Oligodendroglial Epigenetics, from Lineage Specification to Activity-Dependent Myelination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
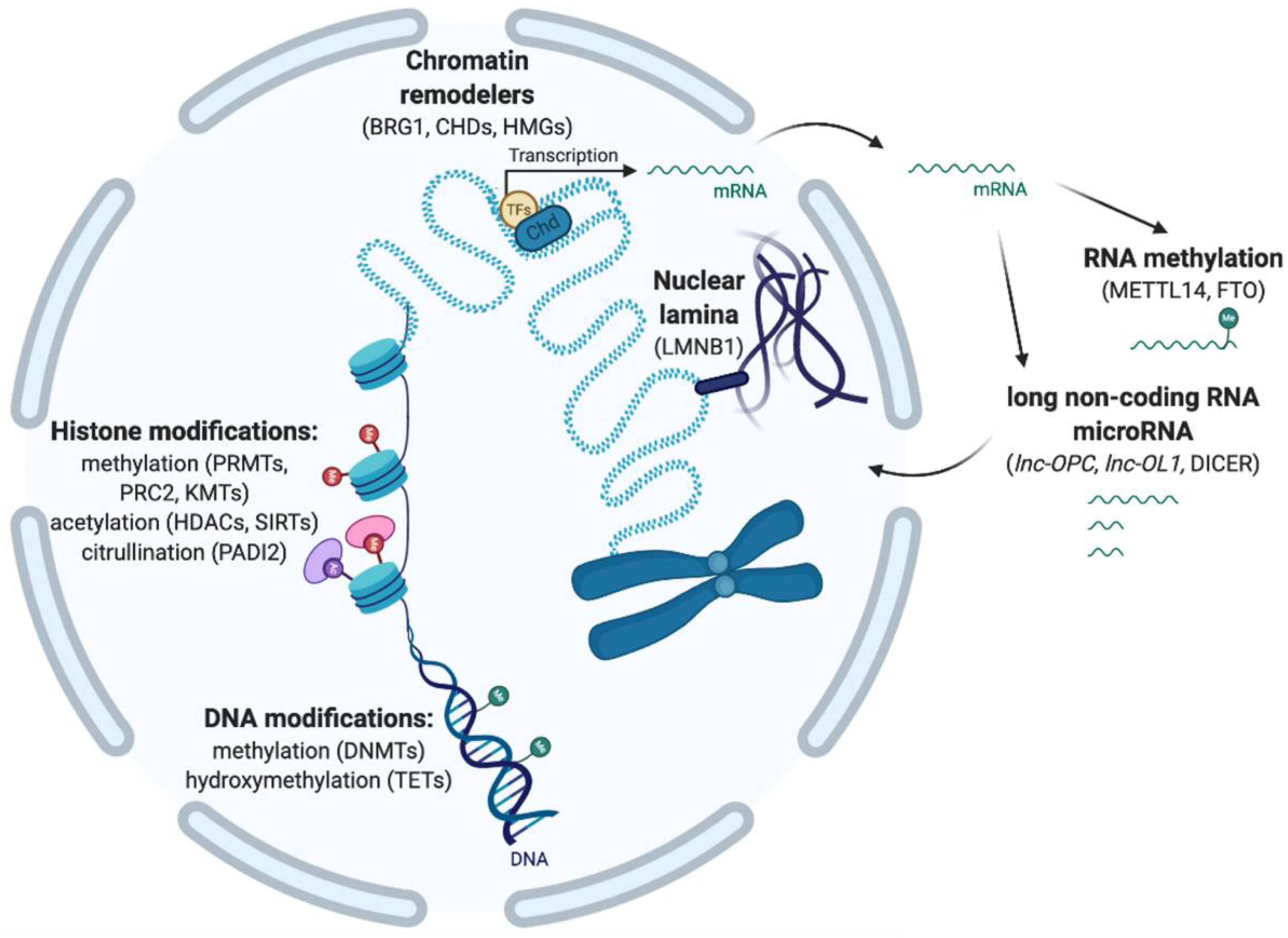
2. Epigenetic Modifications Involved in Chromatin Accessibility and the Regulation of Gene Expression
2.1. DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation
2.2. Histone Post-Translational Modifications
2.3. Chromatin Remodeling
2.4. 3D Chromatin Organization with Nuclear Lamina
2.5. Post-Transcriptional Modifications
3. Epigenetic Marks with Roles in Oligodendroglial Cell Lineage
3.1. DNA Methylation Waves in NSC Differentiation to OPCs
| DNA Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA methylation | Negative role in NSCs differentiation to glia | Repression of astrogliogenesis (Stat3 binding element in Gfap promoter) | In vitro neuroepithelial cells | BS PCR on neuroepithelial cells | Takizawa et al. [85] | |
| DNMT1 | Negative role in NPCs differentiation to glia | Control of the timing of astrogliogenesis by repression of astrocyte-specific genes (Gfap, Stat1) | Nestin-cre;Dnmt1flox NPCs | BS PCR on Nestin-cre;Dnmt1flox NPCs | Fan et al. [86] | |
| Positive role in NSCs differentiation to glia | Repression of neuron-specific genes (Dlx1, Dlx2, Trb1) | Sox2-EGFP mice | WGBS on NS/PCs from Sox2-EGFP transgenic mice | Sanosaka et al. [84] | ||
| DNMT1 | Positive role in NSCs specification to OPCs | Repression of neuron-specific (Ndrg4, Camk1, Ephb2) and astrocyte-specific (Aldh1l1, Pax6, Rfx4) genes | Olig1cre;Dnmt1flox mice | RNA-Seq and ERRBS on sorted neonatal OPCs and OLs, RNA-Seq on sorted Olig1cre;Dnmt1flox OPCs | Moyon et al. [91] | |
| DNA demethylation | Positive role in ESCs transition to NSCs | Activation of transcription factors (Sox2, Sox21, Ascl1) | Sox2-EGFP mice | WGBS on NS/PCs from Sox2-EGFP transgenic mice | Sanosaka et al. [84] | |
| Positive role in NSCs differentiation to glia | Activation of gliogenic promoters (NFI, Tcf3, Gfap, Kcnj10, Sox8) | |||||
| Activation of gliogenic promoters (Stat3 binding site in Gfap promoter, Aldoc) | In vitro NPCs and astrocytes from mice | MIAMI and BS on NPCs and astrocytes | Hatada et al. [87] | |||
| DNA hydroxymethylation | TET1 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Activation of OL genes (Olig1, Sox10, Id2/4) | Olig1cre;Tet1flox mice | hMeDIP-Seq on in vitro neonatal NSCs and OPCs, RNA-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Tet1flox OPCs | Zhang et al. [92] |
| Histone Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Histone methylation | PRC2 (EZH2) (H3K27me3) | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | In vitro primary cultures + Olineu + Ezh2 expression vector/shRNA | Sher et al. [94] | ||
| Repression of neuronal (NeuroD2, Tlx3), astrocytic (Tal1), OL (Olig2, Pdgfra, Nkx2.2) genes | In vitro NSCs and OPCs + shRNA | ChIP-Seq on in vitro NSCs and OLs | Sher et al. [95] | |||
| PRC2 (EED) (H3K27me3) | Positive role in astrocyte–OPC fate switch | Olig1cre;Eedflox and PdgfracreRT;Eedflox mice | Wang et al. [96] | |||
| H3K27me3 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Repression of global lineage alternative choice | In vitro OPCs; Cnp-EGFP mice | ChIP-Seq on in vitro OPCs and OLs (H3K27me3) | Liu et al. [97] | |
| PRMT1 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Nestin-cre;Prmt1flox mice | Hashimoto et al. [98] | |||
| Histone (de)acetylation | CBP (H3K9/K14ac) | Positive role in NSCs differentiation | Sequential activation of promoters of neuronal (Tuba1a), astrocytes (Gfap), OL (Mbp) | In vitro cortical precursors + siRNA/inhibitors; cbp+/− mice | ChIP-qPCR on cbp+/− cortices | Wang et al. [99] |
| HDACs | Positive role in oligodendrogenesis | In vivo HDAC inhibition in rats | Liu et al. [100] | |||
| HDAC1/HDAC2 | Positive role in Shh-induced oligodendrogenesis | Repression of genes associated with Notch signaling (Hey1, Hey2) and Wnt signaling (Tbx3) | In vitro OPCs, Olineu cells + shRNA/inhibitors | ChIP on in vitro Olineu and GeneChip on in vitro OPCs | Wu et al. [101] | |
| HDAC2 (H3K9deac) | Negative role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Repression of oligodendroglial differentiation genes (Sox10) in the presence of thyroid hormone | In vitro NSCs, Olineu, OPCs + siRNA/inhibitors | ChIP-Seq on in vitro NSCs | Castelo-Branco et al. [102] | |
| HDAC3 | Positive role in astrocyte–OL fate switch | Activation of enhancers of OPC genes (Olig2, Ng2) and repression of astrogliogeneis genes (Stat3) and neuronal genes (Bdnf) | In vitro astrocytes and OPCs + inhibitors/expression vectors; Olig1Cre;Hdac3flox, PDGFRaCreERT2;Hdac3flox; Syn1Cre;Hdac3flox mice | ChIP-Seq on in vitro OPCs and OL; RNA-Seq on optic nerves from Olig1cre;Hdac3flox mice | Zhang et al. [103] | |
| SIRT1 (H3K9deac) | Negative role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Repression of differentiation to OPCs (deacetylation at the Pdgfrα promoter) | In vitro OPCs, NS/PCs + inhibitors; NestinCre;Sirt1flox mice | ChIP-qPCR on in vitro NS/PCs | Rafalski et al. [104] | |
| Chromatin Organization | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Chromatin remodelers | HMGA1, 2 | Negative role in NPCs differentiation to glia | Repression of astrogenic transition | In vitro and in vivo NPCs + shRNA/overexpression | Kishi et al. [105] | |
| HMGB1, 2, 3, 4 | Dynamically expressed in NSCs | In vitro NSCs, Nestin-GFP mice, HMGB2−/− mice | IHC, qPCR, shotgun proteomics on in vitro NSCs | Abraham et al. [106] | ||
| HMGB2 | Possible role in NSCs proliferation and maintenance | In vitro NSCs, Nestin-GFP mice, HMGB2−/− mice | IHC, qPCR, shotgun proteomics on in vitro NSCs | Abraham et al. [106] | ||
| Role in neuron–glia fate switch | In vitro NS/PCs, HMGB2−/− mice | Bronstein et al. [107] | ||||
| HMGB4 | Negative role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Regulation of neuronal, astrocyte, oligodendrocyte genes (Fabp7, NeuroD1, Gfap, Ppp1r14a) | In vitro neurons, neurospheres and various cell lines + lentivirus; HMGB4 Vivo-Morpholinos | Microarray on HMGB4-EGFP over-expressing HEK 293T cells | Rouhiainen et al. [108] | |
| HMGN family | Positive role in neuron–glia fate switch | Modulation of the response to gliogenic signals | In vitro NPCs + shRNA/overexpression | qPCR, IHC, BS and microarray on in vitro NPCs | Nagao et al. [109] | |
| BRG1 | Positive role in NSCs maintenance and gliogenesis | Repression of neuronal differentiation in NSCs | In vitro NSCs, NestinCre;Brg1flox mice | IHC; DNA microarray on CNS tissues of NestinCre;Brg1flox mice | Matsumoto et al. [110] | |
| Positive role in NSCs differentiation to neurons | Activation of neuronal genes (Ngn and NeuroD) | In vitro pluriopotent P19 cells + plasmids, Xenopus + Brg1 morpholino | IHC | Seo at al. [111] | ||
| Limited role in NSCs | zebrafish + Brg1 morpholino | IHC, ISH | Gregg et al. [112] | |||
| Post-Transcriptional Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Long non-coding RNA | lnc-158 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Activation of OL genes (Cnp, Mbp, Mag, Osp) | In vitro NSCs + lnc-158 overexpression and siRNA | Li et al. [113] | |
| lnc-OPC | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Activation of OL genes (Mbp, Plp1, Cnp) | NSCs + shRNA | ChIP-Seq and RNA-Seq on in vitro NSCs | Dong et al. [114] | |
| Neat1 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Activation of OL genes (Olig1, Olig2, Gpr17, Sox8) | Neat1−/− mice | ChIP-Seq on human tissues; RNA-Seq on Neat1−/− mouse brains | Katsel et al. [115] | |
| Sox8OT | Possible role in NSCs differentiation to OPCs | Via Sox8 activation | Descriptive study | Mercer et al. [116] | ||
| MicroRNA | miR-124 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to neurons | Repression of Ezh2 expression | In vitro NSCs + N2a neuroblastoma + P19 cells + overexpression | Microarray on N2a cells | Neo et al. [117] |
| miR-153 | Negative role in NSCs differentiation to glia | Repression of gliogenic genes (Nfia/b) | In vitro ESCs + shRNA + artifical miRNAs | Tsuyama et al. [118] | ||
| miR-17/106 | Positive role in NSCs differentiation to glia | Activation of gliogenesis (p38) | in vitro ESCs and mouse embryos + lentivirus | Naka-Kaneda et al. [119] |
3.2. Histone Modifications
3.2.1. Repression of Lineage-Specific Genes in NSCs by Histone Methylation
3.2.2. Histone Acetylation and Deacetylation Regulate the Lineage Specification
3.3. Chromatin Reorganization during the Differentiation from NSCs to OPCs
3.4. Post-Transcriptional Modifications
4. Epigenetic Marks Maintain an Oligodendroglial Progenitor Cell Pool
4.1. Apoptosis vs. Survival
4.2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation
5. Epigenetic Marks Regulate the Oligodendroglial Progenitor Cell Differentiation into Mature Oligodendrocytes
5.1. Global DNA Demethylation Is Associated with OPC Differentiation
5.2. Chromatin Modifications Are Involved in OPC Differentiation
5.2.1. Chromatin Reorganization Allows for the Accessibility of Differentiation Gene in OPCs
5.2.2. Repressive Marks Regulate the Transition from OPC Proliferation to Differentiation
5.3. Post-Transcriptional Modifications That Are Essential for OPC Differentiation
6. Epigenetic Marks Modulate Myelination and Myelin Remodeling
7. Epigenetic Changes Translate Environmental Cues into Intrinsic Signals in Oligodendroglial Cells
7.1. Chemical and Physical Cues
7.2. Neuronal Activity
7.2.1. Oligodendrocytes Respond to Neuronal Activity
7.2.2. Activity-Dependent Epigenetic Modifications in the CNS
7.2.3. Activity-Dependent Epigenetic Modifications in Oligodendrocytes
7.2.4. Activity-Dependent Epigenetic Modifications in Other Cell Types
