Abstract
Previous studies have suggested that the back-reaction of super-Hubble cosmological fluctuations on a symmetric background space-time, with respect to being homogeneous and isotropic, could behave like a dynamical relaxation of the cosmological constant. Moreover, this mechanism appears to be self-regulatory, potentially leading to oscillatory behavior in the effective DE. Such an effect would occur in any cosmological model with super-Hubble matter fluctuations, including the standard CDM model. Apart from that, recent DESI data, which indicate that DE may be dynamical, have renewed interest in exploring scenarios leading to such an oscillatory behavior. In this study, we propose a parameterization to account for the impact of super-Hubble fluctuations on the background energy density of the Universe. We model the total effective cosmological constant as the sum of a constant and an oscillating contribution. We performed a preliminary comparison of the background dynamics of this model with recent radial BAO data from DESI. We also discuss the status of the tension problem in this model.
1. Introduction
In the current paradigm of cosmology, the CDM model, the dark energy (DE) component, which comprises the majority of today’s cosmological energy density, is parametrized by a positive cosmological constant term, , in the Einstein equations. Despite its apparent simplicity, this interpretation faces conceptual problems. In addition to some well-known problems, such as the cosmological constant problem [1,2,3,4,5], the coincidence problem [3,4,6], and the Hubble tension [7,8,9], a model with a positive cosmological constant (which leads to de Sitter evolution in the far future) faces some conceptual challenges. In particular, there are indications that a de Sitter space might be unstable due to infrared (IR) effects [10,11,12,13,14,15]. In the context of String Theory, there have also been indications that it is not possible to obtain a stable de Sitter phase [16,17,18,19], and the recently suggested “Trans-Planckian Censorship Criterion” [20,21,22] implies that a positive cosmological constant is not consistent from an effective field theory point of view. In the work of Refs. [23,24], it was suggested that the reason our universe (assuming that a bare cosmological constant drives an initial period of inflation) stopped inflating is that IR processes in pure quantum gravity (no matter) tend to screen the bare . However, the authors of [24] found that the screening effects become important only after perturbation theory has broken down. In 1997, the work of Ref. [25] studied the back-reaction of super-Hubble modes of cosmological perturbations induced by matter, finding that the effective energy density associated with these modes would counteract any pre-existing (see also [26,27,28]). Later, in 1999, Ref. [29] speculated that this dynamical relaxation mechanism for could be self-regulating. Note also the related “Everpresent Lambda” scenario, which was proposed by drawing on ideas from causal set theory and unimodular gravity, and which leads to an effective fluctuating cosmological “constant”; see Refs. [30,31,32], for instance. A crucial question that remained at that time was whether this back-reaction effect could be measured locally [33,34,35]. Recent works have shown that super-Hubble fluctuation modes can, in fact, modify the parameters of a local Friedmann cosmology when measured by a clock field [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49]. In the context of the back-reaction of sub-Hubble cosmological fluctuations, a recent analysis can be found, for instance, in Ref. [50]. Another approach to account for the back-reaction effect can be found in the works of Refs. [51,52,53]. In [54], the analysis was extended beyond perturbation theory, showing that the locally measured Hubble expansion rate indeed obtains a negative contribution from the back-reaction of super-Hubble fluctuations. This supports the suggestion that (quasi) de Sitter space-times are unstable and that the back-reaction mechanism might lead to a dynamical relaxation of the cosmological constant. As first speculated in Ref. [29], this is expected to lead to an effective DE density, which oscillates in time around the dominant matter density.
The quest for understanding the nature and dynamics of the accelerated expansion of the Universe has become even more interesting recently, given the new observational measurements that allow us to better constrain the expansion history of the Universe. In particular, the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Year 1 (DR1) [55,56,57] and DESI DR2 [58,59] results were released, officially marking the start of the Stage IV DE era. The cosmological results stem from measurements of baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) in galaxies, quasars, and Lyman- forest tracers. The DESI results, when combined with a number of external probes, provide intriguing hints for a dynamical, time-evolving DE component [55,56,57]. These hints were present already in the DR1 release (see, however, Ref. [60] for caveats). Later, the enhanced statistical power and extended redshift coverage of DESI DR2 sustained the preference for a dynamical DE component, yielding a level of statistical significance comparable to or greater than that reported for DESI DR1 [58,59,61]. These hints may have enormous implications for understanding the nature of DE and align with expectations from certain fundamental theory frameworks [62].
In light of these results, recent works, among them [63,64], have pointed to signals, from late-time cosmological data, of oscillatory/non-monotonic features in the dependence of the expansion rate as a function of redshift z at low redshifts (see, however, Ref. [65] for a warning that oscillatory features in can be induced when fitting for this function given incomplete data. In addition, DESI full-shape modeling does not show a signal [66]). The possibility of oscillating DE has already been addressed in earlier studies, such as in Refs. [56,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86], but without a justification for such oscillations from fundamental physics in mind. In Ref. [64], in light of the recent cosmological data, including DR1, twelve different parameterizations for an oscillatory DE equation of state were analyzed, among them the ones proposed in Refs. [70,71,78,87]. The analysis demonstrated that all the oscillating DE parameterizations considered provide a better fit to the DR1 data when compared to the pure cosmological constant model, although in a Bayesian evidence analysis, they are penalized due to the additional free parameter. In the study of Ref. [63], the late-time expansion history was reconstructed in a way, according to the authors, to be “as model-independent and non-parametric as possible” (see also [88,89]). In their first reconstruction, using DR1 + PantheonPlus data, two features in the unnormalized expansion rate were identified, a bump at redshift , and a depression at (both features were absent when replacing the DESI dataset with the older SDSS one). The depression feature was noticeable in both the DR1+PantheonPlus and DR1+Union3 reconstructions, but not in the DR1+DES Y5 one (for more information on the reconstruction methods, see Ref. [63]). While the Chevallier–Polarski–Linder (CPL) fit (the parameterization often considered when interpreting DESI data) is able to partially capture the data, it cannot fit the oscillator features. Fitting the data may require an oscillatory scaling of the Hubble expansion rate [63]. More recently, some studies (see [90] for instance) have found evidence for an oscillating behavior of the DE equation of state from the more recent DESI DR2 data.
