Abstract
Titania is one of the most comprehensively studied nanostructures due to their widespread applications in the production of catalytic, gas sensing, and corrosion-resistant materials. M-polynomial of nanotubes has been vastly investigated, as it produces many degree-based topological indices, which are numerical parameters capturing structural and chemical properties. These indices are used in the development of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) in which the biological activity and other properties of molecules, such as boiling point, stability, strain energy, etc., are correlated with their structure. In this report, we provide M-polynomials of single-walled titania (SW TiO2) nanotubes and recover important topological degree-based indices to theoretically judge these nanotubes. We also plot surfaces associated to single-walled titania (SW TiO2) nanotubes.
1. Introduction
In chemical graph theory, molecular topology, and mathematical chemistry, a topological index, sometimes known as a connectivity index, is a type of a molecular descriptor which is calculated based on the molecular graph of a chemical compound. A large amount of chemical experiments require a determination of the chemical properties of new compounds and new drugs. Fortunately, the chemical-based experiments indicate that there is strong inherent relationship between the chemical characteristics of chemical compounds and drugs and their molecular structures. Topological indices calculated for these chemical molecular structures can help us to understand the physical features, chemical reactivity, and biological activity.
Titania, TiO2, attracts considerable technological interest due to its unique properties in biology, optics, electronics, and photo-chemistry [1]. Recent experimental studies show that titania nanotubes (NTs) improve TiO2 bulk properties for photocatalysis, hydrogen-sensing, and photo-voltaic applications [2]. Titanium nanotubes have been observed in two types of morphologies: single-walled titanium (SW TiO2) nanotubes and multi-walled (MW TiO2) nanotubes [3]. Here, we are interested only in single-walled TiO2 nanotubes because we consider their chemical graphs to work on molecular descriptors. Titania nanotubes are formed by rolling up the stoichiometric two-periodic (2D) sheets cut from the energetically stable anatase surface, which contains either six or three layers [4].
The is the two-parametric chemical graph of three-layered titania nanotubes, where m and n represent the number of titanium atoms in each row and column, respectively (Figure 1). Big dots correspond to titanium atoms, whereas small dots correspond to oxygen atoms, and edges represent bonds.
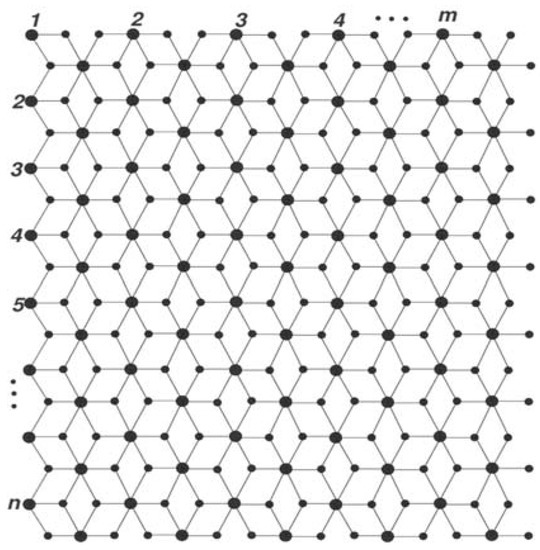
Figure 1.
The graph of three-layered single-walled titania nanotubes.
is the two-parametric chemical graph of a six-layered single-walled titania nanotube, where m and n represent the number of titanium atoms in each column and row, respectively (Figure 2). Here again, big dots correspond to titania atoms, small dots to oxygen, and edges to atomic bonds.
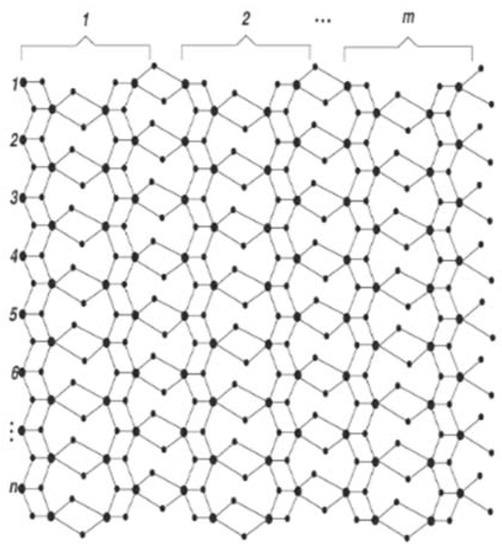
Figure 2.
The graph of six-layered single walled titania nanotubes.
In order to engineer a nanotube endowed with a proposed property, one can have control over structural sensitive properties such as fracture toughness and yield stress. The topological index of a molecule structure can be considered as a non-empirical numerical quantity that quantifies the molecular structure and its branching pattern in many ways. In this point of view, the topological index can be regarded as a score function that maps each molecular structure to a real number and is used as a descriptor of the molecule under testing.
The Wiener index is the first and most studied topological index and is defined as the sum of the distances between all pairs of vertices in G. For more details, see [5,6]. Zagreb indices were introduced by Gutman and Trinajstic [7]. The first Zagreb index M1(G) is defined as the sum of the squares of degrees of a graph G, and the second Zagreb index M2(G) is the sum of the product of all degrees corresponding to each edge in G [7]. The second modified Zagreb index is defined by , where du and dv are the degrees of vertices u and v, respectively [8]. General Randic index of G is defined as the sum of over all edges uv of G, where du denotes the degree of vertex u of G, and , where is an arbitrary real number [9]. Symmetric division index is defined as . These indices can help to characterize the chemical and physical properties of molecules [7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Most recently, Munir et al. computed M-polynomials and related topological indices for Bucktubes [11] and Nanostar dendrimers [19].
In the present article, we compute the closed forms of M-polynomials of single-walled titania nanotubes and represent them graphically using Mapple. As a consequence, we derived some topological degree-based indices. We start by defining the M-polynomial of a general graph [7]. It is important to mention that black titania nanotubes are used to control photo-catalysis and crystalline structures. These tubes have applications in nanotechnology, optics, and electronics. In these areas, computations of topological indices can predict properties of these tubes and avoid a large amount of chemical experiments.
Definition 1.
If is a graph where V denotes vertices and E represents edges of G. Let represent the degree of v in graph G. Let be the number of edges of G such that which means the M-Polynomial of graph G is defined as
Topological indices are numerical parameters of a graph that characterize its topology and are usually graph-invariant. It describes the structure of molecules numerically. Topological indices are used in the development of qualitative structure activity relationships (QSARs). Some degree-based topological indices are derived from M-polynomials [21]. The following Table 1 relates these derivations.

