding nanoparticle when pushed by the tip (nanoparticle sliding). Additionally, also the topography signal recorded during the manipulation of the nanoparticle is shown, which is flat on a sub-nanometer level.
3. Results
In order to characterize and understand the tribological behavior of the NaCl-nanoparticles, two main aspects of our experimental results have to be considered successively. As a first step, we will analyze the specific features of the lateral force traces recorded during nanoparticle manipulation, which often reveal sudden changes in the friction level. As a second step, we will then evaluate, how these different friction levels observed for particles of varying size do fit into a comprehensive representation of the friction versus area scaling.
3.1. Friction Changes during Manipulation
As already indicated in previous publications, the interfacial friction of crystalline particles on a crystalline substrate does not neccessarily need to be constant but can instead be changing almost instantly, an effect that is usually associated with the intricate dependence of energy barriers on the relative orientation between tip and sample [9,23,24].
Similar effects have also been observed for the NaCl-Particles on HOPG. This is illustrated in Figure 3, where a nanoparticle with a contact area of = 28,750 nm has been consecutively manipulated three times as shown by the panels I-IV in Figure 3 (Please note that panels II and III show the same data, albeit using a different y-scale). The result reveals distinct friction levels: For the first manipulation, the lateral force signal (Figure 3I) starts with a pronounced peak of approximately 35 nN, which is only stable for approximately 20–30 nm before the lateral force experiences a sudden drop to a level below 5 nN. But also on this lower level, friction does not remain constant but instead switches five more times with friction changes in the nN-range. We checked if the sudden friction changes can be related to topography features of the surface or the particle dimension but no apparent correlation was found. Therefore, the friction variations must be correlated to intrinsic changes of the interface conditions.
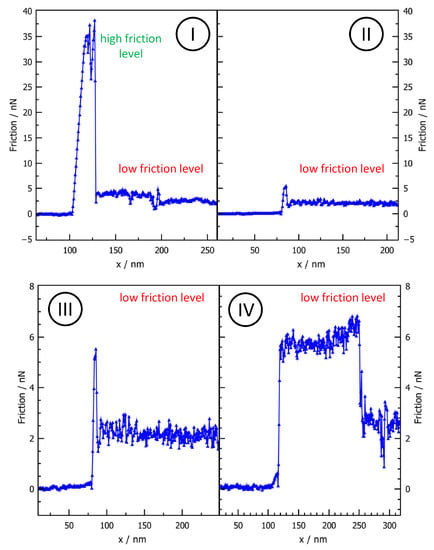
Figure 3.
Multiple manipulation of a NaCl-nanoparticle with a contact Area of = 28,750 nm. The lateral force signal shows several jumps, which constitute different friction levels. Most prominently, panel I shows the transition between the high friction level and the lower firction level, while all further panels reveal friction changes within the lower friction branch. Please note that panels (II) and (III) show the same lateral force trace but use different y-Axis scaling for comparison to the traces shown in panels (I) and (IV).
Figure 3 already highlights two main features that are important in the further course of this work. The first one is the switching between different levels in the lower friction range. This effect was not only observed for the example shown in Figure 3 but was a frequent occurrence throughout our measurements of a larger number of nanoparticles. Interestingly, we found that friction can indeed change back and forth between higher and lower levels in this range (see also Figure 3). The significance of the second main effect (i.e., the existence of a high friction level) is not immediately clear from Figure 3. Here, the initially high friction level might alternatively be interpreted as a static friction peak, despite the fact that friction remains on the high level for at least a few nm. However, the importance of this peak becomes clearer in Figure 4, which shows friction measurements for a previous manipulation of this nanoparticle. Here, friction remains on the elevated level for a distance of approximately 80 nm. Therefore, the high friction level of Figure 3 must rather be considered as a short-lived manifestation of a characteristic sliding state than as a static friction peak (i.e., an aging related threshold force to overcome before sliding). As we will see later on, this classification, which was also applied for other nanomanipulations is further justified by the consistence of the resulting friction versus area scaling, which results in a distinct branch with .
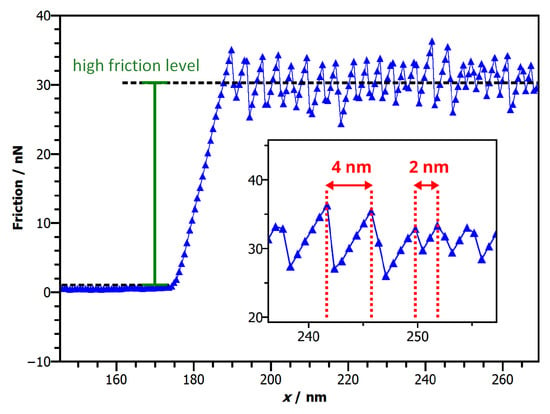
Figure 4.