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valério-Gomes, B.; Guimarães, D.M.; Szczupak, D.; Lent, R. The Absolute Number of Oligodendrocytes in the Adult Mouse Brain. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelvig, D.P.; Pakkenberg, H.; Stark, A.K.; Pakkenberg, B. Neocortical Glial Cell Numbers in Human Brains. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, A.S.; Tzvetavona, I.D.; Trevisiol, A.; Baltan, S.; Dibaj, P.; Kusch, K.; Möbius, W.; Goetze, B.; Jahn, H.M.; Huang, W.; et al. Oligodendroglial NMDA Receptors Regulate Glucose Import and Axonal Energy Metabolism. Neuron 2016, 91, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.E.; Miller, R.H. Local Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Regulates Oligodendrocyte Precursor Appearance in Multiple Ventricular Zone Domains in the Chick Metencephalon. Dev. Biol. 2001, 233, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessaris, N.; Fogarty, M.; Iannarelli, P.; Grist, M.; Wegner, M.; Richardson, W.D. Competing Waves of Oligodendrocytes in the Forebrain and Postnatal Elimination of an Embryonic Lineage. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, N.P.; Yu, W.P.; Howell, M.; Colvin, J.S.; Ornitz, D.M.; Richardson, W.D. Fgfr3 Expression by Astrocytes and Their Precursors: Evidence That Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes Originate in Distinct Neuroepithelial Domains. Development 2003, 130, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron-Curry, P.; Le Douarin, N.M. Oligodendrocyte Precursors Originate from Both the Dorsal and the Ventral Parts of the Spinal Cord. Neuron 1995, 15, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, M.; Richardson, W.D.; Kessaris, N. A Subset of Oligodendrocytes Generated from Radial Glia in the Dorsal Spinal Cord. Development 2005, 132, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, N.P.; Richardson, W.D. A Singularity of PDGF Alpha-Receptor Expression in the Dorsoventral Axis of the Neural Tube May Define the Origin of the Oligodendrocyte Lineage. Development 1993, 117, 525–533. [Google Scholar]
- Barres, B.A.; Lazar, M.A.; Raff, M.C. A Novel Role for Thyroid Hormone, Glucocorticoids and Retinoic Acid in Timing Oligodendrocyte Development. Development 1994, 120, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, A.; Chang, A.; Trapp, B.D. NG2+ Glial Cells: A Novel Glial Cell Population in the Adult Brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 58, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, N.P.; Mudhar, H.S.; Collarini, E.J.; Richardson, W.D. PDGF Receptors in the Rat CNS: During Late Neurogenesis, PDGF Alpha-Receptor Expression Appears to Be Restricted to Glial Cells of the Oligodendrocyte Lineage. Development 1992, 115, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raff, M.C.; Abney, E.R.; Cohen, J.; Lindsay, R.; Noble, M. Two Types of Astrocytes in Cultures of Developing Rat White Matter: Differences in Morphology, Surface Gangliosides, and Growth Characteristics. J. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Barzan, R.; Chen, T.-J.; Kukley, M. Different Patterns of Neuronal Activity Trigger Distinct Responses of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells in the Corpus Callosum. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, S.O.; Sitnikov, S.; Kamen, Y.; Evans, K.A.; Kronenberg-Versteeg, D.; Dietmann, S.; de Faria, O.; Agathou, S.; Káradóttir, R.T. Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells Become Regionally Diverse and Heterogeneous with Age. Neuron 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka, M.; Rivers, L.E.; Fancy, S.P.; Zhao, C.; Tripathi, R.; Jamen, F.; Young, K.; Goncharevich, A.; Pohl, H.; Rizzi, M.; et al. CNS-Resident Glial Progenitor/Stem Cells Produce Schwann Cells as Well as Oligodendrocytes during Repair of CNS Demyelination. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, B.; Agalliu, D.; Cahoy, J.D.; Watkins, T.A.; Dugas, J.C.; Mulinyawe, S.B.; Ibrahim, A.; Ligon, K.L.; Rowitch, D.H.; Barres, B.A. Myelin Gene Regulatory Factor Is a Critical Transcriptional Regulator Required for CNS Myelination. Cell 2009, 138, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dupree, J.; Wang, J.; Sandoval, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Nave, K.A.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. The Transcription Factor Yin Yang 1 Is Essential for Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Differentiation. Neuron 2007, 55, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küspert, M.; Wegner, M. SomethiNG 2 Talk about—Transcriptional Regulation in Embryonic and Adult Oligodendrocyte Precursors. Brain Res. 2016, 1638, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.R.; Sun, T.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, N.; Garcia, M.; Stiles, C.D.; Rowitch, D.H. Common Developmental Requirement for Olig Function Indicates a Motor Neuron/Oligodendrocyte Connection. Cell 2002, 109, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, H.; Martin, E.; Hassani, H.; Clavairoly, A.; Maire, C.L.; Viadieu, A.; Kerninon, C.; Delmasure, A.; Frah, M.; Weber, M.; et al. Ascl1/Mash1 Promotes Brain Oligodendrogenesis during Myelination and Remyelination. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 9752–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, E.M.; Purger, D.; Mount, C.W.; Goldstein, A.K.; Lin, G.L.; Wood, L.S.; Inema, I.; Miller, S.E.; Bieri, G.; Zuchero, J.B.; et al. Neuronal Activity Promotes Oligodendrogenesis and Adaptive Myelination in the Mammalian Brain. Science 2014, 344, 1252304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacmeister, C.M.; Barr, H.J.; McClain, C.R.; Thornton, M.A.; Nettles, D.; Welle, C.G.; Hughes, E.G. Motor Learning Promotes Remyelination via New and Surviving Oligodendrocytes. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, S.L.; Nagy, Z.; Skare, S.; Forsman, L.; Forssberg, H.; Ullén, F. Extensive Piano Practicing Has Regionally Specific Effects on White Matter Development. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, I.A.; Ohayon, D.; Li, H.; de Faria, J.P.; Emery, B.; Tohyama, K.; Richardson, W.D. Motor Skill Learning Requires Active Central Myelination. Science 2014, 346, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, I.D.; Radcliff, A. Remyelination Therapy for Demyelinating Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, I.; Peter, C.J.; Mitchell, A.; Straubhaar, J.; Rogaev, E.; Akbarian, S. Epigenetics in the Human Brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Qi, Z.; Sang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Deng, Y. The Role of MRNA M6A Methylation in the Nervous System. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, S.; Cedar, H. Role of DNA Methylation in the Regulation of Transcription. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1994, 4, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Uehara, Y.; Kurishita, A.; Tawa, R.; Sakurai, H. Biological Significance of DNA Methylation in the Ageing Process. Age Ageing 1993, 22, S34–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawa, R.; Ono, T.; Kurishita, A.; Okada, S.; Hirose, S. Changes of DNA Methylation Level during Pre- and Postnatal Periods in Mice. Differentiation 1990, 45, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schübeler, D. Function and Information Content of DNA Methylation. Nature 2015, 517, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: Roles in Mammalian Development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K.P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Liu, D.R.; Aravind, L.; et al. Conversion of 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mammalian DNA by MLL Partner TET1. Science 2009, 324, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Dai, J.; Ma, Y.; Mi, Y.; Cui, D.; Ju, G.; Macklin, W.B.; Jin, W. Dynamics of Ten-Eleven Translocation Hydroxylase Family Proteins and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Glia 2014, 62, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shao, N.; Szulwach, K.E.; Vialou, V.; Huynh, J.; Zhong, C.; Le, T.; Ferguson, D.; Cahill, M.E.; Li, Y.; et al. Role of Tet1 and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cocaine Action. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulwach, K.E.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Song, C.-X.; Wu, H.; Dai, Q.; Irier, H.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Gearing, M.; Levey, A.I.; et al. 5-HmC-Mediated Epigenetic Dynamics during Postnatal Neurodevelopment and Aging. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin Modifications and Their Function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kan, P.-Y.; Voigt, P.; Ma, L.; Shi, X.; Reinberg, D.; Lee, M.G. Trans-Tail Regulation of MLL4-Catalyzed H3K4 Methylation by H4R3 Symmetric Dimethylation Is Mediated by a Tandem PHD of MLL4. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, M.D.; Zhang, J.; He, M.; Ho, M.-C.; Zheng, Y.G. The Intricate Effects of Alpha-Amino and Lysine Modifications on Arginine Methylation on the N-Terminal Tail of Histone H4. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 3539–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Lee, M.G. Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferases and Demethylases in Self-Renewal Anddifferentiation of Stem Cells. Cell Biosci. 2013, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guccione, E.; Bassi, C.; Casadio, F.; Martinato, F.; Cesaroni, M.; Schuchlautz, H.; Lüscher, B.; Amati, B. Methylation of Histone H3R2 by PRMT6 and H3K4 by an MLL Complex Are Mutually Exclusive. Nature 2007, 449, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyllus, D.; Stein, C.; Schnabel, K.; Schiltz, E.; Imhof, A.; Dou, Y.; Hsieh, J.; Bauer, U.-M. PRMT6-Mediated Methylation of R2 in Histone H3 Antagonizes H3 K4 Trimethylation. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 3369–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margueron, R.; Reinberg, D. The Polycomb Complex PRC2 and Its Mark in Life. Nature 2011, 469, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, B.E.; Kamal, M.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Bekiranov, S.; Bailey, D.K.; Huebert, D.J.; McMahon, S.; Karlsson, E.K.; Kulbokas, E.J.; Gingeras, T.R.; et al. Genomic Maps and Comparative Analysis of Histone Modifications in Human and Mouse. Cell 2005, 120, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Torres, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Pollock, R.E. An Overview of Chromatin-Regulating Proteins in Cells. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2016, 17, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creyghton, M.P.; Cheng, A.W.; Welstead, G.G.; Kooistra, T.; Carey, B.W.; Steine, E.J.; Hanna, J.; Lodato, M.A.; Frampton, G.M.; Sharp, P.A.; et al. Histone H3K27ac Separates Active from Poised Enhancers and Predicts Developmental State. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21931–21936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenuwein, T.; Allis, C.D. Translating the Histone Code. Science 2001, 293, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, A.D.; Bedford, M.T. Histone Arginine Methylation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, T.S.; Ku, M.; Jaffe, D.B.; Issac, B.; Lieberman, E.; Giannoukos, G.; Alvarez, P.; Brockman, W.; Kim, T.