Overexpression of EIF5A2 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
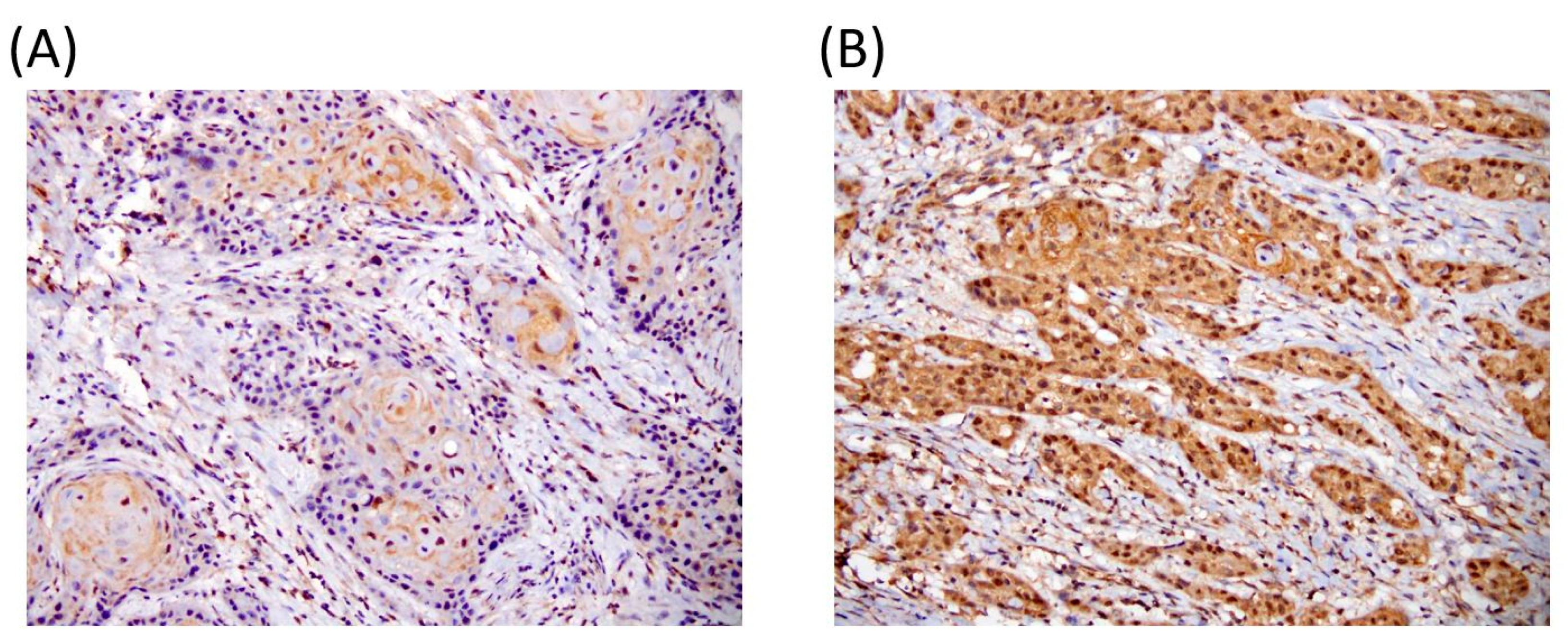
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.3. Patient and Public Involvement
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Relationships Between EIF5A2 Expression and Clinical Parameters in Oral Cancer Patients
3.2. EIF5A2 Expression of is Associated with EMT Markers in Oral Cancer Specimens
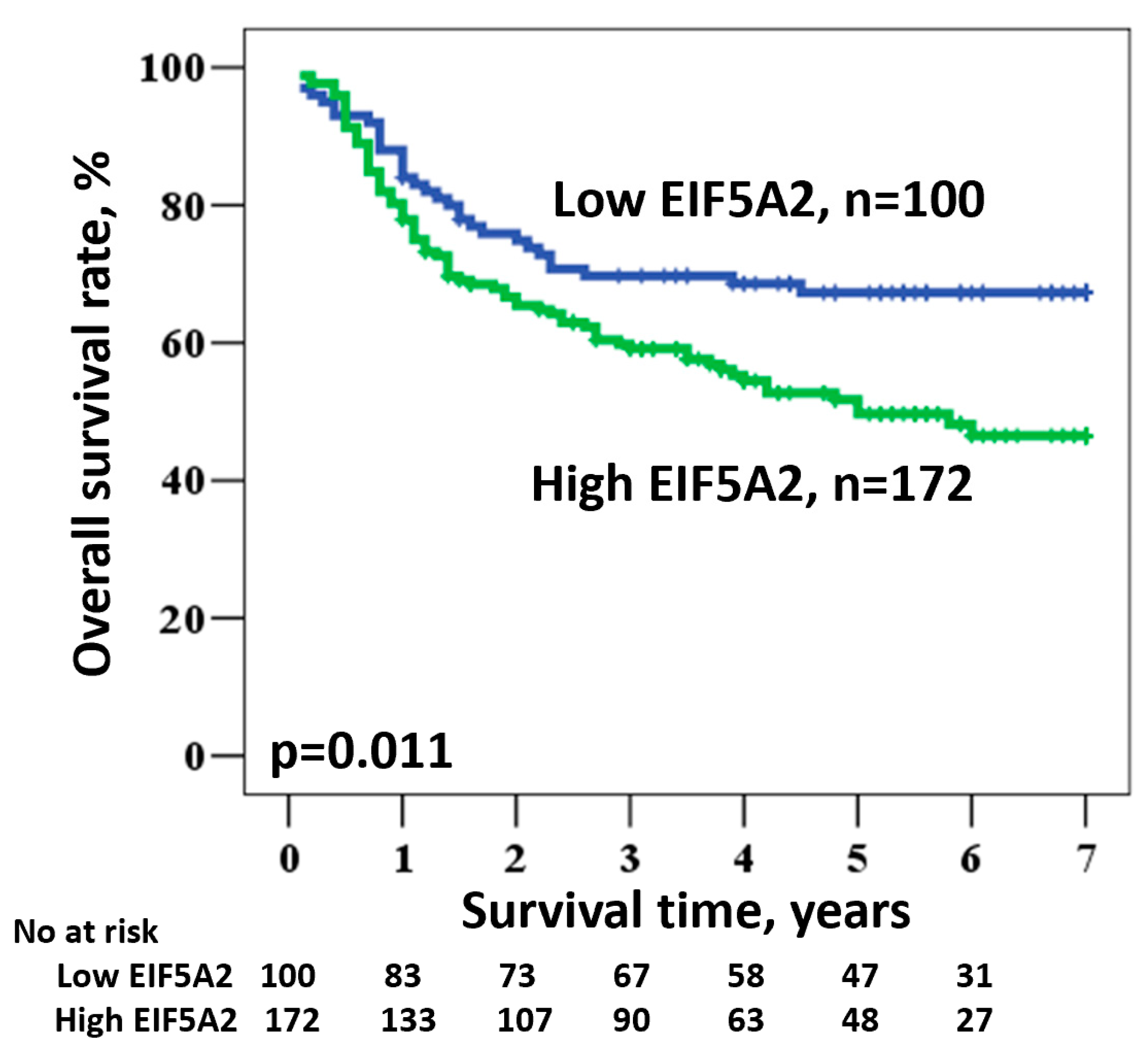
3.3. EIF5A2 is an Independent Factor Associated with Oral Cancer Overall Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.W.; Warnakulasuriya, S.; Gupta, P.C.; Dimba, E.; Chindia, M.; Otoh, E.C.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Califano, J.; Kowalski, L. Global Oral Health Inequalities in Incidence and Outcomes for Oral Cancer: Causes and Solutions. Adv. Dent. Res. 2011, 23, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.; Kowalski, L.P.; Agra, I.M.G.; Pontes, E.; Campos, O.D.; Pellizzon, A.C.A. Treatment results on advanced neck metastasis (N3) from head and neck squamous carcinoma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 132, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, S.D.; Hier, M.; Mlynarek, A.; Kowalski, L.P.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. Recurrent oral cancer: Current and emerging therapeutic approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosh, A.; Jones, T.; Harvey, J. A review on oral cancer biomarkers: Understanding the past and learning from the present. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almangush, A.; Heikkinen, I.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Coletta, R.D.; Läärä, E.; Leivo, I.; Salo, T. Prognostic biomarkers for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, H.W.; Chen, Y.; Wei, J.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Feng, Z.H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Luo, J.H.; Fang, Y. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 is highly expressed in prostate cancer and predicts poor prognosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.Y.; Zeng, T.T.; Ban, X.; Li, M.Q.; Zhang, B.Z.; Zhu, Y.H.; Hua, W.F.; Mai, H.Q.; Zhang, L.; Guan, X.Y.; et al. Expression of EIF5A2 associates with poor survival of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with induction chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, Z.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ni, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, S.; Teng, F.; et al. eIF5A2 regulates the resistance of gastric cancer cells to cisplatin via induction of EMT. