Structural and Functional Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities in Forest–Wetland Ecotones: A Case Study of the Lesser Khingan Mountains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput 16S rRNA Gene Paired-End Sequencing
2.5. Sequencing Data Processing and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Analysis of Soil Bacterial Structure in Different Forest–Wetland Ecotones
3.3. Microbial Alpha and Beta Diversity
3.4. Correlation Between Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and the Relative Abundance of Microbial Communities
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Soil Bacteria with Soil Physical and Chemical Factors
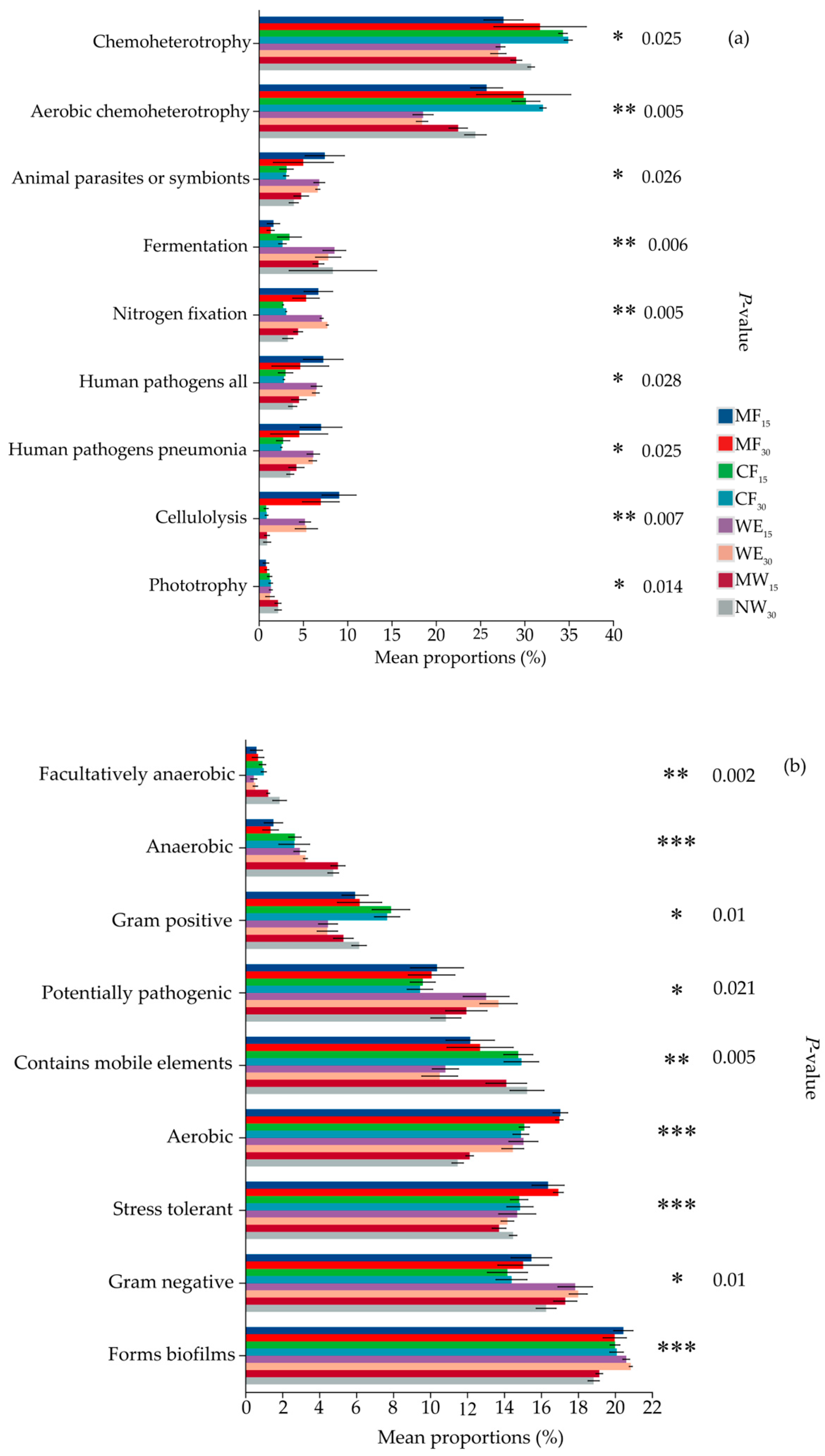
3.6. Phenotypic Prediction and Functional Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between Soil Physicochemical Properties and Diversity
4.2. Environmental Factors Influencing Soil Microbial Community Structure
4.3. Functional Prediction Analysis of Soil Bacterial Communities in Forest–Wetland Ecotones
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mauchamp, A.; Bonis, A.; Crabot, J.; Bergerot, B.; Gore, O.; Paillisson, J.M. Interplay between water regime components and wet grassland plant communities. Wetlands 2024, 44, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Boughton, E.H.; Bohlman, S.; Bernacchi, C.; Bohlen, P.J.; Boughton, R.; Delucia, E.; Fauth, J.E.; Gomez-Casanovas, N.; Jenkins, D.G.; et al. Grassland intensification effects cascade to alter multifunctionality of wetlands within metaecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.R.; Zhou, H.M.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, G.D.; Ma, W.; Wang, Q. Exploration of vegetation change trend in the Greater Khingan Mountains area of China based on EEMD method. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, L.N.; Wan, L.H. Water quality analysis and evaluation of eutrophication in a swamp wetland in the permafrost region of the lesser khingan mountains, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomako, M.O.; Roiloa, S.; Yu, F.H. Potential roles of soil microorganisms in regulating the effect of soil nutrient heterogeneity on plant performance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.M.; Sattar, K.; Lü, G.H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.D. Different contributions of plant diversity and soil properties to the community stability in the arid desert ecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 969852. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Colin, P.; Hulshof, C.M. Ecotones as windows into organismal-to-biome scale responses across neotropical forests. Plants 2024, 13, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.C.; Walentowitz, A.; Beierkuhnlein, C. The biome inventory–Standardizing global biogeographical land units. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 2172–2183. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Bai, H.; Zhao, C.H.; Peng, M.; Chi, Q.; Dai, Y.P.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, M.M.; Niu, B. The characteristics of soil microbial co-occurrence networks across a high-latitude forested wetland ecotone in China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1160683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.X.; Hu, Y.D. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors Analysis of Habitat Quality: A Case Study in Harbin, China. Land 2024, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smrithy, V.; Kulkarni, A.; Shigwan, B.K.; Shetti, R.; Datar, M.N. Floristic composition and plant functional type diversity of the basalt cliffs of Western Ghats, India. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2025, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gatti, R.C. Ecological Peace Corridors: A new conservation strategy to protect human and biological diversity. Biol. Conserv. 2025, 302, 110947. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, M.K.; Wong, C.K.; Chu, K.H.; Kwan, H.S. Community structure, dynamics and interactions of bacteria, archaea and fungi in subtropical coastal wetland sediments. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14397. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, W.S.; Huang, L.N. Microbial diversity in extreme environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viceli, J.M.; Acosta, A.C.B.; Pocojeski, E.; Casali, C.A.; Kessler, N.C.H.; Tessaro, D. Influence of soil water content on chemical and microbiological characteristics of selected riparian forests in southern Brazil. Wet. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 33, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M.M.; Kan, J.; Plante, A.F. Parent material and vegetation influence bacterial community structure and nitrogen functional genes along deep tropical soil profiles at the Luquillo Critical Zone Observatory. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Dong, X.F.; Wu, X.D.; Ma, D.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Man, H.R.; Li, M.; Zang, S.Y. Response of carbon emissions and the bacterial community to freeze–thaw cycles in a permafrost-affected forest–wetland ecotone in Northeast China. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wutzler, T.; Zaehle, S.; Schrumpf, M.; Ahrens, B.; Reichstein, M. Adaptation of microbial resource allocation affects modelled long term soil organic matter and nutrient cycling. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 322–336. [Google Scholar]
- Philippot, L.; Griffiths, B.S.; Langenheder, S. Microbial community resilience across ecosystems and multiple disturbances. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00026-20. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, S.T.; Luo, P.P.; Xie, D.N.; Zhu, W. Watershed ecohydrological processes in a changing environment: Opportunities and challenges. Water 2022, 14, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.; Wei, G. Linking phylogenetic niche conservatism to soil archaeal biogeography, community assembly and species coexistence. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.Y.; Xie, R.F.; Ma, D.L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, L. Variations in soil microbial community structure and extracellular enzymatic activities along a forest–wetland ecotone in high-latitude permafrost regions. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diwan, D.; Rashid, M.M.; Vaishnav, A. Current understanding of plant-microbe interaction through the lenses of multi-omics approaches and their benefits in sustainable agriculture. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 265, 127180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, G.; Tafese, T.; Abda, E.M.; Kamaraj, M.; Assefa, F. Factors influencing the bacterial bioremediation of hydrocarbon contaminants in the soil: Mechanisms and impacts. J. Chem. 2021, 1, 9823362. [Google Scholar]
- Do, D.T.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Do, X.S. Sustainable development in Mekong Delta, Vietnam: Designing resilient cities based on landscape ecological principles. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamrikova, E.V.; Vanchikova, E.V.; Kyzyurova, E.V.; Zhangurov, E.V. Methods for measuring organic carbon content in carbonate-containing soils: A review. Eurasian Soil. Sci. 2024, 57, 380–394. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.W.; Biswas, A.; Wen, M.Y.; Si, B.C. Predicting bulk density in deep unsaturated soils based on multiple scale decomposition. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114859. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Qu, Y.Y.; Shen, W.L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, D.X.; Li, H.J.; Zhou, J.T. Bacterial community compositions of coking wastewater treatment plants in steel industry revealed by Illumina high-throughput sequencing. Bioresource Technol. 2015, 179, 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, D.; Armas, C.; Pueyo, J.J.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Hernández, T. Soil total nitrogen and its relation to land use changes. Geoderma 2023, 411, 115699. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. Optimization of the Ammonium Acetate Extraction Method for Available Potassium in Soils. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.F.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.L.; Fan, H.Z.; Shi, X.J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X.J.; Liu, G.R.