A Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Identification of CTX-M-Producing Enterobacterales from Culture Plates and Positive Blood Cultures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Monoclonal Antibodies
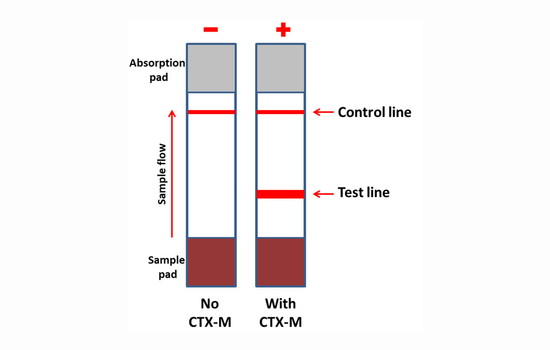
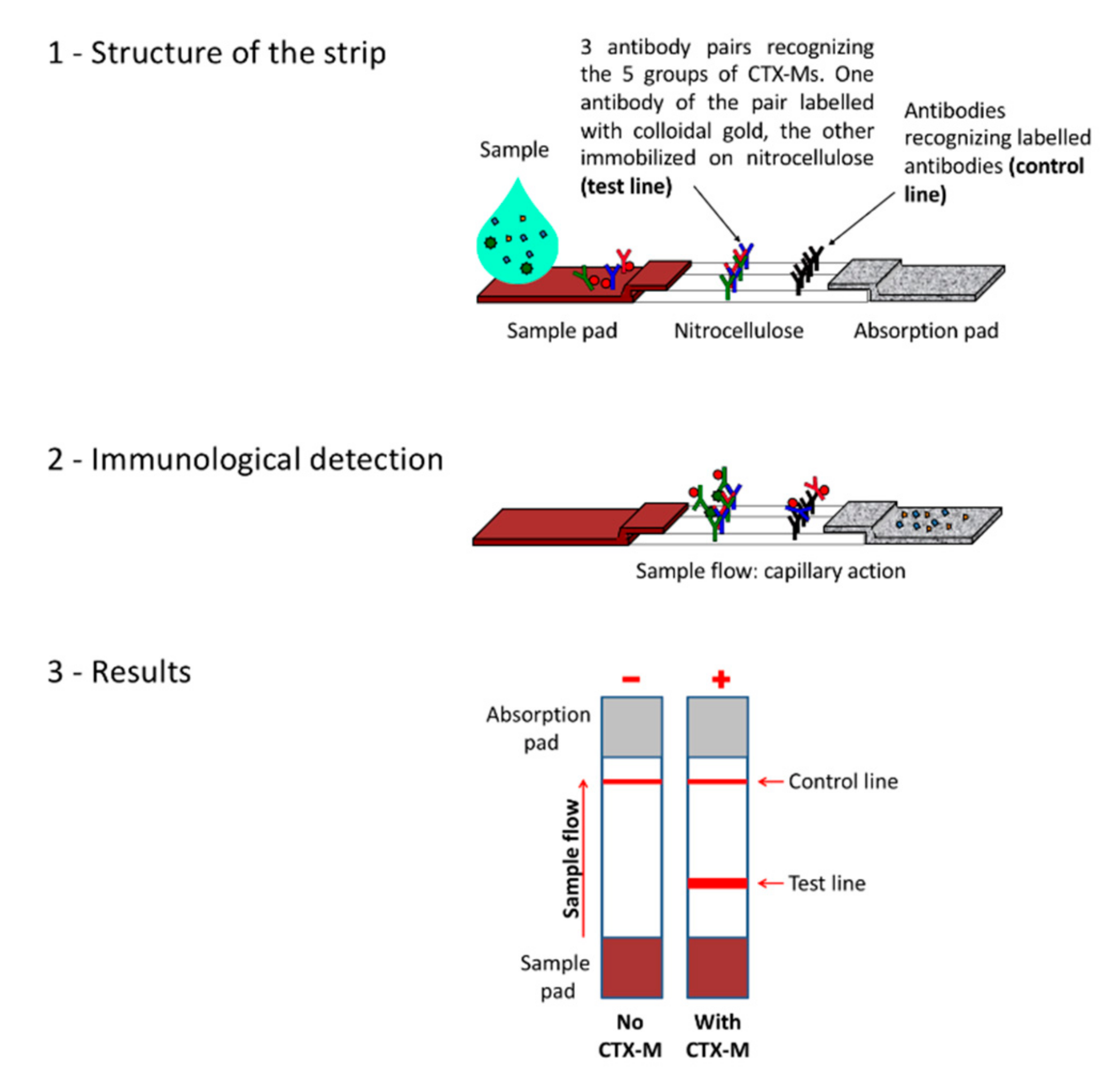
2.3. NG-Test CTX-M MULTI Assay and Protocol
2.4. Bacterial Strains
2.5. Positive Blood Cultures, Isolate Identification and Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Resistance Gene Detection
2.7. Culture Media Tested
3. Results
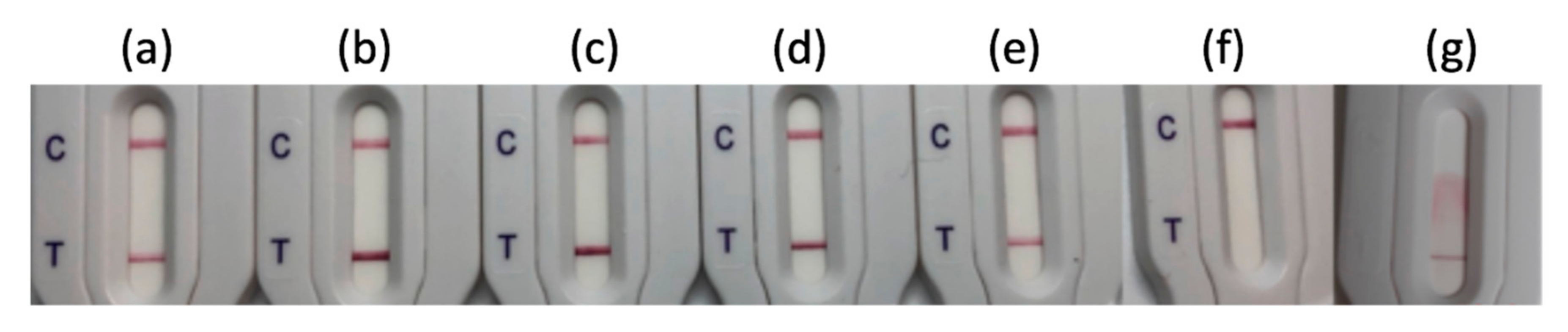
3.1. Retrospective Evaluation on Well-Characterized Isolates
3.2. Evaluation of NG-Test CTX-M MULTI Results on Different Culture Media
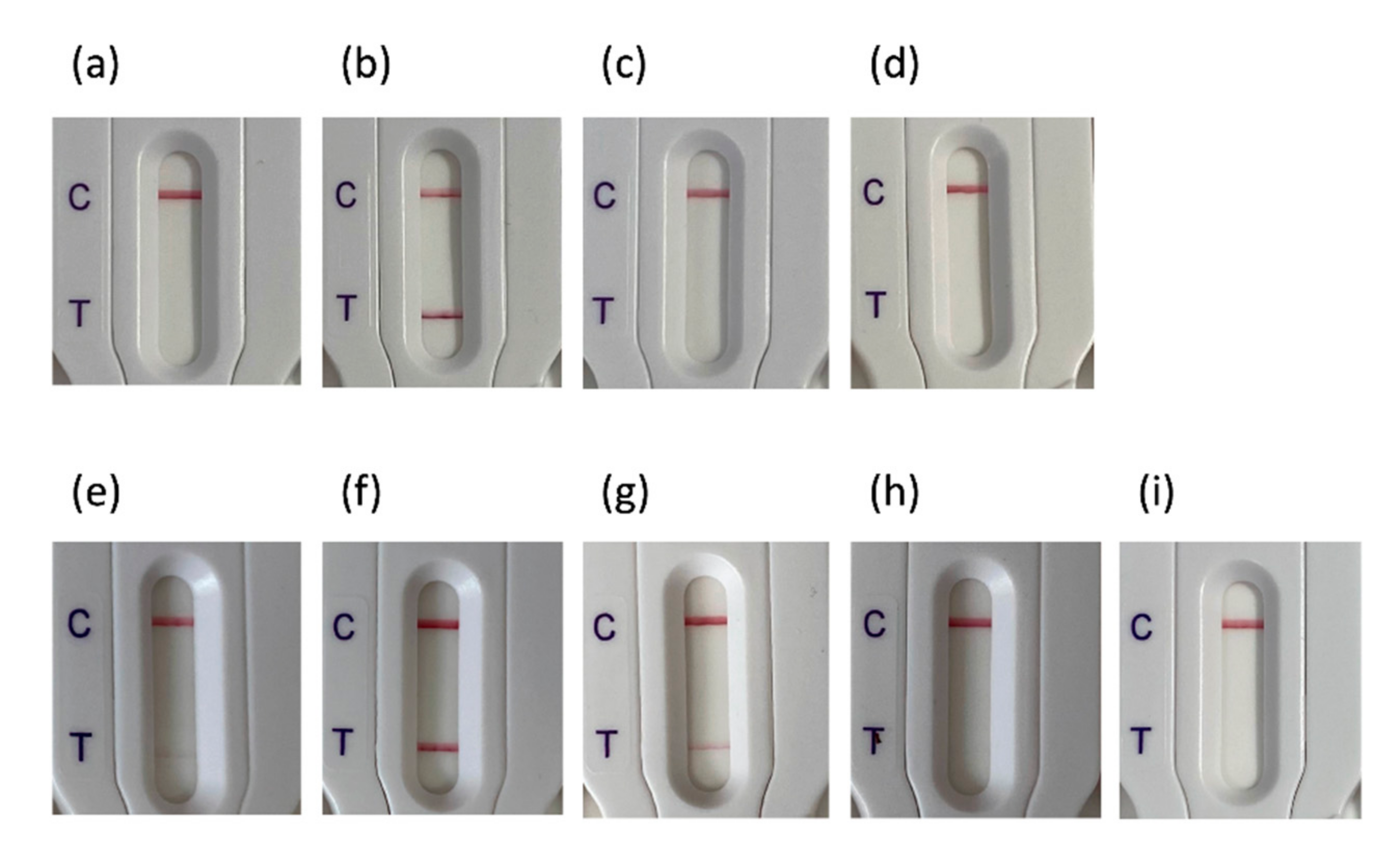
3.3. Prospective Evaluation on Routine Antibiograms
3.4. Prospective Evaluation on Blood Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paterson, D.L. Resistance in gram-negative bacteria: Enterobacteriaceae. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2006, 34 (Suppl. 1), S20–S28, discussion S64–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/threat-report-2013/index.html (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Bauernfeind, A.; Grimm, H.; Schweighart, S. A new plasmidic cefotaximase in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Infection 1990, 18, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, R. Growing group of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: The CTX-M enzymes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cantón, R.; Coque, T.M. The CTX-M β-lactamase pandemic. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantón, R.; González-Alba, J.M.; Galán, J.C. CTX-M Enzymes: Origin and Diffusion. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevan, E.R.; Jones, A.M.; Hawkey, P.M. Global epidemiology of CTX-M β-lactamases: Temporal and geographical shifts in genotype. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Duse, A.; Wattal, C.; Zaidi, A.K.; Wertheim, H.F.; Sumpradit, N.; Vlieghe, E.; Hara, G.L.; Gould, I.M.; Goossens, H.; et al. Antibiotic resistance—The need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 1057–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkey, P.M. Multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: A product of globalization. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 89, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Cataldo, M.A.; Dancer, S.J.; De Angelis, G.; Falcone, M.; Frank, U.; Kahlmeter, G.; Pan, A.; Petrosillo, N.