A Collaborative Optimization Strategy for Photovoltaic Array Layout Based on the Lemur Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel PV array design framework that combines the Perez anisotropic irradiance model with a dynamic shading irradiance geometric model to jointly model the irradiance and shading is proposed, thereby enabling the accurate estimation of long-term effective irradiance.
- The proposed framework introduces tilt angle, azimuth angle, and row spacing as coupled decision variables, incorporating land area, shading loss, and maintenance constraints into the optimization problem to enhance engineering practicality and application feasibility.
- The proposed framework employs the LO algorithm to effectively solve the three-variable PV array layout problem, demonstrating superior convergence efficiency and solution quality compared with conventional optimization algorithms such as PSO and GA, thereby validating the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed design methodology.
2. Collaborative Optimization Framework for PV Array Layout Design
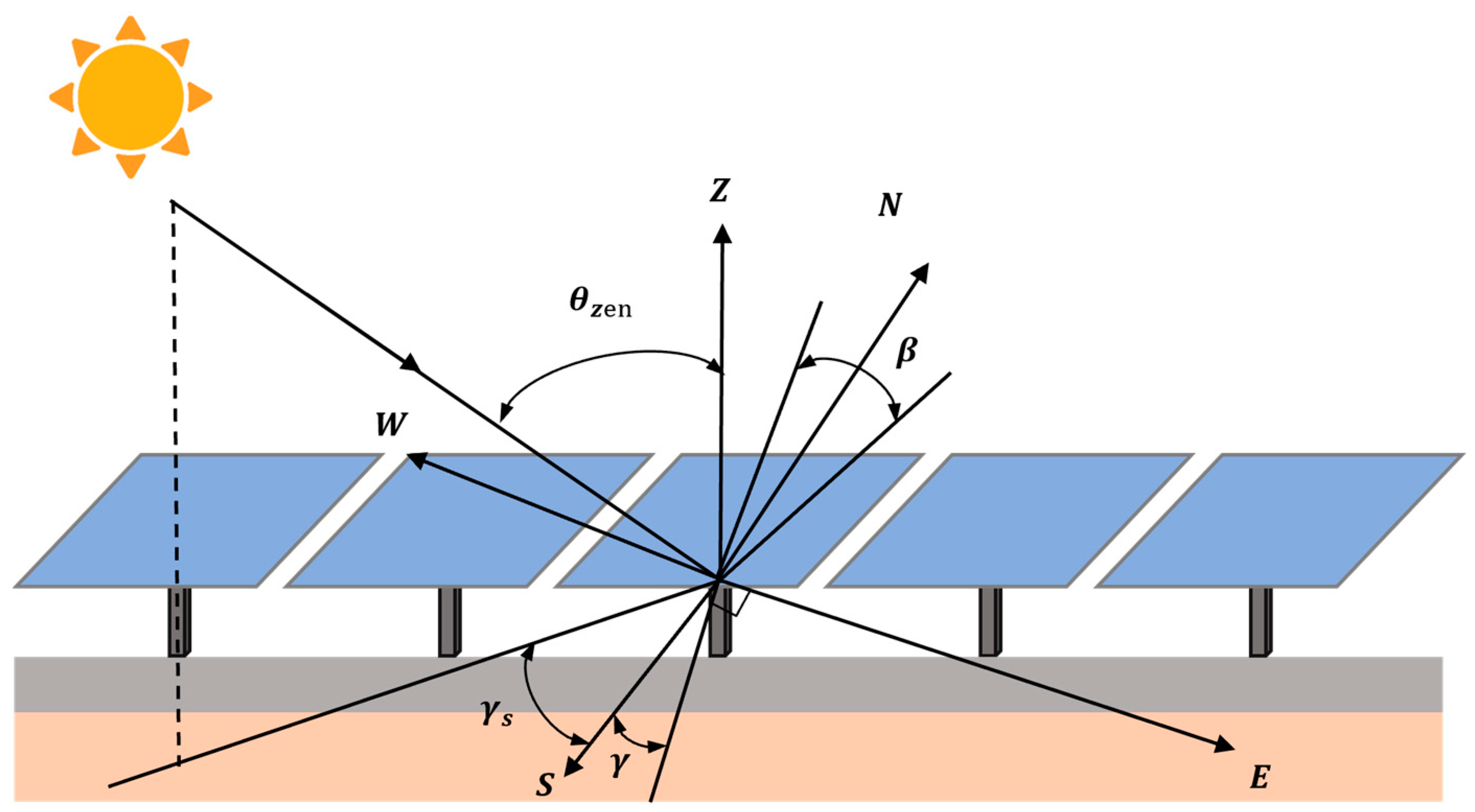
2.1. Mathematical Model of Solar Angles
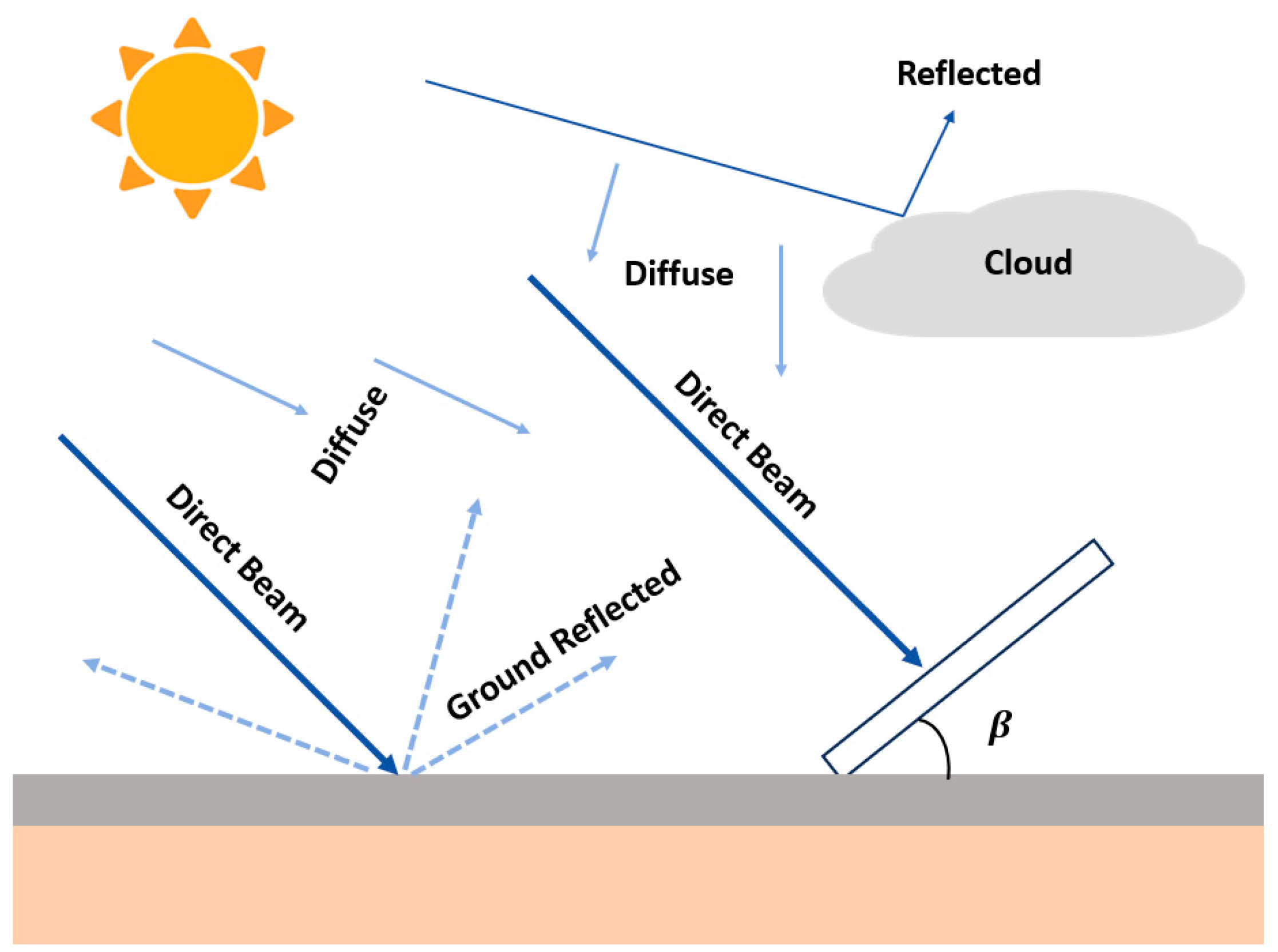
2.2. Solar Radiation Modeling Based on the Perez Anisotropic Irradiance Model
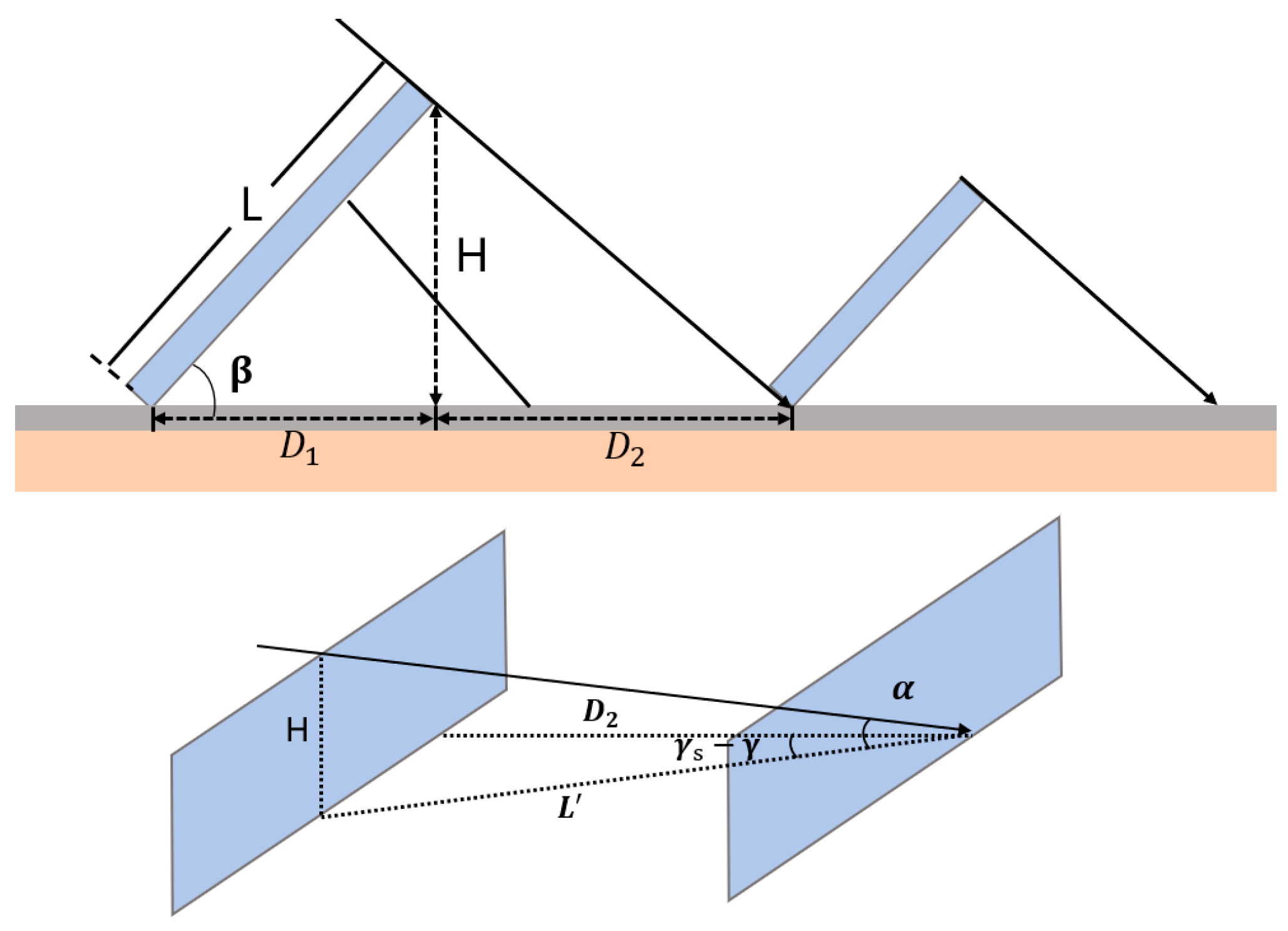
2.3. Dynamic Shading Irradiance Geometric Model
2.4. Objective Function and Constraints
