Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of flipping left corneas topography and analysethem quantitively along with fellow right corneas based on the assumption that they are mirror images of each other. Methods: The study involved scanning both eyes of 177 healthy participants (aged 35.3 ± 15.8) and 75 keratoconic participants (aged 33.9 ± 17.8). Clinical tomography data were collected for both eyes using the Pentacam HR and processed by a fully automated custom-built MATLAB code. For every case, the right eye was used as a datum fixed surface while the left cornea was flipped around in the superior–inferior direction. In this position, the root-mean-squared difference (RMS) between the flipped left cornea and the right cornea was initially determined for both the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces. Next, the iterative closest point transformation algorithm was applied on the three-dimensional flipped cornea to allow the flipped left corneal anterior surface to translate and rotate, minimising the difference between it and the right corneal anterior surface. Then, the RMS differences were recalculated and compared. Results: A comparison of the dioptric powers showed a significant difference between the RMS of both the flipped left eyes and the right eyes in the healthy and the KC groups (p < 0.001). The RMS of the surfaces of the flipped left corneas and the right corneas was 0.6 ± 0.4 D among the healthy group and 4.1 ± 2.3 among the KC group. After transforming the flipped left corneas, the RMS was recorded as 0.5 ± 0.3 D and 2.4 ± 2 D among the healthy and KC groups, respectively. Conclusions: Although fellow eyes are highly related in their clinical parameters, they should be treated with care when one eye topography is flipped and processed with the other eye topography in an optic-related research analysis where translation might be needed. In KC, an asymmetric disease, it was observed that a portion of the asymmetry was due to a corneal apex shift interfering with the image acquisition. Therefore, transforming the flipped left eyes by rotation and translation results in a fairer comparison between the fellow KC corneas.
1. Introduction
It is a common practice in anterior ocular topography-based studies that left eyes are superiorly–inferiorly flipped and quantitively analysed along with right eyes through the same analytical approach [1,2]. This left eye mirror-imaging technique of analysing corneal topography is well justified in the literature, as bilateral fellow eyes have always been found to be mirror-symmetric [3,4,5,6]. Conversely, and despite several findings that the right and the mirrored image of the left anterior eye topographies are highly correlated, they are believed to not be equally aligned in topography scans [7]. Even a small difference in their raw elevations, as measured, could make the right and left eyes differ in their dioptric powers and astigmatic axes [8]. Additionally, two-thirds of the population are right-eye dominant [9,10,11,12,13], and the visual field of right eyes is different from that of left eyes [14]. Beyond the eye globe, the image-merging processes carried out within the brain for the two eyes are different [15,16]. These differences require the two eyes to perform differently during the fixation process [17], where dominant eyes have been believed to be dynamic during the fixation process.
The current study accepts the existence of mirror symmetry among fellow eyes, but investigates if only flipping the left corneal topography data around a superior–inferior axis is an effective strategy for quantitively analysing right and flipped left corneas together, or if there should be an additional adjustment to compensate for the different eye alignments during the fixation process associated with the corneal topography and tomography scans. The study gives a clear pathway for the ocular-anterior eye research community to enable analysing flipped left corneas with right corneas, if necessary, without affecting the results with misalignment artefacts.
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Participants
The study involved scanning the fellow eyes of 177 healthy participants (aged 35.3 ± 15.8) and 75 keratoconic participants (aged 33.9 ± 17.8), selected from referrals to Instituto de Olhos Renato Ambrósio (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). The current study utilises fully anonymised records retrospectively evaluated in solely secondary analyses. No clinical data were collected especially for this study; therefore, no ethical approval was required according to of the policy of the University of Liverpool on research ethics. Nevertheless, the study was conducted in accordance with the standards set in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Before being anonymised, clinical topography data were collected for both eyes of normal and KC participants using the Pentacam HR (OCULUS Optikgeräte GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). Participants with no history of ocular disease, trauma, or ocular surgery were selected for the healthy group. Participants with a clear presence of keratoconus and with no previous ocular procedures, such as collagen cross-linking, were selected for the keratoconic group. Those with intraocular pressure (IOP) higher than 21 mmHg as measured by the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer, those who wore soft contact lenses until less than two weeks before measurement, and those who wore rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses until less than four weeks before measurements were excluded.
At least three successive scans were taken for each eye with a total approximate period of 30 s between them. The measurements continued until three scans with an instrument-generated quality factor of at least 95% and 90% were obtained for the anterior and posterior surfaces, respectively. The scan with the highest quality was then selected for analysis in the current study. Pentacam HR raw elevation data for the anterior surface were exported in comma-separated values (CSV) format and analysed using custom-built MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA) codes.
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
Pentacam HR data were extracted over a mesh grid covering −7 to 7 mm in 141 steps in both nasal–temporal and superior–inferior directions, with missing raw elevation values around corners and edges set to NaN, which stands for “not a number”. A fully computerised custom-built MATLAB code was written especially for this study. The code was able to read the CSV files of both the right and left corneas of every participant before processing them. For every case, the right eye was used as a datum fixed surface while the left corneal was flipped around in the superior–inferior direction. In this position, the root-mean-squared (RMS) difference between the flipped left cornea and the right cornea was initially determined for both the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces. The RMS difference was calculated as in Equation (1) as
where is the flipped left corneal raw elevation surface height, is the measured raw elevation right corneal surface height, and is the number of non-missing data points. In this context, the Latin notation OD stands for oculus dextrus which means the right eye, and OS stands for oculus sinister which means the left eye.
Later, the iterative closest point (ICP) transformation algorithm was applied on the three-dimensional (3D) flipped cornea to allow the flipped left corneal anterior surface to translate and rotate in order to minimise the difference between it and the right cornea anterior surface. The number of ICP iterations was set to 20 based on a preliminary study and the process outputted two matrices representing the 3D translation and the rotation. The flipped left cornea was then rotated (Equation (2)) and translated (Equation (3)) accordingly. As a result, the flipped left eye coordinates became unaligned with the right eye that was used as a datum. To allow a common coordinate among the right and the flipped left eyes, 3D triangulation-based cubic interpolation [18] was used to reconstruct the flipped left cornea that had been rotated and translated to be aligned with the right cornea.
