Measurement of Oral Epithelial Thickness by Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
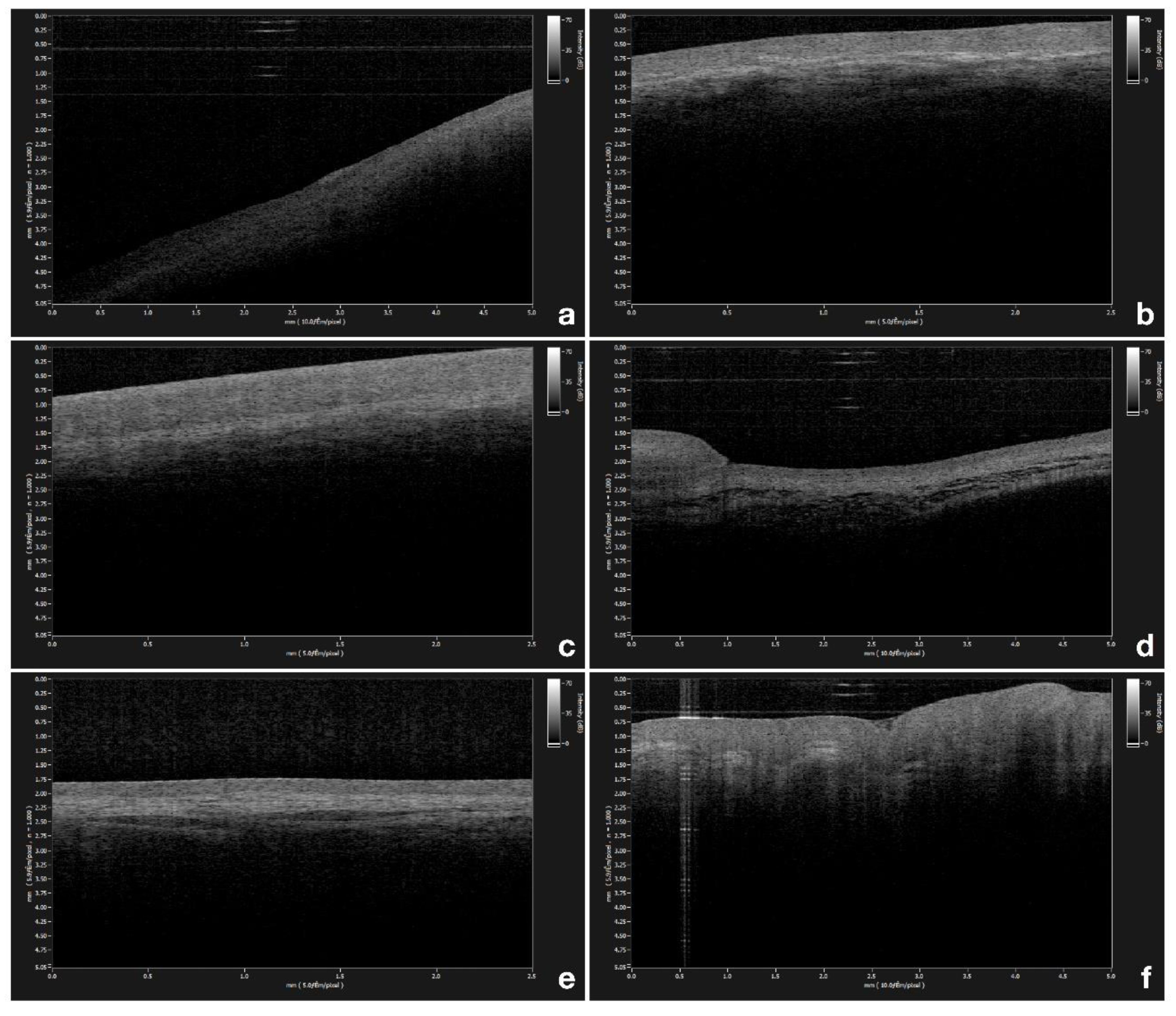
2.1. Epithelial Thickness Mesurement
2.2. OCT System
2.3. Statistical Analysis
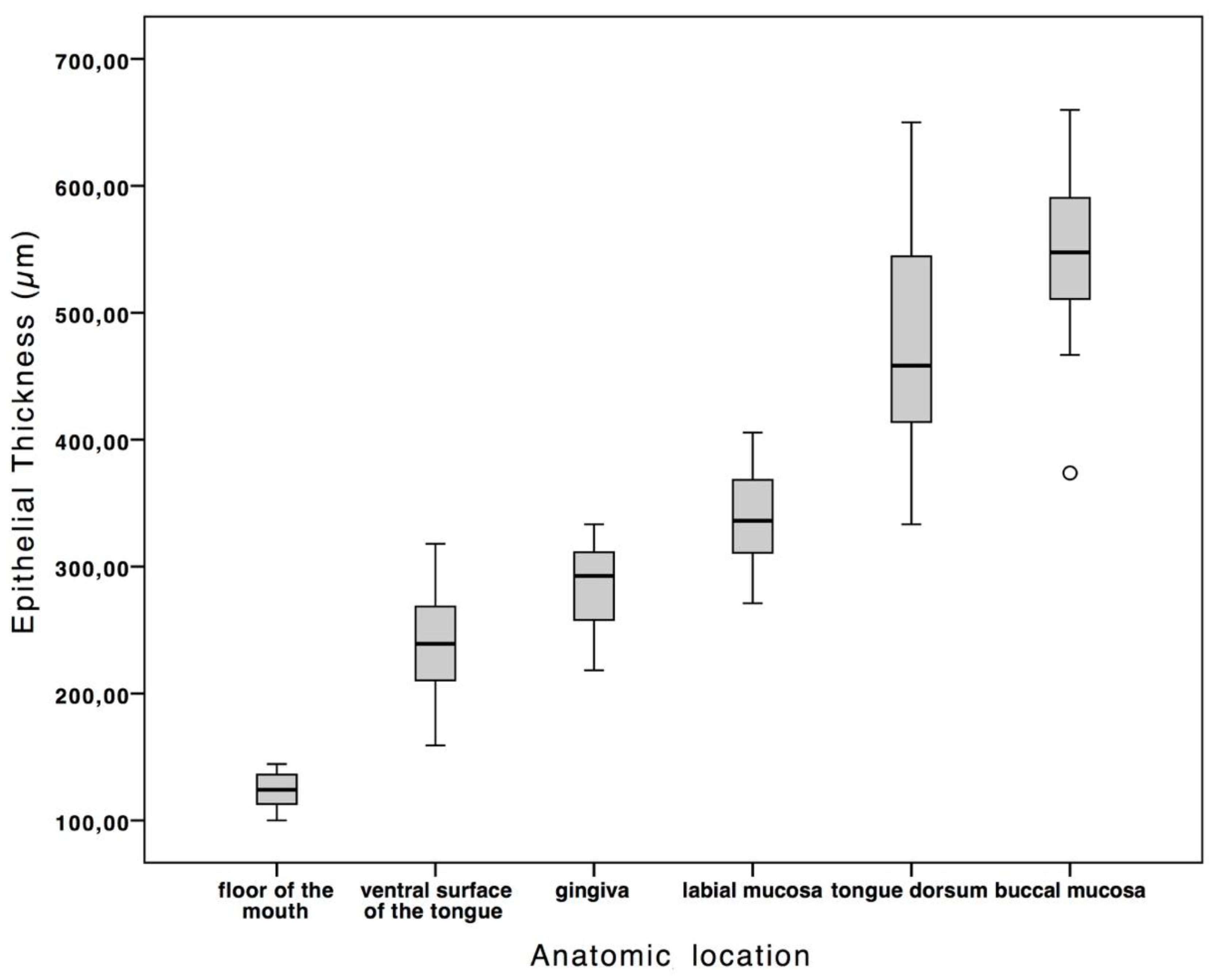
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gentile, E.; Maio, C.; Romano, A.; Laino, L.; Lucchese, A. The potential role of in vivo optical coherence tomography for evaluating oral soft tissue: A systematic review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldchtein, F.I.; Gelikonov, V.M.; Iksanov, R.R.; Gelikonov, G.V.; Kuranov, R.V.; Sergeev, A.M.; Gladkova, N.D.; Ourutina, M.N.; Reitze, D.H.; Warren, J.A.; et al. In vivo OCT imaging of hard and soft tissue of the oral cavity. Opt. Express 1998, 3, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, T.O.; Meyers, A. Early Detection of Premalignant Lesions and Oral Cancer. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 44, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-S.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chuang, C.-C.; Tsai, J.; Lin, K.-F.; Sun, C.-W. Dental optical coherence tomography. Sensors (Basel). 2013, 13, 8928–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.; Cho, N.; Kim, S.-H.; Jeong, H.; Kim, J.; Ahn, Y.-C. Simple Spectral Calibration Method and Its Application Using an Index Array for Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2011, 15, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Park, B.H.; Maguluri, G.N.; Lee, T.W.; Rogomentich, F.J.; Bancu, M.G.; Bouma, B.E.; de Boer, J.F.; Bernstein, J.J. Two-axis magnetically-driven MEMS scanning catheter for endoscopic high-speed optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 18130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.; Adler, D.C.; Fujimoto, J.G. Buffered Fourier domain mode locking: Unidirectional swept laser sources for optical coherence tomography imaging at 370,000 lines/s. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.J.; Wang, R.K. In vivo imaging of functional microvasculature within tissue beds of oral and nasal cavities by swept-source optical coherence tomography with a forward/side-viewing probe. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibhai, A.Y.; Or, C.; Witkin, A.J. Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography: A Review. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2018, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Deegan, A.J.; Chang, J.; Wang, R.K. Comparing imaging capabilities of spectral domain and swept source optical coherence tomography angiography in healthy subjects and central serous retinopathy. Eye Vis. 2018, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arens, C.; Glanz, H.; Wönckhaus, J.; Hersemeyer, K.; Kraft, M. Histologic assessment of epithelial thickness in early laryngeal cancer or precursor lesions and its impact on endoscopic imaging. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-T.; Lee, H.-C.; Lee, C.-K.; Yu, C.-H.; Chen, H.-M.; Chiang, C.-P.; Chang, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, C.C. Effective indicators for diagnosis of oral cancer using optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 15847–15862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prestin, S.; Rothschild, S.I.; Betz, C.S.; Kraft, M. Measurement of epithelial thickness within the oral cavity using optical coherence tomography. Head Neck 2012, 34, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, J.M.; Armstrong, W.B.; Guo, S.; Mahmood, U.; Su, J.; Jackson, R.P.; Shibuya, T.; Crumley, R.L.; Gu, M.; Chen, Z.; et al. In Vivo Optical Coherence Tomography of the Human Oral Cavity and Oropharynx. Arch. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilder-Smith, P.; Lee, K.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Osann, K.; Chen, Z.; Messadi, D. In vivo diagnosis of oral dysplasia and malignancy using optical coherence tomography: Preliminary studies in 50 patients. Lasers Surg. Med. 2009, 41, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Paparella, R.; Franco, R.; Montella, M.; Serpico, R.; Lucchese, A. Ultrasound imaging of oral fibroma: A case report. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogt, M.; Knüttel, A.; Hoffmann, K.; Altmeyer, P.; Ermert, H. Comparison of high frequency ultrasound and optical coherence tomography as modalities for high resolution and non invasive skin imaging. Biomed. Tech. (Berl). 2003, 48, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warszawik-Hendzel, O.; Olszewska, M.; Maj, M.; Rakowska, A.; Czuwara, J.; Rudnicka, L. Non-invasive diagnostic techniques in the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Case Rep. 2015, 9, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinformatics 2017, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Romano, A.; Salerno, C.; Minervini, G.; Minervini, G.; Gentile, E.; Serpico, R.; Lucchese, A. In vivo characterization of oral pemphigus vulgaris by optical coherence tomography. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Boer, J.F.; Leitgeb, R.; Wojtkowski, M. Twenty-five years of optical coherence tomography: The paradigm shift in sensitivity and speed provided by Fourier domain OCT [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchese, A.; Gentile, E.; Romano, A.; Maio, C.; Laino, L.; Serpico, R. The potential role of in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy for evaluating oral cavity lesions: A systematic review. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassia, V.; Gentile, E.; Di Stasio, D.; Jamilian, A.; Matarese, G.; D’Apuzzo, F.; Santoro, R.; Perillo, L.; Serpico, R.; Lucchese, A. In vivo confocal microscopy analysis of enamel defects after orthodontic treatment: A preliminary study. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2016, 40, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, A.; Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Santoro, R.; Marotta, A.; Itro, A.; Lucchese, A. Non-invasive analysis of bleaching effect of hydrogen peroxide on enamel by reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM): Study of series of cases. Odontology 2019, 107, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.D.; Cahill, L.; Liu, K.; MacAulay, C.; Poh, C.; Lane, P. Wide-field in vivo oral OCT imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, F.; Thale, A. Epithelial-connective tissue boundary in the oral part of the human soft palate. J. Anat. 1998, 193, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Schroeder, H.E. Architecture and density of the connective tissue papillae of the human oral mucosa. J. Anat. 1977, 123, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kraft, M.; Glanz, H.; von Gerlach, S.; Wisweh, H.; Lubatschowski, H.; Arens, C. Clinical value of optical coherence tomography in laryngology. Head Neck 2008, 30, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Anatomic Location | Thickness (µm) | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| gingiva | Mean | 285.04 | ± 32.98 |
| Min | 218.30 | ||
| Max | 333.33 | ||
| labial mucosa | Mean | 339.83 | ± 36.44 |
| Min | 271.19 | ||
| Max | 405.56 | ||
| buccal mucosa | Mean | 545.40 | ± 62.45 |
| Min | 373.75 | ||
| Max | 659.79 | ||
| ventral surface of the tongue | Mean | 239.79 | ± 37.30 |
| Min | 159.09 | ||
| Max | 318.00 | ||
| floor of the mouth | Mean | 124.09 | ± 13.53 |
| Min | 100.07 | ||
| Max | 144.44 | ||
| tongue dorsum | Mean | 479.32 | ± 83.56 |
| Min | 333.33 | ||
| Max | 650.02 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Stasio, D.; Lauritano, D.; Iquebal, H.; Romano, A.; Gentile, E.; Lucchese, A. Measurement of Oral Epithelial Thickness by Optical Coherence Tomography. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9030090
Di Stasio D, Lauritano D, Iquebal H, Romano A, Gentile E, Lucchese A. Measurement of Oral Epithelial Thickness by Optical Coherence Tomography. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(3):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Stasio, Dario, Dorina Lauritano, Hasan Iquebal, Antonio Romano, Enrica Gentile, and Alberta Lucchese. 2019. "Measurement of Oral Epithelial Thickness by Optical Coherence Tomography" Diagnostics 9, no. 3: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9030090
APA StyleDi Stasio, D., Lauritano, D., Iquebal, H., Romano, A., Gentile, E., & Lucchese, A. (2019). Measurement of Oral Epithelial Thickness by Optical Coherence Tomography. Diagnostics, 9(3), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9030090







