Abstract
The source of cancerous mutations and the relationship to telomeres is explained in an alternative way. We define the smallest subunit in the genetic code as a loop braid group element. The loop braid group is suitable to be defined as a configuration space in the process of converting the information written in the DNA into the structure of a folded protein. This smallest subunit, or a flying ring in our definition, is a representation of 8-spinor field in the supermanifold of the genetic code. The image of spectral analysis from the tensor correlation of mutation genes as our biological system is produced. We apply the loop braid group for biology and authentication in quantum cryptography to understand the cell cocycle and division mechanism of telomerase aging. A quantum biological cryptosystem is used to detect cancer signatures in 36 genotypes of the bone ALX1 cancer gene. The loop braid group with the RSA algorithm is applied for the calculation of public and private keys as cancer signatures in genes. The key role of this approach is the use of the Chern–Simons current and then the fiber bundle representation of the genetic code that allows a quantization procedure.
1. Introduction
For a long time, scientists have been trying to understand the source of self and nonself authentication keys [1] for cancer cells and the immune system’s recognition cells. It might be related to information encryption [2] inside 64 codons and a repeated sequence in the non-protein-coding DNA as key pairs [3] of a biological cipher in the cancer quantum public-key cryptosystem—some information from the genus of an ancient organism. This information is a biological Chern–Simons current [4,5] induced from an adaptive behavior field in the genetic code. Some questions arise from a new theory of cell biology. What is the smallest subunit used for a representations of the structures of the folded proteins in a living organism? Is it possible to quantize such a structure by adopting standard procedures of theoretical physics? We try to show that it can be done by a new way of unifying triplet states of DNA, RNA, and protein. The new approach of the Chern–Simons current in the genotype with a mathematical model of the hidden state in a genome [6] is trying to answer some questions. The suppersymetry approach [7] was also used for the model of graphene wormhole and for the computation of the Chern–Simons current in a Josephson junction of superconductor states in the graphene. Additionally, the applications of neural networks for density estimation [8] outperformed parametric and non-parametric approaches.
The information in a genetic code can serve as the public key encryption used for authentication of the correct creation of the structure of a folded protein. The loop braid group [9] is suitable for defining the configuration space of this undivided small subunit in the genetic code as a so-called flying ring between the DNA and RNA. We redefine this transition as an anyon state in the process of protein folding over underlying Hopf fibration in Kolmogorov space [10] of biological time series data. As opposed to protein chemistry, in this paper, by "protein folding" we mean the entire process of translating the DNA sequence into the three-dimensional structure of a folded protein.
Recently, scientists applied the loop braid group to studying the anyon [11] in topological quantum computer architecture [12]. We borrow this theory to redefine a new model of the asymmetric key between public and private keys in protein–protein interactions as a new moduli state space model in quantum cryptography for biology. The anyon in biology can be associated with a phase transition of DNA–RNA–protein with a quaternionic state with two fermion pairs in the genetic code. Nowadays, a topological quantum cryptography is the most secure cryptography concept with the highest impact on computer security, business, and society, but it is rarely used in biology. Experimental quantum cryptography narrows the gap and it approaches the implementation of theoretical knowledge outside the laboratories, e.g., by the investigation of quantum key distribution with finite decoy states [13,14].
In the loop structure of telomeres [7], there exist layers of G-quadruplex (G4) [15]. Their structures are similar to the structure with the loop braid group in the standard model [16,17]. The G letter (guanine) can be suitably chosen as the hidden time scale in a biological clock. The nature of the telomerase enzyme is that it reacts like a retrotransposon hidden in transition state in the non-protein-coding DNA area. The loop braid group’s operation is the composition of braids representing the translation of an amino acid being the disjoint component operator that is convenient for representing G-quadruplex in 4-dimensional coordinates of spacetime curvature in a protein folding. We investigate why cancer and the adaptive behavior of the immune system are involved with a hidden feedback control mechanism in the trash DNA-like status.
The numbers of four letters in the DNA alphabet cannot be completely separated like transition levels of energy-momentum of gene expression. The natural process of transcription and reversed transcription in extended central dogma [18] we can describe by providing definitions of the relative natures of the genes involved with three objects: DNA, RNA, and protein. These three things can not be separated from one another as these three molecules are interconnected into a 4-dimensional coordinate system of living things. We can unify them as a loop braid group in the genetic code. Based on the analogies from the theory of general relativity (e.g., a definition of connection), we combine some more properties of the braid group and Khovanov cohomology [19,20] to them. We redefine the loop braid group by adding some extra properties to them for visualizing the folding structure in the amino acids [21]. We can apply the anyon [22] states of the pair between DNA and RNA as braid groups in anyon–geneonic pair states in the genetic code. The codon can be related to a table of public keys which can release noncoding RNA [23] as the private key for correctly translating a DNA sequence into a folded protein for the specific docking site in the antigen–antibody immune system.