-K.; Koche, R.P.; et al. Genome-Wide Maps of Chromatin State in Pluripotent and Lineage-Committed Cells. Nature 2007, 448, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada-Iglesias, A.; Bajpai, R.; Swigut, T.; Brugmann, S.A.; Flynn, R.A.; Wysocka, J. A Unique Chromatin Signature Uncovers Early Developmental Enhancers in Humans. Nature 2011, 470, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilatifard, A. Chromatin Modifications by Methylation and Ubiquitination: Implications in the Regulation of Gene Expression. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 243–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D. The Language of Covalent Histone Modifications. Nature 2000, 403, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Zhang, Y. The Diverse Functions of Histone Lysine Methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, A.M.; Meijer, M.; Scaglione, A.; Rinwa, P.; Agirre, E.; Liang, J.; Larsen, S.C.; Heskol, A.; Frawley, R.; Klingener, M.; et al. PAD2-Mediated Citrullination Contributes to Efficient Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1090–1102.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodage, T.; Basrai, M.A.; Baxevanis, A.D.; Hieter, P.; Collins, F.S. Characterization of the CHD Family of Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11472–11477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, M.; Weider, M.; Küspert, M.; Nave, K.-A.; Wegner, M. Brg1-Dependent Chromatin Remodelling Is Not Essentially Required during Oligodendroglial Differentiation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, D.C.; Crabtree, G.R. ATP-Dependent Chromatin Remodeling: Genetics, Genomics and Mechanisms. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 396–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Marie, C.; Zhao, C.; Kim, B.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Clavairoly, A.; Frah, M.; Wang, H.; He, X.; et al. Chd7 Cooperates with Sox10 and Regulates the Onset of CNS Myelination and Remyelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Crabtree, G.R. Chromatin Remodelling during Development. Nature 2010, 463, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, C.; Clavairoly, A.; Frah, M.; Hmidan, H.; Yan, J.; Zhao, C.; Van Steenwinckel, J.; Daveau, R.; Zalc, B.; Hassan, B.; et al. Oligodendrocyte Precursor Survival and Differentiation Requires Chromatin Remodeling by Chd7 and Chd8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 201802620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kim, B.; Wang, H.; Zhao, C.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.M.; Mao, M.; et al. Olig2 Targets Chromatin Remodelers to Enhancers to Initiate Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Cell 2013, 152, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapier, C.R.; Cairns, B.R. The Biology of Chromatin Remodeling Complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 273–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catez, F.; Yang, H.; Tracey, K.J.; Reeves, R.; Misteli, T.; Bustin, M. Network of Dynamic Interactions between Histone H1 and High-Mobility-Group Proteins in Chromatin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Fedele, M. Roles of HMGA Proteins in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechat, T.; Adam, S.A.; Goldman, R.D. Nuclear Lamins and Chromatin: When Structure Meets Function. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2009, 49, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naetar, N.; Ferraioli, S.; Foisner, R. Lamins in the Nuclear Interior—Life Outside the Lamina. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yattah, C.; Hernandez, M.; Huang, D.; Park, H.; Liao, W.; Casaccia, P. Dynamic Lamin B1-Gene Association During Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Differentiation. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. The Long Non-Coding RNAs: A New (P)Layer in the “Dark Matter”. Front. Genet. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Sunkin, S.M.; Mehler, M.F.; Mattick, J.S. Specific Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs in the Mouse Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.A.; Mehler, M.F. Emerging Roles of Non-Coding RNAs in Brain Evolution, Development, Plasticity and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaratiegui, M.; Irvine, D.V.; Martienssen, R.A. Noncoding RNAs and Gene Silencing. Cell 2007, 128, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.P.; Lau, N.C.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Grimson, A.; Schelter, J.M.; Castle, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Linsley, P.S.; Johnson, J.M. Microarray Analysis Shows That Some MicroRNAs Downregulate Large Numbers of Target MRNAs. Nature 2005, 433, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Guerrero, C.R.; Zhong, N.; Amato, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Cai, Q.; Ji, D.; Jin, S.-G.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; et al. Tet-Mediated Formation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in RNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11582–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dominissini, D.; Rechavi, G.; He, C. Gene Expression Regulation Mediated through Reversible M6A RNA Methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Adhikari, S.; Dahal, U.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hao, Y.-J.; Sun, B.-F.; Sun, H.-Y.; Li, A.; Ping, X.-L.; Lai, W.-Y.; et al. Nuclear m 6 A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates MRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; He, C. RNA N6-Methyladenosine Methylation in Post-Transcriptional Gene Expression Regulation. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B.-F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.; Hao, Y.-J.; Ping, X.-L.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wang, W.-J.; et al. FTO-Dependent Demethylation of N6-Methyladenosine Regulates MRNA Splicing and Is Required for Adipogenesis. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jia, G. Methylation Modifications in Eukaryotic Messenger RNA. J. Genet. Genom. 2014, 41, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liu, F.; Lu, Z.; Fei, Q.; Ai, Y.; He, P.C.; Shi, H.; Cui, X.; Su, R.; Klungland, A.; et al. Differential M6A, M6Am, and M1A Demethylation Mediated by FTO in the Cell Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 973–985.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, F.H. Mammalian Neural Stem Cells. Science 2000, 287, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murao, N.; Noguchi, H.; Nakashima, K. Epigenetic Regulation of Neural Stem Cell Property from Embryo to Adult. Neuroepigenetics 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Wada, Y.; Katada, S.; Kishi, Y. Epigenetic Regulation for Acquiring Glial Identity by Neural Stem Cells during Cortical Development. Glia 2020, 68, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanosaka, T.; Imamura, T.; Hamazaki, N.; Chai, M.; Igarashi, K.; Ideta-Otsuka, M.; Miura, F.; Ito, T.; Fujii, N.; Ikeo, K.; et al. DNA Methylome Analysis Identifies Transcription Factor-Based Epigenomic Signatures of Multilineage Competence in Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2992–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, T.; Nakashima, K.; Namihira, M.; Ochiai, W.; Uemura, A.; Yanagisawa, M.; Fujita, N.; Nakao, M.; Taga, T. DNA Methylation Is a Critical Cell-Intrinsic Determinant of Astrocyte Differentiation in the Fetal Brain. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Martinowich, K.; Chin, M.H.; He, F.; Fouse, S.D.; Hutnick, L.; Hattori, D.; Ge, W.; Shen, Y.; Wu, H.; et al. DNA Methylation Controls the Timing of Astrogliogenesis through Regulation of JAK-STAT Signaling. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2005, 132, 3345–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatada, I.; Namihira, M.; Morita, S.; Kimura, M.; Horii, T.; Nakashima, K. Astrocyte-Specific Genes Are Generally Demethylated in Neural Precursor Cells Prior to Astrocytic Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namihira, M.; Kohyama, J.; Semi, K.; Sanosaka, T.; Deneen, B.; Taga, T.; Nakashima, K. Committed Neuronal Precursors Confer Astrocytic Potential on Residual Neural Precursor Cells. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teter, B.; Rozovsky, I.; Krohn, K.; Anderson, C.; Osterburg, H.; Finch, C. Methylation of the glial fibrillary acidic protein gene shows novel biphasic changes during brain development. Glia 1996, 17, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheldon, L.M.; Abakir, A.; Ferjentsik, Z.; Dudnakova, T.; Strohbuecker, S.; Christie, D.; Dai, N.; Guan, S.; Foster, J.M.; Corrêa, I.R.; et al. Transient Accumulation of 5-Carboxylcytosine Indicates Involvement of Active Demethylation in Lineage Specification of Neural Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyon, S.; Huynh, J.; Yoo, S.; Dutta, D.; Zhang, F.; Ma, D.; Yoo, S.; Lawrence, R.; Wegner, M.; John, G.; et al. Functional Characterization of DNA Methylation in the Oligodendrocyte Lineage. Cell Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Lu, G.; Xu, L.; Ren, K.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xing, J.; Gao, X.; et al. TET1-Mediated Oligodendrocyte Homeostasis Regulates Myelination and Synaptic Functions. bioRxiv 2019, 821496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Wu, S.; Zhao, X. Immunoprecipitation and Mass Spectrometry Define TET1 Interactome during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, F.; Rößler, R.; Brouwer, N.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Boddeke, E.; Copray, S. Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Oligodendrocytes: Involvement of the Polycomb Group Protein Ezh2. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, F.; Boddeke, E.; Olah, M.; Copray, S. Dynamic Changes in Ezh2 Gene Occupancy Underlie Its Involvement in Neural Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation towards Oligodendrocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Dong, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Weng, Q.; Zhao, C.; Xin, M.; Lu, Q.R. EED-Mediated Histone Methylation Is Critical for CNS Myelination and Remyelination by Inhibiting WNT, BMP, and Senescence Pathways. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Magri, L.; Zhang, F.; Marsh, N.O.; Albrecht, S.; Huynh, J.L.; Kaur, J.; Kuhlmann, T.; Zhang, W.; Slesinger, P.A.; et al. Chromatin Landscape Defined by Repressive Histone Methylation during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Murata, K.; Ishida, J.; Kanou, A.; Kasuya, Y.; Fukamizu, A. Severe Hypomyelination and Developmental Defects Are Caused in Mice Lacking Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) in the Central Nervous System. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Weaver, I.C.G.; Gauthier-Fisher, A.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Yeomans, J.; Wondisford, F.; Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. CBP Histone Acetyltransferase Activity Regulates Embryonic Neural Differentiation in the Normal and Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome Brain. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Han, Y.R.; Li, J.; Sun, D.; Ouyang, M.; Plummer, M.R.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. The Glial or Neuronal Fate Choice of Oligodendrocyte Progenitors Is Modulated by Their Ability to Acquire an Epigenetic Memory. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 7339–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hernandez, M.; Shen, S.; Sabo, J.K.; Kelkar, D.; Wang, J.; O’Leary, R.; Phillips, G.R.; Cate, H.S.; Casaccia, P. Differential Modulation of the Oligodendrocyte Transcriptome by Sonic Hedgehog and Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 via Opposing Effects on Histone Acetylation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6651–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo-Branco, G.; Lilja, T.; Wallenborg, K.; Falcão, A.M.; Marques, S.C.; Gracias, A.; Solum, D.; Paap, R.; Walfridsson, J.; Teixeira, A.I.; et al. Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Is Dictated by Distinct Actions of Nuclear Receptor Corepressors and Histone Deacetylases. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 3, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; He, D.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, X.; Hassan, A.; et al. Hdac3 Interaction with P300 Histone Acetyltransferase Regulates the Oligodendrocyte and Astrocyte Lineage Fate Switch. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafalski, V.A.; Ho, P.P.; Brett, J.O.; Ucar, D.; Dugas, J.C.; Pollina, E.A.; Chow, L.M.L.; Ibrahim, A.; Baker, S.J.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Expansion of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells Following SIRT1 Inactivation in the Adult Brain. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Gotoh, Y. HMGA Regulates the Global Chromatin State and Neurogenic Potential in Neocortical Precursor Cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.B.; Bronstein, R.; Reddy, A.S.; Maletic-Savatic, M.; Aguirre, A.; Tsirka, S.E. Aberrant Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Increased Adult Neurogenesis in Mice Lacking Chromatin Protein HMGB2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, R.; Kyle, J.; Abraham, A.B.; Tsirka, S.E. Neurogenic to Gliogenic Fate Transition Perturbed by Loss of HMGB2. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhiainen, A.; Zhao, X.; Vanttola, P.; Qian, K.; Kulesskiy, E.; Kuja-Panula, J.; Gransalke, K.; Grönholm, M.; Unni, E.; Meistrich, M.; et al. HMGB4 Is Expressed by Neuronal Cells and Affects the Expression of Genes Involved in Neural Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M.; Lanjakornsiripan, D.; Itoh, Y.; Kishi, Y.; Ogata, T.; Gotoh, Y. High Mobility Group Nucleosome-Binding Family Proteins Promote Astrocyte Differentiation of Neural Precursor Cells. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2983–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; Banine, F.; Struve, J.; Xing, R.; Adams, C.; Liu, Y.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Rao, M.S.; Sherman, L.S. Brg1 Is Required for Murine Neural Stem Cell Maintenance and Gliogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2006, 289, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Richardson, G.A.; Kroll, K.L. The SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Protein Brg1 Is Required for Vertebrate Neurogenesis and Mediates Transactivation of Ngn and NeuroD. Development 2005, 132, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, R.G.; Willer, G.B.; Fadool, J.M.; Dowling, J.E.; Link, B.A. Positional Cloning of the Young Mutation Identifies an Essential Role for the Brahma Chromatin Remodeling Complex in Mediating Retinal Cell Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6535–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Yang, R.; Xiao, Z.; Gao, X.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Luo, Y. A Novel Long Noncoding RNA Lnc158 Promotes the Differentiation of Mouse Neural Precursor Cells into Oligodendrocytes by Targeting Nuclear Factor-IB. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chen, K.; Cuevas-Diaz Duran, R.; You, Y.; Sloan, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, S.; Cao, Q.; Barres, B.A.; Wu, J.Q. Comprehensive Identification of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Purified Cell Types from the Brain Reveals Functional LncRNA in OPC Fate Determination. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsel, P.; Roussos, P.; Fam, P.; Khan, S.; Tan, W.; Hirose, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Haroutunian, V. The Expression of Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Is Reduced in Schizophrenia and Modulates Oligodendrocytes Transcription. NPJ Schizophr. 2019, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Qureshi, I.A.; Gokhan, S.; Dinger, M.E.; Li, G.; Mattick, J.S.; Mehler, M.F. Long Noncoding RNAs in Neuronal-Glial Fate Specification and Oligodendrocyte Lineage Maturation. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, W.H.; Yap, K.; Lee, S.H.; Looi, L.S.; Khandelia, P.; Neo, S.X.; Makeyev, E.V.; Su, I. MicroRNA MiR-124 Controls the Choice between Neuronal and Astrocyte Differentiation by Fine-Tuning Ezh2 Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20788–20801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyama, J.; Bunt, J.; Richards, L.J.; Iwanari, H.; Mochizuki, Y.; Hamakubo, T.; Shimazaki, T.; Okano, H. MicroRNA-153 Regulates the Acquisition of Gliogenic Competence by Neural Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naka-Kaneda, H.; Nakamura, S.; Igarashi, M.; Aoi, H.; Kanki, H.; Tsuyama, J.; Tsutsumi, S.; Aburatani, H.; Shimazaki, T.; Okano, H. The MiR-17/106–P38 Axis Is a Key Regulator of the Neurogenic-to-Gliogenic Transition in Developing Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.L.; Hsieh, J.; Barbosa, A.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 Control the Progression of Neural Precursors to Neurons during Brain Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7876–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Chen, Y.; Hoang, T.; Montgomery, R.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Bu, H.; Hu, T.; Taketo, M.M.; van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H.; et al. HDAC1 and HDAC2 Regulate Oligodendrocyte Differentiation by Disrupting the Beta-Catenin-TCF Interaction. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, E.G.; Kang, S.H.; Fukaya, M.; Bergles, D.E. Oligodendrocyte Progenitors Balance Growth with Self-Repulsion to Achieve Homeostasis in the Adult Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barres, B.A.; Burne, J.F.; Holtmann, B.; Thoenen, H.; Sendtner, M.; Raff, M.C. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Enhances the Rate of Oligodendrocyte Generation. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996, 8, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoll, P.D.; Musacchio, J.M.; Hardy, R.; Reynolds, R.; Marchionni, M.A.; Salzer, J.L. GGF/Neuregulin Is a Neuronal Signal That Promotes the Proliferation and Survival and Inhibits the Differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Progenitors. Neuron 1996, 17, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemel, L.T.; Jackson, S.J.; Cuzner, M.L. Role for TGF-Beta1, FGF-2 and PDGF-AA in a Myelination of CNS Aggregate Cultures Enriched with Macrophages. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 74, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, M.; Murray, K.; Stroobant, P.; Waterfield, M.D.; Riddle, P. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Promotes Division and Motility and Inhibits Premature Differentiation of the Oligodendrocyte/Type-2 Astrocyte Progenitor Cell. Nature 1988, 333, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohya, W.; Funakoshi, H.; Kurosawa, T.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) Promotes Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Its Differentiation during Postnatal Development in the Rat. Brain Res. 2007, 1147, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A.; Raff, M.C. Proliferation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells Depends on Electrical Activity in Axons. Nature 1993, 361, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerens, C.; Stankoff, B.; Logak, M.; Anglade, P.; Allinquant, B.; Couraud, F.; Zalc, B.; Lubetzki, C. Induction of Myelination in the Central Nervous System by Electrical Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9887–9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.; Zhou, J.M.; McBain, C.J.; Wright, P.; Knutson, P.L.; Armstrong, R.C. Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Lineage Progression Are Regulated by Glutamate Receptor-Mediated K+ Channel Block. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Brus-Ramer, M.; Martin, J.H.; McDonald, J.W. Electrical Stimulation of the Medullary Pyramid Promotes Proliferation and Differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells in the Corticospinal Tract of the Adult Rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 479, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, N.; Shindo, A.; Hikawa, R.; Kinoshita, H.; Liang, A.C.; Itoh, K.; Lok, J.; Maki, T.; Takahashi, R.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Differential Roles of Epigenetic Regulators in the Survival and Differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Glia 2019, 67, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyon, S.; Frawley, R.; Marshall-Phelps, K.L.; Kegel, L.; Bostrand, S.M.; Sadowski, B.; Huang, D.