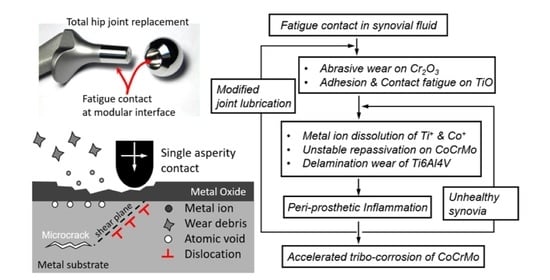
Sliding Corrosion Fatigue of Metallic Joint Implants: A Comparative Study of CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V in Simulated Synovial Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials Description
Experimental Details
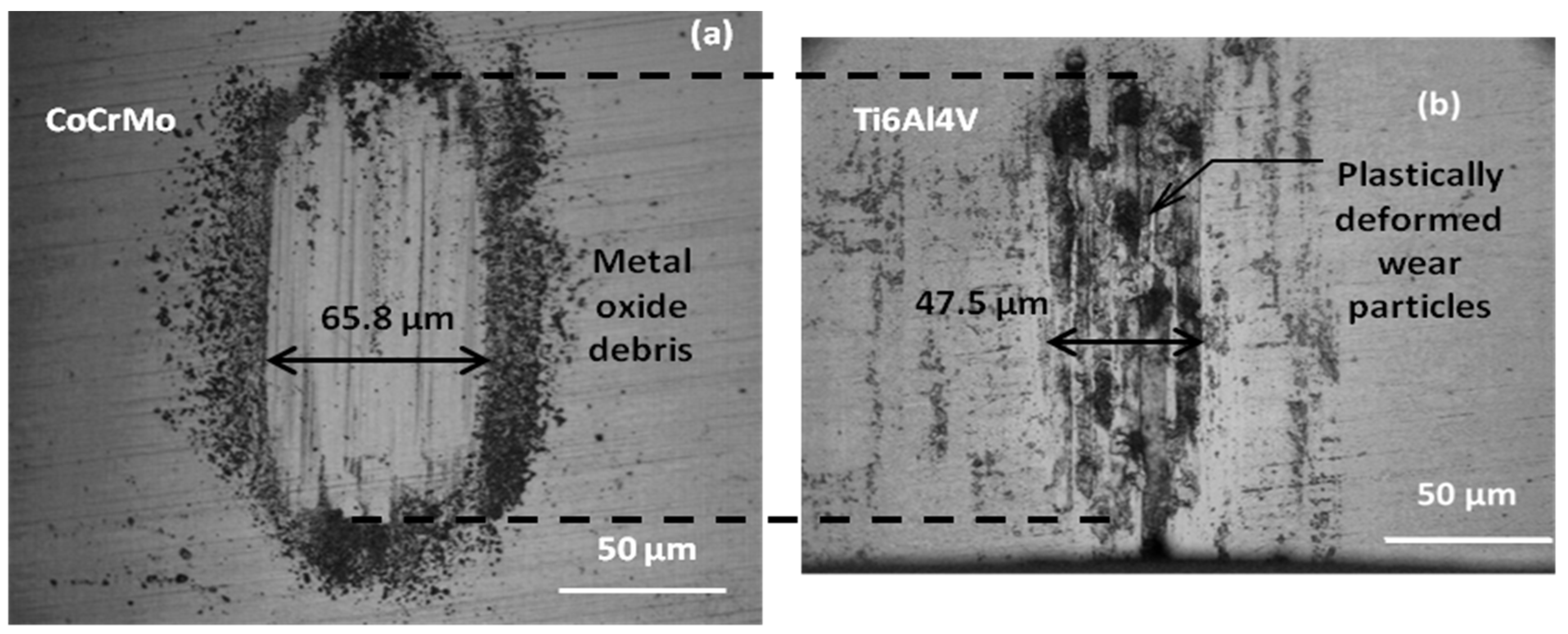
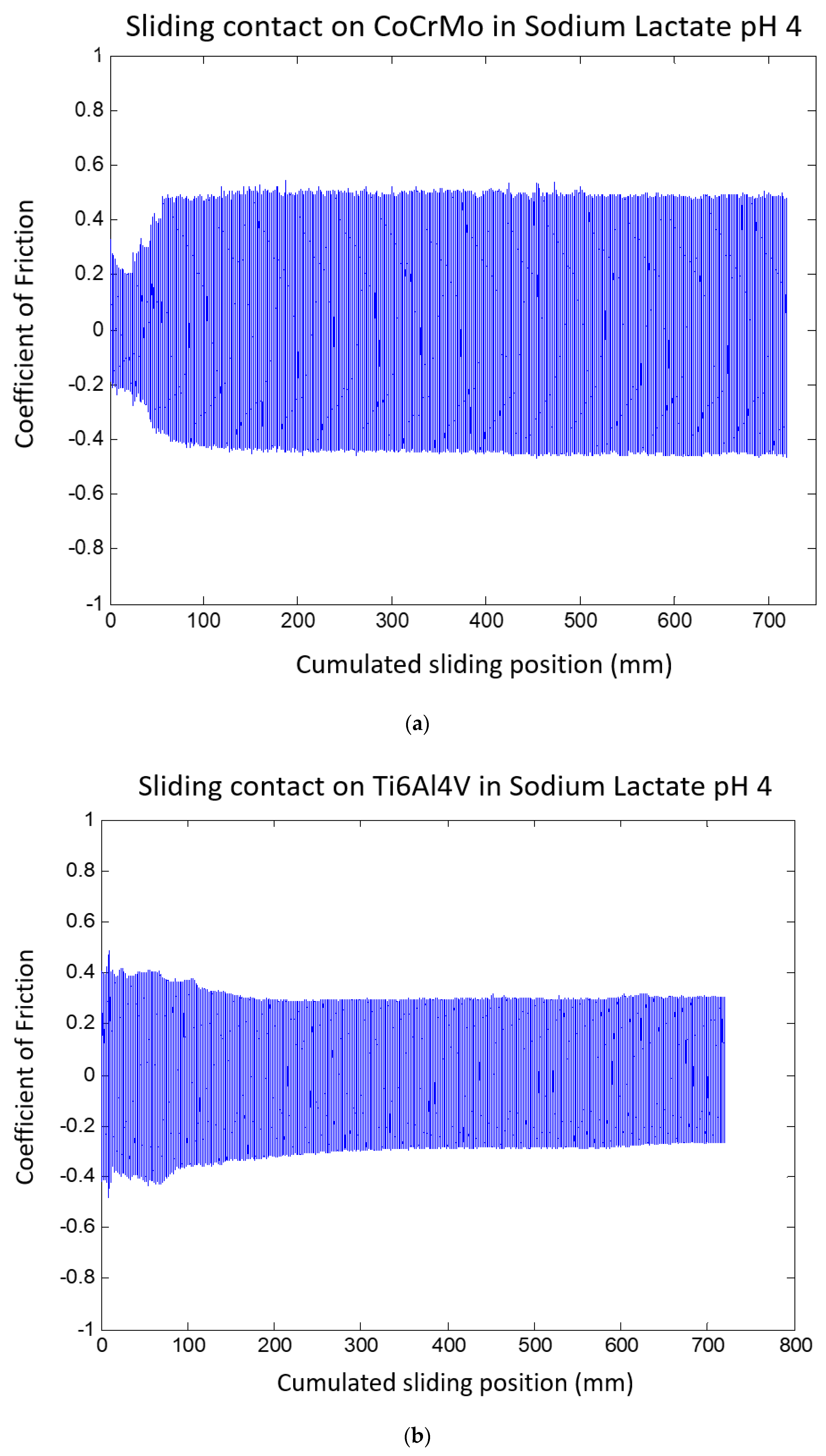
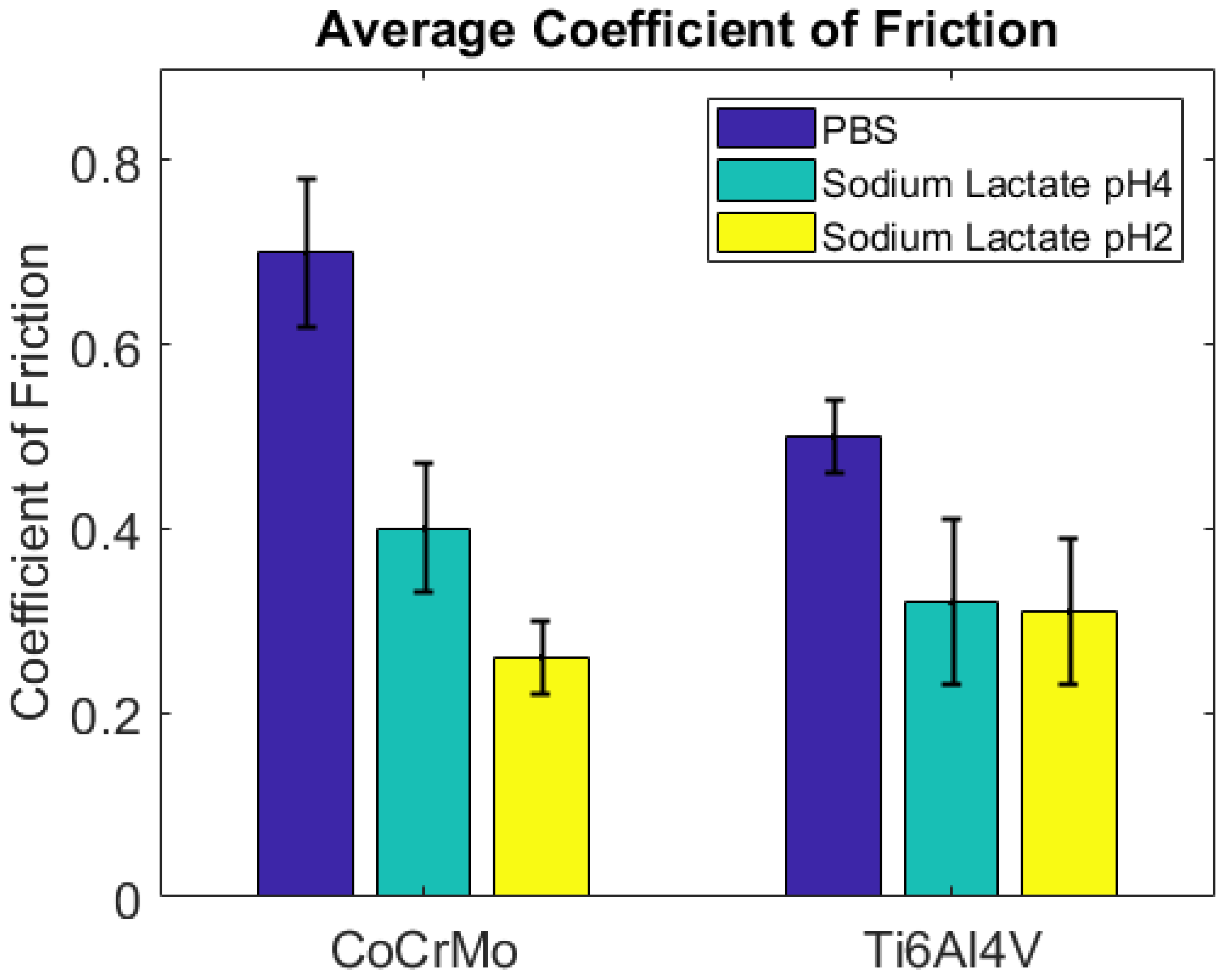
3. Results and Discussion
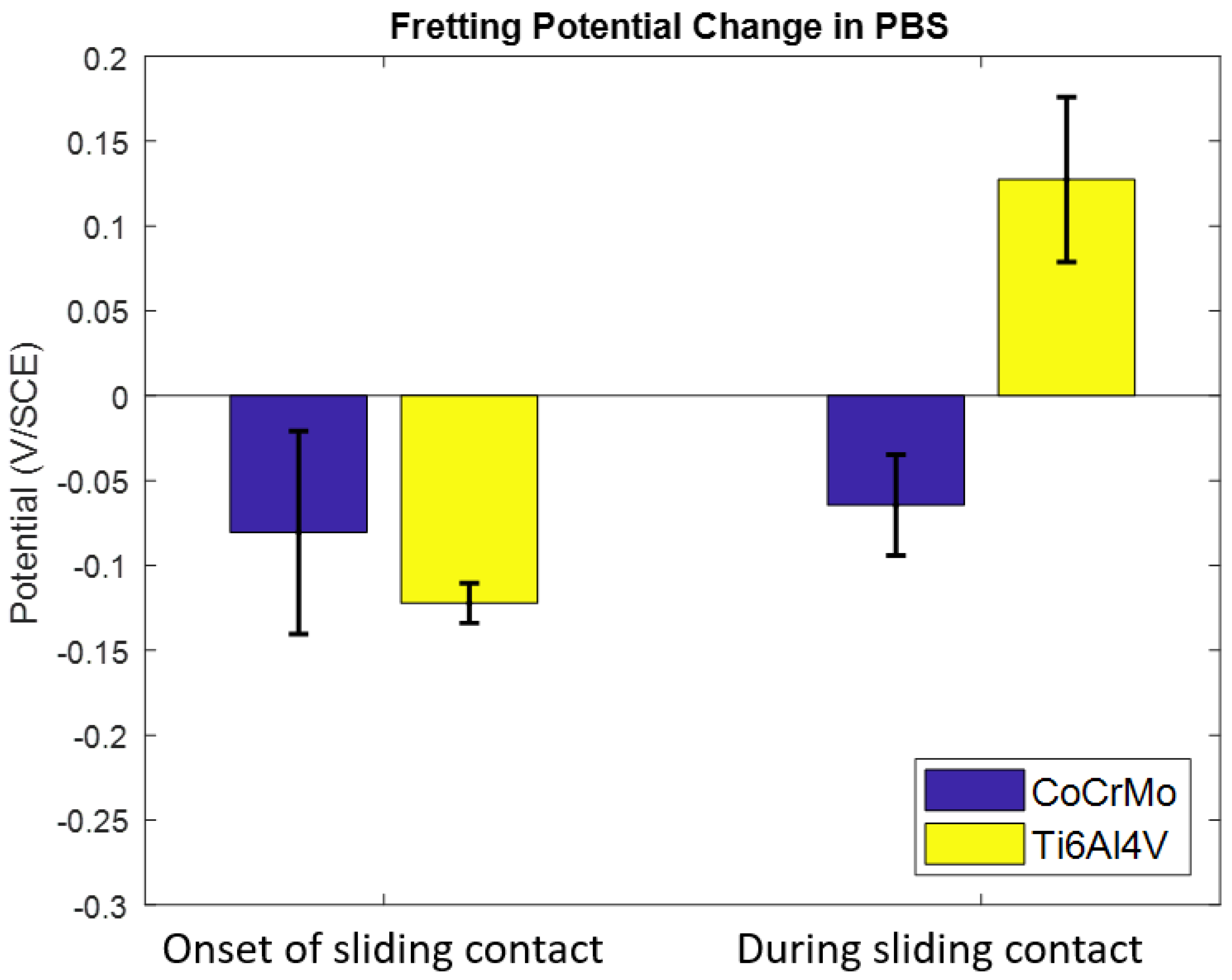
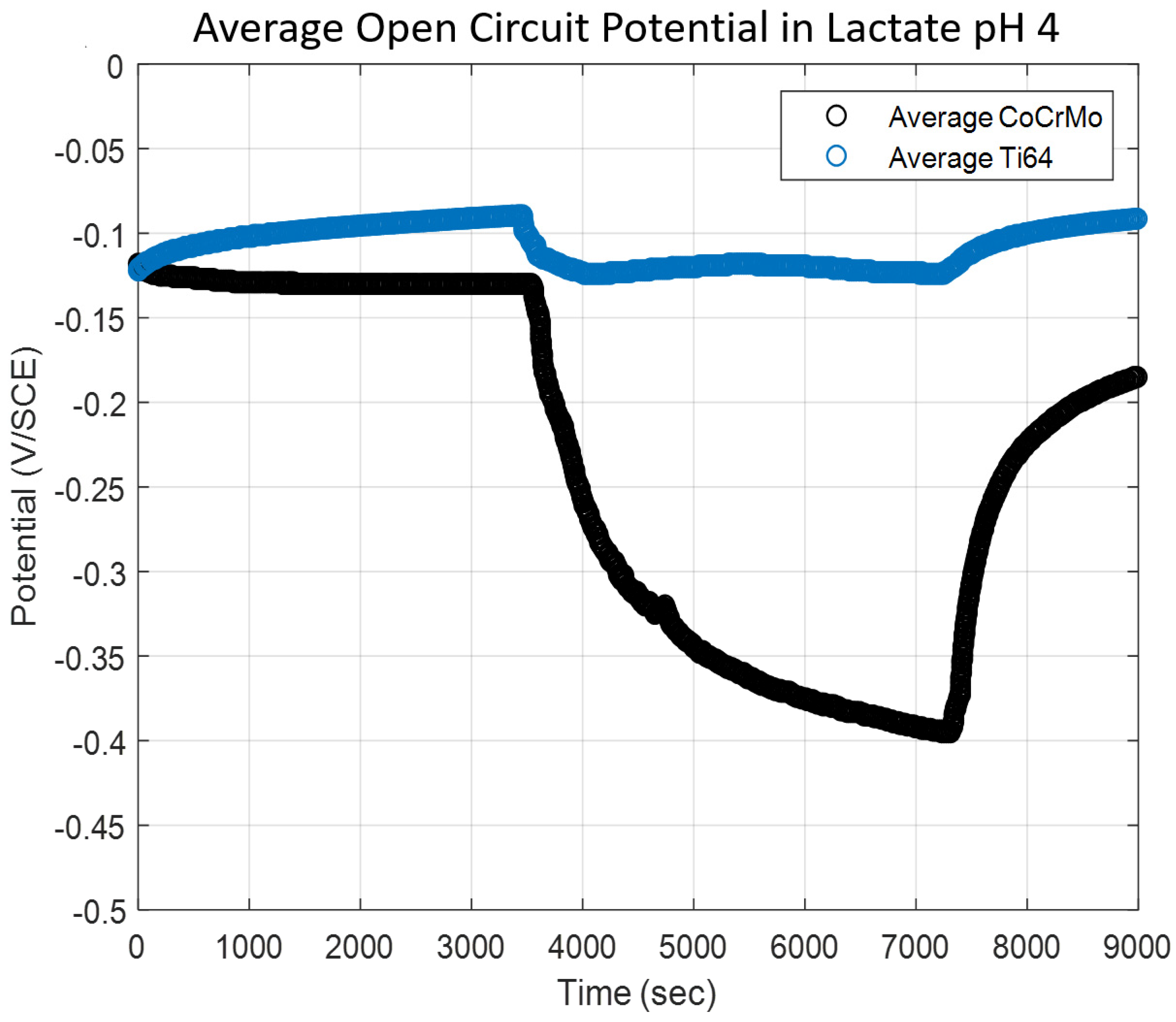
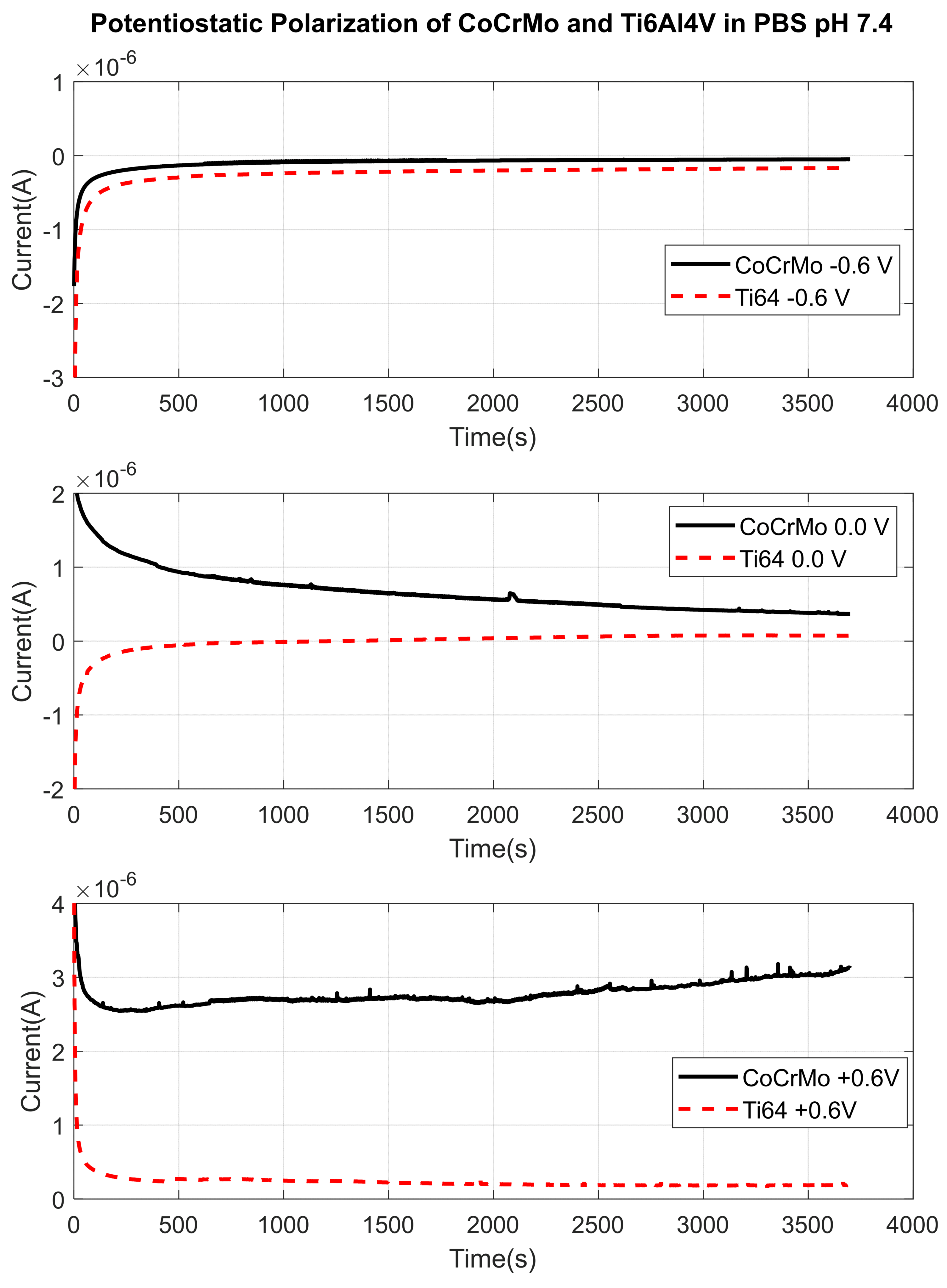
3.1. Open Circuit Potential Measurement
3.1.1. Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS) Solution pH 7.4
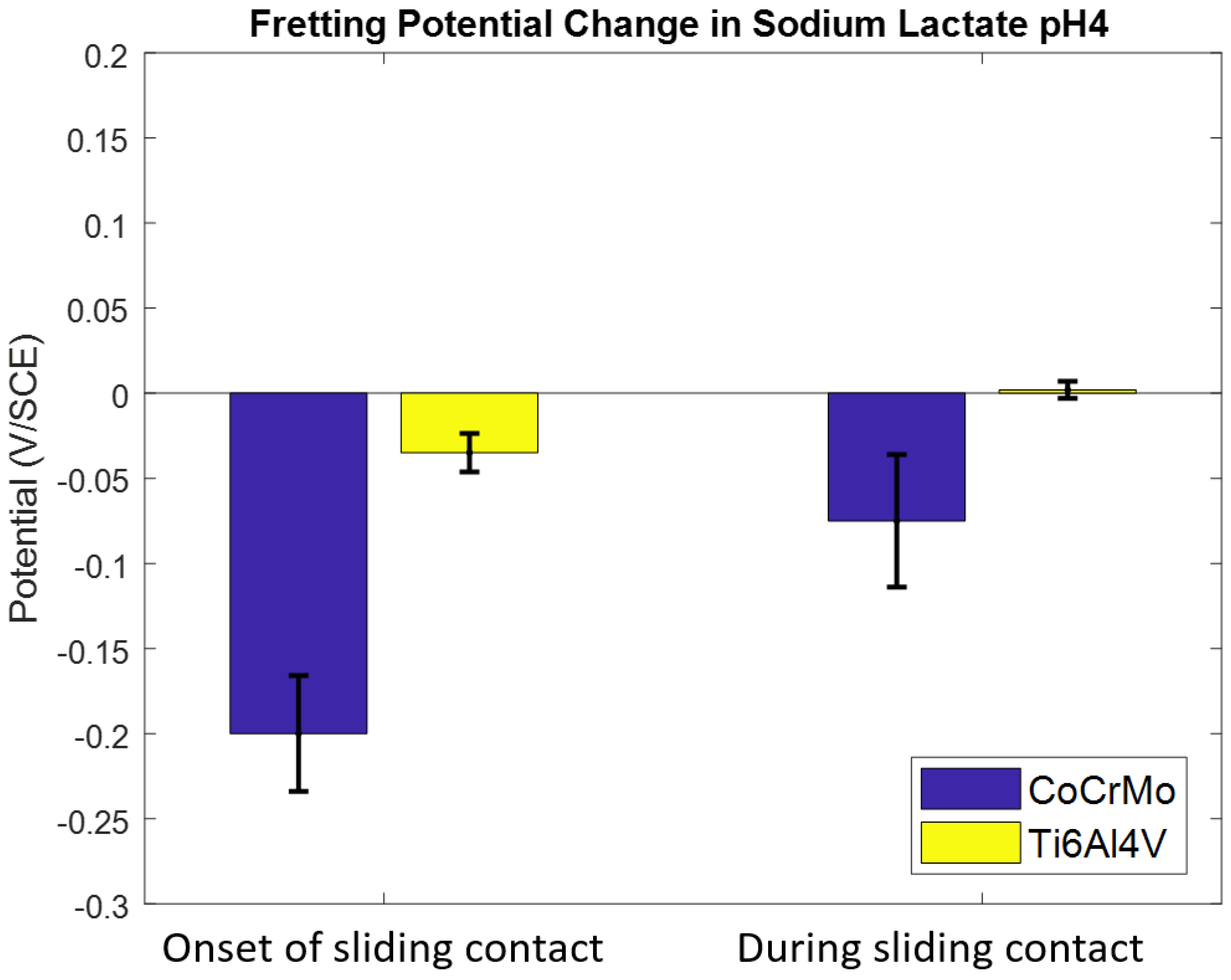
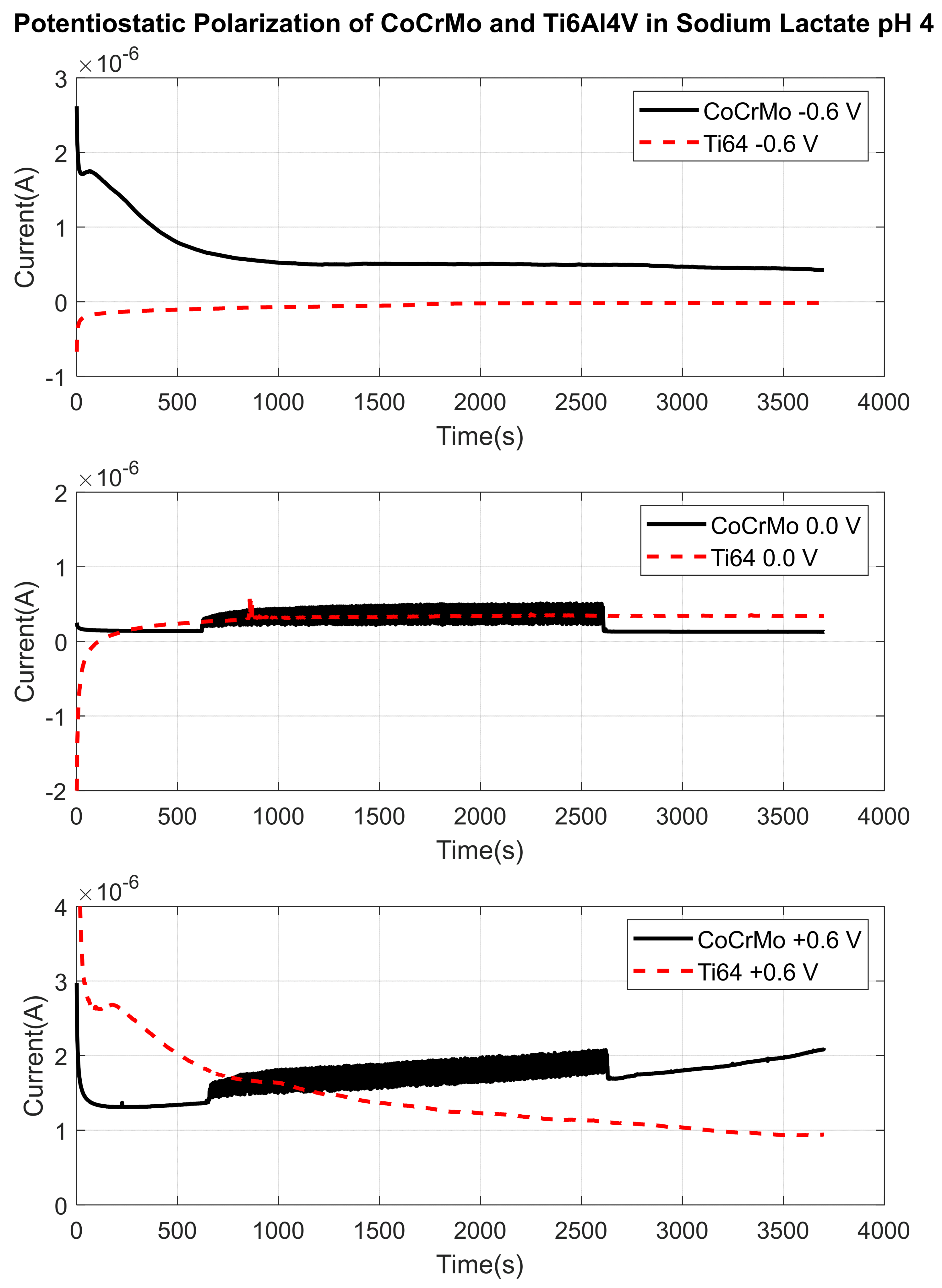
3.1.2. Sodium Lactate pH 4
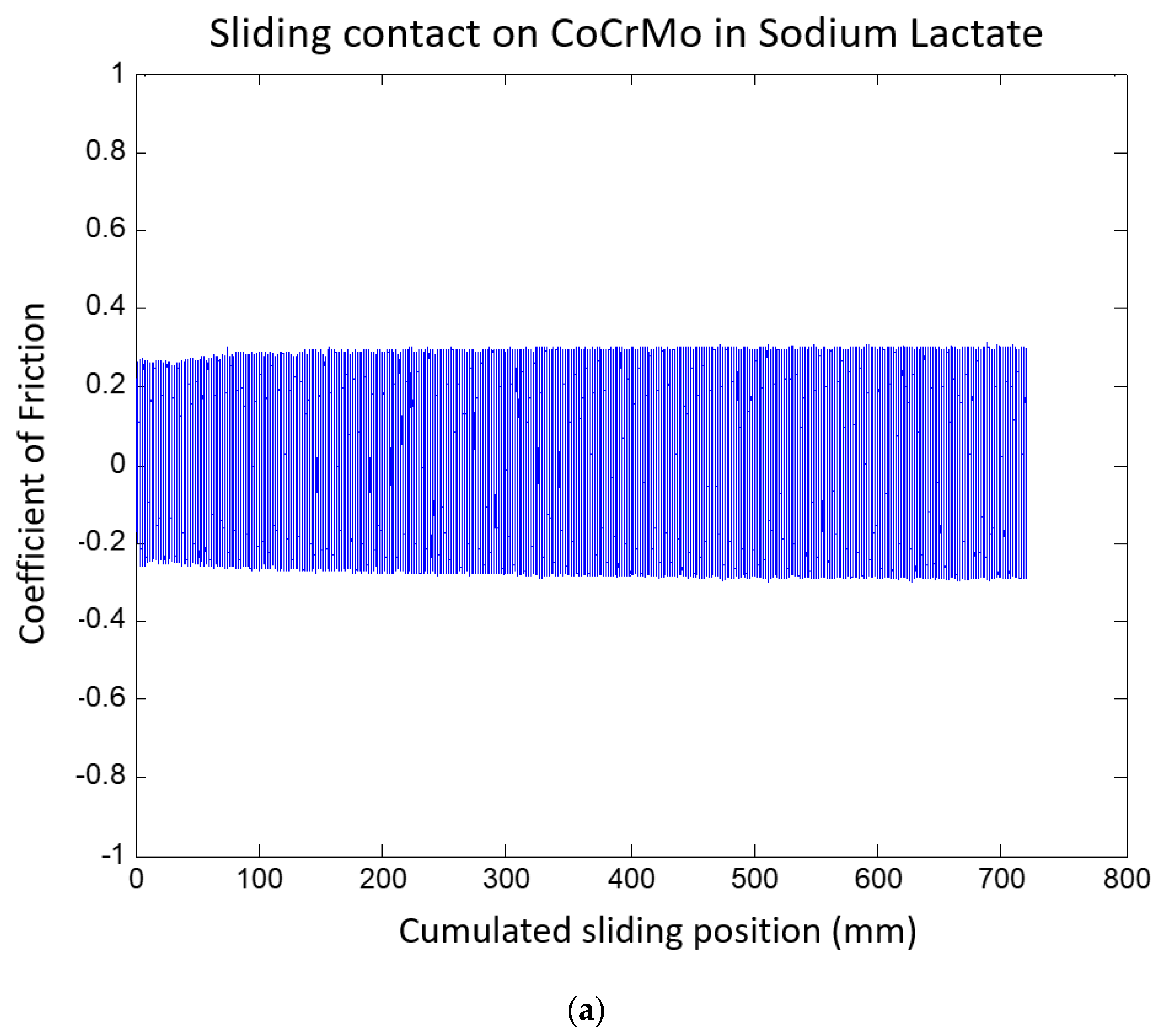
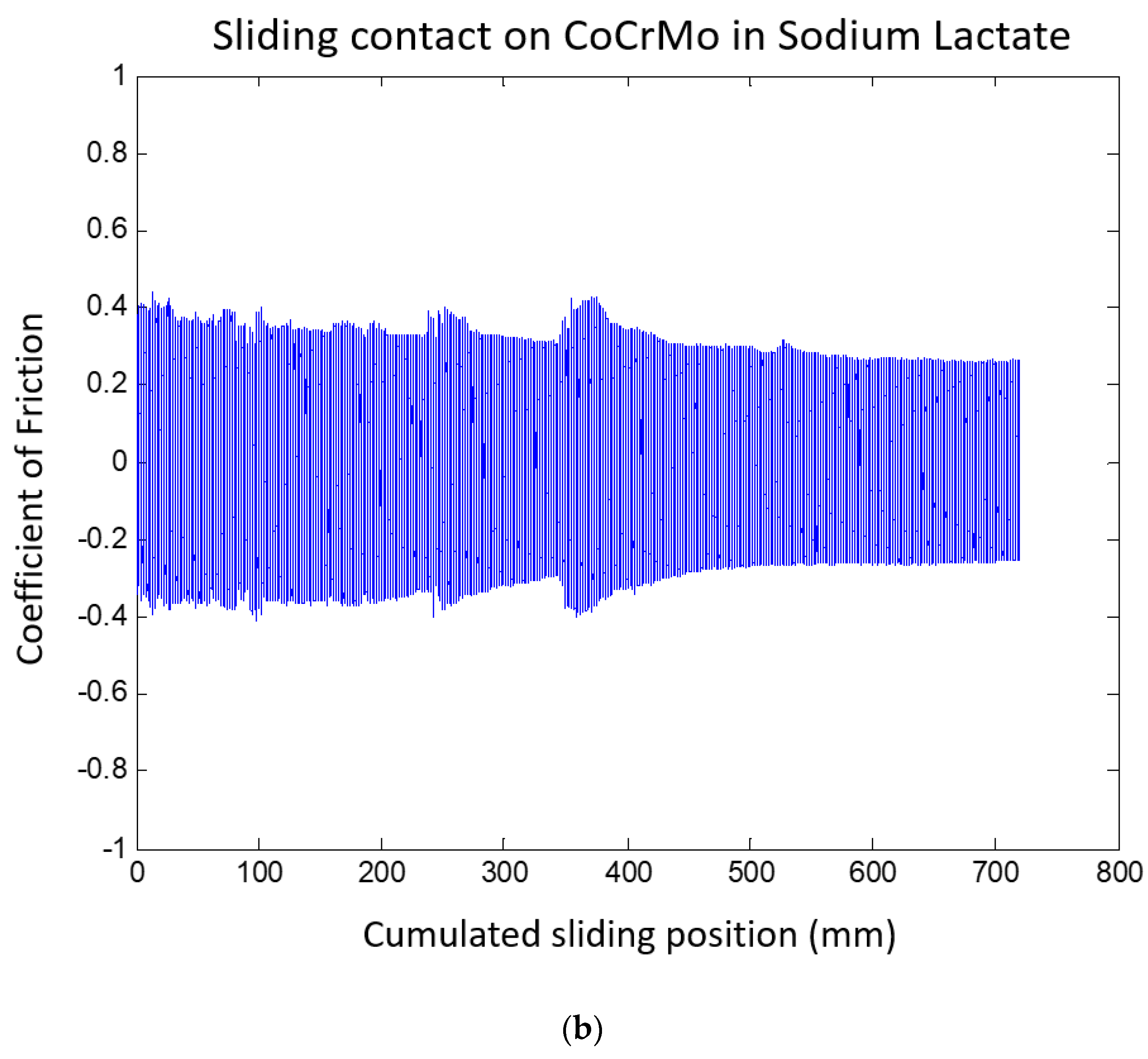
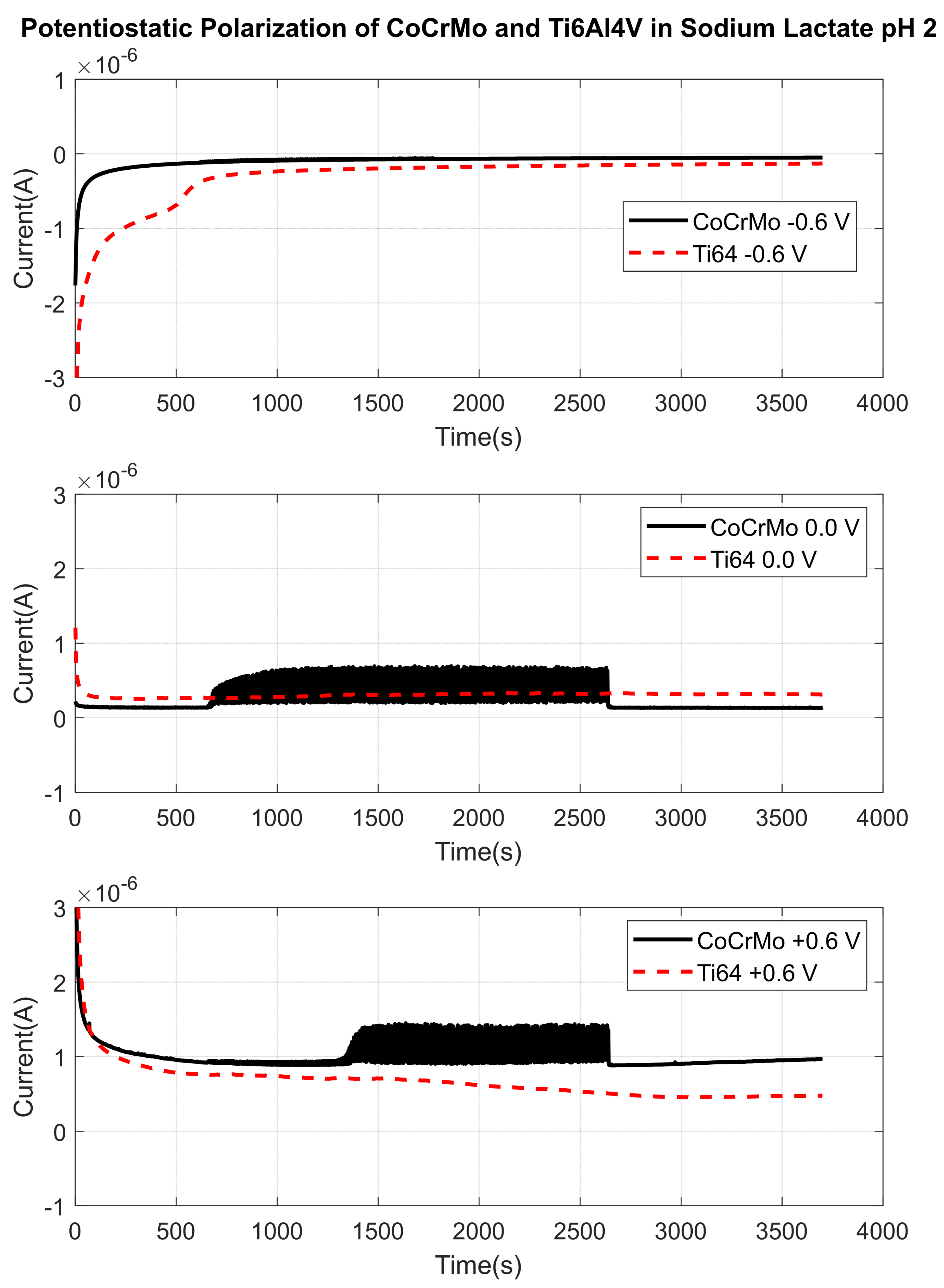
3.1.3. Sodium Lactate pH 2
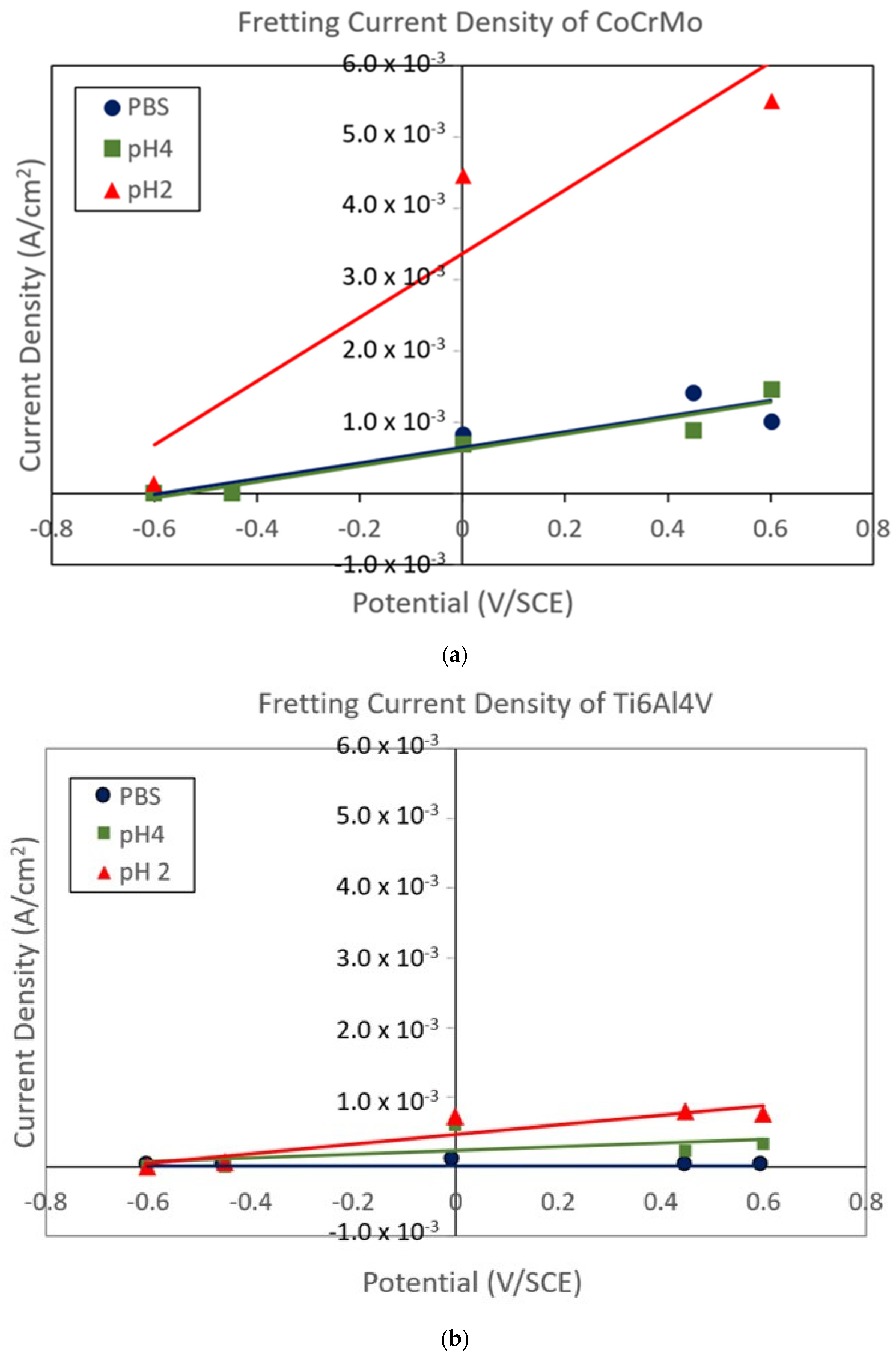
3.2. Fretting Static Current
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathew, M.; Nagelli, C.; Pourzal, R.; Fischer, A.; Laurent, M.; Jacobs, J.; Wimmer, M. Tribolayer formation in a metal-on-metal (MoM) hip joint: An electrochemical investigation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 29, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallab, N.J.; Messina, C.; Skipor, A.; Jacobs, J.J. Differences