Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin, Silibinin, and Crocetin in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of MASLD: The Role of CD36 and PLIN3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
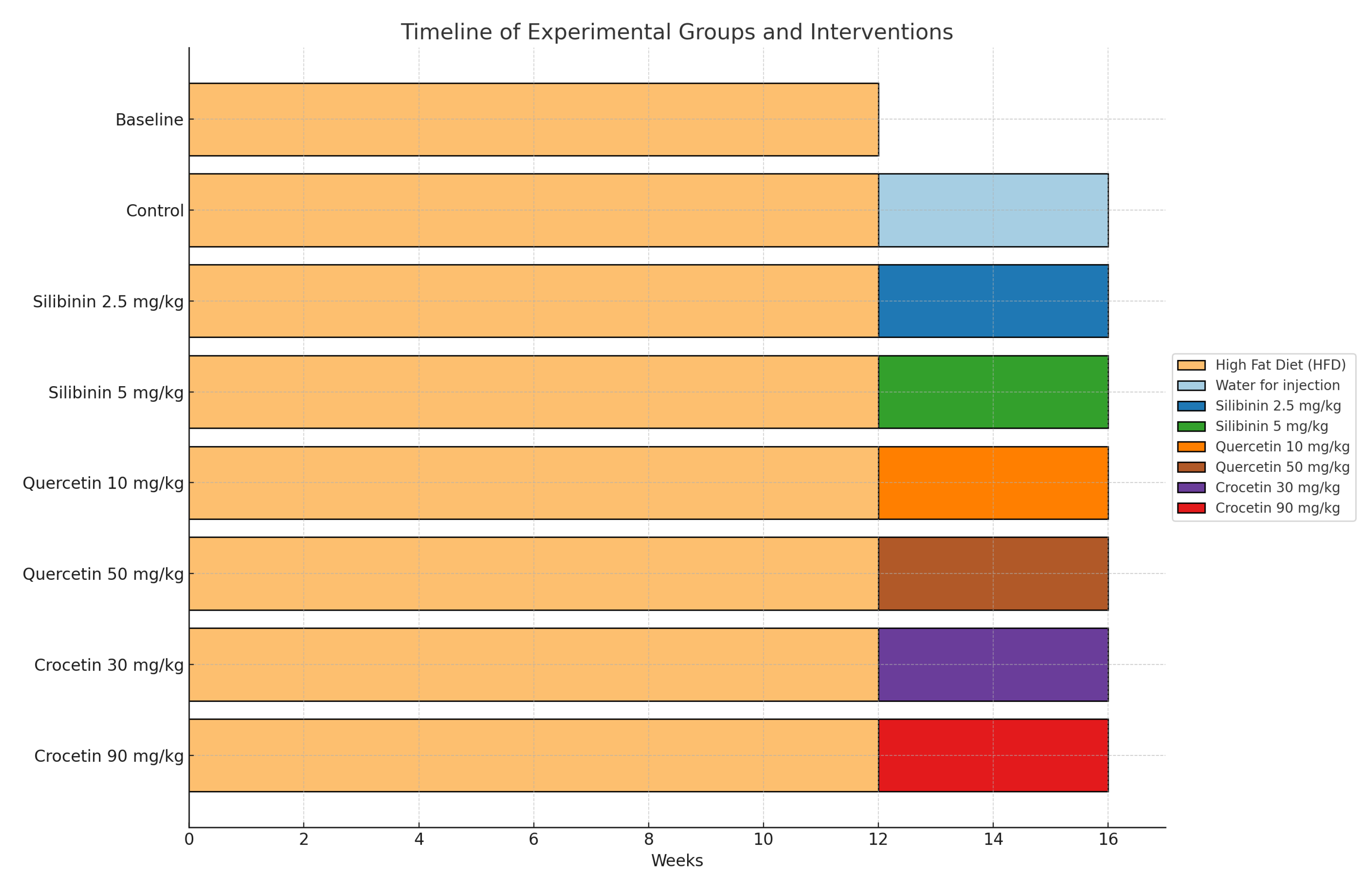
2.1. Experimental Model
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Preparation of QUE-HP-β-CD and SLB-HP-β-CD Lyophilized Product
2.4. Preparation of Saffron Aqueous Extract
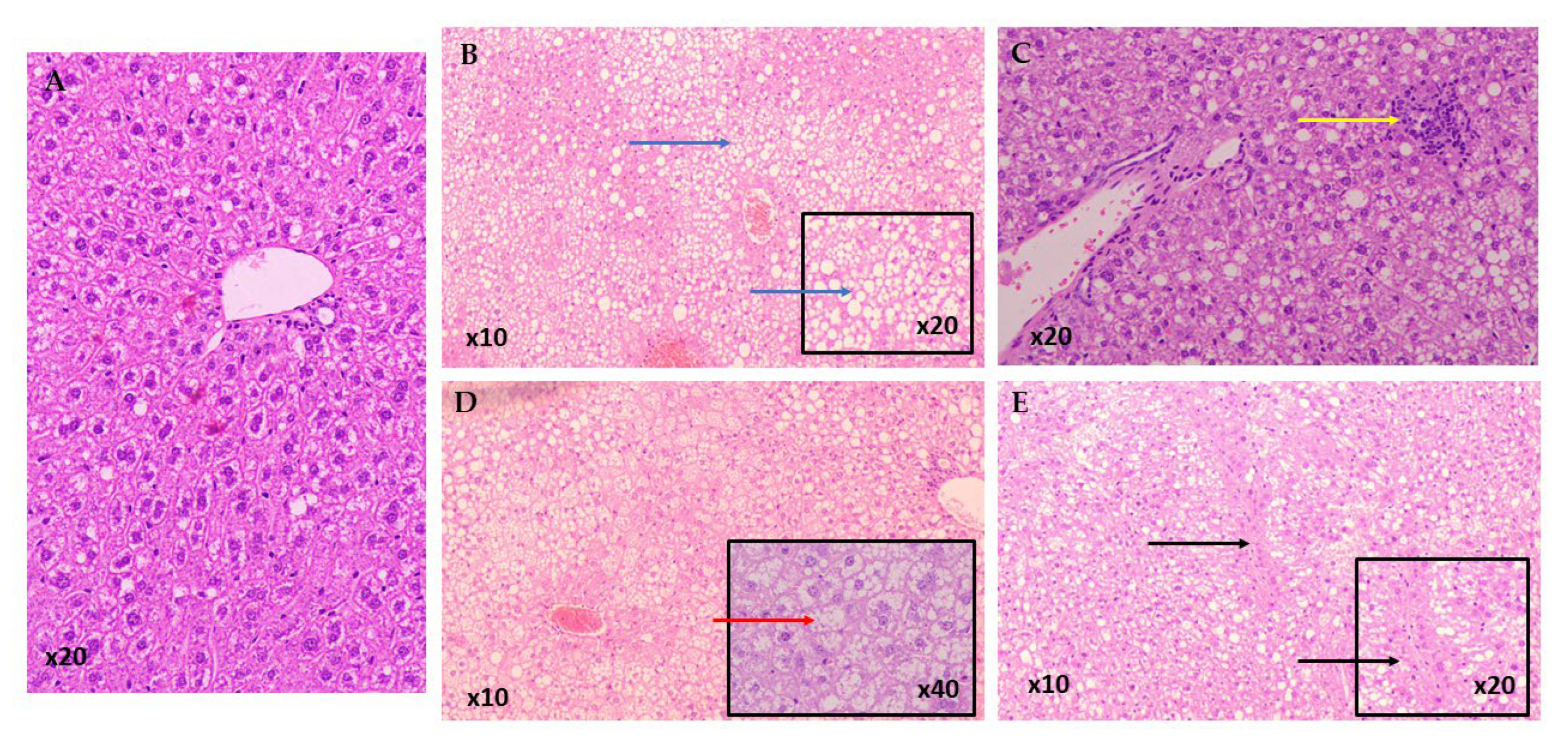
2.5. NAFLD Activity Score
2.6. Immunohistochemistry (Methods)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
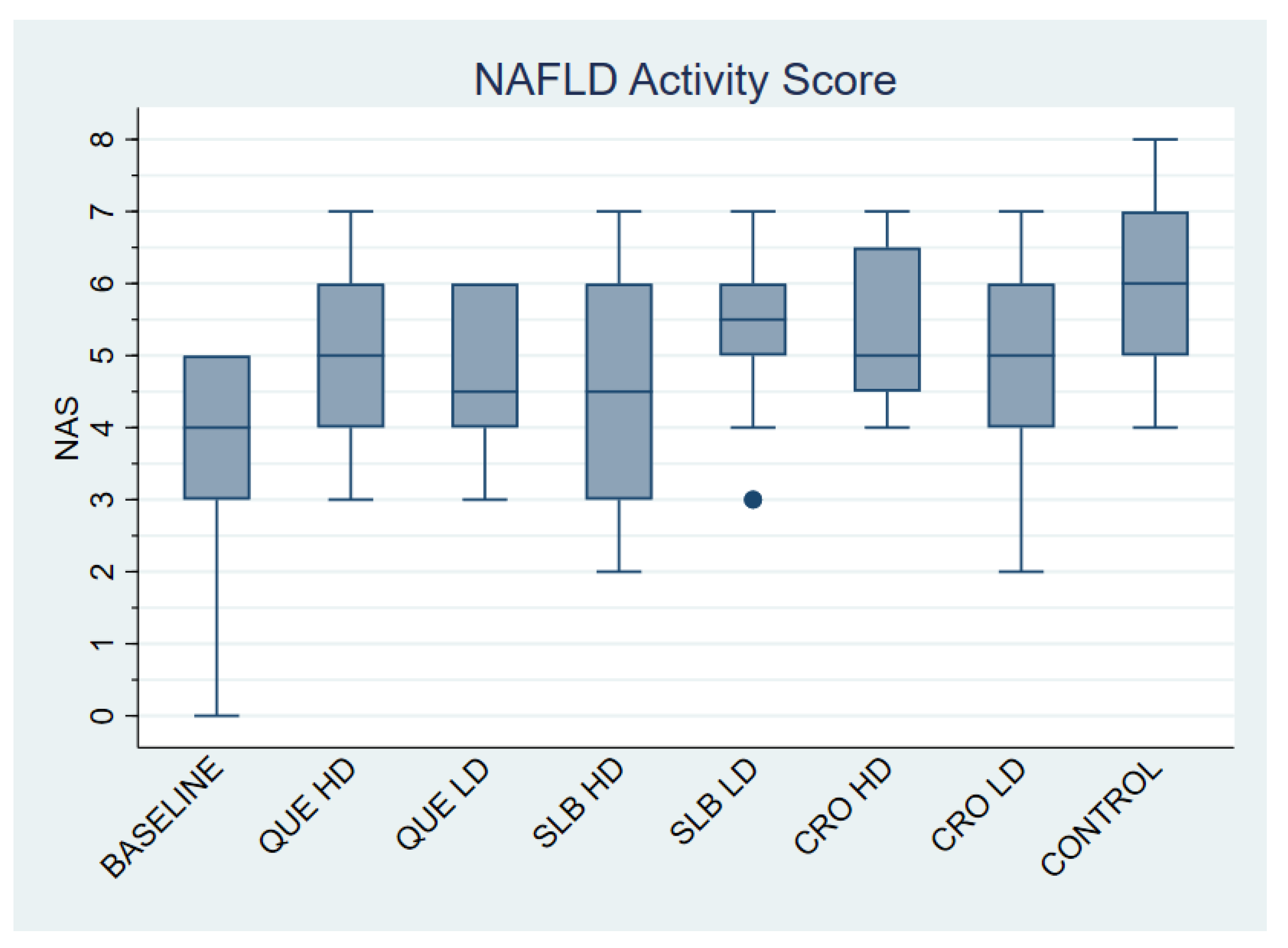
3.1. NAFLD Activity Score (NAS)
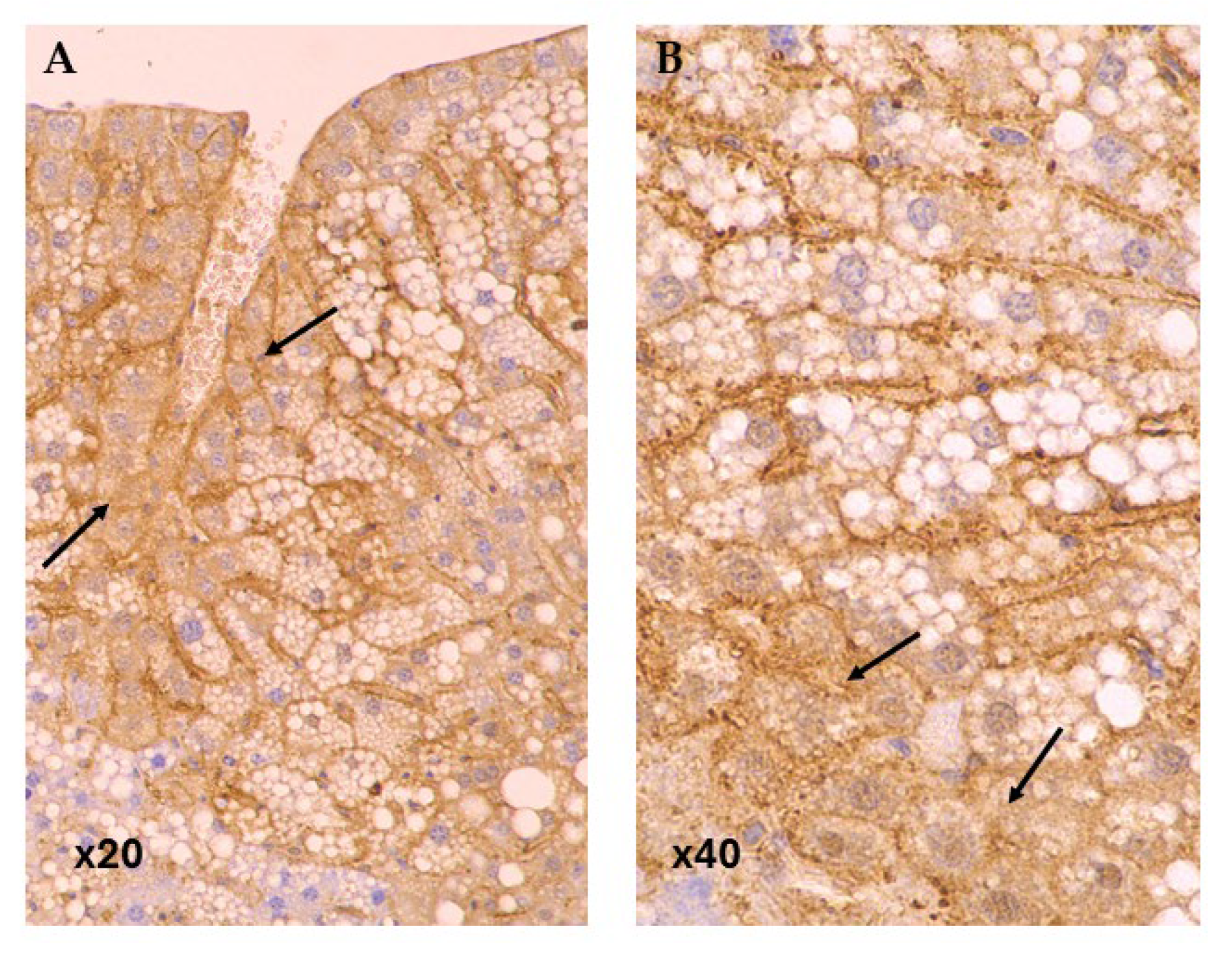
3.2. Immunohistochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Association for the Study of Diabetes; European Association for the Study of Obesity. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Executive Summary. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 2375–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metab. Clin. Exp. 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.A. Autophagy: A Cellular Guardian against Hepatic Lipotoxicity. Genes 2023, 14, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, L.; Yang, J.; Fernandes, G.; Stepanova, M.; Nader, F. The Growing Economic and Clinical Burden of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) in the United States. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 13, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, T.G.; Charlton, M. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis After Liver Transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2020, 26, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Schick, F.; Häring, H.U. Causes, Characteristics, and Consequences of Metabolically Unhealthy Normal Weight in Humans. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M.; Pagano, G. Meta-analysis: Natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for liver disease severity. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 617–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam-Larsen, S.; Franzmann, M.; Andersen, I.B.; Christoffersen, P.; Jensen, L.B.; Sørensen, T.I.; Becker, U.; Bendtsen, F. Long term prognosis of fatty liver: Risk of chronic liver disease and death. Gut 2004, 53, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Nasr, P.; Widman, L.; Hagström, H. Risk of cardiovascular disease and loss in life expectancy in NAFLD. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1495–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsaros, I.