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; et al. ESCMID guidelines for the management of the infection control measures to reduce transmission of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in hospitalized patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruppé, E.; Hem, S.; Lath, S.; Gautier, V.; Ariey, F.; Sarthou, J.L.; Monchy, D.; Arlet, G. CTX-M β-Lactamases in Escherichia coli from Community-acquired Urinary Tract Infections, Cambodia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, M.M.; Arena, F.; Pallecchi, L.; Rossolini, G.M. CTX-M-type β-lactamases: A successful story of antibiotic resistance. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordmann, P.; Dortet, L.; Poirel, L. Carbapenem resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Here is the storm! Trends Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, V. Phenotypic and Genotypic Methods for Detection of Extended Spectrum β Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Ventilator Associated Pneumonia. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, K.; Emami, A.; Bazargani, A.; Moattari, A. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of CTX-M extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolates in Shiraz, Iran. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2015, 48, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, N.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Langereis, P.C.; Raangs, E.G.C.; Kluytmans, J.A.; Friedrich, A.W.; Veenemans, J.; Sinha, B. Evaluation of an Accelerated Workflow for Surveillance of ESBL (CTX-M)-Producing Escherichia coli Using Amplicon-Based Next-Generation Sequencing and Automated Analysis. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naas, T.; Cuzon, G.; Bogaerts, P.; Glupczynski, Y.; Nordmann, P. Evaluation of a DNA microarray (Check-MDR CT102) for rapid detection of TEM, SHV, and CTX-M extended-spectrum β-lactamases and of KPC, OXA-48, VIM, IMP, and NDM-1 carbapenemases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girlich, D.; Bernabeu, S.; Fortineau, N.; Dortet, L.; Naas, T. Evaluation of the CRE and ESBL ELITe MGB® kits for the accurate detection of carbapenemase- or CTX-M-producing bacteria. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 92, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, T.; Oxacelay, C.; Nordmann, P. Identification of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase genes using real-time PCR and pyrosequencing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxacelay, C.; Ergani, A.