in the fretting corrosion of metal–metal and ceramic–metal modular junctions of total hip replacements. J. Orthop. Res. 2004, 22, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, M.M.; Hube, R.; Wassilew, G.; Prange, F.; Huber, G.; Perka, C. Taper corrosion: A complication of total hip arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, K.M.N.; Krause, W.E.; Jones, R.L.; Colby, R.H. Rheopexy of synovial fluid and protein aggregation. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Usami, H.; Niimi, T.; Sawae, Y.; Krupka, I.; Hartl, M. Running-in friction of hip joint replacements can be significantly reduced: The effect of surface-textured acetabular cup. Friction 2020, 8, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.B.; Burr, D.B.; Sharkey, N.A.; Fyhrie, D.P. Skeletal Tissue Mechanics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hallab, N.; Jacobs, J. Orthopedic Implant Fretting Corrosion. Corros. Rev. 2003, 21, 183–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, M.; Vasconcelos, D.; Sousa, D.M.; Sousa, B.; Conceição, F.; Neto, E.; Lamghari, M.; Alves, C.J. The Mechanisms Underlying the Biological Response to Wear Debris in Periprosthetic Inflammation. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xu, N.; Zhang, C. Characteristics of copper corrosion in simulated uterine fluid in the presence of protein. Adv. Contracept. 