Abstract
Railway catenary layout drawings (RCLDs) have the characteristics of upper and lower symmetry, a large drawing size, a small size, high similarity among target symbols, and an uneven distribution of symbol categories. These factors make the symbol detection task more complex and challenging. To address the aforementioned challenges, this paper proposes three enhancements to YOLOv8n to improve symbol detection performance and integrates an improved denoising diffusion probabilistic model (IDDPM) to mitigate the imbalance in symbol category distribution. First, the multi-scale dilated attention (MSDA) is introduced in the Neck part to enhance the model’s perception of the global context in complex RCLD scenes, so that it can more effectively capture the symbol information distributed in different scales and backgrounds. Secondly, the receptive field attention convolution (RFAConv) is used in the detection head to replace the standard convolution, to improve the ability to focus on the target symbols in RCLDs and effectively alleviate the occlusion interference between symbols. Finally, the dynamic upsampler (DySample) is used to enhance the clarity and positioning accuracy of the edge area of small target symbols in RCLDs and enhance the detection of small targets. The above design made targeted optimizations to resolve the problems of symbol and background interference, character overlap, and symbol category imbalances in complex scenes in RCLDs, effectively improving the overall detection performance of the model. Compared with the baseline YOLOv8n model, the improved YOLOv8n achieves increases of 2.9% in F1, 1.9% in mAP@0.5, and 1.7% in mAP@0.5:0.95. With the introduction of synthetic data, the recognition of minority-class symbols is further enhanced, leading to additional gains of 4%, 3.8%, and 14% in F1, mAP@0.5, and mAP@0.5:0.95, respectively. These results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method in improving detection performance.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of rail transportation, the catenary distribution range has been expanding in recent years. Catenary is an important part of electric locomotives as it can obtain electric energy, which is vital to ensure the normal and stable operation of electric locomotives [1]. RCLDs serve as the basis for construction, operations, and maintenance, and contain key information such as equipment symbols’ locations, models, and layout. However, the automatic symbol recognition of RCLDs faces many challenges, including the large drawing sizes, dense symbols, complex backgrounds, small sizes, and similarities in their appearance. Problems such as the uneven distribution of categories also further aggravate the difficulty of detection. Currently, the interpretation of engineering drawings largely depends on manual analysis by professionals. This method is not only time-consuming and labor-intensive but is also susceptible to human error, which increases reliance on experts [2,3].
In recent decades, numerous researchers have proposed various methods to process, analyze, and interpret these engineering drawings automatically [4,5,6,7]. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, deep learning, especially convolutional neural networks (CNNs), has made breakthroughs in the fields of image recognition and medical image analysis [8]. In 2018, Moreno-García et al. noted that emerging technologies in machine vision, such as machine learning, should be effectively introduced into the processing and analysis of engineering drawings to promote their intelligent development [9]. Currently, the world is in an era of intelligent digital transformation, and the railroad industry is also actively undergoing intelligent transformation. Through the introduction of artificial intelligence, building information modeling, and other cutting-edge technologies, the intelligent construction of railroads could lead to the comprehensive digital management of the entire life cycle, promoting overall upgrades to the railroad industry [10].
Many deep learning methods have also been applied to technical drawings [11], construction drawings [12], engineering documents [13], and engineering drawings [14,15], and have improved automation to some extent. According to Laura Jamieson et al., despite the progress brought by the use of deep learning in automating engineering drawing digitization, several critical challenges still need to be addressed. For instance, the complex background of engineering drawings and symbols’ tendency to overlap and suffer from noise interference can lead to inter-class confusion. Moreover, the imbalanced symbol category distribution can lead to model bias toward the majority class, while the limited availability of public datasets hinders further research in this area [16].
Although existing studies have made progress in modeling complex backgrounds, small target detection, or sample enhancement, most of them focus on a single problem. A unified solution that simultaneously addresses small target occlusion and category imbalances is still lacking. Especially when dealing with complex RCLDs, existing methods cannot fully address these challenges, which restricts their ability to provide an efficient analysis and their intelligent application within the deep learning framework.
To cope with these problems, this paper aims to construct an efficient symbol detection framework for RCLDs. It focuses on three key challenges: the limitations of model input caused by large drawing sizes, the impact of small target occlusion on detection accuracy, and the difficulty in recognizing minority classes due to category imbalances. The goal is to improve overall detection performance against complex backgrounds. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- Improve the baseline model YOLOv8n, then sequentially introduce MSDA, RFAConv, and Dysample to improve the feature extraction ability and small target identification effect in difficult scenarios.
- Differing from traditional GAN-based sample generation methods, this paper introduces IDDPM for symbol recognition in RCLDs. This generates higher-quality, more stable samples for minority classes, helping to alleviate category imbalances and enhance recognition performance for minority symbols.
- Based on the improved YOLOv8n model, the original dataset and the dataset with the addition of synthetic data are trained separately to evaluate the detection performance and perform a comprehensive analysis and comparison.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents a discussion of recently published research results, Section 3 details our proposed methodology, Section 4 describes the experimental design and its results, and Section 5 provides an in-depth discussion of the findings and suggestions for future research.
2. Related Work
This section discusses the most recent research breakthroughs on this subject and examines several deep-learning algorithms used in engineering drawing inspections.
2.1. Development of Object Detection Algorithms
Target detection algorithms are mainly divided into two categories: two-stage target detection and single-stage target detection. Two-stage methods have high accuracy; for example, Faster R-CNN introduces a region proposal network (RPN) to improve detection [17], and Mask R-CNN adds mask branches to realize pixel-level target segmentation [18]. Single-stage target detection algorithms emphasize real-time detection and high efficiency, such as YOLO, which transforms detection into a regression problem to achieve fast predictions [19], while SSD directly predicts the target location and category through multi-layer feature maps, avoiding the computation of the region proposal network (RPN) and non-maxima suppression (NMS) to improve detection speed [20] and DETR introduces the Transformer model, removing the anchor frames and NMS, further improving the detection efficiency [21]. YOLOv4 achieves a balance between accuracy and speed through feature fusion [22]. On this basis, Ji et al. introduced MCS-YOLOv4, an improved small-object detection algorithm derived from YOLOv4 [23]. The incorporation of multi-scale contextual features, extended receptive field blocks, and attention mechanisms notably enhances its performance in detecting small objects. YOLOv5, on the other hand, achieves a lightweight design through the adaptive anchor frame mechanism, which improves the inference speed and ensures high accuracy, and YOLOv8 optimizes the network structure based on YOLOv5, reduces the number of model parameters, and improves the computational efficiency; this method is now widely used in many types of research [24]. For example, Wang et al. used a YOLOv8 surveillance video for the detection of non-standard mining behaviors and improved it by introducing techniques such as deformable convolution and SimAM, which enhanced the overall performance of the model [25]. Hao et al. enhanced the detection of lesions across various scales—particularly multiple small lesions—by improving YOLOv8’s backbone network and incorporating attention mechanisms [26].
Currently, improvements in generalized target detection models are mainly focused on the field of natural images. However, these models show poor adaptability when dealing with engineering drawings, especially when confronted with severe occlusions between symbols, morphological similarities, and large differences in the number of categories.
2.2. Symbol Detection Methods Using Engineering Drawings
Many studies on engineering drawings have recommended various strategies for enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of symbol recognition and detection. Tan et al. employed Local Binary Patterns (LBP) and Spatial Pyramid Matching (SPM) to automatically recognize components in piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs) [27]. Moreno-García et al. used the Canny edge detector combined with a sequential heuristic symbol localization method to effectively identify and isolate symbols in images, improving the character detection effect after separating symbols and text [28]. Moon et al. combined the RetinaNet model to enhance the recognition of line objects and arrows in pipeline and instrument diagrams [29]. Bhanbhro et al. obtained 95% accuracy using YOLOv8 to localize and recognize symbols in single-line diagrams [30]. Su et al. used YOLOv5 + SE for pipeline identification and improved the accuracy of pipeline identification [31]. Yang et al. integrated the Swin Transformer into the Faster R-CNN model to further enhance the precision and recall of single-line symbol detection [32].
Although existing methods have made some progress in drawing recognition, most of them rely on a generalized detection framework, which makes it difficult for them to effectively deal with symbol class imbalances and occlusion problems. Notably, there are still limitations regarding misrecognition and omission in the detection of a few classes of symbols, and more targeted improvements are urgently needed.