It is the empirical fact that only 2% of human genetic material is expressed, but another 98% does not change into any proteins. This material is called the non-protein-coding DNA area, or in analogy with physics, the dark matter of the genetic code [24]. Recently, experiments confirmed that this DNA area is very important to the development of the brain in humans, and reproductive systems. It is possible that this area has an important part in controlling protein formation and acts like a big center for issuing instructions and verifying cryptography in the process of decoding genes. Additionally, the noncoding genome can generate or form three-dimensional structures in such a way as to generate protein molecular systems associated with disease (cancer). Our purpose is to build suitable new methodology for detection of such secondary and tertiary DNA structures in noncoding regions.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2 we define the concept of using a loop braid group for the genetic code. We discuss the source of translating the DNA sequence into a folded protein by using loop braid group operation. In Section 3 we define new asymmetric cryptography for biology, as a source of the public and private keys in the system of protein–protein interactions. We apply the moduli state space model to RSA algorithm to calculate public and private keys in asymmetric cryptography for biology for samples of 36 genes as a new signature. We use tensor correlation for gene expression to generate the image of a geneonic spectral sequence for a mutation gene signature in Section 4 and an empirical analysis with some concrete cases is developed. For brevity and easier understanding of the issue, we are using the term cancer gene for all genetic mutations and the term cancer signature defines all patterns for known types of damage and abnormalities. In the last section we conclude and discuss all results, giving future perspectives of this approach. Some technical aspects of our model are discussed in Appendix A and Appendix B. Amino acid sequences are given in Appendix C and Appendix D; the cipher text for the encryption of a gene is reported in Appendix E.
2. Algebraic Construction of G-Quadruplex in Telomere
In each cell division, the telomeres (see Figure 1a,b) are shortened [25] and the total length of DNA becomes shorter. As the result of the shorter biological clock from cell division, living things die. In order to understand the cell cocycle and the division mechanism of telomerase aging, we are looking on the source of cancer as the source of age acceleration and we relate it to the telomere shortening mechanism [26,27] (also see Figure 2 for detail of the biological clock), which is a source of braid group operation [28]—so-called self-diffeomorphism—in the genetic code. In the next part we are also trying to explain the real source and state of cancer as damage to the biological clock which can induce age acceleration [29]. The age acceleration is a relative measurement between the chronological clock and the biological clock in the telomere [30]. Up to now, scientists understood telomeres and telomerase as remnants of ancient viruses that rely on DNA in the chromosomes of living organisms. The telomere is composed of the repeated sequence of where . The size of the duplicate sequence at the end of this open chromosome is amplified by six braids caused by six superspaces in time series data of organisms. It is naturally selected by the evolution of transgenic reproduction in all possible directions of the transcription process. The G alphabet might be suitable for the hidden time scale in the biological clock.
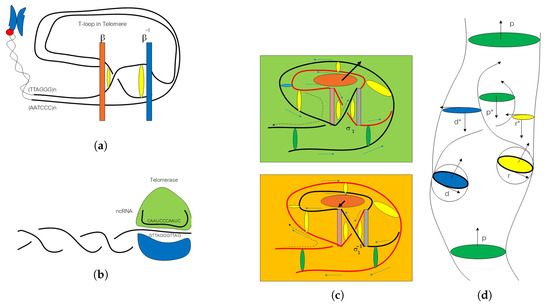
Figure 1.
(a) T-loop in a telomere as a loop braid group in a genetic code. (b) Noncoding RNA in a telomerase. It is an example of reverse transcription from RNA to DNA in extended central dogma. (c) The upper picture demonstrates an active state of gene expression with an open switch in a telomere braid group element. The bottom picture shows an inactive state of gene expression with a closed switch in a telomere braid group element. (d) The picture represents a flying ring between two rings.
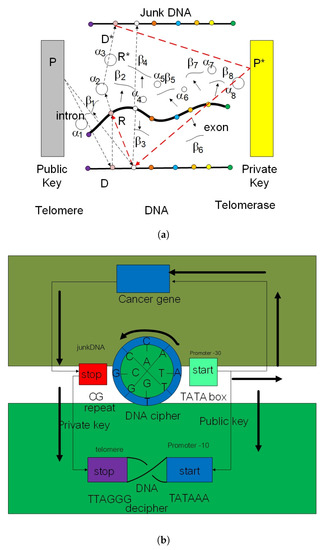
Figure 2.
The left picture (a) shows a vierbien diagram of gene expression in a eukaryotic cell. The immature mRNA is composed of intron and exon states. The intron state is an analogy of the public key in gene expression and the exon state with private key. (b) The genetic code is produced from the rotation of biological clock as a signal generation represented by circular disk in the middle of right diagram.
Definition 1.
Let be a superspace of DNA, be a superspace of RNA, and be a superspace of protein. We have a Wigner ray [31] of biological time series data of living organism defined by ,
The protein structure can be considered a transition state. It is a partition function with , an equivalent class of homotopic paths of gene expression in DNA, .
Definition 2.
Let be a biological clock time scale in four corners of G-quadruplex. We denote , , , to be a possible pair of times in four corners of G-quadraplex.