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.M.; et al. Soil potassium regulation by changes in potassium balance and iron and aluminum oxides in paddy soils subjected to long-term fertilization regimes. Soil. Till Res. 2021, 214, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Plant, R.E. Applications of apparent soil electrical conductivity in precision agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.N. Soil nitrogen transformation and functional microbial abundance in an agricultural soil amended with biochar. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2023, 47, e0220156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Weber, C.F. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent community analysis tools. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.W.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Kennedy, P.G. Fun Guild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.C.; Deng, J.J.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W. Functional distribution of bacterial community under different land use patterns based on FaProTax function prediction. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Q.; Kang, P.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.X.; Li, X.R. Response of the soil bacterial community to seasonal variations and land reclamation in a desert grassland. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jonge, I.K.; Veldhuis, M.P.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Berg, M.P.; Olff, H. The metamicrobiome: Key determinant of the homeostasis of nutrient recycling. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Graphene oxide enters the rice roots and disturbs the endophytic bacterial communities. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 192, 110304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Furtak, K. Soil–Plant–Microbe interactions determine soil biological fertility by altering rhizospheric nutrient cycling and biocrust formation. Sustainability 2022, 15, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ameen, F.; Verma, P. Unraveling the shift in bacterial communities profile grown in sediments co-contaminated with chlorolignin waste of pulp-paper mill by metagenomics approach. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1350164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmano, R.F.; Damian, J.M.; de Marchi Soares, T.; Colzato, M.; Antonangelo, J.A.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Soares, M.R.; Alleoni, L.R.F. Chemical Drivers of Molybdate-Unreactive Phosphorus in Subtropical Forest Soils: Insights from P Tests, Chemical Properties and XANES. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 1281–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yan, Y.; Dong, H.Y.; Lei, W.K. Experimental Study on Infiltration Characteristics of Shallow Rainwater in Expansive Soil Slopes at Different Gradients. Water 2025, 17, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah-Antwi, C.; Kwiatkowska-Malina, J.; Szara, E.; Fenton, O.; Thornton, S.F.; Malina, G. Assessing factors controlling structural changes of humic acids in soils amended with organic materials to improve soil functionality. Agronomy 2022, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, A.; Huang, J.X.; Li, S.D.; Lu, X.H.; Guo, R.J. Hot viewpoint on how soil texture, soil nutrient availability, and root exudates interact to shape microbial dynamics and plant health. Plant Soil 2024, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Furman, A. Soil redox dynamics under dynamic hydrologic regimes-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143026. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Effects of forest management on soil acidification in cedar plantation. Geoderma 2022, 424, 115967. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Yu, Q.; Wang, R.Z.; Cao, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, L.J.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Jiang, Y. Decoupling of plant and soil metal nutrients as affected by nitrogen addition in a meadow steppe. Plant Soil 2019, 443, 337–351. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, M.; Bhardwaj, S.; Kumar, V.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Lichens as effective bioindicators for monitoring environmental changes: A comprehensive review. Total Environ. Adv. 2024, 9, 200085. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, R.W.; Shu, H.; Naz, I.; Quddoos, A.; Yaseen, A.; Gulshad, K.; Alarifi, S.S. Machine learning-based wetland vulnerability assessment in the sindh province ramsar site using remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, A.; Khalid, N.; Aqeel, M.; Noman, A.; Naeem, N.; Sarfraz, W.; Ejza, U.; Qaiser, Z.; Khalid, A. Nitrogen dynamics in wetland systems and its impact on biodiversity. Nitrogen 2021, 2, 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Kohout, P. Forest microbiome and global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 487–501. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.P.; Yan, Q.; Wang, J.; Shao, M.A.; Li, Z.; Jia, H. Biodegradable plastics fragments induce positive effects on the decomposition of soil organic matter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naylor, D.; McClure, R.; Jansson, J. Trends in microbial community composition and function by soil depth. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Guo, X.T. Impact of soil structure and texture on occurrence of microplastics in agricultural soils of karst areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166189. [Google Scholar]
- Wilpert, K.V. Forest soils—what’s their peculiarity? Soil. Syst. 2022, 6, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.T.; Lennon, J.T.; Lu, X.; Ruan, A.D. Anthropogenic activities mediate stratification and stability of microbial communities in freshwater sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Hiiesalu, I.; Schweichhart, J.; Angel, R.; Davison, J.; Doležal, J.; Kopecký, M.; Macek, M.; Řehakova, K. Plant-symbiotic fungal diversity tracks variation in vegetation and the abiotic environment along an extended elevational gradient in the Himalayas. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad092. [Google Scholar]
- Minghelli, A.; Vadakke-Chanat, S.; Chami, M.; Guillaume, M.; Migne, E.; Grillas, P.; Boutron, O. Estimation of bathymetry and benthic habitat composition from hyperspectral remote sensing data (BIODIVERSITY) using a semi-analytical approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.C.; Wu, J.Z.; Lin, W.S. Long-Term Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics and Driving Force Analysis of Landscape Stability in the Forest–Grassland Ecotone of the Greater Khingan Mountains, Inner Mongolia, China. Land 2025, 14, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Zeng, Q.S.; Wang, W.Q.; Zheng, Y.; Sardans, J.; Xue, K.; Zeng, F.J.; Tariq, A.; Peñuelas, J. Soil carbon pools and microbial network stability depletion associated with wetland conversion into aquaculture ponds in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.X.; Xie, S.R.; Song, Z.L.; Xia, S.P.; Åström, M.E. Biogeochemical cycling of iron (hydr-) oxides and its impact on organic carbon turnover in coastal wetlands: A global synthesis and perspective. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103658. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.C.; Niu, W.Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhang, E.; Wang, J. Soil moisture and nitrogen content influence wheat yield through their effects on the root system and soil bacterial diversity under drip irrigation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3062–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Bai, J.H.; Zhang, Z.S.; Xie, T.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.Z.; Liu, Z. Plant invasion strengthens the linkages between dissolved organic matter composition and the microbial community in coastal wetland soils. Catena 2023, 232, 107449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.N.; Yu, S.P. Stochastic Processes Dominate the Assembly of Soil Bacterial Communities of Land Use Patterns in Lesser Khingan Mountains, Northeast China. Life 2024, 14, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, A.; Bohlen, P.J. Hydro-ecological controls on soil carbon storage in subtropical freshwater depressional wetlands. Wetlands 2021, 41, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.T.; Liu, R.; Zhou, X.X.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.T.; Zou, P.; Bi, X.Y.; Li, S.B. Role of lake aquatic–terrestrial ecotones in the ecological restoration of eutrophic water bodies. Toxics 2023, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiqige, B.; Liu, J.J.; Li, M.; Hu, X.S.; Guo, W.W.; Wang, P.; Ding, Y.; Zhi, Q.Y.; Wu, Y.X.; Guan, X.; et al. Different Flooding Conditions Affected Microbial Diversity in Riparian Zone of Huihe Wetland. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, F.A.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, W.X. Root effects on soil organic carbon: A double-edged sword. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querejeta, J.I.; Ren, W.; Prieto, I. Vertical decoupling of soil nutrients and water under climate warming reduces plant cumulative nutrient uptake, water-use efficiency and productivity. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1378–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, J.; Rakshit, A.; Ogireddy, S.D.; Singh, S.; Gupta, C.; Chandrakala, J. Microbiome as a key player in sustainable agriculture and human health. Front. Soil. Sci. 2022, 2, 821589. [Google Scholar]
- Marschner, P. Processes in submerged soils–linking redox potential, soil organic matter turnover and plants to nutrient cycling. Plant Soil 2021, 464, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sonke, J.E.; Angot, H.; Zhang, Y.; Poulain, A.; Björn, E.; Schartup, A. Global change effects on biogeochemical mercury cycling. Ambio 2023, 52, 853–876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Daunoras, J.; Kačergius, A.; Gudiukaitė, R. Role of soil microbiota enzymes in soil health and activity changes depending on climate change and the type of soil ecosystem. Biology 2024, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, M.S.M.; Abdelhamid, S.A.; Mohamed, S.S. Secondary metabolites and biodiversity of actinomycetes. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Li, X.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Shi, Y.; Li, H.L. Degradation reduces the diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the alpine wetland on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 939762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Lu, Y.H. Soil pH and temperature regulate assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterial communities in agricultural ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 22, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Naorem, A.; Jayaraman, S.; Dang, Y.P.; Dalal, R.C.; Sinha, N.K.; Rao, C.S.; Patra, A.K. Soil constraints in an arid environment—Challenges, prospects, and implications. Agronomy 2023, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Piao, S.L.; Huntingford, C.; Peñuelas, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, A.P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Keenan, T.F.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global variations in critical drought thresholds that impact vegetation. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad049. [Google Scholar]
- Naz, M.; Dai, Z.C.; Hussain, S.; Tariq, M.; Danish, S.; Khan, I.U.; Qi, S.S.; Du, D. The soil pH and heavy metals revealed their impact on soil microbial community. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115770. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.A.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Pan, X.Z. Soil bacterial community composition rather than diversity exhibits edge effects in a farming-pastoral ecotone. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105722. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, X.; Zhang, R.T.; Frey, B.; Yang, L.B.; Liu, Y.N.; Ni, H.W.; Li, M.H. Soil physicochemical properties drive the variation in soil microbial communities along a forest successional series in a degraded wetland in northeastern China. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.B.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, Q.C.; Bermudez, R.S.; Yu, S.H.; Bu, P.T.; Wang, Z.W.; Chen, D.S.; Feng, J. Effects of plantation type and soil depth on microbial community structure and nutrient cycling function. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 846468. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Al-Mutairi, K.A. Earthworms effect on microbial population and soil fertility as well as their interaction with agriculture practices. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.R.; Zhao, Z.G.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Y.; Guan, Z.