PECNet: A Lightweight Single-Image Super-Resolution Network with Periodic Boundary Padding Shift and Multi-Scale Adaptive Feature Aggregation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
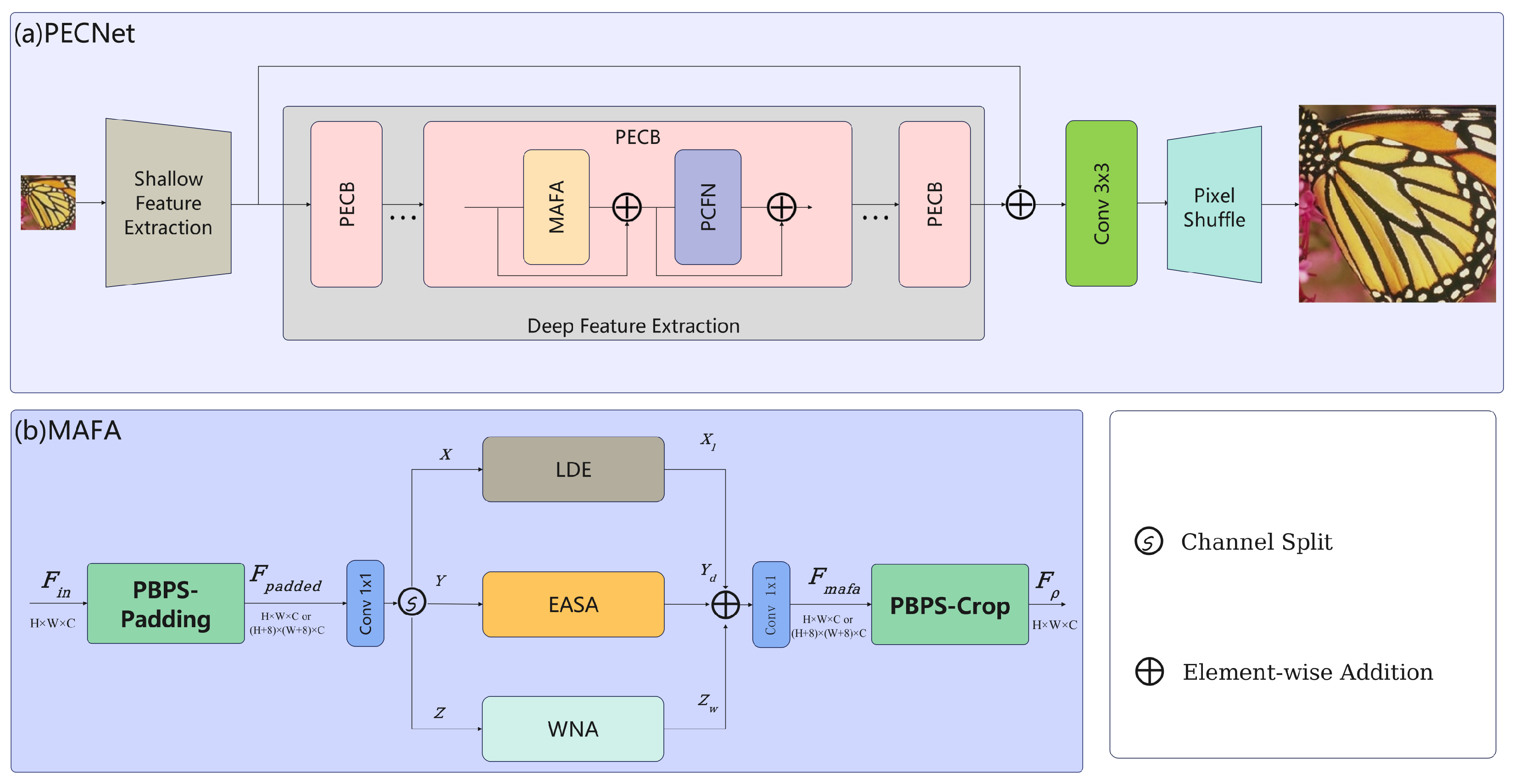
- MAFA integrates local details and global structural information to avoid unremarkable feature synthesis—solving the problem that existing frameworks (even with improvements such as dual-path design) still cannot integrate two complementary features as a whole, namely “distinguishable local details” and “global structural dependencies”, resulting in a disconnection in their extraction. The MAFA module achieves holistic integration through three specialized branches: the local detail estimation (LDE) enhances high-frequency details via depthwise convolution; the effective approximate self-attention (EASA) models long-range dependencies with variance modulation;the Window Nonlocal Attention (WNA) captures intra-window contexts through 8 × 8 attention.
