1. Introduction
CNC machine tools are fundamental to modern manufacturing and support the transition toward intelligent production. The performance of the feed system directly affects the precision of machining and production efficiency [
1]. However, rolling bearings within these systems are highly susceptible to damage due to complex operating conditions and variable loads [
2]. Severe bearing damage not only degrades the performance of the system but also compromises the quality of the machining and the safety of production [
3]. Therefore, developing efficient, real-time, and reliable fault diagnosis methods for rolling bearings is essential to improving the reliability of CNC machine tools and maintaining stable industrial production.
Current fault diagnosis methods for monitoring bearing health are typically classified into traditional machine learning techniques based on signal analysis and modern deep learning-based intelligent diagnostic methods [
4]. Traditional approaches typically follow a “feature extraction–fault classification” paradigm. Features extracted from vibration signals are commonly categorized into three analytical domains: the time domain, the frequency domain, and the time–frequency domain [
5]. These features subsequently serve as inputs to various classifications for fault diagnosis, including Support Vector Machines (SVMs), Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), and K-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) [
6]. Traditional methods provide the distinct advantage of physically interpretable features, yielding transparent diagnostic results [
7]. However, their reliance on expert-designed features limits their ability to capture the complex characteristics [
8]. Furthermore, the performance of classifiers remains sensitive to hyperparameter optimization, thereby limiting their generalization capability across diverse operational conditions and constraining their real-time deployment.
To address the constraints of manual feature engineering, researchers have increasingly adopted end-to-end deep learning approaches. Deep learning-based diagnostic methods can be divided into three types according to their learning strategies. Supervised learning approaches, such as CNNs and Deep Belief Networks (DBNs), can extract discriminative features when labeled datasets are available [
9]. In contrast, unsupervised learning methods are suited for scenarios where labeled data is scarce [
10]. Zero-shot learning can identify fault types that were not present during training [
11]. However, given the accumulation of maintenance data in industrial settings, supervised learning methods demonstrate superior practical applicability in real-world applications [
12].
CNN applications in bearing fault diagnosis primarily comprise two-dimensional CNN (2D-CNN) and one-dimensional CNN (1D-CNN) approaches [
13]. 2D-CNN methodologies typically transform one-dimensional vibration signals into two-dimensional representations before conducting feature learning. For example, Cui et al. [
14] proposed a lightweight CNN framework based on FFT image encoding, integrating empirical mode decomposition and signal denoising techniques to achieve efficient fault diagnosis. Shi et al. [
15] employed Recurrence Binary Plots (RBPs) coupled with a depth-wise separable dilated CNN (DSD-CNN) for fault identification. Zhang et al. [
16] integrated Gram matrix (GM) representations with a multi-scale CNN (MSCNN) to enhance feature extraction capabilities while effectively suppressing noise interference. Although signal-to-image transformation methods have achieved considerable success, they introduce complexity in preprocessing and may lead to the loss of temporal information [
17]. Conversely, 1D-CNN architectures process raw vibration signals directly, thereby preserving full temporal information and minimizing preprocessing requirements, which makes them particularly well-suited for industrial applications [
18]. For instance, Chen et al. [
19] proposed the MRCC-Transformer framework, which integrates multi-scale residual convolution with multi-head self-attention mechanisms, effectively addressing strong coupling issues in high-dimensional features. Xie et al. [
20] designed the lightweight Pyramid Attention Residual Network (PARNet), demonstrating excellent diagnostic performance under conditions of significant speed variations. Kumar et al. [
21] proposed a Multi-width Kernel Convolutional Neural Network (MWK-CNN) for bearing fault diagnosis, addressing the inherent limitations of traditional CNN architectures in capturing both local and global feature representations.
Previous studies have demonstrated that integrating multi-scale feature extraction with attention mechanisms significantly enhances diagnostic performance. For example, Hu et al. [
22] introduced the Multi-scale Convolutional Neural Network with Multiple Attention Mechanisms (MMCNN). This framework integrates enhanced position attention, channel attention, and squeeze-and-excitation modules to overcome traditional CNNs’ limitations in learning discriminative fault features. Shao et al. [
23] developed the Adaptive Multi-scale Attention Convolutional Neural Network (AmaCNN), which integrates multi-level attention mechanisms designed to address feature distribution shifts in cross-domain fault diagnosis under varying load conditions. Guo et al. [
24] proposed the DA-ConvNeXt framework, which deeply integrates parallel multi-scale dilated convolution residual modules with multi-head attention mechanisms, significantly enhancing feature extraction capabilities. Sun et al. [
25] addressed the small sample problem through their Parallel Attention Multi-Scale Residual Network (PA-MSRN), which combines parallel attention mechanisms with multi-scale feature fusion technology. Cui et al. [
26] enhanced bearing fault diagnosis accuracy by developing the Multi-scale Gaussian Enhanced Residual Network (MGE-ResNet), which combines Gaussian pyramid-based multi-scale feature extraction with an Efficient Channel Attention mechanism. Jin et al. [
27] introduced the Spatial Attention Multi-Scale Depth-wise Separable Convolutional Neural Network (SA-MSDSCNN), combining multi-scale depth-wise separable convolutions with spatial attention mechanisms to enhance fault-feature extraction across varying operational conditions. Hu et al. [
28] tackled the challenge of limited training data through their Attention-based Multi-dimensional Fault Information Sharing framework (AMFIS), which employs a shared network architecture with Convolutional Block Attention Module and a Dynamic Adjustment Strategy.