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Rapid detection of CTX-M-producing Enterobacteriaceae in urine samples. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peker, N.; Couto, N.; Sinha, B.; Rossen, J.W. Diagnosis of bloodstream infections from positive blood cultures and directly from blood samples: Recent developments in molecular approaches. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Angelis, G.; Grossi, A.; Menchinelli, G.; Boccia, S.; Sanguinetti, M.; Posteraro, B. Rapid molecular tests for detection of antimicrobial resistance determinants in Gram-negative organisms from positive blood cultures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takissian, J.; Bonnin, R.A.; Naas, T.; Dortet, L. NG-Test Carba 5 for Rapid Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacterales from Positive Blood Cultures. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00011–e00019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutal, H.; Naas, T.; Devilliers, K.; Oueslati, S.; Dortet, L.; Bernabeu, S.; Simon, S.; Volland, H. Development and Validation of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of NDM-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutal, H.; Vogel, A.; Bernabeu, S.; Devilliers, K.; Creton, E.; Cotellon, G.; Plaisance, M.; Oueslati, S.; Dortet, L.; Jousset, A.; et al. A multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid identification of NDM-, KPC-, IMP- and VIM-type and OXA-48-like carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Breakpoints and Dosing of Antibiotics. Available online: https://eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/ (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Naas, T.; Oueslati, S.; Bonnin, R.A.; Dabos, M.L.; Zavala, A.; Dortet, L.; Retailleau, P.; Iorga, B.I. Beta-lactamase database (BLDB)—Structure and function. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 917–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beta-Lactamase DataBase—Structure and Function. Available online: http://www.bldb.eu/ (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Rodriguez, M.M.; Power, P.; Radice, M.; Vay, C.; Famiglietti, A.; Galleni, M.; Ayala, J.A.; Gutkind, G. Chromosome-encoded CTX-M-3 from Kluyvera ascorbata: A possible origin of plasmid-borne CTX-M-1-derived cefotaximases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4895–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazin, M.; Paasch, F.; Goossens, H.; Malhotra-Kumar, S. MOSAR WP2 and SATURN WP1 Study Teams. Current trends in culture-based and molecular detection of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-harboring