While conclusive results will require more precise future data, we believe that it is now important to further investigate the theoretical mechanisms that could account for an oscillatory dynamical behavior of DE. As discussed above, the back-reaction effect of super-Hubble fluctuations is a mechanism based on fundamental physics ideas that could naturally lead to an oscillatory behavior for the DE density, and consequently for the Hubble parameter, without the need for extra ingredients beyond General Relativity coupled to standard matter. This back-reaction effect is present in any cosmological model whenever super-Hubble cosmological fluctuations are present.
In the present work, we investigate the consequences of a parameterization of the Hubble expansion rate that can account for the back-reaction effect of super-Hubble fluctuations by means of an oscillating effective energy density component. This may provide a complete non-perturbative description of the back-reaction effect. We then analyze such a model, considering data from the radial component of the BAO from the recent DESI DR2 data. We compute the Hubble parameter at low redshifts as predicted by this model and compare the results with the data to constrain the amplitude of the oscillations. We also analyze the predictions of the model for the effective DE equation of state, the deceleration parameter, and for .
Our study should be considered a first-step analysis limited to considering background quantities, aiming only to highlight the importance of not neglecting the back-reaction mechanism.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we define a parameterization that can describe the back-reaction of super-Hubble fluctuations in the late universe. In Section 3, we discuss the data analysis methods used to compare our model predictions with the recent DESI results. In Section 4, we present our results, and we conclude in Section 5.
2. A Model for the Back-Reaction of Super-Hubble Fluctuations
The Einstein field equations are well known to be highly nonlinear. Even at the classical level, second-order fluctuations affect the background. This effect is called the back-reaction. Matter fluctuations induce metric fluctuations via the Einstein equations. In our case, these same fluctuations back-react on top of a symmetric space-time with respect to being homogeneous and isotropic. The full evolution of the metric is governed by the Einstein equations
where is the Einstein tensor of the metric , G is Newton’s gravitational constant, and is the energy-momentum tensor of matter.
All that is important for the back-reaction analysis is that there is matter with a non-vanishing average energy density present. For late universe studies, this matter can be treated as being hydrodynamical. Metric and the matter component (taken for simplicity to be a scalar matter field ) can be written, at linear order in the amplitude of cosmological fluctuations, as
and
In the absence of anisotropic stress, the scalar metric fluctuation variables and in Equation (2) are equal. To write the metric, we have chosen a particular coordinate system (longitudinal gauge) (see, e.g., [91] for a review of the theory of cosmological perturbations). In Equation (2), is the background metric of the constant time hypersurfaces. We assume vanishing spatial curvature and then . In the above equations, the background metric is given by the scale factor and the background matter is given by . We will only consider the effects of scalar metric fluctuations.
To determine how the linear fluctuations affect the background, we substitute the ansatz Equations (2) and (3) into the Einstein equations and expand to second order. The zeroth-order terms satisfy the background equations. The linear terms are assumed to obey linear perturbation equations. In this case, the Einstein equations are not satisfied at the quadratic order. The back-reaction is a method to correct this at the quadratic order. The quadratic terms on the left-hand side of Equation (1) can be moved to the right hand side of the equation, where they form an effective energy-momentum tensor when combined with the quadratic terms in [25,92],
where the superscript (2) indicates the order of the terms.
At second order, the linear perturbations modify the background metric. This effect can be described by introducing a modified background metric
where the first term is the original background metric and the second term reflects the quadratic corrections to the background.
By taking the spatial average of the Einstein Equation (1), expanded to the second order, we can describe the corrections to the background. Following the method proposed in [25,92] (and reviewed in [93]), we can write the resulting equation in the form
where the first term on the right-hand side of the equation is the contribution of the background matter field to . Improved studies of the back-reaction of super-Hubble fluctuations focus on physically measurable quantities such as the spatial average of the local Hubble expansion rate [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] even beyond perturbation theory [54]. Some of these results point to a self-adjusting mechanism for the cosmological constant, as first discussed in [29].
The origin of the self-adjustment mechanism for the relaxation of the cosmological constant is as follows [29]: in the accelerating phase, fluctuation modes exit the Hubble radius and freeze out. Cosmological perturbations induced by super-Hubble matter fluctuations contribute to the effective energy-momentum tensor, which has the form of a negative cosmological constant (negligible kinetic and tension energies leading to an effective equation of state , and negative effective energy density-negative since matter induces a potential well and the negativity of the gravitational energy overwhelms the positivity of the matter energy for super-Hubble modes). This induces a decrease in the effective cosmological constant by counteracting the effect of the pre-existing . However, once the energy density in the effective cosmological constant falls below that of matter, the accelerated expansion will stop, the modes will re-enter the Hubble radius, the decline in will halt, and within a fraction of the Hubble time, a renewed buildup of the back-reaction effect will take place. This will lead to oscillations of the effective dark energy density about the dominant matter energy density, which is the dark matter density, at the small redshifts that we are considering. These oscillations are expected to have a period of the order of the Hubble time.
In light of this, we propose the following parameterization for the effective energy density associated with the back-reaction of super-Hubble fluctuations:
where A is a dimensionless amplitude, f plays the role of a frequency of oscillation, is the phase, and is the background density of matter. The proposed expression, given in Equation (7), characterized by an oscillatory cosine term, captures the anticipated periodic behavior, as motivated by the study presented in [29]. Rather than representing a first-principles solution for the energy density of the back-reaction fluid, it serves as a parameterization expected to closely approximate the density function that can be rigorously derived from the effective energy-momentum tensor described in Equation (4). The typical timescale of these oscillations is set by the Hubble time. Furthermore, this ansatz encapsulates the expectation that, following the epoch of matter-radiation equality at redshift , the back-reaction term closely tracks the matter energy density . Note that an oscillatory contribution to the DE density was recently also shown to emerge from a model in which the DE field emerges from the dynamics of a highly curved field space motivated by string theory [94]. This assumption is justified by the recognition that the matter component is primarily responsible for the fluctuations that generate the back-reaction.
Even being hard to address the dynamics precisely (since once the back-reaction effect becomes large, we are in the nonlinear regime of cosmological perturbation theory), if the universe would continue to accelerate, the net dark energy (initial bare cosmological constant plus the contribution of super-Hubble modes) would drop to zero. Before this happens, the matter (or radiation) density will take over, at which point the decrease of would stop. This induces oscillations of which are not overdamped but could be damped. The damping time scale will be the Hubble time since it is the Hubble time which determines the gravitational dynamics.
