A Composite Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Control-Sliding Mode Control Strategy with Nominal Model Compensation for Precision Motion Tracking in Semiconductor Die Attach Machines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling and Identification of the Motion Platform
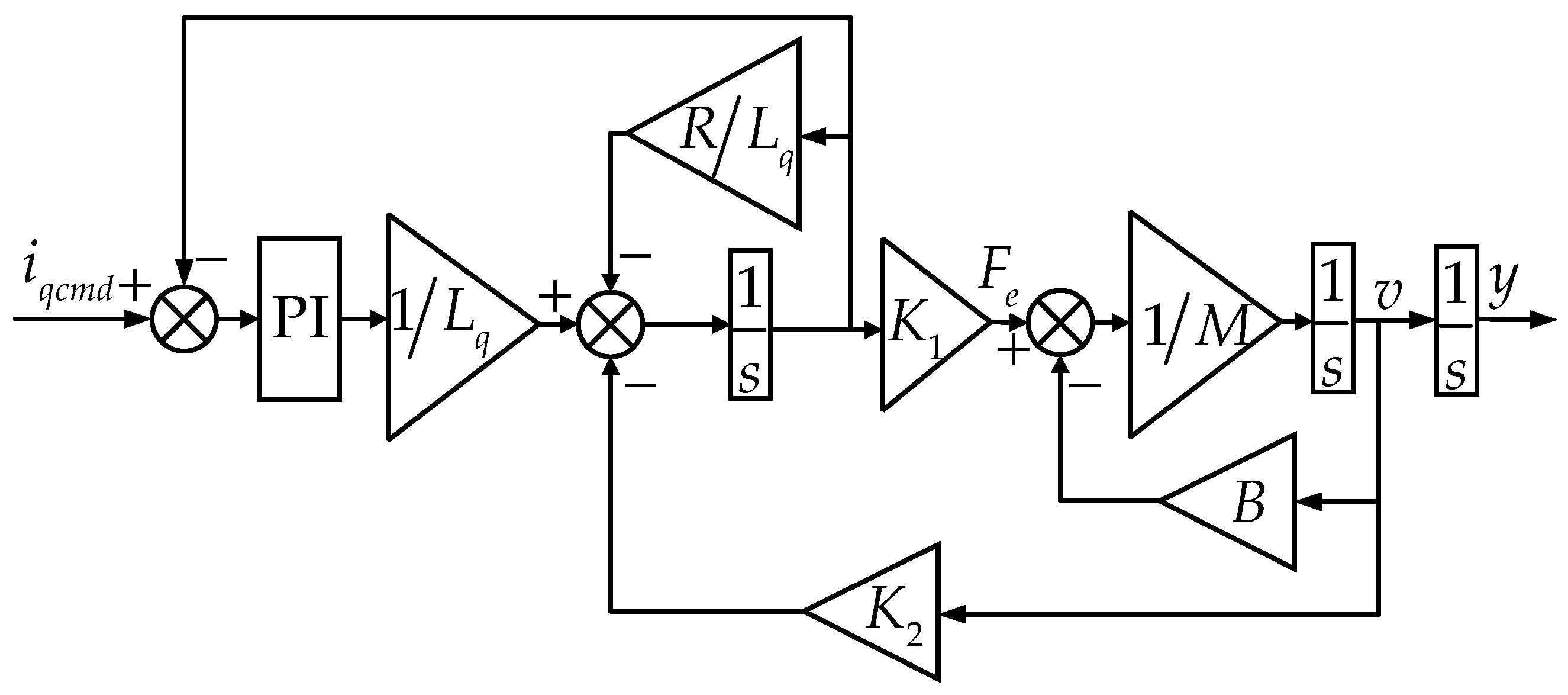
2.1. Mechanistic Model
2.2. Model Identification
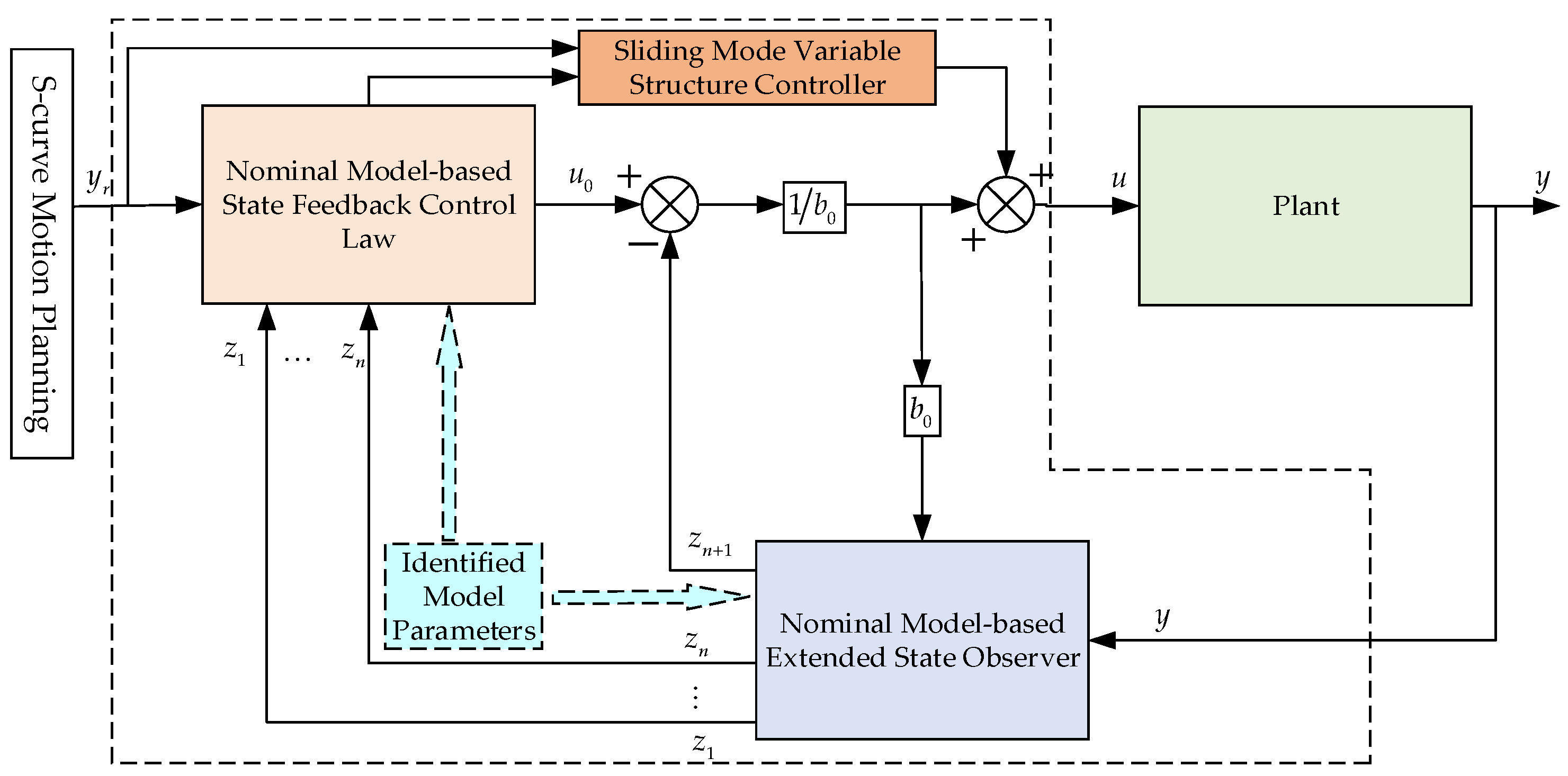
3. The Proposed Composite Control Strategy
3.1. NMLADRC
3.2. SMC
3.3. Stability Analysis
3.3.1. NMESO Stability
3.3.2. SMC Stability
3.3.3. Overall Stability of Composite Control System
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
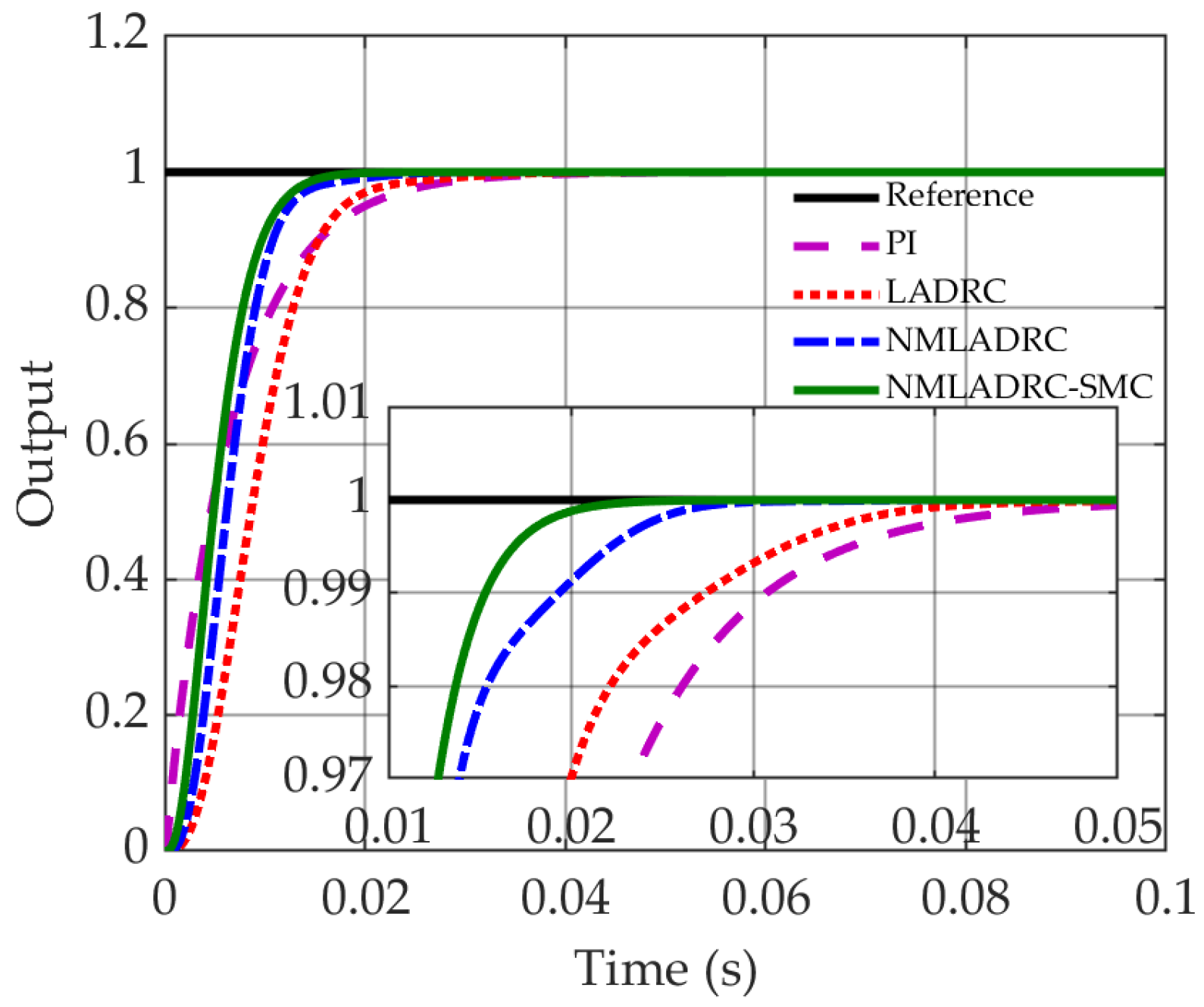
4.1. Dynamic and Static Characteristic Analysis
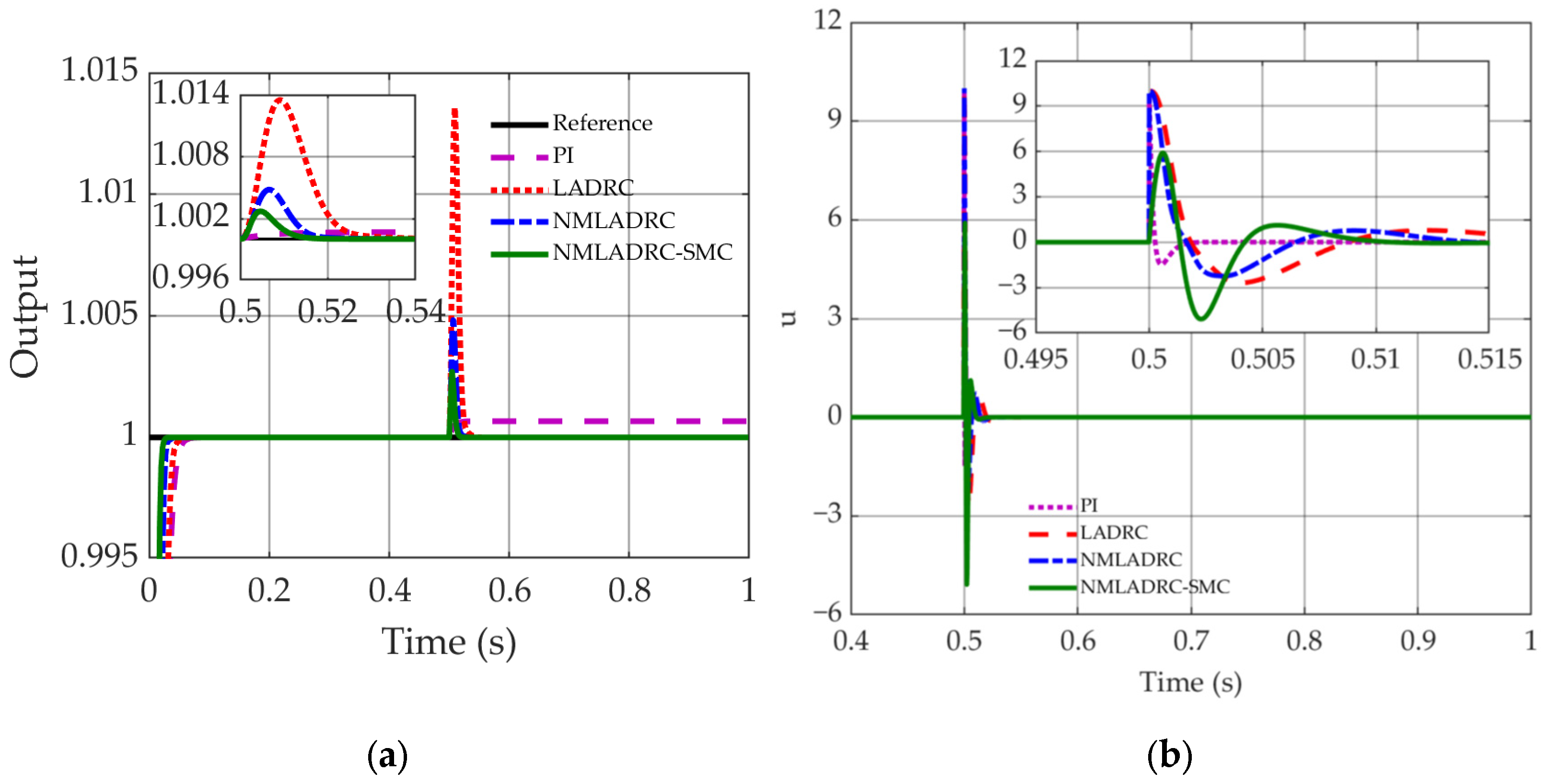
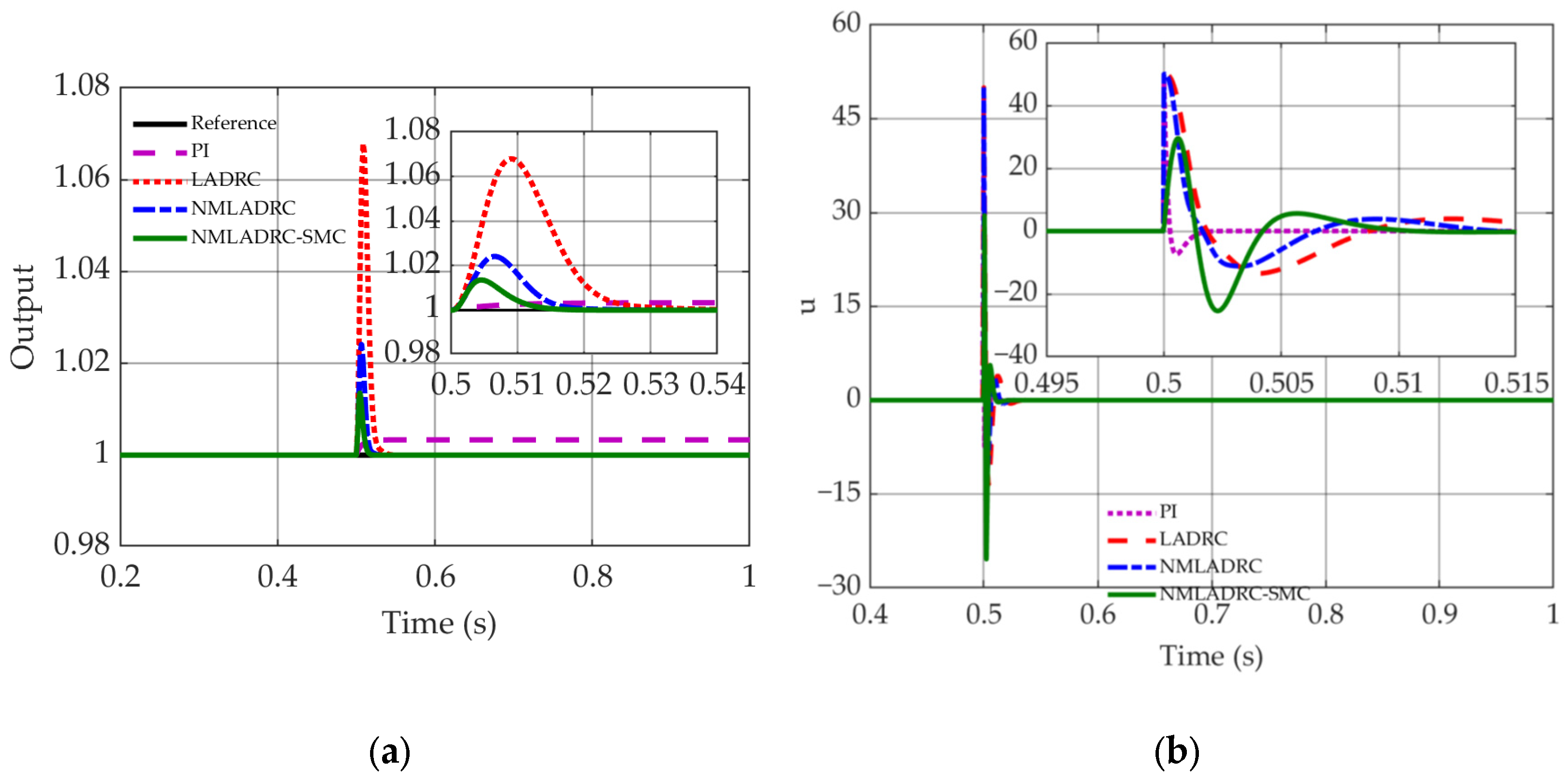
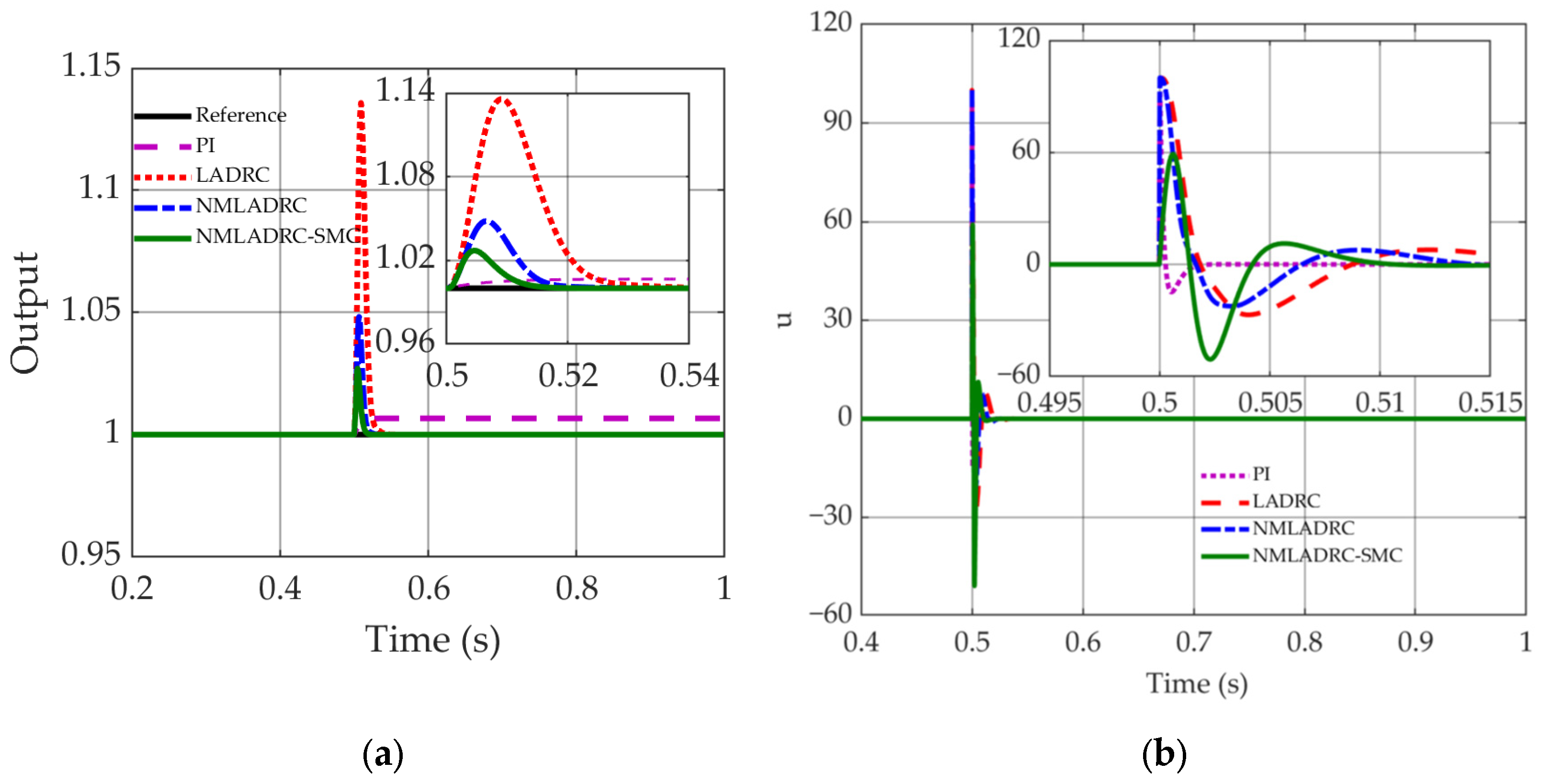
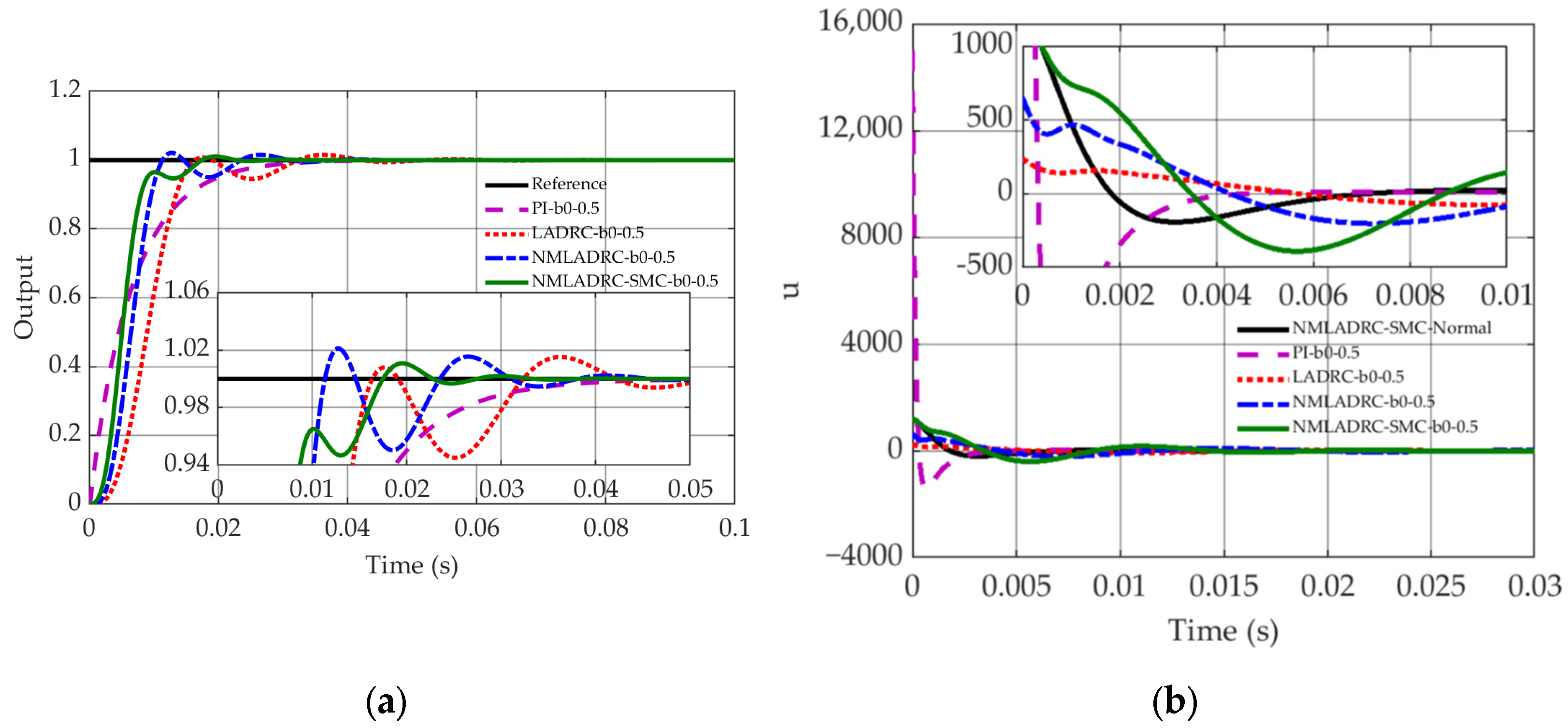
4.2. Robustness Evaluation Under Disturbances and Parametric Uncertainties
4.2.1. External Step Disturbance
4.2.2. Model Parameter Uncertainties
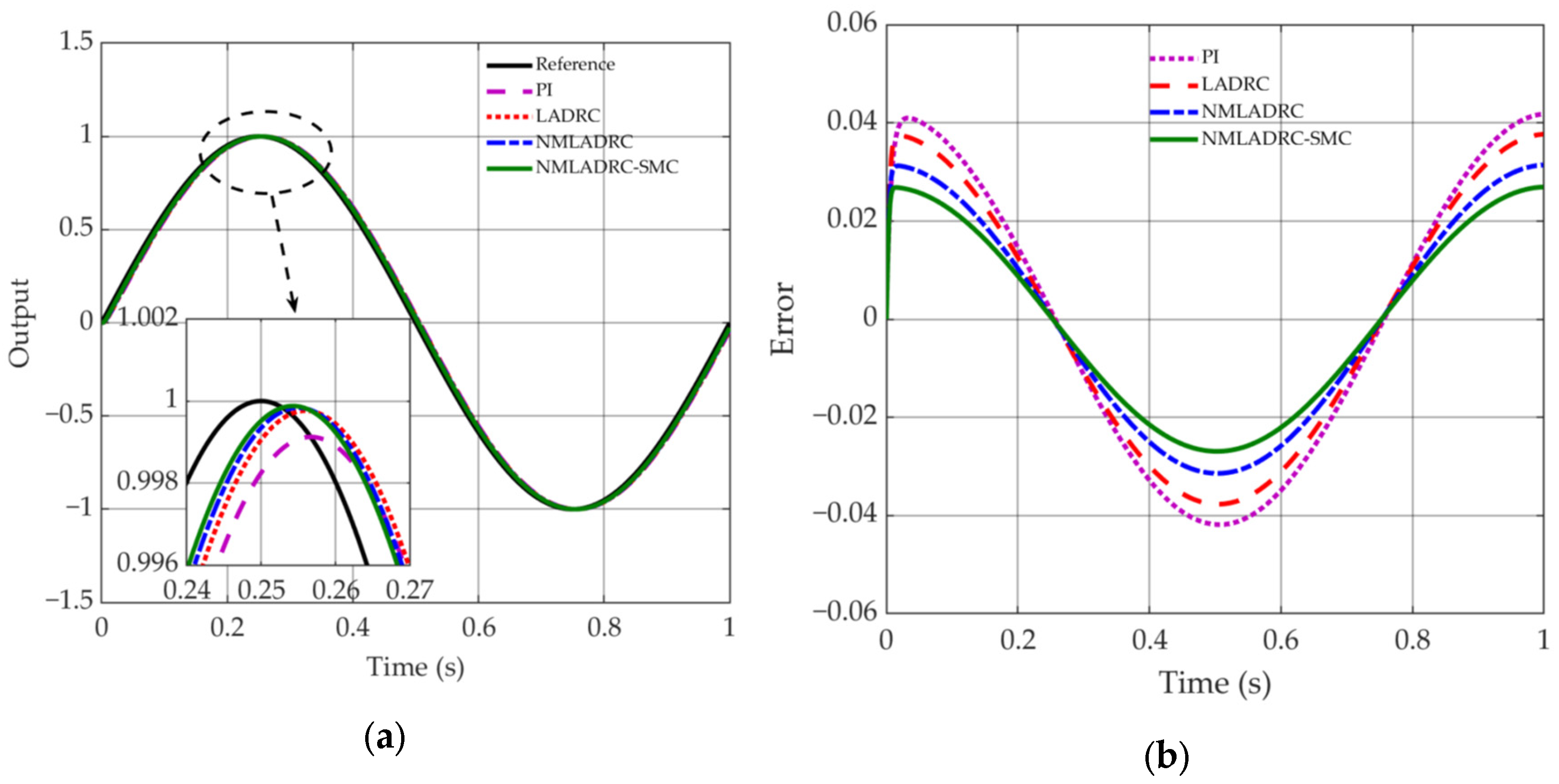
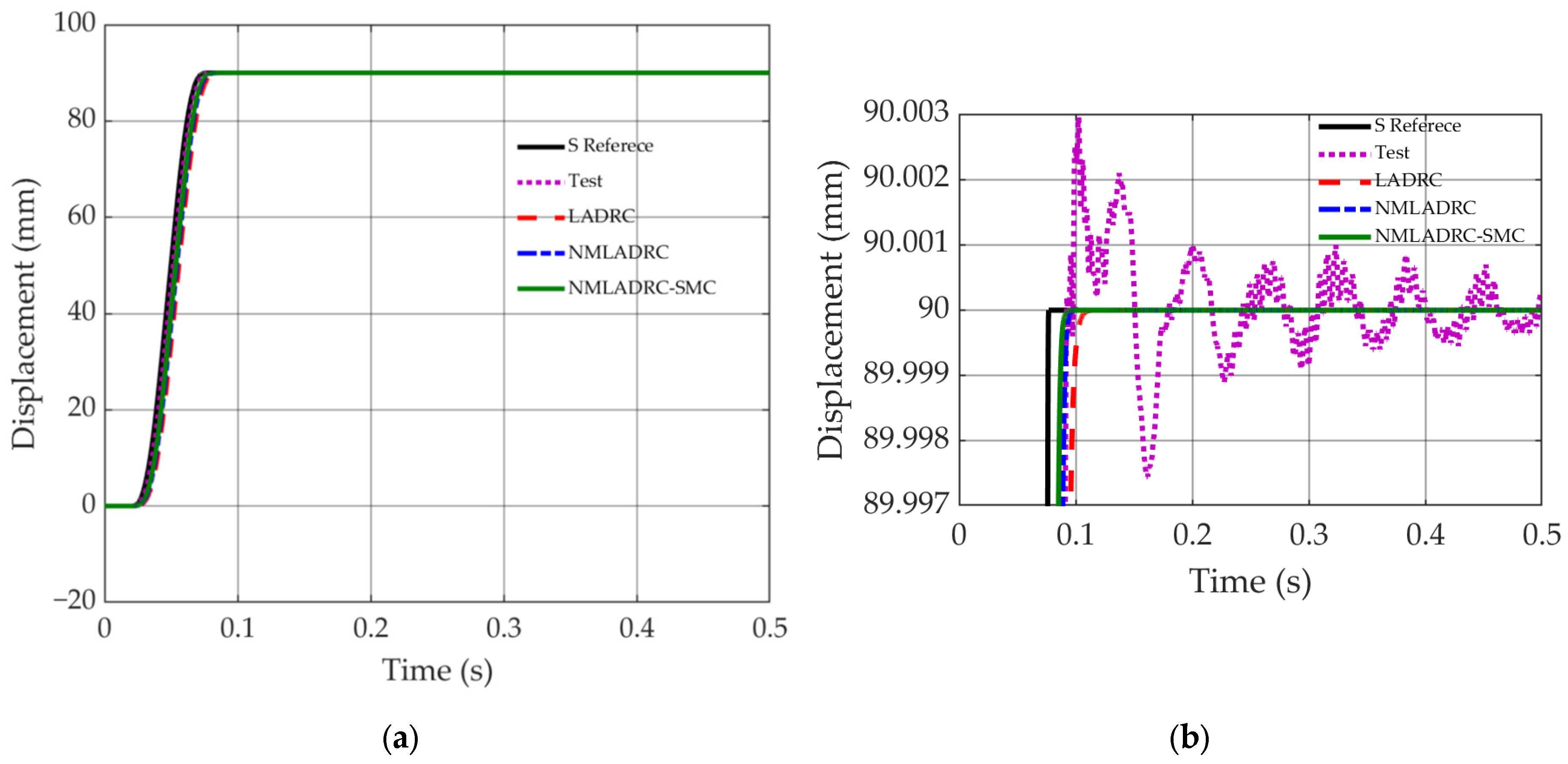
4.3. Servo Tracking Performance Analysis Under High-Acceleration and High-Speed Operating Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guste, R.R.A.; Mariñas, K.A.A.; Ong, A.K.S. Efficiency Analysis of Die Attach Machines Using Overall Equipment