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Vailas, M. Quercetin’s Potential in MASLD: Investigating the Role of Autophagy and Key Molecular Pathways in Liver Steatosis and Inflammation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; E, M.; Qi, H.; et al. Therapeutic application of natural products: NAD(+) metabolism as potential target. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 114, 154768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsaros, I.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Vailas, M.; Papachristou, F.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Grigoriou, M.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Valsami, G.; Tsaroucha, A.; et al. The Effect of Quercetin on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and the Role of Beclin1, P62, and LC3: An Experimental Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qin, Y.; Xin, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Feng, X. The great potential of flavonoids as candidate drugs for NAFLD. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Ruan, R.; Huang, G.; Mi, S.; Cheng, Y. Lipid-Lowering Potential of Almond Hulls (Quercetin, Baicalein, and Kaempferol): Insights from Network Pharmacology and Molecular Dynamics. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Nitzan-Kaluski, D.; Goldsmith, R.; Webb, M.; Blendis, L.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R. Long term nutritional intake and the risk for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A population based study. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadeja, R.N.; Thounaojam, M.C.; Dandekar, D.S.; Devkar, R.V.; Ramachandran, A.V. Clerodendron glandulosum.Coleb extract ameliorates high fat diet/fatty acid induced lipotoxicity in experimental models of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2010, 48, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carresi, C.; Cardamone, A.; Musolino, V.; Mollace, R.; Tavernese, A.; Coppoletta, A.R.; Gliozzi, M.; Mollace, V. The role of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) in MASLD-Induced HFpEF: Mitigate diastolic dysfunction by targeting chronic low-grade inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 190, 118375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, Y.; Sanyal, A.J. Current and upcoming pharmacotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2017, 66, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wah Kheong, C.; Nik Mustapha, N.R.; Mahadeva, S. A Randomized Trial of Silymarin for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2017, 15, 1940–1949.e1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.Y.; Xi, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.G.; Fang, X.H.; Li, Z.X.; Chen, Y.M. Effects