There are two types of cell cocycles (Figure 1c) in the loop structure of G-quadruplex of telomere and in telomerase enzymes; we call them - and - cocycles. They are associated with T-loop and D-loop in G-quadruplex (Figure 2). We visualize the gene expression as an anyon transition state with behavior field . It is the cocycles of the flying ring in geneon wave function (see Figure 3). The sequence of a gene in a protein is separable and can be processed by permutation as the mutation in the new order of the gene with transposon and retrotransposon states . The dark line in the middle of the plot is DNA with the transcription process. We define a DNA flying ring as an orbit of geneonic transition in superspace of DNA , for the RNA flying ring is . The trajectory of intersection between these two rings induces a loop braid group in genetic codes in extra dimensions. The fiber bundle along the trajectory is a folding structure of the secondary protein in a superspace . The upper layer is a starting point for flying; the lower layer is the passive layer of protein folding in the feedback loop. The yRNA and intron are just a result of the Reidemeister move for loop braid group in three trajectories of (Figure 4b).
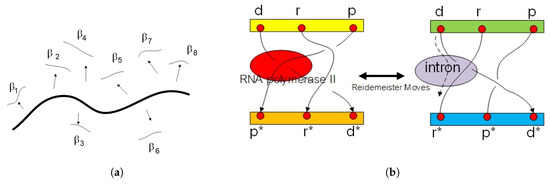
Figure 3.
We define gene expression as a cocycle with behavior field in geneonic wave function (a). It is equivalent tothe exon state in mRNA. In the right picture (b) is a loop braid group diagram for extended central dogma. There exist six superspaces in Kolmogorov space of biological time series data. The trajectory of means DNA, means RNA, and means a protein. The upper layer is an active layer of gene expression with a flying ring along the trajectory as a loop braid element. The Reidemeister move switches state of gene expression between two loop braid group elements in genetic code.
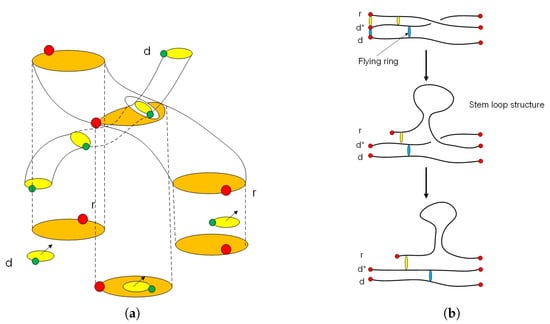
Figure 4.
(a) The picture shows a loop braid group structure in a telomere. The passive layer of a telomerase protein at the end of the chromosome is an element of superspace . Inside the layer of telomerase there exists a flying ring of RNA and DNA . When the cell divides the loop braid group element, the genetic code will fly to the active side of a histone protein . The four circular rings inside the loop braid group are T-loop and D-loop structures in a telomere. (b) The picture shows gene expression from DNA to mRNA with a stem-loop structure. It is an example of a flying ring in loop braid group of a superspace of DNA and RNA.
This interaction of D-brane in a living organism is a coupling in loop space in biological time series data with parasitism state between a host cell of the living organism. One state is used for shortening the telomere, and the other reversed transcription state is used for an adenovirus to prolong the length of telomere during cell division. It is a real function of ncRNA embedded in telomerase. They both have G-quadruplex stabilizers. We can represent the T-loop and D-loop in the end-point of the chromosome by using the loop braid group for biology. The loop braid group for biology is not just a representation for DNA, RNA, and protein transitions (Figure 2). It can be used also to define the intrinsic source of the energy-momentum tensor with undivided properties in genotypes of underlying behavior fields as a flying ring (Figure 1d) in the genetic code.
2.1. Anyon in Biology and Configuration Phase Space for Protein Folding
The permutation of an alphabet code from an evolutional process induces a mutation and it appears as an element of a symmetric group .
Definition 3.
Let and . The permutation of alphabet code in mutation induced a symmetric group as group operation. Let be a loop braid group operation over Kolmogorov space in time series data , as configuration space in the process of converting the DNA sequence into a folded protein
Definition 4.
Let and , , , . We have an anyon in biology defined by the wave function of gene expression with behavior field as the cocycle in adaptive behavior in the immune system.
It is used to define the configuration space in the wave function of the transition state for gene expression by , where anyon fields are induced from the behavior of immune system. In DNA there is a pair of genotypes in the form of a pair of alleles ; it is an adaptive behavior of cocycle of gene expression for undocking behavior in the protein–protein docking system.
2.2. Circular Artin Braid Group Representation for Spinor Field in Genetic Code
In this section, we assume that all genetic code cannot be completely separated. The biological clock in telomere length is parametrized by a hidden state of the number of alphabet in a repeated pattern of the telomere .
The element is Grothendieck topology over an adjoint cofunctor. It is a self-diffeomorphism . The loop braid generator for is a quaternionic field in genetic code. We define their explicit forms and their permutations over the symmetric group by a chosen basis in Clifford algebra.
Definition 5.
Let
and , , . We have
therefore, one can write eight bases for spinor field in the genetic code in braid form as follows.
