An Improved NSGA-II for Three-Stage Distributed Heterogeneous Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling with Flexible Assembly and Discrete Transportation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A mathematical model has been created for the three-stage distributed assembly problem.
- An enhanced version of the Nondominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II, incorporating Q-learning (termed QNSGA), has been introduced to reduce both the makespan and the maximum tardiness. In QNSGA, Q-learning dynamically selects the optimal search strategy to improve the solution set, based on 12 states related to evaluating population quality and 8 actions that represent search operators and effective action selection.
- Heuristics have been designed to produce initial solutions.
- Extensive experiments have been carried out to assess the performance of QNSGA in comparison to other methods found in the literature. The computational results show that the introduction of new strategies, including the Q-learning algorithm, is both effective and efficient, and QNSGA yields promising results for the analyzed three-stage distributed assembly problem.
2. Literature Review
2.1. ASP and DAPFSP
2.2. Reinforcement Learning and NSGA-II for ASP
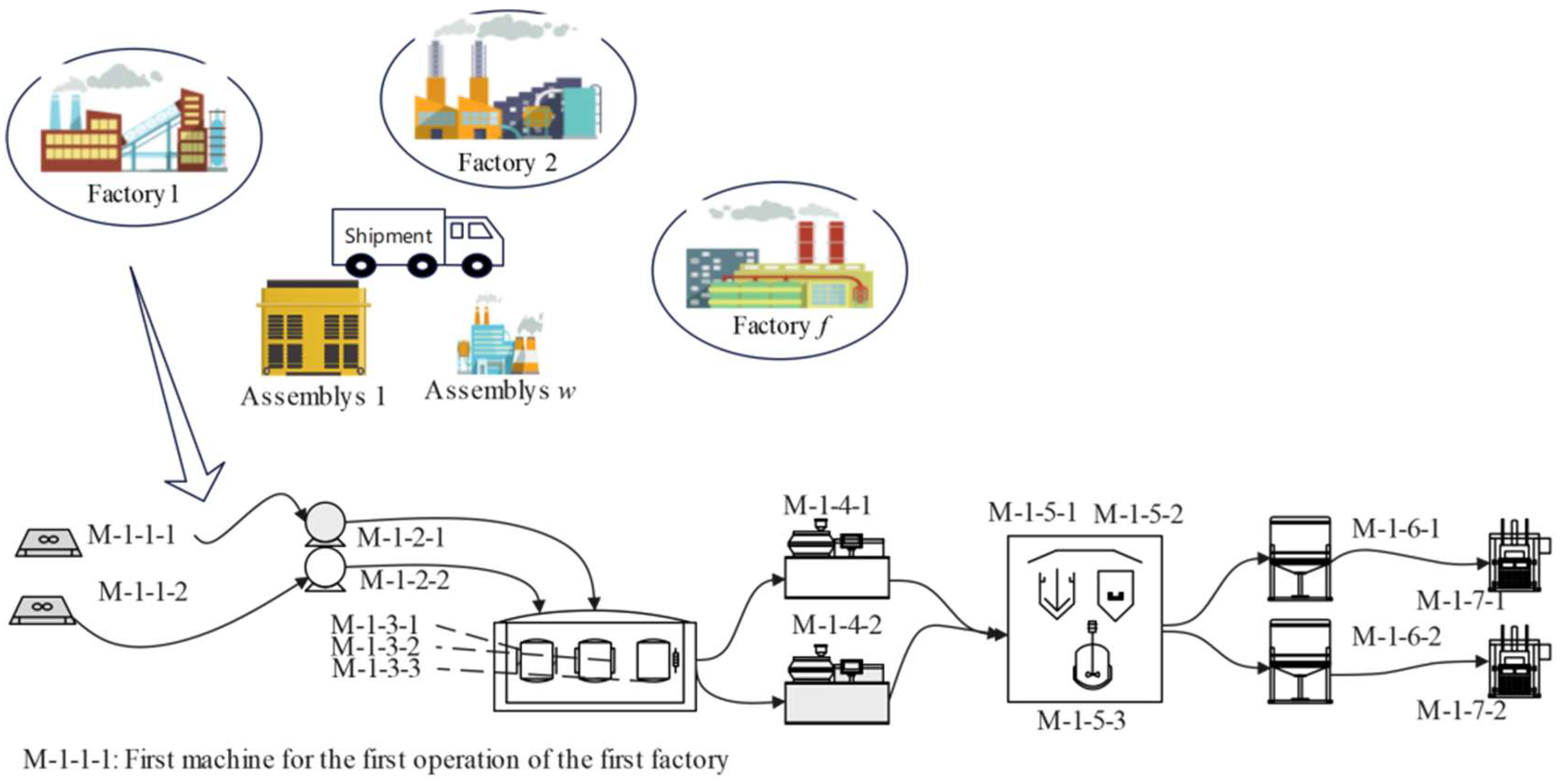
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. Notations
3.2. Mathematical Model
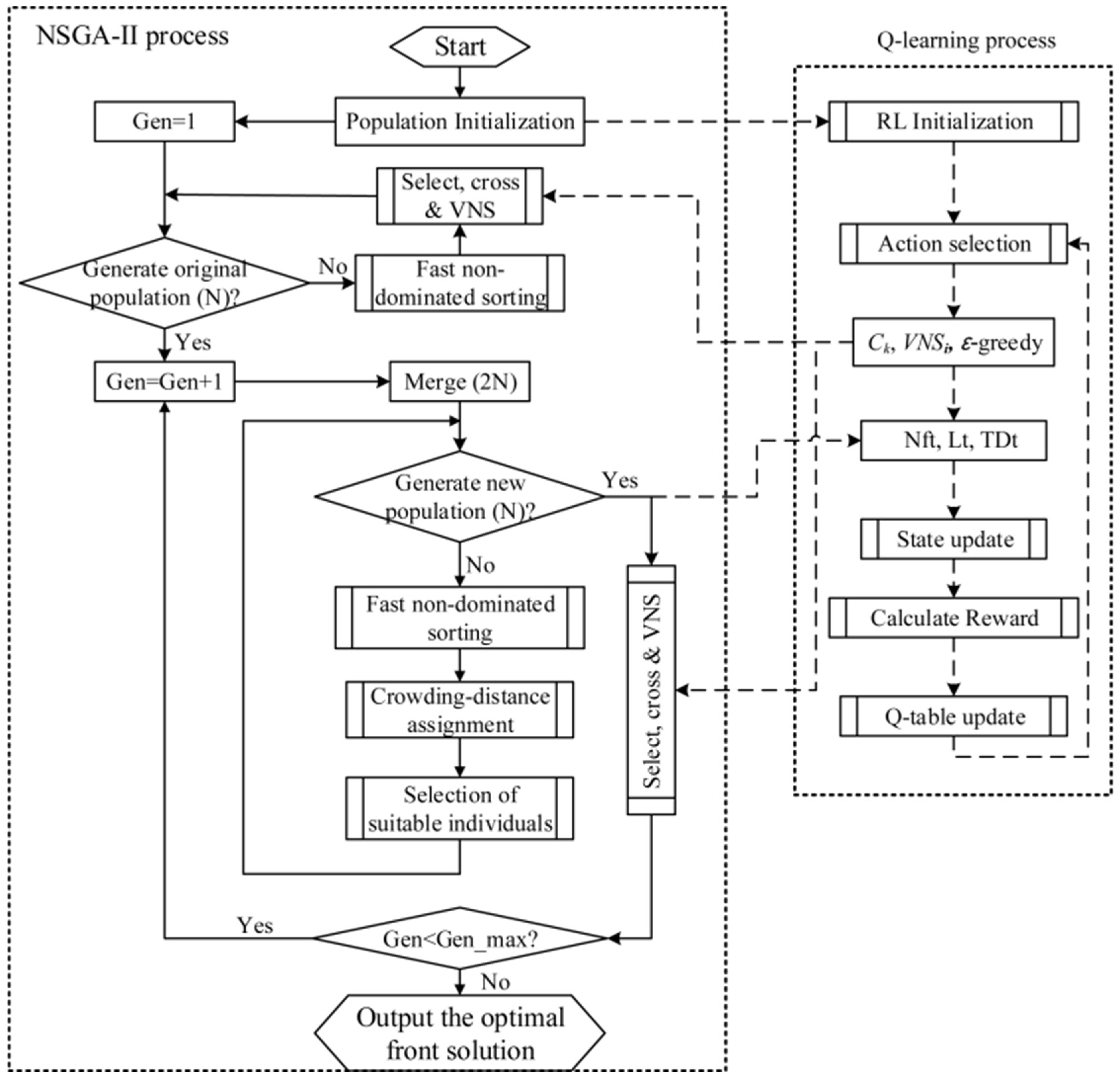
4. Symmetry Analysis of Q-Learning Reinforced NSGA-II
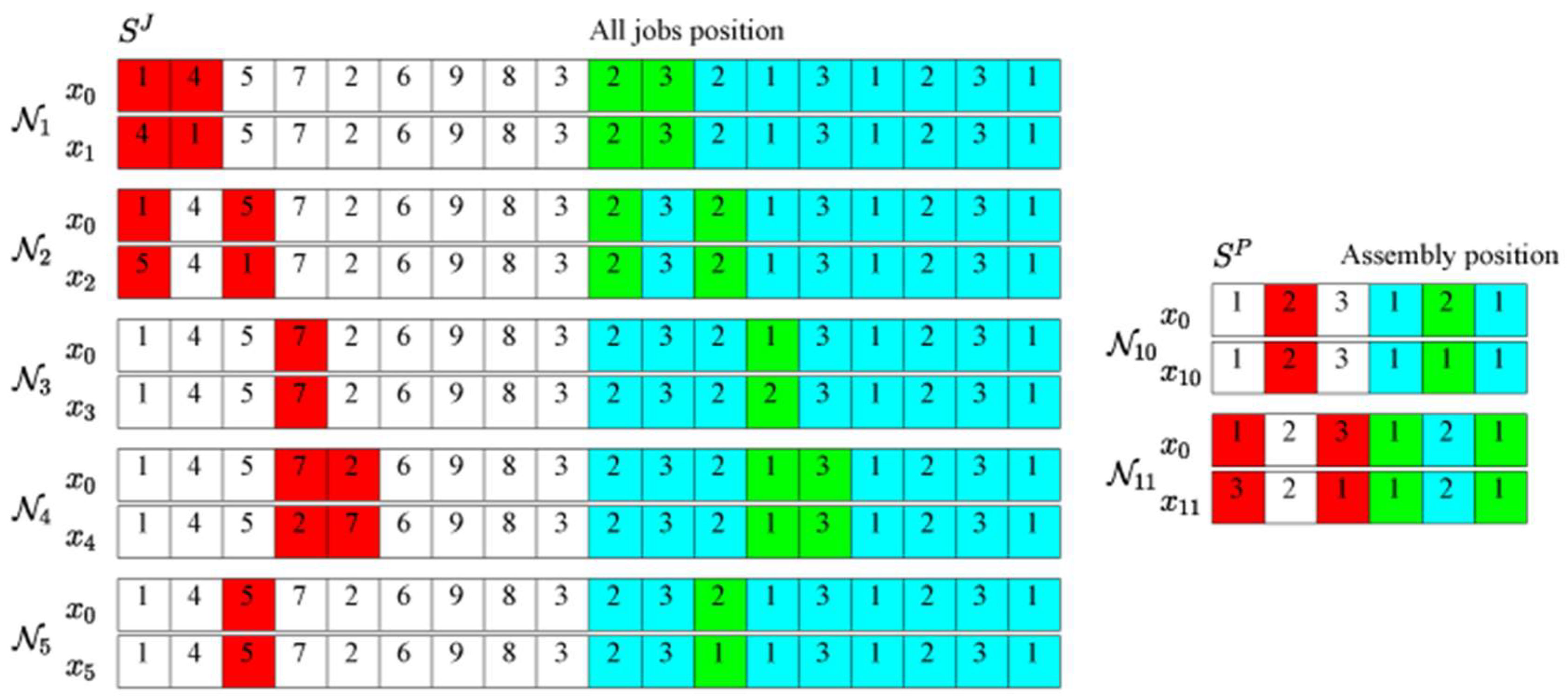
4.1. Symmetric Solution Representation
4.1.1. Subsequence Initialization for Jobs
- Set i = 1;
- Calculate the average processing time of operation Oji in available machines of factory Fg as ;
- Compute the average processing time of Oji across all factories as ;
- Let i = i + 1. If i = m, proceed to the next step; otherwise, return to Step 2;
- Compute the total processing time of job Jj with .