of Silybum marianum, Pueraria lobate, combined with Salvia miltiorrhiza tablets on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: A triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 63, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shu, S. Danshao Shugan Granule therapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambu, B.; Yan, S.; Huda, N.; Liu, G.; Yin, X.M. Autophagy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease. Liver Res. 2018, 2, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kaushik, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Novak, I.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; Cuervo, A.M.; Czaja, M.J. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, A.; Mayoral, R.; Agra, N.; Valdecantos, M.P.; Pardo, V.; Miquilena-Colina, M.E.; Vargas-Castrillón, J.; Lo Iacono, O.; Corazzari, M.; Fimia, G.M.; et al. Impaired autophagic flux is associated with increased endoplasmic reticulum stress during the development of NAFLD. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willy, J.A.; Young, S.K.; Mosley, A.L.; Gawrieh, S.; Stevens, J.L.; Masuoka, H.C.; Wek, R.C. Function of inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase isoform α (IBTKα) in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis links autophagy and the unfolded protein response. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 14050–14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Sun, W.; Sun, F.; Yin, G.; Liang, P.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, F. Biological Mechanisms and Related Natural Inhibitors of CD36 in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 3829–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, T. Role of lipid droplet proteins in liver steatosis. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 67, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, R.; Chen, J.; Xin, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, L.; Tong, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shui, G. Knockdown of hepatocyte Perilipin-3 mitigates hepatic steatosis and steatohepatitis caused by hepatocyte CGI-58 deletion in mice. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 14, mjac055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, E.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Konstandi, O.A.; Kenoutis, C.; Kakazanis, Z.I.; Rizakou, A.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Crocus sativus L. aqueous extract reduces atherogenesis, increases atherosclerotic plaque stability and improves glucose control in diabetic atherosclerotic animals. Atherosclerosis 2018, 268, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Kimura, T.; Fujimori, N.; Nagaya, T.