Abstract
A number of studies have explored visual symmetry processing by measuring event related potentials and neural oscillatory activity. There is a sustained posterior negativity (SPN) related to the presence of symmetry. There is also functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) activity in extrastriate visual areas and in the lateral occipital complex. We summarise the evidence by answering six questions. (1) Is there an automatic and sustained response to symmetry in visual areas? Answer: Yes, and this suggests automatic processing of symmetry. (2) Which brain areas are involved in symmetry perception? Answer: There is an extended network from extrastriate areas to higher areas. (3) Is reflection special? Answer: Reflection is the optimal stimulus for a more general regularity-sensitive network. (4) Is the response to symmetry independent of view angle? Answer: When people classify patterns as symmetrical or random, the response to symmetry is view-invariant. When people attend to other dimensions, the network responds to residual regularity in the image. (5) How are brain rhythms in the two hemispheres altered during symmetry perception? Answer: Symmetry processing (rather than presence) produces more alpha desynchronization in the right posterior regions. Finally, (6) does symmetry processing produce positive affect? Answer: Not in the strongest sense, but behavioural measures reveal implicit positive evaluation of abstract symmetry.
1. Introduction
There have been many studies on perception of symmetry, as reviewed in Tyler [1], Wagemans [2,3], Treder [4] and van der Helm [5]. More recently, researchers have explored the neural basis of symmetry perception in humans. We start with a brief discussion of why symmetry is important in the study of human vision. Next we review what has been learned about symmetry from event related potentials (ERP), neural oscillatory activity, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). As a strategy to review what is known and what remains to be discovered, we pose six questions about the neural processing of symmetry and provide tentative answers.
The six questions, which are dealt in separate sections below, are: (1) is there and automatic and sustained response to symmetry in visual areas? (2) Which brain areas are involved in symmetry perception? (3) Is reflectional symmetry special? (4) Is the response to symmetry view-independent? (5) How are brain rhythms in the two hemispheres altered during symmetry perception? Finally, (6) does symmetry processing produce an automatic emotional response?
1.1. The Importance of Symmetry
Symmetry has fascinated vision researchers and artists for a long time. Perhaps we can identify Ernst Mach as the first to bring attention to the nature of human symmetry perception. In his classic book [6] he pointed out how geometric regularities are perceived differently by human observers. People are more sensitive to reflectional symmetry (mirror symmetry) than to translation or rotation, and to vertical rather than horizontal reflections. The large psychophysical literature on symmetry perception has confirmed these observations (with some caveats [7,8]).
Why is the visual system so sensitive to the reflection between two sides of an object (bilateral symmetry)? From an evolutionary perspective, bilateral symmetry could be a reliable signal of mate quality [9]. Supporting this, humans are attracted to symmetrical faces [10] and symmetrical bodies [11,12]. Although there is also some evidence of publication bias in the human attractiveness studies [13], sensitivity to symmetry, and preference for bilateral symmetry, has been found in many species, both for mating [14] and for food choice [15]. Known symmetry-loving animals include finches [16], bees [17], pigeons [18], starlings [19], swordtail fish [20], and even newborn chicks [21]. There is also evidence that preference for symmetry is present already in human infants [22,23]. This large body of research strongly suggests that a symmetry-sensitive visual system is an adaptive phenotype, promoted by natural selection.
A more basic aspect of symmetry that makes it important for the visual system is that it facilitates image segmentation [24] and it can play a role in object analysis and representation [25]. Of course, there is no reason why these positions are mutually exclusive: symmetry could both play a basic role in image segmentation and indicate genetic quality. Preference for symmetry could also arise through another, indirect route: The fluency hypothesis states that fluent (i.e., rapid, efficient) perceptual processing creates positive hedonic feelings, which are sometimes attributed to the inherent quality of the stimulus [26,27]. People may thus like symmetry simply because it is fluently processed [28].
Human fascination with symmetry can be found in visual art across cultures and across history [29,30]. Ramachandran and Hirstein [31] listed symmetry as one of the fundamental aesthetics principles. This issue is of great interest in the context of neuroaesthetics [32,33] because it could link neural responses to symmetry and aesthetic preference for symmetry. As well as the evolutionary and fluency accounts of symmetry preference, there is also an idea that works of art optimally stimulate the perceptual system [34,35]. It is possible that artists use symmetry because the visual system is well tuned to this type of information. The fluency hypothesis and the optimal stimulation hypothesis are closely related, differing on the emphasis placed on fluency of processing by the individual or on objective stimulus properties. We will return to symmetry preference with our last question, where we will focus on whether symmetry automatically generates a positive emotional response.
1.2. Models of Symmetry Processing in the Brain
Given that a number of empirical facts are well established about perception of symmetry, models have been developed to try and explain human performance. For instance, the importance of the vertical axis of reflectional symmetry has led to the formulation of the callosal hypothesis, according to which the corpus callosum mediates the vertical symmetry advantage [36]. This view has not received much support, as it is not compatible with perception of symmetry when fixation is not on the axis and also with the fact that symmetry becomes more salient when multiple axes of reflection are present [3,4].
Another line of work has analysed the way that spatial filters can be used to extract symmetry from an image. In particular, when an image is subjected to spatial filters and thresholded, it can generate blobs that cluster around the axis of reflection [37,38]. Spatial filters are biologically plausible because receptive fields of cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and simple cells in V1 can be described as linear filters [39]. These linear models can explain human sensitivity to bilateral symmetry, but they fail to explain some other aspects, such as detection of symmetry when elements have opposite luminance polarity (anti-symmetry, [40]). To explain sensitivity to anti-symmetry and to symmetry with very low density of elements, Tyler and Hardage [41] proposed that second-order channels play an important role, and that detection of these second-order properties could involve long-range connections because performance varied little with eccentricity. Other studies, however, have found poor performance for detection of anti-symmetry with dense arrays [42]. A more recent type of filter model has been able to extend the response of the model to closed contours and to faces [43]. In alternative to filter models, other authors have worked on models that extract structural information [5,44]. This section is far from exhaustive, as we cannot review here all models that have been proposed. However, there is not yet a fully tested neural model of symmetry detection.
2. Six Questions
2.1. Question One: Is There an Automatic and Sustained Response to Symmetry in Visual Areas?
We start with a question with a clear answer. A sustained response to visual symmetry has been documented from several electroencephalography (EEG) studies. The interesting pattern is that symmetry modulates only later components of the visual event related potential (ERP) in a consistent way (Figure 1).
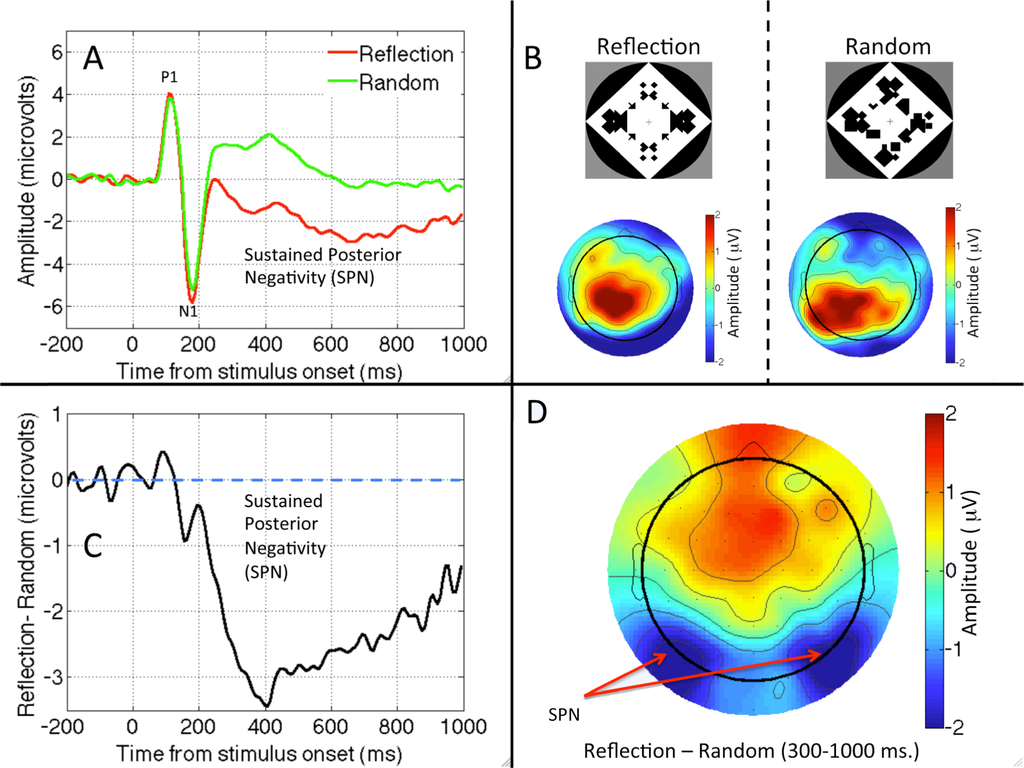
Figure 1.