and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Zwaluw, K.; de Haan, A.; Pluister, G.N.; Bootsma, H.J.; de Neeling, A.J.; Schouls, L.M. The carbapenem inactivation method (CIM), a simple and low-cost alternative for the Carba NP test to assess phenotypic carbapenemase activity in gram-negative rods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianco, G.; Boattini, M.; Iannaccone, M.; Fossati, L.; Cavallo, R.; Costa, C. Direct β-Lactam Inactivation Method: A New Low-Cost Assay for Rapid Detection of Carbapenemase- or Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales Directly from Positive Blood Culture Bottles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 58, e01178-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparbier, K.; Schubert, S.; Weller, U.; Boogen, C.; Kostrzewa, M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry-based functional assay for rapid detection of resistance against β-lactam antibiotics. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dortet, L.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Rapid detection of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in blood cultures. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 21, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renvoisé, A.; Decré, D.; Amarsy-Guerle, R.; Huang, T.D.; Jost, C.; Podglajen, I.; Raskine, L.; Genel, N.; Bogaerts, P.; Jarlier, V.; et al. Evaluation of the β-Lacta test, a rapid test detecting resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical strains of Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4012–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poirel, L.; Fernández, J.; Nordmann, P. Comparison of Three Biochemical Tests for Rapid Detection of Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodman, K.E.; Lessler, J.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Harris, A.D.; Lautenbach, E.; Han, J.H.; Milstone, A.M.; Massey, C.J.; Tamma, P.D. A clinical decision tree to predict whether a bacteremic patient is infected with an extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing organism. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Porter, V.; Mubareka, S.; Kotowich, L.; Simor, A.E. Rapid identification of bacteria directly from positive blood cultures by use of a serum separator tube, smudge plate preparation, and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasso, M.; Porter, V.; Simor, A.E. Evaluation of the β-Lacta Test for Detection of Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Organisms Directly from Positive