One can also use with spin quantum number s to be an integer number for the retrotransposon, so that
The geneon and retrotransposon statistics operators are and respectively. In 2-dimensional position space, the abelian anyonic statistics operators are 1-dimensional representations of eight loop braid elements in circular Artin braid group acting on the space of wave functions (Figure 5).
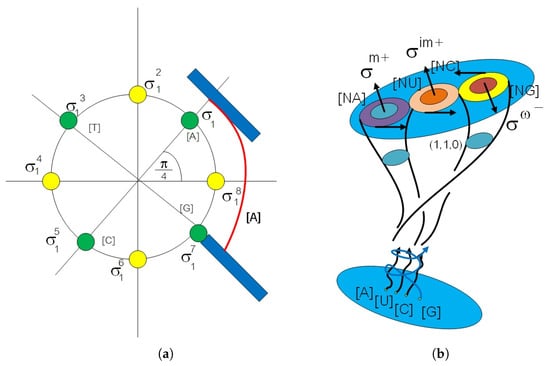
Figure 5.
(a) The picture shows a biological Artin braid element in complex plane . There are eight equivalent classes span by eight orders of . It is a representation of 8 states in 3 genetic codes in codon as braid element in . The red color line represents the curvature from the physiology of biological time series data and blue color represents the active and passive behavior field layers. (b) The picture shows a member of loop braid group. We have three circles . They are a source of closed 3-balls , the structure group of the affine transform of 3 behavioral fields in genetic code action on an affine fiber bundle of the behavioral field in the genetic code , , . The affine group is as a loop braid group in genetic code by .
2.3. Classification of the Loop Braid Group in Genetic Code
One can classify three types of loop braid group operations as representations of an anyon for protein folding. For a two dimensional representation of D-brane in the loop braid group for the genetic code, one can define the abelian anyon for biology in (2 + 1) dimensions. The extra dimensions are used to represent the homotopy path of protein folding.
Definition 6.
The loop braid group, , for a genetic code has three types of generators, , , and . The generators and fulfill following relations
Definition 7.
Let G be a group operation of the genotype. Let ρ be a representation for gene translation as an anyon. We have as a representation in and in . In order to visualize 3D folding structure of the protein, we define three types of loop braid group operations in biology. All loop elements of the representation of amino acids arose from group operations over the superspace of time series data. These tree types are a translation, reflection, and rotation; , , and . For the translation as a string of amino acids, we have the anyon T-I for biology:
Considering an analogy with the action of the symmetric group by permutations, one can find a natural action of the braid group on n-tuples of objects or on the n-folded tensor product that involves some twistors. For this purpose let us consider an arbitrary group G and let X be the set of all n-tuples of elements of G whose product is the identity element of G. The kernel of the homomorphism is a subgroup of called pure loop braid group for biology on n strands and it is denoted as . In the pure braid, the beginning and the end of each strand are in the same position. Pure braid groups fit into a short exact sequence
As is obvious, the sequence splits and therefore pure braid groups are realized as iterated semi-direct products of free groups. The braid group is the universal central extension of the modular group .
Definition 8.
Let , , be active layers over the superspace of DNA, RNA, and protein. Let , , be passive layers. We define a braid group in genetic code by a curvature inside DNA, RNA, or protein structure. It is a source of an acceleration of biological clock in the epigenetic code. We let , , , , , , and , be loop braid group elements in the genetic code. They are the circular Artin braid groups for the genetic code. One can define
In that way, a braid group operation gives
which implies that is in the center of . It is a wave function of protein transition anyon state. If acts on
If acts on , one gets
Additionally, if acts on
From above, it follows that the elements and exchange places in DNA strand by an analogy with genetic variation. One can check that the braid group relations are satisfied and this formula indeed defines a group action of on .
3. Affine Loop Braid Group in Public Key Cryptosystem of Protein Folding
Topological cryptography for biology releases a self versus non-self protein–protein authentication as a public key, a non-protein-coding piece of DNA. An example of such an area of DNA is mitochondrial DNA (miDNA). The genetic codes of tRNA in miDNA and in the chromosome are the same codes but in a different places. The methyl transfer to AdoMet [32] of tRNA represents the role of knot protein as the RSA algorithm in public key biological cryptosystem. The encryption of the moduli state of a protein comes from 20 modulus states in tRNA. The real function of tRNA is a hash function for encrypting the digital signature of biological information.
3.1. Public Key Biological Cryptosystem in Protein–Protein Docking
The system of protein–protein interaction in an immune system can be realized as a public key biological cryptosystem. It is the main application of the loop braid group relations in self and non-self protein–protein authentication in a cryptosystem of antigen-antibody recognition.
Secret information is encoded in the genetic code and immune system with some help from y-RNA. There exists a normal form for the elements of in the terms of generators . It induces the application of loop braid groups in the genetic code to pubic key biological cryptosystem. In order to explain the authentication mechanism of the digital signature in the system of protein–protein interaction, we have to recall the natural phenomena in the immune system. It is a classification between self and non-self cell death program in apoptosis. Unlike the use of a two-factor authentication certificate, the user needs to know the digital signature to authenticate the self and non-self certificate when a cancer cell or virus attacks the immune system. There must be a private key associated with the noncoding y-RNA to transfer the certificate through a nuclear pore, so the immune system will be able to access the defense authentication system.