The sustained posterior negativity (SPN). (A) Grand average waveforms from PO7/PO8 electrodes in Reflection and Random trials. (B) Topographic plot of Reflection and Random conditions. (C) The Grand average SPN as a difference wave (Reflection—Random). (D) SPN plot produced by subtracting the two plots in B. Data from Experiment 1 in [45].
Norcia, Candy, Pettet, Vildavski, and Tyler [46] presented observers with symmetric and random dot patterns. The ERP diverged from about 220 ms after onset, and symmetric stimuli were associated with a more negative wave. Jacobsen and Höfel [47] used abstract black and white patterns. They distinguished three ERP components, one of which was clearly related to symmetry. For occipital electrodes, amplitude was more negative in symmetrical than random trials, with the waves diverging after the P1 and N1 components of the visual evoked potential. This ERP was replicated in [48,49]. We will refer to this Sustained Posterior Negativity as SPN. Note that the SPN is a difference wave, and the term negative is relative, referring to the fact that amplitude is more negative in symmetrical than random conditions. The SPN is illustrated in different ways in Figure 1.
Experiments conducted in our lab in Liverpool have replicated the SPN with different types of symmetrical displays. For example, Makin, Wilton, Pecchinenda and Bertamini [45] used abstract stimuli similar to those used by Jacobsen and Höfel [47] (Figure 1), while Makin, Rampone, Pecchinenda and Bertamini [50] elicited the SPN with dot patterns (Figure 2). Rampone, Makin and Bertamini [51] recorded it with square field stimuli similar to those used by Royer [52], and Makin, Rampone, Wright, Martinovic and Bertamini [53] found it with line drawings (similar to those used in [54]).
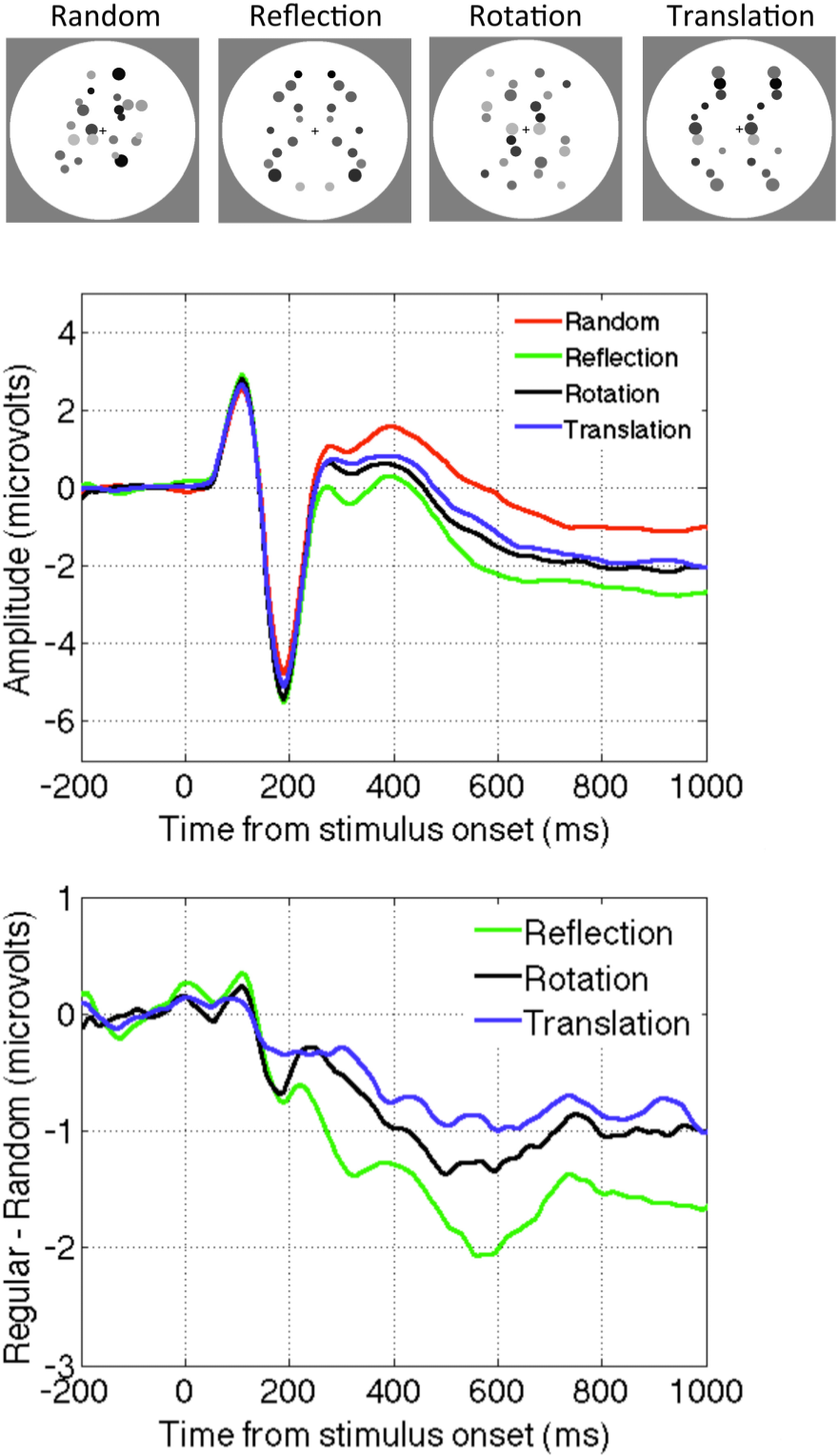
Figure 2.
The SPN for different kinds of regularity (Reflection, Rotation and Translation). Data from [50].
The latency of SPN onset varies from study to study, and different authors have used slightly different windows for analysis (different band-pass filtering of the EEG signal may also affect the apparent time course of the SPN). A typical onset is around 250 ms, and the component reaches maximum amplitude at around 300 ms. Symmetry related ERPs at earlier time points are inconsistent. Makin et al. [45,50] found an N1 modulation that could indicate the beginning of the negative wave. They speculated that this short-latency effect might have been masked in previous studies by large luminance changes at stimulus onset. Nevertheless the N1 effect will require further research to establish whether it represents a unique stage in symmetry processing. Certainly the amplitude of any N1 modulations is smaller than the later SPN (Figures 1 and 2).
In earlier ERP work, Beh and Latimer [55] found several visual evoked potentials components that were larger, and earlier, for horizontal and vertical reflections than asymmetrical or oblique reflection patterns, although this may have been a neural response to axis orientation rather than to symmetry. The sample size (N = 4 or 5), electrodes (O1–O2) and EEG pre-processing procedures used by Beh and Latimer [55] were substantially different from more recent work, perhaps explaining when they did not report a strong SPN.
The long duration of the SPN is also worth discussing. After onset this component is long lasting and stable. This suggests a long integration phase and it is consistent with psychophysical work. In particular Tyler, Hardage and Miller [56] have argued that information about symmetry is integrated over more than a second.
It is unlikely that the SPN is generated by a mechanism that maps spatially corresponding locations in the left and right visual hemifields [36]. Wright et al. [57] compared the SPN with horizontal and vertical orientations. For horizontal patterns the paired elements are presented within the same hemifield, but the SPN was similar irrespective of orientation. Other unpublished work from our lab has shown that a contralateral SPN can be recorded when symmetrical are presented entirely in a single hemifield.
It appears that the SPN is generated in response to symmetry in the image. In other words, the SPN is independent of task requirements, as well as being independent of the way symmetry is depicted. Höfel and Jacobsen [48] recorded the SPN when participants were not asked to categorize the patterns in terms of symmetry, while Höfel and Jacobsen [49] found the SPN when participants deliberately misreported their responses. Makin et al. [50] presented observers with symmetric and random patterns. In one study, participants discriminated regularity, in another, they responded to rare oddballs (an orthogonal visual dimension). The SPN was similar during active regularity discrimination and oddball detection. More recently, comparable SPN waves have been recorded irrespective of whether participants were discriminating regularity or number of objects [53], and whether participants were discriminating regularity or element colour [58]. These results suggest that the neural response to symmetry is automatic—it occurs even when participants are attending to other aspects of the stimulus. However, SPN amplitude can be modulated by attention to some extent. For example, there is a reduced SPN when participants attend to superimposed words presented on top of patterns [51].
