Abstract
This research presents the effects of carbon nanotori structures (CNst) dispersed as reinforcement for metal-working and metal-forming lubricants. Synthetic (SL) and deep drawing (DD) nanolubricants were prepared following a two-step method at 0.01 wt.%, 0.05 wt.%, and 0.10 wt.% filler fractions. Slight increases in viscosity (<6%) for nanolubricants were observed as filler fraction was increased through various measured temperatures. Tribological behavior of nanolubricants displayed superb improvements under antiwear and extreme pressure conditions. The load carrying capacity (poz) increased by 16% and 22% at merely 0.01 wt.% CNst reinforcement and up to 73% and 107% at 0.10 wt.% filler fraction for SL and DD nanolubricants, respectively, compared to conventional materials. Additionally, at 0.10 wt.% wear scar evaluations showed a highest benefit of 16% and 24%, for SL and DD nanolubricants, respectively. This enhancement is attributed to diverse mechanisms such as rolling/sliding and load bearing effects, tribofilm formation, and CNst tribosintering behavior (at high pressures) onto metallic surfaces due to nanostructures size and morphology and their interlayer relationship among conventional lubricants.
1. Introduction
Sustainable and environmentally friendly materials are being developed and incorporated to diverse industrial metal-mechanic manufacturing processes such as grinding, milling, turning, stamping, punching, and hydroforming, among others [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. For lightweight purposes, thinner materials with higher mechanical properties are used in fields such as automotive and agriculture, among others. These materials require higher processing loads, needing a more robust performance of lubrication due to higher friction and wear among tooling and base substrates.
The incorporation of diverse nanostructures to cutting fluids and lubricants for plastic deformation processes has demonstrated great benefits, particularly for improving the efficiency, quality, and production in industrial operations. Through the comparison of tribological properties, researchers have been able to determine effective methods of improving lubricants under specific conditions such as antiwear (AW) and extreme pressures (EP). According to diverse studies, the most relevant advantages and improvements of using nanostructures as additives are: coefficient of friction (COF) and wear reduction, hence, decreasing machining operations cutting forces as well as energy consumption [9,10]. Another critical aspect is the improvement on the surface finishing of the produced components, which has a great impact on quality and post-processing. Tooling and machinery components are also benefited by using nanofluids and nanolubricants, such as also acting as thermal transport of the generated heat by metal-to-metal contact [11,12,13,14].
The reinforcing role of nanostructures in decreasing friction, wear, and improving plastic deformation manufacturing processes [14,15,16] attracts attention and substantial interest for its micro-rolling effect, self-repairability, polishing effect, and tribolayer formation [10,17]. These nanostructures, due to their intrinsic physico-chemical characteristics, convey desired performance characteristics to the conventional materials [16]. Due to the size and morphology of nanostructures, they possess high surface energies; thus, these are susceptible to agglomerate and sediment. The filler fraction of these nanostructures also contributes to this phenomenon, which is very important for machinery and devices.
Lubrication mechanisms using carbonaceous structures such as single wall/multiwall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs/MWCNTs), graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs), carbon fibers (CFs), nanodiamonds (NDs), carbon nano-onions, and carbon nanotori structures (CNst) have attracted significant attention as potential lubrication reinforcement for conventional fluids and lubricants [18,19,20,21,22,23] due to their good corrosion behavior, superb mechanical properties, high thermal conductivity, and excellent lubricating properties. Widely studied carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have demonstrated superb enhancements in tribological behavior when incorporated as additives or reinforced solid material of diverse systems [24], showing enhancement with diverse mechanisms such as tribofilm formation, rolling/sliding, and load bearing effects [7,21,25].
According to Jansson et al. [26] carbon nano-allotropes structures may contribute to the tribochemical layer creation through their chemical reactivity, rather than through their surface functional groups [26]. Conventional fluids and lubricants depend on their intrinsic characteristics such as chemical properties and structural parameters, among others. Ali et al. observed outstanding improvements in wear and friction reduction for diverse fluids and lubricants by adding carbon and graphene nanostructures [27].
