Abstract
This study aimed to examine whether probiotics supplements using Bifidobacterium bifidum (Bf-688) can improve clinical characteristics and gut microbiomes among patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This open-label, single-arm trial consisted of 30 children aged 4–16 years who met the criteria for ADHD diagnosis. Each subject took Bf-688, with one sachet in the morning and one in the evening (daily bacteria count 5 × 109 CFUs), for 8 weeks. Patients’ clinical symptoms were assessed using the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale (SNAP-IV). We collected stool samples at the baseline, the 8th week, and the 12th week for gut microbiota examination. During the 8-week Bf-688 supplement period, patients’ inattention symptoms and hyperactivity/impulsive symptoms improved, and their weights and BMIs increased. For gut microbiota, the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B ratio) decreased significantly. LEfSe analysis revealed that Firmicutes significantly decreased while Proteobacteria significantly increased during the 8-week treatment period. After Bf-688 was discontinued for 4 weeks (12 weeks from baseline), Bacteroidota significantly decreased and Shigella significantly increased. The probiotic Bf-688 supplement was associated with an improvement of clinical symptoms and with weight gain among ADHD children. Furthermore, gut microbiota composition was significantly altered by the Bf-688 supplement. A future randomized control trial is warranted to verify these findings.
1. Introduction
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common mental disorders that occur in childhood. It affects approximately 3 to 10% school-age children around the world [1]. Children with ADHD suffer from failures in academic performance, in interpersonal relationships, and present various psychiatric comorbidities [2]. ADHD may result from multidimensional pathophysiologies [3]. A recent focal point of research has been on the multicomponent bidirectional signaling pathways between the gut and the brain [4]. The “gut–brain axis,” which refers to the link between gut microbiota and the central nervous system, has been suggested to affect neurodevelopmental disorders such as ADHD [5,6,7,8,9]. Therefore, modification of microbiota profiles by using probiotics supplements in patients with ADHD may shed light on the search for novel therapeutic applications [10,11,12,13].
One prospective study showed that supplementing a child’s diet with probiotics (Lactobacillus rhamnosus, LGG) during the first six months of life can reduce the risk of ADHD and autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in later childhood [14]. A clinical trial conducted in Taiwan demonstrated that Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 improved inattentive/hyperactive symptoms in children with ASD [15]. A randomized control trial showed that children and adolescents with ADHD who had received LGG supplementation showed better health-related QoL compared to their peers who received placebos [16]. In one study, researchers observed favorable effects of probiotic supplementation using LGG supplementation on cognitive function in children and adolescents; there was a reduced risk of developing ADHD or autism [17]. In contrast, a study in Sweden reported that both Synbiotic 2000 and placebos improved ADHD symptoms equally well. In adults with ADHD, those with elevated plasma vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) levels proposed a reduction in autism symptoms in children and an improvement of emotional regulation [18]. In a 10-week randomized control trial for micronutrient supplementation in 17 children with ADHD, micronutrient administration modulated Bifidobacterium abundance and had potential implications for modulating and regulating ADHD behavior [19].
A previous case-control study revealed a nominal increase in Bifidobacterium genus in ADHD cases and proposed that altering the gut microbiome may result in dopamine precursor synthesis [20]. The Bifidobacterium bifidum (B. bifidum) species constitutes one of the dominant taxa amongst Bifidobacterial communities [21]. B. bifidum has been demonstrated to improve the quality of life in individuals with rhino-conjunctivitis seasonal allergies [22], and it has been observed to reduce milk allergies in infants [23]. Another clinical trial indicated that the B. bifidum TMC3115 strain (TMC3115) may exhibit beneficial effects on the serum cholesterol metabolism of subjects with dyslipidaemia via the modulation of their intestinal microbiota [24]. Furthermore, heat-inactivated B. bifidum MIMBb75 (SYN-HI-001) has been shown to substantially alleviate the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome [25]. B. bifidum G9-1 (BBG9-1) improves dysbiosis, which results in an increase in organic acids and improved neurotransmission (including dopamine) [26]. In addition, a mixture of probiotics containing Lactobacillus species and B. bifidum could improve rotational behavior, cognitive function, and neuronal damage in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) [27].