Effectiveness Metrics and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis with an Ishikawa Diagram. Machines 2024, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braembussche, P.; Swevers, J.; Brussel, H. Design and Experimental Validation of Robust Controllers for Machine Tool Drives with Linear Motor. Mechatronics 2001, 11, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-H. Adaptive Controller Design for a Linear Motor Control System. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 601–615. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Huang, S.; Dou, H.; Lee, T.; Chin, S.; Lim, S. Adaptive Robust Motion Control for Precise Trajectory Tracking Application. ISA Trans. 2001, 40, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yao, B. Adaptive Robust Precision Motion Control of Linear Motors with Negligible Electrical Dynamics: Theory and Experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2001, 6, 444–452. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wikander, J. Model Reference Discrete-Time Sliding Mode Control of Linear Motor Precision Servo Systems. Int. J. Mechatron. 2004, 14, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. From PID to Active Disturbance Rejection Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Scaling and bandwidth-parameterization based controller tuning. In Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2003; pp. 4989–4996. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ma, P.; Gao, F.; Shi, X. Research on Position Servo System Based on Fractional-Order Extended State Observer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 102748–102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, B.; Cheng, Z.; Fan, H. Cascade ADRC with Neural Network-based ESO for Hypersonic Vehicle. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 9115–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, J.; Mrotek, M.; Pazderski, D.; Kozierski, P.; Retinger, M. Improving Performance of ADRC Control Systems Affected by Measurement Noise Using Kalman Filter-Tuned Extended State Observer. Electronics 2024, 13, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Su, X.; Ren, X. Optimization of Active Disturbance Rejection Control System for Vehicle Servo Platform Based on Artificial Intelligence Algorithm. Electronics 2025, 14, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, Y.; Ma, A. Optimization of Ship Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor ADRC Based on Improved QPSO. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tong, Y. Research on Active Disturbance Rejection Control with Parameter Tuning for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Improved PSO Algorithm. Electronics 2024, 13, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Shen, W.; Dai, Y.; Ye, Y. Parameter tuning of auto disturbance rejection controller based on improved glowworm swarm optimization algorithm. Assem. Autom. 