2.4.1. Formulation of Objective Function
2.4.2. Structural Constraints of PV Array Deployment
3. The Optimization for PV Array Layout Based on the LO Algorithm
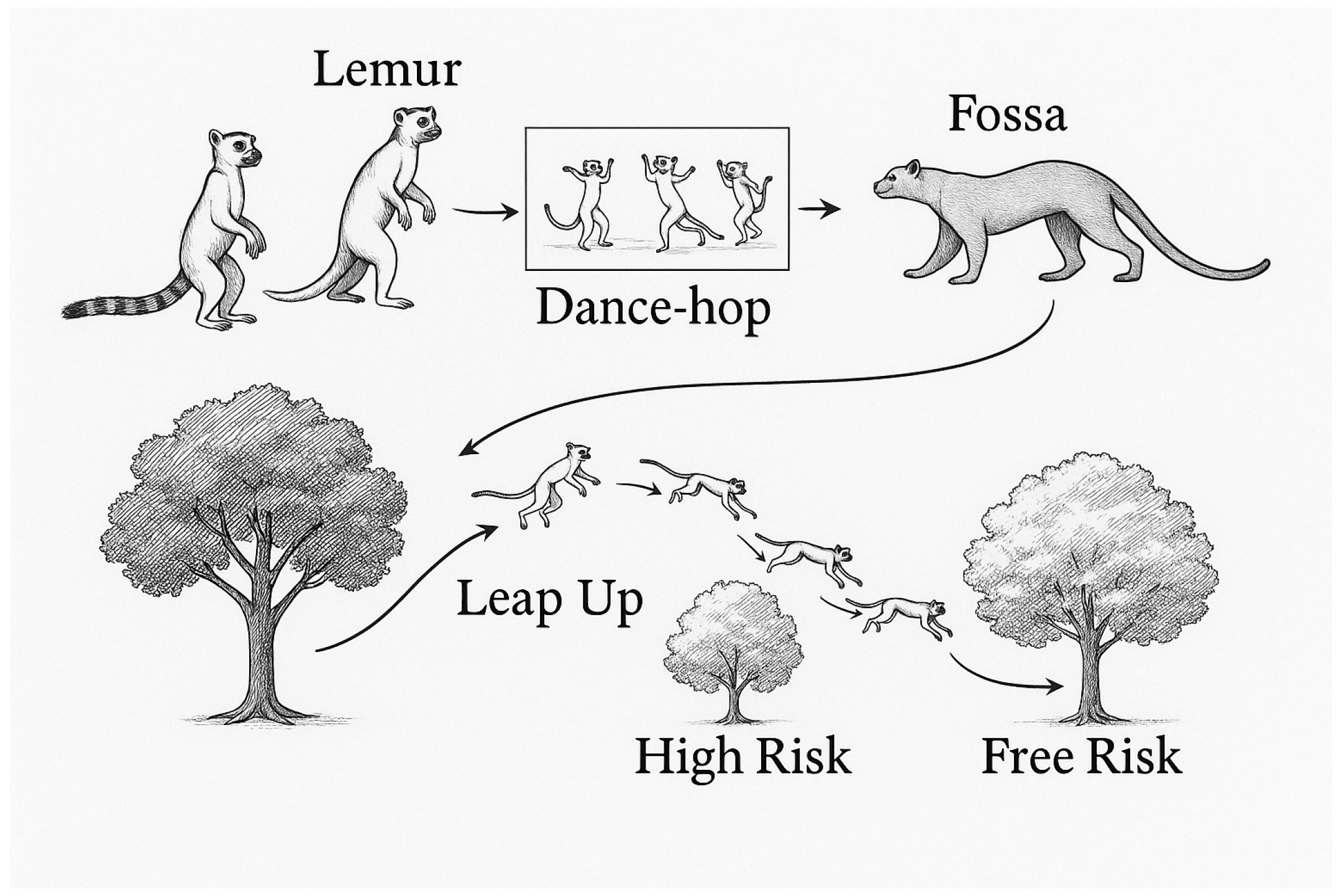
3.1. Fundamental Principles of the Lemurs Optimization Algorithm
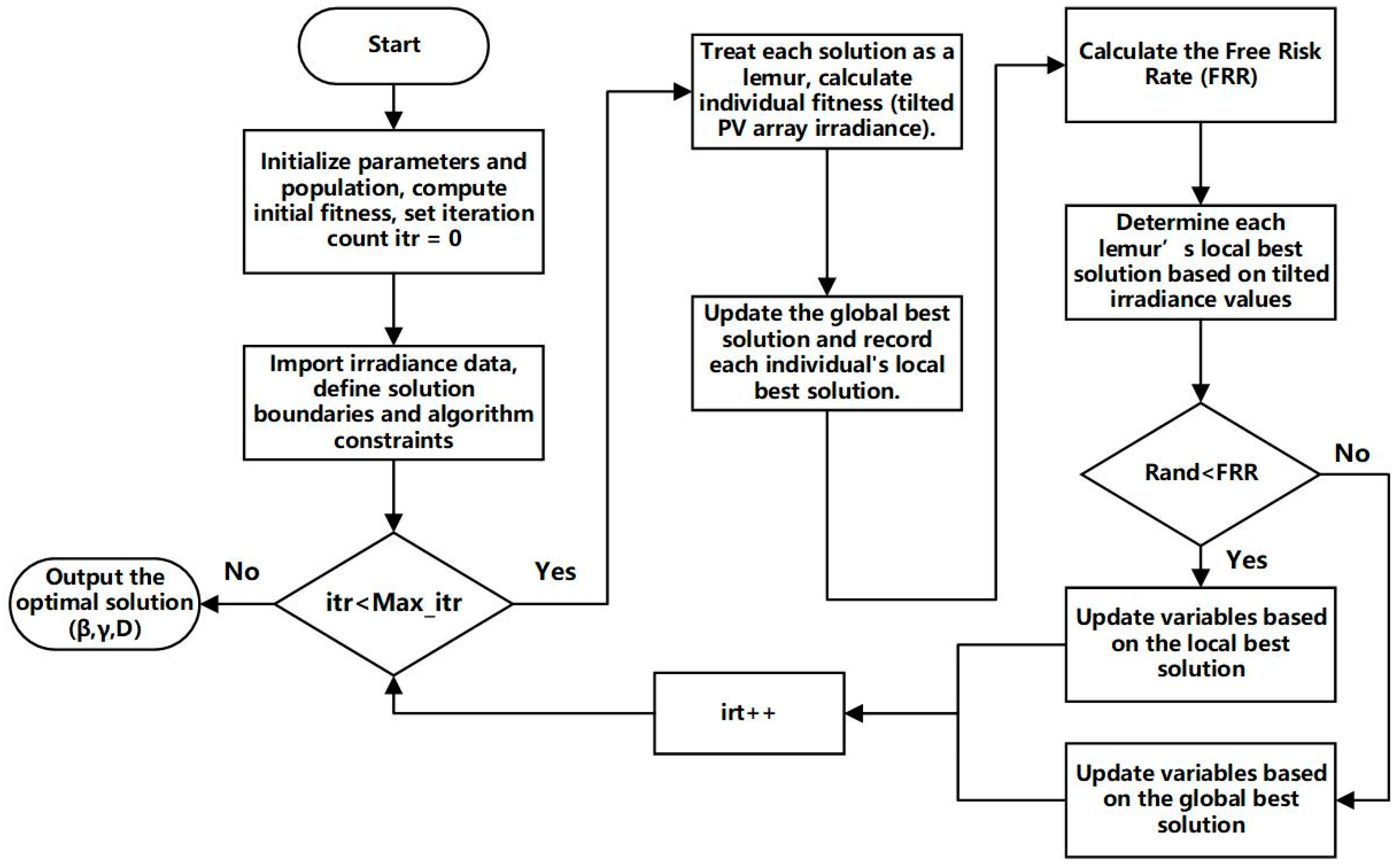
3.2. The Application of the LO Algorithm in PV Array Layout Optimization
- Define the objective as maximizing annual effective irradiance , accounting for dynamic shading;
- Encode each solution as a vector of three variables—tilt angle , azimuth angle , and row spacing ;
- Generate the initial population matrix with candidate solutions, initializing each variable within its physical bounds, as defined in Equation (42).
