Effects of Grooved Surfaces and Lubrication Media on the Performance of Hybrid Gas Journal Bearings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Methods
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Reynolds Equation
2.3. Gas Film Thickness Equation
2.4. FEM Formulation
2.5. Boundary Conditions
- (1)
- The gas pressure at the outer nodes of the bearings was the same as the ambient pressure.
- (2)
- The lubricating gas flow rate at the inlet of the supply hole was equal to the flow through the constant-flow valve restrictor.
- (3)
- The film pressure distribution was periodic in the circumferential direction.
2.6. Solution Procedure
2.7. Bearing Performance Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Verification
3.2. Effects of Different Gases and Grooved Surfaces on Performance Characteristics
3.2.1. Minimum Gas Film Thickness
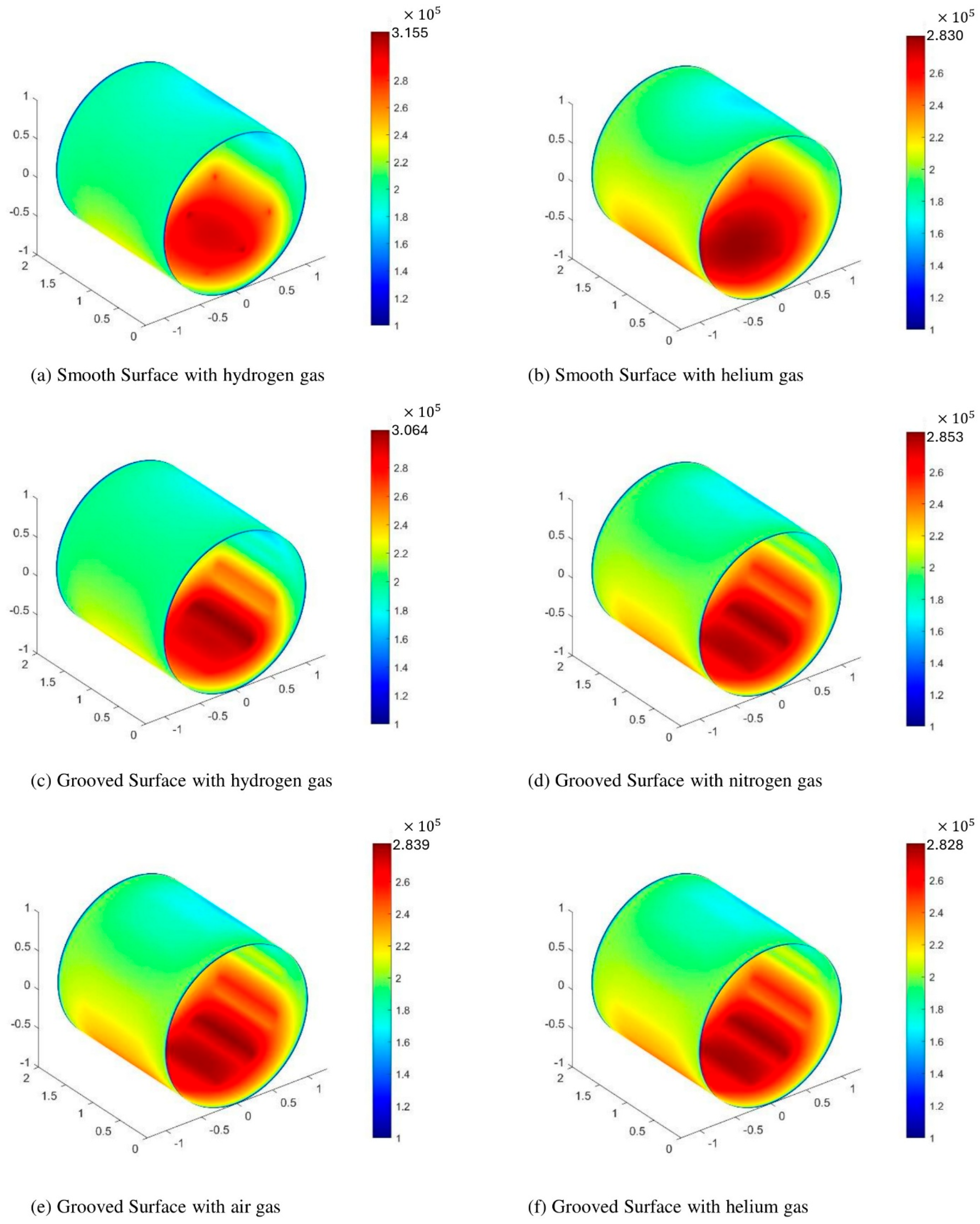
3.2.2. Maximum Gas Film Pressure
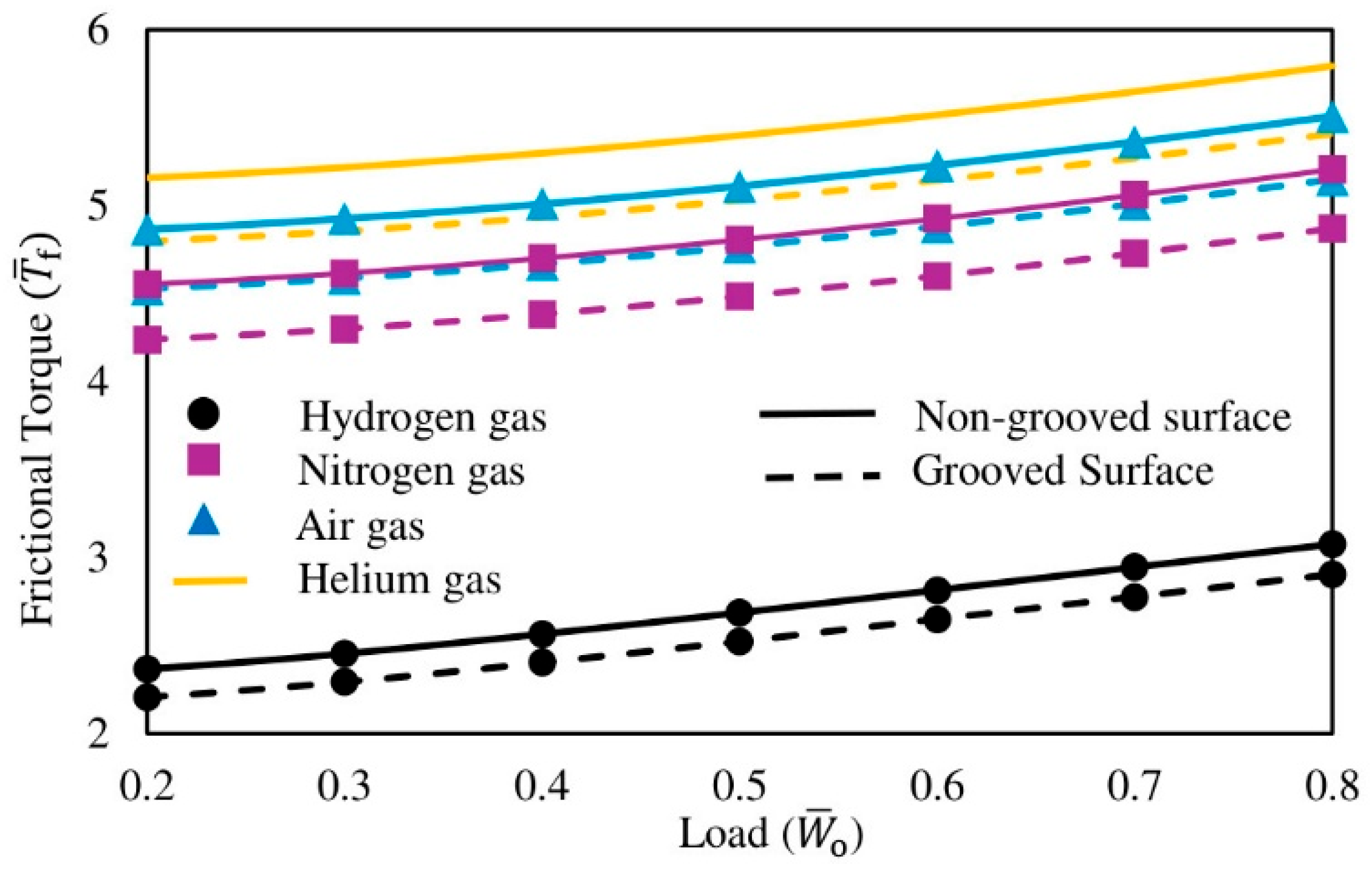
3.2.3. Frictional Torque
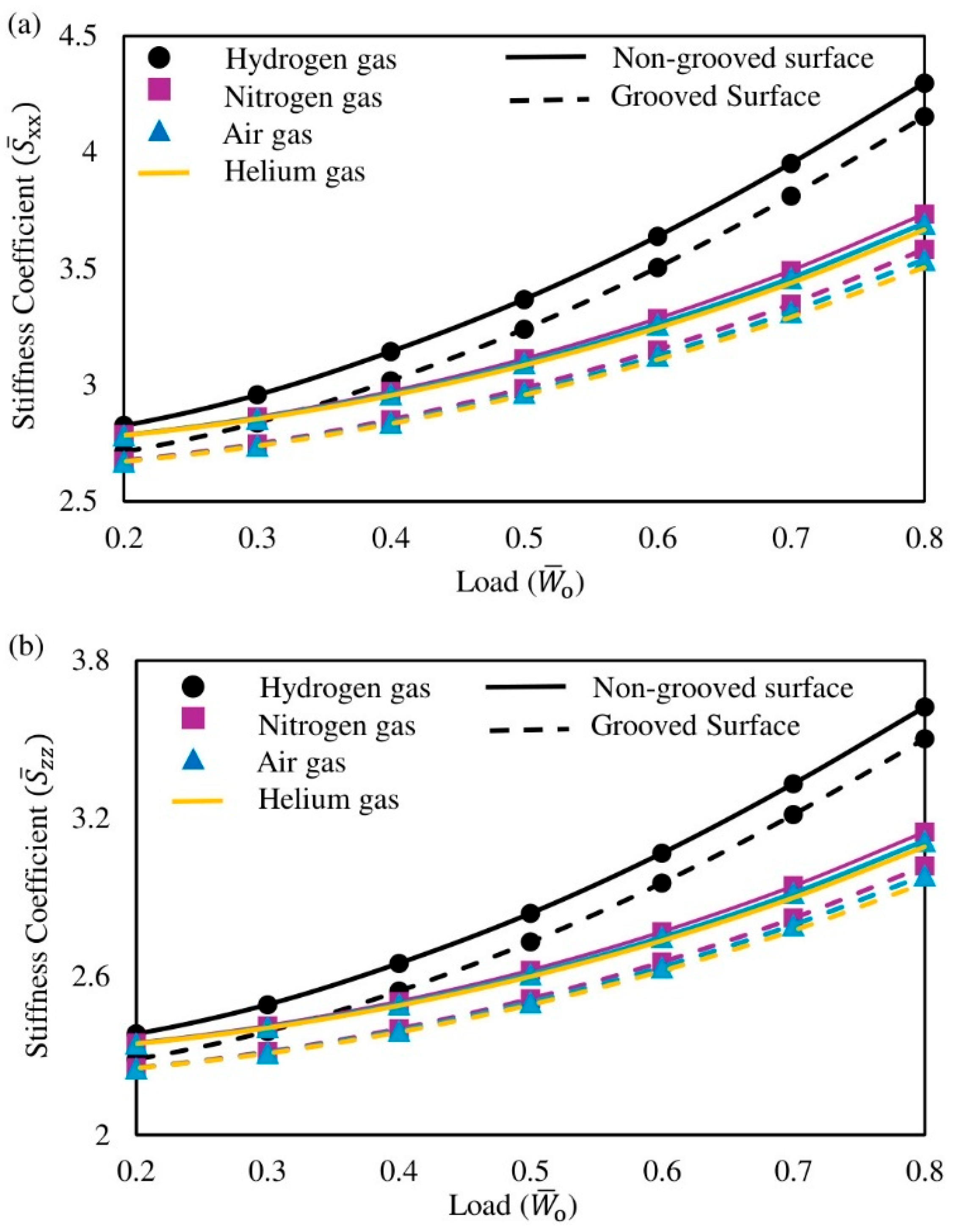
3.2.4. Stiffness Coefficients
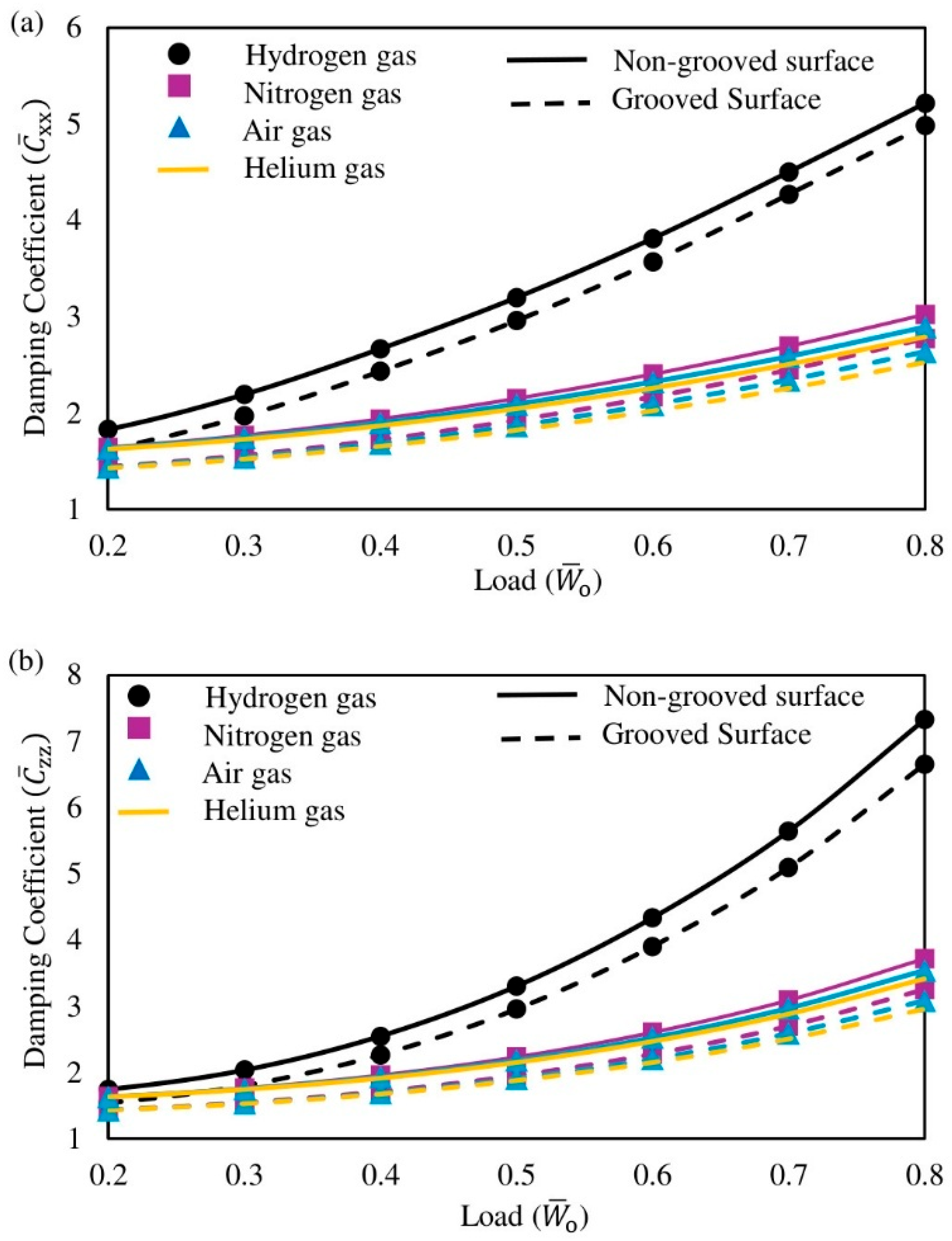
3.2.5. Damping Coefficients
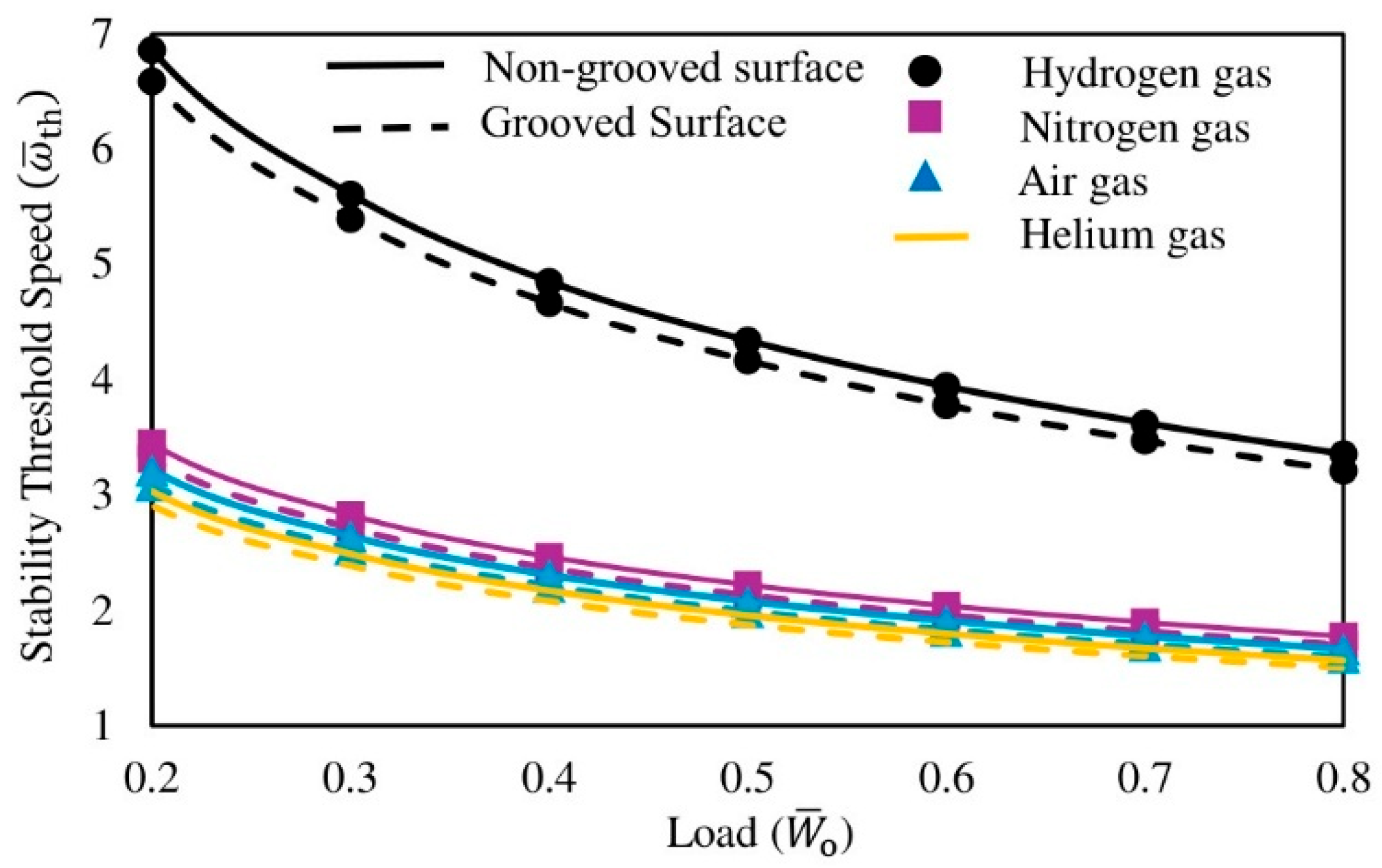
3.2.6. Stability Threshold Speed
4. Conclusions
- Modeling fidelity supports robust parameter studies: The validated FEM framework with constant-flow restrictors provides reliable trends for film thickness, pressure distribution, torque, stiffness/damping, and stability, enabling systematic design exploration. Mesh independence and convergence criteria ensure that observed effects stem from physical parameter variations rather than numerical artifacts.
- Gas selection dominates the performance envelope: Hydrogen-lubricated bearings yield the lowest frictional torque and higher dynamic coefficients. Helium favors a larger minimum film thickness. Lower viscosity reduces shear stress (lower torque) but requires higher peak pressures at a smaller film thickness to sustain the load. Higher viscosity increases hydrodynamic support and film thickness, moderating peak pressures.
