Petrographic, Geochemical, and Geochronological Characteristics of the Granite in Yunnan and Its Constraints on Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Mineralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
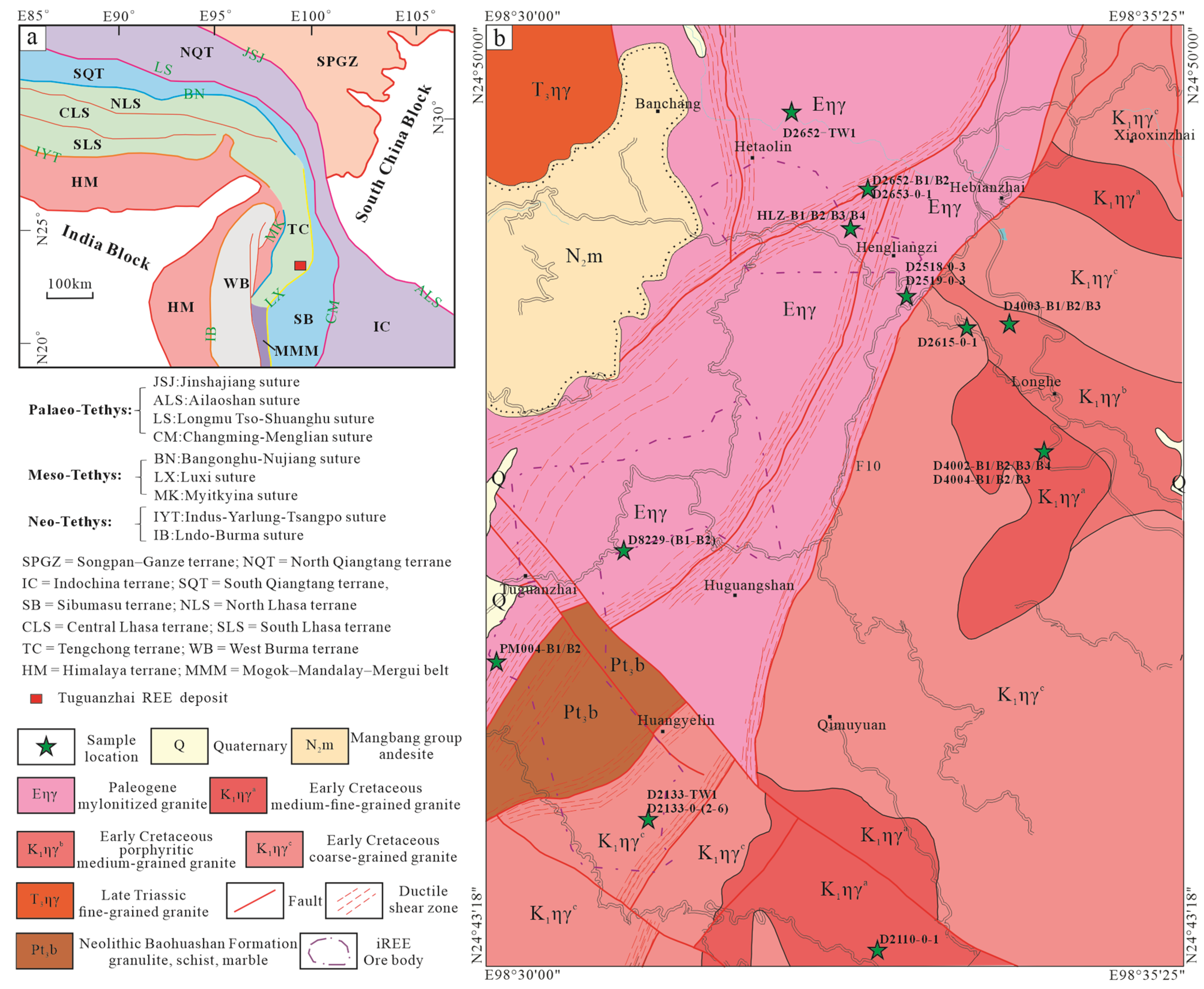
2. Geological Background
2.1. Regional Geology