Blood Cultures by Use of Smudge Plates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 3560–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Compain, F.; Bensekhri, H.; Rostane, H.; Mainardi, J.L.; Lavollay, M. ß-LACTA test for rapid detection of Enterobacteriaceae resistant to third-generation cephalosporins from positive blood cultures using briefly incubated solid medium cultures. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeniuk, C.; Arlet, G.; Gautier, V.; Grimont, P.; Labia, R.; Philippon, A. ß-Lactamases of Kluyvera ascorbata, probable progenitors of some plasmid-encoded CTX-M types. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3045–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luttrell, R.E.; Rannick, G.A.; Soto-Hernandez, J.L.; Verghese, A. Kluyvera species soft tissue infection: Case report and review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 2650–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karadag Oncel, E.; Ozsurekci, Y.; Akyon, Y.; Gur, D.; Cengiz, A.B.; Kara, A. Kluyvera ascorbata infections in children: A case series. Turk. Pediatri Ars. 2015, 50, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, M.F.; Poirel, L.; Aubert, D.; Nordmann, P. In vitro analysis of ISEcp1B-mediated mobilization of naturally occurring beta-lactamase gene blaCTX-M of Kluyvera ascorbata. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nijhuis, R.H.; Oueslati, S.; Zhou, K.; Bosboom, R.W.; Rossen, J.W.; Naas, T. OXY-2-15, a novel variant showing increased ceftazidime hydrolytic activity. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Test Results on Culture Medium a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Species | β-Lactamase | MH | COH | Uri-4 | DRIG | ChromID |
| K. pneumoniae | CTX-M-15 | P b | P | P | P | P |
| E. coli | CTX-M-1 | P | P | P | P | P |
| E. coli | CTX-M-14 | P | P | P | P | P |
| E. coli | CTX-M-9 | P | P | P | P | P |
| E. coli | CTX-M-8 | P | P | P | P | P |
| K. pneumoniae | CTX-M-8 | P | P | P | P | P |
| E. coli | CTX-M-2 | P | P | P | P | P |
| K. pneumoniae | CTX-M-2 | P | P | P | P | P |
| E. coli | SHV-12 | N | N | N | N | N |
| E. coli | TEM-24 | N | N | N | N | N |
| E. coli | KPC-2 | N | N | N | N | N |
| Species | Sample Origin | ESBL Identified | No. of Isolates | NG-Test CTX-M MULTI Results a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | Urine | CTX-M-1 | 4 | P |
| E. coli | Bile | CTX-M-1 | 1 | P |
| E. coli | Urine | CTX-M-14 | 6 | P |
| E. coli | Bile | CTX-M-14 | 1 | P |
| E. coli | blood | CTX-M-14 | 1 | P |
| E. coli | Urine | CTX-M-15 | 18 | P |