Numerous studies have shown that probiotic supplementation can have a positive effect on the course of neurodevelopmental disorders, including ADHD [13]. However, the therapeutic effect of the B. bifidum Bf-688 strain has not yet been investigated in children with ADHD. We hypothesized that altering the dysbiosis of gut microbiota may be associated with improvements in ADHD clinical symptoms. This open-label, single-arm clinical study aimed to examine whether Bf-688 supplementation could improve the clinical symptoms of ADHD and facilitate healthy weight gain. We also investigated whether 8-week Bf-688 supplementation would change gut microbiome composition and whether any changed composition would last for more than four weeks after discontinuing Bf-688.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
This research protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan. Eligible patients with ADHD were recruited from the outpatient Department of Child Psychiatry at Chang Gung Children’s Hospital in Taiwan. We explained the protocols of this study to participants and their parents or guardians prior to their entry into this study; written informed consent was obtained from both the children and their parents/guardians upon their agreement.
The inclusion criteria for patients with ADHD were as follows: (a) a clinical diagnosis of ADHD made by a senior child psychiatrist via structured interviews using the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM–5) [28,29]; (b) age between 4 and 16 years; and (c) no prior history of using any medical treatments for ADHD. The exclusion criteria of this study were as follows: (a) patients with a history of major neuropsychiatric diseases, including intellectual disabilities, autism spectrum disorder, bipolar disorders, major depressive disorders, psychotic disorders, or substance dependence; (b) patients with any major physical illnesses, such as epilepsy, severe head trauma, or gastrointestinal disorders; and (c) patients who are vegetarians or are currently taking any probiotics or antibiotics.
2.2. Study Procedure
This open-label, single-arm trial recruited 30 children aged 4–16 years who met the criteria of ADHD diagnosis. Each subject took Bf-688 for 8 weeks, with one sachet in the morning and one in the evening (daily bacteria count 5 × 109 CFUs). At the baseline, 2nd, 4th, and 8th weeks for each subject, ADHD symptoms were assessed using the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham Rating Scale (SNAP-IV) parent-form [30], and the patients’ heights and weights were measured. We collected stool samples at the baseline and at the 8th week for gut microbiota examination. In order to investigate whether the gut microbiota composition changed after discontinuing Bf-688 for four weeks, patients were also encouraged to provide fecal samples at week 12. Patients were required not to change their diet patterns; moreover, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs were prohibited during the study period.
2.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
ADHD patients were asked to collect fecal samples by scooping a pea-sized piece of feces and placing it in a 50 mL Falcon tube. The samples were stored at 4 °C immediately after collection and then transferred to a −80 °C refrigerator in our laboratory within 24 h. From the DNA samples to the final data, including sample tests, PCR amplification as well as SMRTbell library preparation and sequencing were performed. Each step was applied to determine environmental microbial diversity and differences in microbial communities. Section 2.4, Section 2.5 and Section 2.6 describe each step of the workflow.
2.4. Extraction of Genome DNA, PCR Amplification, and Purification
Total genomic DNA from samples was extracted using the column-based method (i.e., QIAamp PowerFecal DNA Kit, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). DNA concentration was determined by a Qubit 4.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and adjusted to 1 ng/ul for the process described below.
The full-length 16S gene sequence (V1–V9 regions) was amplified by barcoded 16S gene-specific primers. According to the amplification of the full-length 16S gene with barcoded primers for multiplexed SMRTbell library preparation and sequencing procedure (Pacbio), each primer was designed to contain a 5′ buffer sequence (GCATC) with a 5′ phosphate modification, a 16-base barcode, and the degenerate 16S gene-specific forward or reverse primer sequences (Forward:5′Phos/GCATC-16-base barcode-AGRGTTYGATYMTGGCTCAG-3′; Reverse: 5′Phos/GCATC-16-base barcode—RGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′). The degenerate base identities were as follows: R = A, G; Y = C, T; and M = A, C. In brief, 2 ng of gDNA was used for the PCR reaction, which was carried out with KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (Roche) under the following PCR conditions: 95 °C for 3 min; 20~27 cycles (sample dependences) of: 95 °C for 30 s; 57 °C for 30 s; 72 °C for 60 s; and 72 °C for 5 min then held at 4 °C. The PCR products were monitored on a 1% agarose gel. Samples with a bright main strip of around 1500 bp were chosen and purified using AMPure PB beads for the library preparation procedure described below.