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Fang, W.M.; Chen, F.D.; Zhao, S. Optimum nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium fertilizer application increased chrysanthemum growth and quality by reinforcing the soil microbial community and nutrient cycling function. Plants 2023, 12, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Hussain, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Ali, I.; Liu, J.Y.; Bano, H. Microbiology of wetlands and the carbon cycle in coastal wetland mediated by microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 175734. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Chen, Q.F.; Li, Q.; Zhao, C.S.; Feng, Y. Influence of plants and environmental variables on the diversity of soil microbial communities in the Yellow River Delta Wetland, China. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129967. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.L.; Zhou, Y.B. Effects of land use patterns on the bacterial community structure and diversity of wetland soils in the Sanjiang Plain. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liang, K.N.; Huang, G.H.; Wang, X.B.; Lin, M.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.Z. Soil bacterial community shifts are driven by soil nutrient availability along a teak plantation chronosequence in tropical forests in China. Biology 2021, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, S.Y.; Sun, X.Y.; He, L.B.; Zhou, W.Z.; Zhao, G.Y.; Yu, J.T.; Bai, X.T.; Zhang, J. Characteristics of Bacterial Communities under Different Tree Species and Their Response to Soil Physicochemical Properties. Forests 2024, 15, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.T.; Wu, W.C.; Liang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Hou, J.L.; Chen, Y.R.; Elvert, M.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Wang, F.P. Anaerobic degradation of organic carbon supports uncultured microbial populations in estuarine sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogati, K.A.; Golińska, P.; Sewerniak, P.; Burkowska-But, A.; Walczak, M. Deciphering the impact of induced drought in agriculture soils: Changes in microbial community structure, enzymatic and metabolic diversity. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Zhao, R.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.W.; Diao, M.H.; Ji, G.D. Influences of fluctuating nutrient loadings on nitrate-reducing microorganisms in rivers. ISME Commun. 2025, 5, ycae168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, B.E.; Louw, D.C.; Van der Plas, A.K.; Bailey, J.V. Giant sulfur bacteria (Beggiatoaceae) from sediments underlying the Benguela upwelling system host diverse microbiomes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Z.P.; Chu, Y.X.; Tian, G.; He, R. Eutrophication levels increase sulfur biotransformation and emissions from sediments of Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Gao, H.; Xie, Y. Effect of No-Tillage on Soil Bacterial Community Structure in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ju, X.; Wu, Q.; Han, G.D. Effects of Grazing Intensity on Microbial Diversity at Different Soil Depths in Desert Steppe Soils. Agronomy 2025, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Gu, Z.; Liu, X.D.; Li, B.Y. Microenvironment heterogeneity affected by anthropogenic wildfire-perturbed soil mediates bacterial community in Pinus tabulaeformis forests. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1415726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Yao, Q.; Yang, K.J. An optimal combined slow-release nitrogen fertilizer and urea can enhance the decomposition rate of straw and the yield of maize by improving soil bacterial community and structure under full straw returning system. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1358582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Hong, Y.Y.; Li, Q.Z.; Liu, Z.B.; Liu, K.H. Characteristics and driving forces of the soil microbial community during 35 years of natural restoration in abandoned areas of the Daxin manganese mine, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujakić, I.; Piwosz, K.; Koblížek, M. Phylum Gemmatimonadota and its role in the environment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eheneden, I.; Wang, R.C.; Zhao, J.F. Antibiotic removal by microalgae-bacteria consortium: Metabolic pathways and microbial responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.S.; Zou, Q. Deciphering microbial adaptation in the rhizosphere: Insights into niche preference, functional profiles, and cross-kingdom Co-occurrences. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Ros, G.H.; Furtak, K.; Iqbal, H.M.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Soil carbon sequestration–An interplay between soil microbial community and soil organic matter dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akinyede, R.; Taubert, M.; Schrumpf, M.; Trumbore, S.; Küsel, K. Dark CO2 fixation in temperate beech and pine forest soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108526. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Tran, P.Q.; Cowley, E.S.; Trembath-Reichert, E.; Anantharaman, K. Diversity and ecology of microbial sulfur metabolism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 122–140. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, S.; Sindhu, S.S.; Dhanker, R.; Kumari, A. Microbes-mediated sulphur cycling in soil: Impact on soil fertility, crop production and environmental sustainability. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 271, 127340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Sachan, K.; Baskar, P.; Saikanth, D.R.K.; Lytand, W.; Kumar, R.K.M.; Singh, B.V. Soil microbes expertly balancing nutrient demands and environmental preservation and ensuring the delicate stability of our ecosystems-a review. Int. J. Plant Soil. Sci. 2023, 35, 989–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, R.K.; Mattoo, A.K.; Schmidt, M.A. Rhizobial–host interactions and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legume crops toward agriculture sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669404. [Google Scholar]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N. Friends or foes—Microbial interactions in nature. Biology 2021, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.W.; Xu, A.; Zhou, Q.X.; Gong, X.F.; Liang, H. New insights into biofilm formation and microbial communities in hybrid constructed wetlands with functional substrates for treating contaminated surface water. Bioresource Technol. 2025, 416, 131741. [Google Scholar]
- Petronilho, S.; Barros, A.S.; Coimbra, M.A.; Rocha, S.M. Efficient use of non-renewable natural resources for quality wine through sustainable viticulture. In Agricultural Systems in the 21st Century; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 195–230. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Wang, H.; Man, S.S.; Yan, Q. Ferrihydrite regulated nitrogen metabolic pathway at biocathode of bioelectrochemical system–Insight into biofilm formation and bacterial composition. Bioresource Technol. 2025, 424, 132275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Rees, G.N.; Mitchell, A.M.; Watson, G.; Williams, J. The short-term effects of salinization on anaerobic nutrient cycling and microbial community structure in sediment from a freshwater wetland. Wetlands 2006, 26, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, M.Y.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhu, Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Nie, X.R. 16s rDNA sequencing-based insights into the bacterial community structure and function in co-existing soil and coal gangue. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Alam, A.; Rani, M.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Hasnain, S.E. Biofilms: Survival and defense strategy for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
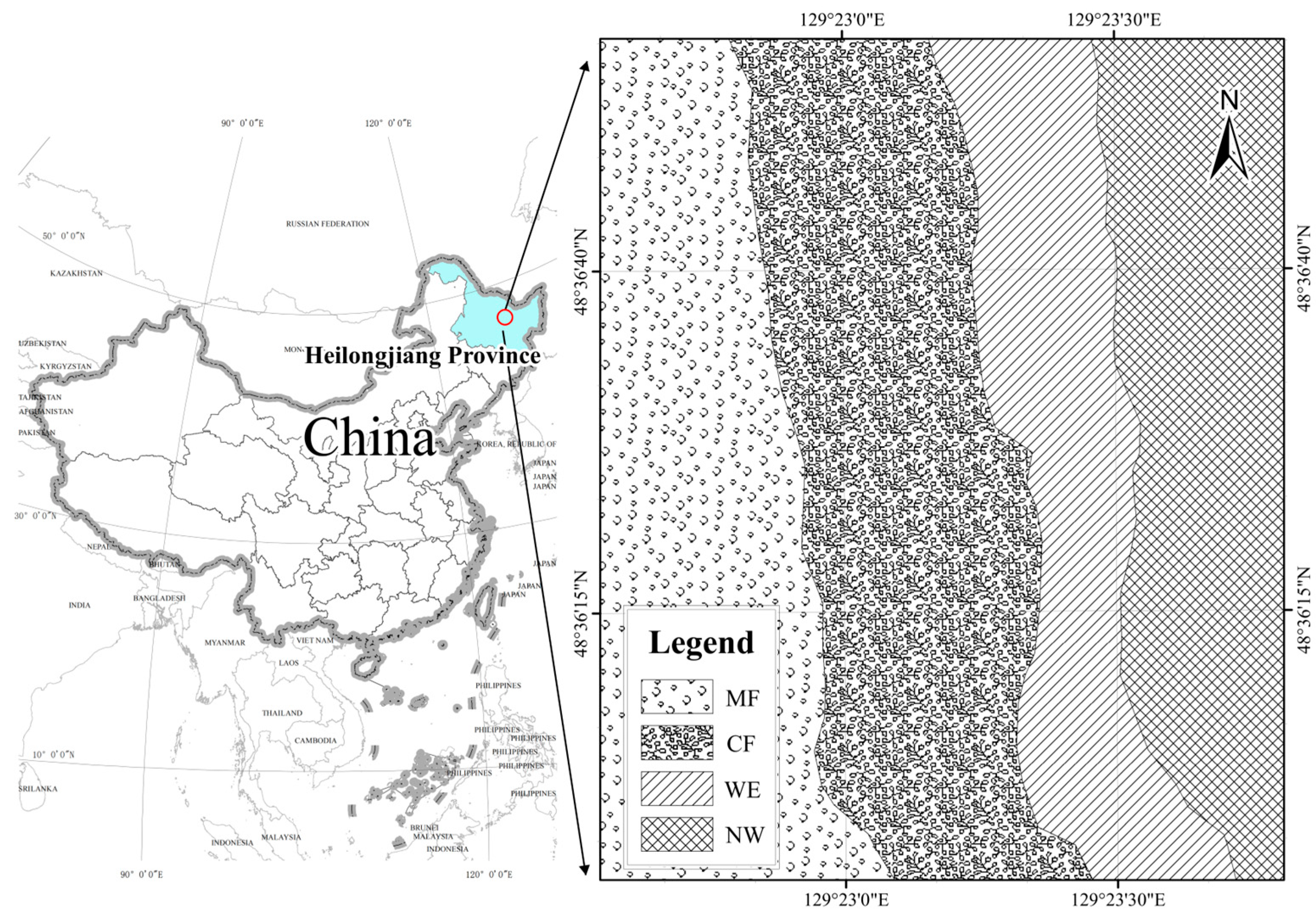
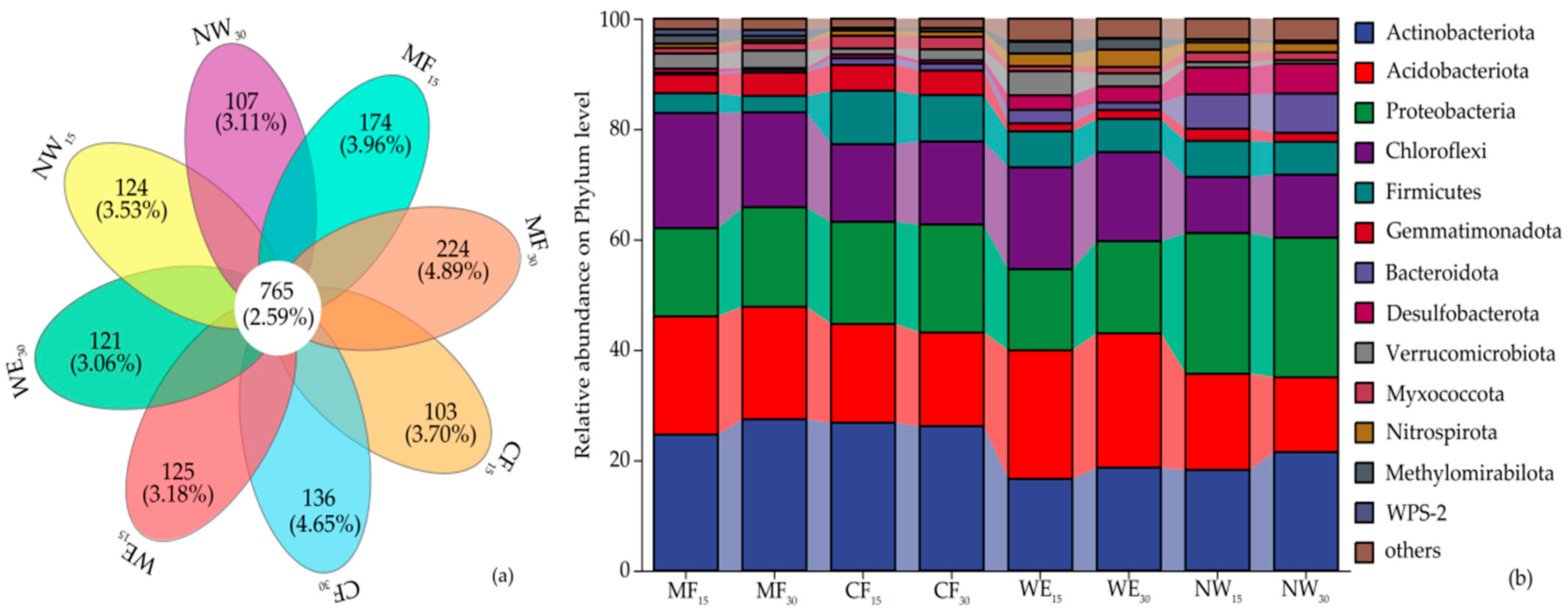
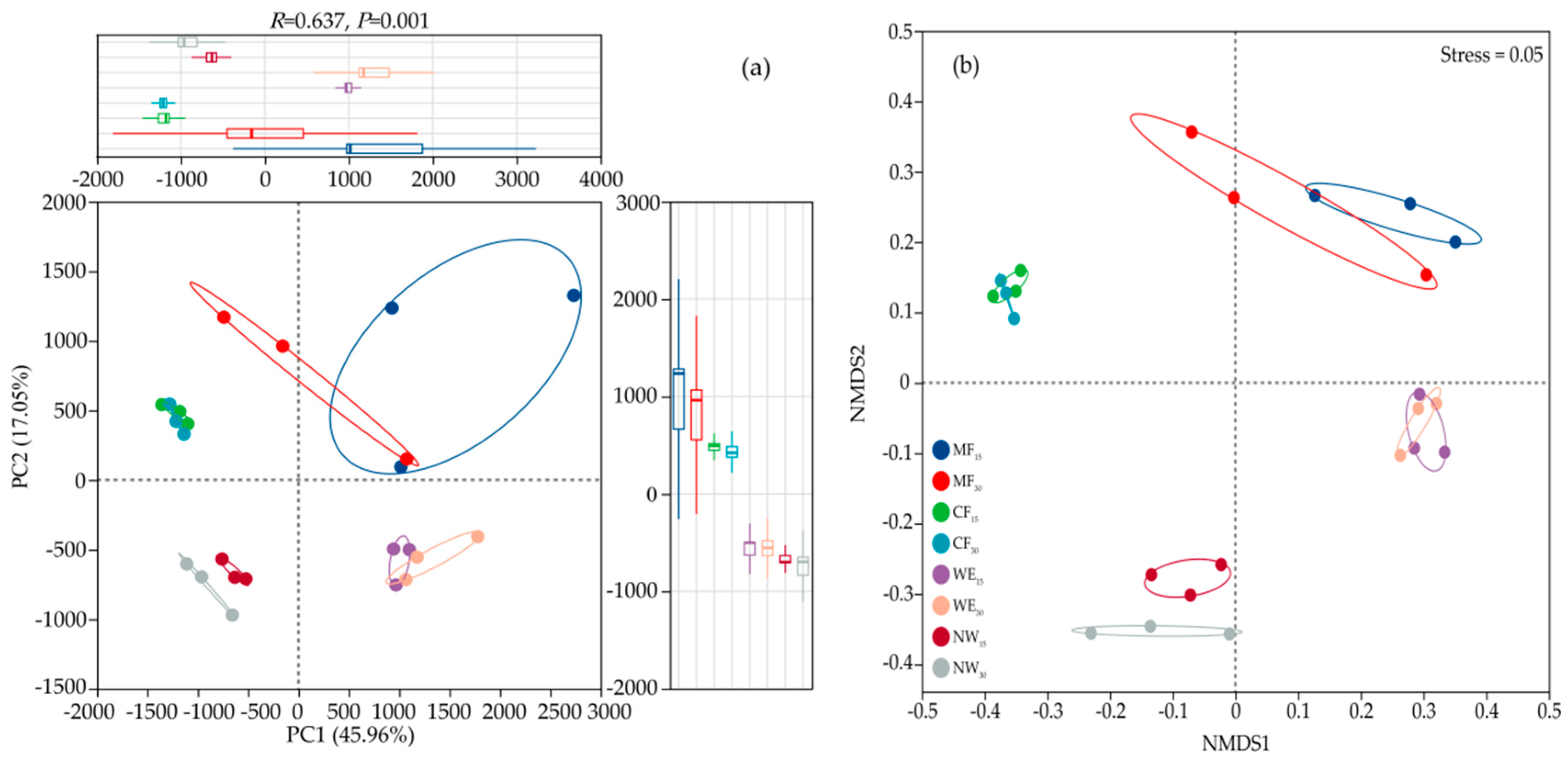
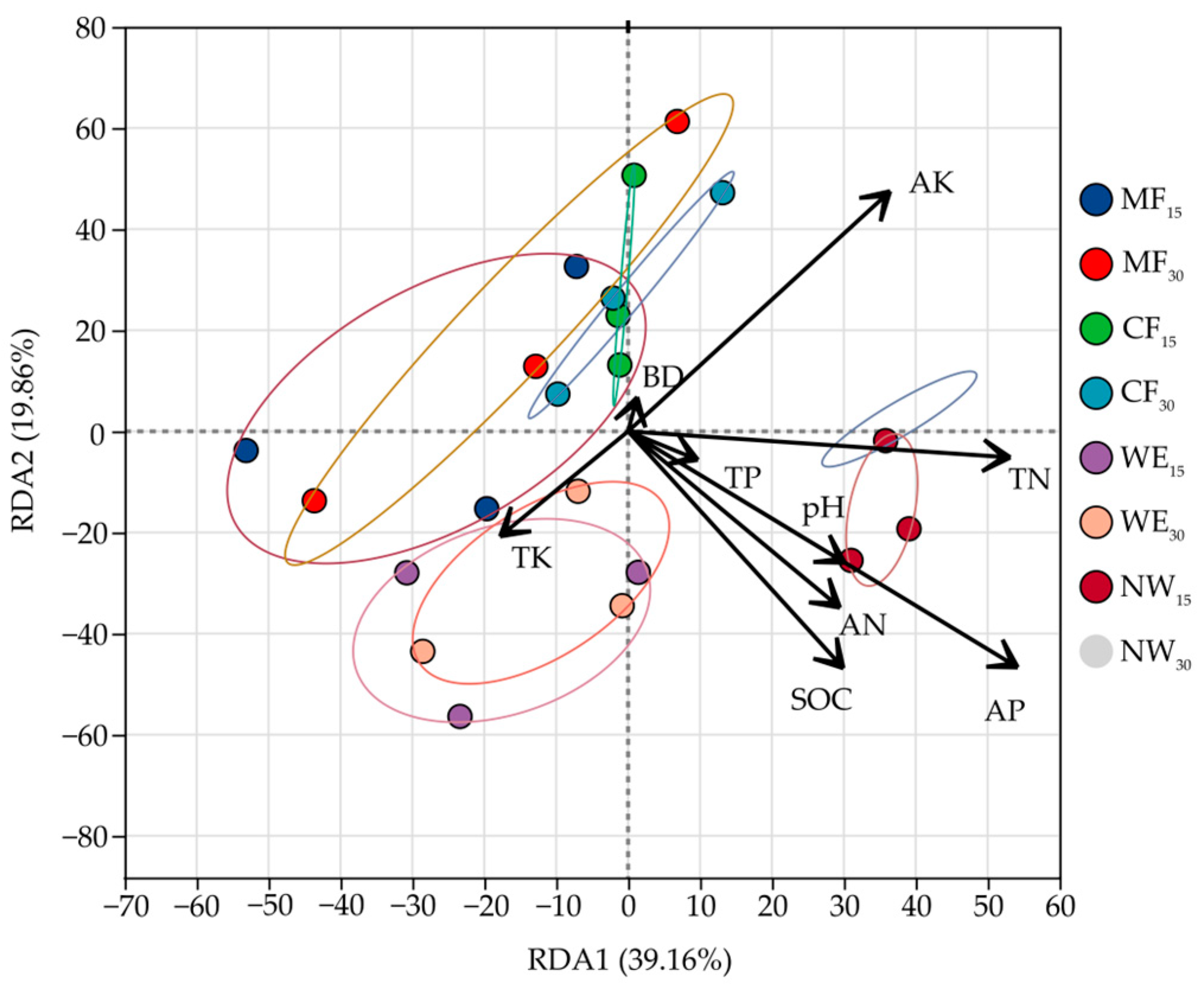

| Ecotones Type | Abbreviation | Plant Composition | Plant Shannon Diversity Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed forest | MF | Betula platyphylla Larix olgensis Picea jezoensis | 0.88 ± 0.03 a |
| Conifer forest | CF | Larix olgensis Lonicera caerulea Spiraea salicifoliab | 0.57 ± 0.03 b |
| Wetland edge | WE | Alnus sibirica Syringa reticulata Prunus padus Anemone dichotoma | 0.54 ± 0.04 b |
| Natural wetland | NW | Carex schmidtii Deyeuxia angustifolia Sanguisorba tenuifolia Filipendula Palmata | 0.52 ± 0.02 b |