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 4269–4279. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.B.; Park, J.H.; Kaevel, J.; Sramkova, M.; Weigert, R.; Park, M.H. The effect of hypusine modification on the intracellular localization of eIF5A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 383, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.-T.; Lin, S.-H.; Fu, L.; Tang, Z.; Che, C.-M.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Ming, X.-Y.; Liu, T.-F.; Tang, X.M.; Tan, B.B.; et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 promotes metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2016, 38, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, Z.A.; Haag, P.G.; Johansson, H.E. Human eIF5A2 on chromosome 3q25-q27 is a phylogenetically conserved vertebrate variant of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A with tissue-specific expression. Genomics 2001, 71, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.; Ma, N.F.; Pan, Z.Z.; Wu, H.X.; Liu, Y.D.; Wu, G.Q.; Kung, H.F.; Guan, X.Y. Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is associated with metastasis of human colorectal carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.F.; Xie, D.; Liu, J.H.; Luo, J.H.; Li, L.J.; Hua, W.F.; Wu, H.M.; Kung, H.F.; Zeng, Y.X.; Guan, X.Y. Expression and amplification of eIF-5A2 in human epithelial ovarian tumors and overexpression of EIF-5A2 is a new independent predictor of outcome in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.-B.; Kang, W.-M.; Yu, J.-C.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Zhou, L.; Cui, Q.-C.; Zhou, W.-X. Overexpression of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) Correlates with Cell Aggressiveness and Poor Survival in Gastric Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.H.; Cao, J.Z.; Zhang, D.; Liao, B.; Zhong, W.M.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.W.; Zhang, J.X.; Tong, Z.T.; Fan, S.; et al. EIF5A2 predicts outcome in localised invasive bladder cancer and promotes bladder cancer cell aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, F.; Chen, W.; Yao, M.; Lv, K.; Fu, P. EIF5A2 is a novel chemoresistance gene in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2015, 22, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Wu, S.; Song, Y.; Li, J. Knockdown of EIF5A2 inhibits the malignant potential of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.J.; Dong, S.S.; Ma, N.F.; Xie, D.; Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Lau, S.H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Guan, X.Y. Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cai, M.Y.; Tong, Z.T.; Dong, S.S.; Mai, S.J.; Liao, Y.J.; Bian, X.W.; Lin, M.C.; Kung, H.F.; Zeng, Y.X.; et al. Overexpression of EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce epithelial-mesenchymaltransition. Gut 2012, 61, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Chen, S.L.; Sung, W.W.; Hsieh, M.J.; Hsu, H.T.; Chen, L.H.; Chen, M.K.; Ko, J.L.; Chen, C.J.; Chou, M.C. PBK/TOPK Expression Predicts Prognosis in Oral Cancer. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Sung, W.W.; Lin, Y.M.; Chen, M.K.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, H.; Yeh, K.T.; Ko, J.L. Gender difference in the prognostic role of interleukin 6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.W.; Lin, Y.M.; Wu, P.R.; Yen, H.H.; Lai, H.W.; Su, T.C.; Huang, R.H.; Wen, C.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.J.; et al. High nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio of Cdk1 expression predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.W.; Lee, M.C.; Yeh, K.T.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. A polymorphic-844T/C in FasL promoter predicts survival and relapse in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5991–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viard-Leveugle, I.; Veyrenc, S.; French, L.E.; Brambilla, C.; Brambilla, E. Frequent loss of Fas expression and function in human lung tumours with overexpression of FasL in small cell lung carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, P.L.; Cheng, Y.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Wu, T.C.; Lee, H. IL-10 promotes tumor aggressiveness via upregulation of CIP2A transcription in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4092–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, M.B.; Hershey, J.W. The translation factor eIF5A and human cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchet, A.; Mocellin, S.; Belluco, C.; Ambrosi, A.; De Marchi, F.; Mammano, E.; Digito, M.; Leon, A.; D’Arrigo, A.; Lise, M.J.A. Gene expression profile of primary gastric cancer: Towards the prediction of lymph node status. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Sun, X.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Q.; Yu, H. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, P.M.J.; Henderson, C.A.; Jenkins, Z.A.; Smit-McBride, Z.; Wolff, E.C.; Hershey, J.W.B.; Park, M.H.; Johansson, H.E. Identification and characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A-2. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 4254–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisanaprakornkit, S.; Iamaroon, A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma. ISRN Oncol. 2012, 2012, 681469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, P.G.; Cristea, S.; Ambatipudi, S.; Desai, R.S.; Kumar, R.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.; Borges, A.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Beerenwinkel, N.; et al. Chromosomal Alterations and Gene Expression Changes Associated with the Progression of Leukoplakia to Advanced Gingivobuccal Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, D.M.; Medici, D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, S.; Wong, R.P.C.; Ardekani, G.S.; Zhang, G.; Martinka, M.; Ong, C.J.; Li, G. Role of EIF5A2, a downstream target of Akt, in promoting melanoma cell invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 110, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Muzio, L.; Pannone, G.; Santarelli, A.; Bambini, F.; Mascitti, M.; Rubini, C.; Testa, N.F.; Dioguardi, M.; Leuci, S.; Bascones, A.; et al. Is expression of p120ctn in oral squamous cell carcinomas a prognostic factor? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Gao, L.; Xie, L.; Xiao, G. GC7 enhances cisplatin sensitivity via STAT3 signaling pathway inhibition and eIF5A2 inactivation in mesenchymal phenotype oral cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EIF5A2 Expression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Case Number | Low | High | p-Value |
| Age (year) | 56.1±12.4 | 56.8±11.0 | 0.655 | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 42 | 15 (35.7) | 27 (64.3) | 0.878 |
| Male | 230 | 85 (37.0) | 145 (63.0) | |
| Smoking | ||||
| No | 160 | 55 (34.4) | 105 (65.6) | 0.329 |
| Yes | 112 | 45 (40.2) | 67 (59.8) | |
| Betel quid chewing | ||||
| No | 220 | 83 (37.7) | 137 (62.3) | 0.498 |
| Yes | 52 | 17 (32.7) | 35 (67.3) | |
| Differentiation | ||||
| Well | 42 | 14 (33.3) | 28 (66.7) | 0.616 |
| Moderate + Poor | 230 | 86 (37.4) | 144 (62.6) | |
| Stage | ||||
| I | 55 | 22 (40.0) | 33 (60.0) | 0.577 |
| II + III + IV | 217 | 78 (35.9) | 139 (64.1) | |
| T value | ||||
| 1 | 71 | 26 (36.6) | 45 (63.4) | 0.976 |
| 2 + 3 + 4 | 201 | 74 (36.8) | 127 (63.2) | |
| N value | ||||
| 0 | 168 | 72 (42.9) | 96 (57.1) | 0.008 |
| 1 + 2 + 3 | 104 | 28 (26.9) | 76 (73.1) | |
| EIF5A2 Expression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Case Number | Low | High | p-Value |
| E-cadherin 1 | ||||
| Low | 120 | 34 (28.3) | 86 (71.7) | 0.046 |
| High | 142 | 57 (40.1) | 85 (59.9) | |
| Beta-catenin 2 | ||||