| E. coli | blood | CTX-M-15 | 3 | P |
| E. coli | Urine | CTX-M-27 | 2 | P |
| E. coli | Urine | CTX-M-32 | 1 | P |
| E. coli | Urine | CTX-M-55 | 1 | P |
| E. coli | blood | CTX-M-9 | 1 | P |
| K. pneumoniae | blood | CTX-M-14 | 1 | P |
| K. pneumoniae | blood | CTX-M-15 | 25 | P |
| K. pneumoniae | Urine | CTX-M-127 | 1 | P |
| K. pneumoniae | blood | CTX-M-15 | 13 | P |
| K. pneumoniae | blood | Hyper SHV-28 | 2 | N |
| E. cloacae | Urine | CTX-M-15 | 7 | P |
| E. cloacae | Urine | CTX-M-9 | 2 | P |
| E. cloacae | blood | CTX-M-15 | 6 | P |
| E. cloacae | blood | CTX-M-3 | 1 | P |
| E. cloacae | blood | SHV-12 | 1 | N |
| C. koseri | Urine | CTX-M-1 | 1 | P |
| C. koseri | Urine | CTX-M-14 | 1 | P |
| Salmonella sp. | blood | CTX-M-9 | 1 | P |
| C. freundii | blood | CTX-M-15 | 1 | P |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernabeu, S.; Ratnam, K.C.; Boutal, H.; Gonzalez, C.; Vogel, A.; Devilliers, K.; Plaisance, M.; Oueslati, S.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Dortet, L.; et al. A Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Identification of CTX-M-Producing Enterobacterales from Culture Plates and Positive Blood Cultures. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100764
Bernabeu S, Ratnam KC, Boutal H, Gonzalez C, Vogel A, Devilliers K, Plaisance M, Oueslati S, Malhotra-Kumar S, Dortet L, et al. A Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Identification of CTX-M-Producing Enterobacterales from Culture Plates and Positive Blood Cultures. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(10):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100764
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernabeu, Sandrine, Kayaththiry Caroline Ratnam, Hervé Boutal, Camille Gonzalez, Anaïs Vogel, Karine Devilliers, Marc Plaisance, Saoussen Oueslati, Surbhi Malhotra-Kumar, Laurent Dortet, and et al. 2020. "A Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Identification of CTX-M-Producing Enterobacterales from Culture Plates and Positive Blood Cultures" Diagnostics 10, no. 10: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100764
APA StyleBernabeu, S., Ratnam, K. C., Boutal, H., Gonzalez, C., Vogel, A., Devilliers, K., Plaisance, M., Oueslati, S., Malhotra-Kumar, S., Dortet, L., Fortineau, N., Simon, S., Volland, H., & Naas, T. (2020). A Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Identification of CTX-M-Producing Enterobacterales from Culture Plates and Positive Blood Cultures. Diagnostics, 10(10), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100764