We have left and right loop braid groups for biology denoted by and . The elements of and are generated by the generators , , and the generators , , respectively. We have commutative properties between left and right supersymmetry of loop braid group as an asymmetric cryptosystem for the authentication public and private keys in the RSA algorithm for biology (see Figure 6c), for any and we have .
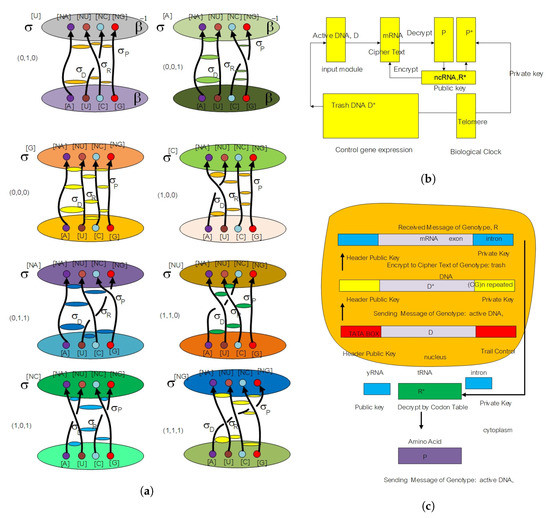
Figure 6.
(a) The picture shows eight anyon smallest subunits in biology. It is a representation of eight spinor fields in the genetic code of living organisms. We define them as a flying ring in the unification between three elements from DNA, RNA, and protein. (b) The picture shows three layers of DNA, RNA, and protein in the asymmetric cryptosystem model for biology. (c) The picture demonstrates the encryption and decryption modules in the public key cryptosystem. The non-protein-coding DNA part is a source of the private key. The telomere is a biological clock subunit; it is equivalent to the modulus part in a moduli state space model.
Let a one-way function of the gene expression be defined by
It is a one-way function to carry public-private keys given by a pair . Now we define key agreement in the protein docking system between the proteins A and B with the help of the braid group version of the Diffie–Hellman key agreement in a quantum cryptosystem for biology. We have the following steps.
- Preparatory step: A suitable pair of integers are chosen, and a sufficiently complicated -loop braid is selected and published through the gene expression.
- Key agreement: A key is shared through the protein folding by performing the following steps each time a shared key is required:
- Protein A chooses a random secret loop braid and sends to B.
- Protein B chooses a random secret loop braid and sends to A.
- Protein A receives and computes the shared key .
- Protein B receives and computes the shared key .
Since , we haveThus both proteins A and B obtain the same loop braid group element with the same curvature. Therefore they can dock to each other; otherwise the system will not be in equilibrium and the moduli state space for the gene expression with control equation will recursively loop back to send the key again.
3.2. Moduli State Space Model for Protein–Protein Interaction
The protein–protein interaction can be realized as a share key agreement in the biological cryptosystem, if we consider the central dogma as the short exact sequence
The moduli state space model for protein–protein interaction with G-quadruplex, , in the D-brane plane, comes from this short exact sequence:
If we approximate this equation with the gene expression at first time period with a short exact sequence, then is the first genotype at time period in the equilibrium moduli state of the gene expression:
We have a recursive loop of reversed transcription of jumping gene of retrotransposon transition state with repeated geneon state by
so we have
For no genetic variation, , we have a recursive loop of repeated jumping gene of retrotransposon in the non-protein-coding DNA as
The initial value equation of moduli state space model for the non-protein-coding DNA with starting state of retrotransposon is
Therefore we have
We have moduli state space model for DNA, , RNA, , and protein,
Let , , , so we have
The definitions of public and private keys in a biological cryptosystem are the following.
Definition 9.
Let the protein A span by the loop braid group and the protein B span by the loop braid group . Let a hash function for biology be from loop braid group in the genetic code to a biological message space. This message space specifies the spinor state of spin up or down over the fiber loop space in the genetic code. The public key biological cryptosystem is composed of three modules
- Key generation module: Protein A and B choose a sufficiently complicated genotype in the loop braid group in genetic code and a hash with a fixed size of 20 amino acids (modulo 20) while transmitting the public key over a two protein docking system. The left protein chooses a genotype with representation in loop braid group in the genetic code . The public key is where .
- Encryption module: Given a biological message authentication code by y-RNA, tRNA, and ncRNA as a hash function with spinor state and the public key , protein B chooses a loop braid group at a rate of random mutation . Biological cipher state is where , .
- Decryption module: Given the biological cipher state and the private key , compute the element .
Because and commute to each other we can recover the information that transmission from DNA to protein by encryption process in RNA by , and therefore we have for , the decryption gets the original message in loop braid group element m.
4. Empirical Analysis of Cancer Gene Signature
Our empirical analysis is based on a novel algorithm based on in time series prediction introduced in [10]. The topological approach to computation on DNA time series data was successfully applied in the empirical mode decomposition of the Chern–Simons current related to genetic variations of viral glycoprotein gene and host T-cell receptor gene [4].