Tribological effects of graphene nanoflakes-blended within engine oil were studied by Rasheed et al. [28]. At merely 0.01 wt.% graphene within conventional engine oil, COF was reduced by 21%. It was also observed that graphene nanostructures also reduce the ring wear over extended hour engine evaluation. Bhaumik et al. [29] observed that adding MWCNTs enhanced the AW characteristics and load-carrying capacity of conventional mineral oil. Wear reduction of 80% was reported for the nanolubricant at 0.05 wt.%. MWCNTs were incorporated as additives for synthetic and mineral oils for metal-working processes. At 0.1 wt.% reinforcement, an enhancement of 21% and 36%, respectively, in the load-carrying capacity was observed [30]. Kumar et al. investigated [31] MWCNTs and SWCNTs as additives in SAE10W40 motor oil. Using these reinforcements, worn scar diameter was reduced by 67% and 38%, respectively. The average COF was also decreased by 48% and 56%, respectively. One important aspect is that nanolubricants viscosity raised by increasing the CNTs filler fraction. Kumar et al. concluded that the AW mechanism is due to the accumulation of SWCNTs and MWCNTs on the material’s surface, reducing shearing stress and improving the tribological performance. Mohamed et al. [32] demonstrated that 1.0 wt.% of CNTs incorporated to lithium grease contributed to improvements in EP performance and load-carrying capacity by 52%, and COF reduction by 82%. Other research on commercial greases reinforced with MWCNTs at various filler fractions showed an increase of 10% at 0.05 wt.% [33]. According to Ni et al. [34], this improvement may be due to the flattening behavior of the nanostructures by compression at high pressures, making them move between surfaces similar to a “tank belt”. Hong et al. [35] investigated the behavior of CNTs-based greases within PAO (polyalphaolefin) oil with incorporation of 1.0 wt.% MoS2 and other commercial greases (lithium, calcium, etc.). A COF reduction of 28% was observed for the CNTs-based grease with MoS2, compared to conventional grease.
Another critical aspect of lubrication is the material’s viscosity. The lubricant viscosity is one parameter for optimizing drawing processes, for instance. Viscosity is related to temperature; a system with high temperature reduces the protecting lubricant layer thickness and generates higher pressures. In diverse studies, dynamic viscosity effects with the addition of nanofillers were observed. In general, viscosity of nanofluids and nanolubricants increases with the addition of solid nanostructures; however, the flow characteristics, such as rheology, depend on diverse parameters and operating circumstances [36,37,38,39]. Sadeghinezhad et al. [40] observed that viscosity performance of GNP-based nanofluids depends on temperature and reinforcement filler fraction. In their study, GNP concentrations vary from 0.025 wt.% to 0.1 wt.%. Viscosity increments were 9−38% compared with distilled water, from room temperature to 60 °C. Similar research by Mehrali et al. [40] demonstrated that viscosity behavior of GNP nanofluids was reduced with filler fraction and temperature increase. Similarly, Moghaddam et al. [41] found that viscosity decreases with shear rate and temperature increments. Particularly, viscosity of GNP nanofluid at 0.1 wt.% was increased by 44%, when compared with conventional material. Afrand et al. [42] studied the effects of hybrid MWCNT- SiO2 nanostructures dispersed in concentrations from 0 to 1 vol.% within SAE40 lubricant. Kinematic viscosity was evaluated over a 25 °C to 60 °C temperature range. In general, viscosity increases with a filler fraction raise, and decrease with temperature increase. The maximum observed improvement in viscosity was 37% for the 1.0 vol.% filler fraction at 60 °C. According to Dhanola et al. [43], the reason for the high viscosity of canola-reinforced lubricants is attributed to the incorporation of small amounts of nanoadditives, which attracted each other due to Van der Waals bonding. Furthermore, agglomeration of additives was observed due to the high concentration of reinforcement, leading to an increase in viscosity [43].