2.2. Geological Characteristics of the Deposit
3. Sample Collection and Testing Methods
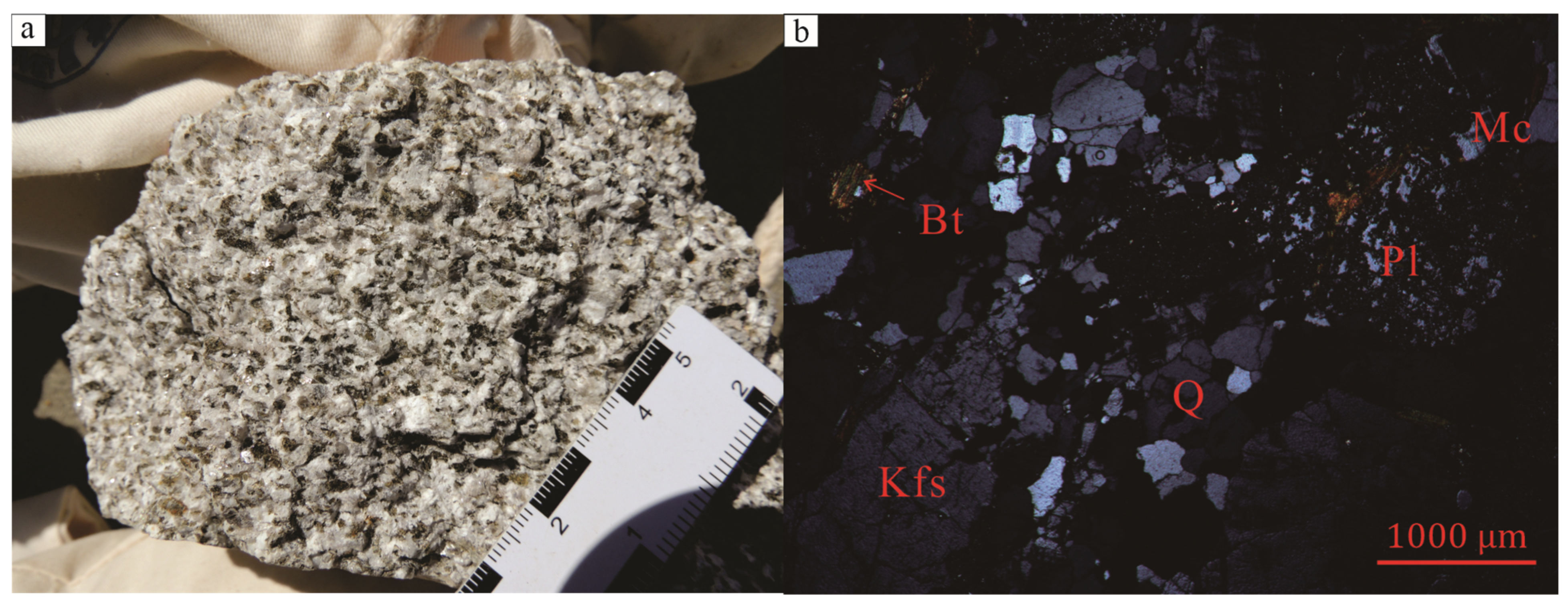
3.1. Sample Collection
3.2. Analytical Methods
4. Results
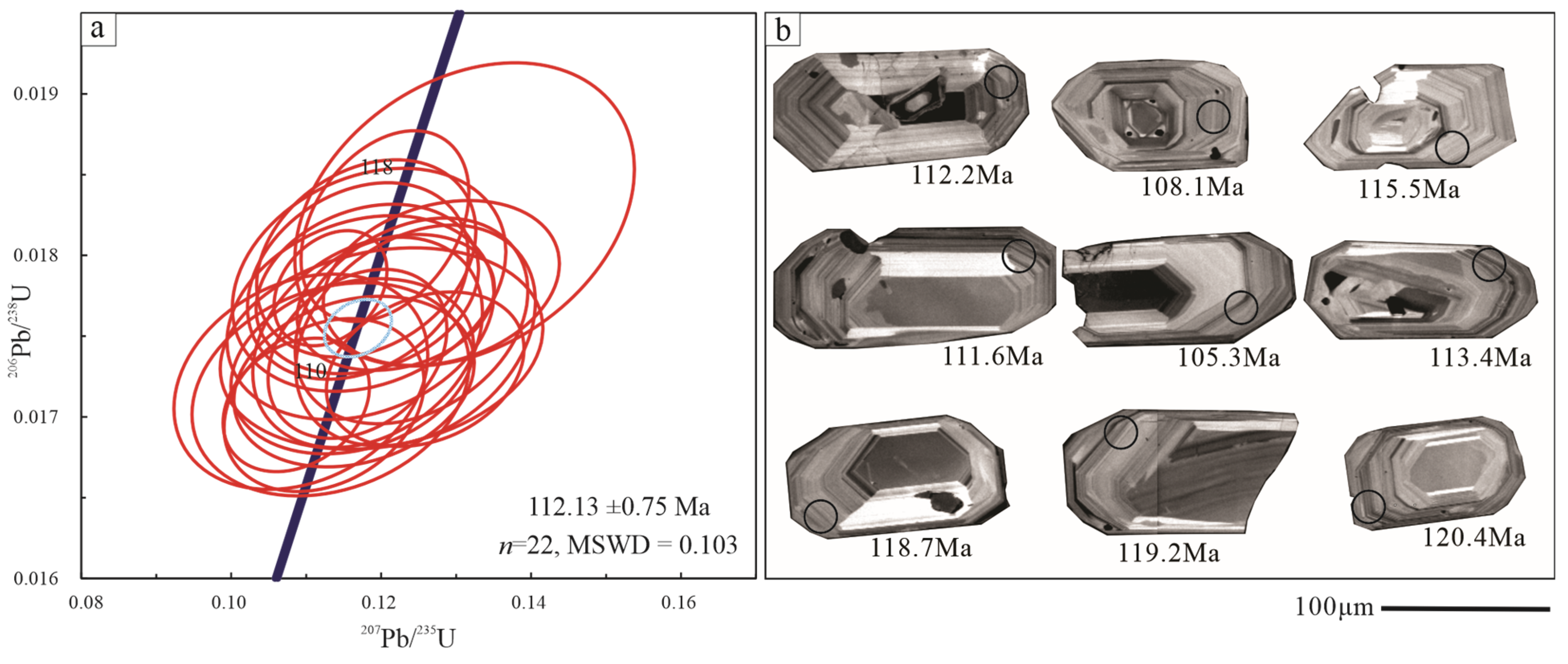
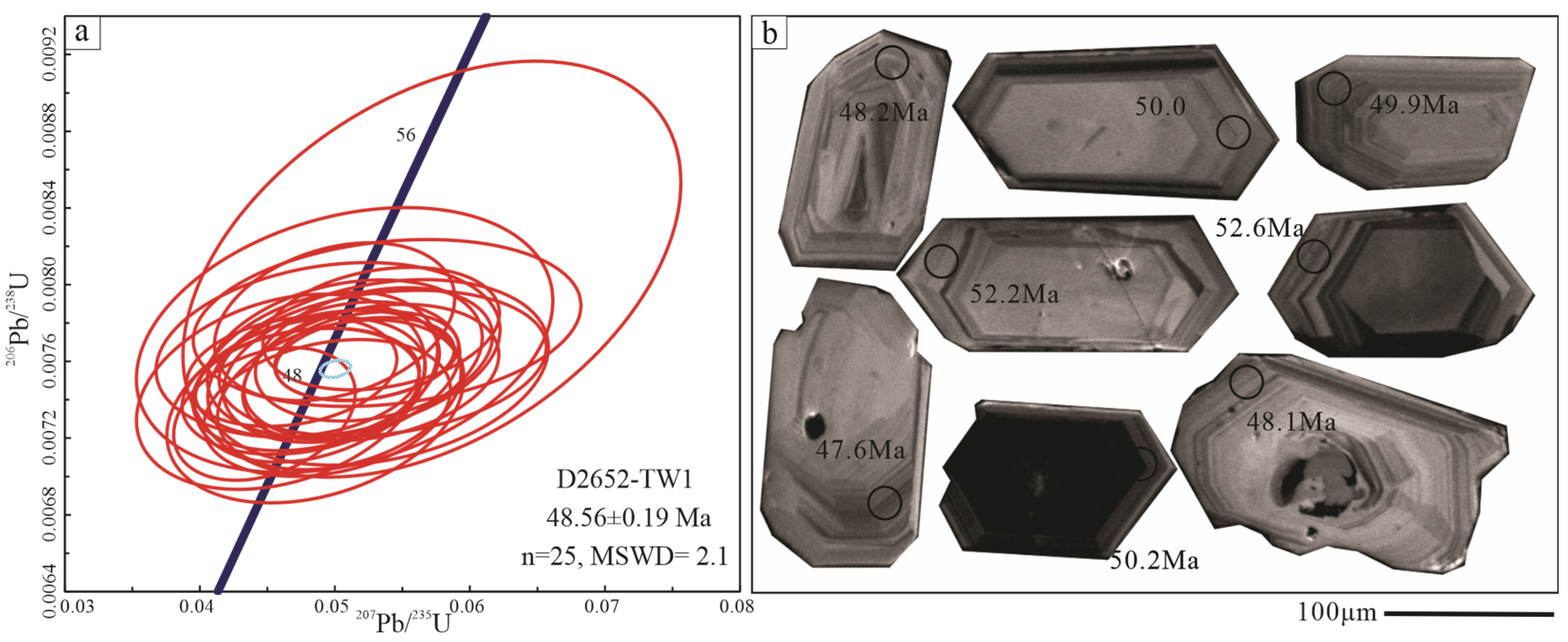
4.1. Chronological Characteristics