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, E. Current status, problems, and perspectives of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease research. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, R. Small Sample Confidence Intervals for the Odds Ratio. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2004, 33, 1095–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Macia, M.; Santos-Ledo, A.; Leslie, J.; Paish, H.L.; Collins, A.L.; Scott, R.S.; Watson, A.; Burgoyne, R.A.; White, S.; French, J.; et al. A Mammalian Target of Rapamycin-Perilipin 3 (mTORC1-Plin3) Pathway is essential to Activate Lipophagy and Protects Against Hepatosteatosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3441–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Kechagia, I.A.; Tzimas, S.; Balafas, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Archontaki, H.; Dokoumetzidis, A.; Valsami, G. Serum and tissue pharmacokinetics of silibinin after per os and i.v. administration to mice as a HP-β-CD lyophilized product. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, K.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Chountoulesi, M.; Diamantis, D.A.; Spaneas, D.; Vakali, V.; Naziris, N.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Andreadelis, I.; Moschovou, K. Preparation and biophysical characterization of quercetin inclusion complexes with β-cyclodextrin derivatives to be formulated as possible nose-to-brain quercetin delivery systems. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4241–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Manta, K.; Kostantini, C.; Kikionis, S.; Banella, S.; Ioannou, E.; Christodoulou, E.; Rekkas, D.M.; Dallas, P.; Vertzoni, M.; et al. Nasal powders of quercetin-β-cyclodextrin derivatives complexes with mannitol/lecithin microparticles for Nose-to-Brain delivery: In vitro and ex vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Georgiou, I.; Kouroupi, M.; Sivridis, E. LC3A, LC3B and Beclin-1 expression in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6827–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Wei, L.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; Chen, Y.; et al. CD36 plays a negative role in the regulation of lipophagy in hepatocytes through an AMPK-dependent pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier-Torres, L.; Fortner, K.A.; Iruzubieta, P.; Delgado, T.C.; Giddings, E.; Chen, Y. Silencing hepatic MCJ attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by increasing mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Yao, P.; Gong, Z. Quercetin Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Accumulation in the Liver: Implication for Autophagy Regulation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 607531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Martínez-Ferreras, Á.