Despite substantial advances in fault diagnosis, existing methods are constrained by limitations in multi-scale modeling, discriminative feature selection, and cross-condition generalization. Current approaches rely on larger convolutional kernels or increased network depth to extract multi-scale features, and lack mechanisms for feature selection. Such architectures not only introduce redundant features but also result in significant parameter expansion, consequently reducing real-time diagnostic performance [
21,
22,
23]. Furthermore, attention mechanisms operate primarily within single dimensions [
25,
26,
27] and lack effective multi-dimensional attention fusion strategies [
24,
28]. Most importantly, these methods tested under idealized conditions such as constant load and fixed speed. When deployed in variable operating environments, their diagnostic accuracy degrades substantially, limiting their applicability in real-world industrial scenarios [
21,
23,
24,
26,
27].
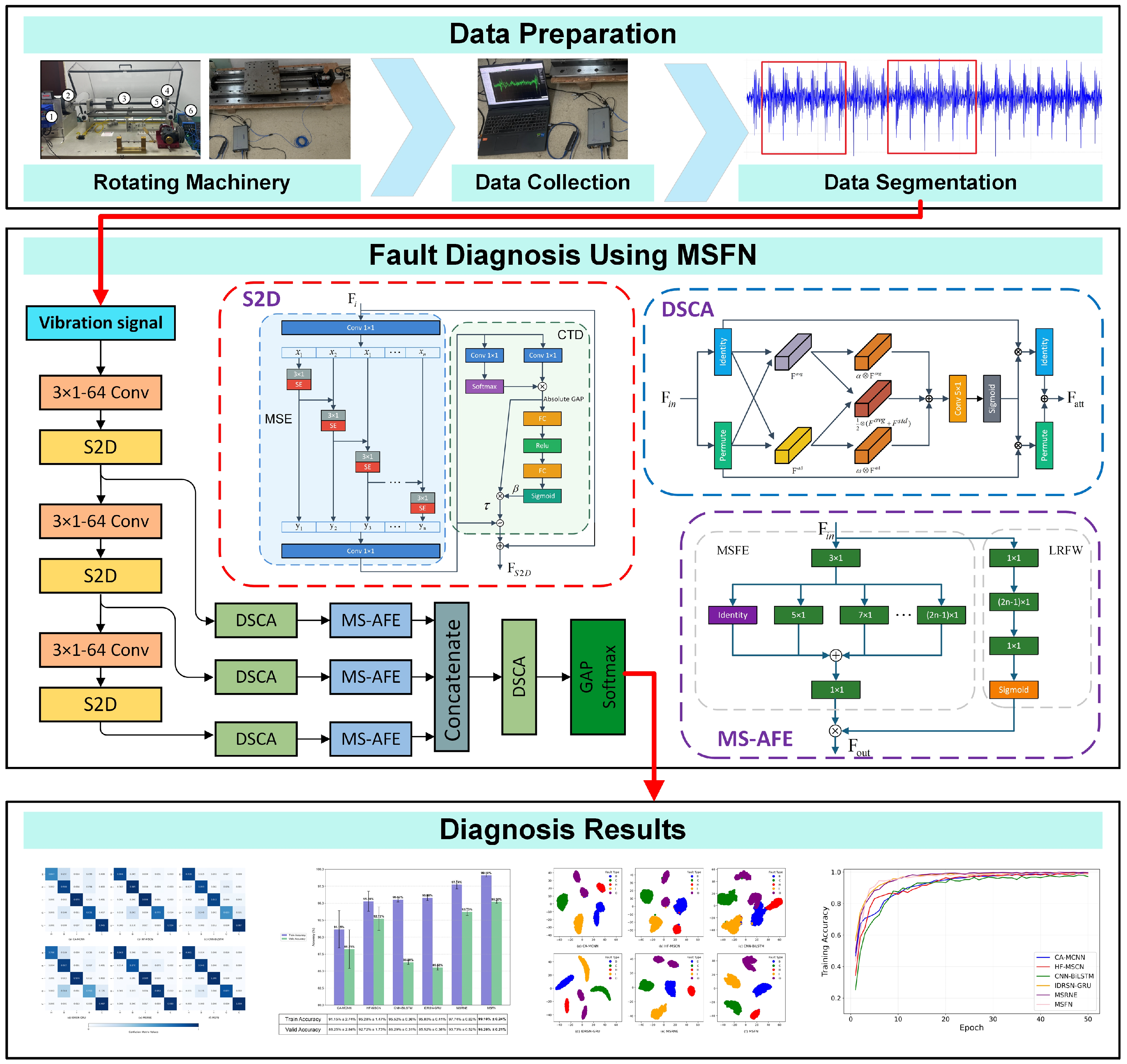
To address the challenges mentioned above, this study proposes a novel CNN-based fault diagnosis model—MSFN—to achieve efficient fault identification of rolling bearings in CNC machine tool feed systems. The main innovations and contributions of this research are as follows:
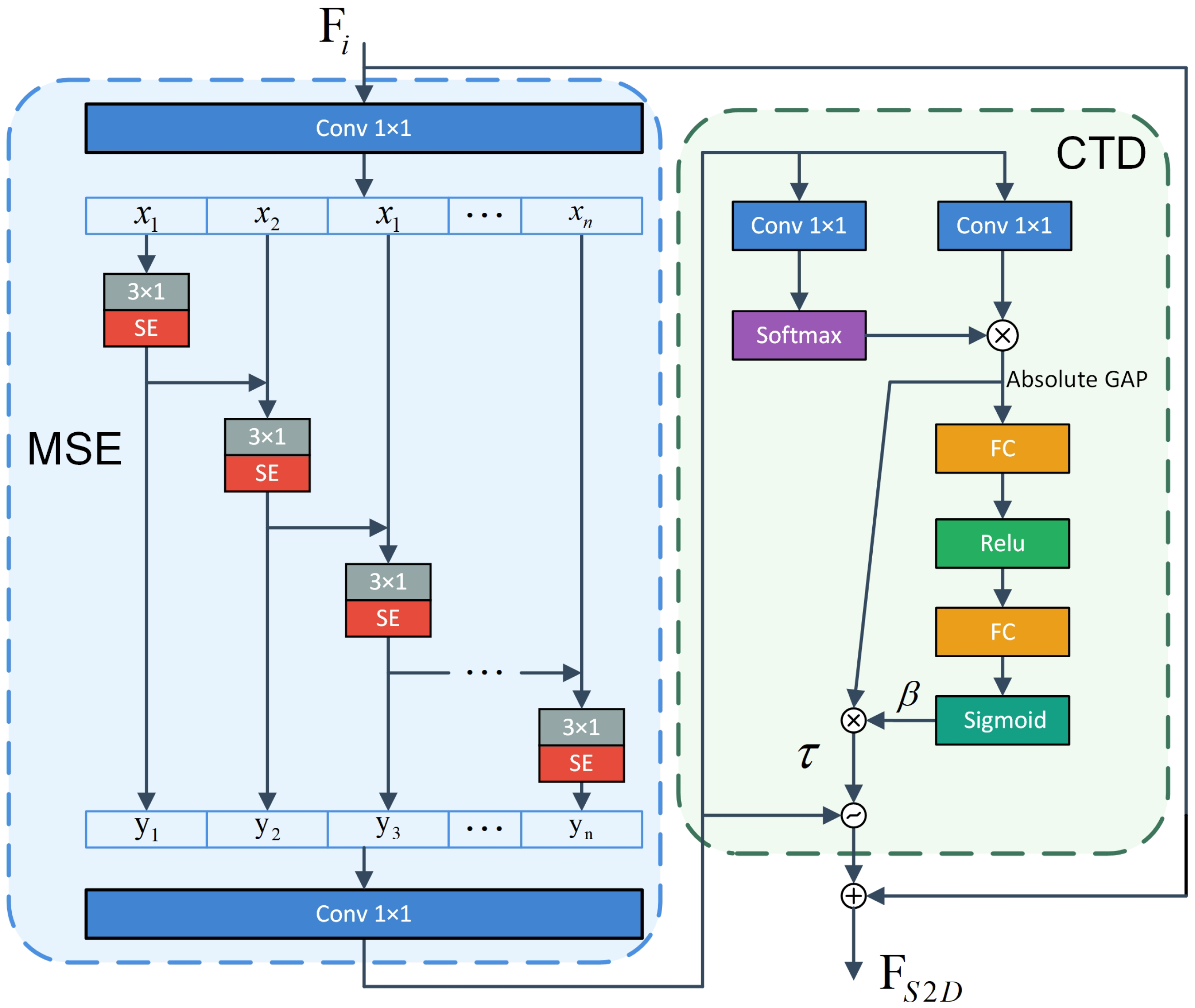
An S2D module is introduced to achieve multi-scale feature extraction through hierarchical cascading and implement feature selection using a channel attention mechanism, enhancing the ability of multi-scale feature representation.
