Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From Past to Present Definition and Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Progressive Definition of AKI
3. Diagnostic Difficulties and Renal Function Evaluation in Cirrhosis-Associated AKI
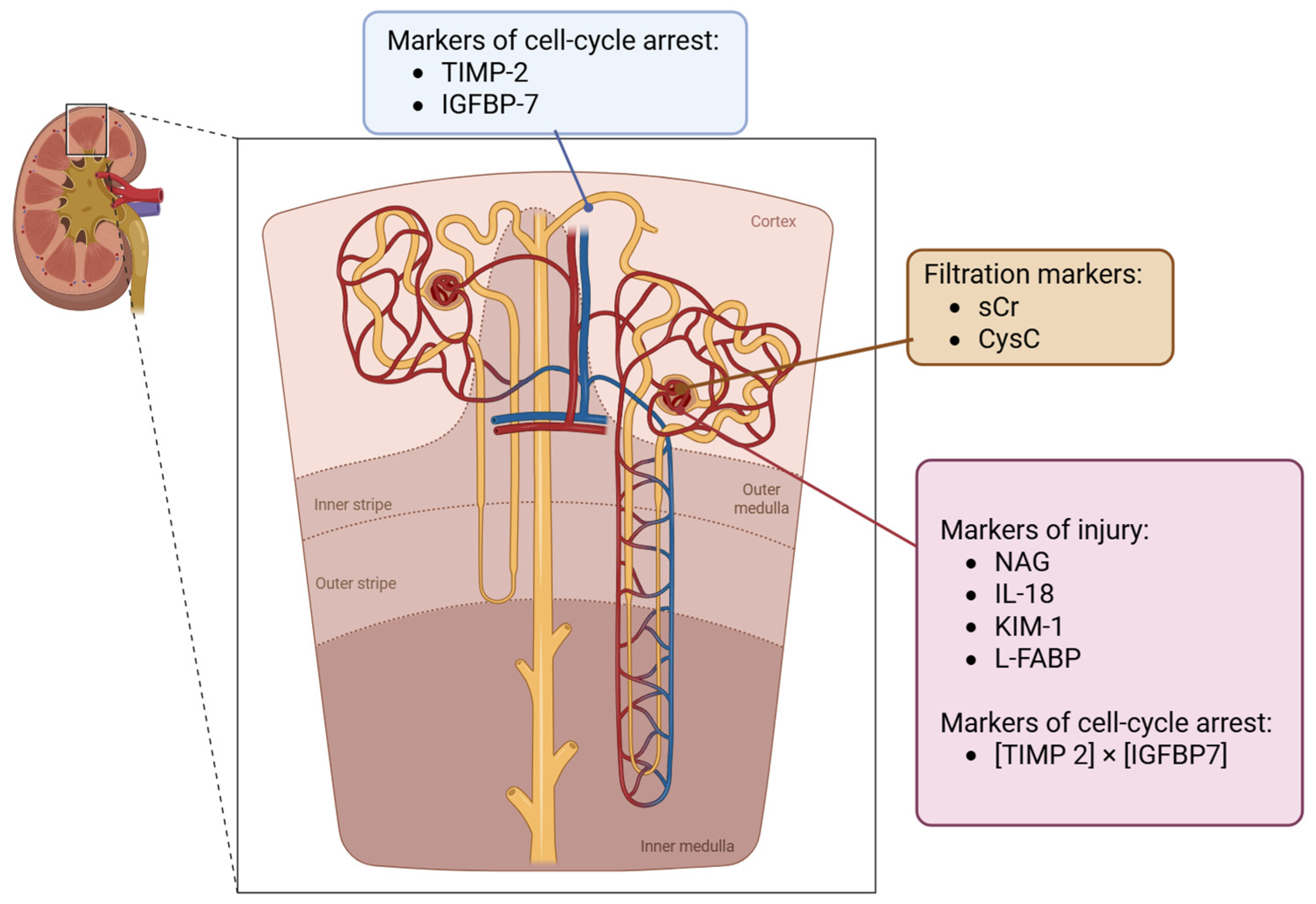
3.1. Biomarkers for the Assessment of Kidney Function
3.2. Biomarkers for Defining the Phenotype of AKI (Tubular Injury Biomarkers)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACLF | Acute-on-chronic liver failure |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| AKIN | Acute Kidney Injury Network |
| ATI | Acute tubular injury |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CLIF-C ACLF | CLIF Consortium ACLF score |
| CysC | Cystatin C |
| DC | Decompensated cirrhosis |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| FENa | Fractional excretion of sodium |
| FEUrea | Fractional excretion of urea |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HRS | Hepatorenal syndrome |
| HRS-AKD | HRS-acute kidney disease |
| HRS-CKD | HRS-chronic kidney disease |
| HRS-AKI | HRS-acute kidney injury |
| HRS-NAKI | Hepatorenal syndrome–non-acute kidney injury |
| ICA | International Club of Ascites |
| IGFBP7 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| KIM-1 | Kidney injury molecule-1 |
| L-FABP | Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein |
| MELD | Model for End-stage Liver Disease |
| MELD-Na | MELD with sodium |
| NAG | N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase |
| NGAL | Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
| RIFLE | Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End-stage Kidney Disease |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
| sCr | Serum creatinine |
| sCysC | Serum cystatin C |
| TIMP-2 | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 |
| uNGAL | Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin |
References
- Velez, J.C.Q.; Therapondos, G.; Juncos, L.A. Reappraising the Spectrum of AKI and Hepatorenal Syndrome in Patients with Cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, T.; Joshita, S.; Shibata, S.; Sugiura, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Fujimori, N.; Matsumoto, A.; Tanaka, E. Renal Impairment Is Associated with Increased Risk of Mortality in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicine 2019, 98, e14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.L.; Techasatian, W.; Hato, T.; Liangpunsakul, S. Role of Endotoxemia in Causing Renal Dysfunction in Cirrhosis. J. Investig. Med. 2020, 68, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanola, A.; Ma, A.T.; Gratacós-Ginès, J.; Soria, A.; Solé, C.; Pose, E.; Ginès, P. Renal Complications in Portal Hypertension. Clin. Liver Dis. 2024, 28, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamm, S.L.; Wong, F.; Ahn, J.; Kamath, P.S. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Evaluation and Management of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Cirrhosis: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2707–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Martin, A. Acute Kidney Injury in Critical Care. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 25, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, C.; Hanouneh, M.; Cervantes, C.E. Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury: A Review of Current Approaches and Emerging Innovations. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadim, M.K.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Hardin, C.C. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matchett, C.L.; Simonetto, D.A.; Kamath, P.S. Renal Insufficiency in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2023, 27, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrier, R.W.; Arroyo, V.; Bernardi, M.; Epstein, M.; Henriksen, J.H.; Rodés, J. Peripheral Arterial Vasodilation Hypothesis: A Proposal for the Initiation of Renal Sodium and Water Retention in Cirrhosis. Hepatology 1988, 8, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegretti, A.S.; Solà, E.; Ginès, P. Clinical Application of Kidney Biomarkers in Cirrhosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.-Y.; Chang, J.W. Hepatorenal Syndrome: Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, P.K. Bilirubin Interference in Serum Creatinine Estimation by Jaffe’s Kinetic Method and Its Rectification in Three Different Kits. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 31, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.M. Hepatorenal Syndrome. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, A.F.; Martin, P. Renal Dysfunction in Cirrhotic Patients. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2019, 114, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Jung, S.E.; Jeong, W.K.; Kim, C.K.; Park, B.K.; Choi, D. Renal Function Impairment in Liver Cirrhosis: Preliminary Results with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging at 3 T. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, P.; Ginès, P.; Wong, F.; Bernardi, M.; Boyer, T.D.; Gerbes, A.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R.; Sarin, S.K.; Piano, S. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Cirrhosis: Revised Consensus Recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. Gut 2015, 64, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Priyadarshi, R.N.; Anand, U. Chronic Renal Dysfunction in Cirrhosis: A New Frontier in Hepatology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognant, N. Evaluation of Renal Function in Patients with Cirrhosis: Where Are We Now? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino, C.; Piano, S.; Stenico, M.; Tonon, M.; Brocca, A.; Calvino, V.; Incicco, S.; Zeni, N.; Gagliardi, R.; Cosma, C. Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Patients with Cirrhosis and Acute Kidney Injury. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, N.R.; Junna, S.; Sharma, P. The Diagnosis and Non-Pharmacological Management of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, S11–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleri, A.; Alessandria, C. Renal Damage in Hepatorenal Syndrome: A Still Unsolved Issue. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullaro, G.; Kanduri, S.R.; Velez, J.C.Q. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, C.; Barreto, R.; Guevara, M.; Garcia, E.; Solà, E.; Rodríguez, E.; Graupera, I.; Ariza, X.; Pereira, G.; Alfaro, I. A Modified Acute Kidney Injury Classification for Diagnosis and Risk Stratification of Impairment of Kidney Function in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrani, S.K.; Shankar, N.; Da Graca, B.; Nadim, M.K.; Cardenas, A. Role of Novel Kidney Biomarkers in Patients with Cirrhosis and After Liver Transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2022, 28, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoz, C.; Nadim, M.K.; Durand, F. Kidney Biomarkers in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassegoda, O.; Huelin, P.; Ariza, X.; Solé, C.; Juanola, A.; Gratacós-Ginès, J.; Carol, M.; Graupera, I.; Pose, E.; Napoleone, L.; et al. Development of Chronic Kidney Disease after Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Cirrhosis Is Common and Impairs Clinical Outcomes. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basthi Mohan, P.; Nagaraju, S.P.; Rangaswamy, D.; Musunuri, B.; Prabhu Attur, R.; Bhat, G.; Shailesh; Shetty, S. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin: Acute Kidney Injury in Liver Cirrhosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, E.L.; Homkrailas, P.; Bunnapradist, S. Evaluation of Renal Disease in Patients with Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, S.; Romano, A.; Di Pascoli, M.; Angeli, P. Why and How to Measure Renal Function in Patients with Liver Disease. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, K.R.; Belcher, J.M.; Regner, K.R.; Hillien, S.A.S.; Simonetto, D.A.; Asrani, S.K.; Neyra, J.A.; Sharma, P.; Velez, J.C.Q.; Wadei, H. Incidence and Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury Including Hepatorenal Syndrome in Hospitalized Patients with Cirrhosis in the US. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.A.; Seo, Y.S. Current Knowledge about Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury in Liver Cirrhosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, D.; Rizzi, F.; Bonetto, S.; Giovo, I.; Roma, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Alessandria, C. Assessment of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Patients with Cirrhosis: Available Tools and Perspectives. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2360–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagheb, M.M.; Namazi, S.; Geramizadeh, B.; Karimzadeh, A.; Oghazian, M.B.; Karimzadeh, I. Serum Cystatin C as a Marker of Renal Function in Critically Ill Patients with Normal Serum Creatinine. Nephro-Urol. Mon. 2014, 6, e15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, K.C.S.; Viau, C.M.; Colares, J.R.; Saffi, J.; Marroni, N.P.; Porawski, M. Cirrhosis Induces Apoptosis in Renal Tissue through Intracellular Oxidative Stress. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2015, 52, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Seo, Y.S.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.W.; et al. Prognosis Predictability of Serum and Urine Renal Markers in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Multicentre Prospective Study. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 3083–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, D.; Holdt, L.; Steib, C.; Benesic, A.; Bendtsen, F.; Bernardi, M.; Moreau, R.; Teupser, D.; Wendon, J.; Nevens, F.; et al. Plasma Cystatin C Is a Predictor of Renal Dysfunction, Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure, and Mortality in Patients with Acutely Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Bhurwal, A.; Law, C.; Ventre, S.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Kabaria, S.; Li, Y.; Tait, C.; Catalano, C.; Rustgi, V.K. Acute Kidney Injury and Hepatorenal Syndrome in Cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.J.; De Kanter, C.T.M.M.; Van Hoek, B.; Arends, J.E.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Burger, D.M. Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy, and Safety of Hepatitis C Virus Drugs in Patients with Liver and/or Renal Impairment. Drug Saf. 2016, 39, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, Y.H.S.; Jagtap, N.; Karyampudi, A.; Rao, N.P.; Deepika, G.; Sharma, M.; Gupta, R.; Tandan, M.; Ramchandani, M.; John, P.; et al. Fractional Excretion of Sodium and Urea in Differentiating Acute Kidney Injury Phenotypes in Decompensated Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, K.R.; Kang, L.; Bajaj, J.S.; Carl, D.; Sanyal, A.J. Fractional Excretion of Urea: A Simple Tool for the Differential Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2018, 68, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, X.; Solà, E.; Elia, C.; Barreto, R.; Moreira, R.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Graupera, I.; Rodríguez, E.; Huelin, P.; Solé, C.; et al. Analysis of a Urinary Biomarker Panel for Clinical Outcomes Assessment in Cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altran, W.S.; de Sousa, L.F.; dos Santos Cortinhas, R.; Ponce, D. The Role of Urinary Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, I.; Barreto, E.F.; Kellum, J.A.; Awdishu, L.; Murray, P.T.; Ostermann, M.; Bihorac, A.; Mehta, R.L.; Goldstein, S.L.; Kashani, K.B.; et al. Moving toward a Contemporary Classification of Drug-Induced Kidney Disease. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staufer, K.; Roedl, K.; Kivaranovic, D.; Drolz, A.; Horvatits, T.; Rasoul-Rockenschaub, S.; Zauner, C.; Trauner, M.; Fuhrmann, V. Renal Replacement Therapy in Critically Ill Liver Cirrhotic Patients—Outcome and Clinical Implications. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romejko, K.; Markowska, M.; Niemczyk, S. The Review of Current Knowledge on Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, E.; Leonardi, A.; Pacifico, F. NGAL as a Potential Target in Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, C.; Pépin, M.-N.; Guevara, M.; Barreto, R.; Casals, G.; Solà, E.; Pereira, G.; Rodríguez, E.; Garcia, E.; Prado, V.; et al. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as Biomarker in the Differential Diagnosis of Impairment of Kidney Function in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, H.S.; El-Ray, A.; Salaheldin, M.; Lasheen, M.; Aboul-Ezz, M.; Abdel-Moaty, A.S.; Abdel-Rahim, A. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, A.J.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Ostermann, M.; Bruce, M.; Sherwood, R.; Musto, R.; Dew, T.; Auzinger, G.; Bernal, W.; O’Grady, J.; et al. Predicting the Development of Acute Kidney Injury in Liver Cirrhosis—An Analysis of Glomerular Filtration Rate, Proteinuria and Kidney Injury Biomarkers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Ong, S.; Satapathy, S.K.; Kamath, P.S.; Wiesner, R.H. Simultaneous Liver Kidney Transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2019, 32, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.M.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Sanyal, A.J.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Peixoto, A.J.; Perazella, M.A.; Ansari, N.; Lim, J.; Coca, S.G.; Parikh, C.R. Urinary Biomarkers and Progression of AKI in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthumana, J.; Ariza, X.; Belcher, J.M.; Graupera, I.; Ginès, P.; Parikh, C.R. Urine Interleukin 18 and Lipocalin 2 Are Biomarkers of Acute Tubular Necrosis in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1003–1013.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelin, P.; Solà, E.; Elia, C.; Solé, C.; Risso, A.; Moreira, R.; Carol, M.; Fabrellas, N.; Bassegoda, O.; Juanola, A.; et al. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin for Assessment of Acute Kidney Injury in Cirrhosis: A Prospective Study. Hepatology 2019, 70, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-J.