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Lyons, D.; Mobius, W.; et al. TET1-Mediated DNA Hydroxy-Methylation Regulates Adult Remyelination. bioRxiv 2019, 819995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, A.; Patzig, J.; Liang, J.; Frawley, R.; Bok, J.; Mela, A.; Yattah, C.; Zhang, J.; Teo, S.X.; Zhou, T.; et al. PRMT5-Mediated Regulation of Developmental Myelination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, L.; Gacias, M.; Wu, M.; Swiss, V.A.; Janssen, W.G.; Casaccia, P. C-Myc-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation of Cell Cycle and Nucleosomal Histones during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Neuroscience 2014, 276, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.D.; O’Bara, M.A.; Vedia, B.H.; Pol, S.U.; Sim, F.J. Histone Deacetylase Activity Is Required for Human Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Differentiation. Glia 2012, 60, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T.; Ogata, T.; Yamauchi, J.; Sawada, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Nagao, M. Chd7 Collaborates with Sox2 to Regulate Activation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 10290–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Dong, C.; Frah, M.; Deng, Y.; Marie, C.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Ma, Z.; Dong, X.; Lin, Y.; et al. Dual Requirement of CHD8 for Chromatin Landscape Establishment and Histone Methyltransferase Recruitment to Promote CNS Myelination and Repair. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 753–768.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsesser, O.; Fröb, F.; Küspert, M.; Tamm, E.R.; Fujii, T.; Fukunaga, R.; Wegner, M. Chromatin Remodeler Ep400 Ensures Oligodendrocyte Survival and Is Required for Myelination in the Vertebrate Central Nervous System. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 6208–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; He, X.; Han, X.; Yu, Y.; Ye, F.; Chen, Y.; Hoang, T.; Xu, X.; Mi, Q.S.; Xin, M.; et al. MicroRNA-Mediated Control of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Neuron 2010, 65, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, A.; Sun, B.; Sun, J.-G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A Novel m6A Reader Prrc2a Controls Oligodendroglial Specification and Myelination. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyon, S.; Ma, D.; Huynh, J.L.; Coutts, D.J.C.; Zhao, C.; Casaccia, P.; Franklin, R.J.M. Efficient Remyelination Requires DNA Methylation. eNeuro 2017, 4, ENEURO.0336-16.2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Husstege, M.; Muggironi, M.; Liu, A.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Histone Deacetylase Activity Is Necessary for Oligodendrocyte Lineage Progression. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10333–10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V. C-Myc Target Genes Involved in Cell Growth, Apoptosis, and Metabolism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guccione, E.; Martinato, F.; Finocchiaro, G.; Luzi, L.; Tizzoni, L.; Dall’ Olio, V.; Zardo, G.; Nervi, C.; Bernard, L.; Amati, B. Myc-Binding-Site Recognition in the Human Genome Is Determined by Chromatin Context. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinato, F.; Cesaroni, M.; Amati, B.; Guccione, E. Analysis of Myc-Induced Histone Modifications on Target Chromatin. PLoS ONE 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.B.; Wood, M.A.; Cole, M.D. The Essential Cofactor TRRAP Recruits the Histone Acetyltransferase HGCN5 to C-Myc. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.A.; Li, A.M.; Grutzendler, J. Lifelong Cortical Myelin Plasticity and Age-Related Degeneration in the Live Mammalian Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, E.G.; Orthmann-Murphy, J.L.; Langseth, A.J.; Bergles, D.E. Myelin Remodeling through Experience-Dependent Oligodendrogenesis in the Adult Somatosensory Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, M.; Itami, C.; Tsumoto, T.; Kimura, F. Change of Conduction Velocity by Regional Myelination Yields Constant Latency Irrespective of Distance between Thalamus and Cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6174–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, A.H.; Rubel, E.W. Systematic and Differential Myelination of Axon Collaterals in the Mammalian Auditory Brainstem. Glia 2016, 64, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassy, G.S.; Berger, D.R.; Chen, H.-H.; Kasthuri, N.; Hayworth, K.J.; Vercelli, A.; Seung, H.S.; Lichtman, J.W.; Arlotta, P. Distinct Profiles of Myelin Distribution Along Single Axons of Pyramidal Neurons in the Neocortex. Science 2014, 344, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonouzi, M.; Berger, D.; Jokhi, V.; Kedaigle, A.; Lichtman, J.; Arlotta, P. Individual Oligodendrocytes Show Bias for Inhibitory Axons in the Neocortex. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2799–2808.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabretta, S.; Vogel, G.; Yu, Z.; Choquet, K.; Darbelli, L.; Nicholson, T.B.; Kleinman, C.L.; Richard, S. Loss of PRMT5 Promotes PDGFRα Degradation during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination. Dev. Cell 2018, 46, 426–440.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Vogel, G.; Yu, Z.; Almazan, G.; Richard, S. Type II Arginine Methyltransferase PRMT5 Regulates Gene Expression of Inhibitors of Differentiation/DNA Binding Id2 and Id4 during Glial Cell Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44424–44432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Li, J.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Histone Modifications Affect Timing of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Differentiation in the Developing Rat Brain. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Sandoval, J.; Swiss, V.; Li, J.; Dupree, J.; Franklin, R.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Age-Dependent Epigenetic Control of Differentiation Inhibitors Is Critical for Remyelination Efficiency. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, M.; Leyk, J.; Richter-Landsberg, C. HDAC6 Inhibition Results in Tau Acetylation and Modulates Tau Phosphorylation and Degradation in Oligodendrocytes. Glia 2014, 62, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; D’ercole, A.J.; Ye, P. Histone Deacetylase 11 Regulates Oligodendrocyte-Specific Gene Expression and Cell Development in OL-1 Oligodendroglia Cells. Glia 2009, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Cao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Guo, J.; Ling, E.-A.; Liang, F. Sirtuin 2, a Mammalian Homolog of Yeast Silent Information Regulator-2 Longevity Regulator, Is an Oligodendroglial Protein That Decelerates Cell Differentiation through Deacetylating α-Tubulin. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2606–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.-C.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Q.R. LncRNA Functional Networks in Oligodendrocytes Reveal Stage-Specific Myelination Control by an LncOL1/Suz12 Complex in the CNS. Neuron 2017, 93, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugas, J.C.; Cuellar, T.L.; Scholze, A.; Ason, B.; Ibrahim, A.; Emery, B.; Zamanian, J.L.; Foo, L.C.; McManus, M.T.; Barres, B.A. Dicer1 and MiR-219 Are Required for Normal Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination. Neuron 2010, 65, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Heng, M.Y.; Ptáček, L.J.; Fu, Y.-H. MicroRNA-23a Promotes Myelination in the Central Nervous System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17468–17473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Howng, S.Y.B.; Ptáček, L.J.; Fu, Y.-H. MiR-32 and Its Target SLC45A3 Regulate the Lipid Metabolism of Oligodendrocytes and Myelin. Neuroscience 2012, 213, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Volsko, C.; Garcia, J.P.; Agirre, E.; Allan, K.C.; Tesar, P.J.; Trapp, B.D.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Sim, F.J.; Dutta, R. Oligodendrocyte Intrinsic MiR-27a Controls Myelination and Remyelination. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 904–919.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Deneen, B.; Tzeng, S.-F. MicroRNA-212 Inhibits Oligodendrocytes during Maturation by down-Regulation of Differentiation-Associated Gene Expression. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecca, D.; Marangon, D.; Coppolino, G.T.; Méndez, A.M.; Finardi, A.; Costa, G.D.; Martinelli, V.; Furlan, R.; Abbracchio, M.P. MiR-125a-3p Timely Inhibits Oligodendroglial Maturation and Is Pathologically up-Regulated in Human Multiple Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Dzhashiashvili, Y.; Shah, A.; Kunjamma, R.B.; Weng, Y.; Elbaz, B.; Fei, Q.; Jones, J.S.; Li, Y.I.; Zhuang, X.; et al. M6A MRNA Methylation Is Essential for Oligodendrocyte Maturation and CNS Myelination. Neuron 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubinska, B.; Laszkiewicz, I.; Royland, J.; Wiggins, R.C.; Konat, G.W. Differentiation-Specific Demethylation of Myelin Associated Glycoprotein Gene in Cultured Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1994, 39, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Bercury, K.K.; Jin, W.; Macklin, W.B. Olig1 Acetylation and Nuclear Export Mediate Oligodendrocyte Development. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 15875–15893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-T.; Fu, Y.-H. MiR-23 Regulation of Lamin B1 Is Crucial for Oligodendrocyte Development and Myelination. Dis. Model. Mech. 2009, 2, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, Y.; Fudge, A.D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Characterization of a Long Noncoding RNA Pcdh17it as a Novel Marker for Immature Premyelinating Oligodendrocytes. Glia 2019, 67, 2166–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Shin, J.-Y.; McManus, M.T.; Ptáček, L.J.; Fu, Y.-H. Dicer Ablation in Oligodendrocytes Provokes Neuronal Impairment in Mice. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Moyano, A.L.; Ma, Z.; Deng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, M.; He, X.; Ma, Z.; et al. MiR-219 Cooperates with MiR-338 in Myelination and Promotes Myelin Repair in the CNS. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 566–582.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.; Healy, E.; Bracken, A.P. PRC2 Mediated H3K27 Methylations in Cellular Identity and Cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 37, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, K.; Chu, P.; Abramowitz, J.; Steger, R.; Ramos, R.L.; Brumberg, J.C. Organization of Myelin in the Mouse Somatosensory Barrel Cortex and the Effects of Sensory Deprivation. Dev. Neurobiol. 2013, 73, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