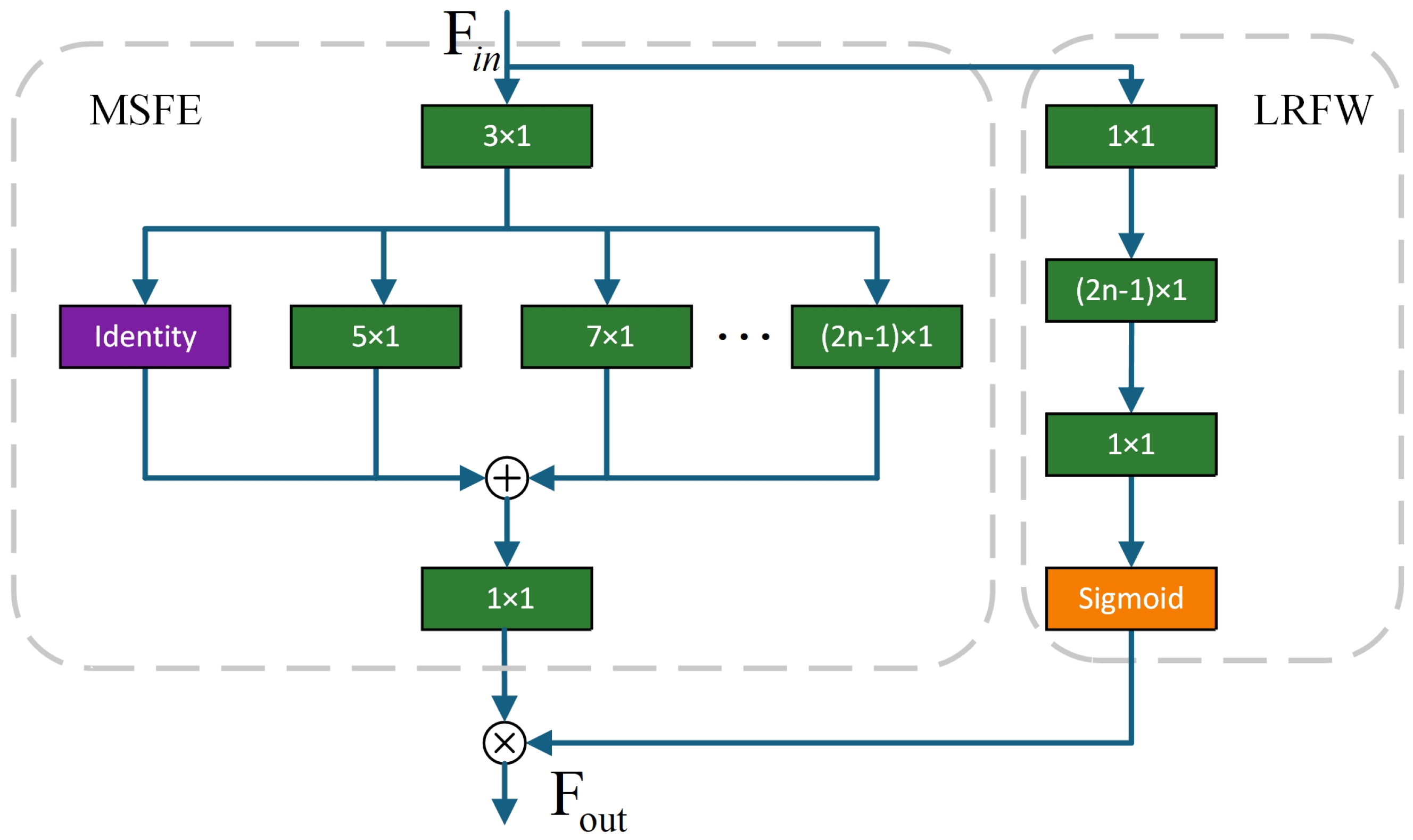
An MS-AFE module is introduced to strengthen the periodic characteristics of fault signals, enhancing the adaptability of the model under varying load and speed conditions.