The rotation matrix R that resulted from the ICP algorithm can be expressed as in Equation (2) as
where is the rotation angle around the X-axis, is the rotation angle around the Y-axis and is the rotation angle around the Z-axis. Likewise, the translation matrix T can be expressed as in Equation (3) as
where and are the translations in the X, Y and Z directions, respectively. Hence, the flipped left cornea coordinate can be expressed as shown in Equation (4) as
before RMS of the difference between the translated, rotated & flipped left cornea and the right cornea was recalculated as shown in Equation (5) as
where is the flipped left corneal raw elevation surface height that has been translated and rotated. Finally, the mean and standard deviation of the healthy and keratoconic participant groups were calculated and compared.
2.3. Axial Radii of Curvature and Refractive Power
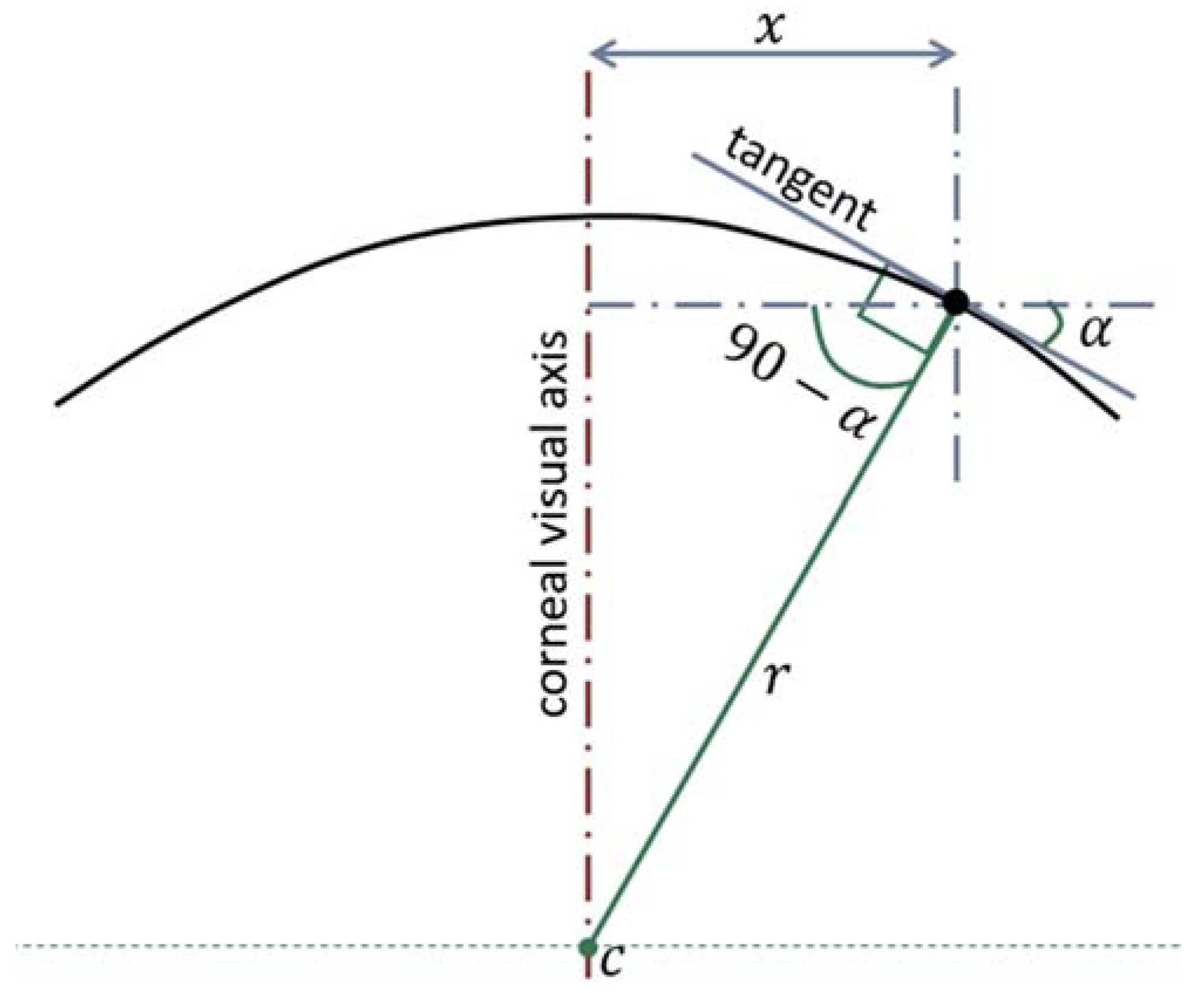
Local axial curvatures were calculated for 359 meridians with a 1.0° angular step covering the assessed area of the cornea up to mm radius. The centres of axial curvatures were assumed to lie on the corneal visual axis [19] as illustrated in Figure 1. The axial radius of curvature at any point was calculated as in Equation (6) as:
where is the tangent angle at this point.
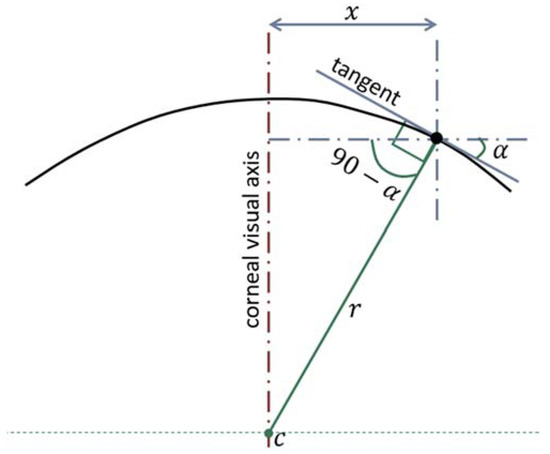
Figure 1.
The determination of the corneal surface axial radius of curvature (r) at a certain meridian plane. In this method, the centre of the curvature (c) was always restricted to the corneal visual axis.
This process was carried out for both the corneal anterior and posterior surfaces and the the corresponding radii of curvature, and , were used to calculate the corneal optical power using the Gaussian optics formula [20,21]:
where the refractive indices of air, , cornea, , and aqueous, , were set at , and , respectively, following the Gullstrand relaxed eye model [22,23]. The central corneal thickness, was determined by subtracting the corneal posterior raw elevation surface from the anterior surface at the corneal apex.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The results were subjected to statistical analysis through the use of the MATLAB Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox. A significance level of 5% was set and the probability of the null hypothesis (p-value) was computed using a two-sample t-test [24]. This calculation was carried out on pairs of data sets to ensure that the observed effects were not occurring as a result of sampling error. Due to the choice of significance level, the observed effects were deemed significant if they achieved a p-value lower than 0.05.