2.3. Synthetic Image Methods Using Engineering Drawings
Although neural networks have made significant progress in drawing recognition with advances in deep learning, challenges remain. Issues like category imbalances and dataset size limitations continue to hinder the accuracy of drawing recognition [33]. As a result, most studies used Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to solve the issue of symbol category imbalances in engineering drawings. For example, Bhanbhro et al. used a multi-pseudo-class generative adversarial network (MFCGAN) to generate a synthetic single-line diagram (SLD) dataset, enhancing the original dataset and solving the class imbalance problem [30]. Elyan et al. used the YOLO model and the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to improve the recognition of minority class symbols [34]. Bhanbhro et al. improved the quality of the dataset and the recognition performance of YOLOV5 by using deep convolutional GAN (DCGAN) and least squares GAN (LSGAN) [35]. Despite their power, GANs require careful regularization and optimization strategies to overcome their instability [36]. In contrast, diffusion modeling (DM) has a much simpler training process. It also narrows the gap between image quality and human perceptual preferences, generating samples with exceptional quality and a realism that surpasses that obtained using previous methods [37]. In recent years, the diffusion model has emerged as a highly regarded deep generative model in computer vision. Its excellent performance in detail portrayal and diversity generation has set new standards, challenging the long-standing dominance of GANs [38]. For example, PIDM, proposed by Bhunia et al., effectively avoids the limitations of GAN in generating realistic textures, handling complex deformations and severe occlusions through a denoising diffusion process, and can generate high-quality, realistic images in challenging scenarios [39]. Wu et al. proposed a DDPM-based super-resolution method for brain MRI, which integrates a self-attention mechanism to optimize the network and enhance image quality. The experimental results demonstrated that the method outperforms existing techniques while reducing image distortion [40].
However, diffusion models have not been fully explored in engineering drawing recognition tasks. Notably, there is still a gap in the generation of synthetic samples for symbol class imbalances.
According to the summary of the review of the related literature, the existing methods for engineering drawing symbol detection are mainly based on the YOLO series. However, most of the methods use a basic architecture, which struggles to cope with challenges such as small targets, occlusion, and complex backgrounds. To address the category imbalance problem, some studies introduced GAN to generate a few class samples to enhance the dataset. These methods suffer from the problems of unstable training and limited generation quality. Additionally, the current research mainly focuses on the recognition and detection of P&ID drawings and single-line diagrams, while relatively few studies have focused on RCLDs. With the advancement of digital transformation in the railroad industry, there is an increasing demand for the efficient parsing and management of RCLDs. Therefore, this paper combines the characteristics of RCLDs and proposes two aspects for improvement. First, small target detection is optimized for the YOLOv8n structure to improve the detection of dense, occluded, and small symbols. Second, IDDPM is used to generate high-quality, few-class synthetic symbols, thus effectively compensating for the performance bottleneck caused by uneven training samples.
3. Methodology
This paper presents a comprehensive solution regarding how to improve symbol detection in RCLDs. Section 3.1 presents information about the dataset used, including the data exploration and preprocessing techniques. Section 3.2 outlines the methodological framework used in this paper. Section 3.3 details the target detection method and improvement strategies. Section 3.4 proposes a solution to the category imbalance problem.
3.1. RCLDs Dataset
In this paper, the experiment selected RCLDs as the research object. RCLDs are technical drawings used in rail transportation to represent the geometric layout and component distribution of the catenary system. They use a two-dimensional planar format to depict the system’s physical structure. A local schematic diagram of the station RCLDs is shown in Figure 1. The drawing shows the relative positions of contact wires, load-bearing cables, guy wires, and other conductors, as well as components like pillars and suspenders. It also indicates the conductor height, anchor section information, and symbol numbers. RCLDs are an important reference for engineers to understand the structure and function of the system during the design, construction, and maintenance of the catenary. These drawings are usually archived as paper documents or images. Interpreting and analyzing them requires a lot of time, effort, and expertise, and misinterpretations can have serious consequences. Therefore, an accurate understanding of RCLDs is critical.
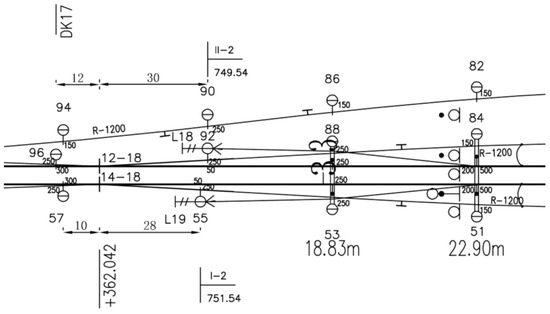
Figure 1.
Localized schematic of the station RCLDs.
To evaluate the performance of the method, the project partners provided 25 RCLDs, covering multiple station and section scenarios. Station drawings are more complex, while section drawings are simpler. To balance the dataset complexity, all station drawings and a selection of section drawings were retained, ensuring representativeness and diversity. The entire dataset was labeled with 11 symbols, as depicted in Figure 2. These were as follows: double tie wire (DTW), catenary pillar outside tunnel (CPOT), fully compensated lower anchor of the catenary outside tunnel (FCLACOT), single tie wire (STW), center anchor knot (CAK), additional conductor suspension point (ACSP), fully compensated lower anchor of bearing cable (FCLABC), fully compensated lower anchor of contact line (FCLACL), uncompensated lower anchor of catenary outside tunnel (ULACOT), additional conductor pair anchor inside tunnel (ACPAIT), and catenary suspension bollard inside tunnel (CSBIT).
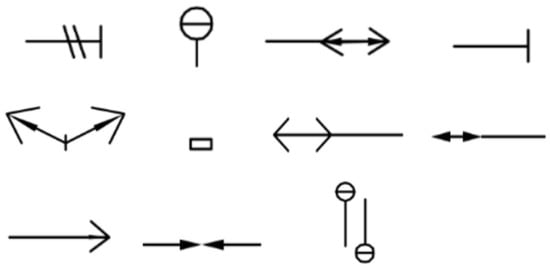
Figure 2.
Examples of typical symbols in RCLDs.
As part of the data preparation, we used IDDPM to generate minority class symbols. The dataset was divided into two categories: the first category contained only real images, and the second category included real images and synthetic images. This dataset is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Data set combinations.
The RCLDs in the original data are large images. The station RCLDs were about 80,000 × 7000 pixels, and the section RCLDs were about 50,000 × 1700 pixels. To facilitate model detection, this paper applied the sliding window method to partition the original image into 1024 × 1024 blocks, with a 0.1 overlap ratio to accelerate training and preserve symbol integrity. This paper used the LabelImg tool to annotate the symbol category and location of the RCLDs, as shown in Figure 3.
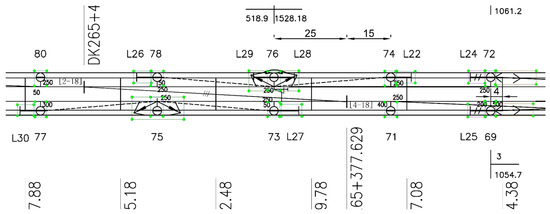
Figure 3.
Symbol information annotation in RCLDs.
Some areas of the station contact network plane design drawings contained vertical symmetry, and the interval layout presented basic symmetrical structural characteristics. Drawing inspiration from this symmetry, the image’s symmetry features were fully leveraged during data augmentation. Operations like horizontal and vertical flipping, as well as center cropping, were applied to improve the model’s ability to recognize symmetrical structures. In addition, by combining techniques such as rotation and the addition of noise, the diversity of the training set was further expanded to simulate the actual transformation of the drawings.
As illustrated in Figure 4, the distribution of various symbols in the original dataset was severely imbalanced. The number of symbols varied significantly. For instance, there were 9561 occurrences of CPOT symbols and 10,495 instances of ACSP symbols. In contrast, ULACOT and ACPAIT symbols were much less frequent, with only 186 and 308 instances, respectively.
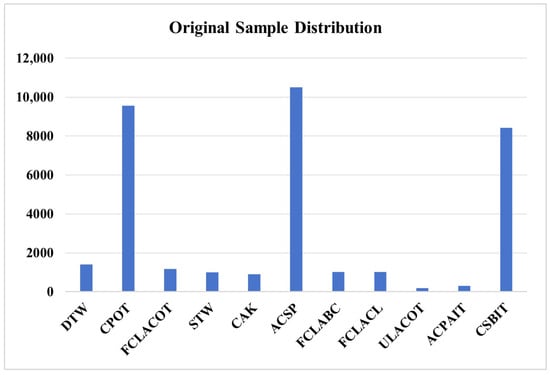
Figure 4.
Distribution of the number of categories in the original dataset.
3.2. Symbol Recognition Methods
As shown in Figure 5, a full description of the approach used in this paper is provided. This paper first used IDDPM to generate synthetic data to supplement the original dataset; secondly, the synthetic data were added to the original dataset, and the improved YOLOv8n was used to recognize the symbols in RCLDs. The experiments were divided into three sections: (a) comparison experiments between the improved YOLOv8n model and other cutting-edge algorithms to verify the effectiveness of this paper’s algorithm; (b) ablation experiments on the improved YOLOv8n model to verify the effectiveness of the improvements in each module; and (c) merging the original image with the synthesized image to verify the training effect of adding the synthesized dataset.