Oka, Victor, Conte and Yanagida [59] reported a different kind of EEG response to symmetry, using the Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential (SSVEP) paradigm. Trials were 36 s of rapidly alternating reflection and random patterns, which participants viewed passively. The stimulus produced a driven oscillation at the presentation frequency (2 Hz) in occipital electrodes. The odd-harmonic was sensitive to symmetry: that is, there was another oscillation with a frequency of 1 Hz, the amplitude of which indexes the brain response to symmetry. In one analysis, they found that this response was proportional to the number of reflection axes present. This is a different kind of automatic and sustained response to symmetry, and its relationship with the SPN will require more research.
It is interesting that similar symmetry-related ERPs have shown up in studies with different research aims [60]. Moreover, the assumption of symmetry for partially occluded objects can lead to prediction errors once the occluder is removed, and this can also be recorded with electrophysiological techniques [61].
Finally, it is worth asking whether the SPN is really specific to symmetry, or whether one could record a comparable response to any stimulus with recognizable structure. The SPN wave closely resembles an object-related Late Component (sometimes divided into L1 and L2). This ERP wave is more negative for recognizable real objects than for matched scrambled images. Moreover, as with the SPN, the late component is found at posterior electrodes, beginning around 230 ms after stimulus onset and persisting until the end to the epoch [62,63]. It is therefore possible that perceptual grouping processes that are not exclusive to symmetry perception contribute to the SPN. However, the SPN response to symmetry cannot merely be one example of the more general Late component: A large SPN is present even when closed contours that have a reflection are compared to closed contours that do not have a reflection [53]. More work is necessary to clarify the relationship between ERP components specific to symmetry from ERP components specific to object identification.
2.2. Question Two: Which Brain Areas Are Involved in Symmetry Perception?
There have been several fMRI studies on symmetry perception. Tyler et al. [64] found a bilateral visual region of occipital cortex that responded strongly to the presence of symmetry compared to random patterns. Importantly, the contrast between symmetric and random patterns produced no activation of the primary visual area V1. A subsequent study [65] found that the network sensitive to symmetry included V3A, V4d/v, V7 and the lateral occipital complex (LO complex), and marginally present in V3. Again, V1 and V2 were not part of the network. The authors noted that the LO complex activation scaled with the proportion of regular elements in noisy images. Moreover, in the same paper the authors were also able to confirm that an analogous fMRI response to symmetry was present in conscious Macaque monkeys. More recently Chen, Kao, and Tyler [66] found that reflectional symmetry (in faces or abstract patterns) activated the intra-occiptal sulcus and medial occipital gyrus (areas overlapping with LO complex), while the right occipital face area was sensitive to symmetry in faces.
Two recent studies have tested the effect of TMS on perception of symmetry [67,68]. The authors argue that fMRI evidence cannot provide evidence for a causal role of any brain area, as it can only measure activity, while TMS allows a temporary localised disruption. Cattaneo et al. [68] used an adaptation paradigm and focused on the role of the dorsolateral occipital complex. They found that bilateral disruption affected perception of reflectional symmetry. Bona et al. [67] confirmed that the LO complex is involved in reflectional symmetry detection, as well as in contour detection. In addition they found a laterality effect—the right LO played a more important role than the left LO in symmetry detection. To explain the lack of laterality in the earlier work they suggested that stimuli with dense arrays might be necessary to show the right hemisphere advantage.
Makin, Wilton et al. [45] employed source localization analysis using low-resolution electromagnetic tomography (LORETA). They analysed the difference between waves (symmetry vs. random), and confirmed that the pattern was largely attributable to sources in the extrastriate visual cortex. We note, however, that this analysis was performed on grand-average difference maps (Figure 1D), and more sophisticated forms of source localization might yield different results. Nevertheless, given then converging evidence with fMRI and TMS, the SPN is likely to be generated by extrastriate and higher visual areas, and can be used as a measure of the symmetry-related activation of these areas. Moreover, these neural correlates support the idea that symmetry is related to object formation given the known role of LO complex in object representation [69].
As noted, the fMRI evidence suggests that symmetry is processed by a network of visual areas, rather than by a unique area. This is consistent with the involvement of feedback connections in form processing. Recent work has highlighted a role of deviation from prediction. Top-down connections carry predictions about the state of the world, while forward connections carry the residual errors between predictions and actual sensory input [70,71]. Redundant information is therefore key to understanding neural responses [72], which is relevant in the case of symmetry because symmetry is defined as self-similarity. In addition, it has been suggested that the first response to the presence of an object is in high-level areas, such as the LO complex, an idea known as inverse hierarchy [73].
Whether the principle of predictive coding apply also to perception of symmetry is an interesting topic for future research. One broadly related phenomenon has already been documented: van der Zwan, Leo, Joung, Latimer and Wenderoth [74] explored tilt after-effects generated by the implicit midline of reflectional symmetry. When the adapting and test patterns were presented to different eyes, an expansion-type tilt after effect was reduced. This could be because monocular cells in the primary visual cortex code the implicit symmetry axis, based on top down signals from symmetry representations in higher areas.
2.3. Question Three: Is Reflection Special?
In everyday language people often equate symmetry with bilateral symmetry, or with reflection, but in more formal terms, symmetry refers to different forms of self-similarity. If we consider the 2D plane, there are four types of symmetric patterns: Reflection, glide reflection, rotation and translation [75]. As we have mentioned, reflection is most salient for the human visual system [6]. It is plausible that sensitivity to abstract reflectional symmetry is a by-product of specialized face recognition/evaluation mechanisms, and thus dedicated networks may process reflectional symmetry alone. Alternatively, reflection might be the optimal stimulus for more general regularity-sensitive networks.
In the study by Sasaki et al. [65] the main findings about fMRI activation was based on comparing four-fold symmetry (reflection across vertical horizontal and oblique axes) and random stimuli. However, in the supplementary materials they also analysed other regularities they compared reflectional to translational symmetry, and found that reflection produced a larger response in the symmetry sensitive network.
Makin et al. [50] presented observers with abstract reflection, rotation, translation and random patterns. The SPN was present for all regularities. However, the amplitude of the SPN was most pronounced for reflection, and somewhat less for rotation and translation (Figure 2). There were some complicated interactions between task and the way random patterns were constructed. In one condition the dots could appear anywhere, in another they were constrained to have similar density and distribution as the symmetry patterns. A full discussion of this issue is outside the scope of this paper, and these considerations do not directly affect the argument. However, the evidence suggests that the neural networks that generate the SPN are sensitive to all regularities, and reflectional symmetry is merely the best stimulus for this regularity-sensitive network. There is no evidence for networks that are exclusively sensitive to reflection.
2.4. Question Four: Is the Neural Response to Symmetry View Invariant?
The evidence reviewed so far suggests that whenever visual symmetry is present at fixation, then the SPN is reliably generated. We have not yet considered whether symmetry has to be present in the image, or whether object-based symmetry will suffice. There is a large literature on how observers achieve view-invariance in the case of object perception and categorisation [76,77]. For symmetry perception, it has been shown that the perspective slant has a negative effect on detection performance. This could be because symmetry analysis follows an effortful and potentially time-consuming normalization process [78], or because symmetry analysis is based on the degraded structure in the retinal image after slanting. Van der Vloed, Csathó and van der Helm [79] argued in favour of the retinal structure hypothesis, and against the normalization hypothesis.
Makin, Rampone and Bertamini [58] revisited these competing accounts by measuring the SPN when patterns were presented in the frontoparallel plane or slanted by ±50 degrees (Figure 3A). One group of observers discriminated symmetry from random; another group reported the colour of the same stimuli (light red or dark red). For the group discriminating regularity the SPN was view-invariant: It was approximately the same size for frontoparallel and slanted presentations (Figure 3B). Conversely, for the group discriminating colour, the SPN was view-selective: Amplitude was reduced by approximately 50% in the slanted condition (Figure 3C). Makin, Rampone and Bertamini [58] concluded that the normalization account describes active symmetry discrimination, whereas the retinal structure hypothesis describes symmetry perception when people are attending to colour. Here the symmetry detection mechanism is still online, and still generates the SPN, but it only responds to residual structure in the image.