2.5. SMRTbell Library Construction and Sequencing
The SMRTbell library was prepared according to the amplification of full-length 16S gene with barcoded primers for multiplexed SMRTbell library preparation and sequencing procedure (Pacbio). In brief, an equal molar of each barcoded PCR product was pooled and then 500–1000 ng of the pooled amplicon sample was used for DNA damage repair followed by End Repair/A-tailing and ligation steps in order to introduce universal hairpin adapters onto the double-stranded DNA fragments. After purification with AMPure PB beads to remove adapter dimers, the SMRTbell library was incubated with sequencing primer v4 and sequel II Binding Kit 2.1 for primer annealing and polymerase binding. Finally, we performed sequencing using the circular consensus sequence (CCS) mode on a PacBio Sequel Iie instrument to generate HiFi reads with predicted accuracy (Phred Scale) = 30.
2.6. Data Analysis
The circular consensus sequence (CCS) reads were determined using a minimum predicted accuracy of 0.9 and a minimum number of 3 passes in the official workflow of PacBio via the SMRT Link software. After demultiplexing, the CCS reads were further processed with DADA2 in order to obtain amplicons with single-nucleotide resolutions [31,32]. The DADA2 workflow included quality filtering, dereplication, learning the dataset-specific error model, ASV inference, and chimera removal. Trimming and filtering were performed with a maximum of two expected errors per read (maxEE = 2). The DADA2 algorithm resolved exact amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) with single-nucleotide resolutions from the full-length 16S rRNA gene with a near-zero error rate. For each representative sequence, we used the feature-classifier [33] and classify-consensus-vsearch algorithm in QIIME2 [34] in order to annotate taxonomy classification based on the information retrieved from the NCBI database. In order to analyze sequence similarities among different ASVs, multiple sequence alignments were conducted by using the QIIME2 alignment MAFFT [35] against the NCBI database [36,37]. A phylogenetic tree was constructed with a set of sequences that were representative of the ASVs using the QIIME2 phylogeny FastTree [38].
Alpha diversity indicates species complexity within individual samples based on seven different criteria outputs, including the following: observed-species; Menhinick’s Richness; Margalef’s richness; Shannon index; Simpson index; PD whole tree; and good coverage. Observed-species is the number of different species represented in the microbial community. Community richness was assessed using both Menhinick’s richness and Margalef’s richness, and the relative abundance and evenness accounting for diversity were evaluated by Shannon and Simpson indices. We constructed a rarefaction curve using random selection of a certain amount of sequencing data from each sample to represent the number of observed species [39].
For statistical analysis, significance of all species among groups at various taxonomic levels was detected using differential abundance analysis with a zero-inflated Gaussian (ZIG) log-normal model as implemented in the “fitFeatureModel” function of the Bioconductor metagenomeSeq package [40]. Furthermore, Welch’s t-test was performed using STAMP software [41]. Statistically significant biomarkers were identified by the use of LefSe analysis [42]. In brief, LefSe is an approach based on an algorithm that performs the non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test and Wilcoxon rank-sum test in order to identify bacterial taxa for which their relative abundance is significantly different between the control and interest groups. LefSe applies LDA to bacterial taxa identified as significantly different and further assesses the effect size of each differentially abundant taxon. In this study, taxa with an LDA score (log 10) > 4 were considered significant. Anosim and MRPP analyses were applied to determine whether community structures significantly differed among and within groups.
3. Results
In total, 30 children with ADHD (mean age: 6.9 years old, 80% male) were recruited for this study (Table 1). In our study sample, a high male-to-female ratio was found (4:1), which corresponds to an ADHD prevalence ratio ranging from 2:1 to 10:1 [43,44]. Among them, 23 patients completed the 8-week trial and provided fecal samples for gut microbiome analysis. Moreover, seven patients provided an additional fecal sample for analysis 4 weeks after completing the trial (12 weeks after baseline).

Table 1.
Characteristics at baseline among ADHD patients (N = 30) who received 8-week probiotic therapy.
As shown in Figure 1, during the eight-week period of ADHD patients receiving oral probiotic Bf-688, ADHD inattention symptoms (Figure 1A) and hyperactivity/impulsive symptoms (Figure 1B) appeared to significantly improve at both week 4 and week 8 (p < 0.05). During the eight-week period of ADHD patients receiving oral probiotic Bf-688, patients’ body weights (Figure 1C) significantly increased both at week 4 and at week 8, while BMI significantly increased at week 8 (Figure 1D).