4.1.2. Jobs Assignment to the Target Factory and Machines
4.1.3. Products Sequencing and Allocation
4.2. Mechanism and Four-Tuple in Reinforcement-Learning-Enhanced NSGA-II
4.3. States Construction in Q-Learning
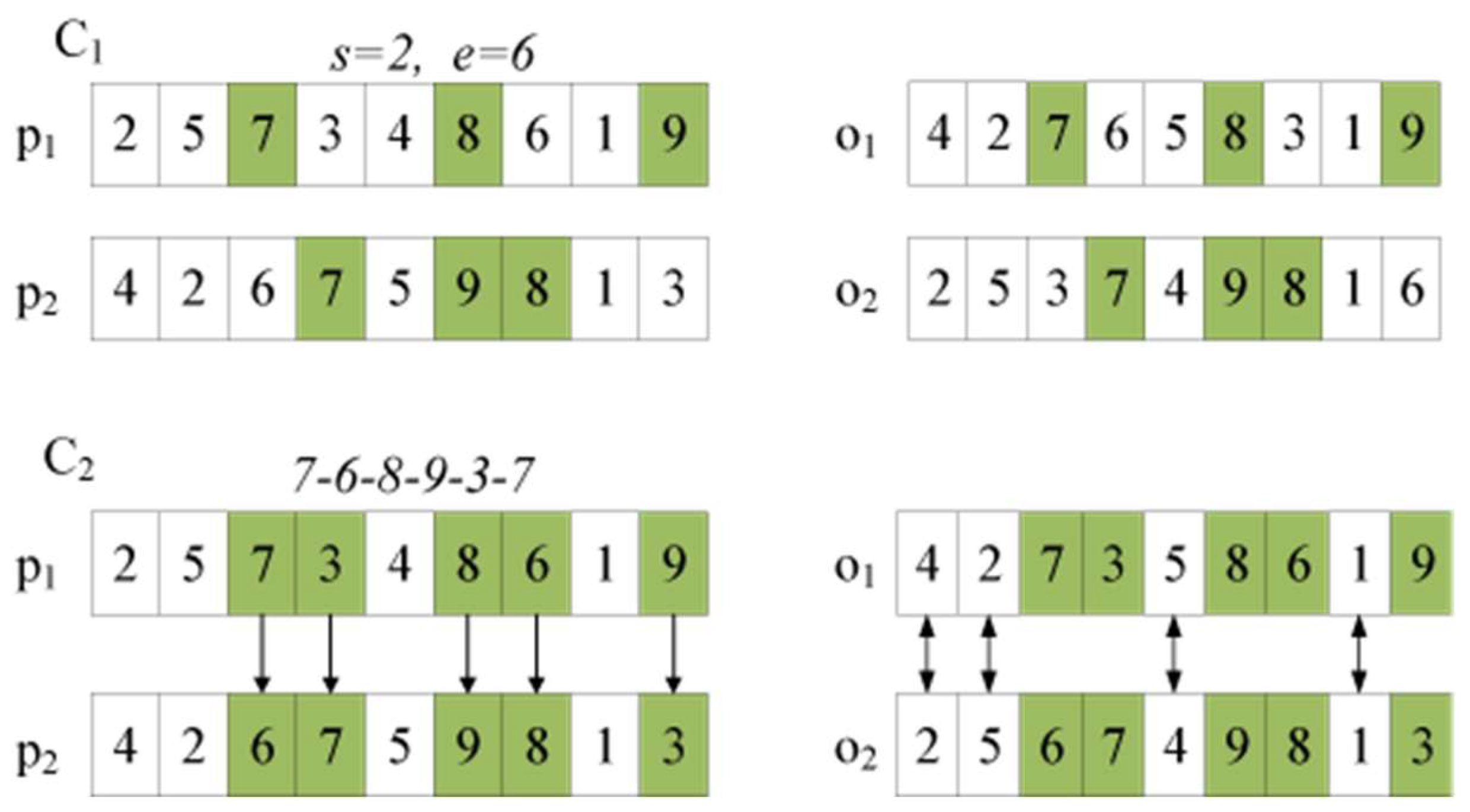
4.4. Actions Symmetry Construction in QNSGA
- Set b = 1 and = 0;
- Generate a solution with a random search based on ;
- If is superior to , update , set , and proceed to Step 5; otherwise, increment b and go to Step 4;
- If b = 11, proceed to Step 5; otherwise, return to Step 2;
- Output the solution and terminate the search.
- Intra-factory symmetry: N2 (job swap in same factory) and N8 (job swap on same machine) share identical permutation logic;
- Cross-stage symmetry: N5 (job transfer between factories) and N11 (product transfer between assembly machines) both implement load-balancing heuristics;
- Unified procedure: Both stages use identical VNS update mechanisms (VNS1, VNS2).
- Randomly select two solutions and from different Pareto fronts, where dominates .
- Generate two offspring solutions and with crossover and compare them with .
- If the dominated one of and can dominate , substitute with the better solution; otherwise, let r = rand(0,1), if r, substitute with the better solution; otherwise, update with based on the -greedy acceptance rule.
4.5. Reward Function Determination
4.6. Procedure of QNSGA
| Algorithm 1: Generate a new population of size N. |
| Require: Original population , selected action at = (Ck, VNSi, Accp) Ensure: A new population while j ≤ N do Select a solution randomly from \NF Select an elite solution x g randomly from NF Cross xr and xg with Ck if xr dominates x g then Append xr to j++ else Randomly generate r ⇐ rand (0, 1) if r is acceptable with Accp then Append xr to set else Search the neighborhood solution of xr with VNSi if xr is acceptable with Accp then Append xr to set P j ++ end if end if end if end while |
| Algorithm 2: QNSGA for the problem |
| Require: Problem environment set, learning rate α, discount factor γ, exploration rate ϵ, maximum running time TM Initialize the population Perform non-dominated sorting and compute the crowding distance. Initialize the Q-table, current time, and state s based on the population P of the initial generation. Select an action a from state s by applying the ϵ-greedy policy informed by the Q-table. while t < TM do Take action a to generate a new population , observe the new state s′ and reward Choose action a′ from s′ using the ϵ-greedy policy derived from the Q-table Perform non-dominated sorting and compute the crowding distance. Update the Q-value for the current state-action pair using Equation (25) Update current state and action: s ← s′, a ← a′ end while |
5. Experimental Evaluation and Industrial Validation
5.1. Experimental Methodology
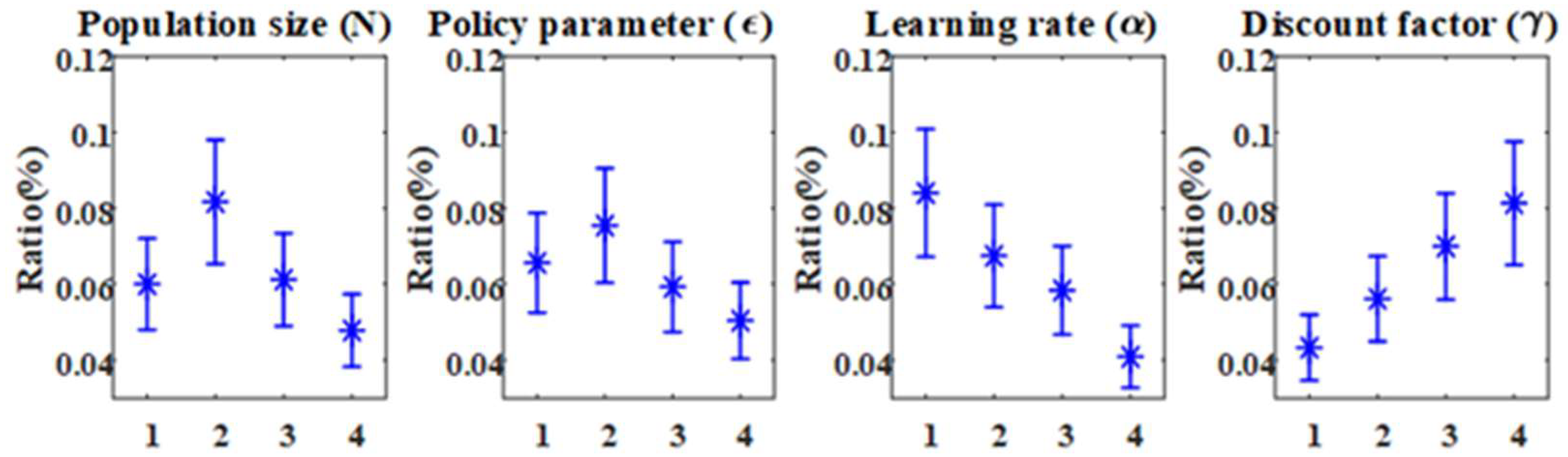
5.2. Calibration of Algorithmic Parameters
5.3. Assessment of the Mathematical Model
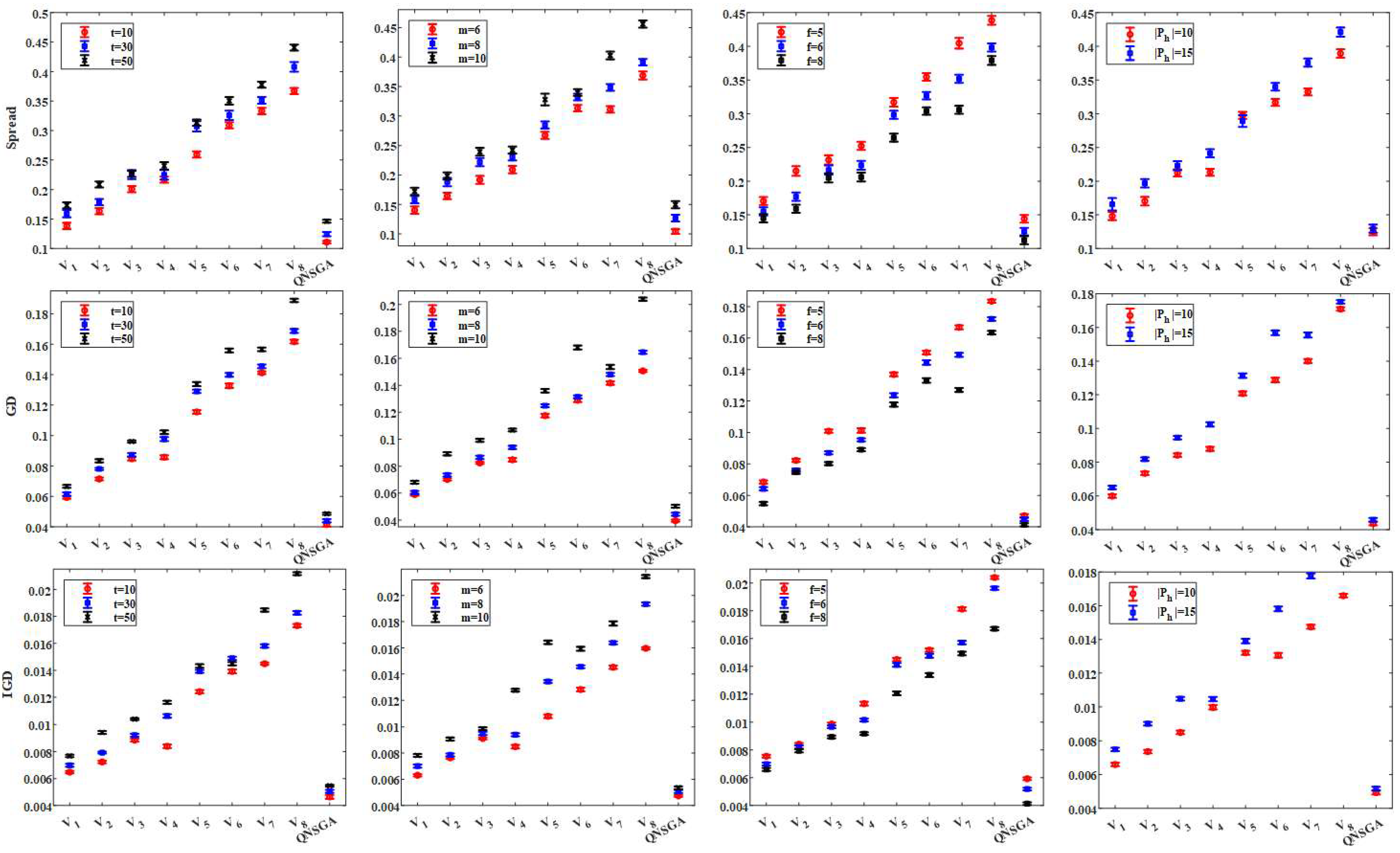
5.4. Effectiveness of Eight Actions
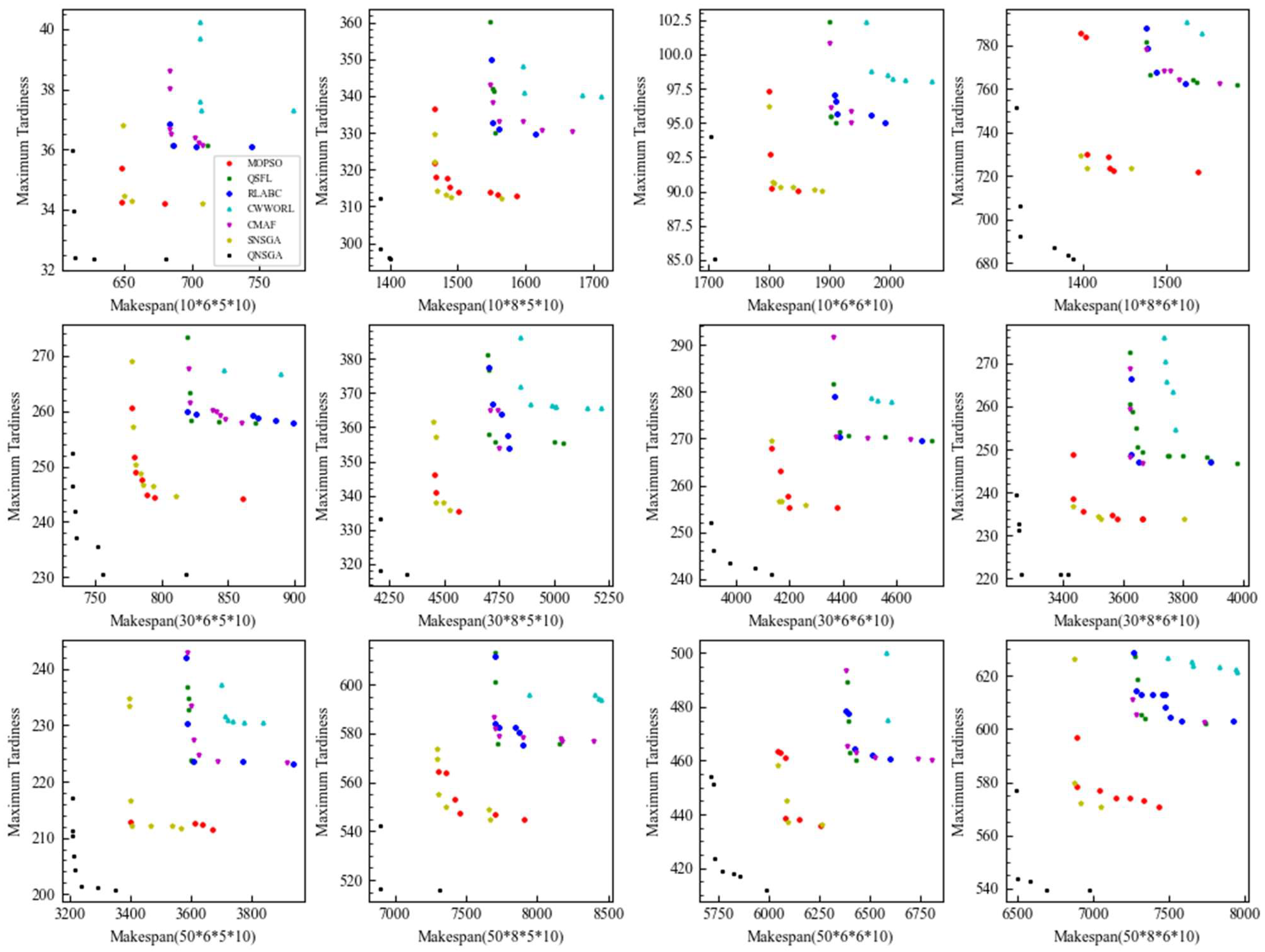
5.5. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Algorithms
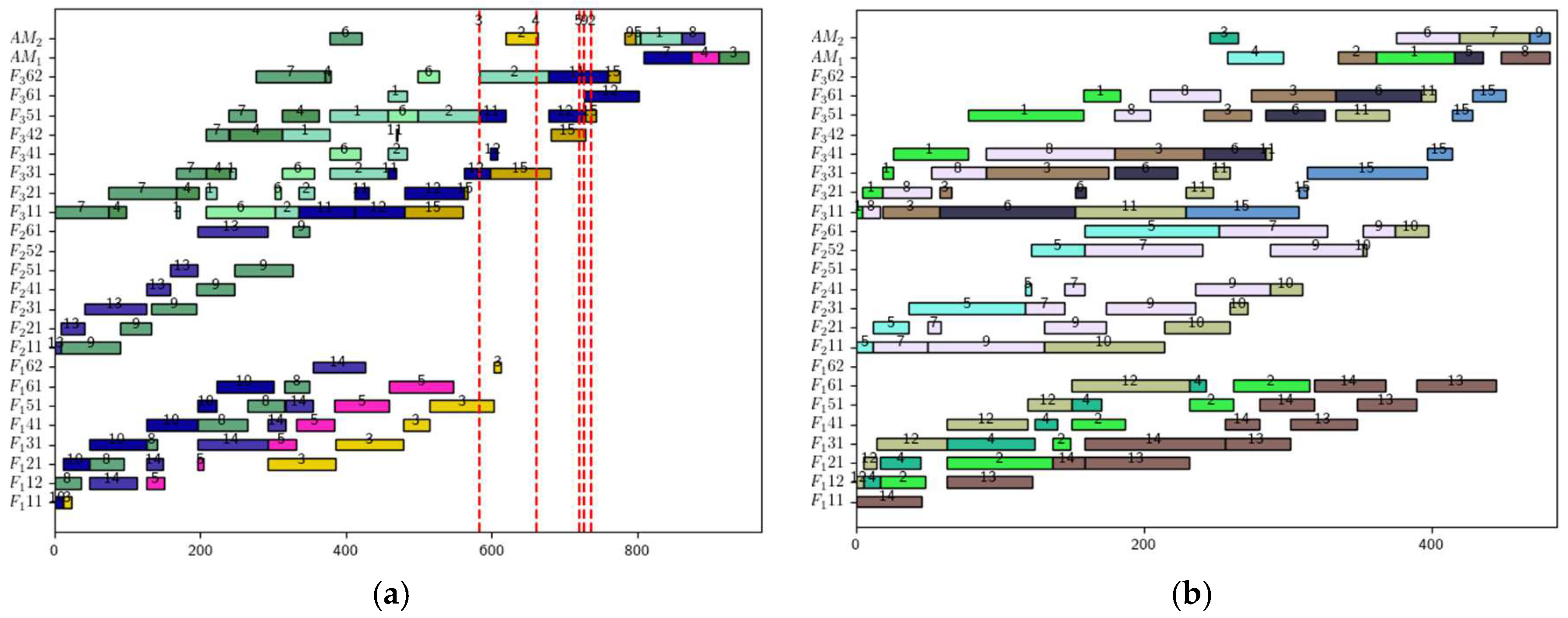
5.6. Industrial Case Study: Wind Turbine Manufacturing Application
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.G.; Yang, N.; Li, W.J.; Lian, J.; Evans, S.; Yin, Y. Training and assignment of multi-skilled workers for implementing seru production systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 937–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xing, K.; Zhang, G.; He, Z. Memetic Algorithm with Meta-Lamarckian Learning and Simplex Search for Distributed Flexible Assembly Permutation Flowshop Scheduling Problem. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 96115–96128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhu, H.; Shen, L.; Zhen, G.; Chen, Z. Research on assembly scheduling problem with nested operations. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 175, 108830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Liu, X.J.; Zhao, N. An improved differential evolution algorithm for solving a distributed assembly flexible job shop scheduling problem. Memetic Comput. 2019, 11, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Sethi, S.P.; Sokolov, B. Scheduling in production, supply chain and Industry 4.0 systems by optimal control: Fundamentals, state-of-the-art and applications. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Hu, R.; Qian, B.; Jin, H.-P.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.