Now about the amplitude parameter in Equation (7), the study of the back-reaction of super-Hubble cosmological perturbations shows that the induced negative contribution to the cosmological constant grows in time as long as the universe is accelerating. So, a priori, it is expected that the amplitude should be time-dependent. However, in the present work, we will focus on the late-time predictions, since we are going to analyze our model in light of data in the range . For this small redshift interval, it is reasonable to consider to be constant. Therefore, in the rest of this paper, we are going to consider the following expression for the effective density from the back-reaction effect
The contribution of the energy density from the back-reaction effect is added to the total energy of the universe, in such a way that the first Friedmann equation can be written as
where we have kept a bare cosmological constant term . We are working in units in which the speed of light c is 1.
By substituting Equation (7) in the above equation, we can write the first Friedmann equation as follows:
where the subscripts 0 indicate the quantities at the present time.
Another important quantity to be analyzed is the deceleration parameter, which must show a transition from a decelerated regime to an accelerated regime as the DE starts to dominate. The deceleration parameter is , where the prime indicates derivative with respect to the redshift. By using the above equation, we obtain for the deceleration parameter the following expression:
Concerning phase , we will choose it such that the back-reaction mechanism is set to 0 at redshift , the redshift of recombination. The choice of this phase is not important for the conclusions drawn in this study.
We can now compute the equation of state associated with the back-reaction effective fluid. The continuity equation is not valid in the usual form for this fluid, because of the energy transfer from the cosmological fluctuations to this effective component [95]. In this case, in order to obtain , we can consider the second Friedmann equation for the total fluid (considering all the components of the Universe):
By isolating in the above equation and considering that , we obtain the following expression for the equation of state,
In Section IV, we illustrate the behavior of the Hubble parameter at low redshifts, the deceleration parameter, and the effective equation of state for the chosen values of the frequency and amplitude in Equation (7).
In this study, we restrict our analysis to the background dynamics. We then do not need to make extra assumptions on the cosmological model at the perturbative level. However, the above expression provides some insights in light of specific datasets, such as the radial component of BAO, which we will discuss in the next section.
3. Methods and Data Analysis
The BAO method is one of the main methods developed to measure the expansion history of the Universe (for a more complete discussion, see, for instance, [96,97,98]). In the pre-recombination Universe, acoustic oscillations in the baryon-photon fluid imprinted a characteristic scale on the clustering of matter, which manifests as a bump in the two-point correlation function of matter (or as a series of oscillations in the power spectrum). The comoving scale of this feature is given by the sound horizon at the end of the baryon drag epoch, . This quantity depends on the photon and baryon content of the universe at this epoch and is well constrained by CMB measurements. The BAO feature can be traced by galaxies, quasars, and the Lyman- forest.
The BAO signature can be measured in two ways: one can use the angular diameter distance to determine the physical length scale corresponding to a certain angle on the sky of the observer, or one can use the difference in redshift to infer some physical radial distance. Therefore, there are measurements of the apparent size of the BAO standard ruler perpendicular and parallel to the line of sight, allowing one to constrain the angular diameter distance and Hubble parameter , respectively. If the Hubble parameter of our universe is different from that predicted by the model considered, then there will be differences in the radial BAO scale.
Therefore, we can decompose the BAO locations into transverse and line-of-sight dilation parameters, denoted by the Alcock–Paczynski-like dilation parameters and , which are linked to the angular diameter distance and the Hubble parameter, respectively, at a given redshift. Here in this work we are interested in the line-of-sight parameter, which is defined as [98]
where the “fid” denotes the quantities measured in the fiducial cosmology, which is the Planck-normalized CDM model used to convert redshifts into distances in the survey. Using the notation of Ref. [58], we can write . In the above, is the comoving sound horizon evaluated at the redshift at which the baryon-drag optical depth is equal to unity, and it depends on quantities at redshifts higher than that. In the case of the back-reaction model presented in Section 2, the quantity will be considered to be equal to the fiducial one, since we are not investigating the effects of back-reaction at earlier times. Therefore, in our analysis, we are going to consider the approximate expression, For a similar analysis in a different context, see, for instance, the work of Ref. [99]:
where . We are going to use information from the DESI DR2 galaxy, quasar, and Lyman- results [58] to interpret the constraints on in terms of constraints on at given redshifts.
The data we considered are described in the following Table 1:

Table 1.
Dataset used for from the DESI DR2 galaxy, quasar, and Lyman- results taken from Ref. [58], and its interpretation in terms of at given redshifts.
Our procedure is as follows: First, we solved Equation (10) (with taken to be the same as in the fiducial cosmology) in order to obtain H(z) predicted by the back-reaction model. From this, we can plot the resulting function for the model, together with the observational values and error bars shown in Table 1. However, to plot the quantity predicted by the back-reaction model, the parameters in Equation (7) must be fixed. As mentioned earlier, the phase is fixed such that is zero at redshift . The amplitude A and the “frequency” f remain to be fixed. We will focus on the values of the amplitude, which are of the order of . Larger amplitude values would give rise to excessively large oscillations of the Hubble parameter, whereas smaller values would not lead to observable differences compared to our fiducial cosmology. We cannot determine the amplitude from the considerations in Section 2 because this would require a non-perturbative calculation that has not yet been achieved. However, the considerations in Section 2 imply that the frequency of oscillation is set by a fraction of the Hubble rate. Hence, we would expect that a non-fine-tuned frequency would correspond to a value of f with an order of magnitude approximately equal to one.
The results obtained are presented in the next section.
4. Results
In this section, we show the predictions of the back-reaction model compared with the data of Ref. [58]. In Figure 1, we show the late-time behavior of the quantity (curves in color) as predicted by the back-reaction model, for values of the amplitude ranging from zero (which represents ) to and for a fixed frequency characterized by the parameter introduced in Equation (10). These predictions were compared with the DESI DR2 results (red dots and error bars). Different shapes of the theoretical curve can be obtained using different values of frequency and amplitude. We choose, just for the sake of illustration, examples of values that provide a shape for the curves that track the DESI data better than the standard CDM model. In addition, in choosing the frequency value to be illustrated in the figures, we selected models that can alleviate the Hubble tension even slightly, and we disregarded models with too high frequencies () since they could lead to smaller simply due to overfitting. Among the frequency values that satisfy these criteria, we chose the one that provides the smaller , which corresponds to . However, higher values for the frequency can be considered, also providing a value lower than the CDM. Figure A1 in the Appendix A shows the same plot as Figure 1 but for DR1 data. Comparing Figure 1 with Figure A1, we see that the evidence of an oscillating DE component is stronger in DR2 than in DR1.