- The pressure–film coupling sets the load support and peak pressure: For a given load, gases with lower viscosities develop higher local peak pressures at reduced minimum film thicknesses, and higher-viscosity gases distribute pressure more broadly with thicker films. This is because the compressible Reynolds balance links viscosity and film geometry to pressure gradients, and reduced viscous resistance intensifies pressure build-up where clearance is smallest.
- Surface texturing introduces a friction–stability trade-off: Circumferential grooves reduce frictional torque but also reduce stiffness, damping, and the stability threshold speed as grooves act as micro-reservoirs that increase the local nominal film thickness and lower shear, yet they diminish the effective load-bearing land and alter pressure gradients, reducing dynamic support.
- Design implication: Pairing low-viscosity gases with carefully parameterized grooves is advantageous where torque reduction and efficiency are paramount. Non-grooved designs with lower-viscosity gases are preferable when stiffness, damping, and stability margins are critical. Thereby, application-specific weighting of shear losses versus dynamic coefficients should guide the selection of gas properties and groove geometry.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Damping coefficients, N s/mm | |
| Gas film reactions, N | |
| Resultant gas film reaction, N | |
| External load, N | |
| L | Bearing length, mm |
| R | Bearing radius, mm |
| U | Velocity, m/s |
| Shape functions | |
| Stiffness, N/mm | |
| Frictional torque, N-mm | |
| c | Radial clearance, mm |
| Groove depth, mm | |
| Groove length, mm | |
| Groove reference length, mm | |
| Nominal gas film thickness, mm | |
| Journal center, Bearing center | |
| Supply pressure, gas film pressure, N/mm2 | |
| t | Time, s |
| Groove width, mm | |
| Journal center coordinates | |
| Dimensionless parameters | |
| ( μ) | |
| , | |
| Greek symbols | |
| Rotational speed of journal, rad-s−1 | |
| Aspect ratio, | |
| Bearing number | |
| Subscripts and superscripts | |
| Bearing, journal | |
| Dimensionless terms | |
| First-order and second-order derivatives to time | |
References