1999, 15, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gilbert, J.L. The effect of simulated inflammatory conditions and pH on fretting corrosion of CoCrMo alloy surfaces. Wear 2017, 390–391, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebenda, D.; Vrbka, M.; Cípek, P.; Toropitsyn, D.; Necas, D.; Pravda, M.; Hart, M. On the Dependence of Rheology of Hyaluronic Acid Solutions and Frictional Behavior of Articular Cartilage. Materials 2020, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharrami, N.; Langton, D.; Sayginer, O.; Bull, S. Why does titanium alloy wear cobalt chrome alloy despite lower bulk hardness: A nanoindentation study? Thin Solid Films 2013, 549, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalko, W.M.; Haider, H.; Kurtz, S.; Marcolongo, M.; Urish, K. New materials for hip and knee joint replacement: What’s hip and what’s in kneed? J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 38, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.B.; Lakes, R.S. Biomaterials: An Introduction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Langton, D.J.; Sidaginamale, R.; Lord, J.K.; Nargol, A.V.F.; Joyce, T.J. Taper junction failure in large-diameter metal-on-metal bearings. Bone Jt. Res. 2012, 1, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilo, K.C.; Hothi, H.S.; Skinner, J.A.; Hart, A.J. Metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty: Does increasing modularity affect clinical outcome? HIP Int. 2020, 1120700020979275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compte, P. Metallurgical observations of Biomaterials. In Contemporary Biomaterials; Boretos, J.W., Eden, M., Eds.; Noyes Publications: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Dai, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Choi, S.-W. On the microstructure and corrosion behaviors of selective laser melted CP-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy in Hank’s artificial body fluid. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 126521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardelli, J.D.C.; Bolfarini, C.; dos Reis, A.C. Comparative analysis of corrosion resistance between beta titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloys: A systematic review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Terminology Relating to Wear and Erosion. In Annual Book of Standards; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1987; Volume 3, pp. 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsitt, H.A.; Wang, D.Y. The effects of interstitial solute atoms on the fatigue limit behavior of titanium. Trans. AIME 1961, 221, 918. [Google Scholar]