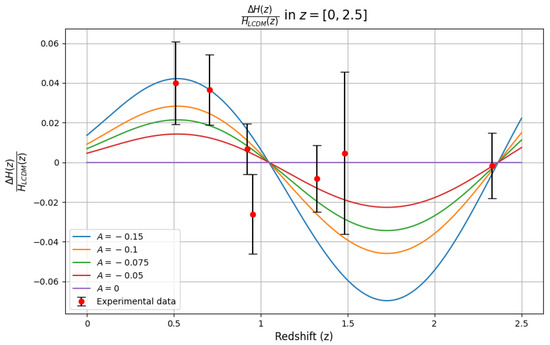
Figure 1.
predicted by the back-reaction model compared with DESI DR2 data.
Note that the values of the free parameters (amplitude and frequency) used are within the range of values that can be considered as “reasonable” from the theoretical point of view. In particular, the frequency was in the range expected from qualitative arguments.
Although the results appear promising, our preliminary analysis should not be viewed as conclusive in terms of statistical evidence. With future data releases, the error bars are expected to shrink, and by combining those with datasets from other sources, it should then be possible to obtain a more solid conclusion on the preference of the data for CDM or a dynamical DE. The objective of Figure 1 is to show the range of amplitudes of the oscillating DE term which can be in agreement with the DESI constraints. We can see that, for the chosen value , values as low as can fit the data within the observational uncertainties.
We performed a minimization of the of the model with respect to the DESI DR2 data points. The method used consists of executing a set of minimization routines, such that for each minimization sequence, we chose the initial values of A to lie within the range , and those of f within . These intervals correspond to the initial guesses of suitable parameter values and are the starting points for parameter exploration.
The expression to be minimized is the of (which expresses the relative difference between the proposed model and the standard cosmological model as a function of redshift) with respect to the experimental data from DESI DR2. As described previously, the DESI experimental results were interpreted in terms of , and the error propagation was calculated. Some minimization results lead to a shape that is more in line with the one indicated by the DESI data than others. However, in practically all the cases considered, for the mentioned initial values, the obtained were smaller than that of the CDM model. However, these analyses were restricted to amplitudes with an order of magnitude or smaller. For larger values of A, the fit is poor. This is shown in Figure 2, where the value of is plotted as a function of the amplitude. From this same figure, we can also see that for values of the amplitude higher than zero and lower than , the back-reaction model provides a fit worse than the standard model (which is recovered for the value , the star in the plot). We can also see from Figure 2 that the minimum value of the is shifted with respect to the CDM value. A similar plot using the data from DR1 is presented in the Appendix A. By comparing the as a function of the amplitude for the two datasets, DR1 and DR2, we see that the minimum value of the does not change significantly. However, from the overall analysis, we obtain that the frequencies that tend to provide best fitting for the DR2 data are generally smaller than the ones that fit better the DR1 data. This general tendency seems to agree with the results of Ref. [100]. While the error bars still do not allow us to conclude that our model performs better than CDM, these results can be viewed as an indication of the importance of further studies of this model rather than a firm statistical conclusion.
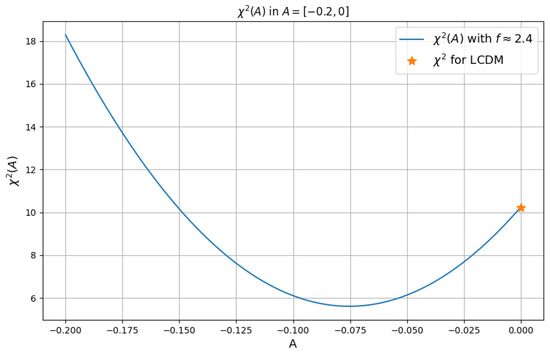
Figure 2.
The value of for the back-reaction model with respect to DESI data as a function of the parameter A. The value for CDM is represented by a star.
In Figure 3 and Figure 4, we plot the deceleration parameter and equation of state (EOS) of the total fluid, all components included, according to the equations in Section 2. The pair of values was chosen as an illustrative example in all these figures. We can see in Figure 3 that this model is able to correctly predict the transition from decelerated to accelerated expansion around the expected redshift.
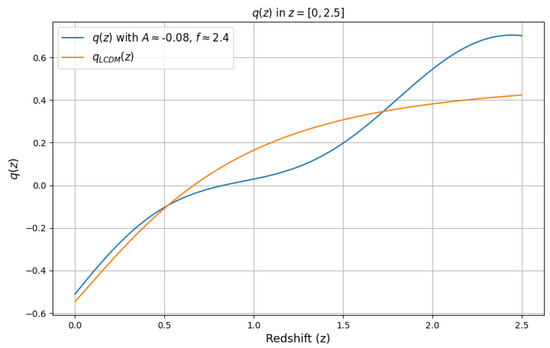
Figure 3.
Deceleration parameter from to predicted by the back-reaction model, together with the CDM prediction.
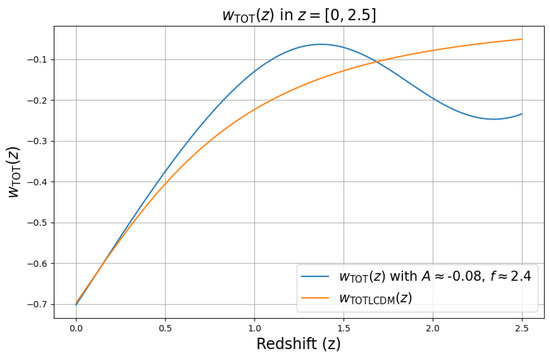
Figure 4.
The evolution of the total effective equation of state predicted by the back-reaction model, together with the CDM prediction.
As explained previously, the self-adjusting behavior of the back-reaction mechanism should have a time-scale of the order of the Hubble time, which determines the gravitational dynamics. The simplest way (which we adopted) to model this dynamic is by an oscillatory (or damped oscillatory) function. One could ask whether the back-reaction mechanism could be described through a different time-dependent function, where the net equation of state changes more sharply than exactly periodically. We do not expect any qualitative differences, in this small redshift range, if the time dependence were slightly different from the oscillatory form we have assumed. On the other hand, if the time dependency was much different than in our parametrization, it would probably lead to too large a deviation from the expected behavior. For instance, as seen in Figure 3, our parametrization, in addition to describing the self-adjusting oscillatory behavior, is able to predict the expected redshift of the transition from acceleration to deceleration.