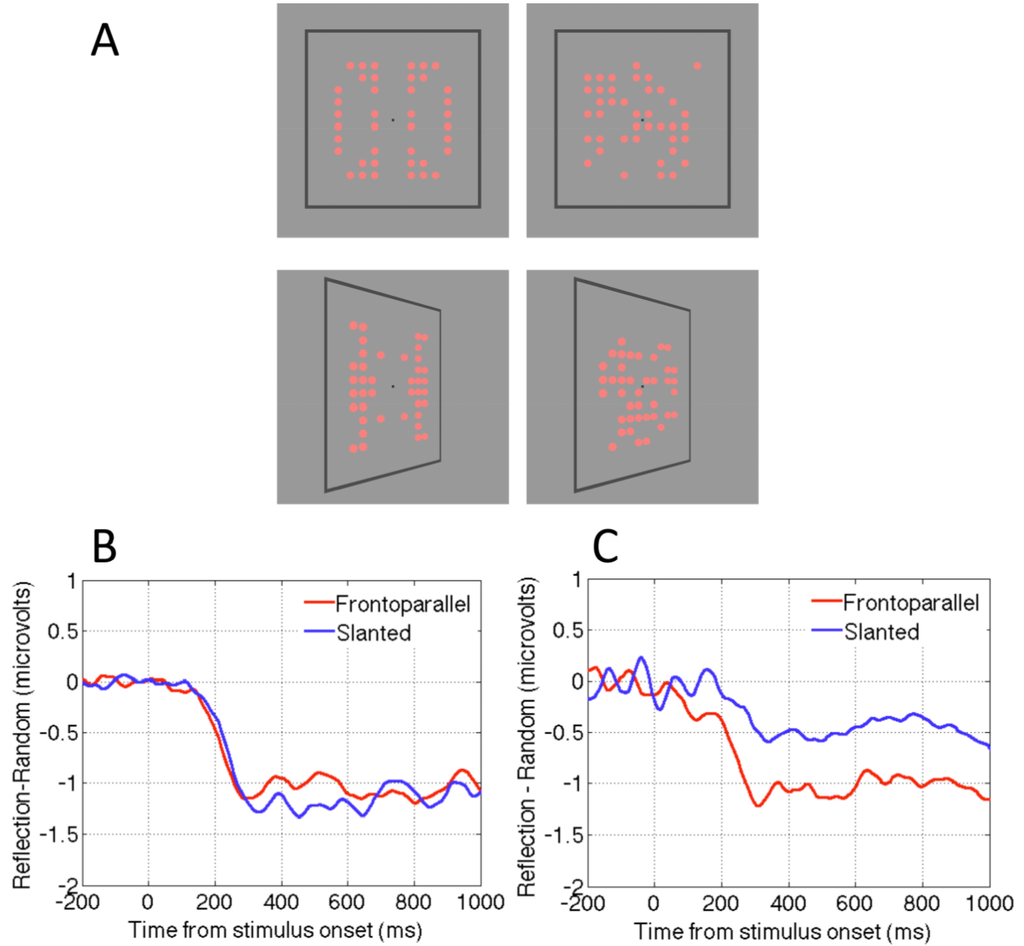
Figure 3.
View invariance and view dependence in the neural response to reflection. (A) Reflection and random patterns viewed in frontoparallel or slanted presentations. (B) The SPN shown as a difference wave (Reflection-Random) in the flat and slanted conditions, when participants were actively classifying trials according to regularity. Note that the response is independent of view angle. (C) The SPN when participants were classifying by colour. Note that the response is now view-selective, and reduced by around 50% for the slanted presentations. Images adapted from [58].
When view invariant responses were recorded in the discriminate regularity group (Figure 3B), the perspective normalization process must have occurred quickly. We do not believe that effortful, time consuming mental object rotation was employed prior to regularity analysis, because this would have delayed SPN onset considerably, and no such delay was observed. Nevertheless, some rapid correction for perspective distortion, perhaps facilitated by the frame, must have preceded the SPN-generating stage of symmetry analysis.
In this experiment the patterns had horizontal and vertical axes of reflection, and slanting destroyed regularity around the vertical axis, leaving horizontal reflection intact. The results of the colour discrimination task were remarkably systematic: 50% reduction in perfect structure for slanted patterns resulted in a ~50% reduction in SPN amplitude (Figure 3C). In a follow-up colour discrimination experiment, a single, vertical axis was used (Figure 4A). A strong prediction was that the SPN would be reduced to near zero in the slanted condition, because there is no intact retinal symmetry. This prediction was confirmed (Figure 4B). By comparing the results of both colour discrimination tasks, it can be seen that addition of an axis of symmetry in the 2D image increases the SPN by approximately 0.5 microvolts (Figure 4C). One has to be careful in interpreting a neat linear relationship given the indirect nature of the signal and the fact that the effect depends on the electrode clusters used for analysis. Nevertheless, the relationship between degree of regularity in the image and SPN amplitude in the colour task is interesting and provides a framework for future studies.
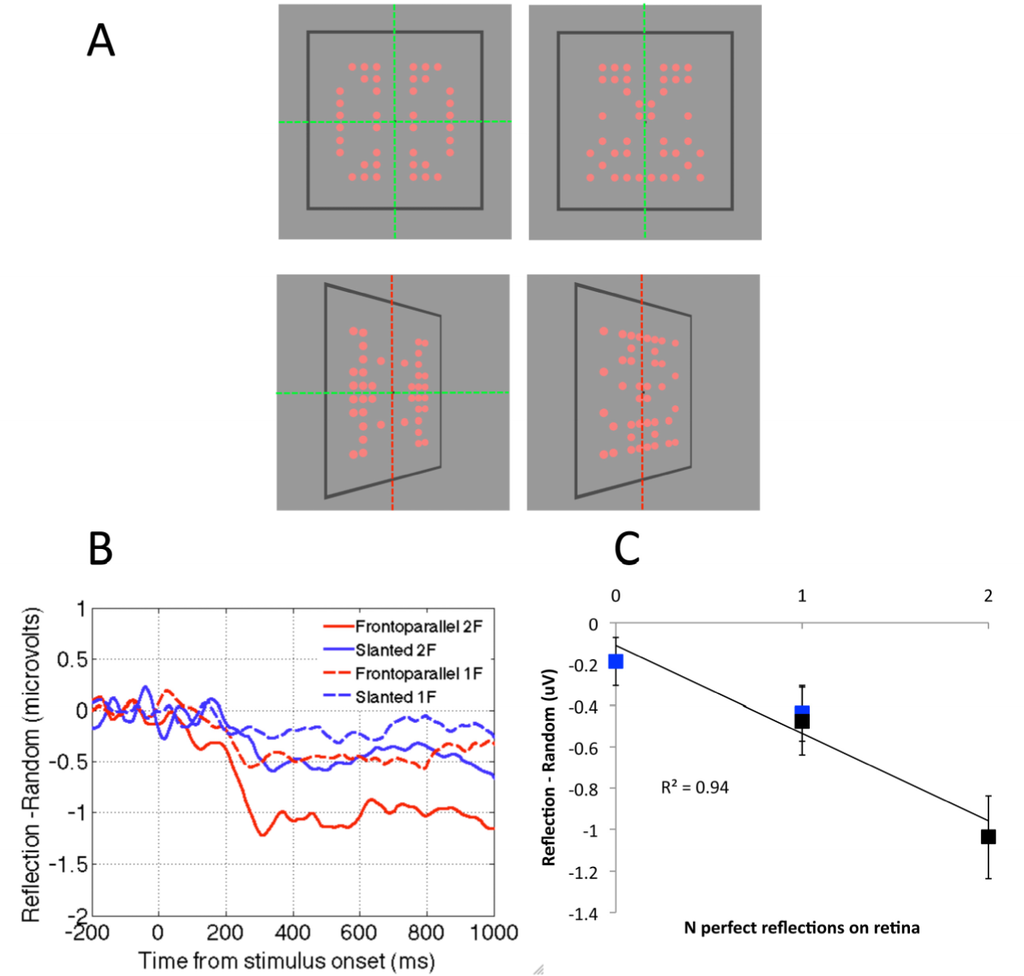
Figure 4.
Relationship between SPN amplitude and the number of axes in the image during colour discrimination tasks. (A) Dotted lines indicate axes of reflection for one and two-fold reflection patterns. Red dotted lines indicate axes that are in the distal object but are absent in the retinal projection. (B) SPN when participants were discriminating colour. Note that the SPN amplitude is related the amount of retinal structure. (C) Relationship between SPN amplitude and number of axes in the image. Error bars = +/−1 standard error of the mean. Images adapted from [58].
In conclusion, there is a view-invariant neural response to symmetry during active symmetry discrimination, and this view invariance is achieved efficiently. When attending to other features, the brain’s symmetry regions respond parametrically to whatever structure remains in the image after perspective distortion.