-B. A matrix cube-based estimation of distribution algorithm for the energy-efficient distributed assembly permutation flow-shop scheduling problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 194, 116484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.H. Distributed assembly permutation flow-shop scheduling problem with non-identical factories and considering budget constraints. Kybernetes 2022, 52, 2018–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. A Hybrid Bat Algorithm for Solving the Three-Stage Distributed Assembly Permutation Flowshop Scheduling Problem. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Z. The distributed assembly permutation flowshop scheduling problem with flexible assembly and batch delivery. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 4053–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, S.; Ruiz, R.; Andres-Romano, C. The Distributed Assembly Permutation Flowshop Scheduling Problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 5292–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, S.; Ruiz García, R.; Romano, C.A. The Distributed Assembly Parallel Machine Scheduling Problem with eligibility constraints. Int. J. Prod. Manag. Eng. 2015, 3, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qian, B.; Hu, R.; Zhang, C. Adaptive hybrid estimation of distribution algorithm for solving a certain kind of three-stage assembly flowshop scheduling problem. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 21, 1829–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-G.; Yu, J.-M.; Lee, D.-H. Scheduling algorithms for remanufacturing systems with parallel flow-shop-type reprocessing lines. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Pan, Q.-K.; Gao, L.; Miao, Z.-H.; Peng, C. A two-phase evolutionary algorithm for multi-objective distributed assembly permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 74, 101128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, P.; Tian, G.; Zhang, C. Integrated remanufacturing scheduling of disassembly, reprocessing and reassembly considering energy efficiency and stochasticity through group teaching optimization and simulation approaches. Eng. Optim. 2024, 56, 2018–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Gonzalez-Neira, E.; Ferone, D.; Hatami, S.; Juan, A.A. A biased-randomized simheuristic for the distributed assembly permutation flowshop problem with stochastic processing times. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2017, 79, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.-Y.; Yan, H.-S. Integrated optimization of production planning and scheduling in uncertain re-entrance environment for fixed-position assembly workshops. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 1705–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Al-Anzi, F.S. Evolutionary heuristics and an algorithm for the two-stage assembly scheduling problem to minimize makespan with setup times. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2006, 44, 4713–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talens, C.; Fernandez-Viagas, V.; Perez-Gonzalez, P.; Framinan, J.M. New efficient constructive heuristics for the two-stage multi-machine assembly scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 140, 106223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhu, H.; Luo, Y. A multi-objective Immune Balancing Algorithm for Distributed Heterogeneous Batching-integrated Assembly Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 259, 125288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xu, H. Multiobjective Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Using Memetic Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H. Dynamic Jobshop Scheduling Algorithm Based on Deep Q Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 122995–123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Sun, G.; Yang, K.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, D.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X. A comprehensive study on integrated optimization of flexible manufacturing system layout and scheduling for nylon components production. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Theory Appl. Pract. 2022, 29, 979–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.; Chen, G.; Lu, Y. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Real-Time Dynamic Production Scheduling in a Robot Assembly Cell. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 7684–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Luo, L.; He, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ji, S. Solving Panel Block Assembly Line Scheduling Problem via a Novel Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Komaki, G.M.; Kayvanfar, V. Multi objective two-stage assembly flow shop with release time. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 124, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chehade, H.; Yalaoui, F.; Amodeo, L. A new method coupling simulation and a hybrid metaheuristic to solve a multiobjective hybrid flowshop scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the EUSFLAT Conference, Aix-les-Bains, France, 18–22 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, S.C.; Arroyo, J.E.C. NSGA-II with iterated greedy for a bi-objective three-stage assembly flowshop scheduling problem. In Proceedings of the 2014 Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–16 July 2014; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, I.; Gandomi, A.H.; Deb, K.; Chen, F.; Nikoo, M.R. Scheduling by NSGA-II: Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Processes 2022, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.-L.; Zhou, W.-J.; Fei, M.-R.; Nee, A.Y.C.; Ong, S.K. Bi-objective scheduling for energy-efficient distributed assembly blocking flow shop. CIRP Ann. 2024, 73, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Lei, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. A novel shuffled frog-leaping algorithm with reinforcement learning for distributed assembly hybrid flow shop scheduling. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 1233–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zhuang, C.; Liu, Z. Digital twin-driven dynamic scheduling for the assembly workshop of complex products with workers allocation. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2024, 89, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Chang, P.C.; Tiwari, M.K.; Kollanoor, N.J. A Pareto block-based estimation and distribution algorithm for multi-objective permutation flow shop scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 793–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Deng, G.L.; Jiang, T.H.; Zhang, S.N. Multi-Objective Parallel Variable Neighborhood Search for Energy Consumption Scheduling in Blocking Flow Shops. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 68686–68700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Lu, C. An integrated job shop scheduling and assembly sequence planning approach for discrete manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 61, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, M.H.; Saghih, A.M.F.; Azimi, Z.N. A fuzzy mathematical model for multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem with new job insertion and earliness/tardiness penalty. Int. J. Ind. Eng.-Theory Appl. Pract. 2021, 28, 256–276. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Y. Dynamic multi-objective scheduling for flexible job shop by deep reinforcement learning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 159, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, Y. Real-Time Scheduling for Dynamic Partial-No-Wait Multiobjective Flexible Job Shop by Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 3020–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; An, D.; Li, D.; Wu, Z. Multistep Multiagent Reinforcement Learning for Optimal Energy Schedule Strategy of Charging Stations in Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 53, 4292–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Tang, J. A cooperative water wave optimization algorithm with reinforcement learning for the distributed assembly no-idle flowshop scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 153, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lei, D.; Cai, J. An adaptive artificial bee colony with reinforcement learning for distributed three-stage assembly scheduling with maintenance. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 117, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhu, H. A self-learning particle swarm optimization for bi-level assembly scheduling of material-sensitive orders. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 195, 110427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulidya, R.; Wangsaputra, R.; Halim, A.H. A Batch Scheduling Model for a Three-stage Hybrid Flowshop Producing Products with Hierarchical Assembly Structures. Int. J. Technol. 2020, 11, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, L. A multi-objective decomposition evolutionary algorithm based on the double-faced mirror boundary for a milk-run material feeding scheduling optimization problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 171, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Xing, K.; Wang, F.; Lei, H.; Han, L. Minimizing the total completion time in a distributed two stage assembly system with setup times. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 47, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, S.; Ruiz García, R.; Romano, C.A. Heuristics and metaheuristics for the distributed assembly permutation flowshop scheduling problem with sequence dependent setup times. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 169, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Wang, L. A cooperative memetic algorithm with feedback for the energy-aware distributed flow-shops with flexible assembly scheduling. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 168, 108126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Meng, L.; Lu, C.; Han, Y.; Sang, H. Automatic design of constructive heuristics for a reconfigurable distributed flowshop group scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2024, 161, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| State | Indicator | State | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Action | Indicator | Action | Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Small | Large |
| t | {3, 5, 8} | {10, 30, 50} |
| m | {2, 3, 4} | {6, 8, 10} |
| f | {2, 3, 4} | {5, 6, 8} |
| |Ph| | {2, 4} | {10, 15} |
| w | ⌈t/2⌉ | ⌈t/2⌉ |
| Kil | RandSelect {1,2,3} | RandSelect {1,2,3,4,5} |
| pjk | U [1,99] | U [1,99] |
| qha | ||
| U [1,49] | U [1,49] | |
| dh |
| No. | N | RV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.09 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.11 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0.09 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0.12 |
| 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0.12 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0.15 |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0.09 |
| 8 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0.08 |
| 9 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0.06 |
| 10 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0.06 |
| 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0.06 |
| 12 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0.03 |
| 13 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0.01 |
| 14 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0.01 |
| 15 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 0.08 |
| 16 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 0.01 |
| I | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
| II | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.07 | |
| III | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | |
| IV | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| R | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Instance | MILP Solver | QNSGA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | Tmax | Time | Cmax | Tmax | Time | ||||||
| Mean | STD | Mean | STD | Mean | STD | Mean | STD | ||||
| t | 3 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 345.21 | 0.084 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.014 | 27 |
| 5 | 0.146 | 0.023 | 0.021 | 0.029 | 1404.29 | 0.150 | 0.022 | 0.045 | 0.022 | 45 | |
| 8 | 0.243 | 0.101 | 0.032 | 0.051 | 1887.67 | 0.153 | 0.025 | 0.079 | 0.041 | 72 | |
| m | 2 | 0.015 | 0.017 | 0.016 | 0.022 | 1162.25 | 0.066 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 32 |
| 3 | 0.127 | 0.025 | 0.022 | 0.032 | 1152.81 | 0.100 | 0.013 | 0.049 | 0.024 | 48 | |
| 4 | 0.300 | 0.043 | 0.030 | 0.055 | 1680.75 | 0.220 | 0.021 | 0.075 | 0.040 | 64 | |
| f | 2 | 0.240 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 1679.10 | 0.174 | 0.022 | 0.078 | 0.035 | 32 |
| 3 | 0.123 | 0.019 | 0.021 | 0.025 | 1248.82 | 0.119 | 0.017 | 0.043 | 0.018 | 48 | |
| 4 | 0.079 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 1067.89 | 0.093 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 64 | |
| |Ph| | 2 | 0.096 | 0.016 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 1297.78 | 0.074 | 0.015 | 0.026 | 0.016 | 48 |
| 4 | 0.199 | 0.027 | 0.032 | 0.044 | 1451.48 | 0.183 | 0.021 | 0.065 | 0.035 | 48 | |
| Average | 0.130 | 0.029 | 0.021 | 0.031 | 1307.1 | 0.129 | 0.018 | 0.046 | 0.025 | 48 | |
| a. Based on the Δ metric | ||||||||||
| Instance | QNSGA | |||||||||
| t | 10 | 0.138 | 0.164 | 0.201 | 0.217 | 0.259 | 0.309 | 0.333 | 0.367 | 0.1110 |
| 30 | 0.159 | 0.179 | 0.225 | 0.225 | 0.307 | 0.326 | 0.351 | 0.408 | 0.1245 | |
| 50 | 0.173 | 0.209 | 0.227 | 0.240 | 0.313 | 0.350 | 0.378 | 0.441 | 0.1464 | |
| m | 6 | 0.140 | 0.164 | 0.192 | 0.209 | 0.267 | 0.313 | 0.311 | 0.369 | 0.1042 |