A toroidal form of carbon nanotubes, or toroidal “crop circles” as some authors name them, were experimentally observed by Liu et al. [44] while investigating laser-grown single-wall carbon nanotube (SWCNT) materials. Carbon nanotori structures are novel configurations of carbon-based materials considered as prospect objects for many investigations, with similar mechanical properties and characteristics as CNTs. These structures have been emerging as a sustainable option for improving industrial manufacturing processes. Most recently, nanotori structures have been utilized in the evaluation of the thermal dissipation of oil-based and synthetic lubricants [45]. These structures have been found to have excellent properties for reinforcing the enhancing thermal transport behavior of common lubricants. This has led to findings that show carbon nanotori structures significantly improve the thermal transport properties of lubricants [46].
Through the comparison of tribological properties, researchers have been able to determine effective methods of improving lubricants under EP and AW conditions. The primary method is preparing lubricants with additives such as carbon nanotori structures. Examining these properties before and after using different additives can help organizations in several ways such as increasing tool life, reducing energy consumption, and decreasing surface damage and COF. The rest of this paper is dedicated to an in-depth review of topics in tribology, focusing on the previous topics mentioned and how they can benefit individual organizations and the industry.
Due to the superb properties of carbon nanotori (CNst) (high mechanical properties such as elastic modulus ~1 TPa and tensile strengths [19]), their characteristics, and likeness to CNTs, these nanostructures are a suitable alternative to reinforce fluids and lubricants for plastic deformation manufacturing processes. In our work, deep drawing (DD) and synthetic (SL) nanolubricants at various concentrations (by weight) of CNst are evaluated for their effect in tribological performance and viscosity behavior over a temperature range of up to 70 °C (343 K).
2. Materials and Methods
Nanolubricants Preparation
Two common lubricants for metal-working and metal-forming processes (stamping, drawing, and punching, among others) (FUCHS Industry) were investigated (see Table 1). The synthetic lubricant (SL) possesses high lubricity properties which reduces the formation of cracks or severe surface damage (galling). The DD lubricant is a pre-emulsified automotive deep drawing compound. The SL and DD medium viscosity lubricants provide a thin protective and effective layer within the metal sheets and tooling to reduce wear and dissipate the generated heat due to friction. Nanolubricants prepared with carbon nanotori homogenously dispersed structures were obtained by a two-step method in three concentrations: 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10 wt.%, according to the procedure by Kharissova [47].

Table 1.
Material Characteristics.
MWNTs with 35–50 nm in diameter were functionalized with carboxylic acid groups. The next step was to dissolve them in a solution of DiW, potassium permanganate, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and sulfuric acid. The solution was maintained in an ice bath which was magnetically stirred for 60 h. Afterwards, the solution was centrifuged and the supernatant was collected to obtain carbon nanotori from other carbon-based materials. Henceforth, nanotori structures were homogeneously incorporated within SL and DD lubricants at various concentrations.
The zeta-potential of the SL and DD nanolubricants at 0.10 wt.% CNst is found to be ~22 mV and 18 mV, indicating the stability of the nanolubricants.
3. Experimental Details
3.1. Tribological Evaluations
A four-ball tribotester was employed to evaluate the load-carrying capacity of nanolubricants under EP conditions and COF. Tests were conducted according to the ITeE-PIB evaluation methodology to evaluate materials under scuffing criteria [48]. This methodology was chosen since it is more sensitive to EP additives [49], and it is also less material and time consuming.