2.5. Question Five: How Are Brain Rhythms in the Two Hemispheres Altered During Symmetry Perception?
Oscillations are ubiquitous in neural networks, and different frequencies have different functional significance [80]. Gamma band oscillations (~25–100 Hz) and beta band oscillations (~15–20 Hz) synchronize task-relevant neural populations during active processing. These high frequency oscillations indicate cortical ON states [81]. Conversely, alpha oscillations (~8–13 Hz) have much higher power, and are associated with top-down inhibition, or cortical OFF states [82]. Therefore alpha and gamma power are inversely related (alpha goes up, gamma goes down, and vice versa). Event Related Desynchronization (ERD, i.e., a reduction) in the occipital alpha rhythm is ubiquitous after a visual onset, and this is thought to indirectly index excitation of visual areas [83,84]. Makin, Wilton et al. [45] have reported occipital alpha ERD from around 400 ms after stimulus onset during their symmetry/random discrimination tasks. This response differs from the SPN in that it is independent of the stimulus type: there is approximately the same occipital alpha ERD whether symmetrical or random images are presented.
With respect to hemispheric differences a clear pattern emerged. The occipital alpha ERD is greater over the right posterior hemisphere than the left during symmetry discrimination. In one study, Makin, Rampone, Wright et al. [53] found right lateralization of occipital alpha ERD during a reflection-translation discrimination task. In an important control experiment, this right lateralization was not observed in another group of participants who were presented with exactly the same stimuli, but were discriminating the number of objects presented. Right lateralization is thus related to the task, not just to the characteristics of the stimuli. It is tempting to conclude that right hemisphere networks are specialized for symmetry discrimination, and that this is linked to the right lateralization for other putatively related tasks, such as mental object rotation [85] and covertly shifting spatial attention [86]. The right lateralized ERD is also consistent with the right hemisphere attentional advantage for magnitude judgments [87]. However, it is thought that the occipital alpha rhythm is produced by loops connecting the thalamus to early visual regions [80], while the above tasks are associated with cerebral asymmetries of the fronto-parietal network. This remains a major ambiguity.
One possible alternative explanation for right lateralized ERD is that participants consistently attend to the left visual hemifield during regularity discrimination tasks, and this enhances visual inputs in the contralateral right hemisphere. Wright et al. [57] have recently tested this idea. Participants were presented with vertical or horizontally oriented patterns (Figure 5A), and made a reflection vs. translation judgement. The scanning from the left hypothesis predicts that alpha ERD should only be lateralized in the vertical condition. In the horizontal trials, corresponding shift of attention would be upwards or downwards, and this would not produce lateralized activity. There was a consistent right lateralization for alpha ERD for horizontal and vertical patterns (Figure 5B). This suggests that the right lateralization is the result of anatomical specialization of the right hemisphere for this task, not the transient enhancement of contralateral inputs.
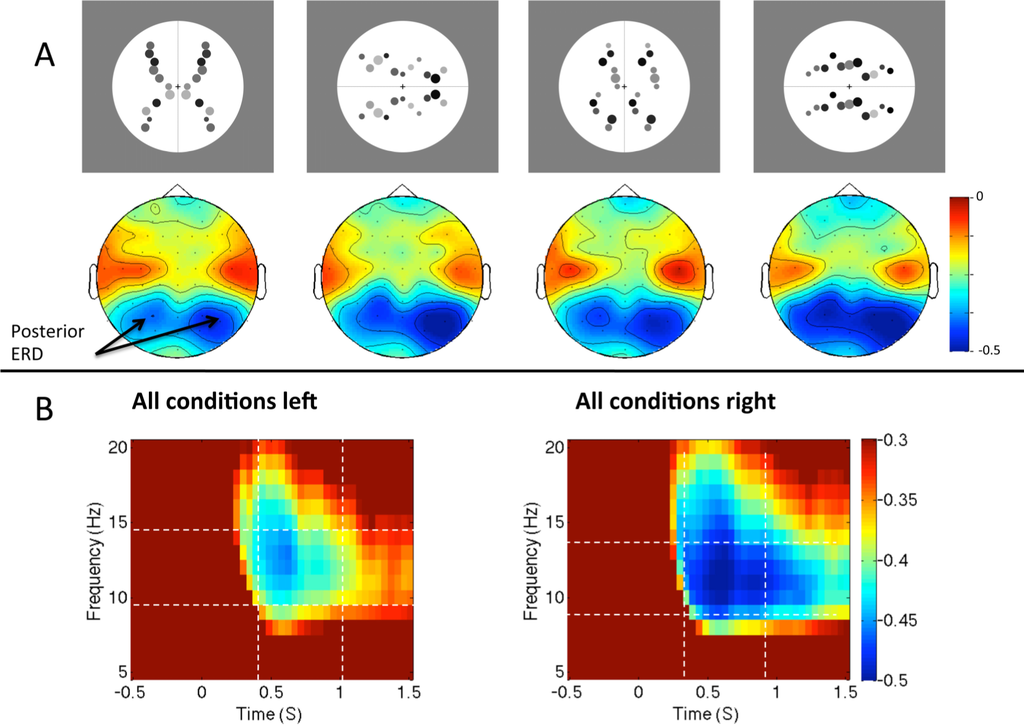
Figure 5.
Alpha desynchronization in response to different regularities. (A) Topographic maps show relative alpha power from 400 to 1000 ms, 10–14 Hz, for the different regularities and orientations (stimuli shown above corresponding maps). (B) Time-frequency spectrograms (averaged across conditions) from left and right posterior electrodes. Images adapted from [57].
Why, then, have other neuroimaging techniques not picked up on this persistent right hemisphere specialization? It is important to note that the right ERD is common to all conditions, so a reflection-random contrast would not show this effect. It is thus unsurprising that Sasaki et al. [65] do not report right lateralization in their fMRI study. This cannot be said of another neuroimaging study by Jacobsen, Schubotz, Höfel and Cramon [88]. They compared fMRI activity in a symmetry discrimination task with aesthetic evaluation and baseline tasks. There was no evidence for right lateralization in the symmetry task, which is inconsistent with the ERD findings. Conversely, there is some evidence for right lateralization from TMS studies, as mentioned above [67]. It could be that there is only a brief window when right hemisphere networks become active during symmetry discrimination (perhaps around 400–1000 ms post stimulus) and fRMI lacks the temporal resolution to detect this.
Is there any evidence for hemispheric specialization from the SPN? Most papers about the SPN have not reported any lateralization, but they may have lacked power. We decided to test this possibility by combined data from previous recordings of the SPN (220 participants in total: 24 participants from [57], 60 participants from [45], 48 participants from [50], and 40 participants from [53], and 48 participants from [58]). All these experiments showed a clear SPN component (averaging across sub conditions when necessary). We re-analyzed this data using the same left and right posterior electrodes and the same SPN time window (250 to 1000 ms). We explored this with a mixed ANOVA. There were two within-subjects factors (Hemisphere (Right, Left) X Regularity (Regular, Less regular)) and one between-subjects factor with 5 levels (Experiment). There was a main effect of Regularity (F(1215) = 123.09, p < 0.001), which was stronger in some experiments than others (F(4215) = 4.933, p = 0.001). Interestingly effect of Regularity was qualified by a Hemisphere X Regularity interaction (F(1215) = 10.795, p = 0.001), which did not interact with the between-subjects factor Experiment (F(1215) < 1, n.s.). Although the SPN was significant on the left (t(219) = 9.543, p < 0.001) and right (t(219) = 11.173, p < 0.001) it was stronger on the right (hence the significant interaction). Therefore, this lateralization is weak and unlikely to be detected in every experiment, but is evident when multiple datasets are combined.
Hemispheric specialization has been a theme in the symmetry perception literature. Corbalis and Roldan [89] found that symmetrical patterns could be detected slightly quicker when presented to the right hemisphere (i.e., in the left visual field). More recently, Verma, van der Haegen and Brysbaert [90] presented symmetrical or asymmetrical shapes to either hemisphere while participants fixated centrally. For neuro-typical participants who were left-hemisphere dominant for language, symmetry detection was superior when images were presented to the right hemisphere. For atypical right-hemisphere language participants, this bias was absent or sometimes reversed. It seems that symmetry detection systems are present in both cerebral hemispheres, but the right hemisphere dominates in most people (see also [91,92]). This literature differs from the ERD lateralization in an important way. It shows that the neural response to symmetry is right lateralized, while alpha ERD is right lateralized when either symmetry or random patterns are presented. However, it is consistent with right lateralization of the SPN, which is a symmetry-specific response. It seems reasonable to conclude that symmetry perception produces slightly greater activity in the right hemisphere than the left, but different neuroimaging techniques are differentially sensitive to this.