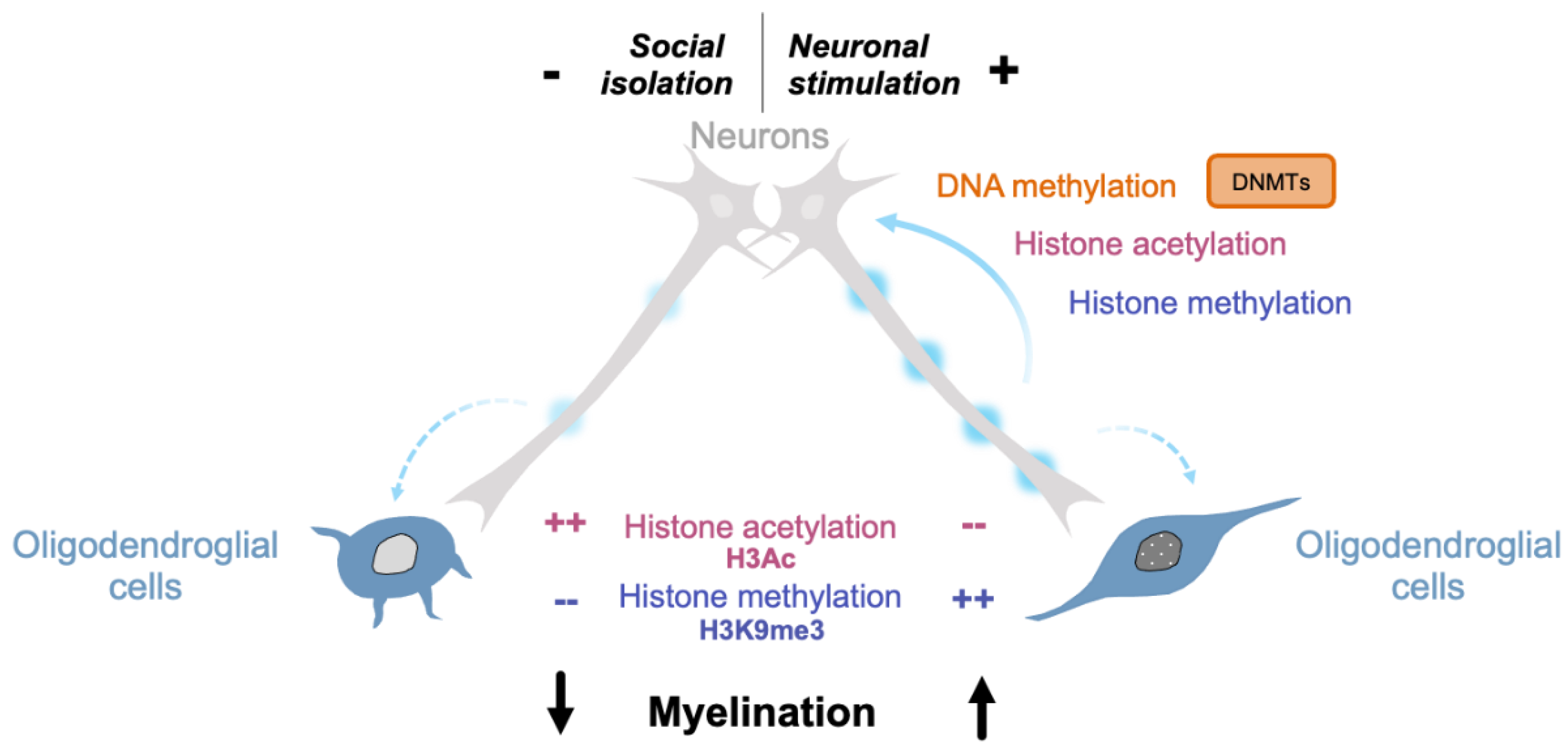
- Liu, J.; Dietz, K.; DeLoyht, J.M.; Pedre, X.; Kelkar, D.; Kaur, J.; Vialou, V.; Lobo, M.K.; Dietz, D.M.; Nestler, E.J.; et al. Impaired Adult Myelination in the Prefrontal Cortex of Socially Isolated Mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinodan, M.; Rosen, K.M.; Ito, S.; Corfas, G. A Critical Period for Social Experience–Dependent Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Myelination. Science 2012, 337, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, J.-M.; Li, P.; Scafidi, J.; Gallo, V. Experience-Dependent Regulation of NG2 Progenitors in the Developing Barrel Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1192–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.M.; Michel, K.; Jokhi, V.; Nedivi, E.; Arlotta, P. Neuron Class–Specific Responses Govern Adaptive Myelin Remodeling in the Neocortex. Science 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, M.; Wood, R.J.; Fletcher, J.L.; Gonsalvez, D.G.; Hannan, A.J.; Murray, S.S.; Xiao, J. Remodeling of Pre-Existing Myelinated Axons and Oligodendrocyte Differentiation Is Stimulated by Environmental Enrichment in the Young Adult Brain. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Leach, M.K.; Redmond, S.A.; Chong, S.Y.; Mellon, S.H.; Tuck, S.J.; Feng, Z.Q.; Corey, J.M.; Chan, J.R. A Culture System to Study Oligodendrocyte Myelination Processes Using Engineered Nanofibers. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Fancy, S.P.J.; Shen, Y.-A.A.; Niu, J.; Zhao, C.; Presley, B.; Miao, E.; Lee, S.; Mayoral, S.R.; Redmond, S.A.; et al. Micropillar Arrays as a High-Throughput Screening Platform for Therapeutics in Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, S.S.; Kelland, E.E.; Tokar, E.; De La Torre, A.R.; Chan, J.R. The Geometric and Spatial Constraints of the Microenvironment Induce Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14662–14667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.; Patzig, J.; Mayoral, S.R.; Costa, K.D.; Chan, J.R.; Casaccia, P. Mechanostimulation Promotes Nuclear and Epigenetic Changes in Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segel, M.; Neumann, B.; Hill, M.F.E.; Weber, I.P.; Viscomi, C.; Zhao, C.; Young, A.; Agley, C.C.; Thompson, A.J.; Gonzalez, G.A.; et al. Niche Stiffness Underlies the Ageing of Central Nervous System Progenitor Cells. Nature 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartline, D.K.; Colman, D.R. Rapid Conduction and the Evolution of Giant Axons and Myelinated Fibers. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, R29–R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fünfschilling, U.; Supplie, L.M.; Mahad, D.; Boretius, S.; Saab, A.S.; Edgar, J.; Brinkmann, B.G.; Kassmann, C.M.; Tzvetanova, I.D.; Möbius, W.; et al. Glycolytic Oligodendrocytes Maintain Myelin and Long-Term Axonal Integrity. Nature 2012, 485, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Morrison, B.M.; Li, Y.; Lengacher, S.; Farah, M.H.; Hoffman, P.N.; Liu, Y.; Tsingalia, A.; Jin, L.; Zhang, P.W.; et al. Oligodendroglia Metabolically Support Axons and Contribute to Neurodegeneration. Nature 2012, 487, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria, A.; Hokanson, K.C.; Dao, D.Q.; Mayoral, S.R.; Mei, F.; Redmond, S.A.; Ullian, E.M.; Chan, J.R. Dynamic Modulation of Myelination in Response to Visual Stimuli Alters Optic Nerve Conduction Velocity. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6937–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitew, S.; Gobius, I.; Fenlon, L.R.; McDougall, S.J.; Hawkes, D.; Xing, Y.L.; Bujalka, H.; Gundlach, A.L.; Richards, L.J.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; et al. Pharmacogenetic Stimulation of Neuronal Activity Increases Myelination in an Axon-Specific Manner. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-De-La-Rocha, I.; Fryatt, G.L.; Rivera, A.D.; Restani, L.; Caleo, M.; Raineteau, O.; Gomez-Nicola, D.; Butt, A.M. Synaptic Silencing Affects the Density and Complexity of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells in the Adult Mouse Hippocampus. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensch, S.; Baraban, M.; Almeida, R.; Czopka, T.; Ausborn, J.; El Manira, A.; Lyons, D.A. Synaptic Vesicle Release Regulates the Number of Myelin Sheaths Made by Individual Oligodendrocytes in Vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, F.C.; Habermacher, C.; Graciarena, M.; Houry, P.-Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Nait Oumesmar, B.; Angulo, M.C. Neuronal Activity in Vivo Enhances Functional Myelin Repair. JCI Insight 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steadman, P.E.; Xia, F.; Ahmed, M.; Mocle, A.J.; Penning, A.R.A.; Geraghty, A.C.; Steenland, H.W.; Monje, M.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Disruption of Oligodendrogenesis Impairs Memory Consolidation in Adult Mice. Neuron 2020, 105, 150–164.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.; Porta, S.; Haak, L.L.; Gallo, V.; Fields, R.D. Adenosine: A Neuron-Glial Transmitter Promoting Myelination in the CNS in Response to Action Potentials. Neuron 2002, 36, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, H.; Lee, P.R.; Fields, R.D. Control of Local Protein Synthesis and Initial Events in Myelination by Action Potentials. Science 2011, 333, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, H.; Ortiz, F.C.; Woo, D.H.; Lee, P.R.; Angulo, M.C.; Fields, R.D. Nonsynaptic Junctions on Myelinating Glia Promote Preferential Myelination of Electrically Active Axons. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-J.; Kula, B.; Nagy, B.; Barzan, R.; Gall, A.; Ehrlich, I.; Kukley, M. In Vivo Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Proliferation and Differentiation by the AMPA-Receptor Subunit GluA2. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 852–861.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swire, M.; Kotelevtsev, Y.; Webb, D.J.; Lyons, D.A.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Endothelin Signalling Mediates Experience-Dependent Myelination in the CNS. eLife 2019, 8, e49493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Y.; Shi, X.-Y.; Qiu, X.; Lu, W.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, G.-H.; Tang, Y. Enriched Environment Increases the Myelinated Nerve Fibers of Aged Rat Corpus Callosum. Anat. Rec. 2012, 295, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio-Baptista, C.; Khrapitchev, A.A.; Foxley, S.; Schlagheck, T.; Scholz, J.; Jbabdi, S.; DeLuca, G.C.; Miller, K.L.; Taylor, A.; Thomas, N.; et al. Motor Skill Learning Induces Changes in White Matter Microstructure and Myelination. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 19499–19503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ohayon, D.; McKenzie, I.A.; Sinclair-Wilson, A.; Wright, J.L.; Fudge, A.D.; Emery, B.; Li, H.; Richardson, W.D. Rapid Production of New Oligodendrocytes Is Required in the Earliest Stages of Motor-Skill Learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stedehouder, J.; Brizee, D.; Shpak, G.; Kushner, S.A. Activity-Dependent Myelination of Parvalbumin Interneurons Mediated by Axonal Morphological Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 3631–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, J.H.; Ravanelli, A.M.; Schwindt, R.; Scott, E.K.; Appel, B. Neuronal Activity Biases Axon Selection for Myelination in Vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechler, M.E.; Byrne, L.; Ffrench-Constant, C. CNS Myelin Sheath Lengths Are an Intrinsic Property of Oligodendrocytes. Curr. Biol. CB 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chong, S.Y.; Tuck, S.J.; Corey, J.M.; Chan, J.R. A Rapid and Reproducible Assay for Modeling Myelination by Oligodendrocytes Using Engineered Nanofibers. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscopo, D.M.; Weible, A.P.; Rothbart, M.K.; Posner, M.I.; Niell, C.M. Changes in White Matter in Mice Resulting from Low-Frequency Brain Stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6339–E6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xu, Y.; Huang, R.; Huang, Y.; Ge, S.; Hu, B. N-Cadherin Is Involved in Neuronal Activity-Dependent Regulation of Myelinating Capacity of Zebrafish Individual Oligodendrocytes In Vivo. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnädelbach, O.; Blaschuk, O.W.; Symonds, M.; Gour, B.J.; Doherty, P.; Fawcett, J.W. N-Cadherin Influences Migration of Oligodendrocytes on Astrocyte Monolayers. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2000, 15, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, H.S.; Johung, T.B.; Caretti, V.; Noll, A.; Tang, Y.; Nagaraja, S.; Gibson, E.M.; Mount, C.W.; Polepalli, J.; Mitra, S.S.; et al. Neuronal Activity Promotes Glioma Growth through Neuroligin-3 Secretion. Cell 2015, 161, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnow, A.M.; Ford, M.C.; Valdivia, L.E.; Wilson, S.W.; Attwell, D. Regulation of Developing Myelin Sheath Elongation by Oligodendrocyte Calcium Transients in Vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M.; Fern, R.F.; Matute, C. Neurotransmitter Signaling in White Matter. Glia 2014, 62, 1762–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, R.D. Imaging Single Photons and Intrinsic Optical Signals for Studies of Vesicular and Non-Vesicular ATP Release from Axons. Front. Neuroanat. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, R.D. Nonsynaptic and Nonvesicular ATP Release from Neurons and Relevance to Neuron–Glia Signaling. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, R.D.; Ni, Y. Nonsynaptic Communication through ATP Release from Volume-Activated Anion Channels in Axons. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrvatin, S.; Hochbaum, D.R.; Nagy, M.A.; Cicconet, M.; Robertson, K.; Cheadle, L.; Zilionis, R.; Ratner, A.; Borges-Monroy, R.; Klein, A.M.