We also calculated the Chern–Simons current in the genotype. We used the genetic code of telomerase RNA component TERC from GenBank [33] (see also Appendix C) and the genetic code of ncRNA in telomerase (Appendix D). The results of the plots for the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code of PD1 and ncRNA are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8. The plots are the Chern–Simons currents in genetic code, for different values of n; they represent the wave functions of retrotransposon states in ncRNA. Higher values of n yield smoother curves; they have parabolic shapes with concave or convex curvature, as one can see from the ncRNA or protein PD1 plots. Similar plot results for the Chern–Simons current can be used to detect a cancer signature, as can be seen in Figure 9.
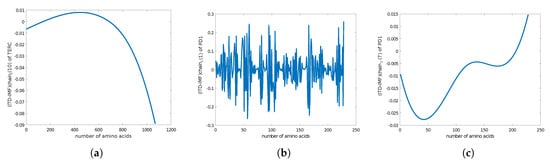
Figure 7.
(a) The plot of of the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code of TERC gene in telomerase with 1069 alphabet codes (Appendix C). (b) The plot of of the Chern–Simons current in PD1 protein. (c) The plot of of the trend of the Chern–Simons current in PD1 protein.
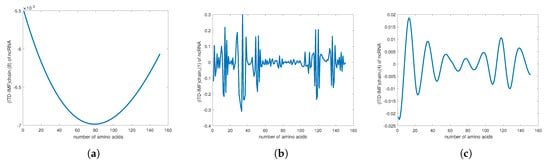
Figure 8.
(a) The plot of retrotransposon state ncRNA in telomerase. It is of the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code of ncRNA. (b) The plot of of telomerase ncRNA. (c) The plot of of telomerase ncRNA.
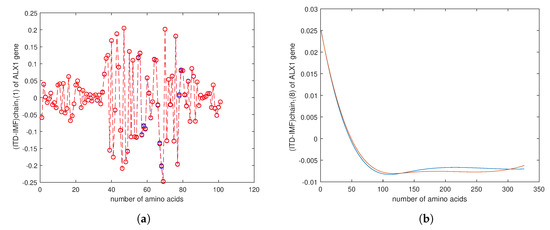
Figure 9.
(a) The plot of the result for computation of the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code of first gene in bone cancer, so-called ALX1 gene, for a cancer gene (red) and normal gene (blue). (b) The plot of the result for computation of of the Chern–Simons current in ALX1 gene. We can notice the difference between two genes by the shift of plotted line.
For that purpose we downloaded data of 36 samples of cancer genes (Table 1) from the online database Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC) with sample name PD7301a and COSMIC sample ID COSS1540693 [34]; the tumour location is in the bone; the pelvis (chondrosarcoma; central); see also Appendix E for the AX1 gene. In Figure 9, one can see the difference in the calculation of the Chern–Simons current in the ALX1 gene for cancer (red) and normal (blue) gene versions; the change is better visible in the computation of . In Figure 10 and Figure 11 are presented results for the tensor correlation of the Chern–Simons current from and between normal (blue) and cancer (red) genes in selected 28 samples of bone cancer. In the region of amino acids 700 and 1000, the mutation area is noticeable. In Figure 12 and Figure 13 are plots of the and of the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code for mutation for samples 33–36 presented in Table 1. Next are presented the images of the spectrum of tensor correlation of 28 cancer genes, computed for the amino acid number 531 (Figure 14) and the amino acid number 9980 (Figure 15). The computation uses canonical tensor correlation structure from to from 28 genes listed in Table 1 with matrix size 19,244. The number 19,244 comes from total sum of all amino acids in 28 samples. One can see the differences in the color patterns. The visualization of comparative difference between the cancer and normal genes can help in building the databases and the classification of different types of genes in the future.

Table 1.
The table shows the result of a public key and the private key calculation for 36 cancer genes compared with 28 normal genes. The result of computation is calculated by the RSA algorithm over genetic codes.
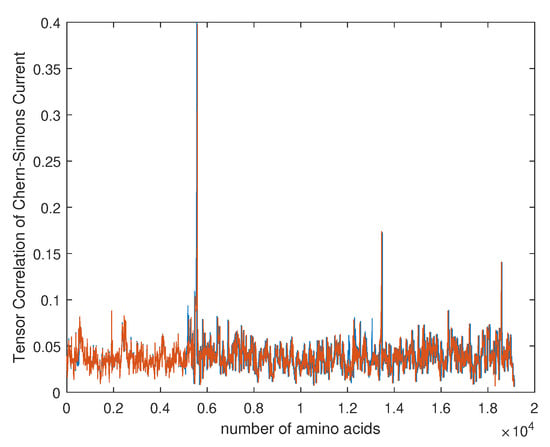
Figure 10.
The picture shows the tensor correlation of the Chern–Simons current from for normal (blue) and cancer (red) genes in 28 selected samples of bone cancer.