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Nam, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, C.W.; Shin, S.K.; Chon, Y.E.; Jang, E.S.; et al. The Role of Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-Glucosaminidase in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakova, T.A.; Sergeeva, N.S.; Kanukoev, K.Y.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Kaprin, A.D. Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1): A Multifunctional Glycoprotein and Biological Marker (Review). Coвpeмeнныe Texнoлoгии B Meдицинe 2021, 13, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanola, A.; Graupera, I.; Elia, C.; Piano, S.; Solé, C.; Carol, M.; Pérez-Guasch, M.; Bassegoda, O.; Escudé, L.; Rubio, A.-B.; et al. Urinary L-FABP Is a Promising Prognostic Biomarker of ACLF and Mortality in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, A.; Faubel, S.; Askenazi, D.J.; Cerda, J.; Fissell, W.H.; Heung, M.; Humphreys, B.D.; Koyner, J.L.; Liu, K.D.; Mour, G.; et al. Clinical Use of the Urine Biomarker [TIMP-2] × [IGFBP7] for Acute Kidney Injury Risk Assessment. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi, L.M.; Bergler, T.; Binnall, B.; Engelman, D.T.; Forni, L.; Germain, M.J.; Gluck, E.; Göcze, I.; Joannidis, M.; Koyner, J.L.; et al. Clinical Use of [TIMP-2]•[IGFBP7] Biomarker Testing to Assess Risk of Acute Kidney Injury in Critical Care: Guidance from an Expert Panel. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksamai, A.; Khaoprasert, S.; Chaiprasert, A.; Chirapongsathorn, S. Urine TIMP2.IGFBP7 Reflects Kidney Injury After Moderate Volume Paracentesis in Patients with Ascites: A Randomized Control Study. JGH Open 2025, 9, e70168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Stage | sCr or GFR Criteria | Urine Output Criteria | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and End-stage Kidney Disease (RIFLE) criteria in 2004 | Stage 1 (Risk) | Increased sCr ≥ 1.5 × baseline or GFR decreased >25% | <0.5 mL/kg/h for ≥6 h | [9,15,16] |
| Stage 2 (Injury) | Increased sCr ≥ 2 × baseline or GFR decreased >50% | <0.5 mL/kg/h for ≥12 h | ||
| Stage 3 (Failure) | Increased sCr ≥ 3 × baseline or GFR decreased >75% | <0.3 mL/kg/h for ≥24 h | ||
| Loss | Persistent acute renal failure > 4 weeks | - | ||
| End-stage | Complete loss of kidney function > 3 months | - | ||
| Acute Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) in 2007 | Stage 1 | Increased sCr ≥ 1.5 × baseline or ≥0.3 mg/dL within 48 h | <0.5 mL/kg/h for ≥6 h | |
| Stage 2 | Increased sCr ≥ 2 × baseline | <0.5 mL/kg/h for ≥12 h | ||
| Stage 3 | Increased sCr ≥ 3 × baseline | <0.3 mL/kg/h for ≥24 h or anuria ≥ 12 h | ||
| Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) in 2012 | Stage 1 | Increased sCr ≥ 1.5–2 × baseline or ≥ 0.3 mg/dL | <0.5 mL/kg/h for ≥6–12 h | |
| Stage 2 | Increased sCr ≥ 2–3 × baseline | <0.5 mL/kg/h for ≥12 h | ||
| Stage 3 | Increased sCr ≥ 3 × baseline or sCr ≥ 4.0 mg/dL | <0.3 mL/kg/h for 24 h or anuria ≥ 12 h |
| Category | Criteria | References |
|---|---|---|
| Definition of baseline sCr | A value of sCr obtained in the previous 3 months. In patients with more than one value, the closest and lowest to hospital admission should be used. In patients without a previous value, the admission value should be used as baseline. | [4,9,19,20] |
| Definition of AKI | Increase in sCr ≥ 0.3 mg/dL (26.5 µmol/L) within 48 h OR Increase in sCr ≥ 50% from baseline within the prior 7 days. | |
| AKI Staging | ||