- Evaluate each individual using the objective function defined in Section 2.4;
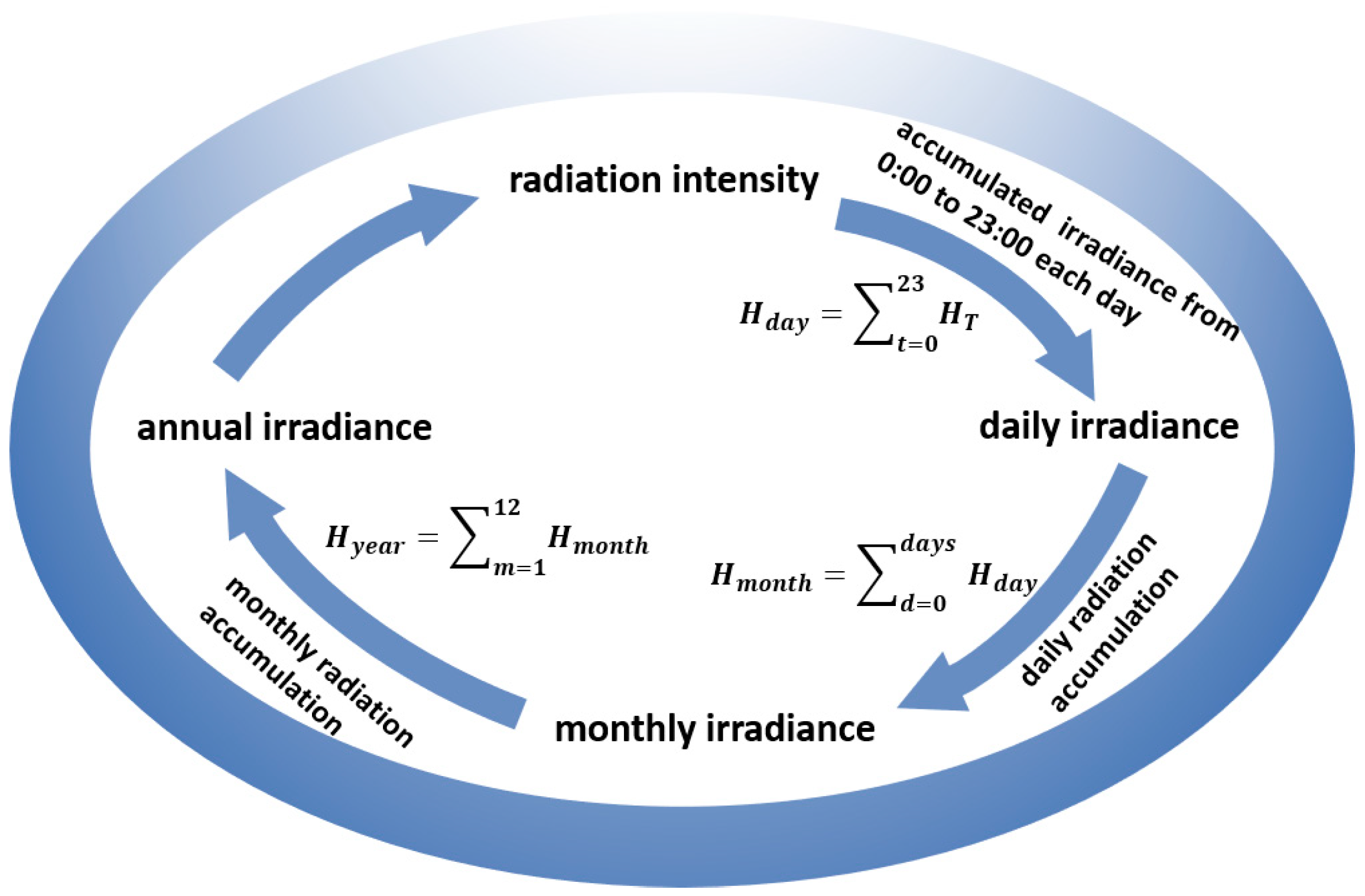
- Irradiance is calculated hourly by first computing the total irradiance on the tilted surface , then applying the shading loss factor to obtain effective irradiance . Summing hourly values yields daily, monthly, and annual totals, which serve as the fitness score;
- Identify the global best individual () with the highest fitness and record local bests () within each neighborhood.
- Update individual positions: iteratively update the position of each individual in the population according to Equation (43);
- Search behavior is controlled by the free risk rate (). If a random number exceeds the , the individual moves toward the global best () with a large exploratory step (leaping upward). If below the , the individual refines its position near the local best (dancing center);
- is adaptively adjusted at each iteration using Equation (45), decreasing linearly from the to the as the iteration count increases. This mechanism enhances early stage exploration and late-stage convergence.
- Repeat Steps 2 and 3 until the termination condition is met, typically when the maximum number of iterations is reached;
- Once terminated, the algorithm outputs the global best solution , representing the optimal layout configuration that maximizes annual energy yield.
4. Case Study and Analysis
4.1. Case Setup and Data Description
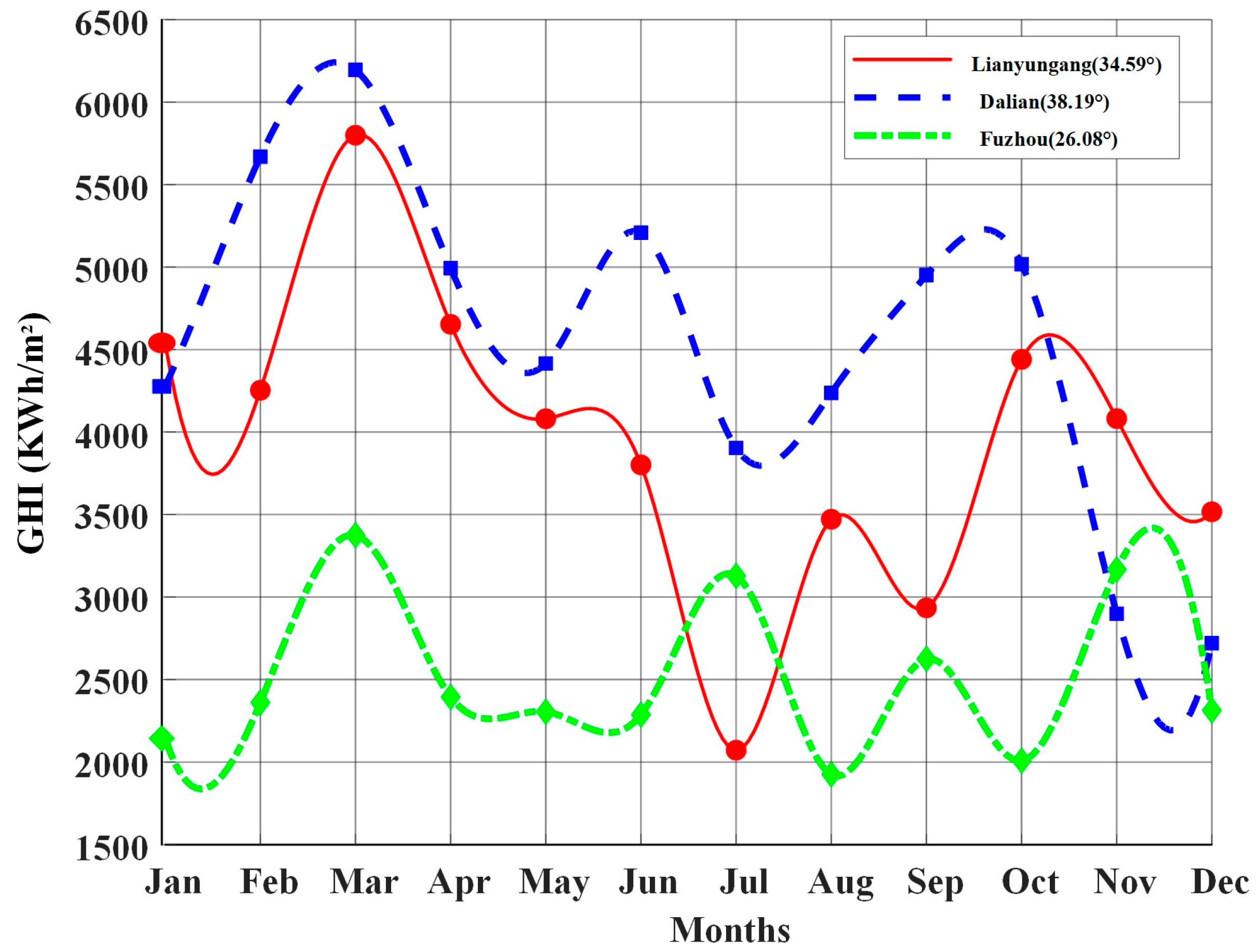
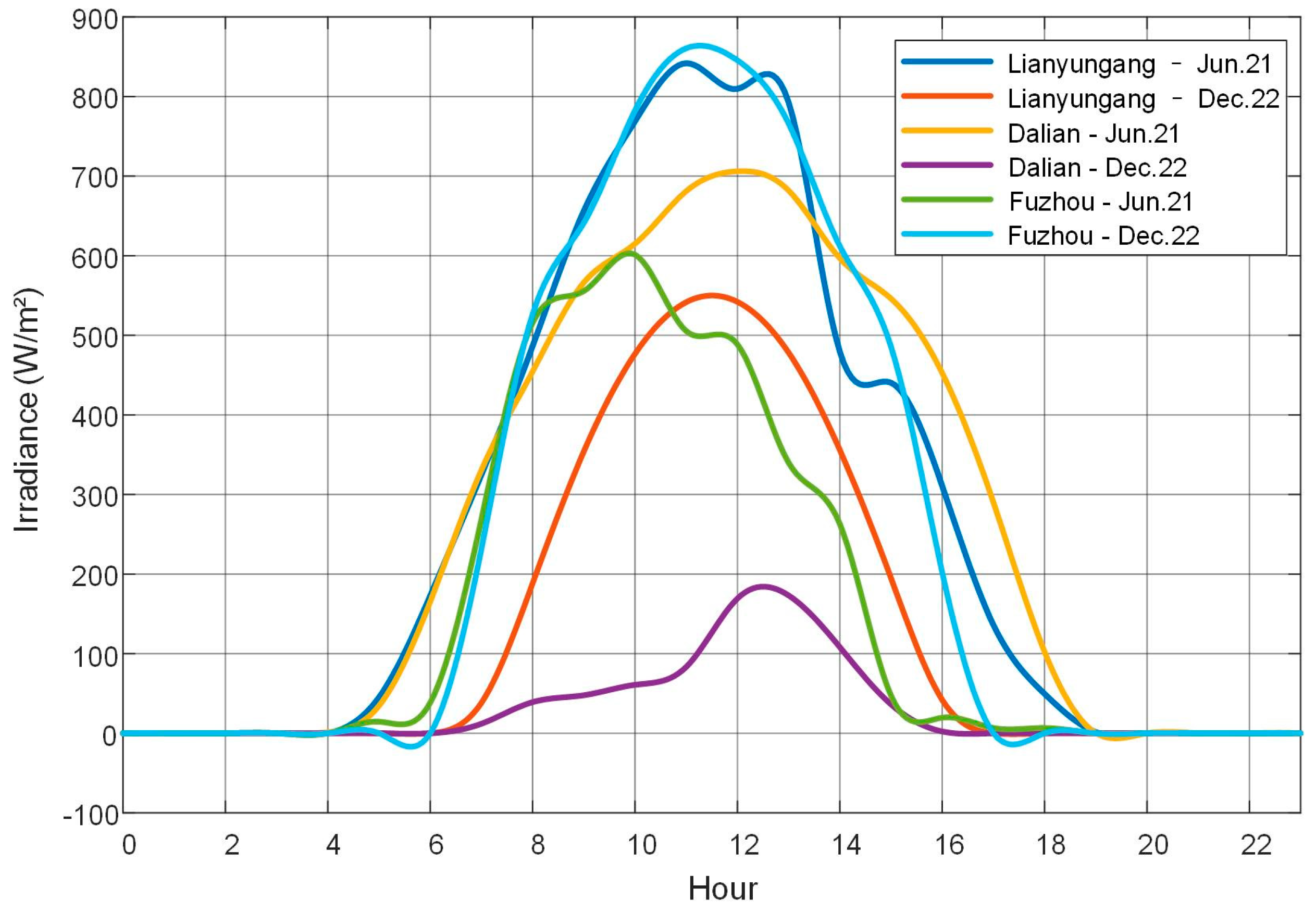
- Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province (34.59° N, 119.22° E), located in a temperate monsoon climate zone;
- Dalian City, Liaoning Province (38.91° N, 121.60° E), characterized by a warm temperate continental monsoon climate;
- Fuzhou City, Fujian Province (26.08° N, 119.30° E), situated in a subtropical monsoon climate zone.
- Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI, W/m2);
- Normal Direct Irradiance (, W/m2);
- Diffuse Irradiance (, W/m2);
- Ambient temperature (, °C).
4.2. Configurations of the Optimization Model
- Tilt angle : 0–90°, covering common ranges for low to mid-latitudes;
- Azimuth angle : −180° to +180°, allowing orientations from southeast to southwest;
- String spacing : 2.0–12.0 m, spanning dense to sparse array layouts.
- Single-sided PV modules, ignoring rear-side reflection;
- No temperature effects on irradiance response;
- Negligible irregular attenuation from dust, shading, or other factors;
- Uniform hourly irradiance distribution over the module surface, ignoring transient changes;
- Ignore component degradation mechanisms such as light-induced degradation (LID) and potential-induced degradation (PID).
- Constant ground reflectance of 0.2, reflecting typical conditions.
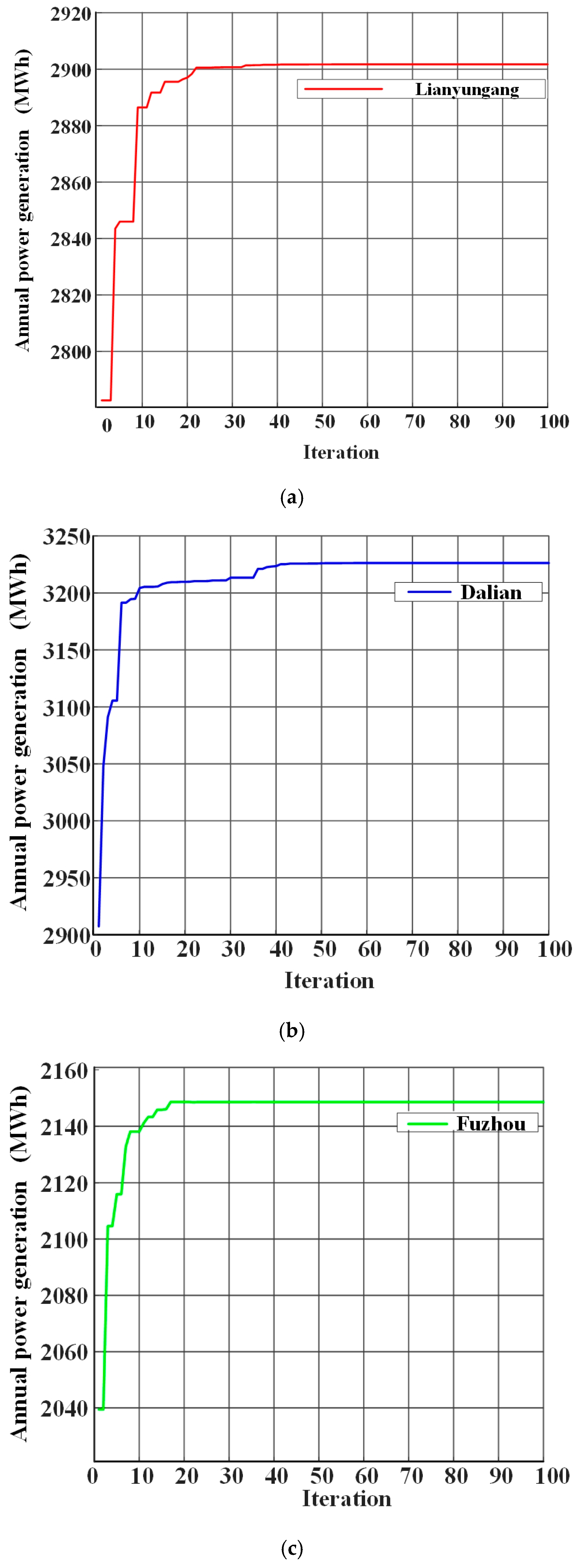
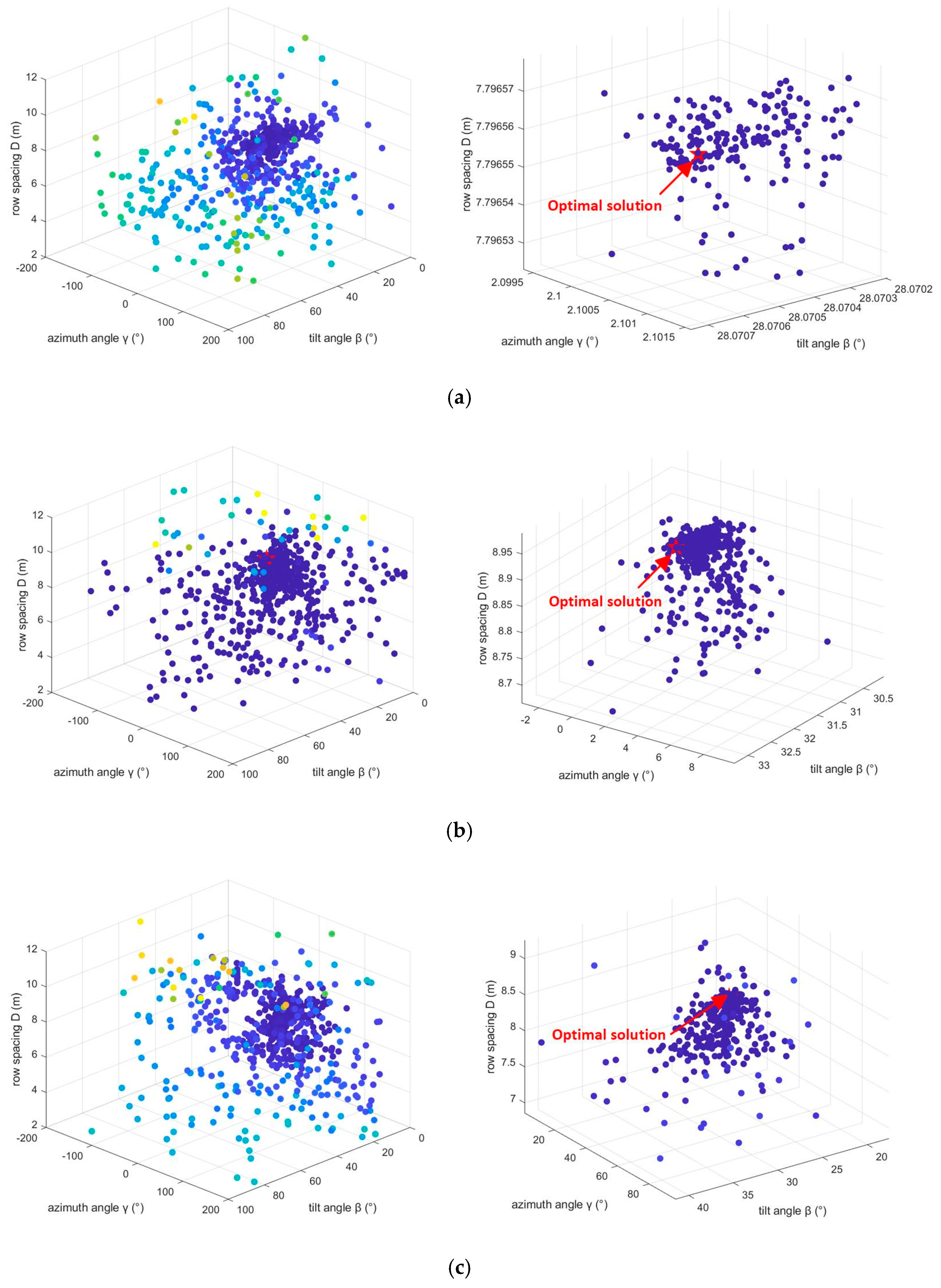
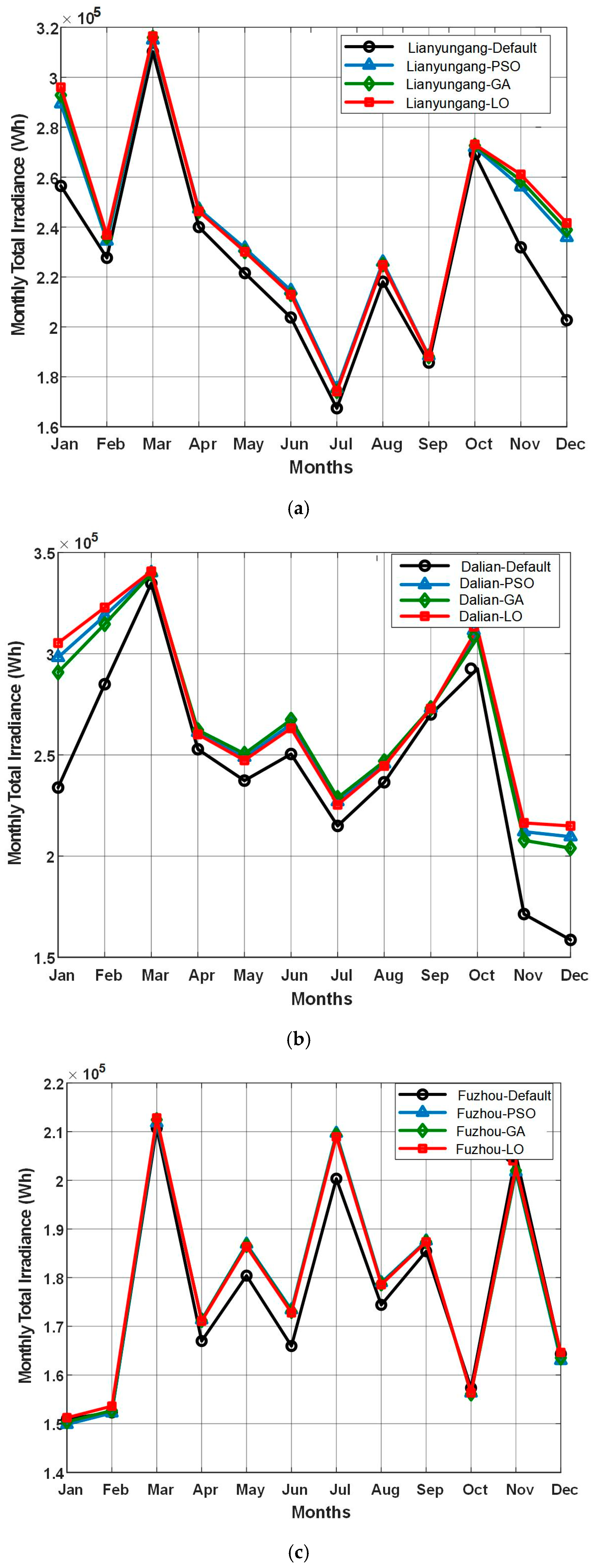
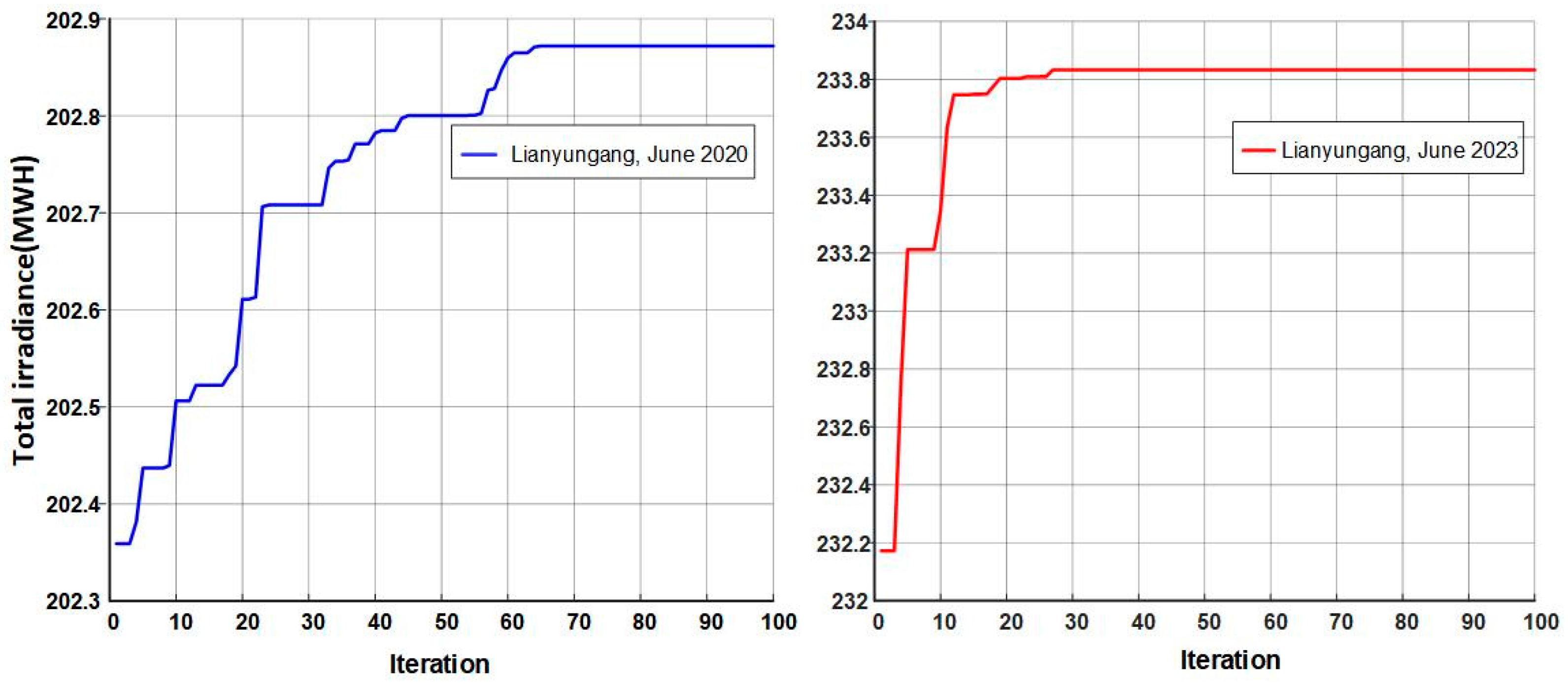
4.3. Simulation Results and Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.; Zheng, R.; Han, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, M.; Shu, H.; Su, S.; Guo, Z. Recent Advances in Fault Diagnosis Techniques for Photovoltaic Systems: A Critical Review. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2024, 9, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B. Two-Stage Hybrid Deep Learning with Strong Adaptability for Detailed Day-Ahead Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Zhang, A.J.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Han, T. Photovoltaic Cell Anomaly Detection Enabled by Scale Distribution Alignment Learning and Multiscale Linear Attention Framework. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 27816–27827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.O.; Souza, F.A.; Carvalho Filho, C.O.; Carvalho, P.C.; AlSkaif, T.; Pereira, R.I. Hybrid Modeling for Photovoltaic Module Operating Temperature Estimation. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2024, 14, 488–496. [Google Scholar]