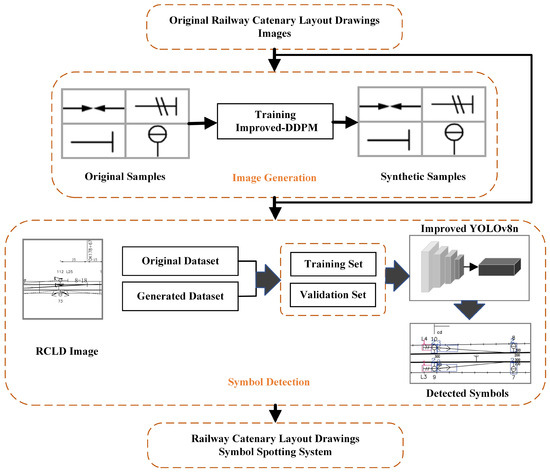
Figure 5.
Structure of the RCLD’s symbol recognition system.
3.3. Improved YOLOV8n
YOLOv8n consists of a Backbone, Neck, and Head, and has a strong target detection ability. However, in the RCLD symbol detection task, symbols are often small and face challenges like overlapping and complex backgrounds. As a result, YOLOv8n faces limitations in local feature extraction, global information modeling, and up-sampling information retention, which impact its accuracy in the detection of small targets.
First, in the Neck structure of YOLOv8n, the C2F module is the key component, which is responsible for fusing multi-scale features to improve detection performance and reduce computational cost. Its core unit, Bottleneck, offers advantages in computational efficiency and feature expression. Nevertheless, it is limited by its fixed receptive field, which hampers its ability to capture long-distance features and weakens the feature-fusion ability of the C2F module, affecting small target detection. Secondly, in the Head structure, the detection head further processes multi-scale features from the C2F module to predict the target category, bounding box, and confidence level. However, the 3 × 3 convolution adopted by YOLOv8n faces limitations in handling small and occluded targets, which restricts the model’s ability to capture fine features. In addition, up-sampling, a key step to recover the resolution of the feature map, is particularly important for small target detection. YOLOv8n’s nearest neighbor interpolation method copies neighboring pixel values, ignoring pixel continuity. This causes blurred edges, particularly at the symbol outline–background junction, affecting the detection accuracy. To address these issues, this paper introduces MSDA [41], RFAConv [42], and Dysample [43], which aim to reduce the misdetection and omission of small targets in RCLDs, enhancing the detection of small and irregular targets. The improved YOLOv8n structure is shown in Figure 6.
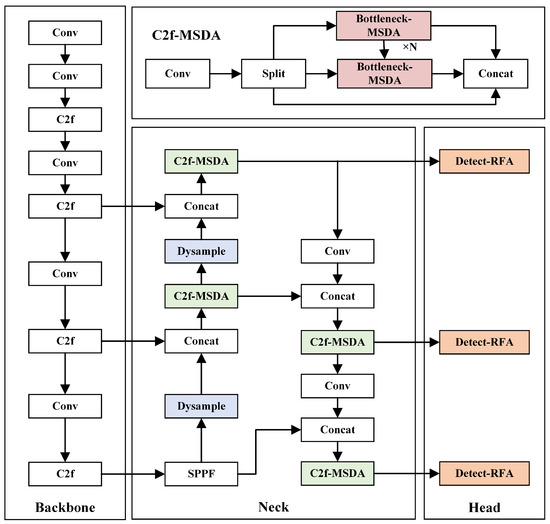
Figure 6.
Structure of the improved YOLOv8n.
3.3.1. C2f-MSDA
RCLDs have complex structures and small symbols, making them a typical small-target detection task. The standard convolution struggles to focus on key information during feature extraction, causing symbols to be obscured by background noise and increasing the risk of missed or false detections. In the YOLOv8n model’s Neck part, the bottleneck layer in the C2F structure uses standard convolution for information fusion. However, global information cannot be fully captured due to the fixed receptive field. As a result, small target features are susceptible to interference from background noise, which affects their detection accuracy. The MSDA module combines multi-scale dilation convolution with the self-attention mechanism, effectively fusing local and global information, improving the model’s ability to recognize small target symbols. Specifically, MSDA adjusts the receptive field of the convolution kernel by setting different dilation rates, enabling the model to model multi-scale contextual information during feature extraction. It simultaneously focuses on both the symbol itself and the surrounding region, allowing for more accurate judgments in scenarios with ambiguous symbol features or severe background interference. Meanwhile, the self-attention mechanism enhances the model’s response to critical regions, helping capture long-range information and improving the representation of small target features. This notably enhances the model’s ability to detect small target symbols in complex scenes. Therefore, in this paper, we improve the C2f module in the Neck network based on YOLOv8n by replacing the standard convolution of its bottleneck layer with MSDA, named Bottleneck-MSDA, whose structure is shown in Figure 7.
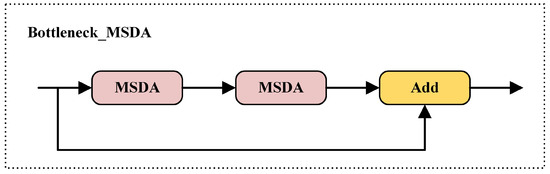
Figure 7.
MSDA replaces standard conv.
The inflated attention block combines the inflated convolution with the self-attention mechanism to enable the model to capture global contextual information across local regions. Specifically, the dilation convolution samples pixel points at regular intervals on the feature map, thus expanding the sensory field. Its pixel index is computed as shown in Equation (1):
where r is the expansion rate, which defines the interval between neighboring sampling points. denotes the coordinates of the current pixel; are the coordinates of the pixel after sampling by expansion; w is the size of the convolution kernel; and p and q control the sampling range. The formula indicates that pixels are sampled within a window centered at , with intervals determined by the dilation rate r. This expands the receptive field without increasing the number of parameters, helping the model capture richer contextual information.
Unlike standard convolutions with a fixed receptive field, MSDA integrates the Dilate Attention mechanism, allowing for features to propagate across scales and enhancing information integration in distant regions. This is achieved through self-attention with multiple dilation rates (dilation = 1, 2, 3, 4). The MSDA module comprises three key steps, as illustrated in Figure 8.
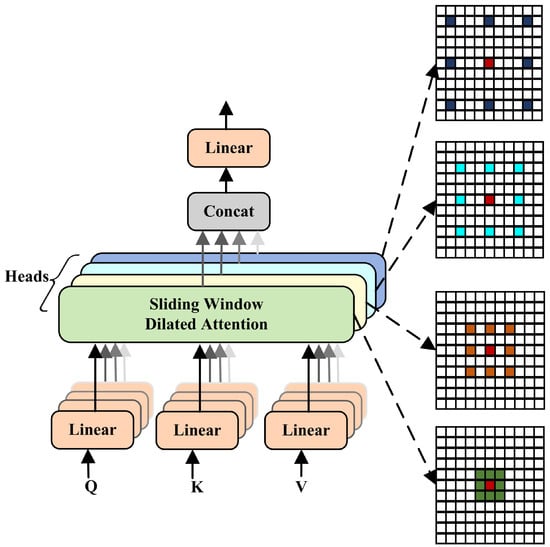
Figure 8.
Structure of MSDA.
First, the input feature map is mapped into three sets of tensors, namely query (Q), key (K), and value (V), using convolutional layers. Second, to address the limitations of a fixed receptive field in a single head, the model employs a multi-head mechanism. It divides the input channel into subspaces, assigning different expansion rates to each, enabling parallel computation, and capturing features at various scales. In this process, features with different expansion rates are dot-producted using Q and K to generate attention scores. Long-range feature associations are established after softmax normalization instead of relying solely on local information. The introduction of a multi-head mechanism allows for multiple heads to process the Q, K, and V tensors independently, forming diverse information pathways. This design reduces redundancy and interference, alleviates the information bottleneck, and enhances the model’s ability to capture complex structural patterns in the data. In addition, this parallel computing method further expands the receptive field, allowing for the model to extract multi-level contextual information at multiple scales and thereby improving its ability to model features of distant areas. Finally, the outputs of multiple heads with multiple dilation rates are merged and projected through the linear layer. To enhance the stability of the attention mechanism, MSDA also introduces a Dropout operation that randomly suppresses some of the attention weights to prevent overfitting and enhance the generalization ability of the model in complex contexts.
Ultimately, the computed attentional weights act on the V to form a weighted feature representation, which optimizes the global information representation in high-complexity and small-objective scenarios. In RCLD’s complex scenarios, MSDA makes the model more robust in small-target detection tasks through remote feature integration, which effectively reduces leakage and false detection problems.