Stick Slip observed for the high friction level. Once the particle starts sliding, at nm, a distinct stick slip behaviour of the lateral force signal can be observed. The inset reveals that the typical slip-lengths can vary and are significantly larger than the periodicity of either highly oriented pyrolithic graphite (HOPG) or NaCl.
Interestingly, we also observe that the lateral force trace of Figure 4 also shows a distinct stick-slip behaviour within the high friction level. However, we find comparatively large periodicities with stick phases ranging from 2–4 nm. These distances are clearly incompatible with the periodicity of either the substrate or the particles. Thus it might seem plausible to correlate the stick-slip pattern with the interface conditions between the nanparticle and the substrate. Crucially these slip-lengths are also similar to that of amorphous Sb-nanoparticles sliding on HOPG [8], where the slip lengths have been attributed to insufficient relaxation of the soft spring within a single lattice constant. Therefore, it is difficult to conclude anything from these slip lengths about lattice parameters in the interface.
Independent of any stick-slip behaviour, the high friction state is also different from the low friction levels since it was exclusively observed, when the particle had not yet switched to a lower friction level. After such a decrease in friction, no evidence was found of switching back to the high friction level and the transitions from higher to the lower levels thus appear to be irreversible.
3.2. Friction versus Area Scaling
All the previously discussed effects must be considered when analyzing the friction versus area scaling based on our nanomanipulation experiments, which consisted of 85 manipulations of 30 nanoparticles. For each nanomanipulation we have analyzed the friction traces recorded during particle manipulation as indicated in Figure 3. The results show two distinct branches of the friction versus area scaling (Figure 5). The low friction branch is well separated from the high friction branch and has a broader spread of friction values.
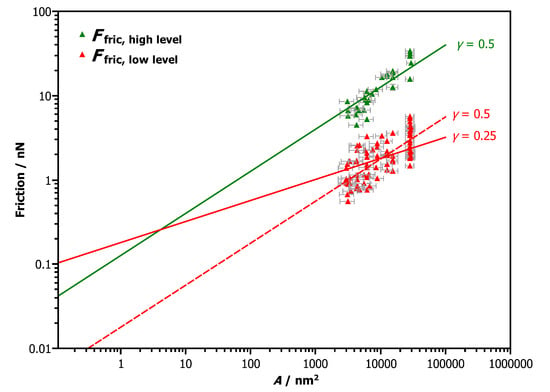
Figure 5.
Friction vs. area scaling extracted from 85 nanomanipulations of 30 particles. The resulting friction values can be distinguished as three different branches as indicated by the different colors. Each branch can be fitted by a scaling law (See Section 4 for details on the choice of the scaling factors and the significance of the different prefactors F0).
The overall very low friction values suggest a scenario involving structural lubricity. In this context it is worthwhile to explore, whether previously described scaling laws [6,11,23] can be applied to this particular system. In general, these scaling laws take the form , where is the energy barrier against sliding for a particle with N interface atoms. The characteristic scaling exponent is controlled by both the relative orientation between particle and substrate as well as the particle’s shape [23,24]. The energy prefactor can depend on the particle shape [24].
Due to the fact that the range of contact areas in the experiment is only one order of magnitude, it is not possible to fit both and with sufficient confidence. We can however determine with certainty that the exponents for both branches are smaller than 1. Moreover, we are helped by the fact that the friction exponents for structural superlubricity found in numerical simulations [23,24] are always , or 1. The high friction branch is most consistent with a scaling exponent of . This corresponds to a barrier of meV per unit cell of NaCl. The low friction branch is more challenging to fit because it is broader. It is statistically consistent with both meV and meV. From our theoretical considerations (see next section) we find that the scaling by is the most plausible one but both are shown in Figure 5.
4. Discussion
We can now use this information to investigate the mechanism behind the switching structural superlubricity in this system. In our previous work [24] with gold on graphite under clean conditions, we have found that the small rotations of the particles can lead to friction changes during superlubric sliding. These changes were reversible and in those previous experiments appeared only within a single friction branch. We observe this kind of switching here as well within the low-friction branch, as can be seen in the bottom part of Figure 3.