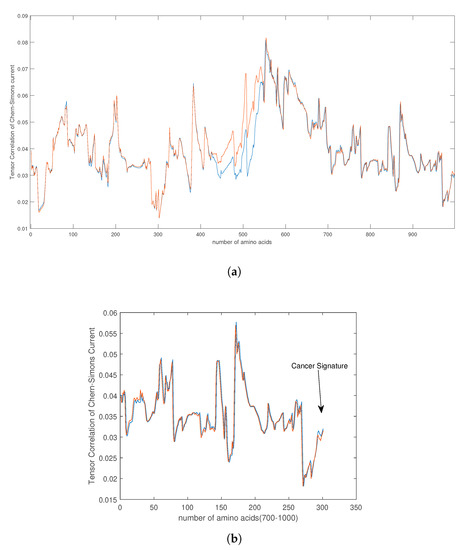
Figure 11.
(a) The picture shows the tensor correlation of the Chern–Simons current from , between normal (blue) and cancer (red) genes in 28 selected samples of bone cancer for the first 1000 amino acids. We can see that the signature of mutation appears between the amino acids 400 and 600. On the plot (b), if we zoom the region between amino acids 700 and 1000 we can also notice some signs of the mutation in that area.
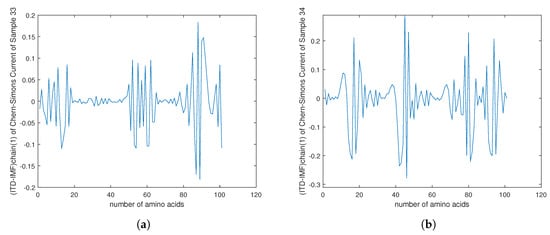
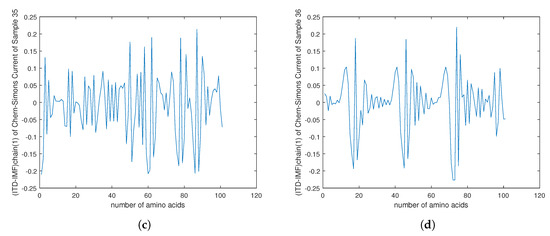
Figure 12.
(a–d) The plots of of the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code of mutation in cancer gene for the samples 33–36 in Table 1.
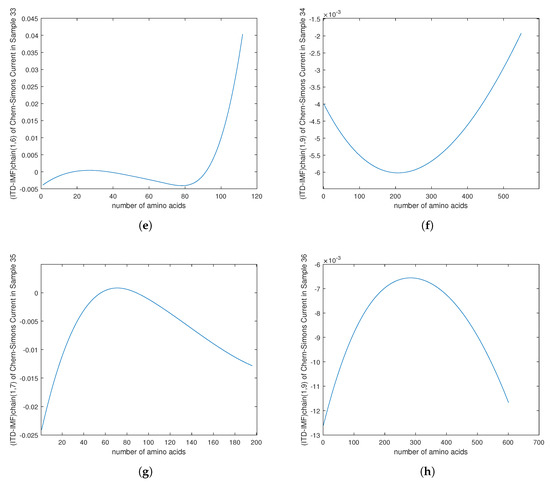
Figure 13.
(e–h) The plots of TREND of of the Chern–Simons current in the genetic code regarding mutation in cancer genes for the samples 33–36 in Table 1.
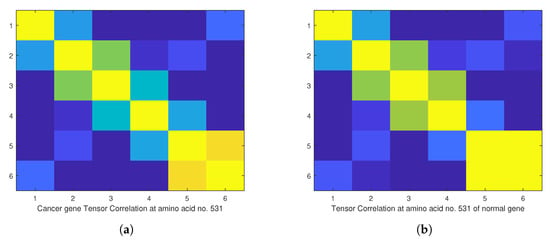
Figure 14.
(a) The image of the spectrum of tensor correlation of 28 cancer genes, computed at amino acid number 531. (b) The same image at the same position of amino acid which we computed from selected 28 normal reference genes. The computation uses canonical tensor correlation structure from to from 28 genes listed in Table 1. We used slide window with the size 6 because we had total samples of amino acids with matrix size 19,244. The number 19,244 comes from total sum of all amino acids in 28 samples.
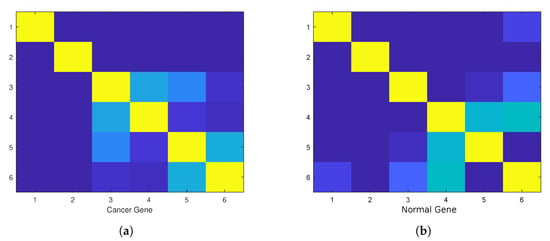
Figure 15.
(a) The image of the spectrum of geneonic transition state of 28 cancer genes at amino acid number 9980 from 19,244 amino acids in tensor correlation. (b) The image of normal 28 genes computed from the same position with slice window size of 6 amino acids. We can use the comparative difference between color patterns as the signature of cancer instead of using only a color diagram, as in [34].