3.3.2. Detect RFA
In RCLDs, overlaps frequently occur between the symbols and the background, between the symbols themselves, and between the symbols and text. These overlaps can lead to the loss of symbolic feature information, thereby increasing the difficulty of recognition. The detection head of YOLOv8n uses standard convolution for feature extraction and classification. However, in complex scenarios, the fixed parameter-sharing mechanism of standard convolution may limit their adaptability to local features.
In contrast, RFAConv integrates a spatial attention mechanism. This enables the convolutional kernels to adaptively adjust their weights according to the spatial distribution of the input features, thereby optimizing the extraction of local information. Specifically, RFAConv does not apply the same convolutional kernel at every location. Instead, it dynamically adjusts the degree of focus of the kernel based on the importance of different regions in the feature map. This adaptive mechanism allows the model to prioritize key regions while suppressing responses to irrelevant areas during feature extraction. This enhances the model’s perception of symbol boundaries and complex backgrounds. RFAConv demonstrates a stronger discriminative ability, especially when dealing with blurred boundaries or structurally similar symbols. This greatly enhances the model’s ability to detect small and occluded targets.
Therefore, this paper introduces RFAConv to the detection head of YOLOv8n, replacing the standard convolution. A new detection head module, named Detect-RFA, was constructed, as illustrated in Figure 9.
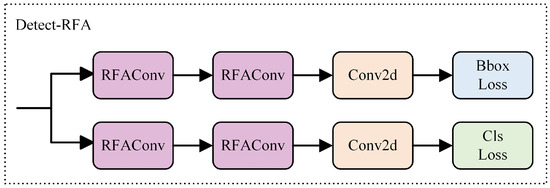
Figure 9.
RFAConv replaces Standard Conv.
The structure of RFAConv is shown in Figure 10; it is divided into three main stages. First, in the dynamic weight generation stage, average pooling is applied to the input image to extract the average features of each region. Then, a 1 × 1 group convolution is used to group the input channels, and the pooled features are mapped to a higher-dimensional space to generate the convolutional kernel weights. After softmax normalization, the dynamic importance of each spatial location is evaluated to optimize the sensory field distribution and enhance the processing capability for complex images. Meanwhile, the original feature maps are processed through 3 × 3 group convolutions, followed by batch normalization and a ReLU activation function. This enhances the model’s nonlinear representation capacity and improves its generalization performance. Secondly, in the weighted feature generation stage, the attention features are multiplied by the receptive field features to achieve dynamic feature weighting. This allows the model to enhance key features while suppressing irrelevant information, thereby optimizing its local sensitivity and improving the expressive power of the feature map. Finally, in the rearrangement and convolution processing stage, the structure of the weighted feature data is adjusted using the rearrange function to accommodate subsequent convolution operations.
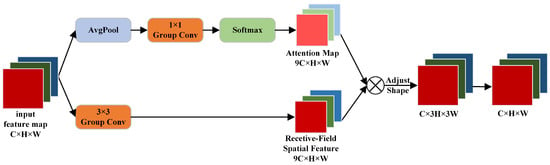
Figure 10.
Structure of RFAConv.
As shown in Figure 11a, the standard convolution uses a fixed parameter-sharing approach when processing images, enabling it to efficiently model generic features. However, when processing complex scenes, this fixed-weight approach may ignore local details, thus limiting its ability to recognize small targets. This can be calculated using Equation (2):
where represents the output value of each convolution slider after calculation; represents the pixel value at the corresponding position in each slider; K represents the convolution kernel; S is the number of parameters in the convolution kernel; and N represents the total number of receptive field sliders. The formula performs feature extraction by sliding the kernel over the image step-by-step. It computes a weighted summation of the pixel values in the local region and the corresponding convolution kernel parameters, generating the response value at the corresponding position in the feature map. This approach helps capture the local structural information of the image.
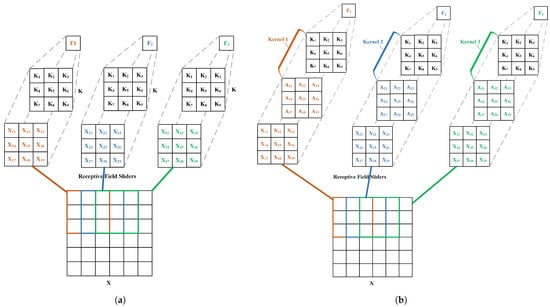
Figure 11.
Standard vs. dynamic convolution. (a) Standard convolution parameter-sharing. (b) RFAConv dynamic convolution weights and spatial attention mechanism.
In contrast, as shown in Figure 11b, RFAConv integrates a spatial attention mechanism, allowing the convolution kernel to adaptively adjust its weights based on its spatial features. This breaks the limitation of fixed weights in standard convolution, enhancing the flexibility of feature representation and improving the modeling of fine-grained information. The corresponding computation is shown in Equation (3).
where denotes the final feature map value obtained by weighting each input value, the corresponding convolutional kernel, and the spatial attention mechanism; represents the weight of the spatial attention mechanism, indicating the amount of attention given to different regions at a particular spatial location. This formula introduces spatial attention weights based on standard convolution operations. It dynamically adjusts the contribution of each position in the input feature map, allowing the model to focus more on critical regions of the image. This mechanism is particularly effective in enhancing the model’s ability to recognize small objects, fine structures, and occluded areas.
Specifically, the spatial attention mechanism can dynamically adjust the convolution kernel weights according to the feature information at different locations, making the convolution operation more adaptable to different regions. This approach not only enhances the attention to key targets but also suppresses background interference and improves the model’s ability to perceive detailed features.
On the other hand, RFAConv employs group convolution to group channel features, which reduces computational complexity, minimizes memory usage, and enhances channel independence. This enables the model to extract spatial features more flexibly and effectively, leading to a more efficient and accurate feature extraction process.
3.3.3. Dysample
Traditional upsampling methods, such as bilinear and nearest-neighbor interpolation, are simple and efficient for generating high-resolution images. However, they often lead to loss of detail and reduced image quality, which limits their performance when detecting small target symbols in complex scenarios like RCLDs. DySample introduces a bias generation mechanism that allows for the flexible adjustment of sampling positions. This enables precise spatial detail recovery and accurate feature alignment. Compared to fixed interpolation methods, DySample offers more accurate feature alignment during upsampling and better captures edges and fine details. It considerably improves the reconstruction of structural and textural information in feature maps, particularly aiding in the detection of small symbols or those with blurred edges. Therefore, this paper adopts the static-range version of DySample to replace traditional upsampling methods, aiming to reduce symbol detail loss and strengthen the model’s perception of small target symbols.
The structure of DySample is illustrated in Figure 12. This module dynamically generates sampling positions, effectively enhancing edge clarity and the expression of detail in images. Traditional upsampling methods typically rely on a fixed grid sampling, ignoring the spatial relationships between sampling points. This often results in uneven sampling distributions and limits the precision of upsampling.
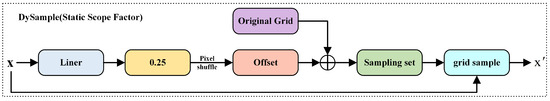
Figure 12.
Structure of Dysample.
To improve sampling adaptability, DySample applies a linear mapping to generate offset values. However, due to the lack of constraints, these offsets may overlap near image boundaries, leading to edge aliasing and feature confusion. Such errors can propagate through deeper layers of the network, ultimately producing artifacts.
To address this issue, DySample introduces a Static Scope Factor. By multiplying the offset values with a fixed coefficient of 0.25, the adjustment range is restricted to local neighborhoods. This coefficient is near the theoretical threshold between the sampling overlap and separation. It maintains flexibility while minimizing boundary blur and interference, greatly enhancing the edge discrimination and detection performance for small symbols, especially in RCLD scenarios.
The final sampling positions are obtained by adding the offsets to the standard grid coordinates, followed by normalization to the [−1, 1] range to fit the input format of the grid_sample. Using the grid_sample function, a bilinear interpolation is performed on the original feature map to generate a higher-resolution output. This process achieves dynamic spatial reconstruction while preserving structural edges and textural details.
Additionally, Pixel Shuffle is used to rearrange the low-resolution offset feature maps to the target resolution, ensuring alignment between the offset and output space. This enhances the feature response in small-object and boundary regions. A channel grouping strategy is also introduced to process the features in groups, reducing the computational overhead and inference latency. This design improves the model’s practicality and deployability under resource-constrained conditions.
3.4. IDDPM Generates Synthetic Images
The diffusion model, introduced by Sohl-Dickstein et al. in 2015, is a parameterized Markov chain learned using variational inference to create samples that match the data distribution [44]. The key idea is to develop a backward-diffusion process that gradually removes noise through the Markov chain to recover the signal, which is the inverse of forward diffusion, as illustrated in Figure 13.