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Fernández, A.; Benet, M.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Quercetin ameliorates dysregulation of lipid metabolism genes via the PI3K/AKT pathway in a diet-induced mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, D.J. What is oxidative stress? Metab. Clin. Exp. 2000, 49, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, M.; Katsaros, I.; Vailas, M.; Lidoriki, I.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.G.; Valsami, G.; Tsaroucha, A.; Schizas, D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of quercetin and its therapeutic implications. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Saudi Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2021, 27, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Manzoor, M.; Yang, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. Silymarin targets the FXR protein through microbial metabolite 7-keto-deoxycholic acid to treat MASLD in obese mice. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 133, 155947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serviddio, G.; Bellanti, F.; Giudetti, A.M.; Gnoni, G.V.; Petrella, A.; Tamborra, R.; Romano, A.D.; Rollo, T.; Vendemiale, G.; Altomare, E. A silybin-phospholipid complex prevents mitochondrial dysfunction in a rodent model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 332, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaky, M.A.; Sirwi, A.; Ismail, S.H.; Awad, H.H.; Gad, S.S. Hepatoprotective Effect of Silver Nanoparticles at Two Different Particle Sizes: Comparative Study with and without Silymarin. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2923–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Federico, A.; Trappoliere, M.; Tuccillo, C.; Sio, I.; Leva, A.; Niosi, M.; D’Auria, M.; Capasso, R.; Blanco, C. The Effect of a Silybin-Vitamin E-Phospholipid Complex on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Fei, W.; Zhen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S.; Ren, L. Quantitative proteomics analysis based on tandem mass tag labeling coupled with labeling coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry discovers the effect of silibinin on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 6750–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Song, G.; Ren, L. Silibinin improves nonalcoholic fatty liver by regulating the expression of miR-122: An in vitro and in vivo study. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D.; Langeswaran, K. Hepatocellular Interactions of Potential Nutraceuticals in the Management of Inflammatory NAFLD. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suguro, R.; Pang, X.C.; Yuan, Z.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Xie, Y. Combinational applicaton of silybin and tangeretin attenuates the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice via modulating lipid metabolism. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, S.; Gong, J.; Feng, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.; You, Y.; Tong, Y.; Wang, P. Exploring the Protective Effects and Mechanism of Crocetin From Saffron Against NAFLD by Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 681391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, S.; Tong, Z.; Chen, S.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, W.; Tong, Y.; Zahra, B.S.; et al. Crocetin ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating mitochondrial dysfunction in L02 cells and zebrafish model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; He, X.M.; Jin, M.H.; Sun, H.N.; Kwon, T. Lipophagy: A potential therapeutic target for nonalcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 672, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, P.; He, Z.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liu, F.; Qi, J. Crocin ameliorates atherosclerosis by promoting the reverse cholesterol transport and inhibiting the foam cell formation via regulating PPARγ/LXR-α. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | N | NAS |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 11 | 3.73 ± 1.56 |
| QUE HD | 12 | 5.17 ± 1.27 |
| QUE LD | 12 | 4.75 ± 1.06 |
| SLB HD | 12 | 4.50 ± 1.57 |
| SLB LD | 12 | 5.42 ± 1.16 |
| CRO HD | 12 | 5.42 ± 1.16 |
| CRO LD | 12 | 4.75 ± 1.66 |
| Control | 12 | 5.83 ± 1.27 |
| Total | 95 | 4.96 ± 1.44 |
| Group | N | Fatty Liver | Steatohepatitis (NAS > 5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 11 | 11 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| QUE HD | 12 | 7 (58.33%) | 5 (41.67%) |
| QUE LD | 12 | 8 (66.67%) | 4 (33.33%) |
| SLB HD | 12 | 8 (66.67%) | 4 (33.33%) |
| SLB LD | 12 | 6 (50.00%) | 6 (50.00%) |
| CRO HD | 12 | 7 (58.33%) | 5 (41.67%) |
| CRO LD | 12 | 8 (66.67%) | 4 (33.33%) |
| Control | 12 | 2 (16.67%) | 10 (83.33%) |
| Total | 95 | 60 (63.20%) | 35 (36.80%) |
| Group | N | CD36 | PLIN3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 11 | 7.82 ± 7.11 | 34.55 ± 9.34 |
| QUE HD | 12 | 4.00 ± 3.95 | 47.5 ± 23.79 |
| QUE LD | 12 | 8.67 ± 5.57 | 52.5 ± 17.65 |
| SLB HD | 12 | 6.83 ± 6.75 | 20.00 ± 8.53 |