We also observe irreversible switching from the high to the low friction branch, which we did not observe in previous experiments. While it is possible for small rotations to switch between different friction branches [23,34], this cannot explain the effect we observe. This is because the high friction branches are always more stable against rotation than the low friction branches [34]. If small rotations were the mechanism for this switching, it would go from low to high friction. We thus conclude that another irreversible mechanism must be at play.
Combined with the structural lubricity and with rotation eliminated, the irreversibility strongly suggests that we are dealing with a structural transition in the interface layer. Given the exponent of the high-friction branch and long stick-slip period, we can surmise that the high-friction branch is the result of an amorphous interface, similar to, for example, antimony [6,23].
The lower friction branch must necessarily have a more crystalline structure. The wide spread in friction values for similar-sized crystals however indicates that something more is going on. In addition, the energy barrier for either scaling option is different from that of the high friction branch. This can be explained by the interface not being monocrystalline but rather polycrystalline with a spread in grain sizes. We can estimate the corrugation and friction of a polycrystalline interface consisting of M grains as the sum over M independent grains. We approximate each grain as a single crystal with random orientation and irregular shape (exponent ), with a contact area with atoms in it. Therefore, the corrugation and with it the friction scale as
In order to confirm this scaling numerically we have computed the potential energy of rigid polycrystalline particles on a rigid substrate. We have studied the dependence on the size of the crystal as well as the grains. For the substrate we used the same hexagonal potential as in References [23,24] with the interactomic distance of graphite, Å. The nanocrystals were circular and consisted of square grains of approximately atoms each. The lattice inside each grain had square symmetry and an orientation chosen from a uniform distribution of angles. The lattice parameter of the nanocrystal was chosen to be Å, which corresponds to the Na-Na spacing in the (100) plane of NaCl.
Figure 6 shows the rescaled corrugation as a function of the contact area for polycrystalline interfaces with grains of various sizes. The lines in the figure show the expected behaviour from Equation (1). For small size, the crystals have only one grain and follow the scaling of circular crystals, with exponent , indicated by the red line. For larger particles, the number of grains grows linearly with the number of atoms, as the grain size is constant, that is, . Hence the corrugation for the larger particles scales as . This scaling is indicated by the other lines in the figure and fits well to the numerical results over more than 8 decades.
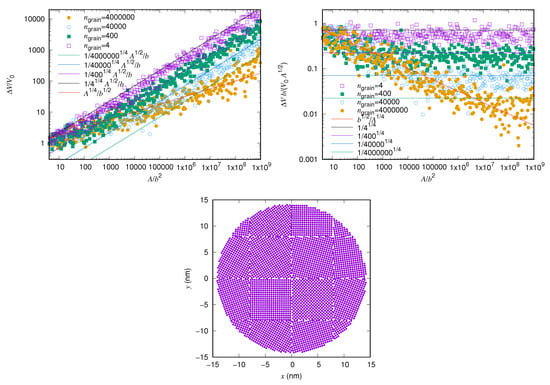
Figure 6.
The corrugation as a function of the contact size for a rigid circular nanocrystal with square grains of area with a randomly oriented square lattice (top left) and rescaled by the single-atom corrugation and for clarity (top right). An example of such a crystal interface with (bottom).
Using Equation (1), we can estimate the number and size of the grains from the energy barriers. The number of grains in a crystal . The number of atoms per grain can also be estimated, . These numbers are consistent with a contact area of several tens of thousands of atoms, which is indeed what one expects from the size of the NaCl particles. It is more difficult to make any reliable estimate about the spread of the grain sizes, because part of the spread of the friction values can be attributed to normal variations due to shape and orienation.
To further explain how this transition from amorphous to polycrystalline may come about, we first make two observations. The first is on the chemical composition of the interface layer. Since the NaCl was exposed to air with some humidity, a layer of water molecules has been formed on the crystal surface. These water molecules cannot be simply removed in vacuum without heating the crystal to above 450 K [35], which has not been done. Moreover, graphite is also weakly hydrophillic. Hence, a layer of water molecules is likely to be present in the interface. While under ambient conditions water is obviously liquid, there is experimental evidence that thin layers of ice can be formed on graphite or graphene [36,37]. Moreover, the regular arrangement of charged ions in the crystal structure of the NaCl could further help stabilise any ice structure.