- Nikolakopoulos, P.G.; Bompos, D.A. Experimental Measurements of Journal Bearing Friction Using Mineral, Synthetic, and Bio-Based Lubricants. Lubricants 2015, 3, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Effect of Groove Structure on Lubrication Performance of Water-Lubricated Stern Tube Bearings. Lubricants 2023, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, C.; Çil, M.A. A study on hydrogen, the clean energy of the future: Hydrogen storage methods. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Guenat, E.; Schiffmann, J. A Review of Grooved Dynamic Gas Bearings. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2020, 72, 010802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Lan, Y.; Bosiakov, S.; Zhuravkov, M.; He, T.; Xia, Y.; Lyu, Y. Investigation on the Coupling Effect of Bionic Micro-Texture Shape and Distribution on the Tribological Performance of Water-Lubricated Sliding Bearings. Lubricants 2025, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elberry, A.M.; Thakur, J.; Santasalo-Aarnio, A.; Larmi, M. Large-scale compressed hydrogen storage as part of renewable electricity storage systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 15671–15690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M. Liquid Hydrogen: A Review on Liquefaction, Storage, Transportation, and Safety. Energies 2021, 14, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Fujioka, H.; Okano, K. Cost analysis of stable electric and hydrogen energy supplies derived from 100% variable renewable resources systems. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhar, U.; Hemmes, K.; Woudstra, T. Exploring the Possibility of Using Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell for the Flexible Coproduction of Hydrogen and Power. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiang, M.; Ding, W.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y. Numerical study on static performance of hydrodynamic bearing in high-speed liquid hydrogen centrifugal pump. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utlu, Z.; Karabuga, A. Conventional and enhanced exergy analysis of a hydrogen liquefaction system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-M.; Kim, B.H.; Choi, B. Hydrogen liquefaction process with Brayton refrigeration cycle to utilize the cold energy of LNG. Cryogenics 2020, 108, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lim, H.; Kim, B.; Jeon, B.; Park, J. Rotordynamic Analysis and Operating Test of an Externally Pressurized Gas Bearing Turbo Expander for Cryogenic Applications. Lubricants 2023, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hou, Y. Numerical and experimental studies on stability of cryogenic turbo-expander with protuberant foil gas bearings. Cryogenics 2018, 96, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Kang, Y.; Hwang, R.-M.; Shyr, S.-S. Influence of orifices on stability of rotor-aerostatic bearing system. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.; Rowe, W.B. Dynamic force coefficients and the mechanism of instability in hydrostatic journal bearings. Wear 1973, 23, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, X.; Ren, Y. Performance analysis of aerostatic journal micro-bearing and its application to high-speed precision micro-spindles. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-H. Performance analysis of high-speed spindle aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S.; Zhang, G.H.; Xu, H.J. Performance analysis of rotating externally pressurized air bearings. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2008, 223, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z. A flow-difference feedback iteration method and its application to high-speed aerostatic journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 2015, 84, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, K.; Chen, S.; Ding, H.; Fu, H. Computational design and analysis of aerostatic journal bearings with application to ultra-high speed spindles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 231, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. Numerical analysis and experimental research on the angular stiffness of aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchehit, B.; Bou-Saïd, B.; Tichy, J. Towards Ecological Alternatives in Bearing Lubrication. Lubricants 2021, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Du, Q.; Huang, S.; Yan, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, S.; Zhang, C. Influence Factor Analysis and Uncertainty Quantification of the Static Characteristics of Organic Working Fluid Aerodynamic Journal Bearings Considering Microscale Effect. Lubricants 2025, 13, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizmer, V.