- (2)
- We propose the Periodic Boundary Padding Shift (PBPS) mechanism in MAFA, which serves as a unified preprocessing backbone to structurally support and align the three complementary branches. As it is difficult to apply window shifting in LDE and singly window shifting to one branch (WNA) will leading unbalance: for odd-indexed blocks, symmetric replicate-padding (4 pixels) expands feature dimensions to induce fixed window offset; even-indexed blocks maintain original resolution followed by center cropping—eliminating explicit shifting operations while equivalently achieving SwinIR-style cross-window communication at zero computational overhead. Feature refinement is enhanced via a Partial Convolution-based Feed-forward Network (PCFN) that selectively processes channels while preserving identity paths. Our experimental evaluation shows that PECNet achieves an outstanding balance between reconstruction quality and computational efficiency across multiple benchmarks (see Figure 1).
- Three-branch aggregation: We design a three-branch aggregation module in MAFA to address the gap in frequency and spatial distance modeling for SISR. the EASA branch captures remote non-local low-frequency information, the LDE branch extracts local high-frequency details and the WNA branch focuses on non-local interactions within the shifted window.
- PBPS mechanism: We propose the PBPS mechanism to integrate the three branches. The PBPS mechanism not only alleviates boundary discontinuity in traditional WNA blocks, but also enhances the generalization capability of LDE and EASA models due to window shifting is also apply in LDE and EASA.
- PECNet algorithm: We propose a lightweight SISR algorithm, PECNet, which employs MAFA as its main block. PECNet extracts multi-frequency and multi-distance features through three specialized branches, with each block operating optimally in its respective domain.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Three-Branch Architecture in MAFA
3.3. Periodic Boundary Padding Shift Mechanism and Its Inverse Operation in MAFA
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets and Implementation
4.2. Ablation Experiment
4.3. Comparisons with State-of-the-Art Methods
5. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hui, Z.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Lightweight Image Super-Resolution with Information Multi-distillation Network. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 2024–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Wu, G. Residual Feature Distillation Network for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cai, H.; Gu, J.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, C. Blueprint Separable Residual Network for Efficient Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 833–843. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Image Super-Resolution via Deep Recursive Residual Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3147–3155. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Lee, K.M. Enhanced Deep Residual Networks for Single Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 286–301. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Timofte, R. SwinIR: Image Restoration Using Swin Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, L. Efficient Long-Range Attention Network for Image Super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 649–667. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Lee, J.; Yang, J. N-gram in swin transformers for efficient lightweight image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2071–2081. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Sun, L.; Dong, J.; Pan, J. SMFANet: A Lightweight Self-Modulation Feature Aggregation Network for Efficient Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.B.; Singh, A.; Ahuja, N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5197–5206. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, Y.; Ito, K.; Aramaki, Y.; Fujimoto, A.; Ogawa, T.; Yamasaki, T.; Aizawa, K. Sketch-based Manga Retrieval using Manga109 Dataset. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 21811–21838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 184–199. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Accelerating the Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z. Real-Time Single Image and Video Super-Resolution Using an Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M. Deeply-Recursive Convolutional Network for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1637–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Shi, J. Lightweight Image Super-Resolution with Adaptive Weighted Learning Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2001.09191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T. OSFFNet: Omni-Stage Feature Fusion Network for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 5660–5668. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F. HiT-SR: Hierarchical Transformer forEfficient Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 483–500. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Pan, J.; Tang, J.; Dong, J. DLGSANet: Lightweight Dynamic Local and Global Self-Attention Networks for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 12792–12801. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhang, F.; Bull, D. MTKD: Multi-Teacher Knowledge Distillation for Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 364–382. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Yuan, K.; Zhao, K.; Xie, Q.; Hao, J.; Sun, M.; Zhou, C. XPSR: Cross-modal Priors for Diffusion-based Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 285–303. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, T.; Xu, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Gao, W. Pre-Trained Image Processing Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12299–12310. [Google Scholar]
- Conde, M.V.; Choi, U.J.; Burchi, M.; Timofte, R. Swin2SR: SwinV2 Transformer for Compressed Image Super-Resolution and Restoration. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 669–687. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Zuo, W.; Shan, S. Shift-Net: Image Inpainting via Deep Feature Rearrangement. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Agustsson, E.; Timofte, R. NTIRE 2017 Challenge on Single Image Super-Resolution: Dataset and Study. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Tang, L.; Wu, Y.; Tretter, D.; Zhou, J. Spatially Adaptive Block-Based Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Ying, X.; Guo, Y. Exploring Sparsity in Image Super-Resolution for Efficient Inference (CVPR’2021). In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4917–4926. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Pan, J.; Tang, J. Shufflemixer: An efficient convnet for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Volume 35, pp. 17314–17326. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhou, K.; Qi, L.; Jiang, N.; Lu, J.; Jia, J. LAPAR: Linearly-Assembled Pixel-Adaptive Regression Network for Single Image Super-resolution and Beyond. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 20343–20355. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Cong, R.; Wu, J.; Bai, H.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y. SRConvNet: A Transformer-Style ConvNet for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Roumy, A.; Guillemot, C.; Morel, A. Low-Complexity Single Image Super-Resolution Based on Nonnegative Neighbor Embedding. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, UK, 3–7 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeyde, R.; Elad, M.; Protter, M. On Single Image Scale-Up Using Sparse-Representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Curves and Surfaces, Oslo, Norway, 28 June–3 July 2012; pp. 711–730. [Google Scholar]
- Arbeláez, P.; Maire, M.; Fowlkes, C.; Malik, J. Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Dong, J.; Tang, J.; Pan, J. Spatially-Adaptive Feature Modulation for Efficient Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 13190–13199. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Restarts. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Core Architecture | High-Frequency | Global Modeling | Window Shift | Key Innovations and Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SwinIR | Pure Transformer | Window self-attention | Window self-attention + explicit shift | Explicit | Pioneered shift-window, but self-attention insensitive to high-frequency details, explicit shifting is not suitable for multiple branches |
| NGswin | Conv + Transformer Hybrid | Partial relief via conv priors | N-Gram context + explicit shift | Explicit | Effective fusion, but explicit shifting, lacks dedicated high-frequency branch |
| SAFMN | Pure CNN (Single-path) | Spatial adaptive modulation | Large-kernel conv (limited receptive field) | None | Simple and efficient, but limited long-range dependencies |
| SMFANet | CNN (Dual-path) | Dedicated path for high-freq details | Dedicated path for low-freq structures | None | Feature separation via dual-path, but insufficient inter-path interaction |
| PECNet (Ours) | Collaborative Three-Branch Hybrid | Dedicated LDE branch | Dual-path: EASA + WNA | PBPS Implicit | Innovation 1: Three-branch collaboration with clear division of labor Innovation 2: PBPS enables implicit global shifting, uniformly supports all branches |