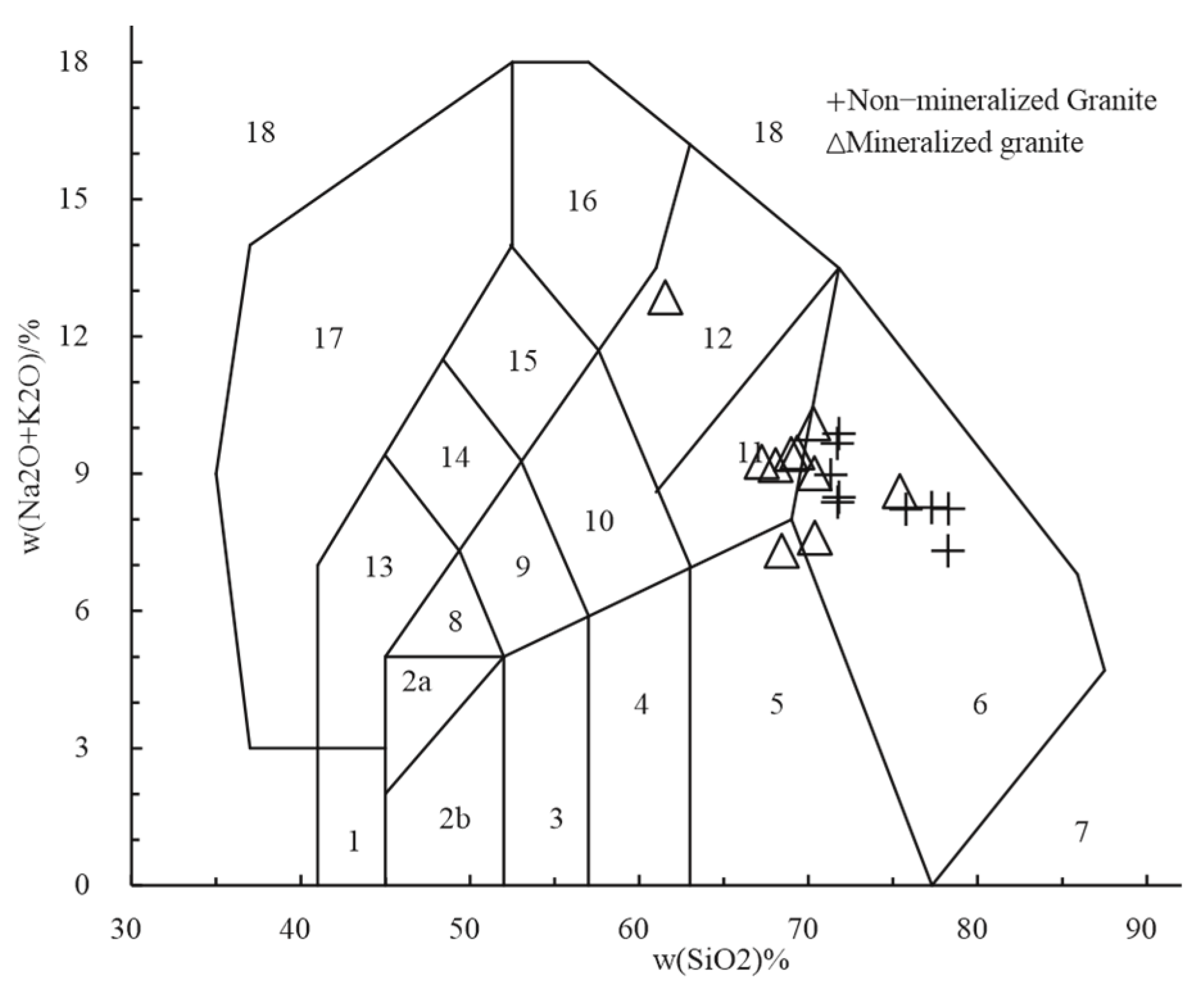
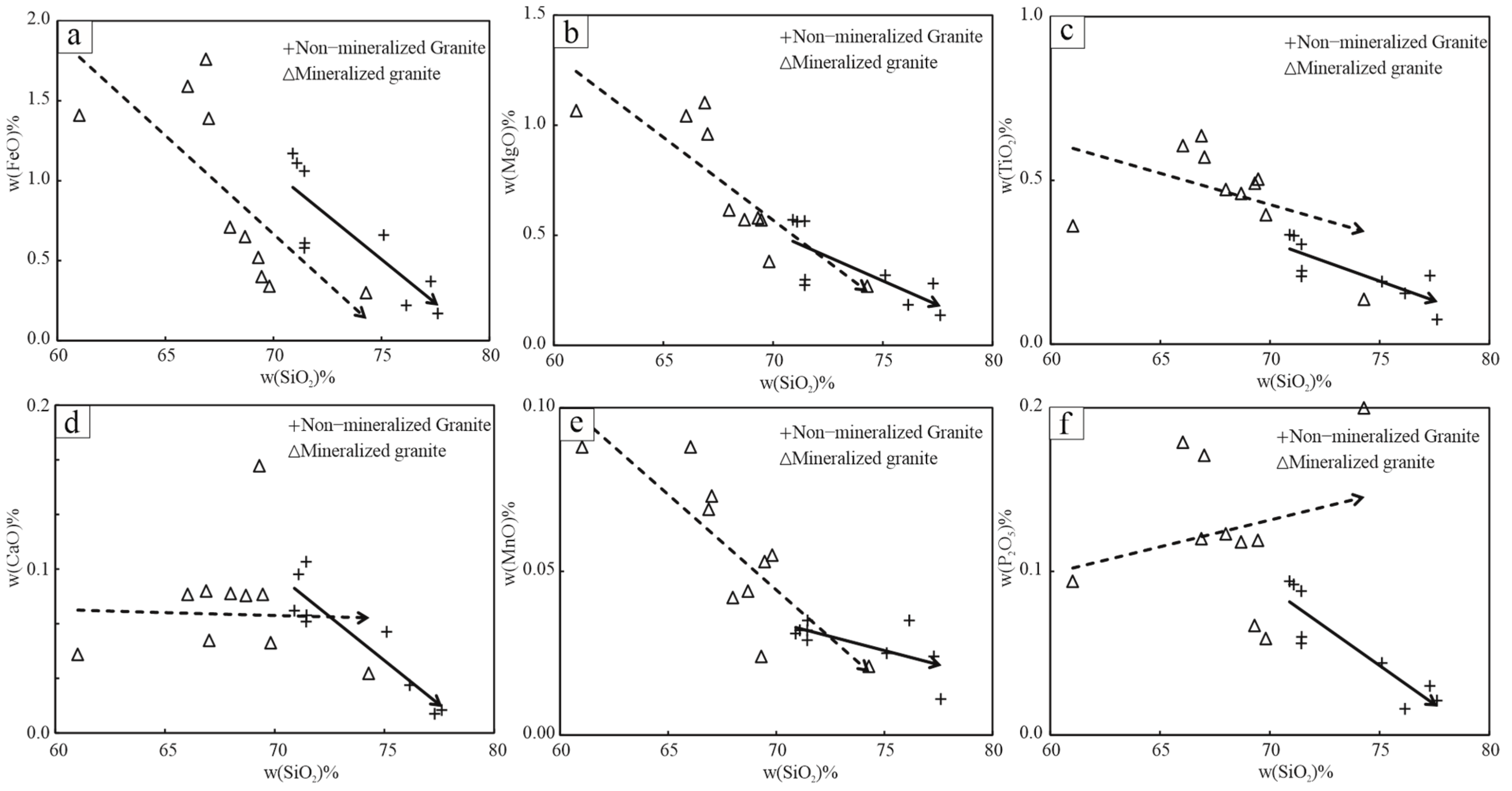
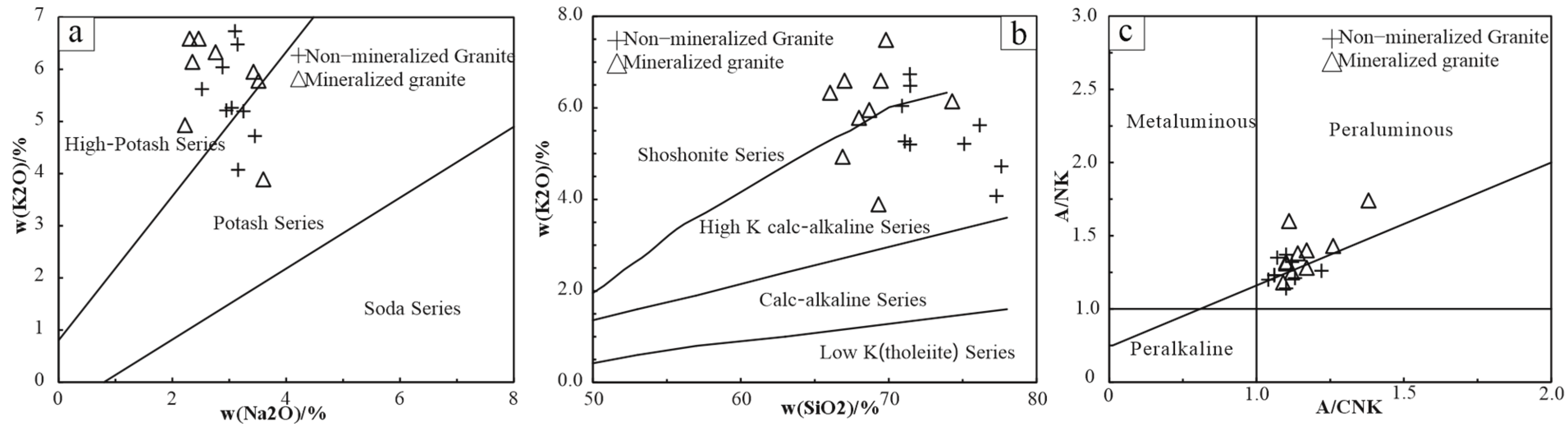
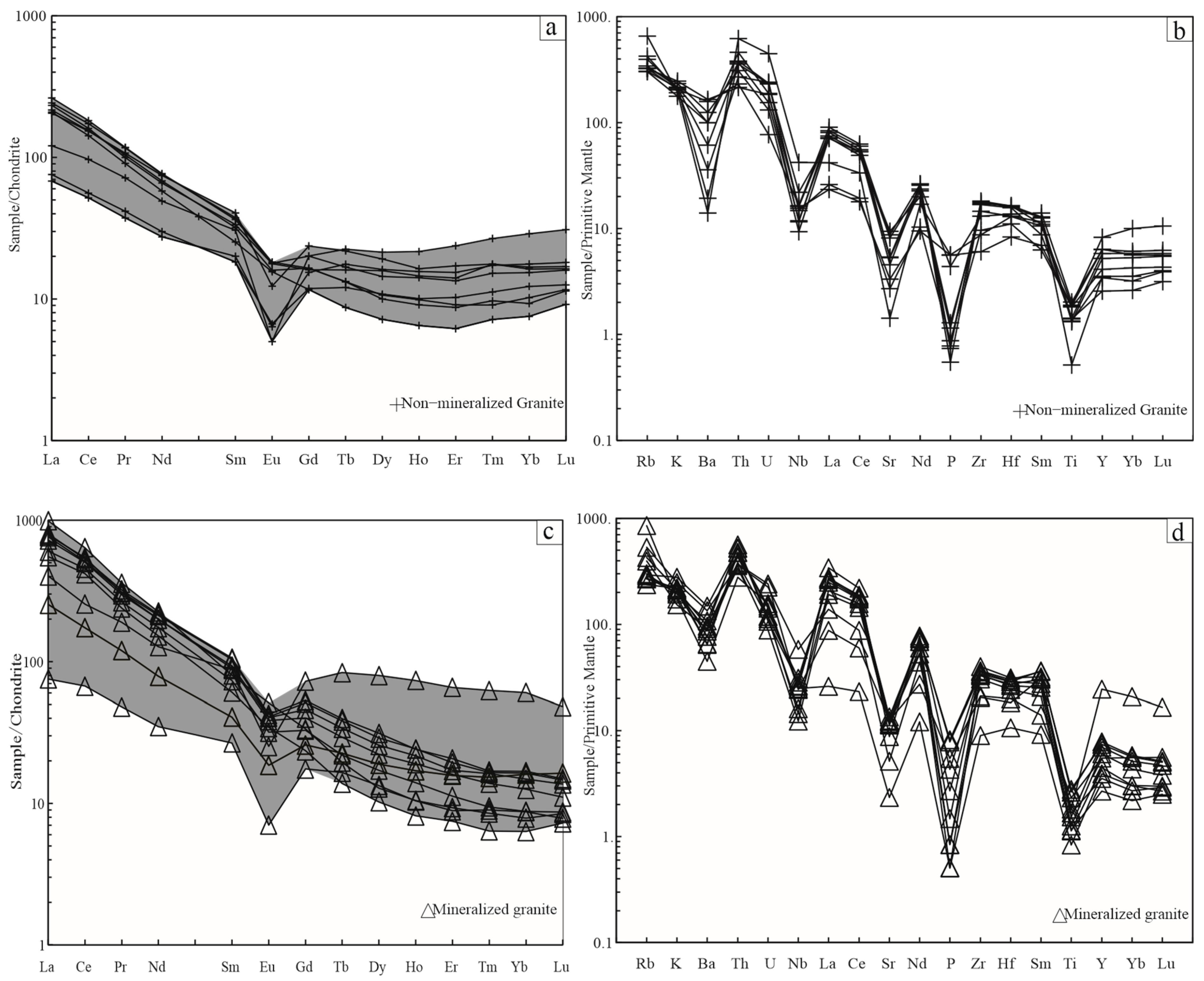
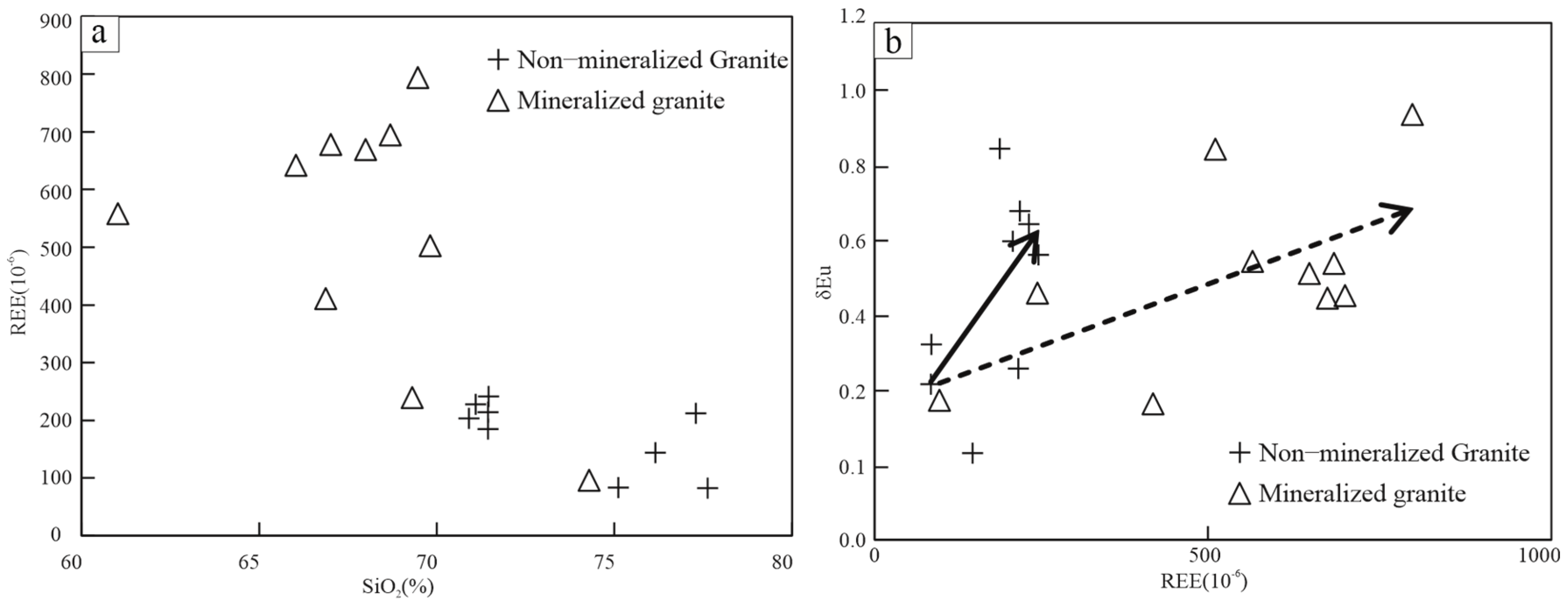
4.2. Geochemical Compositions
4.3. Characteristics of REE-Bearing Minerals
5. Discussion
5.1. Chronological Characteristics and iREE Mineralization
5.2. Genetic Relationships Between Whole-Rock Geochemical Compositions and iREE Mineralization
5.3. Genetic Relationships Between REE-Bearing Minerals and iREE Mineralization
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The zircon U-Pb ages of the mineralized granites in the Tuguanzhai area are 112.13 ± 0.75 Ma (n = 22, MSWD = 0.103), 52.78 ± 0.28 Ma (n = 28, MSWD = 12), and 48.56 ± 0.19 Ma (n = 25, MSWD = 2.1). We first confirm that the Early Cretaceous granites have potential for iREE mineralization in the Tengchong-Lianghe region of western Yunnan, China.