Table 1.
Derivations of degree-based indices.
2. Results
In this section, we use the symmetric structures of single-walled titania nanotubes to determine the M-polynomials and then derive topological indices for these tubes.
Proposition 1.
Let be the three-layered single-walled titania nanotube. Therefore,
Proof.
Let be the three-layered single-walled titania nanotube, where m and n are the number of titanium atoms in each row and column, respectively. The graph has number of vertices and edges. The following are the tables for the vertex and edge partitions of nanotubes.
From Table 2, we see that there are four partitions, , and for the vertex set with size and , respectively.

Table 2.
The partition of V(G) of .

Table 3.
Edge partition of edge set of .
Thus, the M-polynomial of is
Proposition 2.
Let be the six-layered single walled titania nanotube. Therefore,
Proof.


Let be the six-layered single walled titania nanotube, where m and n are the number of titanium atoms in each row and column, respectively. The graph has number of vertices and edges. Table 4 provides the edge partitions of , and Table 5 provides Vertex partitions.

Table 4.
Edge partition of edge set of .

Table 5.
The partition of of .
From Table 4, we see that the partitions of of are , and for the vertex set with size and , respectively. From Table 5, the edge set of can be written as
and
The following results provide the computation of the topological indices of the three-layered and six-layered single-walled titania nanotubes.
Proposition 3.
For the three-layered single-walled titania nanotube we have
Proof.
Let be the M-polynomial of . Therefore,
Proposition 4.
For the six-layered single-walled titania nanotube we have
Proof.
Let be M-polynomial of . Therefore,
3. Conclusions
In this article, we computed the connectivity of titania nanotubes through degree-based topological indices. In Figure 3 and Figure 4, we gave graphically representation of M-polynomial of 3-layered single walled titania nanotbes and 6-layered single walled titania nanotubes. The topological indices thus calculated for these titania nanotubes can help us to understand their physical features, chemical reactivity, and biological activities. From this point of view, topological indices can be regarded as a score function that maps each molecular structure to a real number and are used as descriptors of the molecule under testing. These results can also play a vital role in the determination of the significance of single-walled titania nanotubes in pharmaceutical industry [22,23]. In addition, a comparison between three- and six-layered titania nanotubes can be launched with the help of careful analysis of the above results. The methodology described above can be extended to emerging types of neontubes: aluminosilicate/aluminugerminate [20,24,25,26].
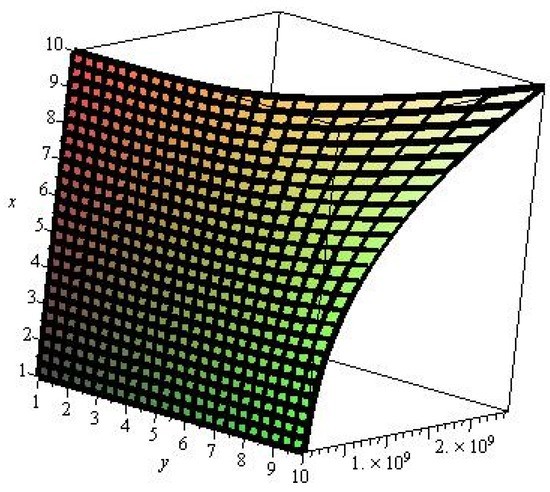
Figure 3.
M-polynomial of 3-layered single walled titania nanotbes.
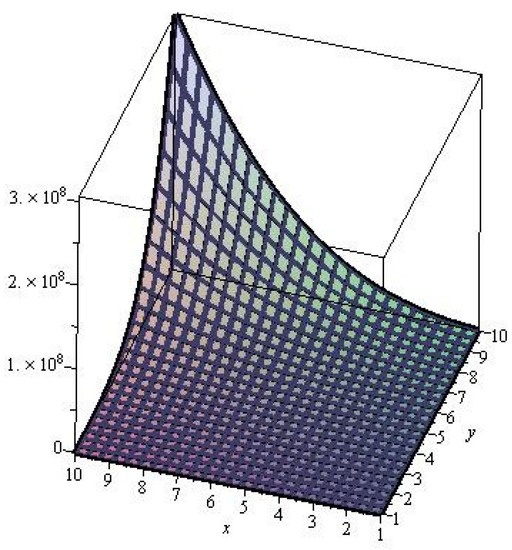
Figure 4.
M-Polynomials of 6-layered single walled titania nanotubes.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 52828, Korea.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work. All authors wrote, reviewed and commented on the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Y.Z.; Lee, N.H.; Lee, E.G.; Song, J.S.; Kim, S.J. The characterization and photocatalytic properties of mesoporous rutile TiO2 powder synthesized through cell assembly of nanocrystals. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 389, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavykin, D.V.; Friedrich, J.M.; Walash, F.C. Protonated titanates and TiO2 nanostructured materials: Synthesis, properties and applications. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2807–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Varghese, O.K.; Paulsose, M.; Grimes, C.A. A study on the growth and structure of Titania nonotubes. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evarestov, R.A.; Bandura, A.V.; Losev, M.V.; Piskunov, S.; Zhukovskii, Y.F. Titania nanotubes modeled from 3-layered and 6-layered(101) anatase sheets: Line group symmetry and comparative ab initio LCAO calculataions. Physica E 2010, 43, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, I. Degree based topological indices. Croat. Chem. Acta 2013, 89, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, H.J. Structural determination of paraffin boiling points. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutman, I.; Trinajstic, N. Graph theory and molecular orbitals total f-electron energy of alternant hydrocarbons. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1972, 17, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J. Theorems about Zagreb Indices and Modified Zagreb Indices. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2011, 65, 659–670. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shi, Y. A Survey on the Randic Index. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2008, 59, 127–156. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Liu, M.; Das, K.C.; Gutman, I.; Furtula, B. A survey on graphs extremal with respect to distance-based topological indices. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2014, 71, 461–508. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.; Nazeer, W.; Nizami, A.R.; Rafique, S.; Kang, S.M. M-polynomial and degree-based topological indices of Buckytubes. Symmetry 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasi, M.; Iranmanesh, A.; Gutman, I. Multiplicative version of first Zagreb index. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2012, 68, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Furtula, B.; Gutman, I.; Dehmer, M. On structure-sensitivity of degree-based topological indices. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 219, 8973–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, I.; Das, K.C. Some properties of the Second Zagreb Index. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2004, 50, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Gao, W.; Li, J.S. General harmonic index and general sum connectivity index of polyomino chains and nanotubes. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2015, 12, 3940–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shi, L. Wiener index of gear fan graph and gear wheel graph. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 3397–3400. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Wang, W. Second atom-bond connectivity index of special chemical molecular structures. J. Chem. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, W.F. The vertex version of weighted wiener number for bicyclic molecular structures. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.; Nazeer, W.; Rafique, S.; Kang, S.M. M-polynomial and degree-based topological indices of Nanostar dendrimers. Symmetry 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K.H.; Kang, D.Y. Defective Single-Walled Aluminosilicate Nanotubes: Structural Stability and Mechanical Properties. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavzar, S.; Deutsch, E. M-Polynomial and Degree-Based Topological Indices. Iran. J. Math. Chem. 2015, 6, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V.; Mannhold, R.; Kubinyi, H.; Timmerman, H. Handbook of Molecular Descriptors; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L.H.; Kier, L.B. Molecular Connectivity in Chemistry and Drug Research; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, K.H.; Tsou, N.T.; Kang, D.Y. Relationships among the structural topology, bond strength, and mechanical properties of single-walled aluminosilicate nanotubes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16222–16229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paineau, E.; Krapf, M.E.M.; Amara, M.S.; Matskova, N.V.; Dozov, I.; Rouzie`re, S.; Thill, A.; Launois, P.; Davidson, P. A liquid-crystalline hexagonal columnar phase in highly-dilute suspensions of imogolite nanotubes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thill, A.; Maillet, P.; Guiose, B.; Spalla, O.; Belloni, L.; Chaurand, P.; Auffan, M.; Olivi, L.; Rose, J. Physico-chemical Control over the Single- or Double-Wall Structure of Aluminogermanate Imogolite-like Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3780–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).