We do not yet know the role of high-frequency gamma band oscillations during symmetry perception. Theoretical work on gamma suggests that neurons coding each pattern element should oscillate between high and low excitatory states at a high frequency, and, crucially, that the phase of these gamma oscillations should be synchronized across the population of relevant cells. This synchronized neural ensemble could underlie perceptual binding, and facilitate memory formation or communication with downstream populations involved in classification or verbal report [80,93]. As indirect evidence for this, we note that the latency of the symmetry related SPN and alpha ERD is similar to the typical latency of the induced gamma band response during object recognition [62].
2.6. Question Six: Does Symmetry Processing Produce an Automatic Affective Response?
This final question may seem very different from the other five questions, as we are now interested in whether there is any evidence of a positive affective response to symmetry. When people are asked to explicitly evaluate the aesthetic appeal of abstract patterns, symmetry is a good predictor of preference [94]. As discussed earlier, symmetry is often mentioned in relation to aesthetics, and even as one of the fundamental laws of artistic experience [31]. Meanwhile, symmetrical faces and bodies signal that development has proceeded according to the genetic template, with minimal environmental perturbation from parasites and accidents. Reflectional symmetry is thus a truthful signal of health and many animals are sensitive to this information [9]. For this and the other reasons reviewed in the introduction, there could be a generalized emotional response to abstract symmetry.
The ERP study by Jacobsen and Höfel [47] compared two conditions, called “descriptive” and “evaluative”. In the descriptive condition participants classified patterns as symmetrical or random. In the evaluative condition, they classified patterns as beautiful or not beautiful. In addition to the symmetry-SPN, the authors reported two additional ERPs related to aesthetic evaluation. The subjectively “not beautiful” patterns produced frontocentral negativity, at around 300–400 ms. All conditions produced a Late Positive Potential (LPP), but this was right lateralized in the evaluation conditions only. A later study Höfel and Jacobsen [48] re-examined these ERPs. They showed the patterns in a pure viewing condition and in an aesthetic contemplation condition. The frontocentral negativity was completely absent in all conditions, indicating that it is generated by aesthetic categorization. Lateralized LPP was only present in the aesthetic contemplation condition. Both ERP correlates of aesthetic evaluation were absent in the viewing condition, leading the authors to conclude that: “Aesthetic appreciation of beauty appears to require intention and is not spontaneous in character” (p. 30).
Jacobsen, Schubotz, Höfel, and Cramon [88] used fMRI to record the correlates of aesthetic judgment of beauty for abstract stimuli. They found that the aesthetic judgment led to activations in several areas, including the frontomedian cortex, bilateral prefrontal, and posterior cingulate. These activations were different from those observed when people classified the symmetry of the stimuli, although there was a degree of overlap. Their conclusion can be seen as pointing away from an automatic evaluation of symmetry: “Brain activations during aesthetic judgment cannot be reduced to an assessment of symmetry but are actually due to a particular mode of judgment” (p. 284).
Makin, Wilton et al. [45] recorded Electromyography (EMG) signals from the Zygomaticus Major muscle, which is responsible for smiling [95]. Participants were merely classifying the patterns as symmetrical or random, and were not asked to form any aesthetic judgement. Nevertheless, the smiling response was larger in the symmetrical trials, indicating an automatic positive response to symmetry. Moreover, the size of this response correlated with the size of the SPN. This result could be interpreted as evidence that participants whose brains are more sensitive to symmetry also like it more! However, Experiment 2 of that study led to different conclusions. Participants were given “Yes” and “No” buttons. Half the participants pressed “Yes” for symmetry and “No” for random. For the other participants, the response mapping was reversed (“No” for symmetry, “Yes” for random). Interestingly, the Zygomaticus Major response followed the response mapping, not the stimuli: Participants smiled for whichever patterns required them to press the “Yes” button. We conclude that in two alternative forced-choice tasks (2AFC), one option takes on the status of target [96], and people may like it when they find what they are looking for. There was no evidence therefore of an automatic affective response to symmetry per se.
To clarify this research question, it is essential to distinguish between different potential readings of the term “automatic affective response”. The strongest claim would be that symmetrical patterns spontaneously produce an emotional reaction, as a reflex, incorporating both peripheral physiological arousal and the subjective experience of positive hedonic tone. A weaker, and more plausible, claim is that people may spontaneously, but coldly and cognitively, classify patterns as positive or negative, even without any requirement to consider or report aesthetic merit [97].
Despite the fact that symmetry is so often mentioned as a basic principle of aesthetics, we are not aware of any evidence for the strong kind of automatic emotional response to symmetry, using any kind of physiological measure. However, there is evidence for qualified forms of automatic evaluation. This has been tested with the Implicit Association Test (IAT) [98]. Makin, Pecchinenda et al. [28] asked people to classify stimuli using two buttons. In some trials, people classified patterns as symmetrical or random. On interleaved trials, they classified words as positive or negative. On congruent blocks, the same key was used to report symmetry and positive, and the other key was used to report random and negative. On incongruent blocks, the response mapping was reversed (random or positive vs. symmetry or negative). Participants were faster in the congruent blocks, indicating implicit preference for symmetry over random. This effect was robust, and the size of the implicit preference for different kinds of regularity was correlated with the perceptual fluency of these regularities, while there was some divergence between implicit and explicit preferences. Further Implicit Association Test experiments have shown that the symmetry is also associated with high arousal words and simple, easy mathematical equations [99]. The IAT certainly shows a form of implicit evaluation; however these studies are not evidence for automatic affective response to symmetry in the strongest sense. By its nature the IAT measure strength of association for categories that people have to actively classify.
Affective priming studies can be used to measure implicit evaluation of briefly presented abstract symmetry. Here symmetrical or random patterns are presented as primes, rapidly followed by positive or negative words. Participants have to classify the word as quickly as possible. One would predict a congruency effect: Faster responses to positive words following symmetry and faster responses to negative words following random. Bertamini, Makin and Pecchinenda [100] found this congruency effect, but only in a modified version of the procedure, when observers had to classify the regularity of the prime pattern after responding to the word. There is no evidence that symmetrical patterns are evaluated when they are not attended or classified. Conversely, Pecchinenda, Bertamini, Makin and Ruta [101] did find evidence for automatic evaluation using the affect misattribution procedure (AMP). This is a variant of the affective priming paradigm. In this procedure symmetric and random patterns are presented as primes and targets are unfamiliar and neutral. The affective response to the prime was misattributed to the neutral targets.
Rampone et al. [51] investigated pattern-word congruency effects with EEG. Symmetrical or random patterns were presented, with positive or negative words superimposed. Participants either discriminated regularity (reflection or random) or word valence (positive or negative). The crucial finding here was a congruency wave. Posterior ERPs distinguish between congruent (Reflection with positive or random with negative) and incongruent (Reflection with negative or random with positive) presentations, even though the component stimuli were identical in both conditions. This suggests that the brain rapidly and spontaneously codes the relationship between pattern and word valence, even though this was not a task requirement. However, the congruence effect was only found in the word discrimination task. One explanation is that when people are evaluating words, they automatically evaluate the background as well. The results also bear other interpretations: It could be that this posterior ERP was the SPN response to symmetry, which was attenuated in the word discrimination task, but more so when participants read negative words than positive words. The congruence ERPs reported by [51] are interesting, but not conclusive.
In summary, there is little evidence for an automatic emotional response to abstract symmetry in humans in the strongest sense, despite its undoubted aesthetic appeal and biological significance. Nevertheless, people have a near-universal preference for symmetrical over random patterns, and this can be measured indirectly with IAT and with modified affective priming procedures.
3. Conclusions
We reviewed work in symmetry perception focusing in particular on electrophysiological and imaging studies. We asked and tried to address six questions. (1) Is there and automatic and sustained response to symmetry in visual areas? Yes, such a response has been reliably replicated in at least ten ERP studies, with no known failures to replicate. There is issue open for future studies: this response to symmetry could be related to (although not reduced to) similar changes to visual networks following the segmentation of a meaningful gestalt. (2) Which brain areas are involved in symmetry perception? Symmetry perception is mediated by extrastriate visual networks, which can be imaged with fMRI and disrupted by TMS. These networks probably generate the SPN. V1 may only be involved in coding the implicit orientation of the axis, based on top down signals from this network. (3) Is reflectional symmetry special? Perhaps surprisingly, there is no evidence that reflection is detected by specialized mechanisms. Instead, reflection is the optimal stimulus for a more general regularity sensitive network. (4) Is the neural response to symmetry view-invariant? During active symmetry classification, the answer is yes. The brain responds in the same way to symmetry whatever the view angle. Conversely, when people are attending to other pattern features, symmetry networks are still online, but respond to the remaining structure in the image. (5) How are brain rhythms altered during symmetry perception? Whenever a symmetrical or random pattern is presented, there is a generic desynchronization of the alpha rhythm over posterior electrodes. This ERD is right lateralized during symmetry discrimination. This is partially consistent with other evidence that symmetry discrimination is a right hemisphere task. It is plausible, but untested, whether representations of pattern elements are bound by gamma band synchronization during symmetry perception. Finally, (6) does symmetry processing produce an automatic emotional response? There is no evidence for this in the strongest sense. Mere presentation of symmetry does not produce a physiologically detectable emotional reaction. However, people reliably prefer symmetrical to random abstract patterns, and this can be recorded with implicit behavioural techniques.