3. Results
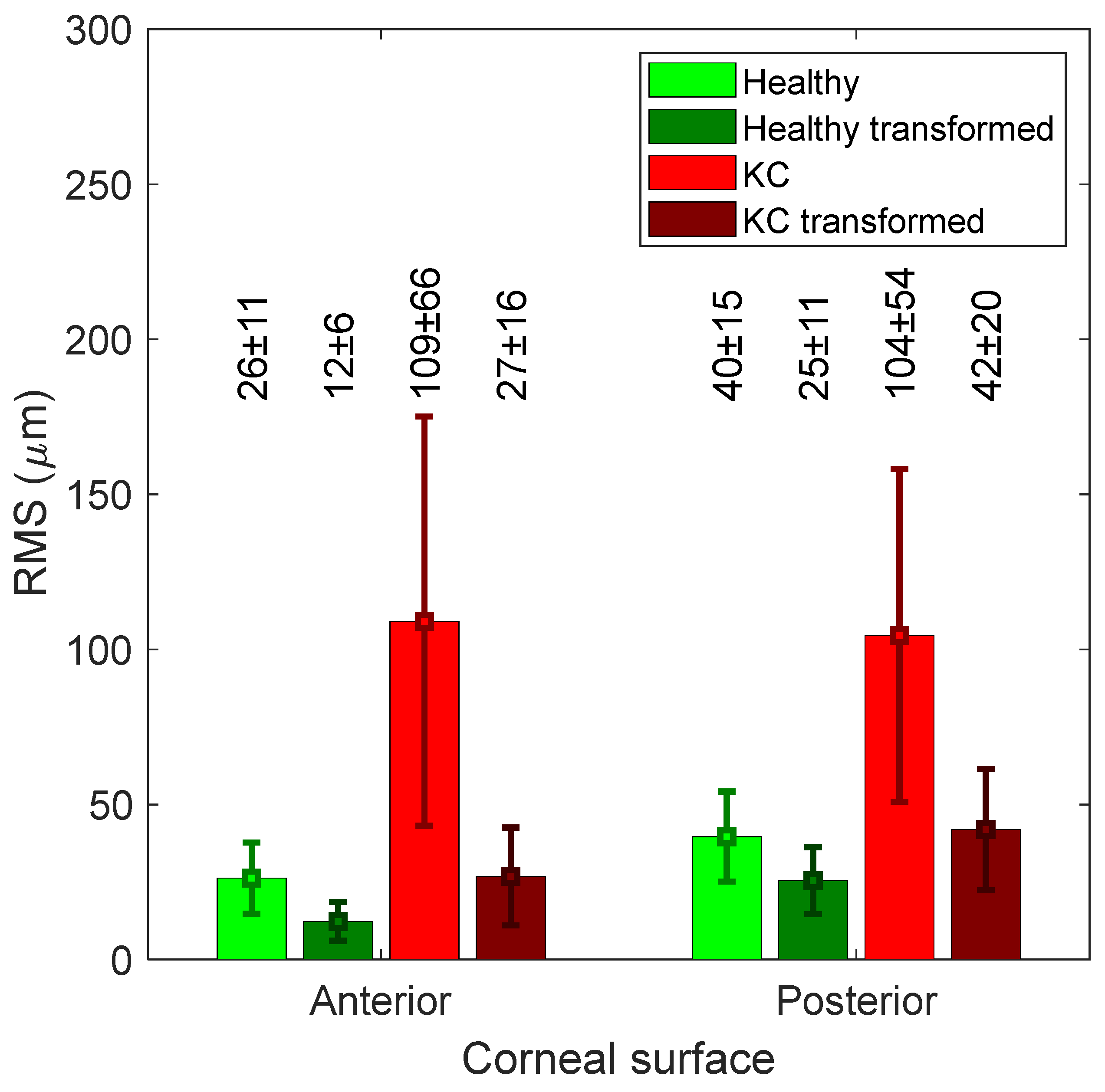
When the left corneas were only flipped around the superior–inferior axis, the healthy corneas recorded RMS differences in raw elevation between the flipped left corneas and right corneas of 26.3 ± 11.5 and 39.6 ± 14.5 µm for the anterior and posterior surfaces respectively. The values of RMS were up to 109.11 ± 66 (anterior) and 104.5 ± 53.6 (posterior) among KC corneas (Figure 2). Once the ICP algorithm was applied, RMS values went down to 12.3 ± 6, 25.4 ± 10.8 µm among healthy corneas and 26.8 ± 15.8, 41.9 ± 19.6 µm among KC corneas for anterior and posterior corneas, respectively (Figure 3).
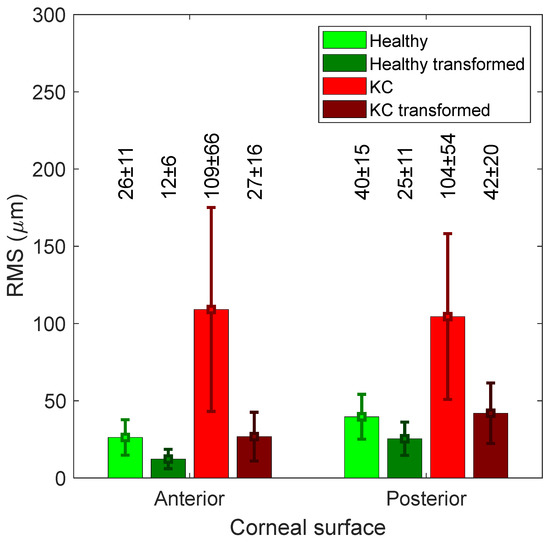
Figure 2.
RMS difference between the flipped left corneas and right corneas for both anterior and posterior surfaces. It shows the difference before and after the flipped left corneas were transformed (rotated and translated).