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. A Laser Surface Textured Parallel Thrust Bearing. Tribol. Trans. 2003, 46, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I.; Shinkarenko, A. Improving Tribological Performance of Piston Rings by Partial Surface Texturing. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropper, D.; Wang, L.; Harvey, T.J. Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured surfaces: A review of modeling techniques and key findings. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Hsu, S.M.; Costa, H.L. A critical assessment of surface texturing for friction and wear improvement. Wear 2017, 372–373, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Almqvist, A.; Rosenkranz, A.; Fillon, M. Numerical micro-texture optimization for lubricated contacts—A critical discussion. Friction 2022, 10, 1772–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirs, G.G. The Load Capacity and Stability Characteristics of Hydrodynamic Grooved Journal Bearings. ASLE Trans. 1965, 8, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Khonsari, M.M. An Experimental Investigation of Dimple Effect on the Stribeck Curve of Journal Bearings. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, C.I.; Efstathiou, E.E.; Nikolakopoulos, P.G.; Kaiktsis, L. Geometry Optimization of Textured Three-Dimensional Micro-Thrust Bearings. J. Tribol. 2011, 133, 041702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Jin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xiao, M. Study on influencing factors of lubrication performance of water-lubricated micro-groove bearing. Tribol. Int. 2019, 129, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, A.K.; Sahu, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Marian, M. Slot-entry herringbone grooved hybrid conical bearings under piezo-viscous lubrication. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 305, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizmer, V.; Kligerman, Y. A Laser Surface Textured Journal Bearing. J. Tribol. 