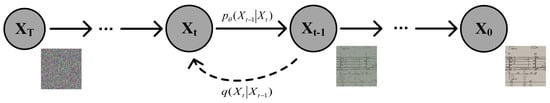
Figure 13.
Forward diffusion and reverse generation process of the diffusion model.
In the forward diffusion process, the signal begins with the data distribution and gradually adds noise over T steps, eventually becoming covered by noise. The specific formula is as follows (4):
where denotes the initial data distribution and describes the process of adding noise to the current state on top of the previous step at each step t. The formula establishes a gradual transition from clear to noisy data as a forward-diffusion process.
The generated distribution starts from the final state of the diffusion process and gradually restores to the initial data through the reverse conditional probability. The specific formula is as follows (5):
where is the distribution of the final noise states, and describes how the previous step is predicted by the current state at each step t, i.e., the backward-diffusion process. This formula, grounded in the forward-diffusion process, describes the reverse procedure for recovering the original data from a noisy state, thereby accomplishing the denoising process.
Diffusion models are generated from noisy samples for data distributions by modeling the reverse-diffusion path. Despite their theoretical novelty, diffusion models have low sampling efficiency, poor generation quality, and a high computational cost, resulting in much slower generation than other generative models, such as GANs. In 2020, Ho et al. proposed the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM), which provides a key improvement to traditional diffusion models [45]. Its core lies in changing the prediction goal of the inverse process from directly predicting the mean to predicting the noise, which simplifies the training goal and improves the generation performance. Meanwhile, DDPM avoids the problem of explicitly modeling complex conditional distributions through noise prediction objective functions, improves the training stability and generation quality, and is becoming a new hotspot in the field of image generation.
IDDPM further improves the quality and efficiency of image generation based on DDPM [46]. IDDPM introduces a flexible noise variance prediction mechanism, which adjusts the noise variance produced by the network output vector v. The specific formula for the noise variance is as follows (6):
where is the noise variance in the inverse-diffusion process, which directly affects the quality and diversity of the generated images. The vector v is the result of the network output, which determines how to adjust the selection of the two noise variances, and , via interpolation. represents the initially set noise variance, and denotes the corrected noise variance. By applying the exponential function exp, the term remains positive. This effectively regulates the magnitude of noise during generation, balancing the preservation of detail and removal of noise in the generated images.
Parameterizing the noise variance as an interpolated form of and instead of a fixed value enables the model to flexibly control the noise variance at each time step. This dynamic adjustment not only avoids the problem of noise spreading too fast but also helps the model to more accurately predict the noise level at each time step. This improvement enhances the quality and diversity of the generated images while also reducing unnecessary computational overhead during training, thus indirectly speeding up the training process.
IDDPM adopts a noise-scheduling method based on the cosine function. The core of noise scheduling is , which varies with time step t, as follows (7):
where parameter is scheduled using a cosine function based on the variation in the timestep t, controlling the intensity of the noise in the reverse-diffusion process. Function represents the value of the cosine function at time step t = 0, which reflects the noise intensity at the initial stage of the back-diffusion process. The function is then defined as the cosine function , where s is a small offset to regulate the variation in the noise over the time series, ensures the smoothness and continuity of the noise variation, T is the total number of diffusion steps, and t is the current diffusion step. Compared to traditional linear scheduling, this cosine scheduling strategy reduces interference from noise at later stages of diffusion while preserving the smooth scheduling. This enhances the naturalness and quality of the generated images while also decreasing the computation time required for their generation.
Compared to DDPM and GAN, although DDPM generates high-quality images, it has a lower generation efficiency and higher computational cost. On the other hand, GAN has the advantage of faster generation but often suffers from instability during training, which can lead to issues such as mode collapse. Additionally, the generation quality of GAN is heavily influenced by the training data and network design. Considering the generation’s quality, efficiency, and stability, IDDPM is a more suitable choice as the generative model. In particular, for the minority class symbol generation task in this paper, IDDPM can stably generate high-quality images with fewer samples and provides a more stable generation process. Based on these advantages, this paper chose to use IDDPM to generate synthetic images to alleviate the class imbalance problem in RCLDs.
4. Experiments
This section describes the experimental environment and process. First, in this paper, a comparison experiment between the improved YOLOv8n model and other state-of-the-art models was conducted to evaluate the performance enhancement. Secondly, ablation experiments were designed and implemented to verify the improvement in each module. Finally, the effect of using synthetic images generated by the IDDPM model and the performance of the improved YOLOv8n model on synthetic datasets are presented.
4.1. Evaluation of the Improved YOLOv8n
4.1.1. Experimental Environment
The experimental environment was based on the Ubuntu 20.04 operating system, using an NVIDIA RTX 4060 GPU (8 GB of video memory). Model training and validation were performed on the PyTorch 2.0.0 framework with Python version 3.8 and CUDA version 11.8. The input images were uniformly resized to 1024 × 1024. The network training settings were as follows: batch size 4, SGD optimizer, cosine decay strategy for learning rate, initial learning rate , final learning rate , momentum parameter 0.9, weight decay 0.0001, and confidence level 0.5. No pre-trained weights were used, and the total training batch contained 500 epochs to ensure full convergence of the model.
4.1.2. Data Preprocessing
The original dataset used for the experiment was provided by Beijing Railway Communication Signal Research and Design Institute Group Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), and contained 25 catenary drawings. More than 800 images were obtained after slicing. The dataset was divided into a training set and a validation set with a ratio of 8:2, with the training set accounting for 80% and the validation set accounting for 20%. To improve the detection accuracy and robustness of the model, data enhancement processing was performed on the training set. After data enhancement, the training set was extended to more than 2600 images, which ensured that the model maintained a high recognition accuracy and stability under complex conditions.
4.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
In this experiment, the model performance was evaluated using the metrics of Precision (P), Recall (R), Mean Average Precision (mAP), Gigafloating Point Operations per Second (GFLOPs), and Frames Per Second (FPS). P refers to the proportion of actual positive samples among all the samples predicted to be positive by the model, measuring the accuracy of the model when predicting positives. High precision indicates that the model is more reliable, reducing the number of false positives. R refers to the proportion of samples that were actually positive and were successfully predicted as positive by the model, measuring the model’s ability to capture positives. High recall means the model can identify more positive cases, reducing the number of false negatives. The specific calculation formulas are shown in (8) and (9). TP is the number of samples correctly predicted as positive, TN is the number of samples correctly predicted as negative, FP is the number of negative samples incorrectly predicted as positive, and FN is the number of positive samples incorrectly predicted as negative.
Average precision (AP) measures the overall precision of the model across the entire recall range by calculating the area under the precision-recall (PR) curve. A larger area indicates better classifier performance. A higher AP means that the model can maintain high precision across different recall rates. The specific formula is as follows (10):
mAP is the mean AP of all the categories, which is used to comprehensively measure the detection performance of the model in different categories. The specific formula is as follows (11):
Since P and R are often in conflict in detection tasks, the F1 score was used as their harmonic mean to comprehensively evaluate the model’s classification performance. Therefore, F1 was introduced as a comprehensive evaluation metric. The specific formula is as follows (12):
4.1.4. Improved YOLOv8n Experimental Results Analysis
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed model, this paper used the improved algorithm on the RCLDs dataset and compared it with several detection algorithms. The main methods used were as follows: two-stage detection method, Faster RCNN, and single-stage detection methods, YOLOv4, YOLOv5n, YOLOv5s, YOLOv6n, YOLOv8n, and YOLOv10n.
The experimental results, as shown in Table 2, demonstrate the improvements in YOLOv8n’s performance on the RCLDs dataset. The model achieved mAP@0.5, mAP@0.5:0.95, and mAP@0.75 scores of 93.6%, 94.7%, and 68.3%, respectively. Compared with Faster RCNN, F1 and mAP@0.5 improved by 64.1% and 63.3%, respectively. Compared to YOLOv4, YOLOv5n, YOLOv5s, YOLOv6n, YOLOv8n, and YOLOv10n, the improved YOLOv8n showed improvements of 19.2%, 3.4%, 2%, 2.2%, 2.9%, and 3.1%, respectively, on F1; while, for mAP@0.5, improvements of 6.2%, 6%, 5.8%, 3.4%, 1.9%, 1.9%, respectively, were obtained, and improvements of 4%, 7.5%, 4.1%, 4%, 1.7%, 0.5% were obtained for mAP@0.5:0.95.

Table 2.
Comparative experimental results.
In summary, the improved YOLOv8n demonstrates notable gains over both traditional and recent YOLO series algorithms across several metrics, including F1, mAP@0.5, and mAP@0.5:0.95. Since there is no publicly available RCLDs dataset, in this paper, the classical network model was chosen to experimentally reproduce the RCLDs dataset to validate the detection performance of this method on this dataset.