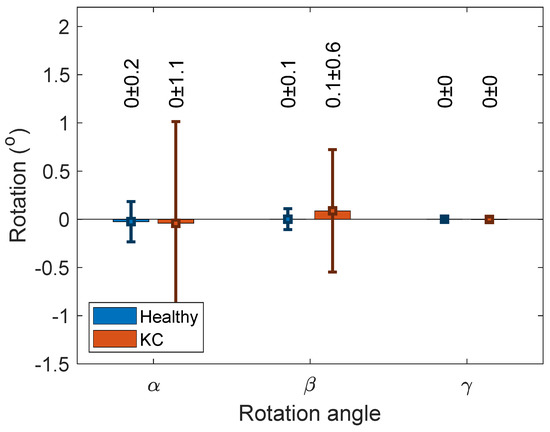
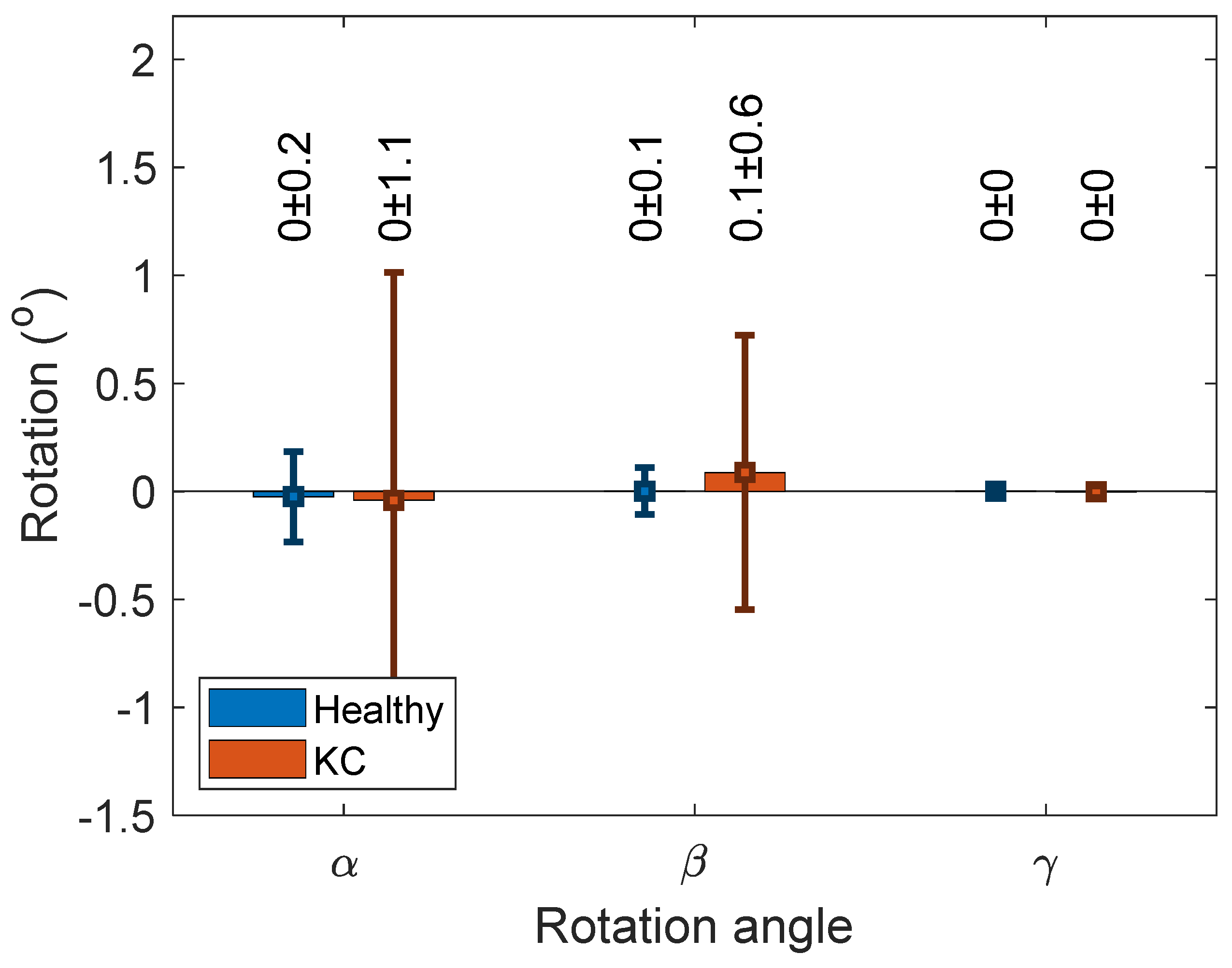
Figure 3.
Flipped left cornea rotation angles around X, Y and Z axes, respectively.
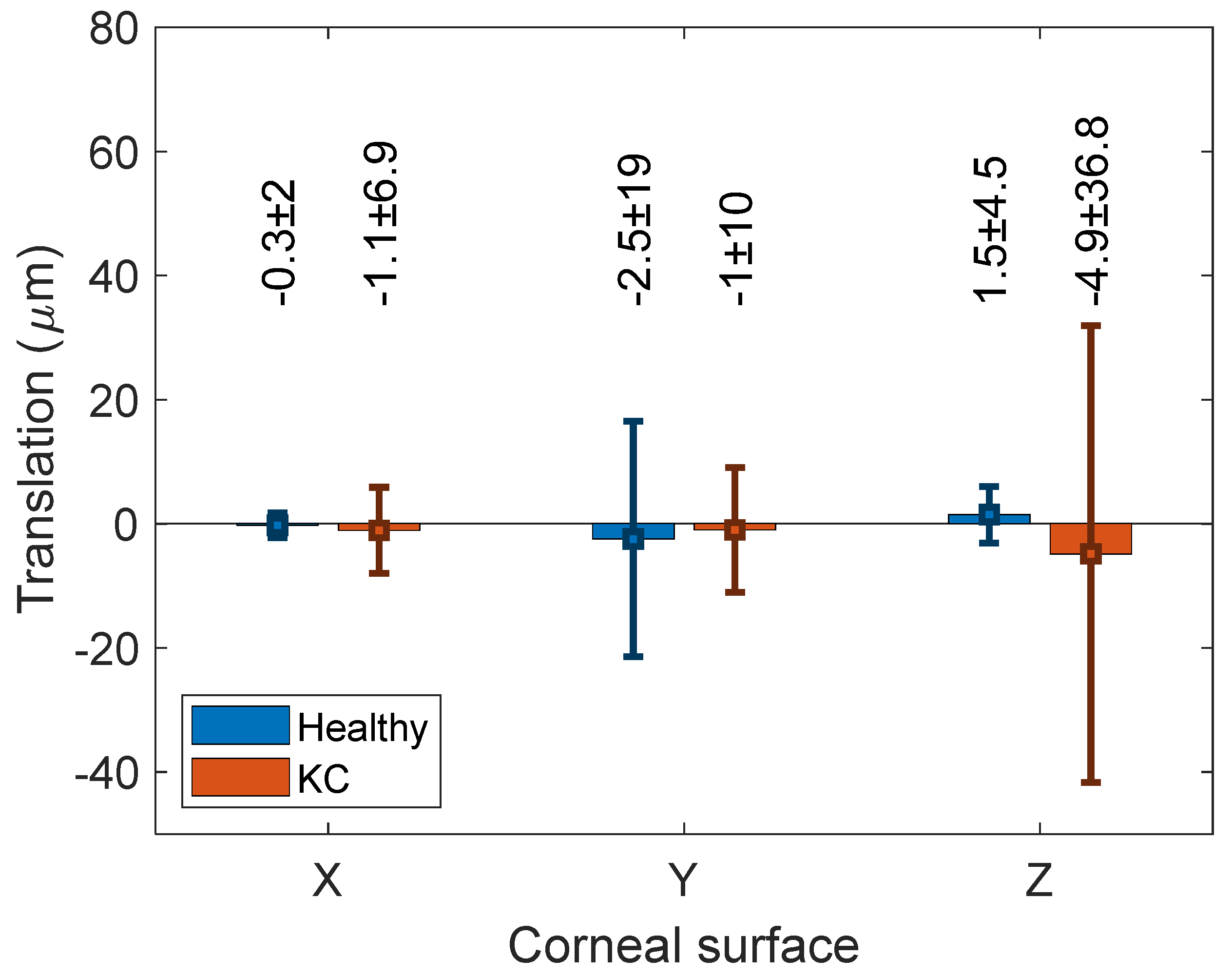
The rotations associated with the ICP algorithm were hardly observable, as can be seen in Figure 3. The associated translation with the ICP transformation algorithm recorded −0.27 ± 2, 2.5 ± 19 and 1.5 ± 5 µm among healthy corneas and −1.1 ± 7, −1 ± 10 and −4.9 ± 36.8 µm among KC corneas (Figure 4). When the RMS values were compared without and with the use of the ICP transformation algorithm, it was found that using the ICP transformation algorithm reduced the RMS significantly among both healthy (p < 0.001) and KC groups (p < 0.001) for both anterior and posterior surfaces.