The effective equation of state for the total fluid exhibited the expected overall behavior, as shown in Figure 4, i.e., it oscillates around the prediction.
Another major challenge that has become more pressing following the DESI data is the Hubble tension problem [101,102,103]. Recent results from DR2 bolster the case for a dynamical DE scenario that exhibits phantom crossing behavior. This framework yields a lower inferred value of the Hubble constant, thereby intensifying the Hubble tension, which can be regarded as a symptom of potential underlying inconsistencies in the standard model. Therefore, it is interesting to analyze in which cases and for which values of the parameters the back-reaction model considered can provide some relief to the Hubble tension. To shed some light on this question, we perform an analysis of the value of predicted for different combinations of the parameters f and A. The analysis used the method described previously. In Figure 5, we show a plot of () as a function of A, where is the value of f chosen from the minimization method performed. We can see in the plot that, for the representative chosen values of the parameters, the predicted by our model is very close to the CDM one. This is partly due to the choice of the fixed A and f and also due to the fact that the back-reaction contribution is proportional to , therefore decreasing at later times, causing the difference in our model with respect to CDM also to decrease.
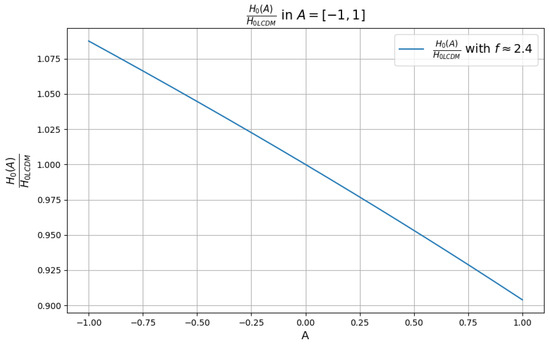
Figure 5.
as a function of A, for f chosen from the minimization method performed.
From all the results of our minimizations, the highest value that was obtained was , which was achieved for and . For the amplitude , for instance, we obtain ; that is, it is basically indistinguishable from . Nevertheless, it may be possible to solve the Hubble tension given sufficiently high absolute values of the amplitude. However, from Figure 1 we can see that such high absolute values of A do not provide a good fit to the DESI data. If we extrapolate and investigate the Hubble constant value for an amplitude as low as , we obtain , considering .
It is important to emphasize again that a priori, there is no reason that the amplitude A should be independent of time. In fact, considering the back-reaction, it is not unreasonable to expect that the effective amplitude of the oscillating contribution to DE performs damped oscillations. In this case, A could be large at early times and then slowly decay to a value consistent with the current late-time data. Therefore, this extended scenario might provide a solution to the Hubble tension. However, without a careful analysis of the fluctuations produced in the model, it is not possible to gauge whether such a scenario would be consistent with other constraints; for example, the value of . Our results then show that the inclusion of back-reaction effects from super-Hubble fluctuations can offer valuable insights in light of recent observational data.
5. Conclusions
In the present work, we studied a parameterization of oscillating DE, motivated by the back-reaction of super-Hubble fluctuations in the late universe. This model takes into account the back-reaction effect on the background cosmology and is based on the conjectured dynamical scaling fixed-point solution describing the back-reaction effect at a fully non-perturbative level. We computed the Hubble parameter at low redshifts predicted by the model, obtaining oscillatory dynamics. We also compared the resulting background cosmology with the data from the radial component of the BAO obtained from the recent DESI survey [58]. We found that, for a frequency scale expected from theoretical considerations, a fit to the recent observations can be obtained for a certain range of the amplitude of the oscillation, which is a free parameter in the analysis, and for a frequency of oscillation that is motivated by the theory. Currently, the observational error bars are still too large to observe a statistically significant advantage of our model over the standard CDM cosmology. However, with upcoming observations, the error bars will shrink and may lead to a way to reliably extract a non-vanishing amplitude of an oscillating component of DE.
We also investigated the impact of our model on the Hubble tension. We found that for a large amplitude A of the oscillatory component (such that the energy density in the oscillating term is comparable to the matter energy density), a sufficiently large change in is observed, explaining the Hubble tension. However, such a high amplitude does not provide a good fit to the data. On the other hand, if A depends on time and decreases from a large value near the time of recombination to a small value at the present time, the Hubble constant tension might be successfully addressed.
The next step should be to analyze the perturbations in our scenario. This would allow us to make comparisons with other observable quantities, such as CMB anisotropies, and in particular, the Integrated Sachs–Wolfe (ISW) effect. In this context, in [77], the behavior of several cosmological observables, such as the linear growth factor, ISW effect, number counts of massive structures, and matter and cosmic shear power spectra, were estimated for several oscillating DE models. It was shown that for several of the models considered, independent of the amplitude and frequency of the DE oscillations, none of these observables showed a significant imprint of the oscillating behavior of . This is a consequence of the fact that such observables are integrals over functions of the expansion rate along cosmic history, consequently smoothing oscillatory features below the level of detectability. This analysis was performed under certain assumptions, such as the assumption that DE does not cluster on the scales of interest. In addition, the models studied in that reference have a different behavior compared to the back-reaction model we consider in our work. We believe it might be possible that the main conclusions of [77] might also hold for our model. As the observables mentioned are integrals over functions of the expansion rate along the cosmic history, we expect that in our scenario, the oscillatory features will also be smoothed, keeping the ISW effect in agreement with current observations.
The main goal of this work was to highlight the importance of further investigating the back-reaction effects of super-Hubble fluctuations in the late Universe. Such effects are expected to be present in any realistic scenario, and we have shown that they can provide an interesting and useful dynamical behavior in light of the recent DESI results. These results served as a motivation, as they have reignited the debate on alternatives to a pure cosmological constant description. At present, we are developing a more comprehensive analysis incorporating datasets from BAO, SNe, CMB, and others, which will serve as a follow-up to the present study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.B. and L.L.G.; methodology, R.B. and M.A.A.; software, M.A.A.; validation, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A.; formal analysis, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A.; investigation, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A.; resources, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A.; data curation, L.L.G. and M.A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L.G.; writing—review and editing, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A.; visualization, M.A.A.; supervision, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A.; project administration, R.B., L.L.G. and M.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.A.A. is supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). L.L.G is supported by research grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Grant No. 307636/2023-2, and from the Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), Grant No. E-26/204.598/2024. R.B. is supported in part by NSERC and the CRC program.