To comprehensively evaluate the detection of the improved YOLOv8n model on the RCLDs dataset, this paper analyzes three aspects: the loss curves during training and validation, the PR curves, and the normalized confusion matrix.
As shown in Figure 14, the loss values in both the training and validation phases continuously decreased and gradually stabilized, indicating that the model successfully converged and possesses a good generalization ability. Figure 15 illustrates that the PR curves exhibited an excellent overall performance, with an mAP@0.5 reaching 94.7%. However, for class 10 "ACPAIT", the mAP@0.5 was only 62.1%, with a sharp drop in precision observed in the low-recall range, indicating a weak detection ability for this class.
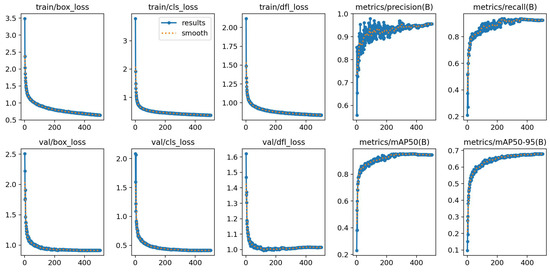
Figure 14.
Result curve.
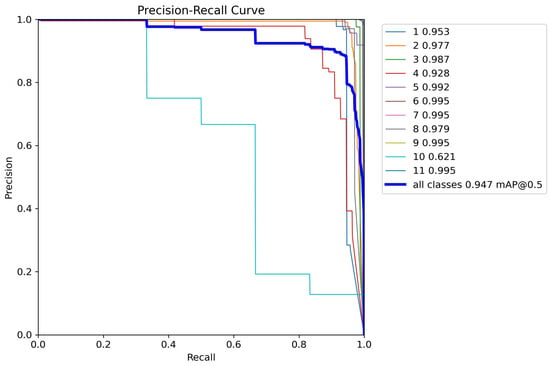
Figure 15.
Precision–recall (PR) curves.
As depicted in Figure 16, the confusion matrix further reveals the model’s limited performance in minority classes. For class 4 "STW", the accuracy was 84%, with 11% misclassified as background and 5% as "DTW". Class 9 "ULACOT" shows an accuracy of 89%, with 11% also misidentified as background. Class 10 "ACPAIT" presents the lowest accuracy, at 67%, with 33% of the samples misclassified as background. In contrast, the remaining symbol classes achieved accuracies above 95%, with most mAP@0.5 scores exceeding 92%, demonstrating a stable and reliable performance across most categories.
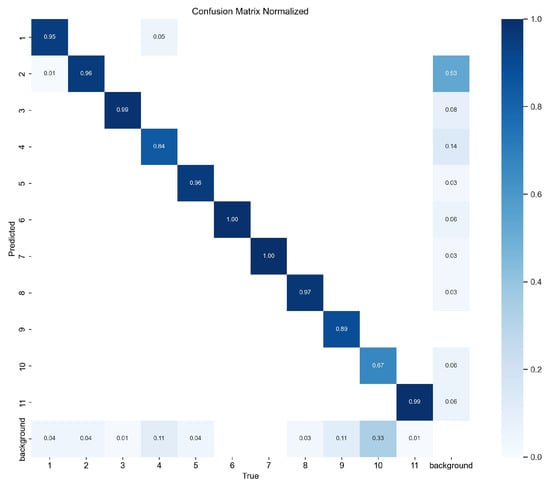
Figure 16.
Normalized confusion matrix.
In conclusion, although the model demonstrated an outstanding detection performance across most categories, its accuracy in minority and easily confused categories still needs improvement. This is primarily due to the limited number of training samples and the overlap between symbols and complex background elements, which increases the risk of their being misclassified as background or other categories. These findings provide a clear direction for future optimization efforts.
To validate the effectiveness of the improved modules, this section presents the experimental evaluations of various modules using the RCLDs dataset, with the results presented in Table 3. The original YOLOv8n algorithm achieved an F1 score of 90.7%, mAP@0.5 of 92.8%, and mAP@0.5:0.95 of 66.6% on the RCLDs dataset. The model had approximately 3 M parameters, 8.1 GFLOPs, and an FPS of 175.6. After introducing MSDA, the feature map processing and fusion capabilities were enhanced, leading to notable improvements in its accuracy in the detection of complex symbols. MSDA expands the receptive field using dilated convolutions while reducing redundant computations, resulting in a 1.7% improvement in mAP@0.5:0.95, with the number of parameters reduced to 2.8 M and GFLOPs decreased to 7.6. However, the multi-scale dilated convolution and self-attention mechanisms introduced in MSDA caused a drop in FPS from 175.6 to 71.5. In the head network, substituting standard convolutions with RFAConv effectively boosted feature extraction accuracy and strengthened the model’s ability to focus on key regions, yielding improvements of 1.9% in F1, 1% in mAP@0.5, and 1.6% in mAP@0.5:0.95. However, the spatial attention mechanism introduced by RFAConv increased the computational load, resulting in approximately 3.1M parameters, 8.7 GFLOPs, and a decrease in FPS to 38.9. Finally, replacing the upsampling with DySample optimized the sampling process and improved the model’s ability to extract detailed features from small target symbols. This allowed the model to maintain approximately 3 M parameters, 8.2 GFLOPs, and 154.4 FPS, while achieving a 1% increase in F1, a 1% increase in mAP@0.5, and a 0.6% increase in mAP@0.5:0.95.

Table 3.
Results of ablation experiments on the RCLDs dataset.
With the integration of the above improvements, the enhanced YOLOv8n algorithm achieved a 2.9% increase in F1 score, a 1.9% increase in mAP@0.5, and a 1.7% increase in mAP@0.5:0.95 compared to the baseline YOLOv8n. Despite these performance gains, the number of parameters and GFLOPs remained nearly unchanged, maintaining the model’s lightweight characteristics and demonstrating its good adaptability for deployment. Although the introduction of MSDA, RFAConv, and DySample reduced the FPS from 175.6 to 28, the model achieved a favorable balance between detection performance and computational cost. As symbol recognition accuracy is the primary objective in the RCLD task, this notable improvement in detection performance further enhances the model’s practicality and application value.
4.2. RCLDs Dataset Supplement
4.2.1. Synthetic Images
In the experiments, the following key hyper parameters were set to optimize model performance and ensure generation quality: an image size of 256 was chosen to accommodate the lightweight network architecture and reduce computational overhead, the number of channels was set to 128, and three residual blocks were used to maintain the model’s representational capacity while controlling the number of parameters. A diffusion step count of 5000 was adopted, along with cosine noise scheduling, which allows for the smoother injection of noise during the later stages of generation, thereby enhancing the preservation of fine details in the generated images. The learning rate was set to and the batch size to 128, balancing training efficiency and stability.
All input data were first pre-processed, including resizing and normalization. Specifically, all data were resized to a 256 × 256 resolution to fit the input requirements of the model and normalized to ensure stability during training. In the model training stage, the mean square error (MSE) loss was used to measure the error between the generated images and the real data. The specific formula of the MSE loss function is as follows (13):
where and denote the pixel values of the real image and the generated image at position , respectively, and M and N denote the height and width of the image, respectively. By minimizing this loss function, the model can gradually optimize the difference between the generated image and the real image.
In addition, the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) technique was used to optimize the convergence and stability of the model to make the generated images more coherent. To enhance data diversity and model generalization, we applied various data augmentation strategies and combined real and synthetic data. The dataset was then re-divided to create richer, more balanced training samples.
To quantify the validity of the synthesized data, we calculated the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID), Inception Score (IS), Structural Similarity Index Metric (SSIM), Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), and Learned Perceptual Image Block Similarity (LPIPS) for use as evaluation metrics.
FID was used to measure how close the generated data were to the real data distribution. The calculation formula is as follows (14):
where and are the feature means of the real image and the generated image, respectively, and and are their covariance matrices. The FID judges the similarities between the generated image and the real image by measuring the difference between the means and covariances of the two.
IS measures the clarity and diversity of an image by calculating the classification probability distribution of the Inception network that generated the image. The formula is as follows (15):
where denotes the image sampled from the generative model . is the category probability distribution of the image computed by the Inception network, which represents the probability that the image belongs to each category.
SSIM mainly measures the similarities between the structural information, which is calculated by the following Formula (16):
where and are the means of the two images, and are the variances, is the covariance, and and are constants to prevent the denominator from being zero.
PSNR evaluates the image quality using pixel-level errors, which are calculated by the following Formula (17):
where is the maximum possible pixel value of the image and MSE is the mean square error, which measures the difference between the original image and the generated image.