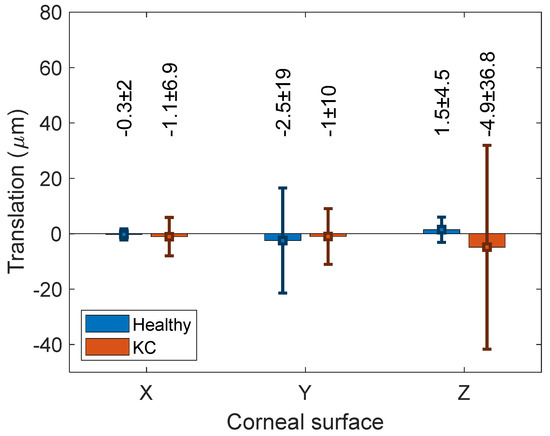
Figure 4.
Flipped left cornea translation in X, Y and Z directions, respectively.
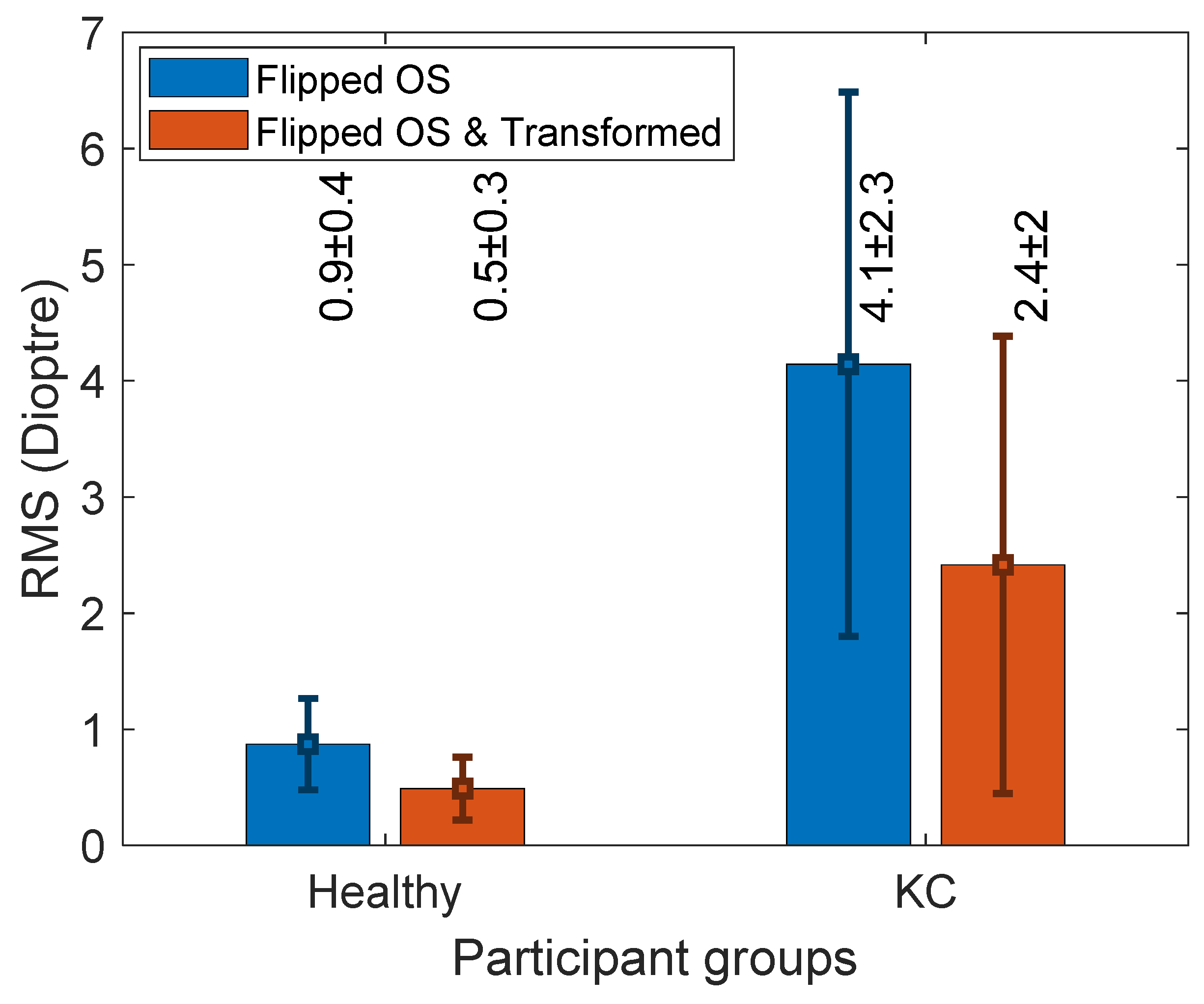
Comparing the dioptric powers showed a significant difference between the RMS of the flipped left corneas and right corneas for both the healthy and the KC group (p < 0.001). The RMS of the surfaces of the flipped left corneas and the right corneas was 0.6 ± 0.4 D among the healthy group and 4.1 ± 2.3 D among the KC group. After transforming the flipped left corneas, RMS recorded 0.5 ± 0.3 D and 2.4 ± 2 D among the healthy and KC groups, respectively (Figure 5).