The second observation is about the amount of energy that is available for a structural transition. The energy released during a slip at the high friction level can be determined from the force trace (see Figure 4). During a typical stick-slip motion, energy is stored in the spring system of the cantilever during sticking and then released during the slip. The amount of energy released during a slip is equal to the work done during the sticking, which can be estimated by , with F the average lateral force and the typical distance between slips. Since the energy is released abruptly and only once per stick-slip period, it is equal to the energy dissipated during one stick-slip period, that is, 30 nN of force for 4 nm is around J. When this energy is released, it briefly heats up the interface. Assuming that this water layer is approximately 0.3 nm thick (one molecule), there are between and water molecules in the interface. There is thus enough energy available to heat the water instantaneously by around 90 K, which is sufficient for a structural transition. In the low friction branch, however, with its lower friction and unobservable stick-slip period, at least an order of magnitude less energy is released.
We can thus provide a speculative explanation for the observed switching effect. In the high friction branch, the water layer between the NaCl and graphite is amorphous or nearly amorphous in structure. During a sufficiently violent slip, it is heated up and then cools down and crystallises into a number of grains. The reverse effect, melting the crystalline interface and refereezing in an amorphous structure, does not appear to happen. This may be because there is less energy available for heating the layer, due to the lower friction of the crystalline interface. It is also likely that the ordered structure is the more energetically favourable than the amorphous one.
5. Conclusions
All in all, our study has revealed NaCl-particles on HOPG as a new material combination, where exposure to ambient conditions is an integral aspect in the formation of interfaces showing superlubricity. By applying AFM-based nanomanipulation techniques, we can observe very low friction values and a sublinear friction versus area scaling, which are both considered to be crucial characteristics for the identification of superlubricity [4,6,20,24]. Especially the occurrence of two branches in the friction versus area scaling then allows deeper insight into the potential interface processes. More specifically, the results can consistently be explained by a theoretical model, where an interfacial water layer that exists as a result of the preparation process, can switch between amorphous and polycrystalline structure, thereby facilitating the occurrence of two friction branches. Interestingly, these results also shed a new light on the role of interface contamination for the occurrence of superlubricity. Usually, it is assumed that interface contamination can inhibit the collective force cancellation effects of superlubricity [4,5]. However, our results now hint at a new mechanism, where larger amounts of interface contaminants can re-trigger superlubricity by forming a new incommensurate interface. In future experiments, it would be interesting to test this hypothesis, which might then constitute a previously unrecognized route to superlubricity.
Author Contributions
F.H., D.D. and A.S. conceived the study, performed the experiments and analyzed the data. A.S.d.W. developed the theoretical model and performed the simulations. All authors discussed on the results and contributed to writing the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the German Research Foundation (DFG Project DI917/5-1, DI917/7-1) and in part by the COST Action MP1303 and the Laboratory of Materials Research (LaMa) of JLU Giessen.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HOPG | Highly oriented pyrolythic grpahite |
| AFM | Atomic force microscope |
| NC-AFM | Non-contact atomic force microscope |
| VT | Variable temperature |
| UHV | Ultra high vacuum |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
References
- Vanossi, A.; Dietzel, D.; Schirmeisen, A.; Meyer, E.; Pawlak, R.; Glatzel, T.; Kisiel, M.; Kawai, S.; Manini, N. Recent highlights in nanoscale and mesoscale friction. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1995–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baykara, M.Z.; Vazirisereshk, M.R.; Martini, A. Emerging superlubricity: A review of the state of the art and perspectives on future research. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 041102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, D.; Schwarz, U.D.; Schirmeisen, A. Nanotribological studies using nanoparticle manipulation: Principles and application to structural lubricity. Friction 2014, 2, 114–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müser, M.; Wenning, L.; Robbins, M. Simple Microscopic Theory of Amontons’s Laws for Static Friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzel, D.; Ritter, C.; Mönninghoff, T.; Fuchs, H.; Schirmeisen, A.; Schwarz, U. Frictional Duality Observed during Nanoparticle Sliding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 125505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzel, D.; Feldmann, M.; Schwarz, U.D.; Fuchs, H.; Schirmeisen, A. Scaling Laws of Structural Lubricity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 235502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, M.; Dietzel, D.; Fuchs, H.; Schirmeisen, A. Influence of Contact Aging on Nanoparticle Friction Kinetics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 155503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, M.; Dietzel, D.; Tekiel, A.; Topple, J.; Grütter, P.; Schirmeisen, A. Universal Aging Mechanism for Static and Sliding Friction of Metallic Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillitzsch, F.; Guerra, R.; Janas, A.; Manini, N.; Krok, F.; Gnecco, E. Directional and angular locking in the driven motion of Au islands on MoS 2. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, D.; Brndiar, J.; Stich, I.; Schirmeisen, A. Limitations of Structural Superlubricity: Chemical Bonds versus Contact Size. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7642–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihan, E.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Baykara, M.Z. Structural lubricity under ambient conditions. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özogul, A.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Baykara, M.Z. Structural superlubricity of platinum on graphite under ambient conditions: The effects of chemistry and geometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 211602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Jiang, B.; Liu, S.; Weng, Y.; Lu, L.; Xue, Q.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, S.; Peng, L. Self-Retracting Motion of Graphite Microflakes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 067205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Grey, F.; Liu, J.Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Q. Observation of Microscale Superlubricity in Graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 205503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Grey, F.; Zheng, Q. The high-speed sliding friction of graphene and novel routes to persistent superlubricity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, C.C.; Zhang, S.; Urbakh, M.; Li, Q.; He, Q.C.; Zheng, Q. Observation of normal-force-independent superlubricity in mesoscopic graphite contacts. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 081405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Sokolov, I.M.; Wang, W.; Filippov, A.E.; Zheng, Q.; Urbakh, M. Diffusion through Bifurcations in Oscillating Nano- and Microscale Contacts: Fundamentals and Applications. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 031020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Ma, M.; Song, Y.; He, Q.; Zheng, Q. Structural superlubricity in graphite flakes assembled under ambient conditions. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 14314–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Mandelli, D.; Hod, O.; Urbakh, M.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Q. Robust microscale superlubricity in graphite/hexagonal boron nitride layered heterojunctions. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müser, M.H. Theoretical Aspects of Superlubricity. In Fundamentals of Friction and Wear; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 177–199. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, T.A.; Pastewka, L.; Robbins, M.O. Elasticity limits structural superlubricity in large contacts. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 121402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienwiebel, M.; Verhoeven, G.; Pradeep, N.; Frenken, J.; Heimberg, J.; Zandbergen, H. Superlubricity of Graphite. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wijn, A.S. (In)commensurability, scaling, and multiplicity of friction in nanocrystals and application to gold nanocrystals on graphite. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 085429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, D.; de Wijn, A.S.; Vorholzer, M.; Schirmeisen, A. Friction fluctuations of gold nanoparticles in the superlubric regime. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 155702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varini, N.; Vanossi, A.; Guerra, R.; Mandelli, D.; Capozza, R.; Tosatti, E. Static friction scaling of physisorbed islands: The key is in the edge. Nanoscale 2014, 7, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, R.; Tosatti, E.; Vanossi, A. Slider thickness promotes lubricity: From 2D islands to 3D clusters. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11108–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Benassi, A.; Vanossi, A.; Urbakh, M. Critical Length Limiting Superlow Friction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zint, S.; Ebeling, D.; Ahles, S.; Wegner, H.A.; Schirmeisen, A. Subsurface-Controlled Angular Rotation: Triphenylene Molecules on Au(111) Substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Xu, K.; Varghese, J.O.; Heath, J.R. The Microscopic Structure of Adsorbed Water on Hydrophobic Surfaces under Ambient Conditions. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5581–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.; Rieutord, F.; Melman, N.A.; Dai, Q.; Salmeron, M. Adsorption of Water on Alkali Halide Surfaces Studied by Scanning Polarization Force Microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 6793–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, L.; Pöschl, U.; Niessner, R. Microstructural rearrangement of sodium chloride condensation aerosol particles on interaction with water vapor. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate, C.M.; Mcclelland, G.M.; Erlandsson, R.; Chiang, S. Atomic-Scale Friction of a Tungsten Tip on a Graphite Surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 1942–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varenberg, M.; Etsion, I.; Halperin, G. An improved wedge calibration method for lateral force in atomic force microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wijn, A.S.; Fusco, C.; Fasolino, A. Stability of superlubric sliding on graphite. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 046105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.W.; Grünbauma, E. The structure of gold films grown in ultra-high vacuum on sodium chloride substrates. Philos. Mag. A J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys. 1965, 11, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinesh, K.B.; Frenken, J.W.M. Experimental Evidence for Ice Formation at Room Temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 036101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, G.A.; Matthiesen, J.; Baer, M.; Mundy, C.J.; Petrik, N.G.; Dohnálek, Z.; Kay, B.D. No Confinement Needed: Observation of a Metastable Hydrophobic Wetting Two-Layer Ice on Graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12838–12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: All samples and materials used in this work are readily available from commercial sources. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).