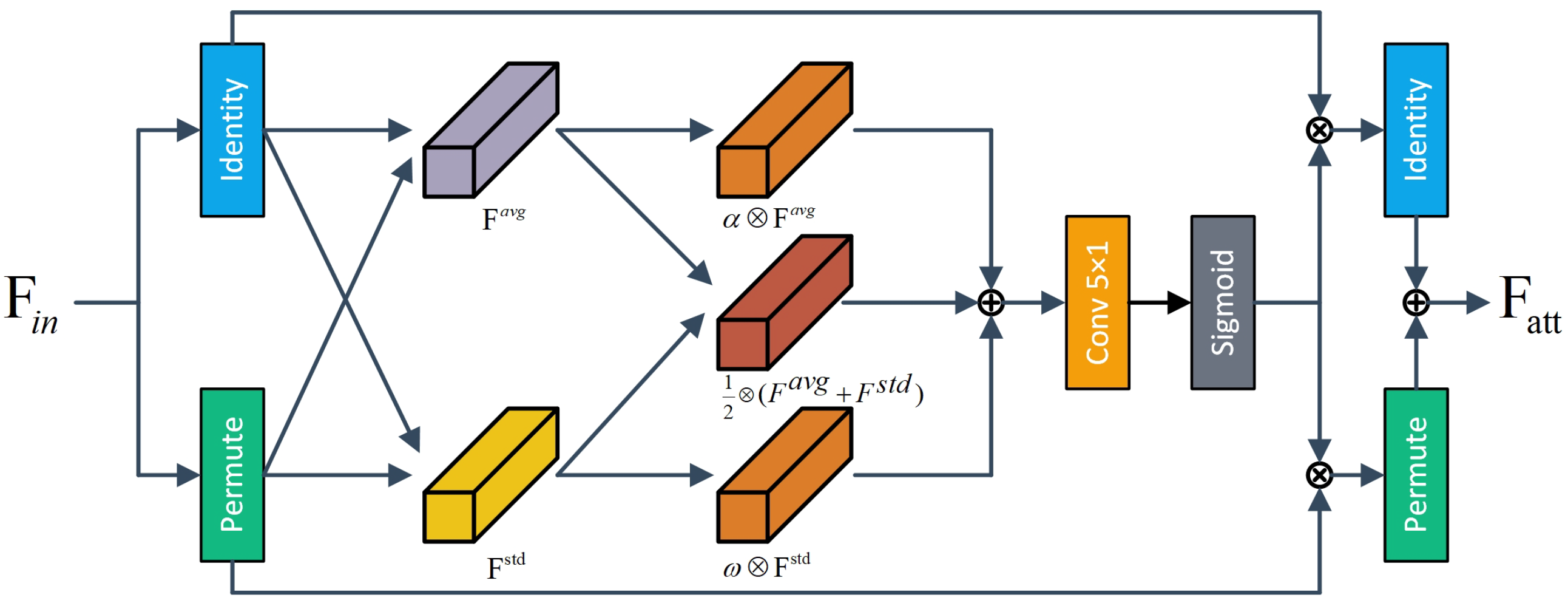
A DSCA module is designed to further improve the representation of fault features using a two-dimensional cooperative attention mechanism, thus enhancing the robustness and generalization capabilities of the model across different operating conditions.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 provides a detailed description of the proposed MSFN, including the architecture and functionality of each core component.