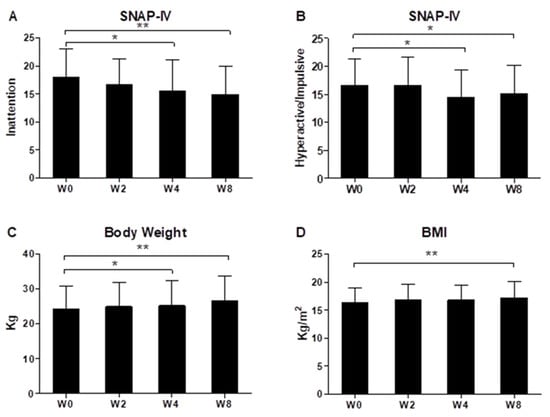
Figure 1.
ADHD inattention symptoms (A), hyperactivity/impulsive symptoms (B), patients’ body weight (C) and BMI (D) during the eight-week period of ADHD patients receiving oral probiotic supplements (Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bf-688). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
With regard to gut microbiota data, sequencing depth was evaluated using a rarefaction curve to confirm the suitability of each sample. Species rarefaction curves showed a tendency toward saturation, indicating that the sequencing depth was sufficient (Figure S1A). In addition, Figure S1B shows the richness of probiotics for the different weeks. Figure S1C represents the species accumulation curve. The sequencing depth achieved included considerable information about total species richness.
Figure 2 shows the abundance of the most prevalent bacteria at the phylum level in the fecal samples of ADHD patients at the baseline, week 8, and week 12. We observed that the main phyla were Actinobacteriota, Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Fusobacteriota. The Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B ratio), a relevant microbial biomarker of ADHD, significantly decreased from baseline to week 8 (p = 0.0012) (Figure 3). The F/B ratio increased after patients discontinued the Bf-688 supplement (from week 8 to week 12, p = 0.0026).
Figure 2.
Abundance of the most prevalent bacteria at the phylum level in the fecal samples of ADHD patients at baseline, week 8, and week 12.
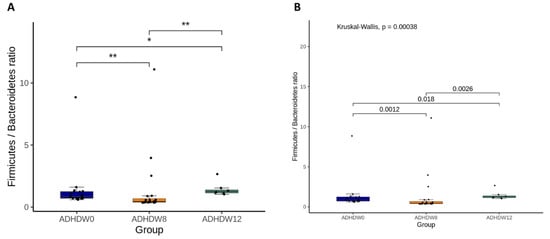
Figure 3.
The Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B ratio) at baseline, week 8, and week 12. Statistical analyses used analysis of variance (ANOVA) (A) and the Kruskal–Wallis test (B). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Figure 4 illustrates the bacterial taxonomic distributions of phylum levels in ADHD patients along with time. The most abundant families are Bacteroidota, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria, respectively. Figure S2 shows the bacterial taxonomic distributions at the species level in ADHD patients at baseline, week 8, and week 12. Bacteroides vulgatus, Bacteroides steroids, Bacteroides uniformis, Bacteroides fragilis, and Shigella flexneri were the five most abundant species among patients.
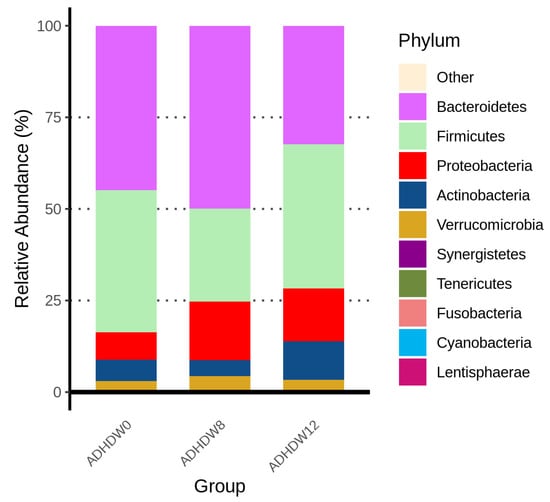
Figure 4.
Bacterial taxonomic distributions of phylum levels in ADHD patients at baseline, week 8, and week 12.