- (2)
- Both the non-mineralized and mineralized granites of Tuguanzhai exhibit high K2O + Na2O and K contents, along with low Ti and Ca contents. Magmatic differentiation does not significantly influence the variation of REE contents in these rocks.
- (3)
- The type and abundance of REE-bearing minerals, including zircon, rutile, ilmenite, titanite, apatite, and monazite, influence the REE distribution in granites. Among these minerals, the high concentration of easily dissociable REE minerals, such as titanite, apatite, and monazite, is a critical factor for mineralization in this region.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; He, X.; Tan, W.; Ma, L.; Zhao, F. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Ion-Adsorption Type REE Deposit in the Lincang Granite, Yunnan Province. Geol. China 2022, 49, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, G.; Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, C.-K. Are South China Granites Special in Forming Ion-Adsorption REE Deposits? Gondwana Res. 2024, 125, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Dai, J.; Deng, M.; Zhao, T.; Liu, L. Exploration and Research Progress on Ion-Adsorption Type REE Deposit in South China. China Geol. 2018, 1, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, C.D.; Marquis, E.; Smith, M.P.; Li, M.Y.H.; Estrade, G.; Goodenough, K.M. Ion Adsorption Mineralisation in Regolith-Hosted REE Deposits. In Mineral Resource Reviews; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.N.; Song, X. A Review of Major Rare Earth Element and Yttrium Deposits in China. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 69, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Long, F.; Chen, Z.; Chi, R. Rare Earth Occurrence States of Weathered Crust Elution-Deposited Rare Earth Ores in Southern Yunnan. Minerals 2023, 13, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, X.P.; Zhang, B.H.; Gao, R.D.; Zeng, Z.J.; Ma, G.T. Geochemical Characteristics of Tuguanzhai Ion-Adsorption Type REE Deposit in Tengchong, Yunnan. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 491–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Xu, X. Geochemical and Geochronological Constraints on the Genesis of Ion-Adsorption-Type REE Mineralization in the Lincang Pluton, SW China. Minerals 2020, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.-W.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhang, S.-T.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, L.-K.; Tang, L.; Pei, Q.-M. Late Cretaceous Magmatism and Related Metallogeny in the Tengchong Area: Evidence from Geochronological, Isotopic and Geochemical Data from the Xiaolonghe Sn Deposit, Western Yunnan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hou, Z.; Goldfarb, R.J.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Rare Earth Element Deposits in China; Society of Economic Geologists Headquarters: Littleton, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, W. A Prolonged Subduction-Accretion in the Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insights from Anatomy and Tectonic Affinity for the Beishan Complex. Gondwana Res. 2021, 95, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liang, X.; Cheng, H. Review of Rare Earth Element (REE) Adsorption on and Desorption from Clay Minerals: Application to Formation and Mining of Ion-Adsorption REE Deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 157, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, G.T.; Gao, R.D.; Zeng, Z.J.; Wang, L.; Zuo, Z.L.; Huang, S.K. Formation Conditions and Prospecting Prediction of Tuguanzhai Ion-Adsorption Type REE Deposit in Tengchong-Lianghe Area. Earth Sci. 2018, 43, 2628–2637. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.M.; Zhao, W.W.; Zhou, M.-F. Nature of Parent Rocks, Mineralization Styles and Ore Genesis of Regolith-Hosted REE Deposits in South China: An Integrated Genetic Model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 148, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, B.; Ma, G.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, B. Mineralization of Ion-Adsorption Type Rare Earth Deposits in Western Yunnan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 148, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.G.; Pan, G.T.; Sun, Z.M. Genesis and Evolution of the Structural Systems during the Cenozoic in the Sanjiang Orogenic Belt, Southwest China. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2021, 41, 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Q.; Wang, B.D.; Li, G.M.; Wang, D.B.; Peng, Z.M. Major Progresses of Geological Survey and Research in East Tethys: An Overview. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2021, 41, 283–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.-X.; Li, W.-C. Evolution and Metallogeny of the Sanjiang Arc-Back Arc Basin System in the Eastern Tethys: An Introduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 222, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, J.-W.; Cawood, P.A.; Fan, W.-M.; Tohver, E.; Wang, Y.-J.; McCuaig, T.C.; Peng, T.-P. Late Permian-Triassic Magmatic Evolution in the Jinshajiang Orogenic Belt, SW China and Implications for Orogenic Processes Following Closure of the Paleo-Tethys. Am. J. Sci. 2013, 313, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, S.; Santosh, M.; Jahn, B. Orogenic Belts in Central Asia: Correlations and Connections. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Li, T. Paleogene Magmatism and Gold Metallogeny of the Jinping Terrane in the Ailaoshan Ore Belt, Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen (SW China): Geology, Deposit Type and Tectonic Setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 620–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Tang, J.; Lin, B.; Yang, C.; Sun, H. Metallogeny in the Bangong–Nujiang Belt, Central Tibet, China: A Review. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1139941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Santosh, M. Cenozoic Tectono-Magmatic and Metallogenic Processes in the Sanjiang Region, Southwestern China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 268–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Leonard, N.; Tao, W.; Tan, S. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of the Early Cretaceous Granitoids in the Eastern Tengchong Terrane, SW China: Constraint on the Evolution of Meso-Tethys. Lithosphere 2020, 12, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, G.; Sun, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Ding, X. In situ elemental and Sr-O isotopic studies on apatite from the xu-huai intrusion at the southern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for petrogenesis and metallogeny. Chem. Geol. 2019, 510, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-J.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Cong, Y.-N.; Zhang, L.-P.; Sun, W.-D.; Li, C.-Y.; Ding, X. Analogous Diagenetic Conditions of Dark Enclave and Its Host Granite Derived by Magma Mixing: Evidence for a Post-Mixing Magmatic Process. Lithos 2020, 356, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Sun, S.-J.; Zhang, L.-P.; Deng, J.-H.; Li, S.; Sun, W.-D. Origin of Transitional IA-Type Syenite and Its Relationship to a-Type Intrusions in the Luzong Basin, the Lower Yangtze River Belt: Insights from Geochemistry. Chem. Geol. 2023, 626, 121458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, P.W.; Schaltegger, U. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2003, 53, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubatto, D. Zircon Trace Element Geochemistry: Partitioning with Garnet and the Link between U–Pb Ages and Metamorphism. Chem. Geol. 2002, 184, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Qin, L.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, C. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Cretaceous–Eocene Granites, Tengchong Block (SW China): Petrogenesis and Implications for Mesozoic-Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of Eastern Tethys. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudovich, Y.E.; Ketris, M.P. Fundamentals of Lithochemistry; RUSSIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, Ural Branch, Komi Scientific Center Institute of Geology: Syktyvkar, Russia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Middlemost, E.A. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongalsky, B.; Krivolutskaya, N. World-Class Mineral Deposits of Northeastern Transbaikalia, Siberia, Russia; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-03559-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Mo, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y. Petrogenesis of Highly Fractionated I-Type Granites in the Zayu Area of Eastern Gangdese, Tibet: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes. Sci. China Ser. Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1223–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, G.; Dong, S.; Qian, L.; Ou, L. Sources and Enrichment Mechanisms of Rare-Earth Elements in the Mosuoying Granites, Sichuan Province, Southwest China. Minerals 2025, 15, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhou, J.; Du, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, W.; Tian, M.; Chen, B. The Characteristics and Enrichment Process of Dabu Ion-Adsorption Heavy Rare-Earth Element (HREE) Deposits in Jiangxi Province, South China. Minerals 2024, 14, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togizov, K.; Issayeva, L.; Muratkhanov, D.; Kurmangazhina, M.; Swęd, M.; Duczmal-Czernikiewicz, A. Rare Earth Elements in the Shok-Karagay Ore Fields (Syrymbet Ore District, Northern Kazakhstan) and Visualisation of the Deposits Using the Geography Information System. Minerals 2023, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, K.X.; Chen, L.K.; Zhu, P.; Ouyang, H. Overview of Metallogenic Features of Ion-Adsorption Type REE Deposits in Southern Jiangxi Province. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths 2015, 33, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, D.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Guo, N.X.; Liu, X.X.; He, H.H. Metallogenic Specialization of Rare Earth Mineralized Igneous Rocks in the Eastern Nanling Region. Geotecton. Metallog. 2014, 38, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Yan, B.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhu, L.; Tan, S.; Ding, D.; Jiang, H. Geochemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Ion-Adsorption Type REE Mineralization in the Mosuoying Granite, Panxi Area, Southwest China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Remobilization and Transferring of Rare Earth Elements in the Formation of Regolith-Hosted REE Deposits. J. Geomech. 