LPIPS measures the perceived distance in deep feature space and is calculated as follows (18):
where x and y are the two input images. is the trained weight parameter used to adjust the contribution of different layer features. computes the Euclidean distance between the two images in the feature space. This formula measures the perceptual similarity between two images by computing a weighted sum of the distances between multi-layer deep features.
The experimental results are shown in Table 4; the synthetic data generated in this paper performed well in several indicators, but there is still some room for improvement. Specifically, the FID value was 55.7077, indicating a gap between the distribution of the synthetic data and real data, but they were still found to be similar; the IS value was 3.2188, showing that the clarity and diversity of the generated images are acceptable and the SSIM value was 0.8843, indicating that the synthetic data were closer to the real data in terms of structural information. The PSNR value was 29.06, indicating a certain level of error between the generated image and the real image, but the visual quality was good; the LPIPS value was 0.1995, reflecting that the synthetic data are closer to the real data in the perceptual feature space. Overall, although some indicators can still be optimized, the generated data can effectively provide a strong supplement to the minority class symbols in the RCLDs dataset.

Table 4.
Synthetic data quality assessment indicators.
The generation effect is shown in Figure 17. Because of their high clarity and lifelike details, the generated images are difficult to differentiate from real photographs, providing valuable data for model training. To increase YOLOv8n’s recognition of symbols, IDDPM-generated synthetic images were merged with real photos.
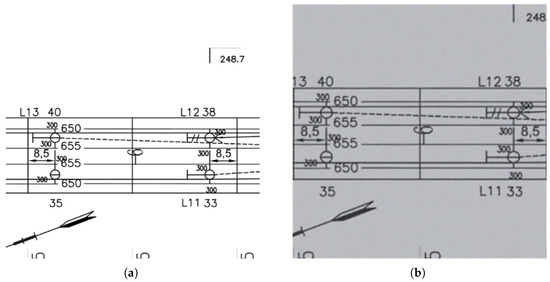
Figure 17.
Comparison of the original image and the synthesized image: (a) original image; (b) synthetic images.
4.2.2. Distribution of RCLDs Dataset
After adding the synthetic images, the RCLDs dataset contained more than 5000 images. The recognition of minority symbols (DTW, STW, ULACOT, ACPAIT, etc.) was poor, primarily due to the limited number of samples in these categories. Additionally, there were similarities between the symbols, which further complicated recognition. Therefore, this paper used IDDPM to generate samples of minority category symbols. After incorporating the synthetic data into the dataset, the class distribution was substantially balanced.
Through IDDPM, more than 2500 images were generated, mainly supplementing the minority category samples. As shown in Figure 18, these images include more than 700 DTW, more than 700 STW, more than 800 ULACOT, and more than 1000 ACPAIT samples. The synthetic data enhances the representation of minority symbols, addressing class imbalances and improving the quality and balance of the training dataset.
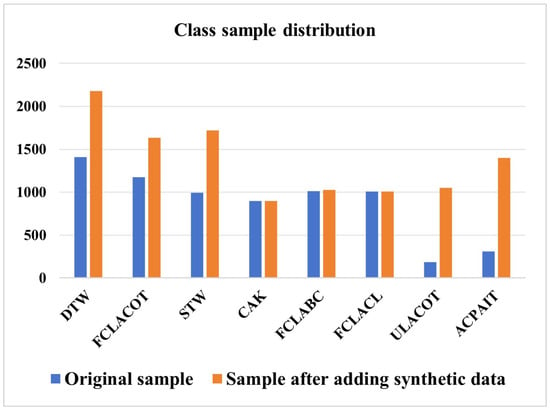
Figure 18.
Comparative analysis of the sample size before and after adding synthetic data.
4.3. Analysis of Experimental Results After Adding Synthetic Images
Since the validation set has fewer samples in the original dataset, the synthesized dataset was re-divided in a ratio of 8:2 to balance the distribution of samples in the training set and validation set. After repartitioning, the number of samples in the validation set increased considerably, and the class distribution became more balanced. Figure 19 presents the sample number distribution before and after the reclassification.
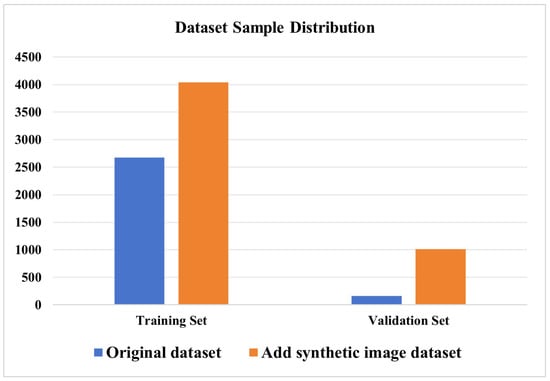
Figure 19.
Proportion of distribution of original and synthetic samples.
As shown in Table 5, the recognition performance for minority-class symbols was notably enhanced. Specifically, the F1 score for STW increased by 10.6%, with mAP@0.5 and mAP@0.5:0.95 improving by 6.5% and 20%, respectively. For ACPAIT, the F1 score rose by 34.1%, while mAP@0.5 and mAP@0.5:0.95 increased by 37.4% and 51.2%. These improvements in minority-class symbol recognition also contributed to the model’s overall performance, with the F1 score rising by 4%, mAP@0.5 by 3.8%, and mAP@0.5:0.95 by 14%.

Table 5.
Comparison of experimental results before and after the addition of synthetic samples.
Visualization of Experimental Results
To verify the performance of the model in the RCLDs recognition task, the original YOLOv8n, the improved YOLOv8n, and the YOLOv8n with synthetic data were used to detect RCLDs. Due to the large size of the RCLDs, some areas were cropped for display in this experiment.
As shown in Figure 20, Figure 21 and Figure 22, the improved YOLOv8n algorithm extracted more features than the original version. It performed better in distinguishing targets with high similarity and occlusion, significantly reducing false detections and missed detections. As shown in Figure 20a, the original YOLOv8n was unable to distinguish "FCLACOT" and "ULACOT", which are two targets with high similarity. As shown in Figure 20b, the improved YOLOv8n could distinguish them accurately. However, due to the sparse features of certain symbols and their tendency to blend with the background, missed detections may still occur. As shown in Figure 20b, although the improved YOLOv8n algorithm reduced the missed detection of the STW symbol to an extent, certain omissions still persisted.
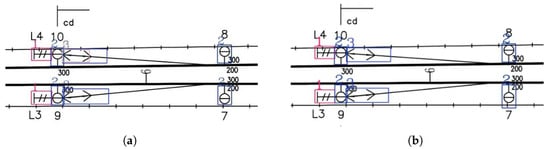
Figure 20.
Comparison of results for the first set of RCLDs: (a) YOLOv8n results; (b) improved YOLOv8n results.
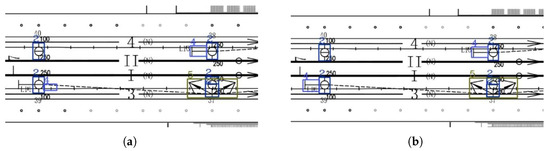
Figure 21.
Comparison of results for the second set of RCLDs: (a) YOLOv8n results; (b) improved YOLOv8n results.
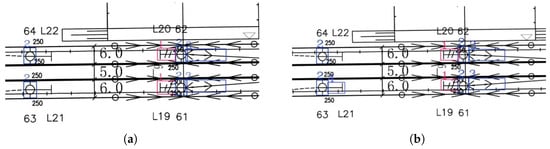
Figure 22.
Comparison of results for the third set of RCLDs: (a) YOLOv8n results; (b) improved YOLOv8n results.
Furthermore, as illustrated in Figure 23, the improved YOLOv8n still has an insufficient detection effect for targets with a small number, such as "ACPAIT". As illustrated in Figure 23b, the YOLOv8n, with the inclusion of synthetic data, can better distinguish diverse target types, particularly those with a small number of targets, improving the model’s overall detection capabilities.
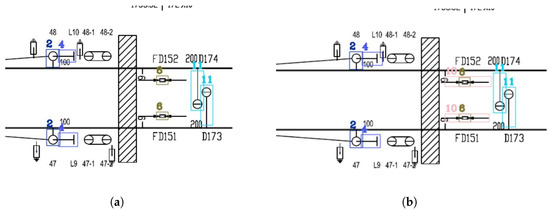
Figure 23.