The evaluation involves the application of a load over a top ball, which acts against a set of three stationary bottom balls on a cylindrical container (oil cup) (Figure 1), which are fully covered with the sample nanolubricant while the upper ball rotates at 500 rpms, at room temperature (~24 °C). The applied load increased progressively up to 7200 N in a period of 18 s. For each set of evaluations, four to six evaluations are performed. Each test consisted of pouring 12.5 mL of nanolubricant over the bottom stationary balls. Ball material is an AISI 52,100 steel grade, 12.7 mm in diameter, with surface roughness average (Ra) of 0.29 µm and 63 HRc. If a seizure occurred, the loading would stop, which means that the protective lubricant film on the balls was damaged or destroyed. This point is where the torque reached 10 N m. Here, the load corresponds to the seizure load (Poz). If the 10 N m frictional torque is not achieved, Poz is considered as the maximum load of 7200 N. After the evaluation is performed, the wear scar diameter (WSD) is measured for the three bottom balls with the aid of an optical microscope. Average values are then employed to determine the load-carrying capacity (poz) of the nanolubricants according to the following equation:

Figure 1.
Schematic of four-ball testing setup.
Furthermore, the nanolubricant with the better tribological characteristics will be obtained with the greater load-carrying capacity. This evaluation helps to determine the EP behavior of nanolubricants, the load, and time at which the loss of lubricant film and wear occur.
3.2. Viscosity Evaluations
Rheological performance of nanolubricants has remarkable importance due to the relationship among shear rates, viscosity, pressure drop, and other characteristics. For instance, viscosity is associated with temperature, pressure, and tribofilm form [25]. Higher viscosity indicates higher flow resistance. Hence, as lubricant viscosity increases, a thicker tribofilm is created [50]. It controls the sealing effect of lubricants and the oil consumption rate. It also determines the ease of machine operation under varying temperature conditions, particularly in cold environments.
Therefore, in our research, the viscosity of nanolubricants is investigated. Shear viscosity evaluations were measured with an ARES rheometer (TA Instruments) with a Couette holder configuration. Temperature-dependent evaluations were obtained at room temperature (~300 K), 30 °C (303 K), 40 °C (313 K), 50 °C (323 K), 60 °C (333 K), and 70 °C (343 K) as well as varying filler fraction as reinforcement of the metal-working and metal-forming lubricants.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Tribological Performance
Improvements in tribological behavior with the incorporation of CNst within SL and DD lubricant systems have been obtained. Figure 2 depicts the scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of worn steel balls for SL and DD nanolubricants at the evaluated concentrations. For SL material, a reduction of 16% in the WSD was shown for the 0.10 wt.% nanolubricant. Furthermore, DD lubricants reflected a 24% improvement at the same filler fraction of CNst. This behavior for both lubricants is mainly associated with the size and morphology of the incorporated carbon nanotori structures, whose sliding-rolling effect acted as a promotor for reducing wear and minimizing COF. Viscosity of base lubricants also played a paramount factor, together with its relationship to applied pressure and temperature, which are responsible for the formed tribolayer thickness and, subsequently, the effect on the tribological properties.
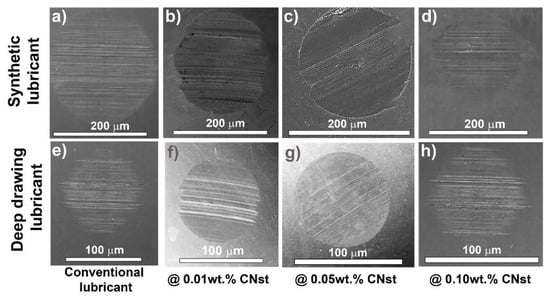
Figure 2.
SEM images of evaluated steel balls wear scars for SL (a–d) and DD (e–h) nanolubricants.