- Sonntag, R.; Reinders, J.; Gibmeier, J.; Kretzer, J.P. Fatigue Performance of Medical Ti6Al4V Alloy after Mechanical Surface Treatments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B.D. Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine; Elsevier, Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oungoulian, S.R.; Durney, K.M.; Jones, B.K.; Ahmad, C.S.; Hung, C.T.; Ateshian, G.A. Wear and damage of articular cartilage with friction against orthopedic implant materials. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.L. Electrochemical behavior of metals in the biological milieu. In Comprehensive Biomaterials; Healy, K.E., Ducheyne, P., Kirkpatrick, C.J., Eds.; Elsevier Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Chapter 13. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamleh, M.M.; Wu, X.; Alnazzawi, A.; Watson, J.; Watts, D. Surface characteristics and biocompatibility of cranioplasty titanium implants following different surface treatments. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmber, M.A.; Radice, S.; Janssen, D.; Fischer, A. Fretting-corrosion of CoCr-alloys against Ti6Al4V: The importance of molybdenum in oxidative biological environments. Wear 2021, 477, 203813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiram, G.; Gindri, I.M.; Kerwell, S.; Shull, K.; Mathew, M.T.; Rodrigues, D.C. Nanoscale Mechanical Evaluation of Electrochemically Generated Tribolayer on CoCrMo Alloy for Hip Joint Application. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2016, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sasikumar, Y.; Indira, K.; Rajendran, N. Surface Modification Methods for Titanium and Its Alloys and Their Corrosion Behavior in Biological Environment: A Review. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2019, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragetti, S.; Villa, F. Corrosion Fatigue of High-Strength Titanium Alloys under Different Stress Gradients. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2015, 67, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beevers, C.J.; Robinson, J.L. Some observations on the influence of oxygen content on the fatigue behavior of α-titanium. J. Less Common Met. 1969, 17, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, O.M.; Tate, R.J.; Meek, R.D.; Grant, M.H. In Vitro Analyses of the Toxicity, Immunological, and Gene Expression Effects of Cobalt-Chromium Alloy Wear Debris and Co Ions Derived from Metal-on-Metal Hip Implants. Lubricants 2015, 3, 539–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Ryu, J.; Karra, P.; Shrotriya, P.; Weik, T. Electrochemical dissolution of biomedical grade Ti6Al4V: Influence of stress and environment. CIRP Ann. 2009, 58, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Shrotriya, P. Mechanical load assisted dissolution response of biomedical cobalt–chromium and titanium metallic alloys: Influence of in-plane stress and chemical environment. Wear 2015, 332–333, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.J.; Shrotriya, P. Influence of roughness on surface instability of medical grade cobalt–chromium alloy (CoCrMo) during contact corrosion–fatigue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Letchuman, S.; Shrotriya, P. Roughness evolution of metallic implant surfaces under contact loading and nanometer-scale chemical etching. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 14, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, R. Surface Wear—Analysis, Treatment, and Prevention; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
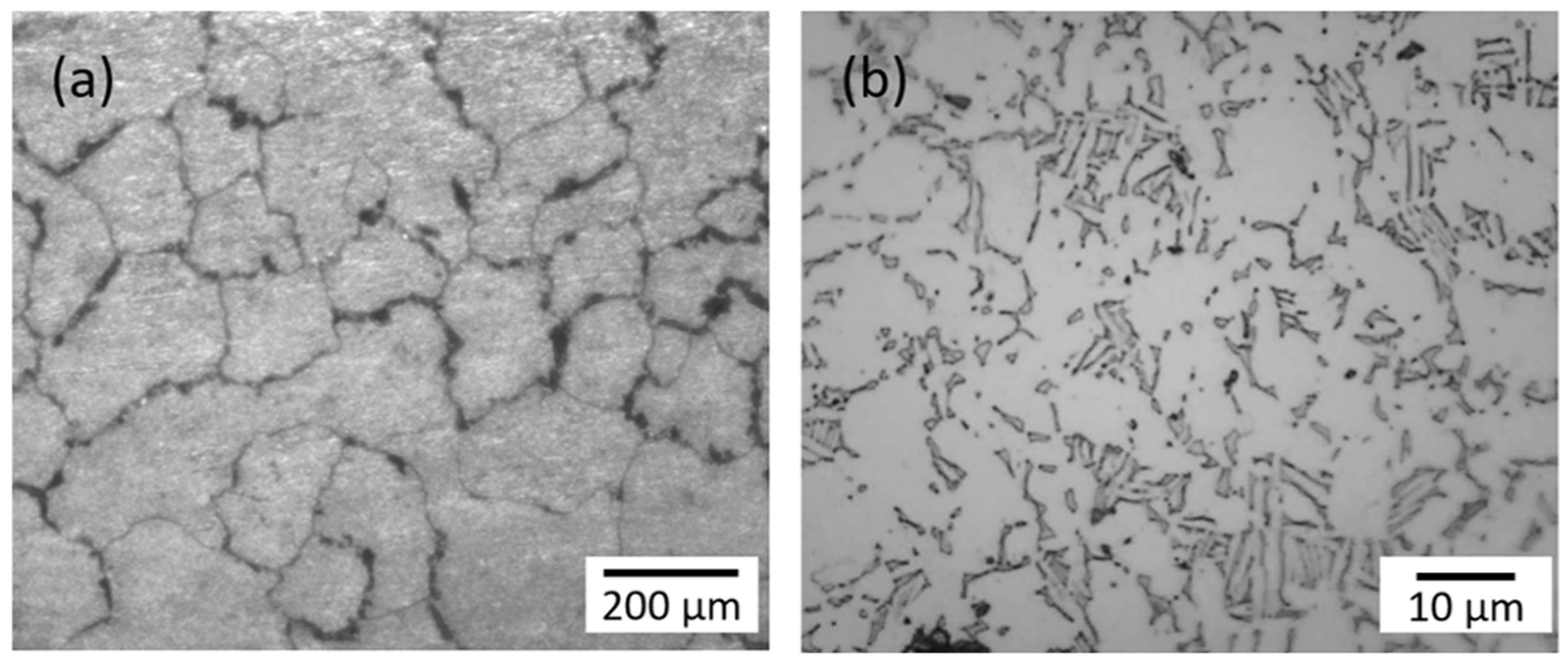
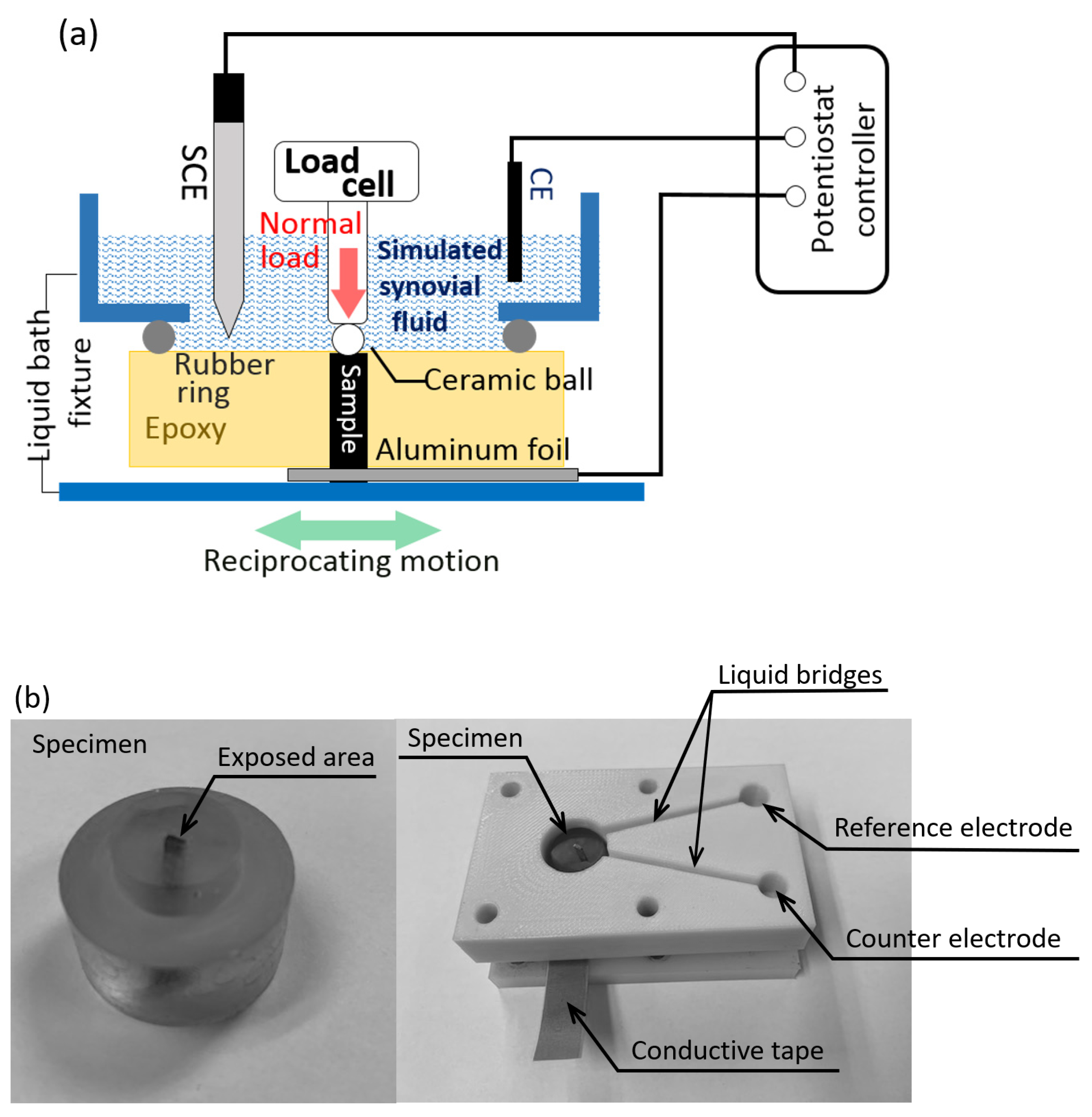




| Ti6Al4V | Ti | Al | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α phase | wt.% | 89.77 | 6.04 | 4.19 |
| at.% | 85.96 | 10.26 | 3.78 | |
| β phase | wt.% | 86.29 | 5.27 | 8.44 |
| at.% | 83.29 | 9.04 | 7.67 | |
| CoCrMo | Co | Cr | Mo | |
| wt.% | 27.72 | 26.90 | 06.91 | |
| at % | 52.71 | 25.63 | 3.84 | |
| Materials | Roughness (Ra, nm) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Hardness (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti6Al4V | 36 ± 8 | 134 ± 21 | 5.07 ± 0.25 |
| CoCrMo | 40 ± 12 | 299 ± 13 | 6.96 ± 0.16 |
| Method | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Contact mode | Reciprocating |
| Contact load | Constant normal at 143 mN |
| Sliding distance | 200 µm |
| Sliding speed | 12 mm/min |
| Sliding cycles | 1800 cycles |
| Environment | PBS (pH 7.4), SL (pH 4 and 2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, J.J.; Cudjoe, E.; Patel, M.V.; Caputo, M. Sliding Corrosion Fatigue of Metallic Joint Implants: A Comparative Study of CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V in Simulated Synovial Environments. Lubricants 2022, 10, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10040065
Ryu JJ, Cudjoe E, Patel MV, Caputo M. Sliding Corrosion Fatigue of Metallic Joint Implants: A Comparative Study of CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V in Simulated Synovial Environments. Lubricants. 2022; 10(4):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10040065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Jae Joong, Edward Cudjoe, Mihir V. Patel, and Matt Caputo. 2022. "Sliding Corrosion Fatigue of Metallic Joint Implants: A Comparative Study of CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V in Simulated Synovial Environments" Lubricants 10, no. 4: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10040065
APA StyleRyu, J. J., Cudjoe, E., Patel, M. V., & Caputo, M. (2022). Sliding Corrosion Fatigue of Metallic Joint Implants: A Comparative Study of CoCrMo and Ti6Al4V in Simulated Synovial Environments. Lubricants, 10(4), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10040065