| 8 | 0.158 | 0.188 | 0.222 | 0.231 | 0.285 | 0.332 | 0.348 | 0.391 | 0.1269 | |
| 10 | 0.172 | 0.198 | 0.239 | 0.242 | 0.328 | 0.340 | 0.403 | 0.456 | 0.1499 | |
| f | 5 | 0.170 | 0.215 | 0.232 | 0.252 | 0.317 | 0.355 | 0.405 | 0.439 | 0.1442 |
| 6 | 0.155 | 0.177 | 0.216 | 0.223 | 0.298 | 0.327 | 0.352 | 0.398 | 0.1253 | |
| 8 | 0.145 | 0.159 | 0.205 | 0.206 | 0.265 | 0.304 | 0.306 | 0.379 | 0.1124 | |
| |Ph| | 10 | 0.148 | 0.170 | 0.212 | 0.213 | 0.298 | 0.317 | 0.332 | 0.389 | 0.1250 |
| 15 | 0.166 | 0.197 | 0.223 | 0.241 | 0.289 | 0.340 | 0.376 | 0.421 | 0.1296 | |
| Average | 0.157 | 0.184 | 0.218 | 0.227 | 0.293 | 0.328 | 0.354 | 0.405 | 0.1273 | |
| b. Based on the GD metric | ||||||||||
| Instance | QNSGA | |||||||||
| t | 10 | 0.059 | 0.071 | 0.085 | 0.086 | 0.115 | 0.133 | 0.141 | 0.162 | 0.042 |
| 30 | 0.062 | 0.078 | 0.087 | 0.098 | 0.129 | 0.140 | 0.145 | 0.169 | 0.044 | |
| 50 | 0.067 | 0.083 | 0.096 | 0.102 | 0.134 | 0.156 | 0.157 | 0.189 | 0.049 | |
| m | 6 | 0.059 | 0.070 | 0.082 | 0.085 | 0.117 | 0.129 | 0.142 | 0.151 | 0.040 |
| 8 | 0.060 | 0.073 | 0.087 | 0.094 | 0.125 | 0.131 | 0.148 | 0.165 | 0.044 | |
| 10 | 0.068 | 0.089 | 0.099 | 0.107 | 0.136 | 0.168 | 0.154 | 0.204 | 0.050 | |
| f | 5 | 0.068 | 0.082 | 0.101 | 0.101 | 0.137 | 0.151 | 0.167 | 0.183 | 0.047 |
| 6 | 0.064 | 0.076 | 0.087 | 0.095 | 0.124 | 0.144 | 0.149 | 0.172 | 0.045 | |
| 8 | 0.055 | 0.075 | 0.080 | 0.089 | 0.118 | 0.133 | 0.127 | 0.163 | 0.041 | |
| |Ph| | 10 | 0.060 | 0.073 | 0.084 | 0.088 | 0.121 | 0.129 | 0.140 | 0.171 | 0.044 |
| 15 | 0.065 | 0.082 | 0.095 | 0.102 | 0.131 | 0.157 | 0.155 | 0.175 | 0.046 | |
| Average | 0.062 | 0.078 | 0.089 | 0.095 | 0.126 | 0.143 | 0.148 | 0.173 | 0.045 | |
| c. Based on the IGD metric | ||||||||||
| Instance | QNSGA | |||||||||
| t | 10 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.005 |
| 30 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.005 | |
| 50 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.005 | |
| m | 6 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.005 |
| 8 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.019 | 0.005 | |
| 10 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.005 | |
| f | 5 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.018 | 0.020 | 0.006 |
| 6 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.020 | 0.005 | |
| 8 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.017 | 0.004 | |
| |Ph| | 10 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.017 | 0.005 |
| 15 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.021 | 0.005 | |
| Average | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.016 | 0.019 | 0.005 | |
| Metric | QNSGA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | 3.421 | 3.768 | 4.308 | 4.207 | 5.607 | 6.445 | 7.105 | 8.339 | 2.902 |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||||||||
| GD | 2.914 | 3.320 | 4.342 | 4.341 | 6.143 | 6.512 | 6.692 | 7.966 | 2.068 |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||||||||
| IGD | 2.893 | 3.173 | 4.311 | 4.511 | 6.100 | 6.597 | 7.374 | 8.588 | 2.375 |
| p-value | 0.000 |
| a. Based on the Δ metric | ||||||||
| Instance | MOPSO | QSFL | RLABC | CWWORL | CMAF | SNSGA | QNSGA | |
| t | 10 | 5.68 × 10−3 | 5.14 × 10−3 | 6.18 × 10−3 | 6.40 × 10−3 | 5.54 × 10−3 | 3.02 × 10−3 | 3.15 × 10−3 |
| 30 | 8.14 × 10−3 | 7.06 × 10−3 | 7.87 × 10−3 | 7.80 × 10−3 | 7.87 × 10−3 | 6.31 × 10−3 | 5.22 × 10−3 | |
| 50 | 1.13 × 10−2 | 1.01 × 10−2 | 1.08 × 10−2 | 9.04 × 10−3 | 9.42 × 10−3 | 9.25 × 10−3 | 9.19 × 10−3 | |
| m | 6 | 5.64 × 10−3 | 5.29 × 10−3 | 6.06 × 10−3 | 6.38 × 10−3 | 5.67 × 10−3 | 3.12 × 10−3 | 3.17 × 10−3 |
| 8 | 7.85 × 10−3 | 7.15 × 10−3 | 7.90 × 10−3 | 8.09 × 10−3 | 8.10 × 10−3 | 6.95 × 10−3 | 6.22 × 10−3 | |
| 10 | 1.16 × 10−2 | 9.86 × 10−3 | 1.09 × 10−2 | 8.77 × 10−3 | 9.07 × 10−3 | 8.52 × 10−3 | 8.18 × 10−3 | |
| f | 5 | 1.15 × 10−2 | 1.01 × 10−2 | 1.04 × 10−2 | 9.34 × 10−3 | 9.52 × 10−3 | 9.06 × 10−3 | 8.67 × 10−3 |
| 6 | 7.86 × 10−3 | 6.99 × 10−3 | 8.16 × 10−3 | 7.51 × 10−3 | 7.65 × 10−3 | 6.55 × 10−3 | 5.95 × 10−3 | |
| 8 | 5.79 × 10−3 | 5.18 × 10−3 | 6.30 × 10−3 | 6.39 × 10−3 | 5.67 × 10−3 | 2.97 × 10−3 | 2.94 × 10−3 | |
| |Ph| | 10 | 6.91 × 10−3 | 6.10 × 10−3 | 7.02 × 10−3 | 7.10 × 10−3 | 6.71 × 10−3 | 4.13 × 10−3 | 4.09 × 10−3 |
| 15 | 9.85 × 10−3 | 8.77 × 10−3 | 9.55 × 10−3 | 8.40 × 10−3 | 8.52 × 10−3 | 8.25 × 10−3 | 7.62 × 10−3 | |
| Average | 8.38 × 10−3 | 7.44 × 10−3 | 8.28 × 10−3 | 7.75 × 10−3 | 7.61 × 10−3 | 6.19 × 10−3 | 5.86 × 10−3 | |
| b. Based on the GD metric | ||||||||
| Instance | MOPSO | QSFL | RLABC | CWWORL | CMAF | SNSGA | QNSGA | |