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Experience-Dependent Transcriptomic States in Mouse Visual Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Fabyanic, E.; Kwon, D.; Tang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, H. Dissecting Cell-Type Composition and Activity-Dependent Transcriptional State in Mammalian Brains by Massively Parallel Single-Nucleus RNA-Seq. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 1006–1015.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppieters, N.; Dieriks, B.V.; Lill, C.; Faull, R.L.M.; Curtis, M.A.; Dragunow, M. Global Changes in DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Alzheimer’s Disease Human Brain. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdhar, K.; Hoffman, G.E.; Jiang, Y.; Brown, L.; Kundakovic, M.; Hauberg, M.E.; Francoeur, N.J.; Wang, Y.; Shah, H.; Kavanagh, D.H.; et al. Cell-Specific Histone Modification Maps in the Human Frontal Lobe Link Schizophrenia Risk to the Neuronal Epigenome. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.L.; Garg, P.; Thin, T.H.; Yoo, S.; Dutta, R.; Trapp, B.D.; Haroutunian, V.; Zhu, J.; Donovan, M.J.; Sharp, A.J.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Differences in Pathology-Free Regions of Multiple Sclerosis-Affected Brains. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.E.; Gao, Y.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Tao, R.; Hyde, T.M.; Weinberger, D.R.; Kleinman, J.E. Mapping DNA Methylation across Development, Genotype and Schizophrenia in the Human Frontal Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2015; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semick, S.A.; Bharadwaj, R.A.; Collado-Torres, L.; Tao, R.; Shin, J.H.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Weiss, J.R.; Weinberger, D.R.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E.; et al. Integrated DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Profiling across Multiple Brain Regions Implicate Novel Genes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenkiel, B.R.; Peca, J.; Davison, I.G.; Feliciano, C.; Deisseroth, K.; Augustine, G.J.; Ehlers, M.D.; Feng, G. In Vivo Light-Induced Activation of Neural Circuitry in Transgenic Mice Expressing Channelrhodopsin-2. Neuron 2007, 54, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargin, D.; Oliver, D.K.; Lambe, E.K. Chronic Social Isolation Reduces 5-HT Neuronal Activity via Upregulated SK3 Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels. eLife 2016, 5, e21416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefil, V.; Dietz, K.; Amatruda, M.; Wentling, M.; Aubry, A.V.; Dupree, J.L.; Temple, G.; Park, H.-J.; Burghardt, N.S.; Casaccia, P.; et al. Region-Specific Myelin Differences Define Behavioral Consequences of Chronic Social Defeat Stress in Mice. eLife 2019, 8, e40855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäkel, S.; Agirre, E.; Falcão, A.M.; van Bruggen, D.; Lee, K.W.; Knuesel, I.; Malhotra, D.; Ffrench-Constant, C.; Williams, A.; Castelo-Branco, G. Altered Human Oligodendrocyte Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis. Nature 2019, 566, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marisca, R.; Hoche, T.; Agirre, E.; Hoodless, L.J.; Barkey, W.; Auer, F.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Czopka, T. Functionally Distinct Subgroups of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells Integrate Neural Activity and Execute Myelin Formation. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.; Zeisel, A.; Codeluppi, S.; van Bruggen, D.; Falcão, A.M.; Xiao, L.; Li, H.; Häring, M.; Hochgerner, H.; Romanov, R.A.; et al. Oligodendrocyte Heterogeneity in the Mouse Juvenile and Adult Central Nervous System. Science 2016, 352, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maag, J.L.V.; Kaczorowski, D.C.; Panja, D.; Peters, T.J.; Bramham, C.R.; Wibrand, K.; Dinger, M.E. Widespread Promoter Methylation of Synaptic Plasticity Genes in Long-Term Potentiation in the Adult Brain in Vivo. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Wang, Y.; Ju, L.-H.; Chen, M. Epigenetic Regulation of Reelin and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Genes in Long-Term Potentiation in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2012, 97, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.; Vanhoutte, P.; Arnold, F.J.L.; Huang, C.L.-H.; Bading, H. Neuronal Activity-Dependent Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling of HDAC4 and HDAC5. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-B.; Yi, S.-H.; Rhee, Y.-H.; Kim, H.; Han, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, H.; Park, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Richardson, E.; et al. Prolonged Membrane Depolarization Enhances Midbrain Dopamine Neuron Differentiation via Epigenetic Histone Modifications. Stem Cells 2011, 29, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinowich, K.; Hattori, D.; Wu, H.; Fouse, S.; He, F.; Hu, Y.; Fan, G.; Sun, Y.E. DNA Methylation-Related Chromatin Remodeling in Activity-Dependent Bdnf Gene Regulation. Science 2003, 302, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.P.; Tun, N.; Grayson, D.R. Depolarization Induces Downregulation of DNMT1 and DNMT3 in Primary Cortical Cultures. Epigenetics 2008, 3, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, T.C.; Vigeland, M.D.; Hjorthaug, H.S.; Etholm, L.; Nome, C.G.; Taubøll, E.; Heuser, K.; Selmer, K.K. Neuronal and Glial DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Changes in Early Epileptogenesis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Ma, D.K.; Mo, H.; Ball, M.P.; Jang, M.-H.; Bonaguidi, M.A.; Balazer, J.A.; Eaves, H.L.; Xie, B.; Ford, E.; et al. Neuronal Activity Modifies DNA Methylation Landscape in the Adult Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, K.; Wang, J.; Lu, Q.R. Epigenetic Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Myelination in Developmental Disorders and Neurodegenerative Diseases. F1000Research 2020, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samudyata; Castelo-Branco, G.; Liu, J. Epigenetic Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation: From Development to Demyelinating Disorders. Glia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiane, A.; Schepers, M.; Rombaut, B.; Hupperts, R.; Prickaerts, J.; Hellings, N.; van den Hove, D.; Vanmierlo, T. From OPC to Oligodendrocyte: An Epigenetic Journey. Cells 2019, 8, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DNA Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA methylation | DNMT1/DNMT3A | Positive role in OPC survival and proliferation | In vitro OPCs + siRNA | Egawa et al. [132] | ||
| No effect on OPC survival | Olig1cre;Dnmt1flox and Olig1cre;Dnmt3flox mice | Moyon et al. [91] | ||||
| DNMT1 | Positive role in OPC proliferation | Increased DNA methylation and downregulation of cell cycle and cell proliferation genes (Cdc6, Meis2) | Olig1cre;Dnmt1flox mice | RNA-Seq and ERRBS on sorted neonatal OPCs and OLs, RNA-Seq on sorted Olig1cre;Tet1flox OPCs | Moyon et al. [91] | |
| DNA demethylation | 5cac mark | 5cac enriched in glial cells during NSCs differentiation (Gfap, Olig1/2) | Descriptive study in vivo | Wheldon et al. [90] | ||
| DNA hydroxymethylation | TET1 | Slight positive role during developmental OPC proliferation | Olig1cre;Tet1flox mice | Zhang et al. [92] | ||
| No role in adult OPC proliferation | Olig1cre;Tet1flox and PdgfracreRT;Tet1flox mice | Moyon et al. [133] | ||||
| Histone Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Histone methylation | PRC2 (EED) (H3K27me3) | Positive role in OPC proliferation (in brain, not spinal cord) | Olig1cre;Eedflox and PdgfracreRT;Eedflox mice | Wang et al. [96] | ||
| PRMT5 | Positive role in OPC survival | Inhibition of p53 pathway | Olig1cre;Prmt5flox mice and in vitro OPCs + siRNA | RNA-Seq on in vitro PRMT5-CRISPRKO OPCs | Scaglione et al. [134] | |
| Histone (de)acetylation | H3K9ac/H3K14ac marks | Activation of cell cycle genes | In vitro OPCs + cMyc silencing | Magri et al. [135] | ||
| HDACs | Positive role in OPC proliferation | In vitro O4+ cells + HDAC inhibitors | Conway et al. [136] | |||
| Chromatin Organization | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Chromatin remodelers | CHD7 | Positive role in OPC survival | Regulation of cell cycle genes (Ccnd1, Cdk4 and Cdk6) and of cell survival/apoptosis genes (e.g., p53/Trp53, Bax, Apaf1) | PdgfracreRT;Chd7flox mice | RNA-Seq on in vitro PdgfracreRT;Chd7flox OPCs | Marie et al. [61] |
| Positive role in OPC proliferation | PdgfracreRT;Chd7flox mice | Doi et al. [137] | ||||
| No role in OPC survival or proliferation | Olig1cre;Chd7flox mice | He et al. [59] | ||||
| CHD8 | Positive role in adult OPC survival and proliferation in spinal cord | Olig1cre;Chd8flox and PdgfracreRT;Chd8flox mice | Zhao et al. [138] | |||
| EP400 | Positive role in OPC survival | Cnpcre;Ep400flox mice | Elsesser et al. [139] | |||
| Post-Transcriptional Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| MicroRNA | DICER | Positive role in OPC proliferation | Olig1cre;Dicerflox mice | Zhao et al. [140] | ||
| m6A RNA methylation | PPRC2A | Positive role in OPC proliferation | Olig2cre;Pprc2aflox and Nescre;Pprc2aflox mice | Wu et al. [141] |
| DNA Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA methylation | DNMT1 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | In vitro OPCs + siRNA | Egawa et al. [132] | ||
| Negative role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Decreased DNA methylation and upregulation of lipid synthesis and myelin formation genes (Mog, Mag, Gpr37) | Olig1cre;Dnmt1flox mice (no phenotype in Cnpcre;Dnmt1flox mice) | RNA-Seq and ERRBS on sorted neonatal OPCs and OLs, RNA-Seq on sorted Olig1cre;Dnmt1flox OPCs | Moyon et al. [91] | ||
| DNMT1/DNMT3A | Positive role in OPC differentiation and remyelination | PlpcreRT;Dnmt1flox;Dnmt3flox mice | Moyon et al. [142] | |||
| DNA hydroxymethylation | TET1/TET2/TET3 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | In vitro OPCs + siRNAs | Zhao et al. [35] | ||
| TET1 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and (re)myelination (no role for TET3) | Activation of cell differentiation genes (Mag) | Olig1cre;Tet1flox mice | hMeDIP-Seq on in vitro neonatal NSCs and OPCs, RNA-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Tet1flox OPCs | Zhang et al. [92] | |