2022, 42, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hou, Q.; Lee, C.H.T. Smooth speed control of permanent magnet synchronous machine using back propagation neural network. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. An ADRC parameters self-tuning controller based on RBF neural network for multi-color register system. Machines 2023, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, S.; Hu, J.; Huang, D. A novel active disturbance rejection control of PMSM based on deep reinforcement learning for more electric aircraft. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Tan, P.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M.; Sun, Q. Deep reinforcement learning based active disturbance rejection control for ship course control. Neurocomputing 2022, 484, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Bacha, S.; Alamir, M. A review on ADRC based PMSM control designs. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017—43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1747–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Fareh, R.; Khadraoui, S.; Abdallah, M.Y.; Baziyad, M.; Bettayeb, M. Active disturbance rejection control for robotic systems: A review. Mechatronics 2021, 80, 102671. [Google Scholar]
- Khadraoui, S.; Fareh, R.; Baziyad, M.; Elbeltagy, M.B.; Bettayeb, M. A Comprehensive Review and Applications of Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 185851–185868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Wang, R.; Su, W. Active Disturbance Rejection Control—New Trends in Agricultural Cybernetics in the Future: A Comprehensive Review. Machines 2025, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Mao, Q.; Mao, Y. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Piezoelectric Smart Structures: A Review. Machines 2023, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Hu, S.; Jiang, F. A Novel Motion Control Design Approach Based on Active Disturbance Rejection. In Proceedings of the 40th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (Cat. No. 01Ch37228), Orlando, FL, USA, 4–7 December 2001; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume 5, pp. 4877–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Madonski, R.; Lakomy, K.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y. Add-on Module of Active Disturbance Rejection for Set-Point Tracking of Motion Control Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 4028–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, R.; Luna, L. Robust ultra-precision motion control of linear ultrasonic motors: A combined ADRC-Luenberger observer approach. Control. Eng. Pract. 