| Methods | LDE Branch | EASA Branch | WNA Branch | #Params (K) | #FLOPs (G) | Set5 (PSNR/SSIM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S_LDE | ✓ | 241 | 10 | 31.49/0.8837 | ||
| S_EASA | ✓ | 241 | 6 | 31.52/0.8857 | ||
| S_WNA | ✓ | 241 | 11 | 31.79/0.8890 | ||
| D_L+E | ✓ | ✓ | 251 | 11 | 31.77/0.8873 | |
| D_E+W | ✓ | ✓ | 251 | 12 | 31.93/0.8905 | |
| D_L+W | ✓ | ✓ | 251 | 15 | 31.87/0.8901 | |
| T_L+E+W | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 262 | 16 | 31.94/0.8909 |
| (our MAFA) |
| Methods | Explicit Window Shifting | PBPS | #Params (K) | #FLOPs (G) | Set5 (PSNR/SSIM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T_L+E+W | 262 | 16 | 31.94/0.8909 | ||
| WNA-shift | ✓ | 260 | 14 | 31.79/0.8889 | |
| PBPS(our) | ✓ | 262 | 16 | 32.02/0.8917 |
| Padding Methods | #Params (K) | #FLOPs (G) | Set5 (PSNR/SSIM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| replicate | 262 | 16 | 32.02/0.8917 |
| circular | 262 | 16 | 32.00/0.8916 |
| reflect | 262 | 16 | 31.98/0.8914 |
| constant = 0 | 262 | 16 | 31.98/0.8914 |
| Scale | Methods | #Params (K) | #FLOPs (G) | Set5 | Set14 | B100 | Urban100 | Manga109 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMSR | 985 | 132 | 38.00/0.9601 | 33.64/0.9197 | 32.17/0.8990 | 32.19/0.9284 | 38.76/0.9771 | |
| ShuffleMixer | 394 | 91 | 38.01/0.9606 | 33.63/0.9180 | 32.17/0.8995 | 31.89/0.9257 | 38.83/0.9774 | |
| SAFMN | 228 | 52 | 38.00/0.9605 | 33.54/0.9177 | 32.16/0.8995 | 31.84/0.9256 | 38.71/0.9771 | |
| SMFANet | 186 | 41 | 38.08/0.9607 | 33.65/0.9185 | 32.22/0.9002 | 32.20/0.9282 | 39.11/0.9779 | |
| LAPAR-A | 584 | 171 | 38.01/0.9605 | 33.62/0.9183 | 32.19/0.8999 | 32.10/0.9283 | 38.67/0.9772 | |
| NGswin | 998 | 146 | 38.05/0.9610 | 33.79/0.9199 | 32.27/0.9008 | 32.53/0.9324 | 38.97/0.9777 | |
| SRConvNet | 387 | 74 | 38.00/0.9605 | 33.58/0.9186 | 32.16/0.8995 | 32.05/0.9272 | 38.87/0.9774 | |
| PECNet(ours) | 250 | 61 | 38.09/0.9611 | 33.82/0.9201 | 32.24/0.9005 | 32.46/0.9309 | 39.19/0.9783 | |
| SMSR | 993 | 68 | 34.40/0.9270 | 30.33/0.8412 | 29.10/0.8050 | 28.25/0.8536 | 33.68/0.9445 | |
| ShuffleMixer | 415 | 43 | 34.40/0.9272 | 30.37/0.8423 | 29.12/0.8051 | 28.08/0.8498 | 33.69/0.9448 | |
| SAFMN | 233 | 23 | 34.34/0.9267 | 30.33/0.8418 | 29.08/0.8048 | 27.95/0.8474 | 33.52/0.9437 | |
| SMFANet | 191 | 19 | 34.42/0.9274 | 30.41/0.8430 | 29.16/0.8065 | 28.22/0.8523 | 33.96/0.9460 | |
| LAPAR-A | 594 | 114 | 34.36/0.9267 | 30.34/0.8412 | 29.11/0.8054 | 28.15/0.8523 | 33.51/0.9441 | |
| NGswin | 1007 | 66 | 34.52/0.9282 | 30.53/0.8456 | 29.19/0.8078 | 28.52/0.8603 | 33.89/0.9470 | |
| SRConvNet | 387 | 33 | 34.40/0.9272 | 30.30/0.8416 | 29.07/0.8047 | 28.04/0.8500 | 33.56/0.9443 | |
| PECNet(ours) | 255 | 28 | 34.51/0.9284 | 30.53/0.8453 | 29.20/0.8079 | 28.43/0.8565 | 34.18/0.9476 | |
| SMSR | 1006 | 42 | 32.12/0.8932 | 28.55/0.7808 | 27.55/0.7351 | 26.11/0.7868 | 30.54/0.9085 | |
| ShuffleMixer | 411 | 28 | 32.21/0.8953 | 28.66/0.7827 | 27.61/0.7366 | 26.08/0.7835 | 30.65/0.9093 | |
| SAFMN | 240 | 14 | 32.18/0.8948 | 28.60/0.7813 | 27.58/0.7359 | 25.97/0.7809 | 30.43/0.9063 | |
| SMFANet | 197 | 11 | 32.25/0.8956 | 28.71/0.7833 | 27.64/0.7377 | 26.18/0.7862 | 30.82/0.9104 | |
| LAPAR-A | 659 | 94 | 32.15/0.8944 | 28.61/0.7818 | 27.61/0.7366 | 26.14/0.7871 | 30.42/0.9074 | |
| NGswin | 1019 | 40 | 32.33/0.8963 | 28.78/0.7859 | 27.66/0.7396 | 26.45/0.7963 | 30.80/0.9128 | |
| SRConvNet | 382 | 22 | 32.18/0.8951 | 28.61/0.7818 | 27.57/0.7359 | 26.06/0.7845 | 30.35/0.9075 | |
| PECNet(ours) | 262 | 16 | 32.38/0.8969 | 28.81/0.7857 | 27.69/0.7396 | 26.35/0.7916 | 31.05/0.9136 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, T.; Liu, Y. PECNet: A Lightweight Single-Image Super-Resolution Network with Periodic Boundary Padding Shift and Multi-Scale Adaptive Feature Aggregation. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111833
Gao T, Liu Y. PECNet: A Lightweight Single-Image Super-Resolution Network with Periodic Boundary Padding Shift and Multi-Scale Adaptive Feature Aggregation. Symmetry. 2025; 17(11):1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111833
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Tianyu, and Yuhao Liu. 2025. "PECNet: A Lightweight Single-Image Super-Resolution Network with Periodic Boundary Padding Shift and Multi-Scale Adaptive Feature Aggregation" Symmetry 17, no. 11: 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111833
APA StyleGao, T., & Liu, Y. (2025). PECNet: A Lightweight Single-Image Super-Resolution Network with Periodic Boundary Padding Shift and Multi-Scale Adaptive Feature Aggregation. Symmetry, 17(11), 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17111833