- Mignoni, N.; Carli, R.; Dotoli, M. Layout Optimization for Photovoltaic Panels in Solar Power Plants via a MINLP Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 18148–18161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Choi, J.; Ahn, S.H.; Hyun, J.H.; Cha, H.L.; Lim, B.Y.; Ahn, H.K. Optimal Inclination and Azimuth Angles of a Photovoltaic Module with Load Patterns for Improved Power System Stability. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2024, 14, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Su, S.F.; Yang, W.; Xie, L. A Novel Hybrid Transformer-Based Framework for Solar Irradiance Forecasting Under Incomplete Data Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 8605–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimd, B.D.; Völler, S.; Midtgård, O.M.; Cali, U.; Sevault, A. Quantification of the Impact of Azimuth and Tilt Angle on the Performance of a PV Output Power Forecasting Model for BIPVs. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2024, 14, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, R.; Parenti, M.; Memme, S.; Fossa, M.; Morchio, S. A Review and Comparative Analysis of Solar Tracking Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovics, D.; Mayer, M.J. Comparison of Machine Learning Methods for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Based on Numerical Weather Prediction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldivar-Aguilera, T.Q.; Valentín-Coronado, L.M.; Peña-Cruz, M.I.; Diaz-Ponce, A.; Dena-Aguilar, J.A. Novel Closed-Loop Dual Control Algorithm for Solar Trackers of Parabolic Trough Collector Systems. Sol. Energy 2023, 259, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.J.; Milidonis, K.; Bonanos, A.M. Updating the PSA Sun Position Algorithm. Sol. Energy 2020, 212, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouholamini, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, C. Modeling, Configuration, and Grid Integration Analysis of Bifacial PV Arrays. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driesse, A.; Jensen, A.R.; Perez, R. A Continuous Form of the Perez Diffuse Sky Model for Forward and Reverse Transposition. Sol. Energy 2024, 267, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, I.; de Blas, M.; Hernández, B.; Sáenz, C.; Torres, J.L. Diffuse Irradiance on Tilted Planes in Urban Environments: Evaluation of Models Modified with Sky and Circumsolar View Factors. Renew. Energy 2021, 180, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynoson, M.; Lu, S.M.; Munkhammar, J.; Campana, P.E. Evaluation of Reverse Transposition and Separation Methods for Global Tilted Irradiance: Insights from High-Latitude Data. Sol. Energy 2025, 297, 113597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Song, Z.; Dong, Q.; Zhao, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; et al. Energy Performance and Fire Risk of Solar PV Panels under Partial Shading: An Experimental Study. Renew. Energy 2025, 246, 122910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, P.; Sharma, R.; Satpathy, P.R.; Thanikanti, S.B.; Nwulu, N.I. A Dimension-Independent Array Relocation (DIAR) Approach for Partial Shading Losses Minimization in Asymmetrical Photovoltaic Arrays. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 63176–63196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecl, K.; Bokalič, M.; Topič, M. Annual Energy Losses Due to Partial Shading in PV Modules with Cut Wafer-Based Si Solar Cells. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcañiz, A.; van Kouwen, M.I.; Isabella, O.; Ziar, H. Wide-Area Sky View Factor Analysis and Fourier-Based Decomposition Model for Optimizing Irradiance Sensors Allocation in European Solar Photovoltaic Farms: A Software Tool. Sol. Energy 2025, 286, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulos, P.; Dhake, H.; Kartoudi, D.; Tsavalos, A.; Koutsantoni, P.; Katranitsas, A.; Lavdakis, N.; Mengou, E.; Kashyap, Y. Ray-Tracing Modeling for Urban Photovoltaic Energy Planning and Management. Appl. Energy 2024, 369, 123516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofstad-Lie, V.; Marstein, E.S.; Simonsen, A.; Skauli, T. Cost-Effective Flight Strategy for Aerial Thermography Inspection of Photovoltaic Power Plants. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2022, 12, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukač, N.; Mongus, D.; Žalik, B.; Štumberger, G.; Bizjak, M. Novel GPU-Accelerated High-Resolution Solar Potential Estimation in Urban Areas by Using a Modified Diffuse Irradiance Model. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Sahu, H.S.; Kumar, S.; Nayak, S.K.; Mishra, M.K. Maximum Energy Harvest From a TCT Connected PV Array Under Nonhomogeneous Irradiation Conditions. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 5441–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Han, D.S.; Lee, Z. Solar Panel Tilt Angle Optimization Using Machine Learning Model: A Case Study of Daegu City, South Korea. Energies 2020, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quraan, A.; Al-Mahmodi, M.; Alzaareer, K.; El-Bayeh, C.; Eicker, U. Minimizing the Utilized Area of PV Systems by Generating the Optimal Inter-Row Spacing Factor. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojkumar, R.; Kumar, C.; Ganguly, S. Optimal Demand Response in a Residential PV Storage System Using Energy Pricing Limits. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, R.B.; Khan, M.A.M.; Alsulaiman, F.A.; Mansour, R.B. Optimizing the Solar PV Tilt Angle to Maximize the Power Output: A Case Study for Saudi Arabia. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 15914–15928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonita, E.M.; Russell, A.C.; Valdivia, C.E.; Hinzer, K. Optimal Ground Coverage Ratios for Tracked, Fixed-Tilt, and Vertical Photovoltaic Systems for Latitudes up to 75° N. Sol. Energy 2023, 258, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prilliman, M.; Smith, S.E.; Stanislawski, B.J.; Keith, J.M.; Silverman, T.J.; Calaf, M.; Cal, R.B. Technoeconomic Analysis of Changing PV Array Convective Cooling Through Changing Array Spacing. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2022, 12, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A.; Wright, D. Optimal Orientation Angles for Maximizing Energy Yield for Solar PV in Saudi Arabia. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, Z.; Butt, N.Z. Implications of Spatial-Temporal Shading in Agrivoltaics under Fixed Tilt & Tracking Bifacial Photovoltaic Panels. Renew. Energy 2022, 190, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, R.; Mulalic, I.; Soutar, I.; Weinand, J.M.; Price, J.; Petrović, S.; Mainzer, K. Exploring Trade-Offs Between Landscape Impact, Land Use and Resource Quality for Onshore Variable Renewable Energy: An Application to Great Britain. Energy 2022, 250, 123754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.J. Effects of the Meteorological Data Resolution and Aggregation on the Optimal Design of Photovoltaic Power Plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 241, 114313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Hu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; He, Z. Hierarchical Energy Management of Networked Flexible Traction Substations for Efficient RBE and PV Energy Utilization Within ERs. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 14, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, Z.; Alharbi, A.; Habib, A.H.; de Weck, O.L. Site Assessment and Layout Optimization for Rooftop Solar Energy Generation in WorldView-3 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnawal, P.J.; Lal, V.N.; Singh, R.K. A Dual Half-Active Bridge Resonant Converter for Solar PV Integration Using Grey Wolf Optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 7087–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liang, F.; Song, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, X.P.; Guo, L.; Gu, X. Impact of the PV Location in Distribution Networks on Network Power Losses and Voltage Fluctuations with PSO Analysis. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 8, 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Y.; Nainar, K.; Bendtsen, J.D.; Diewald, N.; Iov, F.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F.; Xue, Y.; Liu, J.; Hong, T.; et al. Voltage Support With PV Inverters in Low-Voltage Distribution Networks: An Overview. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 1503–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. PSOPruner: PSO-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network Pruning Method for PV Module Defects Classification. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2022, 12, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, E.; Buerhop-Lutz, C.; Bennett, S.; Christlein, V.; Hauch, J.; Brabec, C.J.; Peters, I.M. PV Polaris—Automated PV System Orientation Prediction. IEEE Photonics J. 2025, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Niu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Duan, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, G. Prediction Method of Direct Normal Irradiance for Solar Thermal Power Plants Based on VMD-WOA-DELM. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Du, E.; Li, S.; Li, Z. Coordinated Operation of Concentrating Solar Power Plant and Wind Farm for Frequency Regulation. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božiková, M.; Bilčík, M.; Madola, V.; Szabóová, T.; Kubík, Ľ.; Lendelová, J.; Cviklovič, V. The Effect of Azimuth and Tilt Angle Changes on the Energy Balance of Photovoltaic System Installed in the Southern Slovakia Region. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, L.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, M.; Li, Q. Evaluation of 12 Transposition Models Using Observations of Solar Radiation and Power Generation. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2022, 12, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolai, A.; Grimaccia, F.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Araneo, R.; Ughi, F.; Polenghi, M. A Review of Floating PV Systems With a Techno-Economic Analysis. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2024, 14, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abasi, A.K.; Makhadmeh, S.N.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Alomari, O.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Alyasser, Z.A.A.; Doush, I.A.; Elnagar, A.; Alkhammash, E.H.; Hadjouni, M. Lemurs Optimizer: A New Metaheuristic Algorithm for Global Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A.; Kambezidis, H.D.; Kampezidou, S.I. Effect of the Ground Albedo on the Estimation of Solar Radiation on Tilted Flat-Plate Surfaces: The Case of Saudi Arabia. Energies 2023, 16, 7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, H.; Salim, K.M.E.; Gül, M. Multi-Objective Design of Grid-Tied Solar Photovoltaics for Commercial Flat Rooftops Using Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, A.M.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Naderipour, A.; Ekanayake, J.B. Comparative Analysis of Two-Step GA-Based PV Array Reconfiguration Technique and Other Reconfiguration Techniques. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 230, 113806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of PV cells () | 132 |
| Open circuit voltage () | 44.80 V |
| Short circuit current () | 18.350 A |
| Voltage at maximum power point () | 37.70 V |
| Circuit at maximum power point () | 17.110 A |
| Maximum power () | 645 W |
| Circuit temperature coefficient () | 9.1 mA/°C |
| Efficiency of the PV module | 21.4% |
| System derating factor | 10% |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Lower Bound | [0, −180, 2] |
| Upper Bound | [90°, 180°, 12] |
| Maximum Iterations | 200 |
| Dimensions | 3 |
| Low Risk Rate | 0.1 |
| High Risk Rate | 0.5 |
| Selected City | Parameter Settings | Annual Irradiance (MW) | Improvement Magnitude (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lianyungang | Default | 34.59 | 0 | 6.00 | 2734.81 | - |
| PSO | 26.76 | 1.54 | 7.20 | 2885.79 | +5.52 | |
| GA | 27.98 | 2.30 | 7.62 | 2895.44 | +5.87 | |
| LO | 28.07 | 2.10 | 7.80 | 2901.67 | +6.10 | |
| Dalian | Default | 38.19 | 0 | 6.00 | 2946.51 | - |
| PSO | 30.56 | 1.47 | 8.20 | 3210.17 | +8.95 | |
| GA | 29.00 | 1.76 | 7.69 | 3193.64 | +8.38 | |
| LO | 31.82 | 1.65 | 8.92 | 3226.27 | +9.49 | |
| Fuzhou | Default | 26.08 | 0 | 6.00 | 2036.59 | - |
| PSO | 17.84 | 1.63 | 6.50 | 2142.58 | +5.20 | |
| GA | 18.21 | 2.82 | 6.65 | 2135.42 | +4.85 | |
| LO | 18.59 | 2.75 | 7.16 | 2148.57 | +5.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, G.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, X. A Collaborative Optimization Strategy for Photovoltaic Array Layout Based on the Lemur Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111870
Dai G, Chen Q, Chen Y, Wang Y, Shen Z, Li X. A Collaborative Optimization Strategy for Photovoltaic Array Layout Based on the Lemur Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry. 2025; 17(11):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111870
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Guanhong, Qianhan Chen, Yangyu Chen, Yu Wang, Zhan Shen, and Xiaoqiang Li. 2025. "A Collaborative Optimization Strategy for Photovoltaic Array Layout Based on the Lemur Optimization Algorithm" Symmetry 17, no. 11: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111870
APA StyleDai, G., Chen, Q., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Shen, Z., & Li, X. (2025). A Collaborative Optimization Strategy for Photovoltaic Array Layout Based on the Lemur Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry, 17(11), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111870