2024, 30, 707–722. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, T.X.; Tang, Z.; Bao, C.F.; Li, R.; Zhan, D.Q.; Yang, Q.B.; Hao, X.F.; Yu, H.J. Prospect, Research Progress and Distribution Characteristics of REE-bearing minerals in Yunnan Province. J. Chin. Soc. Rare Earths 2022, 40, 577. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Ming, T.; Li, R.; He, X.; Wen, H.; Yu, W. Petrogenesis of Eocene A-Type Granite Associated with the Yingpanshan–Damanbie Regolith-Hosted Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Deposit in the Tengchong Block, Southwest China. Minerals 2024, 14, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
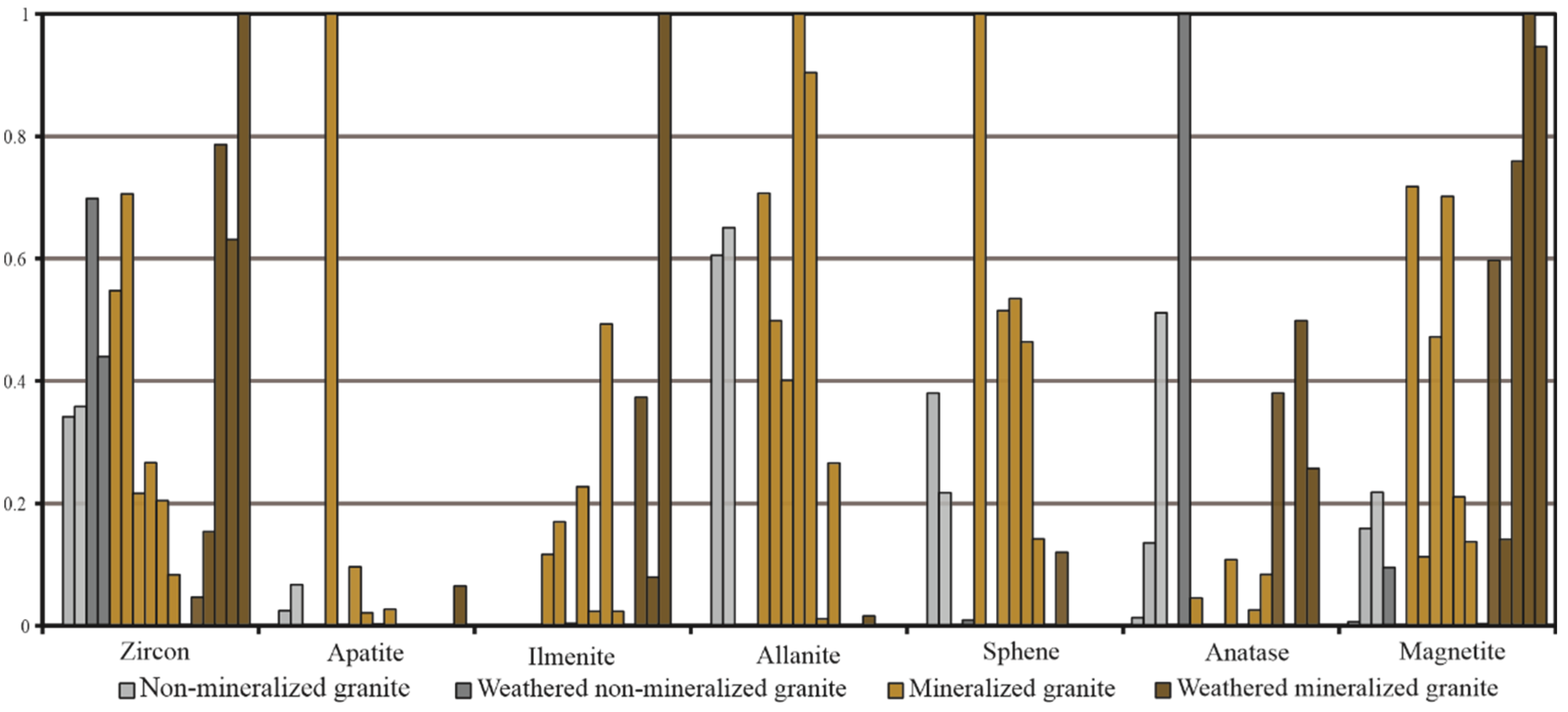
| Sample | Rock Name | Remarks | Zircon | Apatite | Ilmenite | Allanite | Epidote | Magnetite | Limonite | Sphene | Rutile | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | |||
| D4002 (B1–B4) | Medium–Fine-Grained Granite | Non-mineralized | 0.97 | minor | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 80.10 | 17.28 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 10.78 |
| D4004 (B1–B3) | Medium-Grained Granite | Non-mineralized | 124.86 | 3.24 | 0.00 | 353.08 | 39.54 | 1620.89 | 13.41 | 112.61 | 1.15 | 43.47 |
| D4003 (B1–B3) | Medium–Coarse-Grained Granite | Non-mineralized | 130.78 | 8.72 | 0.00 | 379.27 | 13.95 | 2216.02 | 46.79 | 64.52 | 4.36 | 41.85 |
| D2615-0-1 | Intensely Weathered Medium–Coarse-Grained Granite | Non-mineralized | 254.16 | minor | 0.00 | 0.00 | 137.67 | 975.70 | 3.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 50.46 |
| D2110-0-1 | Intensely Weathered Medium–Fine-Grained Granite | Non-mineralized | 160.51 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 6.21 | 17.91 | 543.43 | 2.66 | 8.51 | 69.08 |
| D2518-0-3 | Medium-Grained Granite | Mineralized | 199.61 | 129.88 | 17.43 | 412.30 | 59.27 | 7239.19 | 35.74 | 296.37 | 0.39 | 162.13 |
| D2133-0-(2-6) | Fragmented Medium-Grained Granite | Mineralized | 256.83 | minor | 25.47 | 290.48 | minor | 1150.36 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 44.95 |
| D8229-(B1–B2) | Fragmented Medium-Grained Granite | Mineralized | 79.49 | 12.49 | 0.57 | 233.93 | 27.25 | 4768.36 | 116.97 | 152.74 | 0.00 | 285.03 |
| HLZ (B1–B4) | Fragmented Medium-Grained Granite | Mineralized | 97.65 | 2.76 | 34.08 | 583.10 | 343.59 | 7081.91 | 86.59 | 158.44 | 0.92 | 746.14 |
| D2653-0-1 | Mylonitized Medium-Grained Granite | Mineralized | 75.12 | 0.35 | 3.53 | 526.91 | 328.00 | 2138.70 | 47.26 | 137.55 | 0.00 | 269.10 |
| PM004-B2 | Granitic Mylonite | Mineralized | 31.04 | 3.52 | 73.94 | 6.82 | 21.14 | 1396.55 | 486.80 | 42.05 | 0.22 | 39.41 |
| PM004-B1 | Granitic Ultra-mylonite | Mineralized | 1.42 | minor | 3.52 | 154.93 | 17.59 | 49.28 | 1.75 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 20.76 |
| HCZ008-(H14/H16) | Semi-Weathered Granite | Mineralized | 17.81 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 977.61 | 6025.94 | 674.14 | 35.61 | 3.24 | 322.91 |
| TCZ-025-H6 | Semi-Weathered Granite | Mineralized | 56.79 | 0.00 | 55.93 | 0.00 | 5.83 | 1441.18 | 93.17 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 62.63 |
| HCZ008-(H7/H9, H11/H13) | Intensely Weathered Granite | Mineralized | 286.00 | 0.00 | 11.88 | 9.33 | 9.33 | 7654.92 | 193.50 | 0.00 | 4.25 | 316.55 |
| TGZ-H1 | Intensely Weathered Granite | Mineralized | 229.85 | 0.00 | 149.95 | 0.00 | 12.04 | 10,080.35 | 187.16 | 0.00 | 2.19 | 264.87 |
| HCZ008-(H3/H5) | Completely Weathered Granite | Mineralized | 363.49 | minor | 0.00 | 0.00 | 11.55 | 9540.26 | 355.09 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 225.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Niu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, X.; Gao, R.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Y. Petrographic, Geochemical, and Geochronological Characteristics of the Granite in Yunnan and Its Constraints on Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Mineralization. Minerals 2025, 15, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080872
Zhang B, Niu H, Zhang L, Zhang B, Zhu X, Gao R, Yang Y, Zou Y. Petrographic, Geochemical, and Geochronological Characteristics of the Granite in Yunnan and Its Constraints on Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Mineralization. Minerals. 2025; 15(8):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080872
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bin, Haobin Niu, Linkui Zhang, Binhui Zhang, Xiangping Zhu, Rudong Gao, Yongfei Yang, and Yinggui Zou. 2025. "Petrographic, Geochemical, and Geochronological Characteristics of the Granite in Yunnan and Its Constraints on Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Mineralization" Minerals 15, no. 8: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080872
APA StyleZhang, B., Niu, H., Zhang, L., Zhang, B., Zhu, X., Gao, R., Yang, Y., & Zou, Y. (2025). Petrographic, Geochemical, and Geochronological Characteristics of the Granite in Yunnan and Its Constraints on Ion-Adsorption Rare Earth Element Mineralization. Minerals, 15(8), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080872