Data Availability Statement
Part of the data produced in this article is available on Table 1 and the other part (the results from the minimization routines) will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Elisa Ferreira for extensive discussions and E. Colgain for important feedback on the first draft of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Previous DESI DR1 Analysis
In this Appendix, we show the analysis of the back-reaction model in light of the previous DR1 results for comparison. Using the DR1 data, we produce the table below with the values for from Refs. [98,104], and its interpretation in terms of at given redshifts.

Table A1.
Dataset used for from the DESI first-year galaxy and quasar results [98], and the Lyman- forest [104], and its interpretation in terms of at given redshifts.
Table A1.
Dataset used for from the DESI first-year galaxy and quasar results [98], and the Lyman- forest [104], and its interpretation in terms of at given redshifts.
| Tracer | Redshift | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LRG 1 | 0.4–0.6 | ||
| LRG 2 | 0.6–0.8 | ||
| LRG 3 | 0.8–1.1 | ||
| ELG 2 | 1.1–1.6 | ||
| Lyman- | ∼2.33 |
In Figure A1, we show the late-time behavior of the function (curves in color) as predicted by the back-reaction model, for values of the parameter A ranging from zero to and for a fixed value of . These predictions are compared with the DESI DR1 results (red dots and error bars). Different shapes of the theoretical curve can be obtained using different values of the frequency and amplitude. To illustrate the method, we selected specific sets of parameter values that resulted in curve shapes that more closely aligned with the DESI DR1 data.
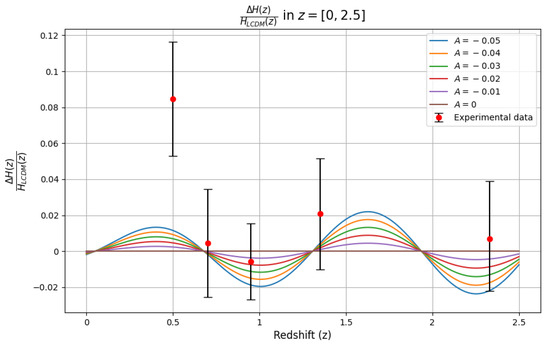
Figure A1.
predicted by the back-reaction model compared with DR1 data. In all the curves, we considered the value .
We performed a test minimizing the of the model with respect to the DR1 data using the same method described in Section IV. In Figure A2, we show the value of plotted as a function of the amplitude. As in the analysis for DR2 shown in Figure 1, we can see that also in this case, higher values of the amplitude of the back-reaction model provide a fit that is worse than that of the standard model. Again, we can see that the minimum value of the is shifted with respect to the CDM value (which is recovered for the value A = 0). The minimum is achieved for an amplitude slightly smaller in modulus than that in the case of DR2, as shown in Figure 2.
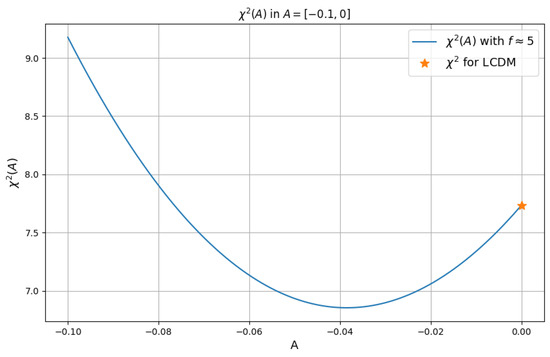
Figure A2.
The value of for the back-reaction model with respect to DR1 data as a function of parameter A. The value for CDM is represented by a star.
Although the best-fit frequency and amplitude of our model show slight variations when using DESI DR2 instead of DR1, and a modest improvement in the value is observed relative to the CDM model when using DR2, the overall conclusions remain consistent across both data releases.
References
- Weinberg, S. The Cosmological Constant Problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M. The Cosmological constant. Living Rev. Relativ. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, S. The Cosmological constant problems. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Sources and Detection of Dark Matter in the Universe (DM 2000), Marina del Rey, CA, USA, 23–25 February 2000; pp. 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, X.D.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Dark Energy. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2011, 56, 525–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J. Everything You Always Wanted To Know About The Cosmological Constant Problem (But Were Afraid To Ask). Comptes Rendus Phys. 2012, 13, 566–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, H.E.S.; vom Marttens, R.F.; Zimdahl, W. Aspects of the cosmological “coincidence problem”. Eur. Phys. J. C 2014, 74, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Said, J.L.; Riess, A.; Pollo, A.; Poulin, V.; Gómez-Valent, A.; Weltman, A.; Palmese, A.; Huang, C.D.; van de Bruck, C.; et al. The CosmoVerse White Paper: Addressing observational tensions in cosmology with systematics and fundamental physics. Phys. Dark Universe 2025, 49, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Imtiaz, B.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.F. Testing the coupling of dark radiations in light of the Hubble tension. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Valentino, E.; Mena, O.; Pan, S.; Visinelli, L.; Yang, W.; Melchiorri, A.; Mota, D.F.; Riess, A.G.; Silk, J. In the realm of the Hubble tension—A review of solutions. Class. Quantum Gravity 2021, 38, 153001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A.M. Infrared instability of the de Sitter space. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1209.4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A.M. De Sitter space and eternity. Nucl. Phys. B 2008, 797, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, P.; Mottola, E. Spontaneous Breaking of De Sitter Symmetry by Radiative Effects. Nucl. Phys. B 1986, 278, 694–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottola, E. THERMODYNAMIC INSTABILITY OF DE SITTER SPACE. Phys. Rev. D 1986, 33, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottola, E. Particle Creation in de Sitter Space. Phys. Rev. D 1985, 31, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsamis, N.C.; Woodard, R.P. Strong infrared effects in quantum gravity. Ann. Phys. 1995, 238, 1–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obied, G.; Ooguri, H.; Spodyneiko, L.; Vafa, C. De Sitter Space and the Swampland. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.08362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvali, G.; Gomez, C. Quantum Exclusion of Positive Cosmological Constant? Ann. Phys. 2016, 528, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, U.H.; Van Riet, T. What if string theory has no de Sitter vacua? Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2018, 27, 1830007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, K.; Emelin, M.; McDonough, E.; Tatar, R. Quantum Corrections and the de Sitter Swampland Conjecture. J. High Energy Phys. 2019, 01, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedroya, A.; Vafa, C. Trans-Planckian Censorship and the Swampland. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 09, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedroya, A.; Brandenberger, R.; Loverde, M.; Vafa, C. Trans-Planckian Censorship and Inflationary Cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R. Trans-Planckian Censorship Conjecture and Early Universe Cosmology. Lett. High Energy Phys. 2021, 2021, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamis, N.C.; Woodard, R.P. Relaxing the cosmological constant. Phys. Lett. B 1993, 301, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamis, N.C.; Woodard, R.P. Quantum gravity slows inflation. Nucl. Phys. B 1996, 474, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, L.R.W.; Brandenberger, R.H.; Mukhanov, V.F. The Energy - momentum tensor for cosmological perturbations. Phys. Rev. D 1997, 56, 3248–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finelli, F.; Marozzi, G.; Vacca, G.P.; Venturi, G. Energy momentum tensor of field fluctuations in massive chaotic inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finelli, F.; Marozzi, G.; Vacca, G.P.; Venturi, G. Energy momentum tensor of cosmological fluctuations during inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozzi, G. Back-reaction of Cosmological Fluctuations during Power-Law Inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R.H. Back reaction of cosmological perturbations. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Particle Physics and the Early Universe, Trieste, Italy, 27 September–3 October 1999; pp. 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Dodelson, S.; Greene, P.B.; Sorkin, R. Everpresent Λ. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 103523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Nasiri, A.; Yazdi, Y.K. Aspects of Everpresent Λ. Part I. A fluctuating cosmological constant from spacetime discreteness. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 10, 047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Nasiri, A.; Yazdi, Y.K. Aspects of Everpresent Λ (II): Cosmological Tests of Current Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, W. Cosmological long wavelength perturbations. arXiv 1998, arXiv:9802323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geshnizjani, G.; Brandenberger, R. Back reaction and local cosmological expansion rate. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 123507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, L.R.; Woodard, R.P. No one loop back reaction in chaotic inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 063515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geshnizjani, G.; Brandenberger, R. Back reaction of perturbations in two scalar field inflationary models. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2005, 04, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozzi, G.; Vacca, G.P.; Brandenberger, R.H. Cosmological Backreaction for a Test Field Observer in a Chaotic Inflationary Model. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 02, 027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finelli, F.; Marozzi, G.; Vacca, G.P.; Venturi, G. Backreaction during inflation: A Physical gauge invariant formulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 121304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, M.; Marozzi, G.; Veneziano, G. Gauge invariant averages for the cosmological backreaction. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 03, 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M.; Marozzi, G.; Veneziano, G. A Covariant and gauge invariant formulation of the cosmological ‘backreaction’. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 02, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozzi, G. The cosmological backreaction: Gauge (in)dependence, observers and scalars. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 01, 012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozzi, G.; Vacca, G.P. Isotropic Observers and the Inflationary Backreaction Problem. Class. Quantum Gravity 2012, 29, 115007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abramo, L.R.; Woodard, R.P. Back reaction is for real. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 65, 063516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, B.; Unruh, W.G. Long-wavelength metric backreactions in slow-roll inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 123510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, B.; Unruh, W.G. On leading order gravitational backreactions in de Sitter spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 023511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R.H.; Lam, C.S. Back-reaction of cosmological perturbations in the infinite wavelength approximation. arXiv 2004, arXiv:0407048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshordi, N.; Brandenberger, R.H. Super Hubble nonlinear perturbations during inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 63, 123505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, V. Perturbative Correction to the Average Expansion Rate of Spacetimes with Perfect Fluids. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, V.; Brandenberger, R. Back-reaction of long-wavelength cosmological fluctuations as measured by a clock field. Eur. Phys. J. C 2024, 84, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, L.; Von Marttens, R.; Camilleri, R. A novel approach to cosmological non-linearities as an effective fluid. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.15295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, E.W.; Marra, V.; Matarrese, S. Cosmological background solutions and cosmological backreactions. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2010, 42, 1399–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kolb, E.W. Backreaction of inhomogeneities can mimic dark energy. Class. Quantum Gravity 2011, 28, 164009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, V.; Notari, A. Observational constraints on inhomogeneous cosmological models without dark energy. Class. Quantum Gravity 2011, 28, 164004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R.; Graef, L.L.; Marozzi, G.; Vacca, G.P. Backreaction of super-Hubble cosmological perturbations beyond perturbation theory. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 103523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, R.; Lodha, K.; Shafieloo, A.; Linder, E.; Sohn, W.; de Mattia, A.; Cervantes-Cota, J.; Crittenden, R.; Davis, T.; Ishak, M.; et al. DESI 2024: Reconstructing Dark Energy using Crossing Statistics with DESI DR1 BAO data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.04216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, K.; Shafieloo, A.; Calderon, R.; Linder, E.; Sohn, W.; Cervantes-Cota, J.L.; De Mattia, A.; García-Bellido, J.; Ishak, M.; Matthewson, W.; et al. DESI 2024: Constraints on Physics-Focused Aspects of Dark Energy using DESI DR1 BAO Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI 2024 VI: Cosmological Constraints from the Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.03002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Karim, M.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Allen, L.; Allende Prieto, C.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI DR2 Results II: Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations and Cosmological Constraints. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14738. [Google Scholar]
- Lodha, K.; Calderon, R.; Matthewson, W.L.; Shafieloo, A.; Ishak, M.; Pan, J.; Garcia-Quintero, C.; Huterer, D.; Valogiannis, G.; Ureña-López, L.A.; et al. Extended Dark Energy analysis using DESI DR2 BAO measurements. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14743. [Google Scholar]
- Payeur, G.; McDonough, E.; Brandenberger, R. Do Observations Prefer Thawing Quintessence? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.B.; Pogosian, L.; Koyama, K.; Peacock, J.A.; Cai, Z.; Cervantes-Cota, J.L.; Zhao, R.; et al. Dynamical Dark Energy in light of the DESI DR2 Baryonic Acoustic Oscillations Measurements. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.06118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R. Why the DESI Results Should Not Be A Surprise. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.17659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Pedrotti, D.; da Costa, S.S.; Vagnozzi, S. Non-parametric late-time expansion history reconstruction and implications for the Hubble tension in light of DESI. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.02365. [Google Scholar]