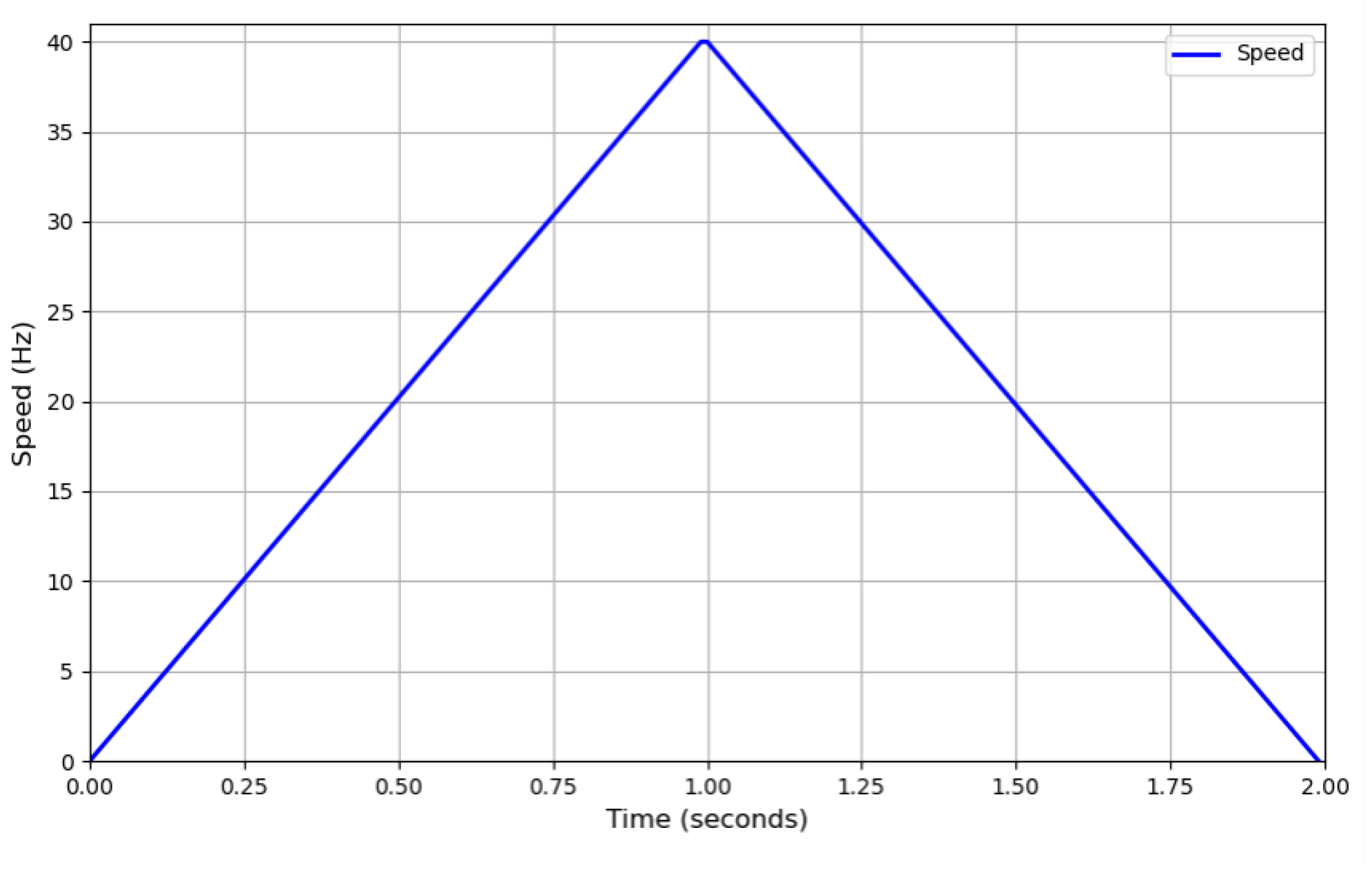
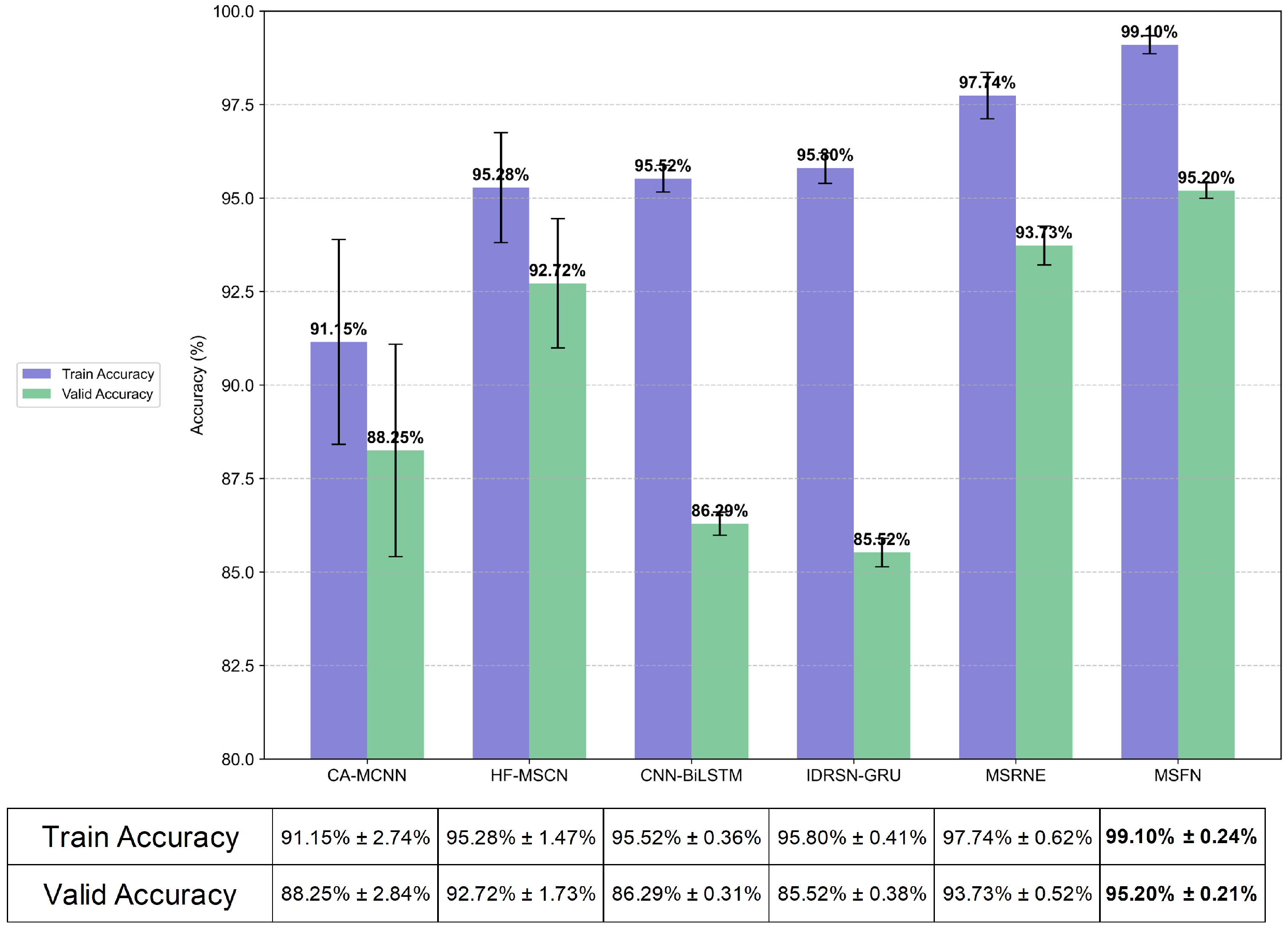
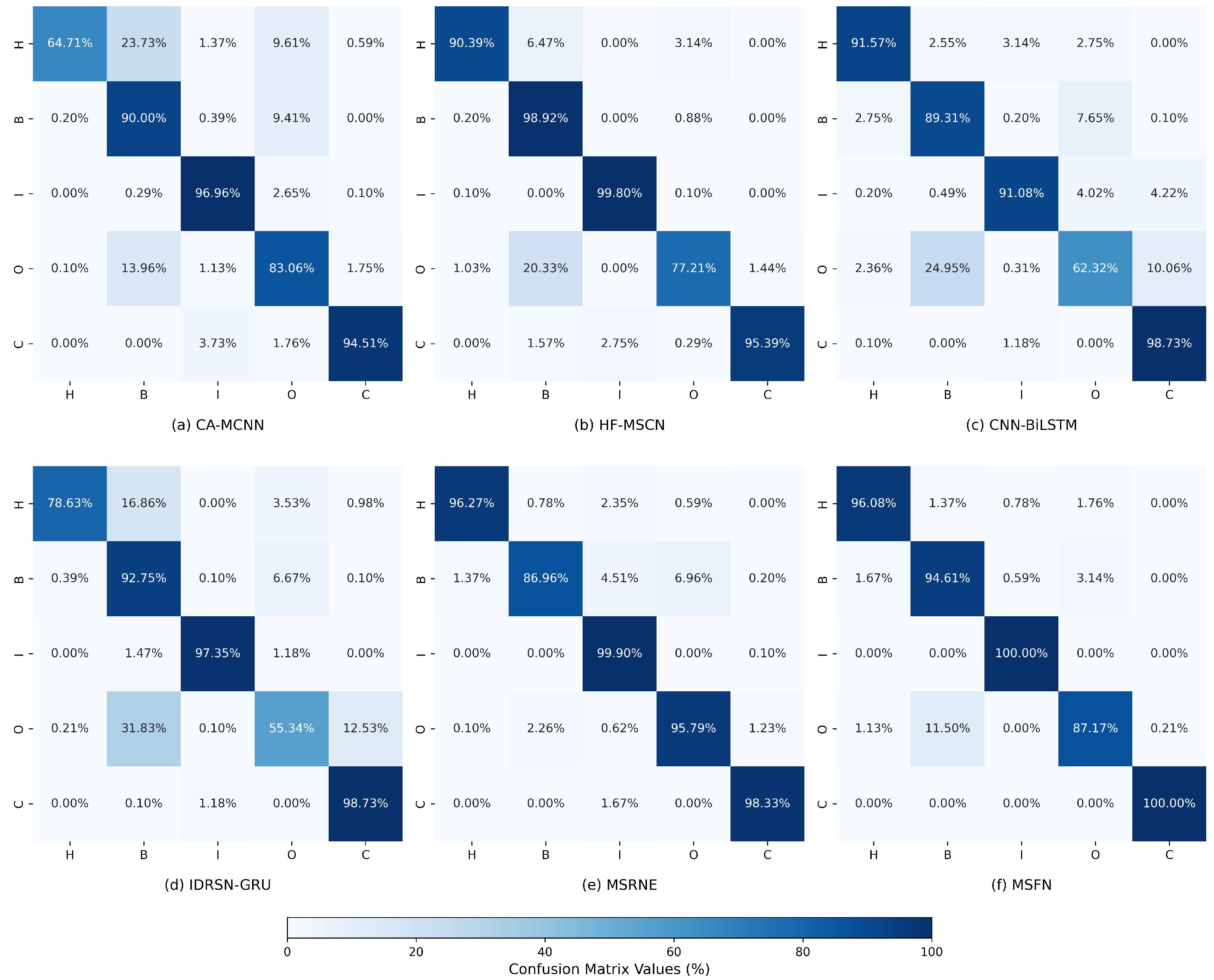