| Variables | MF15 | MF30 | CF15 | CF30 | WE15 | WE30 | NW15 | NW30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.4 ± 0.0 b | 5.3 ± 0.1 b | 5.6 ± 0.1 ab | 5.8 ± 0.1 ab | 5.8 ± 0.1 ab | 5.8 ± 0.2 ab | 5.6 ± 0.3 ab | 6.1 ± 0.4 a |
| SOC (g·kg−1) | 51.3 ± 2.7 b | 41.8 ± 0.6 c | 35.7 ± 2.1 d | 33.2 ± 0.4 d | 50.1 ± 1.2 b | 43.2 ± 1.5 c | 59.8 ± 1.8 a | 53.5 ± 1.9 b |
| BD (g·cm−3) | 1.2 ± 0.1 a | 1.5 ± 0.6 a | 1.1 ± 0.17 a | 1.3 ± 0.0 a | 1.2 ± 0.0 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 a |
| TN (g·kg−1) | 4.3 ± 0.8 b | 4.5 ± 0.1 b | 3.1 ± 1.0 c | 2.9 ± 0.1 c | 3.3 ± 0.1 c | 1.7 ± 0.3 d | 6.7 ± 0.3 a | 6.5 ± 0.0 a |
| AN (mg·kg−1) | 122.7 ± 5.1 b | 93.7 ± 11.6 b | 64.3 ± 5.2 c | 51.5 ± 2.5 c | 108.4 ± 2.0 b | 76.3 ± 4.8 c | 168.9 ± 3.4 a | 105.9 ± 2.8 b |
| TP (g·kg−1) | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 b | 0.3 ± 0.0 c | 0.2 ± 0.0 c | 0.3 ± 0.0 c | 0.2 ± 0.0 c | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 b |
| AP (mg·kg−1) | 53.0 ± 0.4 d | 47.1 ± 2.4 d | 41.1 ± 2.4 e | 31.7 ± 0.5 f | 73.2 ± 2.1 b | 68.2 ± 0.2 c | 115.1 ± 9.2 a | 105.7 ± 2.6 a |
| TK (g·kg−1) | 7.1 ± 0.3 a | 5.1 ± 0.3 b | 2.4 ± 0.2 d | 2.1 ± 0.3 d | 4.0 ± 0.1 c | 3.3 ± 0.7 c | 5.4 ± 1.1 b | 3.7 ± 1.2 c |
| AK (mg·kg−1) | 164.7 ± 2.1 b | 143.2 ± 1.9 c | 152.5 ± 2.5 bc | 148.7 ± 2.7 c | 91.3 ± 5.2 d | 75.2 ± 8.0 e | 183.4 ± 11.2 a | 156.4 ± 4.8 b |
| Soil Sample | Sobs | Shannon | Ace | Chao1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF15 | 1032.7 ± 101.2 d | 5.5 ± 0.1 c | 1139.7 ± 122.1 d | 1149.4 ± 116.9 d |
| MF30 | 1081.3 ± 66.6 d | 5.7 ± 0.1 c | 1207.0 ± 63.2 d | 1221.0 ± 74.8 d |
| CF15 | 1412.3 ± 62.3 bc | 6.2 ± 0.1 b | 1517.8 ± 49.8 b | 1566.4 ± 22.6 b |
| CF30 | 1448.3 ± 18.2 b | 6.2 ± 0.0 b | 1543.5 ± 17.1 b | 1573.0 ± 13.5 b |
| WE15 | 1276.7 ± 91.2 c | 5.8 ± 0.0 c | 1419.3 ± 94.3 bc | 1465.3 ± 85.1 bc |
| WE30 | 1277.7 ± 27.7 c | 5.8 ± 0.1 c | 1420.3 ± 31.0 c | 1457.7 ± 14.7 c |
| NW15 | 1611.7 ± 82.3 a | 6.4 ± 0.0 a | 1751.5 ± 68.1 a | 1785.3 ± 58.5 a |
| NW30 | 1651.0 ± 33.1 a | 6.4 ± 0.1 ab | 1806.1 ± 25.7 a | 1852.3 ± 35.7 a |
| Phylum | BD | TP | TK | TN | AK | pH | AN | SOC | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinobacteriota | 0.111 | −0.094 | −0.132 | −0.172 | 0.156 | −0.296 | −0.451 | −0.585 | −0.749 |
| Acidobacteriota | −0.103 | −0.135 | 0.171 | −0.368 | −0.525 | 0.047 | 0.010 | −0.126 | −0.044 |
| Proteobacteria | −0.026 | 0.142 | 0.001 | 0.571 | 0.547 | 0.072 | 0.229 | 0.351 | 0.355 |
| Chloroflexi | 0.061 | −0.100 | 0.163 | −0.389 | −0.354 | −0.226 | −0.192 | −0.290 | −0.397 |
| Firmicutes | −0.091 | −0.484 | −0.741 | −0.291 | −0.038 | 0.306 | −0.511 | −0.361 | −0.232 |
| Gemmatimonadota | −0.049 | −0.017 | 0.026 | −0.130 | 0.307 | −0.374 | −0.366 | −0.528 | −0.727 |
| Bacteroidota | −0.079 | 0.011 | −0.279 | 0.424 | 0.213 | 0.441 | 0.262 | 0.463 | 0.654 |
| Desulfobacterota | −0.174 | 0.195 | 0.016 | 0.406 | 0.226 | 0.305 | 0.492 | 0.701 | 0.853 |
| Verrucomicrobiota | −0.031 | 0.025 | 0.239 | −0.306 | −0.548 | −0.047 | 0.021 | −0.155 | −0.173 |
| Myxococcota | −0.025 | −0.375 | −0.570 | −0.087 | 0.257 | 0.135 | −0.439 | −0.431 | −0.370 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, J.; Yu, S. Structural and Functional Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities in Forest–Wetland Ecotones: A Case Study of the Lesser Khingan Mountains. Life 2025, 15, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040570
Ding J, Yu S. Structural and Functional Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities in Forest–Wetland Ecotones: A Case Study of the Lesser Khingan Mountains. Life. 2025; 15(4):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040570
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Junnan, and Shaopeng Yu. 2025. "Structural and Functional Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities in Forest–Wetland Ecotones: A Case Study of the Lesser Khingan Mountains" Life 15, no. 4: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040570
APA StyleDing, J., & Yu, S. (2025). Structural and Functional Characteristics of Soil Microbial Communities in Forest–Wetland Ecotones: A Case Study of the Lesser Khingan Mountains. Life, 15(4), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040570