| Low | 135 | 58 (43.0) | 77 (57.0) | 0.020 |
| High | 133 | 39 (29.3) | 94 (70.7) | |
| Overall Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Category | 5-year Survival (%) | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | ≥57/<57 | 60.9/61.0 | 1.061 | 0.749–1.503 | 0.739 |
| Gender | Male/Female | 59.7/71.4 | 1.477 | 0.862–2.531 | 0.156 |
| Smoking | Yes/No | 60.4/62.1 | 1.017 | 0.716–1.445 | 0.924 |
| Betel quid chewing | Yes/No | 62.6/60.9 | 0.851 | 0.533–1.359 | 0.500 |
| Stage | II+III+IV/I | 57.9/74.4 | 1.762 | 1.082–2.868 | 0.023 |
| N value | 1+2+3/0 | 36.8/68.4 | 2.770 | 1.906–4.024 | <0.001 |
| EIF5A2 | High/Low | 49.7/67.3 | 1.696 | 1.126–2.554 | 0.011 |
| Overall Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Category | Mean Survival (years) | HR * | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | ≥57/<57 | 4.8/4.9 | 0.837 | 0.570–1.230 | 0.365 |
| Gender | Male/Female | 4.8/5.5 | 1.347 | 0.736–2.468 | 0.334 |
| Smoking | Yes/No | 4.9/4.9 | 0.805 | 0.510–1.271 | 0.351 |
| Betel quid chewing | Yes/No | 4.8/5.1 | 0.750 | 0.416–1.352 | 0.338 |
| Stage | II+III+IV/I | 4.7/5.6 | 1.950 | 1.123–3.387 | 0.018 |
| EIF5A2 | High/Low | 4.3/5.2 | 1.714 | 1.134–2.590 | 0.011 |
| Overall Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Category | Mean Survival (yrs) | HR * | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | ≥57/<57 | 4.8/4.9 | 0.913 | 0.622–1.339 | 0.640 |
| Gender | Male/Female | 4.8/5.5 | 1.704 | 0.931–3.119 | 0.084 |
| Smoking | Yes/No | 4.9/4.9 | 0.809 | 0.514–1.274 | 0.361 |
| Betel quid chewing | Yes/No | 4.8/5.1 | 0.779 | 0.434–1.397 | 0.402 |
| N value | 1+2+3/0 | 3.4/5.4 | 2.699 | 1.847–3.943 | <0.001 |
| EIF5A2 | High/Low | 4.3/5.2 | 1.520 | 1.002–2.307 | 0.049 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-M.; Chen, M.-L.; Chen, C.-L.; Yeh, C.-M.; Sung, W.-W. Overexpression of EIF5A2 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070436
Lin Y-M, Chen M-L, Chen C-L, Yeh C-M, Sung W-W. Overexpression of EIF5A2 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(7):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yueh-Min, Mei-Ling Chen, Chia-Lo Chen, Chung-Min Yeh, and Wen-Wei Sung. 2020. "Overexpression of EIF5A2 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Diagnostics 10, no. 7: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070436
APA StyleLin, Y.-M., Chen, M.-L., Chen, C.-L., Yeh, C.-M., & Sung, W.-W. (2020). Overexpression of EIF5A2 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Diagnostics, 10(7), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10070436