2012, 134, 031702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P.; Koskinen, J.; Varjus, S.; Gerbig, Y.; Haefke, H.; Georgiou, S.; Zhmud, B.; Buss, W. Microlubrication effect by laser-textured steel surfaces. Wear 2007, 262, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, W.; Li, L.; Xia, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Tan, C. Enhancing the wettability for 4043 aluminum alloy on 301L stainless steel via chemical-etched surface texturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 305, 117577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y.; Du, X. Regulation of surface texturization through copper-assisted chemical etching for silicon solar cells. Sol. Energy 2020, 201, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Raphaelson, S.; Ehmann, K.; Wang, Q.J.; Lin, C. Surface Texturing of Tribological Interfaces Using the Vibromechanical Texturing Method. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2009, 131, 061005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.G.; Ruiz, J.Á.; Azpeitia, D.B.; González, J.I.M.; Fernández, L.G. Friction improvement via grinding wheel texturing by dressing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 4939–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.F.G.; Bottene, A.C.; França, T.V. A novel dressing technique for texturing of ground surfaces. CIRP Ann. 2010, 59, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneau, D.; Huitric, J.; Tournerie, B. Finite Element Analysis of Grooved Gas Thrust Bearings and Grooved Gas Face Seals. J. Tribol. 1993, 115, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Yau, H.-T.; Jang, M.-J.; Yeh, Y.-L. Theoretical analysis of the non-linear behavior of a flexible rotor supported by herringbone grooved gas journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Huang, W.L.; Chen, Y.P. Design of the aerostatic linear guideway with a passive disk-spring compensator for PCB drilling machine. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, T.; To, S. Improvement on load performance of externally pressurized gas journal bearings by opening pressure-equalizing grooves. Tribol. Int. 2014, 73, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F. Effect of herringbone groove structure parameters on the static performance of gas foil herringbone groove thrust bearings. Tribol. Int. 2023, 177, 107979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, C.B.; Sharma, S.C. Analysis of textured multi-lobe non-recessed hybrid journal bearings with various restrictors. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 145, 258–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinhasan, R.; Wadhwa, S.; Singh, D. Dynamic performance of non-circular gas bearings. Period. Polytech. Mech. Eng. 1984, 28, 367–389. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Ye, Y.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, C. Numerical Analysis on the Static Performance of Gas Journal Bearing by Using Finite Element Method. Nanomanuf. Metrol. 2024, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, K.-Q.; Wang, X.-L. On the non-linear stability of self-acting gas journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Tomar, A.K. Effect of bearing shell deformation and ER fluid behavior on two-lobed slot-entry hybrid journal bearing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2024, 238, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosar, A.; Klemenc, J.; Nagode, M.; Oman, S. On the importance of the experimental setup design in hydrodynamic journal bearing friction measurement. Tribol. Int. 2024, 197, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Schmid, S.R.; Jacobson, B.O. Fundamentals of Fluid Film Lubrication; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, K.; Tomar, A.K.; Sharma, S.C. Effect of textured shapes on slot entry hybrid conical journal bearing with ER lubricant behavior. Tribol. Trans. 2024, 67, 615–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
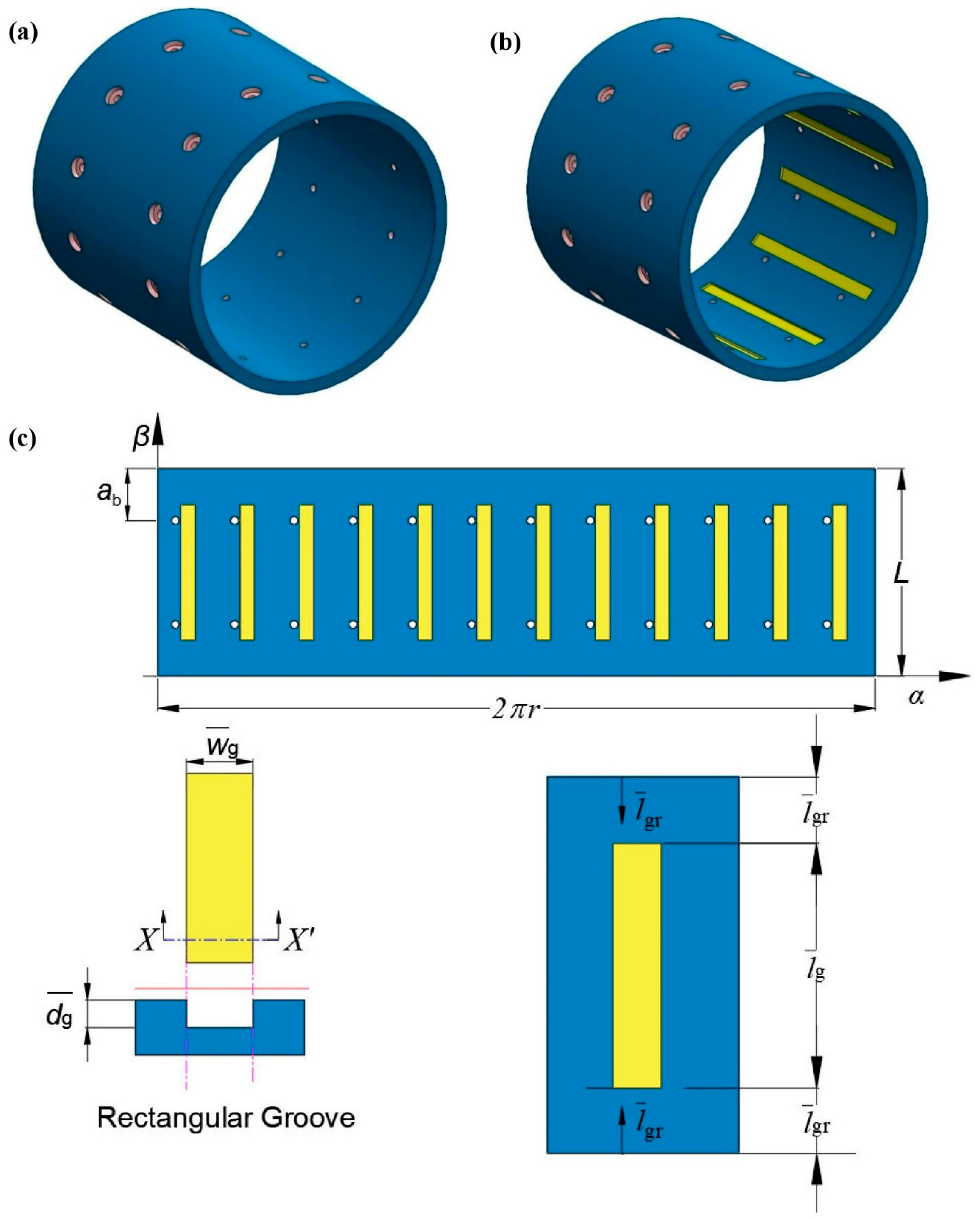
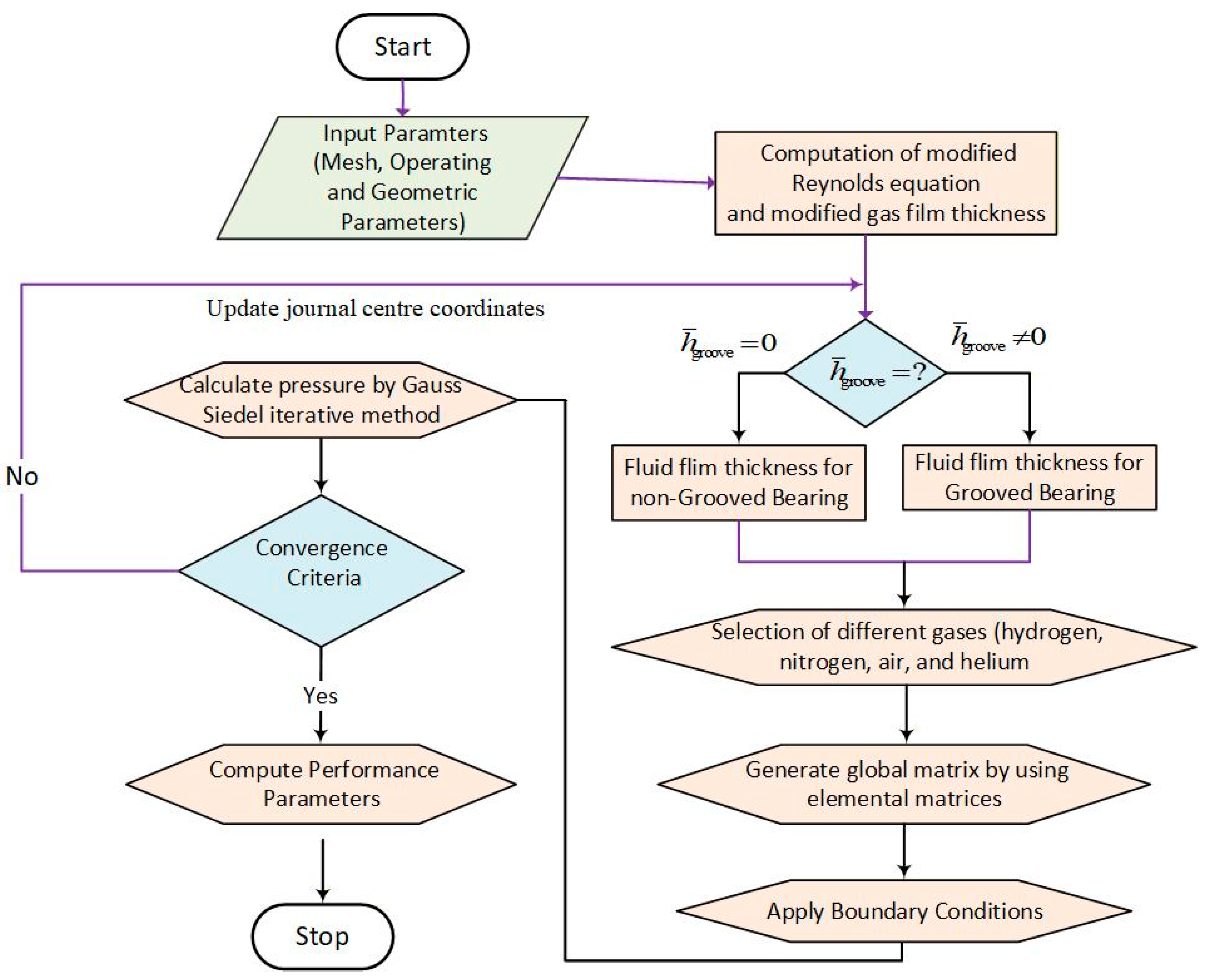

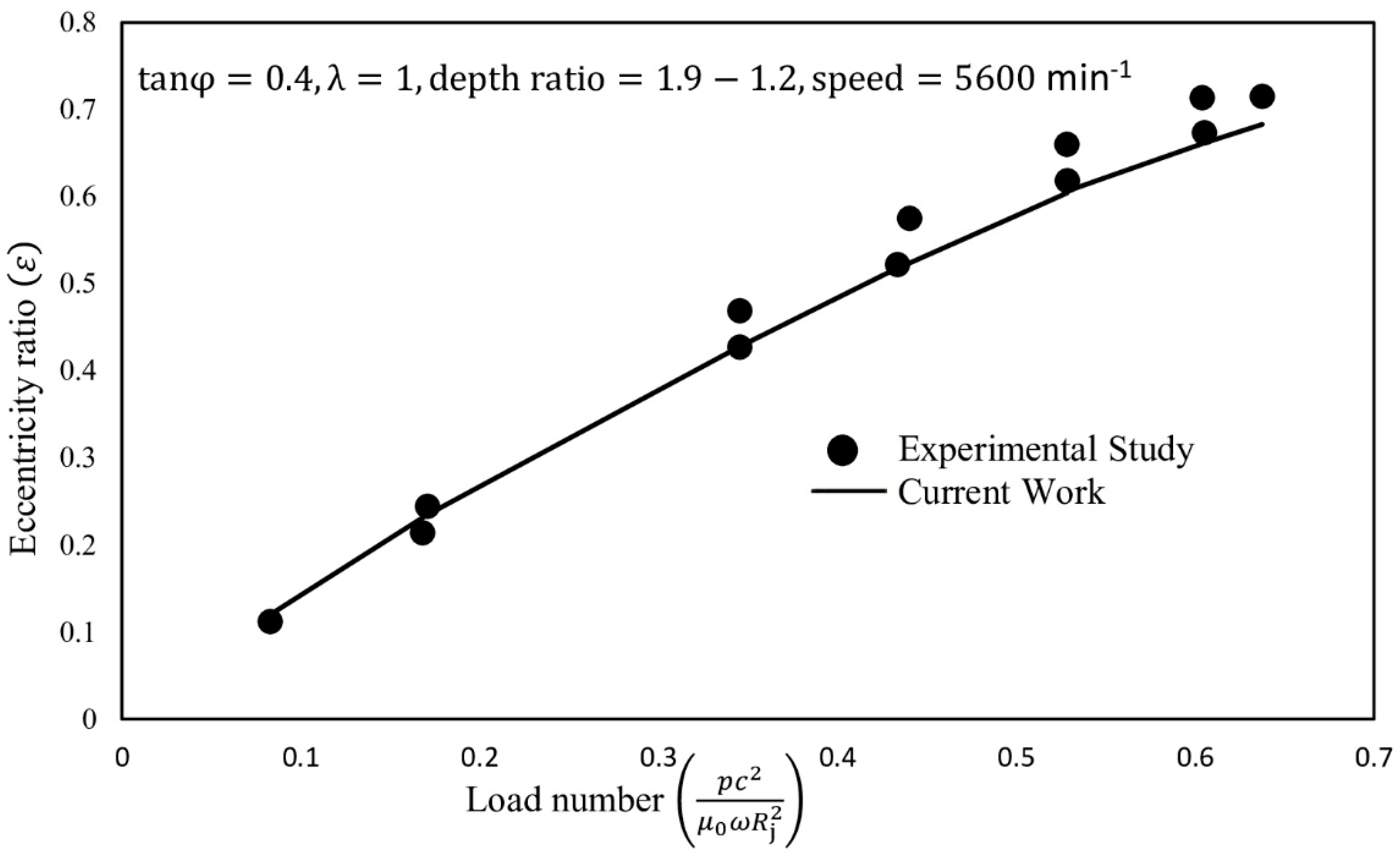
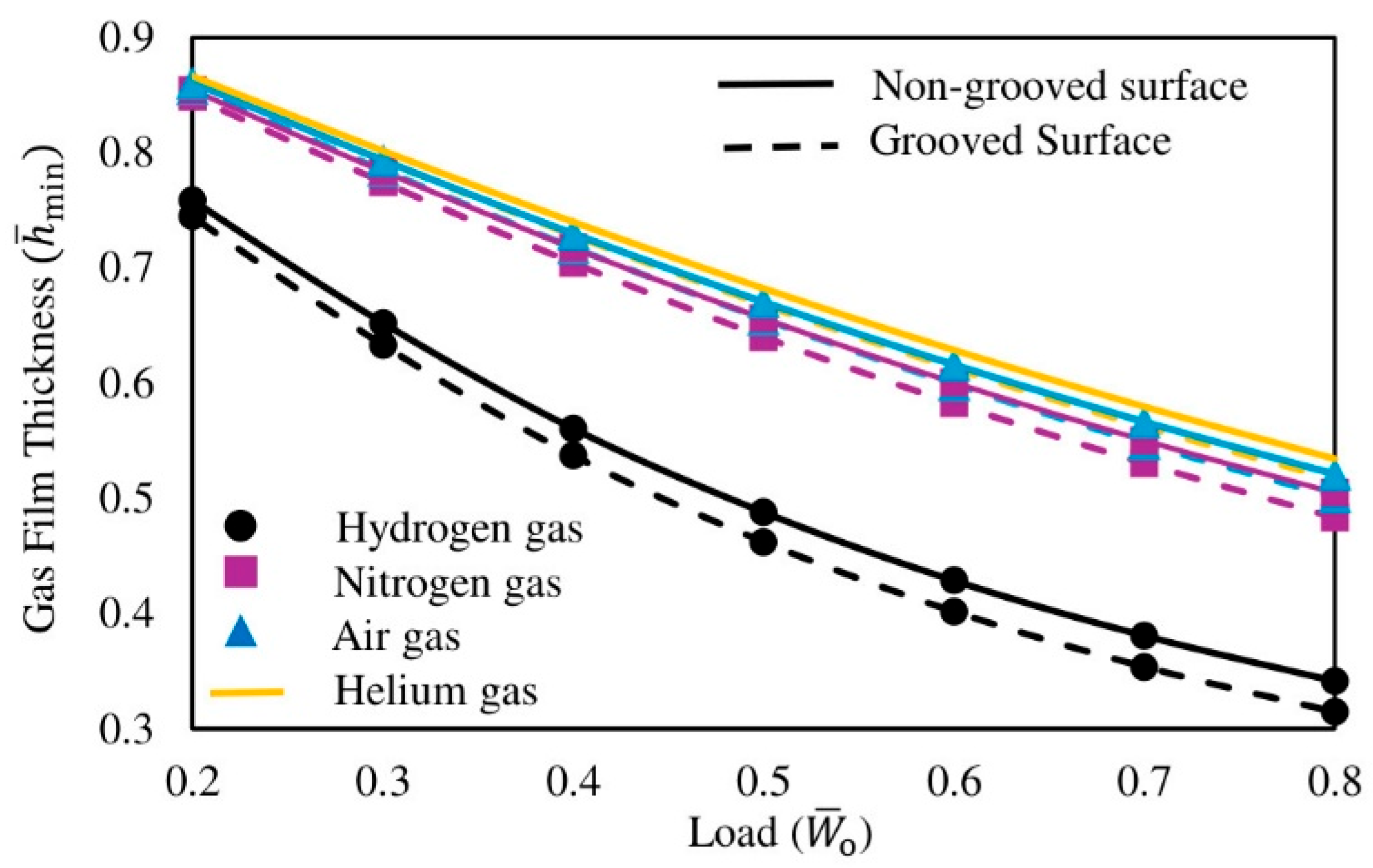
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Bearing radius (R) | 20 mm |
| Land width ratio | 0.25 |
| Clearance (c) | 20 μm |
| Supply pressure | 4 MPa |
| Concentric design pressure ratio | 0.5 |
| Speed | 80,000 min−1 |
| No. of supply holes in a row | 12 |