As filler fraction increases, a favorable benefit is reflected in the SL nanolubricants. For instance, at merely 0.01 wt.% an enhancement of 16% is observed, achieving a maximum increment of 73% at 0.10 wt.%. DD nanolubricants displayed a similar effect on load-carrying capacity. Figure 3 shows the effect of the incorporation of CNst at various concentrations. In this case, load carrying capacity was higher than observed for SL lubricants, which is attributed to the affinity of carbon nanotori structures to deep drawing lubricant. Therefore, their dispersion is easy without using additives or surfactants. For instance, at 0.01 wt.% a reduction of 22% was observed, increasing to 53% at 0.05 wt.% and reaching a maximum improvement of 107% at 0.10 wt.%.
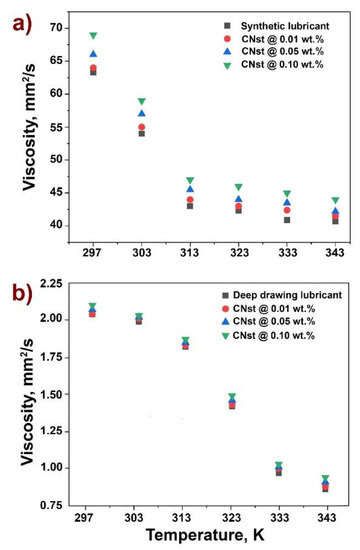
Figure 3.
Temperature-dependence evaluation for viscosity behavior. (a) SL lubricants; (b) DD lubricants.
Table 2 shows the enhancements during four-ball evaluations by carbon nanotori structures reinforcing SL and DD lubricants under EP conditions. Seizure load (Poz), pressure loss limit (poz), and WSD are integrated into this table, with enhancement in parentheses. The solid nanostructures are pushed into the metal contacts, forming a protective film, as other authors have also seen and called the tribo-sintering effect [51,52,53]. The observed improvements can be attributed to this tribo-sintering effect of the carbon nanotori structures onto worn areas, filling valleys or vacancies and the shearing mechanism of captured nanostructures at the surfaces interface, hence providing smoothness and reducing the frictional forces. Another critical characteristic can be associated with the substrate hardness and the tribo-layer formation, as other authors have also described [7,45,47,52,53,54].

Table 2.
Enhancements by CNst reinforcement to SL and DD lubricants under EP conditions.
As previously explained, during the four-ball evaluations an extreme pressure is applied. A tribo-membrane is formed, resulting from a chemical response among the nanolubricants and the working surfaces. Due to the carbon nanotori morphology, higher loads could be supported, maintaining the lubrication layer between metal components. The load-bearing effect provided by the CNst-nanolubricants due to the high elastic modules is promoted at EP conditions.
4.2. Viscosity Evaluations
Temperature-dependent measurements for shear viscosity behavior for various filler fractions of nanolubricants are shown in Figure 3. Viscosity slightly increased with reinforcement of carbon nanotori structures to both lubricants, as expected. Moreover, for SL lubricants (Figure 3a), viscosity is reduced with temperature raise (from 63 mm2/s at room temperature to 40 mm2/s at 70 °C), while a slight increment in viscosity due to the incorporation of carbon nanotori (<6%) was observed.
Similar to reported research [37,55,56,57,58], an incremental viscosity behavior trend is seen as filler fraction is increased, as well as a decrease in viscosity with temperature raise. Figure 3b shows the viscosity behavior for DD nanolubricants over the evaluated temperatures. In this case, due to the initial low viscosity of the DD lubricant, viscosity increments due to the incorporation of reinforcing nanostructures is minimal, at less than 4%.