Comparison of RCLD results before and after adding synthetic images. (a) Improved YOLOv8n results. (b) Detection effect of YOLOv8n after adding the synthetic image.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, an improved YOLOv8n detection method is proposed to address the challenges presented by the small target occlusion problem and the low recognition accuracy of minority class symbols in RCLDs. Additionally, IDDPM is introduced to generate synthetic samples of minority class symbols to improve the model’s recognition of minority classes. The experimental results show that the proposed method performs well in terms of feature extraction, small target detection, and inter-class equalization. The method effectively minimizes the leakage and false detection rates of small target symbols and improves the model’s detection performance for minority-class symbols. In addition, the method has good potential for engineering applications. It supports the intelligent analysis of CAD drawings in the railroad industry and facilitates the automation and standardization of symbol recognition. This, in turn, helps reduce the manual annotation costs and enhances the efficiency of drawing digital processing and the intelligence level of engineering audits. Nevertheless, the model still has some limitations. The presented experiments were limited to drawing samples provided by Beijing All-Road Communication Signal Research and Design Institute Group Co., Ltd. Further evaluation is required to assess the model’s adaptability to other drawing formats, symbol styles, and industry standards. Meanwhile, the computational efficiency of the model in the inference stage still needs to be further optimized to meet the demand for real-time performance in practical engineering applications.
Future research can be extended in several directions. First, exploring more efficient network architectures and attention mechanisms may greatly enhance the model’s ability to extract features, improving detection accuracy against complex backgrounds and in symbol-dense regions. Second, the introduction of more expressive generative models could improve the visual realism and diversity of synthetic samples, thereby better addressing the performance limitations caused by class imbalances. In addition, constructing a symbol–text joint modeling framework by leveraging the semantic associations between symbols and textual information in drawings can enable comprehensive semantic parsing and the structured representation of drawing content. Integrating optical character recognition techniques to support joint symbol–text parsing will further enhance the model’s capacity to understand and process diverse symbol systems. Finally, a lightweight model design and optimized deployment remain essential for real-world applications, ensuring the model can meet the requirements for real-time performance, computational efficiency, and stability in embedded devices or on-site tool systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.S. and M.L.; methodology, M.Z.; software, M.Z. and W.D.; validation, M.Z. and W.D.; formal analysis, G.L.; investigation, G.L.; resources, G.L.; data curation, M.Z. and G.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, Q.S., M.L. and W.D.; supervision, Q.S. and M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, grant number 22JR11RA160.
Data Availability Statement
Our dataset is provided by Beijing Railway Signal and Communication Research and Design Institute Group Co., Ltd. It involves the plane design drawings of the overhead contact network in the railway industry. As this data is considered internal and confidential to the industry, it cannot be made publicly available. For access to the dataset, please contact the Beijing Railway Signal and Communication Research and Design Institute Group Co., Ltd.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Gaoju Li is employed by China Railway Signal and Communication Research and Design Institute Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors (Qi Sun, Mengxin Zhu, Minzhi Li, and Weizhi Deng) declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Feng, D.; Yu, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhu, H.; Lin, S.; Liang, J. Risk assessment for electrified railway catenary system under comprehensive influence of geographical and meteorological factors. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, S.; Jain, A.; Sharma, M.; Vig, L. Digitize-PID: Automatic digitization of piping and instrumentation diagrams. In Proceedings of the Trends and Applications in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining: PAKDD 2021 Workshops, WSPA, MLMEIN, SDPRA, DARAI, and AI4EPT, Delhi, India, 11 May 2021; pp. 168–180. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, S.; Sharma, M.; Vig, L. OSSR-PID: One-shot symbol recognition in P&ID sheets using path sampling and GCN. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, A.; Kondo, T.; Mori, K.; Tsunekawa, S.; Kawamoto, E. An automatic circuit diagram reader with loop-structure-based symbol recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1988, 10, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablameyko, S.V.; Uchida, S. Recognition of engineering drawing entities: Review of approaches. Int. J. Image Graph. 2007, 7, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.O.; Lee, E.B.; Baek, H.K. A digitization and conversion tool for imaged drawings to intelligent piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&ID). Energies 2019, 12, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, J.K.; Rainio, K.; Numminen, J.P.; Syrjänen, T.; Paganus, N.; Honkoila, K. Object detection in design diagrams with machine learning. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Recognition Systems (CORES 2019), Polanica Zdroj, Poland, 20–22 May 2020; pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Manakitsa, N.; Maraslidis, G.S.; Moysis, L.; Fragulis, G.F. A review of machine learning and deep learning for object detection, semantic segmentation, and human action recognition in machine and robotic vision. Technologies 2024, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-García, C.F.; Elyan, E.; Jayne, C. New trends on digitisation of complex engineering drawings. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 1695–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xue, R.; Shao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y. Current state and predicted technological trends in global railway intelligent digital transformation. Railw. Sci. 2023, 2, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Pham, V.L.; Nguyen, C.C.; Nguyen, V.V. Object Detection and Text Recognition in Large-Scale Technical Drawings. 2021. Available online: https://eprints.uet.vnu.edu.vn/eprints/id/eprint/4603/ (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Faltin, B.; Schönfelder, P.; König, M. Inferring interconnections of construction drawings for bridges using deep learning-based methods. In ECPPM 2022-eWork and eBusiness in Architecture, Engineering and Construction 2022; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, M.; Eglin, V.; Biou, M. Text detection and post-OCR correction in engineering documents. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, La Rochelle, France, 22–25 May 2022; pp. 726–740. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Pandey, P.; Kar, S. Automatic detection and classification of symbols in engineering drawings. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.13277. [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel, B.; Mangler, J.; Rinderle-Ma, S. Extraction of dimension requirements from engineering drawings for supporting quality control in production processes. Comput. Ind. 2021, 129, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, L.; Francisco Moreno-García, C.; Elyan, E. A review of deep learning methods for digitisation of complex documents and engineering diagrams. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.J.; Ling, Q.H.; Han, F. An improved algorithm for small object detection based on YOLO v4 and multi-scale contextual information. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. YOLOv8. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Duan, S.; Pan, H. An efficient detection of non-standard miner behavior using improved YOLOv8. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 112, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Li, X.; Peng, W.; Fan, Z.; Ji, Z.; Ganchev, I. YOLO-CXR: A novel detection network for locating multiple small lesions in chest X-ray images. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 156003–156019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.C.; Chen, I.M.; Tan, H.K. Automated identification of components in raster piping and instrumentation diagram with minimal pre-processing. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 21–24 August 2016; pp. 1301–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-García, C.F.; Elyan, E.; Jayne, C. Heuristics-based detection to improve text/graphics segmentation in complex engineering drawings. In Proceedings of the Engineering Applications of Neural Networks: 18th International Conference, EANN 2017, Athens, Greece, 25–27 August 2017; pp. 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, Y.; Lee, J.; Mun, D.; Lim, S. Deep learning-based method to recognize line objects and flow arrows from image-format piping and instrumentation diagrams for digitization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanbhro, H.; Hooi, Y.K.; Kusakunniran, W.; Amur, Z.H. Symbol Detection in a Multi-class Dataset Based on Single Line Diagrams using Deep Learning Models. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Zhao, S.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, Z. Image format pipeline and instrument diagram recognition method based on deep learning. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2024, 4, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, C.; Shi, D. Practical single-line diagram recognition based on digital image processing and deep vision models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazed, M.S.M.; Shaubari, E.F.A.; Yap, M.H. A Review of Neural Network Approach on Engineering Drawing Recognition and Future Directions. JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis. 2023, 7, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Elyan, E.; Jamieson, L.; Ali-Gombe, A. Deep learning for symbols detection and classification in engineering drawings. Neural Netw. 2020, 129, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanbhro, H.; Kwang Hooi, Y.; Kusakunniran, W.; Amur, Z.H. A Symbol Recognition System for Single-Line Diagrams Developed Using a Deep-Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, S.; Hinz, T.; Raue, F.; Hees, J.; Dengel, A. Adversarial text-to-image synthesis: A review. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, B.; Shanbhag, A.; Raue, F.; Frolov, S.; Palacio, S.; Dengel, A. Diffusion models in image super-resolution and everything: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.00736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, F.A.; Hondru, V.; Ionescu, R.T.; Shah, M. Diffusion models in vision: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10850–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, A.K.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Anwer, R.M.; Laaksonen, J.; Shah, M.; Khan, F.S. Person image synthesis via denoising diffusion model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5968–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Shen, J.; Zeng, Y. Super-resolution of brain MRI images based on denoising diffusion probabilistic model. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 85, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Tang, Y.M.; Lin, K.Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.S. Dilateformer: Multi-scale dilated transformer for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 8906–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Song, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, K.; Song, Y. RFAConv: Innovating spatial attention and standard convolutional operation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03198. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Fu, H.; Cao, Z. Learning to upsample by learning to sample. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 6027–6037. [Google Scholar]
- Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Weiss, E.; Maheswaranathan, N.; Ganguli, S. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2256–2265. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.Q.; Dhariwal, P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8162–8171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).