| SLB LD | 12 | 2.67 ± 2.84 | 49.17 ± 19.29 |
| CRO HD | 12 | 4.42 ± 3.6 | 62.5 ± 11.38 |
| CRO LD | 12 | 4.33 ± 3.52 | 31.67 ± 19.46 |
| Control | 12 | 8.08 ± 7.17 | 27.50 ± 14.22 |
| Total | 95 | 5.83 ± 5.53 | 40.74 ± 20.80 |
| CD36 | PLIN3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| weak | strong | weak | strong | |
| Baseline | 4 (36.36%) | 7 (63.64%) | 5 (45.45%) | 6 (54.55%) |
| QUE HD | 9 (75.00%) | 3 (25.00%) | 5 (41.67%) | 7 (58.33%) |
| QUE LD | 3 (25.00%) | 9 (75.00%) | 2 (16.67%) | 10 (83.33%) |
| SLB HD | 7 (58.33%) | 5 (41.67%) | 12 (100.00%) | 0 (0.00%) |
| SLB LD | 11 (91.67%) | 1 (8.33%) | 2 (16.67%) | 10 (83.33%) |
| CRO HD | 8 (66.67%) | 4 (33.33%) | 0 (0.00%) | 12 (100.00%) |
| CRO LD | 8 (66.67%) | 4 (33.33%) | 7 (58.33%) | 5 (41.67%) |
| Control | 6 (50.00%) | 6 (50.00%) | 9 (75.00%) | 3 (25.00%) |
| Total | 56 (58.95%) | 39 (41.05%) | 42 (44.21%) | 53 (55.79%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotiropoulou, M.; Katsaros, I.; Vailas, M.; Papachristou, F.; Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Valsami, G.; Tsaroucha, A.; Schizas, D. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin, Silibinin, and Crocetin in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of MASLD: The Role of CD36 and PLIN3. Life 2025, 15, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101523
Sotiropoulou M, Katsaros I, Vailas M, Papachristou F, Papakyriakopoulou P, Kostomitsopoulos N, Giatromanolaki A, Valsami G, Tsaroucha A, Schizas D. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin, Silibinin, and Crocetin in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of MASLD: The Role of CD36 and PLIN3. Life. 2025; 15(10):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101523
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotiropoulou, Maria, Ioannis Katsaros, Michail Vailas, Fotini Papachristou, Paraskevi Papakyriakopoulou, Nikolaos Kostomitsopoulos, Alexandra Giatromanolaki, Georgia Valsami, Alexandra Tsaroucha, and Dimitrios Schizas. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin, Silibinin, and Crocetin in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of MASLD: The Role of CD36 and PLIN3" Life 15, no. 10: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101523
APA StyleSotiropoulou, M., Katsaros, I., Vailas, M., Papachristou, F., Papakyriakopoulou, P., Kostomitsopoulos, N., Giatromanolaki, A., Valsami, G., Tsaroucha, A., & Schizas, D. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin, Silibinin, and Crocetin in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model of MASLD: The Role of CD36 and PLIN3. Life, 15(10), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101523