5. Conclusions
Two common lubricants for metal-working and metal-forming processes were investigated. Carbon nanotori structures (CNst) at diverse concentrations reinforced SL and DD lubricants. CNst demonstrated good affinity and improved tribological behavior under EP conditions, providing a sliding-rolling effect that promotes the wear reduction. Tribological performance was greatly benefited; the load carrying capacity was observed to be enhanced by 16% and 22% at merely 0.01 wt.% reinforcement and up to 73% and 107% at 0.10 wt.% for SL and DD nanolubricants, respectively, compared to pure lubricants. Wear scar evaluations were performed; the highest improvement was found at 0.10 wt.% reinforcement of 16% and 24%, for SL and DD, respectively. This improvement may be due to diverse mechanisms such as rolling effect and their tribo-sintering behavior (at high pressures) onto metal surfaces and their spacer effect due to the size and morphology of nanostructures as well as the interlayer relationship with conventional lubricants. Further investigation is needed to fully show these effects. Viscosity behavior was analyzed by comparing nanolubricants and pure lubricants. The incorporation of nanostructures slightly increased (<6% at 0.10 wt.%) the viscosity of conventional lubricants, as expected. Carbon nanotori as reinforcing material for lubricants in industrial applications such as in metal-mechanic plastic deformation processes is an emerging alternative. Furthermore, predictive simulations and methodologies for tribological performance is an opportunity field in which additional development could be addressed.
Author Contributions
J.J.T.-T. contributed to the conceptualization, project administration, methodology, literature research, measuring campaign, data analysis, data interpretation, validation, formal analysis, resources, investigation, figures, study design, supervision, and writing—original. P.Y.A.-G. contributed to the methodology, resources, validation, formal analysis, investigation, and writing—original. J.M.M. contributed to the measuring campaign, data interpretation, and investigation. D.E. contributed to the investigation, literature research, and formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge Metalsa and Universidad de Monterrey for their support given in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Taha-Tijerina, J.J.; Calderón, R.; Rodríguez, B. Optimization and nanoreinforcements of lubricant Concentration for steel sheet forming process. Int. J. Mod. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 13, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Yusup, S.; Chok, V. A Review on Nanoparticle Addition in Base Fluid for Improvement of Biodegradable Ester-Based Drilling Fluid Properties. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2015, 45, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, I.S.; Sahoo, M. Optimization of Drilling Parameters Using Nanofluid MinimumQuantity Lubrication. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2016, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Minh, D.T.; The, L.T.; Bao, N.T. Performance of Al2O3 nanofluids in minimum quantity lubrication in hard milling of 60Si2Mn steel using cemented carbide tools. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zareh-Desari, B.; Davoodi, B. Assessing the lubrication performance of vegetable oil-based nano-lubricants for environmentally conscious metal forming processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.N.; Li, C.; Huang, C.; Ali, H.M.; Xu, X. Nano-enhanced biolubricant in sustainable manufacturing: From processability to mechanisms. Friction 2021, 10, 803–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Water-Based Nanolubricants. Lubricants 2021, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.N.; Anandan, V.; Babu, M.D.; Muthukrishnan, N. Turning SKD 11 Steel Using Silver Nanofluids with Minimum Quantity Lubrication. Int. J. Manuf. Mater. 2021, 11, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchanikar, S.; Kore, S.S.; Hujare, P. A review on nanofluids in minimum quantity lubrication machining. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 68, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Sun, J.; He, J.; Wu, P. Research Progress of Interface Conditions and Tribological Reactions: A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 94, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Dixit, A.R. Progress of Nanofluid Application in Machining: A Review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Said, L.; Kolsi, L.; Ghachem, K.; Almeshaal, M.; Maatki, C. Application of nanofluids as cutting fluids in machining operations: A brief review. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, H.A.; Hegab, H.; Deiab, I.; Eltaggaz, A. Sustainability assessment during machining Ti-6Al-4V with nano-additives-based minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadirgama, K. A comprehensive review on the application of nanofluids in the machining process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverberi, A.P.; D’Addona, D.M.; Bruzzone, A.A.G.; Teti, R.; Fabiano, B. Nanotechnology in machining processes: Recent advances. Procedia CIRP 2019, 79, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Xie, G.; Luo, J. Mechanical properties of nanoparticles: Basics and applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 13001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, M.J.; Liu, J.L.; Qi, Z.N.; He, J.; Wei, J.J.; Miao, J.Y. Research progress in nanofluids with graphene addition. J. Mater. Eng. 2020, 48, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.L.; Herranz, M.Á.; Martín, N. The nano-forms of carbon. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, J. Toroidal and Coiled Carbon Nanotubes. In Syntheses and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes and Their Composites; Suzuki, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sarapat, P.; Hill, J.; Baowan, D. A Review of Geometry, Construction and Modelling for Carbon Nanotori. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jammoria, N.S.; Ul Haq, M.I.; Raina, A. Carbon-Related Materials for Tribological Application. In Advances in Sustainability Science and Technology, Proceedings of Fourth International Conference on Inventive Material Science Applications, Coimbatore, India, 4–15 May 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 469–483. [Google Scholar]
- Shafi, W.K.; Charoo, M.S. An overall review on the tribological, thermal and rheological properties of nanolubricants. Tribol.-Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 15, 20–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opia, A.C.; Kameil, A.H.M.; Syahrullail, S.; Johnson, C.A.N.; Izmi, M.I.; Mamah, S.C. Tribological behavior of organic formulated anti-wear additive under high frequency reciprocating rig and unidirectional orientations: Particles transport behavior and film formation mechanism. Tribol. Int. 2022, 167, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Lin, H.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, H. Important contributions of multidimensional nanoadditives on the tribofilms: From formation mechanism to tribological behaviors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 234, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jason, Y.J.J.; How, H.G.; Teoh, Y.H.; Chuah, H.G. A Study on the Tribological Performance of Nanolubricants. Processes 2020, 8, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, N. Carbon Nanostructures as Lubricant Additives. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Basheer, A.A.; Kucherova, A.; Memetov, N.; Pasko, T.; Ovchinnikov, K. Advances in carbon nanomaterials as lubricants modifiers. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 279, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.K.; Khalid, M.; Javeed, A.; Rashmi, W.; Gupta, T.C.S.M.; Chan, A. Heat transfer and tribological performance of graphene nanolubricant in an internal combustion engine. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, S.; Prabhu, S.; Singh, K.J. Analysis of Tribological behavior of carbon nanotube based industrial mineral gear oil 250 cSt viscosity. Adv. Tribol. 2014, 2014, 341365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peña-Parás, L.; Taha-Tijerina, J.; García, A.; Maldonado, D.; González, J.A.; Molina, D. Antiwear and Extreme Pressure Properties of Nanofluids for Industrial Applications. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goyal, P. Experimental study of Carbon Nanotubes to enhance Tribological Characteristics of Lubricating Engine Oil SAE 10W40. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1225, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Osman, T.A.; Khattab, A.; Zaki, M. Tribological behavior of carbon nanotubes as an additive on lithium grease. J. Tribol. 2015, 137, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Parás, L.; Taha-Tijerina, J.; García, A.; Maldonado, D.; Nájera, A.; Cantú, P. Thermal transport and tribological properties of nanogreases for metal-mechanic applications. Wear 2015, 332–333, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Sinnott, S.B. Tribological properties of carbon nanotube bundles predicted from atomistic simulations. Surf. Sci. 2001, 487, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Hong, H.; D’urso, V.; Younes, H. Tribological Behavior of Novel CNTs-Based Lubricant Grease in Steady-State and Fretting Sliding Conditions. Lubricants 2021, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.C.; Mukherjee, S.; Nayak, S.K.; Panda, A. A brief review on viscosity of nanofluids. Int. Nano Lett. 2014, 4, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamze, S.; Cabaleiro, D.; Estellé, P. Graphene-based nanofluids: A comprehensive review about rheological behavior and dynamic viscosity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, H.D.; Doganay, S.; Turgut, A.; Tavman, I.H.; Saidur, R.; Mahbubul, I.M. Effect of particle size on the viscosity of nanofluids: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubbi, F.; Das, L.; Habib, K.; Aslfattahi, N.; Saidur, R.; Alam, S.U. A comprehensive review on advances of oil-based nanofluids for concentrating solar thermal collector application. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghinezhad, E.; Mehrali, M.; Tahan, L.S.; Mehrali, M.; Kazi, S.N.; Oon, C.S. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer using graphene nanoplatelet based nanofluids under turbulent flow conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 12455–12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.B.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Entezari, M.H.; Nancarrow, P. Preparation, characterization, and rheological properties of graphene-glycerol nanofluids. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrand, M.; Nazari Najafabadi, K.; Akbari, M. Effects of temperature and solid volume fraction on viscosity of SiO2-MWCNTs/SAE40 hybrid nanofluid as a coolant and lubricant in heat engines. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanola, A.; Garg, H.C. Dispersion stability and rheology study of canola oil containing TiO2 nanoadditives for tribological applications: An experimental approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2020, 235, 1765–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, H.; Hafner, J.H.; Colbert, D.T.; Smalley, R.E. Fullerene “crop circles”. Nature 1997, 385, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Tijerina, J.; Aviña, K.; Martínez, J.M.; Arquieta-Guillén, P.Y.; González-Escobedo, M. Carbon Nanotori Structures for Thermal Transport Applications on Lubricants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Guo, G.Y.; Jayanthi, C.S.; Wu, S.Y. Colossal Paramagnetic Moments in Metallic Carbon Nanotori. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 217206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Garza-Castañón, M.; Kharisov, B.I. Inorganic nanorings and nanotori: State of the art. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 3998–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalczewski, R.; Piekoszewski, W.; Tuszynski, W.; Szczerek, M.; Wulczynski, J. The new methods for scuffing and pitting investigation of coated materials for heavy loaded lubricated elements. In Tribology—Lubricants and Lubrication; Kuo, C.-H., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 305–320. [Google Scholar]
- Szczerek, M.; Tuszynski, W. A method for testing lubricants under conditions of scuffing. Part I. Presentation of the method. Tribotest 2002, 8, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, L.R. Synthetics, Mineral Oils, and Bio-Based Lubricants: Chemistry and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; p. 1194. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, Á.D.; Szabó, Á.I.; Leskó, M.Z.; Rohde-Brandenburger, J.; Kuti, R. Tribological Properties of the Nanoscale Spherical Y2O3 Particles as Lubricant Additives in Automotive Application. Lubricants 2022, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Battez, A.; González, R.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernández, J.E.; Díaz-Fernández, J.M.; Machado, A. CuO, ZrO2 and ZnO nanoparticles as antiwear additive in oil lubricants. Wear 2008, 265, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Komai, K. Tribofilm formation and mild wear by tribo-sintering of nanometer-sized oxide particles on rubbing steel surfaces. Wear 2007, 262, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaso, P.; Ville, F.; Dassenoy, F.; Diaby, M.; Afanasiev, P.; Cavoret, J. Boundary lubrication: Influence of the size and structure of inorganic fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticles on friction and wear reduction. Wear 2014, 320, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Bahman, A.M.; Aljuwayhel, N.F.; Ebrahim, S.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Alsayegh, A. Carbon-based nanofluids and their advances towards heat transfer applications—A review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Saeed, T.; Chu, Y.M.; Ali, H.M.; Cheraghian, G.; Kalbasi, R. Comprehensive study concerned graphene nano-sheets dispersed in ethylene glycol: Experimental study and theoretical prediction of thermal conductivity. Powder Technol. 2021, 386, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.K.; Khalid, M.; Rashmi, W.; Gupta, T.C.S.M.; Chan, A. Graphene based nanofluids and nanolubricants–Review of recent developments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 63, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, B.M.; Tirth, V.; Algahtani, A.; Shiba, M.S.; Mobasher, A.; Hashish, H.A. Optimization of the Rheological Properties and Tribological Performance of SAE 5W-30 Base Oil with Added MWCNTs. Lubricants 2021, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).