2021, 111, 104812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.X.; Zheng, C.H.; Duan, B.Y. Automatic Disturbances Rejection Controller for Precise Motion Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhao, Y. A New Robust Algorithm to Improve the Dynamic Performance on the Position Control of Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Future Computer and Communication, Wuhan, China, 21–24 May 2010; pp. V3-268–V3-272. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.; Liu, C.; Hui, F.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y. A Decoupled Active Disturbance Rejection Controller for PMSM Speed-Regulation System with Position Feedback. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015; pp. 1769–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Luo, D. A New Fuzzy Active-Disturbance Rejection Controller Applied in PMSM Position Servo System. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 2055–2059. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Kuang, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, S.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y. A Novel Position Controller for PMSM Servo System Based on Variable Structure Active Disturbance Rejection Controller. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sira-Ramírez, H.; Linares-Flores, J.; García-Rodríguez, C.; Contreras-Ordaz, M.A. On the Control of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor: An Active Disturbance Rejection Control Approach. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Bustamante, E.W.; Sira-Ramirez, H.; Linares-Flores, J. On the Sensorless Rotor Position Control of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor: An Active Disturbance Rejection Approach. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on Power Electronics (CIEP), Guanajuato, Mexico, 20–23 June 2016; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Tan, W. Tuning of linear ADRC with known plant information. ISA Trans. 2016, 65, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Version | Framework | Control Law |
|---|---|---|
| ADRC | (1) Transient profile generator (2) ESO (3) Nonlinear weighted sum | |
| LADRC | (1) ESO (2) State feedback | |
| NMLADRC | (1) Nominal model-based ESO (2) Nominal model-based state feedback |
| Algorithm | Phase Lag (Degrees) | Maximum Tracking Error (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| NMLADRC-SMC | 1.377 | 0.269 |
| NMLADRC | 1.790 | 0.313 |
| LADRC | 2.163 | 0.375 |
| PI | 2.756 | 0.495 |
| Control Strategy | Positioning Time/ms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ±10 μm | ±5 μm | ±3 μm | ±2 μm | |
| Test | 7.56 | 13.66 | 14.29 | 89.75 |
| LADRC | 15.64 | 17.51 | 18.85 | 19.94 |
| NMLADRC | 9.8 | 11.17 | 12.09 | 12.78 |
| NMLADRC-SMC | 6.56 | 7.65 | 8.43 | 9.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Liang, W. A Composite Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Control-Sliding Mode Control Strategy with Nominal Model Compensation for Precision Motion Tracking in Semiconductor Die Attach Machines. Symmetry 2025, 17, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050636
Chen H, Zhang Y, Li W, Zhang X, Liang W. A Composite Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Control-Sliding Mode Control Strategy with Nominal Model Compensation for Precision Motion Tracking in Semiconductor Die Attach Machines. Symmetry. 2025; 17(5):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050636
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Huairong, Yonghong Zhang, Wen Li, Xiang Zhang, and Weiming Liang. 2025. "A Composite Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Control-Sliding Mode Control Strategy with Nominal Model Compensation for Precision Motion Tracking in Semiconductor Die Attach Machines" Symmetry 17, no. 5: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050636
APA StyleChen, H., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Zhang, X., & Liang, W. (2025). A Composite Linear Active Disturbance Rejection Control-Sliding Mode Control Strategy with Nominal Model Compensation for Precision Motion Tracking in Semiconductor Die Attach Machines. Symmetry, 17(5), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050636