We further analyzed the gut microbiota composition of ADHD subjects. The Shannon index and Simpson index were analyzed in order to determine species richness; we found no significant differences between the baseline, week 8, and week 12 (Figure 5). Figure 6 shows the flora with significant differences between the baseline and the 8th week. Figure 6A shows enriched bacteria identified at the genus level using LEfSe analysis after Bf-688 treatment for 8 weeks. Firmicutes significantly decreased while Proteobacteria significantly increased. Our previous study [45] found a high abundance of Bacteroides ovatus (B. ovatus) in ADHD subjects. In the current study, an 8-week probiotic (Bf-688) supplement reduced the abundance of B. ovatus in ADHD subjects. Figure 6B shows enriched bacteria at the genus level using LEfSe analysis after Bf-688 was discontinued for 4 weeks (12 weeks from baseline). Bacteroidota significantly decreased while Shigella significantly increased.
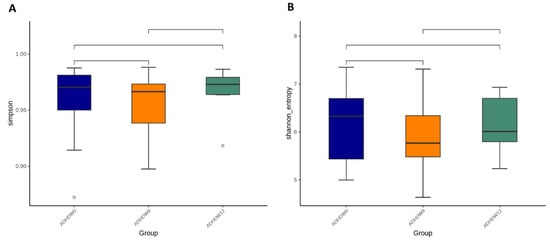
Figure 5.
The Simpson index (A) and Shannon index (B) among ADHD patients at baseline, week 8, and week 12.
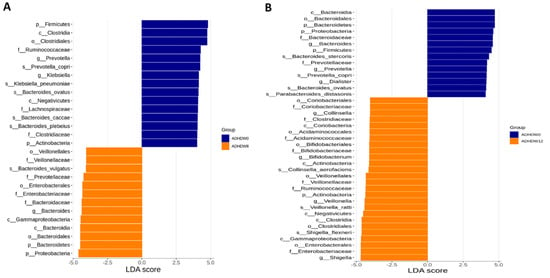
Figure 6.
Flora with significant differences between baseline and the 8th week (A) and between baseline and the 12th week (B). The orange bars represent flora with higher abundances after taking probiotics (week 8). The blue bars show flora with higher expressions at the baseline.
The relative abundances of dominant species are shown in Figure 7. Abundances greater than 1% of the species (ASVs) appearing in at least one sample are illustrated. The values are sorted from small to large, and the top 30 dominant species with differences between groups were selected for the circle chart. Throughout the baseline, week 8, and week 12, Collinsella aerofaciens and Erysipelatoclostridium ramosum were collectively abundant species. However, Clostridium viride showed relatively high abundance in the samples at baseline (week 0). The abundances of Granulicatella elegans and Blautia hydrogenotrophica were relatively high at week 0 and decreased at week 8; then, they were re-elevated at week 12.
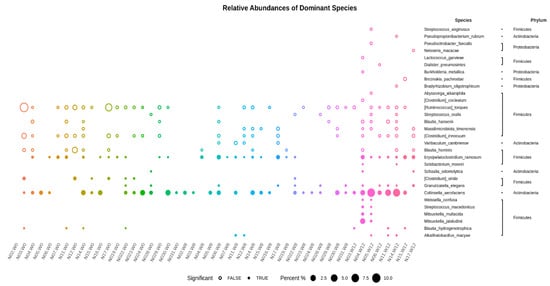
Figure 7.
The dominant species and species abundances of each sample shown with those having abundances greater than 1% of the species (ASVs) appearing in at least one sample. The p-values between the two-group statistics (Wilcoxon rank-sum test) or the multi-group statistics (Kruskal–Wallis test). The values are sorted from small to large, and the top 30 dominant species with differences between groups are selected for the circle chart. A solid circle indicates the statistical threshold reached (p < 0.05), and a hollow circle represents a species under the statistical threshold.
4. Discussion
This study is the first one to use B. bifidum (Bf-688 strain) as a supplement for ADHD, and ADHD symptoms improved during the 8-week test period. Various strains of B. bifidum have been demonstrated to improve several physical conditions, including rhinoconjunctivitis-specific quality of life [22], reducing milk allergies in infants [23], and improving the serum cholesterol metabolism of subjects with dyslipidemia [24], irritable bowel syndrome [25], and Parkinson’s disease (PD) [27]. B. bifidum G9-1 (BBG9-1) potentially improves dysbiosis, which results in modulations of organic acids and neurotransmission (including dopamine) [26]. Furthermore, neurochemical mechanisms that interfere with monoamine neurotransmitter synthesis have been implicated in ADHD pathophysiologies [46]. We proposed that Bf-688 may modulate catecholamine functions indirectly among ADHD patients. Whether ADHD symptoms improve when taking Bf-688 supplements involved in monoamine modulations still warrants further clarification.