- Escamilla, L.A.; Pan, S.; Di Valentino, E.; Paliathanasis, A.; Vázquez, J.A.; Yang, W. Testing an oscillatory behavior of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 111, 023531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, O.; Colgain, E.O.; Özulker, E.; Thakur, S.; Yin, L. Inevitable manifestation of wiggles in the expansion of the late Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 123526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgáin, E.O.; Sheikh-Jabbari, M.M. DESI and SNe: Dynamical Dark Energy, Ωm Tension or Systematics? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.12905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.B.; Raveri, M.; Pogosian, L.; Wang, Y.; Crittenden, R.G.; Handley, W.J.; Percival, W.J.; Beutler, F.; Brinkmann, J.; Chuang, C.H.; et al. Dynamical dark energy in light of the latest observations. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo, D.; Vazquez, J.A. Fourier-series expansion of the dark-energy equation of state. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubano, C.; Scudellaro, P.; Piedipalumbo, E.; Capozziello, S. Oscillating dark energy: A Possible solution to the problem of eternal acceleration. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. On oscillating dark energy. Astropart. Phys. 2006, 25, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, M.; Piao, Y.S.; Zhang, X. Oscillating quintom and the recurrent universe. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 634, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. The Oscillating dark energy: Future singularity and coincidence problem. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 637, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, A.; Hrycyna, O.; Szydlowski, M. Constraints on oscillating dark energy models. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 659, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Dev, A.; Alcaniz, J.S. Cosmological bounds on oscillating dark energy models. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 656, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saez-Gomez, D. Oscillating Universe from inhomogeneous EoS and coupled dark energy. Gravit. Cosmol. 2009, 15, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, A.; Hrycyna, O.; Szydlowski, M. From model dynamics to oscillating dark energy parametrisation. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 690, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Fedeli, C.; Moscardini, L.; Bartelmann, M. Structure formation in cosmologies with oscillating dark energy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Saridakis, E.N.; Yang, W. Observational Constraints on Oscillating Dark-Energy Parametrizations. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 063510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panotopoulos, G.; Rincón, A. Growth index and statefinder diagnostic of Oscillating Dark Energy. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M. Observational constraints on the oscillating dark energy cosmologies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 485, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.Y.; Guo, R.Y.; Zhao, X.Y. Constraining neutrino mass in dynamical dark energy cosmologies with the logarithm parametrization and the oscillating parametrization. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.05956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M. Oscillating Dark Energy in Light of the Latest Observations and Its Impact on the Hubble Tension. Astrophys. J. 2024, 967, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tián, S.X. Cosmological consequences of a scalar field with oscillating equation of state: A possible solution to the fine-tuning and coincidence problems. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 063531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, S.A.; Akarsu, O.; Di Valentino, E.; Nunes, R.C.; Özülker, E.; Sen, A.A.; Specogna, E. Omnipotent dark energy: A phenomenological answer to the Hubble tension. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 023527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbonye, M.R. Is cosmic dynamics self-regulating? Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2023, 32, 2350076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbonye, M.R. The Big Bang: Origins and initial conditions from Self-Regulating Cosmology (SRC) model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.B.; Xia, J.Q.; Li, M.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X. Perturbations of the quintom models of dark energy and the effects on observations. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 123515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisenberg, L.; Bartelmann, M.; Brandenberger, R.; Refregier, A. Model independent analysis of supernova data, dark energy, trans-Planckian censorship and the swampland. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 812, 135990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haude, S.; Salehi, S.; Vidal, S.; Maturi, M.; Bartelmann, M. Model-Independent Determination of the Cosmic Growth Factor. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.04560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, D.A.; Escamilla, L.A.; Pan, S.; Di Valentino, E. One-parameter dynamical dark energy: Hints for oscillations. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.00776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.F.; Feldman, H.A.; Brandenberger, R.H. Theory of cosmological perturbations. Part 1. Classical perturbations. Part 2. Quantum theory of perturbations. Part 3. Extensions. Phys. Rept. 1992, 215, 203–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.F.; Abramo, L.R.W.; Brandenberger, R.H. On the Back reaction problem for gravitational perturbations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1624–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, R.H. Back reaction of cosmological perturbations and the cosmological constant problem. In Proceedings of the 18th IAP Colloquium on the Nature of Dark Energy: Observational and Theoretical Results on the Accelerating Universe, Paris, France, 1–5 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Payeur, G.; McDonough, E.; Brandenberger, R. Swampland conjectures constraints on dark energy from a highly curved field space. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, L.R.W. The Back Reaction of Gravitational Perturbations and Applications in Cosmology. Ph.D. Thesis, Physics Department, Brown University, Providence, RI, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, D.H.; Mortonson, M.J.; Eisenstein, D.J.; Hirata, C.; Riess, A.G.; Rozo, E. Observational Probes of Cosmic Acceleration. Phys. Rept. 2013, 530, 87–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Howlett, C.; White, M.; McDonald, P.; Ross, A.J.; Seo, H.J.; Padmanabhan, N.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; et al. Baryon Acoustic Oscillation Theory and Modelling Systematics for the DESI 2024 results. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.14070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI 2024 III: Baryon Acoustic Oscillations from Galaxies and Quasars. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.03000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Hyatt, N. A radical solution to the Hubble tension problem. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2024, 08, 052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormondroyd, A.N.; Handley, W.J.; Hobson, M.P.; Lasenby, A.N. Comparison of dynamical dark energy with ΛCDM in light of DESI DR2. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.17342. [Google Scholar]
- Colgáin, E.O.; Pourojaghi, S.; Sheikh-Jabbari, M.M.; Yin, L. How much has DESI dark energy evolved since DR1? arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.04417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, V.; Smith, T.L.; Calderón, R.; Simon, T. Impact of ACT DR6 and DESI DR2 for Early Dark Energy and the Hubble tension. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.08051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.G. The Impact of the Hubble Tension on the Evidence for Dynamical Dark Energy. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.21600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI 2024 IV: Baryon Acoustic Oscillations from the Lyman Alpha Forest. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).