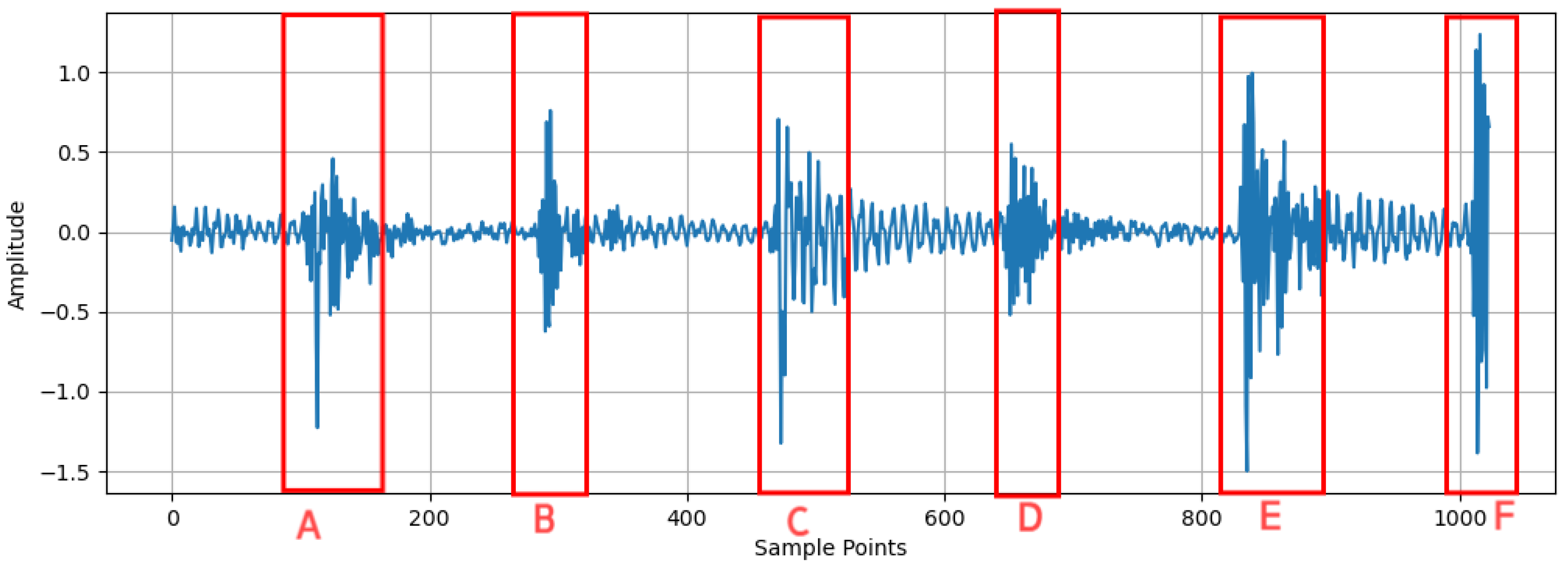
Section 3 assesses the performance of MSFN using publicly available datasets as well as a laboratory-based feed-system dataset. Finally,
Section 4 summarizes the key findings and contributions of this study and discusses potential avenues for future research.