| No. of grooves | 12 |
| No. of supply hole rows | 2 |
| Gases | Hydrogen, nitrogen, air, and helium |
| Viscosity of lubricating gases | Hydrogen: 0.880; nitrogen: 1.730; air: 1.846; and helium: 1.960; ×10−5 Pa-s |
| Groove width | 0.4 |
| Groove depth | 1 |
| Groove reference length | 0.25 |
| Λ | (Reference Work) | (Present Work) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0884 | 0.0879 |
| 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1804 | 0.1798 |
| 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.3976 | 0.3957 |
| 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7332 | 0.7273 |
| 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.6104 | 1.5778 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.34 | 0.3378 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.6948 | 0.6926 |
| 3 | 0.4 | 1.5208 | 1.5173 |
| 3 | 0.6 | 2.8456 | 2.8193 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 6.1456 | 6.0176 |
| 12 | 0.1 | 0.5148 | 0.5123 |
| 12 | 0.2 | 1.0728 | 1.0703 |
| 12 | 0.4 | 2.54 | 2.5325 |
| 12 | 0.6 | 5.0828 | 5.0471 |
| 12 | 0.8 | 11.336 | 11.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomar, A.K.; Sahu, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Marian, M. Effects of Grooved Surfaces and Lubrication Media on the Performance of Hybrid Gas Journal Bearings. Lubricants 2025, 13, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13110492
Tomar AK, Sahu K, Sharma SC, Marian M. Effects of Grooved Surfaces and Lubrication Media on the Performance of Hybrid Gas Journal Bearings. Lubricants. 2025; 13(11):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13110492
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomar, Adesh Kumar, Krishnkant Sahu, Satish C. Sharma, and Max Marian. 2025. "Effects of Grooved Surfaces and Lubrication Media on the Performance of Hybrid Gas Journal Bearings" Lubricants 13, no. 11: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13110492
APA StyleTomar, A. K., Sahu, K., Sharma, S. C., & Marian, M. (2025). Effects of Grooved Surfaces and Lubrication Media on the Performance of Hybrid Gas Journal Bearings. Lubricants, 13(11), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13110492