Our clinical study revealed that ADHD patients’ body weights and BMIs significantly increased after Bf-688 administration. Bifidobacterium species have been proven to reduce the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants [47]. A previous clinical trial found that tolerability and safety of B. bifidum HI-MIMBb75 was rated as very good or good by 91% of participants [25]. ADHD medications have been associated with risks of decreased appetite, weight loss, and abdominal pain in children and adolescents [48]. The results in this study imply that Bifidobacterium may have potential beneficial effects on gastrointestinal symptoms in ADHD patients. Whether supplements of Bf-688 improve ADHD children’s appetite or weight gain requires further validation with a randomized control trial.
Bacterial taxonomic distributions changed during the administration of Bf-688 supplements in ADHD patients. The Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B ratio), a microbial biomarker, significantly decreased from baseline to week 8 and then re-elevated from week 8 to week 12. The F/B ratio evolves during different life stages [49], and a higher F/B ratio has been considered as a biomarker of obesity in animals and humans [50]. A previous clinical trial indicated that a B. bifidum TMC3115 supplement reduced allergic scores, improved anti-inflammatory responses, and reduced the serum levels of IgE in infants. In contrast, a B. bifidum supplement increased the proportion of probiotics and reduced the proportion of pathogens [23]. Another study of older adults revealed that probiotics, including B. bifidum, maintained CD4+ lymphocytes and produced a less inflammatory cytokine profile, possibly as a result of changes in their microbial communities; furthermore, this profile more closely resembled those reported in healthy younger populations [51]. Our case–control study previously demonstrated that the abundances of Bacteroides and Sutterella may be potential gut microbiota markers of ADHD and that dietary content may be associated with gut microbiome composition [45]. Taken together with our current results, B. bifidum supplements changed gut microbial composition (reduced F/B ratio); however, the changed composition diminished after discontinuing B. bifidum supplements.
Our study has certain limitations. First, this study design was an open-label, single-arm study rather than a randomized control trial. The current study lacked a comparison group, and ADHD clinical symptoms were subjectively determined. The therapeutic effect of Bf-688 could have been easily influenced by the placebo effect. Second, the sample size was small. Only 23 patients completed the 8-week study period; thus, statistical power was limited. In addition, the age range of the participants was wide (4–16 years), and changes of gut microbiomes and behavioral patterns may be different between age groups. However, subgroup analyses stratified by age were not performed in this study as a result of the small sample size. Third, dietary habits or lifestyles may influence the gut microbiome. Although we asked patients not to change their dietary patterns and antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs were prohibited, the gut microbiota may still have been altered by other environmental factors. Fourth, cytokine or immunological function levels were not measured in this study. Therefore, the manner probiotics interact with gut microbiota and behavioral symptoms still requires further investigation. Additional studies are needed to clarify the molecular mechanisms that underly the gut–brain axis as the basis for modifying commensal microbiota or their functions for targeting ADHD [52].
5. Conclusions
The results in this study suggest oral probiotic Bf-688 improved clinical symptoms of ADHD and increased body weights and BMIs of ADHD children. Furthermore, gut microbiota composition was significantly altered by the Bf-688 supplement. A future randomized control trial is warranted to verify the treatment effects of probiotics (Bf-688) on ADHD symptoms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jpm12020227/s1, Figure S1. The rarefaction curve of gut microbiome at baseline, week 8, and week 12. Species rarefaction curves showed a tendency toward saturation, indicating that sequencing depth was sufficient (A); the richness of probiotics for different weeks (B); the species accumulation curve (C). Figure S2. The bacterial taxonomic distributions at the species level in the ADHD patients at baseline, week 8, and week 12.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.-J.W. and C.-Y.Y.; methodology, L.-J.W.; formal analysis, L.-J.W.; investigation, L.-J.W., W.-J.C. and C.-S.T., S.-Y.L.; data curation, H.-C.K.; writing—original draft preparation, L.-J.W. and C.-Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.-Y.L.; supervision, H.-C.K.; project administration, L.-J.W., W.-J.C. and C.-S.T.; funding acquisition, L.-J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (research grant CMRPG8K0761 and CMRPG8M0031) and the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 109-2314-B-182-045-MY2).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan (IRB No: 201901479A3C601).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Yu-Lun Kuo at BIOTOOLS Co., Ltd. in Taiwan for kindly supporting the bioinformatics analysis of NGS data; Wei-Tsun Soong for granting us the use of the Chinese version of the K-SADS; and Shur-Fen Gau for granting our use of the Chinese version of the SNAP-IV. We also acknowledge Next-Generating Sequencing Core (grant CLRPD1J0012) at Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Polanczyk, G.V.; Willcutt, E.G.; Salum, G.A.; Kieling, C.; Rohde, L.A. ADHD prevalence estimates across three decades: An updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, T.J.; Biederman, J.; Mick, E. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Diagnosis, lifespan, comorbidities, and neurobiology. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2007, 32, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posner, J.; Polanczyk, G.V.; Sonuga-Barke, E. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 2020, 395, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathee, K.; Cickovski, T.; Deoraj, A.; Stollstorff, M.; Narasimhan, G. The gut microbiome and neuropsychiatric disorders: Implications for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukmajaya, A.C.; Lusida, M.I.; Soetjipto, S.Y. Systematic review of gut microbiota and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2021, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandgren, A.M.; Brummer, R.J.M. ADHD-originating in the gut? The emergence of a new explanatory model. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 120, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, S.A.; Mostert, J.C.; Szopinska-Tokov, J.W.; Bloemendaal, M.; Amato, M.; Arias-Vasquez, A. The role of the gut–brain axis in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchooduang, N.; Louthrenoo, O.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Possible links between gut-microbiota and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders in children and adolescents. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3391–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundgaard-Nielsen, C.; Knudsen, J.; Leutscher, P.D.C.; Lauritsen, M.B.; Nyegaard, M.; Hagstrøm, S.; Sørensen, S. Gut microbiota profiles of autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic literature review. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurek, L.; Sevil, M.; Jay, A.; Schroder, C.; Baghdadli, A.; Hery-Arnaud, G.; Geoffray, M.M. Is there a dysbiosis in individuals with a neurodevelopmental disorder compared to controls over the course of development? A systematic review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2021, 30, 1671–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligezka, A.N.; Sonmez, A.I.; Corral-Frias, M.P.; Golebiowski, R.; Lynch, B.; Croarkin, P.E.; Romanowicz, M. A systematic review of microbiome changes and impact of probiotic supplementation in children and adolescents with neuropsychiatric disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 108, 110187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checa-Ros, A.; Jerez-Calero, A.; Molina-Carballo, A.; Campoy, C.; Munoz-Hoyos, A. Current evidence on the role of the gut microbiome in ADHD pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. Nutrients 2021, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalenik, A.; Kardas, K.; Rahnama, A.; Sirojc, K.; Wolanczyk, T. Gut microbiota and probiotic therapy in ADHD: A review of current knowledge. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 110, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partty, A.; Kalliomaki, M.; Wacklin, P.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. A possible link between early probiotic intervention and the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders later in childhood: A randomized trial. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liong, M.T.; Chung, Y.C.E.; Huang, H.Y.; Peng, W.S.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, Y.Y.; Tsai, Y.C. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on children with autism spectrum disorder in Taiwan: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumperscak, H.G.; Gricar, A.; Ulen, I.; Micetic-Turk, D. A pilot randomized control trial with the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in ADHD: Children and adolescents report better health-related quality of life. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rianda, D.; Agustina, R.; Setiawan, E.A.; Manikam, N.R.M. Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function in children and adolescents: A systematic review of randomised trials. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skott, E.; Yang, L.L.; Stiernborg, M.; Söderström, Å.; Rȕegg, J.; Schalling, M.; Forsell, Y.; Giacobini, M.; Lavebratt, C. Effects of a synbiotic on symptoms, and daily functioning in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder—A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.J.; Purcell, R.V.; Darling, K.A.; Eggleston, M.J.F.; Kennedy, M.A.; Rucklidge, J.J. Human gut microbiome changes during a 10 week randomised control trial for micronutrient supplementation in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, E.; Ederveen, T.; Naaijen, J.; Zwiers, M.P.; Boekhorst, J.; Timmerman, H.M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Netea, M.G.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Franke, B.; et al. Gut microbiome in ADHD and its relation to neural reward anticipation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Milani, C.; Lugli, G.A.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bifidobacterium bifidum: A key member of the early human gut microbiota. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dennis-Wall, J.C.; Culpepper, T.; Nieves, C., Jr.; Rowe, C.C.; Burns, A.M.; Rusch, C.T.; Federico, A.; Ukhanova, M.; Waugh, S.; Mai, V.; et al. Probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri KS-13, Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1, and Bifidobacterium longum MM-2) improve rhinoconjunctivitis-specific quality of life in individuals with seasonal allergies: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W. Bifidobacterium bifidum TMC3115 ameliorates milk protein allergy in by affecting gut microbiota: A randomized double-blind control trial. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ge, L.; Pu, F.; Ma, X.; Cui, W.; Marrota, F.; He, F.; et al. Bifidobacterium bifidum TMC3115 Can Characteristically Influence Glucose and Lipid Profile and Intestinal Microbiota in the Middle-Aged and Elderly. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2019, 11, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, V.; Gschossmann, J.; Layer, P. Heat-inactivated Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 (SYN-HI-001) in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makizaki, Y.; Uemoto, T.; Yokota, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohno, H. Improvement of loperamide-induced slow transit constipation by Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 is mediated by the correction of butyrate production and neurotransmitter profile due to improvement in dysbiosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour Nosrani, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Alibolandi, Z.; Sarkar, P.; Ghazanfari, M.; Azami Tameh, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Banikazemi, Z.; Hadavi, R.; Naderi Taheri, M. Neuroprotective effects of probiotics bacteria on animal model of Parkinson’s disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine: A behavioral, biochemical, and histological study. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2021, 42, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; DSM-5; American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, W.J.; Lin, K.C.; Shen, L.J.; Gau, S.S. Prevalence of DSM-5 mental disorders in a nationally representative sample of children in Taiwan: Methodology and main findings. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 29, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gau, S.S.-F.; Shang, C.-Y.; Liu, S.-K.; Lin, C.-H.; Swanson, J.M.; Liu, Y.-C.; Tu, C.-L. Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Swanson, Nolan, and Pelham, version IV scale–parent form. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 17, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quin, C.; Estaki, M.; Vollman, D.M.; Barnett, J.A.; Gill, S.K.; Gibson, D.L. Probiotic supplementation and associated infant gut microbiome and health: A cautionary retrospective clinical comparison. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balvociute, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT—How do these taxonomies compare? BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gyarmati, P.; Kjellander, C.; Aust, C.; Song, Y.; Ohrmalm, L.; Giske, C.G. Metagenomic analysis of bloodstream infections in patients with acute leukemia and therapy-induced neutropenia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paulson, J.N.; Stine, O.C.; Bravo, H.C.; Pop, M. Differential abundance analysis for microbial marker-gene surveys. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willcutt, E.G. The prevalence of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analytic review. Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yuan, S.-S.; Yang, C.-J.; Yang, K.-C.; Huang, T.-S.; Chou, W.-J.; Chou, M.-C.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, T.-L.; et al. Prevalence rates of youths diagnosed with and medicated for ADHD in a nationwide survey in Taiwan from 2000 to 2011. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2016, 26, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-J.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chou, W.-J.; Lee, M.-J.; Chou, M.-C.; Kuo, H.-C.; Yeh, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Huang, L.-H.; Li, S.-C. Gut microbiota and dietary patterns in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 29, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaei, C.S.; Barone, H.; Kleppe, R.; Betari, N.; Reif, A.; Haavik, J. ADHD symptoms in neurometabolic diseases: Underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 132, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, P.C.; Skelley, J.W. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium species in prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in very-low birth weight infants. A systematic review. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 24, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmskov, M.; Storebø, O.J.; Moreira-Maia, C.R.; Ramstad, E.; Magnusson, F.L.; Krogh, H.B.; Groth, C.; Gillies, D.; Zwi, M.; Skoog, M.; et al. Gastrointestinal adverse events during methylphenidate treatment of children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariat, D.; Firmesse, O.; Levenez, F.; Guimaraes, V.D.; Sokol, H.; Dore, J.; Corthier, G.; Furet, J.-P. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human microbiota changes with age. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaiser, S.J.; Culpepper, T.; Nieves, C., Jr.; Ukhanova, M.; Mai, V.; Percival, S.S.; Christman, M.C.; Langkamp-Henken, B. Lactobacillus gasseri KS-13, Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1, and Bifidobacterium longum MM-2 ingestion induces a less inflammatory cytokine profile and a potentially beneficial shift in gut microbiota in older adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- Hiergeist, A.; Gessner, J.; Gessner, A. Current limitations for the assessment of the role of the gut microbiome for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).