| Stage 1A | Increase in sCr ≥ 0.3 mg/dL (26.5 µmol/L) to a value < 1.5 mg/dL (133 µmol/L) from baseline at AKI diagnosis. | |
| Stage 1B | Increase in sCr ≥ 0.3 mg/dL (26.5 µmol/L) to a value ≥ 1.5 mg/dL (133 µmol/L) from baseline at AKI diagnosis. | |
| Stage 2 | Increase in sCr 2-fold to 3-fold from baseline. | |
| Stage 3 | Increase in sCr ≥ 3-fold from baseline OR sCr ≥ 4.0 mg/dL (353.6 µmol/L) with an acute increase of ≥0.3 mg/dL (26.5 µmol/L) OR Initiation of renal replacement therapy (RRT). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Syndrome/Criteria | Old Term | Definition | HRS Prerequisites | New Term | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKI | HRS-1 | - Stage 1: Increase in baseline sCr of either ≥0.3 mg/dL in 48 h or ≥1.5–1.9 × baseline in the last 7 d or urinary output ≤ 0.5 mg/kg body weight in ≥6 h - Stage 2: ≥2–2.9 × baseline sCr - Stage 3: ≥3 × baseline sCr or sCr ≥ 4 mg/dL or KRT | - Decompensated cirrhosis (DC) - Absence of shock - No treatment with nephrotoxic medications - No response to volume expansion - Absence of parenchymal disease (proteinuria: >500 mg/d; hematuria: <50 RBCs per HPF) - Suggestion of kidney vasoconstriction with FENa < 0.2% | HRS-AKI | [12,23] |
| AKD | HRS-2 | eGFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for <3 mo | Same as AKI | HRS-AKD | |
| CKD | N/A | eGFR < 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 for ≥3 mo | Same as AKI | HRS-CKD | |
| Serum Creatinine Criteria Evolution | N/A | - 1996: sCr > 1.5 mg/dL - 2007: sCr ≥ 2.5 mg/dL - 2015: Increase in sCr ≥ 0.3 mg/dL in 48 h or ≥50% from baseline - 2019: Baseline sCr < 3 months | Varies by year, with evolving inclusion of structural kidney disease, urine sodium levels, and hemodynamic parameters | N/A | |
| Urine Sodium | N/A | - 1996: <10 mEq/L - 2007: <30 mEq/L - 2015: FENa < 0.2% | Absence of structural kidney disease | N/A | |
| Urine Volume | N/A | - 1996: <500 mL/day - 2015: <0.5 mL/kg/h for 6 h | Absence of structural kidney disease | N/A | |
| Urine Sediment | N/A | - 1996: No proteinuria - 2015: No significant proteinuria | No active urinary sediment | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lungu, A.; Sarbu, G.-E.; Cotlet, A.S.; Savin, I.-A.; Damian, I.-R.; Juncu, S.; Muzica, C.; Girleanu, I.; Sîngeap, A.-M.; Stanciu, C.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From Past to Present Definition and Diagnosis. Life 2025, 15, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081249
Lungu A, Sarbu G-E, Cotlet AS, Savin I-A, Damian I-R, Juncu S, Muzica C, Girleanu I, Sîngeap A-M, Stanciu C, et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From Past to Present Definition and Diagnosis. Life. 2025; 15(8):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081249
Chicago/Turabian StyleLungu, Andreea, Georgiana-Elena Sarbu, Alexandru Sebastian Cotlet, Ilie-Andreas Savin, Ioana-Roxana Damian, Simona Juncu, Cristina Muzica, Irina Girleanu, Ana-Maria Sîngeap, Carol Stanciu, and et al. 2025. "Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From Past to Present Definition and Diagnosis" Life 15, no. 8: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081249
APA StyleLungu, A., Sarbu, G.-E., Cotlet, A. S., Savin, I.-A., Damian, I.-R., Juncu, S., Muzica, C., Girleanu, I., Sîngeap, A.-M., Stanciu, C., Trifan, A., & Cojocariu, C. (2025). Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From Past to Present Definition and Diagnosis. Life, 15(8), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081249