| t | 10 | 4.67 × 10−5 | 3.75 × 10−5 | 4.70 × 10−5 | 4.03 × 10−5 | 4.10 × 10−5 | 3.25 × 10−5 | 2.73 × 10−5 |
| 30 | 6.12 × 10−5 | 5.70 × 10−5 | 6.37 × 10−5 | 5.58 × 10−5 | 5.94 × 10−5 | 5.94 × 10−5 | 4.79 × 10−5 | |
| 50 | 7.22 × 10−5 | 8.38 × 10−5 | 8.42 × 10−5 | 8.04 × 10−5 | 8.92 × 10−5 | 7.54 × 10−5 | 7.25 × 10−5 | |
| m | 6 | 4.52 × 10−5 | 3.89 × 10−5 | 4.67 × 10−5 | 4.23 × 10−5 | 4.24 × 10−5 | 3.36 × 10−5 | 2.77 × 10−5 |
| 8 | 6.24 × 10−5 | 5.90 × 10−5 | 6.45 × 10−5 | 5.63 × 10−5 | 5.71 × 10−5 | 6.02 × 10−5 | 4.89 × 10−5 | |
| 10 | 7.24 × 10−5 | 8.05 × 10−5 | 8.37 × 10−5 | 7.80 × 10−5 | 9.01 × 10−5 | 7.35 × 10−5 | 7.11 × 10−5 | |
| f | 5 | 7.24 × 10−5 | 7.05 × 10−5 | 8.37 × 10−5 | 7.80 × 10−5 | 9.01 × 10−5 | 7.35 × 10−5 | 7.61 × 10−5 |
| 6 | 6.03 × 10−5 | 5.99 × 10−5 | 6.35 × 10−5 | 5.76 × 10−5 | 5.85 × 10−5 | 6.29 × 10−5 | 5.02 × 10−5 | |
| 8 | 4.73 × 10−5 | 4.79 × 10−5 | 4.77 × 10−5 | 4.09 × 10−5 | 4.10 × 10−5 | 3.09 × 10−5 | 2.14 × 10−5 | |
| |Ph| | 10 | 5.38 × 10−5 | 4.89 × 10−5 | 5.56 × 10−5 | 4.93 × 10−5 | 4.97 × 10−5 | 4.69 × 10−5 | 3.83 × 10−5 |
| 15 | 6.62 × 10−5 | 7.00 × 10−5 | 7.43 × 10−5 | 6.84 × 10−5 | 7.67 × 10−5 | 6.47 × 10−5 | 6.02 × 10−5 | |
| Average | 6.00 × 10−5 | 5.95 × 10−5 | 6.50 × 10−5 | 5.88 × 10−5 | 6.32 × 10−5 | 5.58 × 10−5 | 4.93 × 10−5 | |
| c. Based on the IGD metric | ||||||||
| Instance | MOPSO | QSFL | RLABC | CWWORL | CMAF | SNSGA | QNSGA | |
| t | 10 | 1.24 × 10−3 | 1.13 × 10−3 | 1.16 × 10−3 | 1.85 × 10−3 | 1.87 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 1.11 × 10−3 |
| 30 | 2.33 × 10−3 | 2.00 × 10−3 | 2.33 × 10−3 | 2.20 × 10−3 | 3.21 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−3 | 1.50 × 10−3 | |
| 50 | 4.07 × 10−3 | 3.53 × 10−3 | 3.76 × 10−3 | 3.37 × 10−3 | 4.27 × 10−3 | 2.95 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−3 | |
| m | 6 | 1.45 × 10−3 | 1.33 × 10−3 | 1.32 × 10−3 | 1.92 × 10−3 | 1.85 × 10−3 | 1.06 × 10−3 | 1.25 × 10−3 |
| 8 | 2.41 × 10−3 | 2.04 × 10−3 | 2.34 × 10−3 | 2.31 × 10−3 | 3.18 × 10−3 | 1.94 × 10−3 | 1.56 × 10−3 | |
| 10 | 3.78 × 10−3 | 3.29 × 10−3 | 3.59 × 10−3 | 3.19 × 10−3 | 4.33 × 10−3 | 2.89 × 10−3 | 2.22 × 10−3 | |
| f | 5 | 3.18 × 10−3 | 3.12 × 10−3 | 3.14 × 10−3 | 3.26 × 10−3 | 4.33 × 10−3 | 2.98 × 10−3 | 2.63 × 10−3 |
| 6 | 2.46 × 10−3 | 2.07 × 10−3 | 2.41 × 10−3 | 2.20 × 10−3 | 3.14 × 10−3 | 1.74 × 10−3 | 1.57 × 10−3 | |
| 8 | 2.00 × 10−3 | 1.47 × 10−3 | 1.70 × 10−3 | 1.96 × 10−3 | 1.89 × 10−3 | 1.17 × 10−3 | 8.34 × 10−4 | |
| |Ph| | 10 | 1.83 × 10−3 | 1.58 × 10−3 | 1.73 × 10−3 | 2.11 × 10−3 | 2.51 × 10−3 | 1.50 × 10−3 | 1.40 × 10−3 |
| 15 | 3.26 × 10−3 | 2.86 × 10−3 | 3.10 × 10−3 | 2.83 × 10−3 | 3.72 × 10−3 | 2.43 × 10−3 | 1.95 × 10−3 | |
| Average | 2.55 × 10−3 | 2.22 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−3 | 2.47 × 10−3 | 3.12 × 10−3 | 1.96 × 10−3 | 1.68 × 10−3 | |
| Metric. | MOPSO | QSFL | RLABC | CWWORL | CMAF | SNSGA | QNSGA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ | 6.555 | 3.043 | 7.504 | 4.212 | 4.139 | 2.567 | 2.184 |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||||||
| GD | 6.077 | 3.041 | 7.416 | 3.999 | 4.296 | 2.790 | 2.347 |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||||||
| IGD | 6.350 | 3.790 | 7.126 | 4.223 | 5.323 | 3.353 | 2.863 |
| p-value | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Chen, H.; Yan, F.; Deng, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Q. An Improved NSGA-II for Three-Stage Distributed Heterogeneous Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling with Flexible Assembly and Discrete Transportation. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081306
Shi Z, Chen H, Yan F, Deng X, Hao H, Zhang J, Yin Q. An Improved NSGA-II for Three-Stage Distributed Heterogeneous Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling with Flexible Assembly and Discrete Transportation. Symmetry. 2025; 17(8):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081306
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhiyuan, Haojie Chen, Fuqian Yan, Xutao Deng, Haiqiang Hao, Jialei Zhang, and Qingwen Yin. 2025. "An Improved NSGA-II for Three-Stage Distributed Heterogeneous Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling with Flexible Assembly and Discrete Transportation" Symmetry 17, no. 8: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081306
APA StyleShi, Z., Chen, H., Yan, F., Deng, X., Hao, H., Zhang, J., & Yin, Q. (2025). An Improved NSGA-II for Three-Stage Distributed Heterogeneous Hybrid Flowshop Scheduling with Flexible Assembly and Discrete Transportation. Symmetry, 17(8), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081306