| Positive role in OPC differentiation and adult remyelination only (no role for TET2) | Activation of cell differentiation, myelination, biosynthesis and neuroglial communication genes (Slc family members, Pcdh family members) | Olig1cre;Tet1flox and PdgfracreRT;Tet1flox mice | RNA-Seq and RRHP on sorted adult OPCs and OLs, RNA-Seq on oligo-enriched Olig1cre;Tet1flox lesioned spinal cord | Moyon et al. [133] | ||
| Histone Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Histone methylation | PRC2 (EED) (H3K27me3) | Negative role in OPC differentiation and (re)myelination | Chromatin silencing of differentiation genes (Bmp, Wnt) | Olig1cre;Eedflox, Plpcre-Eedflox and PdgfracreRT;Eedflox mice | RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Eedflox OPCs | Wang et al. [96] |
| H3K9me3 | Positive role in OPC differentiation (no role for H3K27me3) | In vitro OPCs and OLs | ChIP-Seq on in vitro OPCs and Ols | Liu et al. [97] | ||
| KMT2/MLL (H3K4me3) | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Recruited by CHD8, mark accumulation at promoters of differentiation genes (Tcf7l2, Myrf, Zfp488, Lnc-OL1) | Olig1cre;Chd8flox mice + KDM5 demethylase inhibitors | ChIP-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Chd8flox OPCs | Zhao et al. [138] | |
| PRMT5 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Regulation of OPC differentiation genes | Olig1cre;Prmt5flox mice and in vitro OPCs + siRNA | RNA-Seq on in vitro PRMT5-CRISPRKO OPCs | Scaglione et al. [134] | |
| Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Regulation of OPC differentiation genes | Olig2cre;Prmt5flox mice | RNA-Seq on Olig2cre;Prmt5flox brain | Calabretta et al. [154] | ||
| Positive role in OPC differentiation | Repression of inhibitors of differentiation (Id2/4) | In vitro OPCs and glioma cells + siRNA | Huang et al. [155] | |||
| Histone deacetylation | HDACs | Positive role in OPC differentiation | In vitro O4+ cells + HDAC inhibitors | Conway et al. [136] | ||
| In vitro OPCs + HDAC inhibitors | Marin-Husstege et al. [143] | |||||
| Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | In vivo HDAC inhibitors | Shen et al. [156] | ||||
| Positive role in OPC differentiation and remyelination | Shen et al. [157] | |||||
| HDAC1/HDAC2 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Olig1cre;Hdac1flox;Hdac2flox mice | Ye et al. [121] | |||
| HDAC1 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | In vitro OPCs + siRNA | Egawa et al. [132] | |||
| HDAC2 | Negative role in OPC differentiation | |||||
| HDAC6 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and OL morphology | Deacetylation of alpha-tubulin | In vitro OPCs + siRNA | Noack et al. [158] | ||
| HDAC11 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | In vitro Olineu cells + siRNA | Liu et al. [159] | |||
| SIRT2 | Negative role in OPC differentiation | Deacetylation of alpha-tubulin | In vitro Olineu cells + siRNA | Li et al. [160] | ||
| Histone citrullination | PADI2 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Activation of cell differentiation genes (Septins, Mbp, Sox9/10, Tcf7l2) (+ role on non-histone targets, e.g., myelin proteins) | PdgfracreRT;Padi2flox mice, in vitro OPCs + siRNA, in vitro Olineu + overexpression | Proteomic and ATAC-Seq on in vitro OPCs + siRNA | Falcão et al. [55] |
| Chromatin Organization | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Chromatin remodelers | CHD7 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and (re)myelination | Transcriptional activation of differentiation genes (Sox10, Gpr17, Sirt2, Nkx2.2) | PdgfracreRT;Chd7flox mice | RNA-Seq on in vitro PdgfracreRT;Chd7flox OPCs | Marie et al. [61] |
| PdgfracreRT;Chd7flox mice | Doi et al. [137] | |||||
| Transcriptional activation of differentiation genes (Myrf, Sox10) | Olig1cre;Chd7flox mice | RNA-Seq on Olig1cre;Chd7flox spinal cord | He et al. [59] | |||
| CHD8 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and (re)myelination | Transcriptional activation of differentiation genes (Tcf7l2, Myrf, Zfp488, Lnc-OL1) | Olig1cre;Chd8flox and PdgfracreRT;Chd8flox mice | ChIP-Seq and ATAC-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Chd8flox OPCs | Zhao et al. [138] | |
| BRG1 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Transcriptional activation of differentiation genes (Myrf, Sox10) | Olig1cre;Brg1flox mice | RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq on Olig1cre;Brg1flox optic nerve | Yu et al. [62] | |
| Cnpcre;Brg1flox mice | Bischof et al. [57] | |||||
| EP400 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Transcriptional activation of differentiation genes (Plp1, Mbp, Mog, Myrf, Sox10) | Cnpcre;Ep400flox mice | ChIP-Seq on sorted Cnpcre;Ep400flox OPCs | Elsesser et al. [139] | |
| Nuclear lamina | LMNB1 | Negative role in OPC differentiation | Repression of differentiation genes (cholesterol synthesis, Lss) | In vitro OPCs + LMNB1 overexpression | DamID on in vitro OPCs, combining with LMNB1 maintained expression | Yattah et al. [68] |
| Post-Transcriptional Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Long non-coding RNA | lnc-OL1 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and (re)myelination | Silencing of OPC program during their differentiation (interaction with SUZ12, within PRC2) | In vitro OPCs + lnc-OL1 overexpression and Ezh2 siRNA, Olig1cre;Ezh2flox mice | He et al. [161] | |
| Neat1 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Over-representation of oligodendroglial pathways among differentially expressed genes | Neat1−/− mice | RNA-Seq of Neat1−/− mouse brains | Katsel et al. [115] | |
| lnc-158 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | In vitro NSCs + lnc-158 overexpression and siRNA | Li et al. [113] | |||
| MicroRNA | DICER | Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Olig2cre;Dicerflox and Cnpcre;Dicerflox mice | Dugas et al. [162] | ||
| Positive role in myelination | Olig1cre;Dicerflox mice | Zhao et al. [140] | ||||
| miR-219 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Repression of inhibitors of differentiation (Zfp238, Foxj3) | In vitro OPCs + miR-219 overexpression | Dugas et al. [162] | ||
| miR-338 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Repression of inhibitors of differentiation (Sox6, Hes5) | In vitro OPCs + miR-219 overexpression, in vivo electroporation in chicks and zebrafish | Zhao et al. [140] | ||
| miR-23 | Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Upregulation of myelin genes (Cnp, Plp1, Mag, Mog) and downregulation of OPC and nuclear lamina genes (Pdgfra, Lmnb1) | In vivo miR-23 overexpression in CNP+ cells (mouse model) | RNA-Seq | Lin et al. [163] | |
| miR-32 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Promotes expression of myelin proteins and glucose/lipi metabolism (MBP, SLC45A3) | In vitro OPCs + miR-32 overexpression and shRNA | Shin et al. [164] | ||
| miR-27a | Negative role in OPC differentiation and (re)myelination | Targets mature OL-specific genes (Mbp) | In vitro OPCs + miR-27a overexpression, ex vivo inhibition in cerebellum slices, in vivo intranasal inhibition in mice | RNA-Seq | Tripathi et al. [165] | |
| miR-212 | Negative role in OPC differentiation | Inhibition of oligodendroglial genes (Mbp, Olig1/2, Sox10) | In vitro OPCs + miR-212 overexpression and siRNA | Validation by rtqPCR | Wang et al. [166] | |
| miR-125-3p | Negative role in OPC differentiation | Inhibition of differentiation genes (Fyn, Smad4, Nrg1) | In vitro OPCs + miR-125-3p overexpression and siRNA | Validation by rtqPCR | Lecca et al. [167] | |
| m6A RNA methylation | METTL14 | Positive role in OPC differentiation | Necessary for mature myelin gene expression (Mbp, Mog, Mag, Plp1, Cnp) and regulation of histone modification enzymes (HATs, HMTs, HDACs, KDMs) | Olig2cre;Mettl14flox and Cnpcre;Mettl14flox mice | RNA-Seq on in vitro Olig2cre;Mettl14flox OPCs | Xu et al. [168] |
| FTO | Positive role in OPC differentiation and myelination | Promotes Olig2 degradation | Fto-TG mice | RNA-Seq on Nescre;Prrc2aflox brain and RIP-Seq on Olig2cre;Prrc2aflox brain | Wu et al. [141] |
| DNA Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA hydroxymethylation | TET1 | Positive role in myelination and neuroglial communication | Activation of cell differentiation and cell communication genes (Ca2+ homeostasis) | Olig1cre;Tet1flox mice | hMeDIP-Seq on in vitro neonatal NSCs and OPCs, RNA-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Tet1flox OPCs | Zhang et al. [92] |
| Activation of cell differentiation, myelination, biosynthesis, and neuroglial communication genes (Slc family members, Pcdh family members) | Olig1cre;Tet1flox mice | RNA-Seq and RRHP on sorted adult OPCs and OLs, RNA-Seq on oligo-enriched Olig1cre;Tet1flox lesioned spinal cord | Moyon et al. [133] | |||
| Chromatin Organization | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| Chromatin remodelers | CHD7 | Positive role in myelination | Preferentially binding and increased accessibility of myelinogenesis (Mbp, Plp1 and Cnp) and lipid metabolism genes (Enpp2, Nfya, and Elovl7) | Olig1cre;Chd7flox mice | RNA-Seq on in vitro Olig1cre;Chd7flox spinal cord | He et al. [59] |
| Post-Transcriptional Modification | Enzyme/Mark | Role | Targeted Genes or Functions | Model | Methods | References |
| MicroRNA | DICER | Positive role in myelin maintenance | Induces expression of myelin proteins | PlpcreRT;Dicerflox mice | Shin et al. [173] | |
| m6A RNA methylation | METTL14 | Positive role in myelination and regulation of internodes lenghts | Alternative splicing of glial paranodal genes (Nfasc155) | Olig2cre;Mettl14flox mice | RNA-Seq on in vitro Olig2cre;Mettl14flox OPCs and OLs | Xu et al. [168] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pruvost, M.; Moyon, S. Oligodendroglial Epigenetics, from Lineage Specification to Activity-Dependent Myelination. Life 2021, 11, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010062
Pruvost M, Moyon S. Oligodendroglial Epigenetics, from Lineage Specification to Activity-Dependent Myelination. Life. 2021; 11(1):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010062
Chicago/Turabian StylePruvost, Mathilde, and Sarah Moyon. 2021. "Oligodendroglial Epigenetics, from Lineage Specification to Activity-Dependent Myelination" Life 11, no. 1: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010062
APA StylePruvost, M., & Moyon, S. (2021). Oligodendroglial Epigenetics, from Lineage Specification to Activity-Dependent Myelination. Life, 11(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11010062