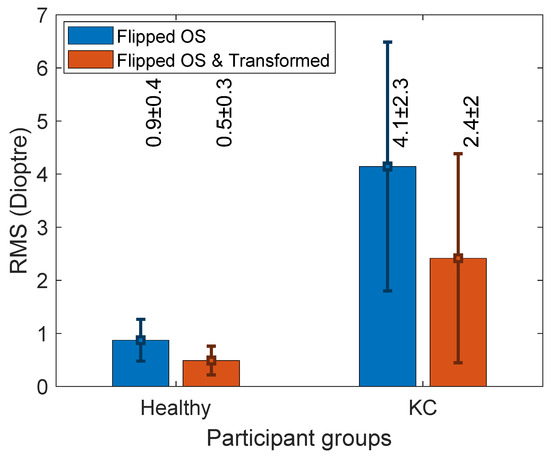
Figure 5.
The axial power RMS difference between right corneas and flipped left corneas without and with ICP transformation.
4. Discussion
The results of the current study confirm the fellow anterior eyes match in terms of their topographical shape (see Appendix A), but suggest fellow corneas should not be considered mirror images of each other in collective analysis without constraints. Flipping the left corneas in order to analyse the right and left corneas together may not be an effective strategy if the aim of the study is related to evaluating corneal optical performance. It was clear from the results that the flipped left eyes needed to be translated a few microns to fit the right eyes, and these small translations caused a change of 0.5 D to 2 D in the corneal optical power. As these power mismatches are high enough to require refractive correction [25], flipped left corneas should not be used as an equivalent to right corneas without further processing. The results suggest that the main mismatch between the flipped left corneas and the right corneas was caused by the surface translation. This indicates that the measured apex position of the flipped left corneas was not a mirror image of the measured right corneas.
When comparing corneal power, the flipped left corneas of the KC participants showed an important asymmetry in the average dioptric power RMS difference of more than 4 D. However, there was a significant reduction of more than 2 D (p < 0.001) when the flipped left corneal surface was transformed using the ICP algorithm. These big differences in the KC cases’ power could be a result of the fact that some KC patients have difficulty focusing on the topographer target during the scan process. This makes the alignment of the KC right and left corneas vary considerably, artificially increasing their asymmetries. This study has some limitations as the ICP algorithm was only applied on the central 8 mm diameter corneal zone, so the peripheral corneal surface effect was not considered. It also used a Scheimpflug imaging tomography instrument, which has limitations such as imaging discrete 2D meridians and using them to reconstruct the corneal surfaces instead of measuring the surfaces in 3D. Finally, the grading of the keratoconus was not taken into account in this study and all keratoconic corneas were analysed together as a single group. The findings of the current study are in agreement with Bao [3], who reported mirror symmetry between fellow corneas among healthy subjects, and with Bussières, who reported both symmetrical and asymmetrical patterns among fellow corneas in patients with keratoconus based on corneal tomography [26]. Dienes [6] also concluded that severe keratoconus patients are more asymmetric in their disease status. In addition, the current study raises the concern that reasonable mirror symmetry in topography does not mean mirror symmetry in refractive power, and a few microns misalignment in topography could cause a significant difference in refractive power calculations.
In conclusion, fellow corneas are highly related in their clinical parameters, but they should be treated with care when one corneal topography is flipped and processed with the other corneal topography in an optic-related research analysis, and translation might be needed. A portion of the asymmetry in KC is due to the corneal apex shift interfering with image acquisition. Therefore, transforming flipped left corneal surfaces by rotation and translation leads to a sensible comparison between the fellow KC corneas since it reduces the power difference between fellow eyes from 4 to 2 D. This can be of relevance to the KC diagnosis since it has historically been described as an asymmetric disease [27,28,29].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.; methodology, A.F.; software, A.A.; validation, B.T.L., R.A.J. and R.W.; formal analysis, A.F.; investigation, B.T.L.; resources, A.A.; data curation, R.A.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F.; writing—review and editing, A.A.; visualization, B.T.L.; supervision, R.W.; project administration, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The current study utilises fully anonymised records retrospectively evaluated in solely secondary analyses. No clinical data were collected especially for this study; therefore, no ethical approval was required according to of the policy of the University of Liverpool on research ethics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Financial Disclosure
None of the authors have financial disclosures.