Acknowledgments
This project was possible thanks to a Grant from the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC, Ref. ES/K000187/1). Makin is funded by a Leverhulme Trust Early Career Fellowship (ECF-2012-721).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tyler, C.W. Empirical aspects of symmetry perception. Spat. Vis 1995, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wagemans, J. Detection of visual symmetries. Spat. Vis 1995, 9, 9–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wagemans, J. Characteristics and models of human symmetry detection. Trends Cogn. Sci 1997, 1, 346–352. [Google Scholar]
- Treder, M.S. Behind the looking glass: A review on human symmetry perception. Symmetry 2010, 2, 510–543. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Helm, P.A. Symmetry perception. In The Oxford Handbook of Perceptual Organization; Wagemans, J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mach, E. The analysis of sensations and the relation of the physical to the psychical; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Bertamini, M. Sensitivity to reflection and translation is modulated by objectness. Perception 2010, 39, 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wenderoth, P. The salience of vertical symmetry. Perception 1994, 23, 221–236. [Google Scholar]
- Grammer, K.; Fink, B.; Møller, A.P.; Thornhill, R. Darwinian aesthetics: Sexual selection and the biology of beauty. Biol. Rev 2003, 78, 385–407. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, G.; Proffitt, F.; Grady, J.M.; Sumich, A. Facial symmetry and the perception of beauty. Psychon. Bull. Rev 1998, 5, 659–669. [Google Scholar]
- Bertamini, M.; Byrne, C.; Bennett, K.M. Attractiveness is influenced by the relationship between postures of the viewer and the viewed person. i-Perception 2013, 4, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Tovee, M.J.; Tasker, K.; Benson, P.J. Is symmetry a visual cue to attractiveness in the human female body? Evol. Hum. Behav 2000, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen, S. Associations between asymmetry and human attractiveness: Possible direct effects of asymmetry and signatures of publication bias. Ann. Hum. Biol 2011, 38, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, A.; Thornhill, R. Bilateral symmetry and sexual selection: A meta-analysis. Am. Nat 1998, 151, 174–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wignall, A.E.; Heiling, A.M.; Cheng, K.; Herberstein, M.E. Flower symmetry preferences in honeybees and their crab spider predators. Ethology 2006, 112, 510–518. [Google Scholar]
- Swaddle, J.P.; Cuthill, I.C. Female zebra finches prefer males with symmetrical chest plumage. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci 1994, 258, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, I.; Gumbert, A.; de Ibarra, N.H.; Kunze, J.; Giurfa, M. Symmetry is in the eye of the “beholder”: Innate preference for bilateral symmetry in flower-naive bumblebees. Naturwissenschaften 2004, 91, 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Delius, J.D.; Habers, G. Symmetry: Can pigeons conceptualize it? Behav. Biol 1978, 22, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Swaddle, J.P.; Ruff, D.A.; Page, L.C.; Frame, A.M.; Long, V.A. A test of receiver perceptual performance: European starlings’ ability to detect asymmetry in a naturalistic trait. Anim. Behav 2008, 76, 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor, M.S.; Morris, M.R. Experience plays a role in female preference for symmetry in the swordtail fish xiphophorus malinche. Ethology 2009, 115, 812–822. [Google Scholar]
- Clara, E.; Regolin, L.; Vallortigara, G. Preference for symmetry is experience dependent in newborn chicks (Gallus gallus). J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process 2007, 33, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein, M.H.; Ferdinandsen, K.; Gross, C.G. Perception of symmetry in infancy. Dev. Psychol 1981, 17, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, G.K.; Humphrey, D.E. The role of structure in infant visual-pattern perception. Can. J. Psychol 1989, 43, 165–182. [Google Scholar]
- Machilsen, B.; Pauwels, M.; Wagemans, J. The role of vertical mirror symmetry in visual shape detection. J. Vis 2009, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Pizlo, Z.; Steinman, R.M. A computational model that recovers the 3D shape of an object from a single 2D retinal representation. Vis. Res 2009, 49, 979–991. [Google Scholar]
- Reber, R. Processing fluency, aesthetic pleasure, and culturally shared taste. In Aesthetic Science: Connecting Mind, Brain, and Experience; Shimamura, A.P., Palmer, S.E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 223–249. [Google Scholar]
- Reber, R.; Winkielman, P.; Schwartz, N. Effects of perceptual fluency on affective judgments. Psychol. Sci 1998, 9, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, A.D.J.; Pecchinenda, A.; Bertamini, M. Implicit affective evaluation of visual symmetry. Emotion 2012, 12, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Washburn, D.K.; Crowe, D.S. Symmetries of Culture; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim, R. Art and Visual Perception: A Psychology of the Creative Eye; University of California Press: Berkley, CA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, V.S.; Hirstein, W. The science of art: A neurological theory of aesthetic experience. J. Conscious. Stud 1999, 6, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A. Neuroaesthetics: A coming of age story. J. Cogn. Neurosci 2011, 23, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Leder, H.; Belke, B.; Oeberst, A.; Augustin, D. A model of aesthetic appreciation and aesthetic judgments. Br. J. Psychol 2004, 95, 489–508. [Google Scholar]
- Zeki, S. Art and the brain. J. Conscious. Stud 1999, 6, 76–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zeki, S. Neural concept formation and art: Dante, Michelangelo, Wagner. J. Conscious. Stud 2002, 9, 53–76. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, A.M.; Humphrey, G.K. Bilateral symmetry detection: Testing a “callosal” hypothesis. Perception 1996, 25, 463–480. [Google Scholar]
- Dakin, S.C.; Hess, R.F. The spatial mechanisms mediating symmetry perception. Vis. Res 1997, 37, 2915–2930. [Google Scholar]
- Dakin, S.C.; Watt, R.J. Detection of bilateral symmetry using spatial filters. Spat. Vis 1994, 8, 393–413. [Google Scholar]
- Movshon, J.A.; Thompson, I.D.; Tolhurst, D.J. Spatial summation in the receptive fields of simple cells in the cat’s striate cortex. J. Physiol 1978, 283, 53–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wenderoth, P. The effects of the contrast polarity of dot-pair partners on the detection of bilateral symmetry. Perception 1996, 25, 757–771. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, C.W.; Hardage, L. Mirror symmetry detection: Predominance of second-order pattern processing throughout the visual field. In Human Symmetry Perception and Its Computational Analysis; Tyler, C.W., Ed.; VSP; Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, S.; Sally, S.L.; Gurnsey, R. Detection of symmetry and anti-symmetry. Vis. Res 2005, 45, 2145–2160. [Google Scholar]
- Poirier, F.J.A.M.; Wilson, H.R. A biologically plausible model of human shape symmetry perception. J. Vis 2010, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wagemans, J.; van Gool, L.; Swinnen, V.; van Horebeek, J. Higher-order structure in regularity detection. Vis. Res 1993, 33, 1067–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, A.D.J.; Wilton, M.M.; Pecchinenda, A.; Bertamini, M. Symmetry perception and affective responses: A combined EEG/EMG study. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 3250–3261. [Google Scholar]
- Norcia, A.M.; Candy, T.R.; Pettet, M.W.; Vildavski, V.Y.; Tyler, C.W. Temporal dynamics of the human response to symmetry. J. Vis 2002, 2, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, T.; Höfel, L. Descriptive and evaluative judgment processes: Behavioral and electrophysiological indices of processing symmetry and aesthetics. Cogn. Affective Behav. Neurosci 2003, 3, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Höfel, L.; Jacobsen, T. Electrophysiological indices of processing aesthetics: Spontaneous or intentional processes? Int. J. Psychophysiol 2007, 65, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Höfel, L.; Jacobsen, T. Electrophysiological indices of processing symmetry and aesthetics: A result of judgment categorization or judgment report? J. Psychophysiol 2007, 21, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, A.D.J.; Rampone, G.; Pecchinenda, A.; Bertamini, M. Electrophysiological responses to visuospatial regularity. Psychophysiology 2013, 50, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Rampone, G.; Makin, A.D.J.; Bertamini, M. Electrophysiological analysis of the affective congruence between pattern regularity and word valence. Neuropsychologia 2014, 58, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Royer, F.L. Detection of symmetry. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform 1981, 7, 1186–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, A.D.J.; Rampone, G.; Wright, A.; Martinovic, J.; Bertamini, M. Visual symmetry in objects and gaps. J. Vis 2014, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bertamini, M.; Friedenberg, J.D.; Kubovy, M. Detection of symmetry and perceptual organization: The way a lock-and-key process works. Acta Psychol 1997, 95, 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Beh, H.C.; Latimer, C.R. Symmetry detection and orientation perception: Electrocortical responses to stimuli with real and implicit axes of orientation. Aust. J. Psychol 1997, 49, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, C.W.; Hardage, L.; Miller, R.T. Multiple mechanisms for the detection of mirror symmetry. Spat. Vis 1995, 9, 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, D.; Makin, A.D.J.; Bertamini, M. Right-lateralized alpha desynchronization during symmetry discrimination: Hemispheric specialization or directed spatial attention? Psychophysiology 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Makin, A.D.J.; Rampone, G.; Bertamini, M. Conditions for view invariance in the neural response to visual symmetry. Psychophysiology 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Victor, J.D.; Conte, M.M.; Yanagida, T. VEPs elicited by local correlations and global symmetry: Characteristics and interactions. Vis. Res 2007, 47, 2212–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Verleger, R.; Görgen, S.; Jaśkowski, P. An ERP indicator of processing relevant gestalts in masked priming. Psychophysiology 2005, 42, 677–690. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, T.C.J.; Bauer, M.; Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; van Lier, R. Cortical responses to contextual influences in amodal completion. Neuroimage 2006, 32, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, T.; Müller, M.M. Oscillatory brain activity dissociates between associative stimulus content in a repetition priming task in the human EEG. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Martinovic, J.; Mordal, J.; Wuerger, S.M. Event-related potentials reveal an early advantage for luminance contours in the processing of objects. J. Vis 2011, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, C.W.; Baseler, H.A.; Kontsevich, L.L.; Likova, L.T.; Wade, A.R.; Wandell, B.A. Predominantly extra-retinotopic cortical response to pattern symmetry. Neuroimage 2005, 24, 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y.; Vanduffel, W.; Knutsen, T.; Tyler, C.W.; Tootell, R. Symmetry activates extrastriate visual cortex in human and nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3159–3163. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Kao, K.L.C.; Tyler, C.W. Face configuration processing in the human brain: The role of symmetry. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Bona, S.; Herbert, A.; Toneatto, C.; Silvanto, J.; Cattaneo, Z. The causal role of the lateral occipital complex in visual mirror symmetry detection and grouping: An fMRI-guided TMS study. Cortex 2014, 51, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, Z.; Mattavelli, G.; Papagno, C.; Herbert, A.; Silvanto, J. The role of the human extrastriate visual cortex in mirror symmetry discrimination: A TMS-adaptation study. Brain Cogn 2011, 77, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kourtzi, Z.; Kanwisher, N. Representation of perceived object shape by the human lateral occipital complex. Science 2001, 293, 1506–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A. Whatever next? Predictive brains, situated agents, and the future of cognitive science. Behav. Brain Sci 2013, 36, 181–204. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, R.P.N.; Ballard, D.H. Predictive coding in the visual cortex: A functional interpretation of some extra-classical receptive-field effects. Nat. Neurosci 1999, 2, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, S.J.; Boynton, G.M.; Murray, S.O. Long-range, pattern-dependent contextual effects in early human visual cortex. Curr. Biol 2012, 22, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein, S.; Ahissar, M. View from the top: Hierarchies and reverse hierarchies in the visual system. Neuron 2002, 36, 791–804. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Zwan, R.; Leo, E.; Joung, W.; Latimer, C.; Wenderoth, P. Evidence that both area V1 and extrastriate visual cortex contribute to symmetry perception. Curr. Biol 1998, 8, 889–892. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.E. On goodness, Gestalt, groups, and Garner: Local symmetry subgroups as a theory of figural goodness. In The Structure of Perception; Lockhead, G., Pomerantz, J., Eds.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Biederman, I.; Gerhardstein, P.C. Recognizing depth-rotated objects—Evidence and conditions for 3-dimensional viewpoint invariance. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform 1993, 19, 1162–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.H.; Gilson, S.J. Recognizing novel three-dimensional objects by summing signals from parts and views. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci 2002, 269, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar]
- Szlyk, J.P.; Rock, I.; Fisher, C.B. Level of processing in the perception of symmetrical forms viewed from different angles. Spat. Vis 1995, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Vloed, G.; Csatho, A.; van der Helm, P.A. Symmetry and repetition in perspective. Acta Psychol 2005, 120, 74–92. [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki, G. Rhythms of the Brain; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, P. A mechanism for cognitive dynamics: Neuronal communication through neuronal coherence. Trends Cogn. Sci 2005, 9, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W.; Sauseng, P.; Hanslmayr, S. EEG alpha oscillations: The inhibition-timing hypothesis. Brain Res. Rev 2007, 53, 63–88. [Google Scholar]
- Laufs, H.; Holt, J.L.; Elfont, R.; Krams, M.; Paul, J.S.; Krakow, K.; Kleinschmidt, A. Where the BOLD signal goes when alpha EEG leaves. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Sauseng, P.; Klimesch, W.; Stadler, W.; Schabus, M.; Doppelmayr, M.; Hanslmayr, S.; Gruber, W.R.; Birbaumer, N. A shift of visual spatial attention is selectively associated with human EEG alpha activity. Eur. J. Neurosci 2005, 22, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, L.M. Superior parietal cortices and varieties of mental rotation. Trends Cogn. Sci 2003, 7, 515–517. [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam, M.M. Functional anatomy of attention and neglect: From neurons to networks. In The Cognitive and Neural Bases of Spatial Neglect; Karnath, H., Milner, D., Vallar, G., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, M.E.; Roberts, G.R. Can free-viewing perceptual asymmetries be explained by scanning, pre-motor or attentional biases? Cortex 2002, 38, 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, T.; Schubotz, R.I.; Höfel, L.; Cramon, D.Y. Brain correlates of aesthetic judgment of beauty. NeuroImage 2006, 29, 276–285. [Google Scholar]
- Corballis, M.C.; Roldan, C.E. Perception of symmetrical and repeated patterns. Percept. Psychophys 1974, 16, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; van der Haegen, L.; Brysbaert, M. Symmetry detection in typically and atypically speech lateralized individuals: A visual half-field study. Neuropsychologia 2013, 51, 2611–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Brysbaert, M. Lateral preferences and visual-field asymmetries—Appearances may have been overstated. Cortex 1994, 30, 413–429. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, D.T.; Halligan, P.W. The effects of stimulus symmetry on landmark judgments in left and right visual fields. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, O.; Kaiser, J.; Lachaux, J.-P. Human gamma-frequency oscillations associated with attention and memory. Trends Neurosci 2007, 30, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, T.; Höfel, L. Aesthetic judgments of novel graphic patterns: Analyses of individual judgments. Percept. Mot. Skills 2002, 95, 755–766. [Google Scholar]
- Winkielman, P.; Cacioppo, J.T. Mind at ease puts a smile on the face: Psychophysiological evidence that processing facilitation elicits positive affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol 2001, 81, 989–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Rothermund, K.; Wentura, D. Underlying processes in the implicit association test: Dissociating salience from associations. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen 2004, 133, 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth, K.L.; Bargh, J.A.; Garcia, M.; Chaiken, S. The automatic evaluation of novel stimuli. Psychol. Sci 2002, 13, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Nosek, B.A.; Greenwald, A.G.; Banaji, M.R. The implicit association test at age 7: A methodological and conceptual review. In Automatic Processes in Social Thinking and Behavior; Bargh, J.A., Ed.; Psychology Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 265–292. [Google Scholar]
- Bertamini, M.; Makin, A.; Rampone, G. Implicit association of symmetry with positive valence, high arousal and simplicity. i-Perception 2013, 45, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Bertamini, M.; Makin, A.D.J.; Pecchinenda, A. Testing Whether and When Abstract Symmetric Patterns Produce Affective Responses. PLoS One 2013, 87, e68403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchinenda, A.; Bertamini, M.; Makin, A.D.J.; Ruta, N. The pleasantness of visual symmetry: Always, never or sometimes. PLoS One 2014, 9, e92685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).