Appendix A
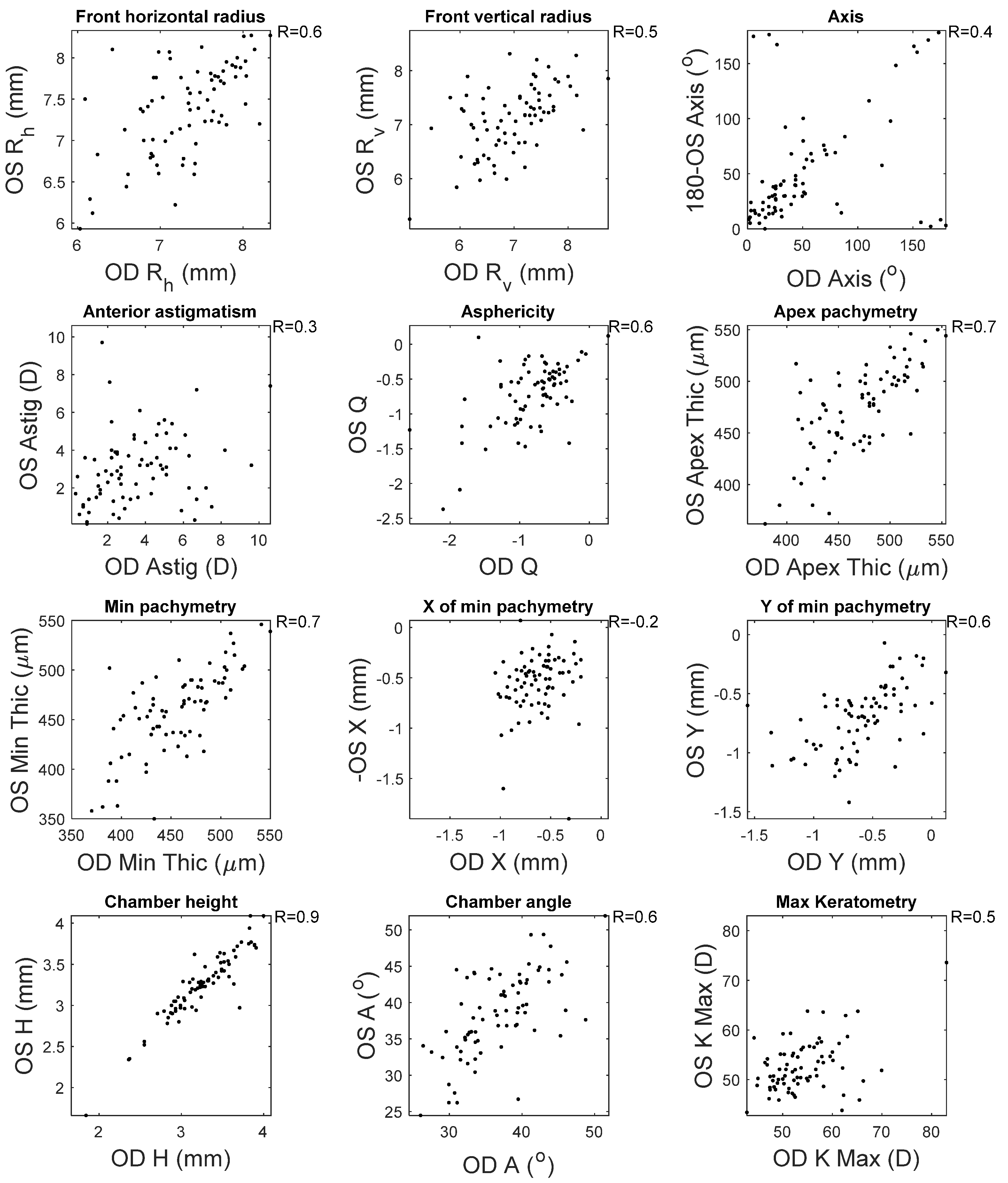
This appendix reports the measured clinical correlation between right (OD) and left (OS) corneas as measured by the Pentacam HR. High correlations were noticed among most of the clinical parameters among healthy subjects, except the location of the minimum pachymetry (R = 0.5) and the astigmatism axes (R = 0.5), where moderate correlations were recorded (Figure A1). When the KC clinical parameters were investigated, only the chamber height recorded a high correlation between right and left corneas. It was clear that the weakest correlations were recorded when the horizontal location of the minimum pachymetry was investigated (R = 0.2) (Figure A2).
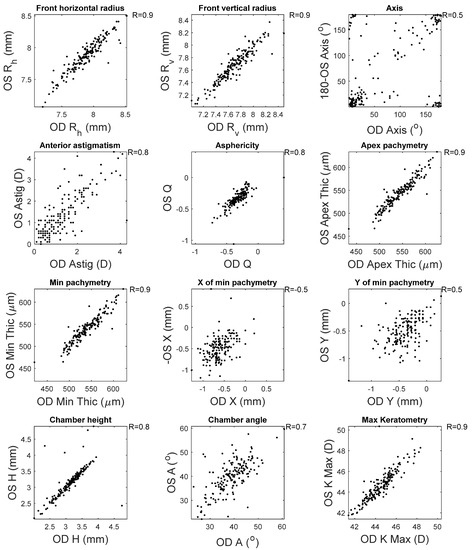
Figure A1.
Correlation between right and left corneas’ clinical parameters among healthy subjects.
Figure A1.
Correlation between right and left corneas’ clinical parameters among healthy subjects.
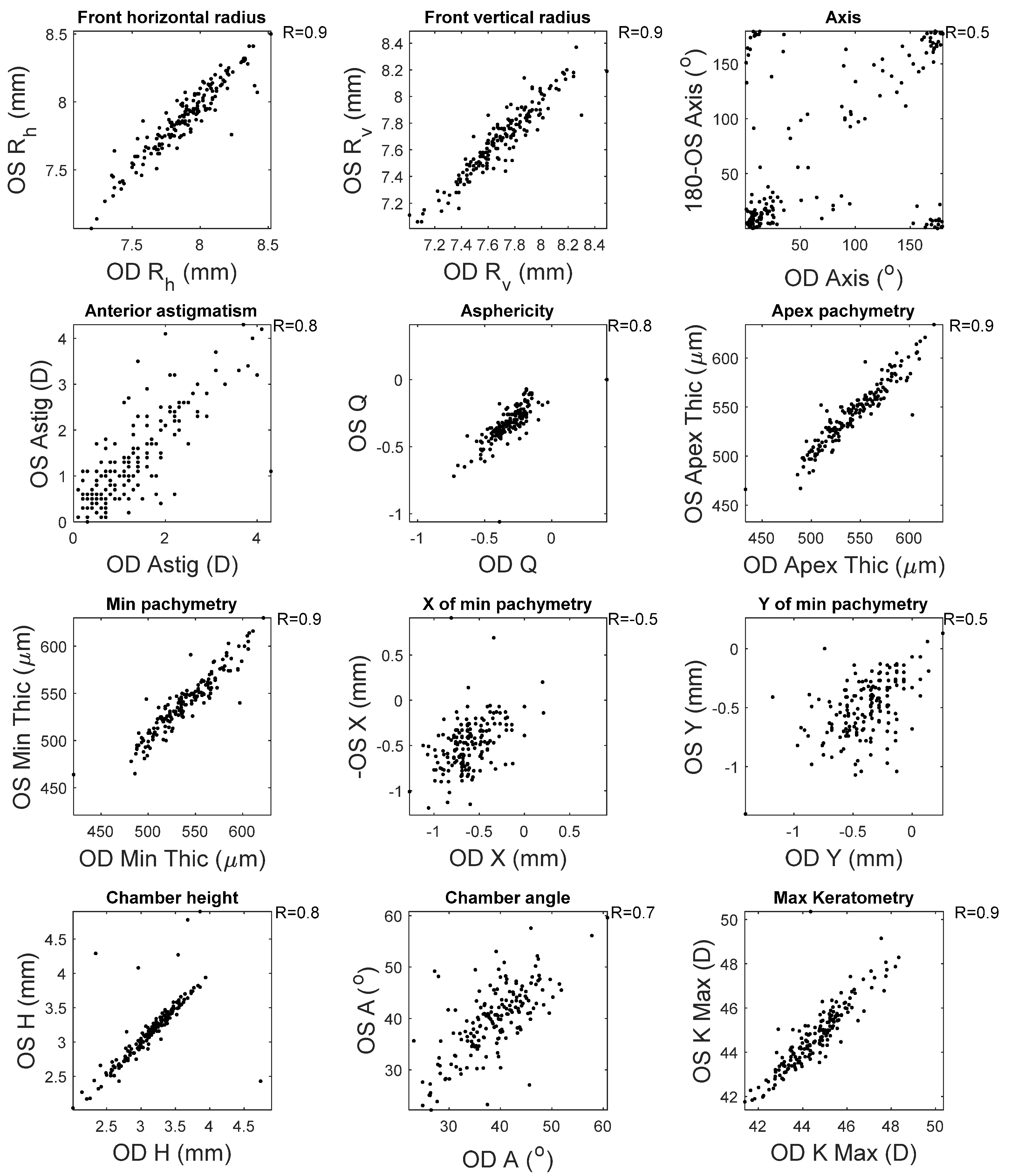
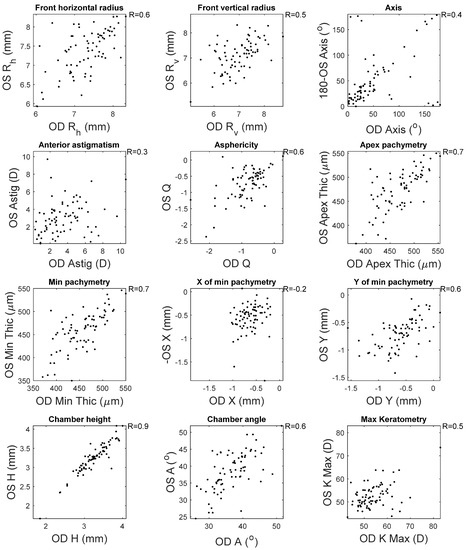
Figure A2.
Correlation between right and left corneas’ clinical parameters among KC subjects.
Figure A2.
Correlation between right and left corneas’ clinical parameters among KC subjects.
References
- Eydelman, M.B.; Drum, B.; Holladay, J.; Hilmantel, G.; Kezirian, G.; Durrie, D.; Stulting, R.D.; Sanders, D.; Wong, B. Standardized Analyses of Correction of Astigmatism by Laser Systems That Reshape the Cornea. J. Refract. Surg. 2006, 22, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolek, M.K.; Klyce, S.D.; Sarver, E.J. Inattention to Nonsuperimposable Midline Symmetry Causes Wavefront Analysis Error. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, F.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Elsheikh, A. Evaluation of the shape symmetry of bilateral normal corneas in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durr, G.M.; Ong, J.; Meunier, J.; Brunette, I.; Auvinet, E. Corneal shape, volume, and interocular symmetry: Parameters to optimize the design of biosynthetic corneal substitutes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavas-Martínez, F.; Piñero, D.P.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Mira, J.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alió, J.L. Assessment of Pattern and Shape Symmetry of Bilateral Normal Corneas by Scheimpflug Technology. Symmetry 2018, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dienes, L.; Kránitz, K.; Juhász, É.; Gyenes, A.; Takács, Á.; Miháltz, K.; Nagy, Z.Z.; Kovács, I. Evaluation of Intereye Corneal Asymmetry in Patients with Keratoconus. A Scheimpflug Imaging Study. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abass, A.; Vinciguerra, R.; Lopes, B.T.; Bao, F.; Vinciguerra, P.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A. Positions of Ocular Geometrical and Visual Axes in Brazilian, Chinese and Italian Populations. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abass, A.; Clamp, J.; Bao, F.; Ambrosio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A. Non-Orthogonal Corneal Astigmatism among Normal and Keratoconic Brazilian and Chinese populations. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, G. Wavefront Optics for Vision Correction; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia, B.D.; Mathur, B.B. Eyedness. Acta Anat. 1976, 96, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, M.R. Ocular dominance: Some family data. Laterality 1997, 2, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenstein, W.H.; Arnold-Schulz-Gahmen, B.E.; Jaschinski, W. Eye preference within the context of binocular functions. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2005, 243, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, I.; Durrie, D.S.; Schwendeman, F.; Stahl, J.E. Association between ocular dominance and refraction. J. Refract. Surg. 2008, 24, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.; Sapru, H.N. Essential Neuroscience; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, E. Advances and Challenges in Multisensor Data and Information Processing; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; 401p. [Google Scholar]
- Barro, S.; Marin, R. Fuzzy Logic in Medicine; Physica-Verlag HD: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamin, O.; Straumann, D. Three-Dimensional Binocular Kinematics of Torsional Vestibular Nystagmus during Convergence on Head-Fixed Targets in Humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.T. Biharmonic spline interpolation of GEOS-3 and SEASAT altimeter data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1987, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavas-Martinez, F.; De la Cruz Sanchez, E.; Nieto Martinez, J.; Fernandez Canavate, F.J.; Fernandez-Pacheco, D.G. Corneal topography in keratoconus: State of the art. Eye Vis. 2016, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsen, T. On the calculation of power from curvature of the cornea. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 70, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.-D.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Tsai, R.J.-F.; Kuo, L.-L.; Tsai, I.L.; Liou, S.-W. Validity of the keratometric index: Evaluation by the Pentacam rotating Scheimpflug camera. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, G.; Atchison, D.A. The Eye and Visual Optical Instruments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Vojniković, B.; Tamajo, E. Gullstrand’s Optical Schematic System of the Eye–Modified by Vojniković & Tamajo. Coll. Antropol. 2013, 37, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, G.; Cook, I. Introducing Statistics; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas, E.A.; Alcón, E.; Artal, P. Minimum amount of astigmatism that should be corrected. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2014, 40, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussières, N.; Ababneh, O.H.; Abu Ameerh, M.A.; Al Bdour, M.D. Keratoconus Asymmetry between Both Eyes Based on Corneal Tomography. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 24, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachmer, J.H.; Feder, R.S.; Belin, M.W. Keratoconus and related non-inflammatory corneal thinning disorders. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1984, 28, 293–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S. Keratoconus. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1998, 42, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas Tur, V.; MacGregor, C.; Jayaswal, R.; O’Brart, D.; Maycock, N. A review of keratoconus: Diagnosis, pathophysiology, and genetics. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2017, 62, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).