5. Discussion and Conclusions
We use loop braid group to define the flying ring in the (3 + 3) extra dimensions of triplet state of transition between the DNA, RNA, and protein. These three molecules are interconnected by combining them into a four-dimensional coordinate system. We can unify them as a loop braid group in genetic code as the smallest subunit in the translating of the DNA sequence into a folded protein. The flying ring is just an 8-spinor field in the homogeneous coordinate of supermanifold in the genetic code.
The interaction between the D-brane of a telomere in the non-protein-coding DNA and the anti-D-brane of the telomerase enzyme with embedded noncoding RNA is the source of the biological clock and cell aging in a living organism. This process of the biological clock generator is the rotation of a homogeneous coordinate in the gene expression. The rotation of the clock produces a spinor field in time series data as a signal for cell transduction. It is the information inside codon which generates the public and private keys in quantum cryptography along the geneonic state. The signal of protein expression is expressed as immune receptors and signal transduction with the public and private keys. The protein state belongs to a superspace P. The gene expression in the eukaryotic cell with mRNA will have approximately eight exon states with cocycle geneonic states.
The other part of noncoding RNA in mRNA is an intron state, denoted as cocycle of retrotransposon state in ncRNA space . The function of intron state is to control the gene expression as public and private keys to deliver the sequence of mRNA out of the nuclear membrane with the help of y-RNA. The keys will match to each other outside the nuclear pore in ribosomes in the rough endoplasmic reticulum for the process of t-RNA to match the public and private keys inside ribosome for the translation process of producing the amino acid. It might be a real function of the non-protein-coding DNA. The acceleration of the life clock is caused by the imbalance of collisions between the telomere and telomerase by passing the energy-momentum tensor in protein–protein interactions.
In this work, a new theory of quantum cryptography for biology has been developed. In particular, we used the loop braid group for biology to visualize the G-quadruplex with six repeated sequences in a telomere. We plotted the Chern–Simons current in the genotypes of all samples to detect the physiology in the biological time series data. We found that the graph of cancer gene has a degree of nonstationary time series data more than the normal gene. The tensor correlation network for 36 cancer genes has been generated and the image of spectra of geneon state in a cancer gene has been produced. We perform RSA image encryption to see the private and public keys over the image of geneon. In our approach, quantum cryptography is applied in biology to find the pattern of mutation genes by using an image encryption method.
We think that this new methodology could evolve into the more practical visualization of genes in the future, instead of showing the sequence of amino acids. DNA (and genes) is permanently changing, it has a dynamic structure. The mutations on the gene level affect the genes, which subsequently can lead to production malfunctions of various proteins. Gene-level mutations are caused by different types of processes. It may be a swapping of one nucleotide for another one, a deleting or omitting of a specific nucleotide from the strand, or an inserting of an extra nucleotide into the replication strand. Besides the single codon substitutions, on the level of codons there exist other categories of mutations. The incorrect amino acids can be inserted into a protein molecule, the synthesis of a protein can be prematurely terminated, and the mutated codon can code the same amino acid as the non-mutated codon. As a consequence of DNA constant change, the difference between the mutated and normal versions of the gene changes over time. We can train our algorithm on the different versions of the genes, on normal genes with non-modified sequences of nucleotides or on their mutated versions as cancer genes, which code different structures than the normal ones.
With our model we are looking for the effective change of topology of proteins, i.e., the stable structures of noncoding DNA binding to genes; this procedure selects only certain structures that can be detected. We hope for the application in cancer genes, but at first the genes on which the measurements can be made must be identified by genetic experts. However, we provide the tool for the terminal measurements incorporated into more complex biophysical experiments. In the future, the application of the methodology can be developed into more practical automatic detection of mutated genes, either for medical purposes or for imaging production of the cancer genome project.
In conclusion, we applied a direct application of algebraic topological quantum cryptography and quantum field theory with loop braid group theory directly to perform the analysis of the ALX1 cancer gene for the detection of a cancer signature. We proposed and used a new theory of quantum public key encryption in a cancer cryptosystem. The result of the computation of the RSA algorithm for public and private keys in normal and cancer genes appeared to be significant for the biological cryptosystem. Finally, we used the Chern–Simons current to plot the tensor correlation and compute the image of spectra for cancer signature.
The relevant point of our approach is the fact that quantum field theory developed for physics, in particular, the Chern–Simons theory, is extremely useful for describing biological systems [35,36], despite the huge difference in orders of magnitude between fundamental particles and genetic code. However, our mathematical method can also be used not only for mapping and determination of the genomes of viruses and subsequent prediction of their mutations, but also in astrophysical and cosmological systems. Following symmetry in biological nature gives us a chance to also compute the structures of biological systems in our description of the mutation genes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.C. and R.P.; investigation: S.C., R.P. and E.B.; writing—original draft preparation: S.C. and R.P.; writing—review and editing: S.C. and E.B.; visualization: E.B.; project administration: S.C. and R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by VEGA grant numbers 2/0009/19 and 2/0153/17.
Acknowledgments
This article is based upon work from CANTATA COST (European Cooperation in Science and Techonology) action CA15117, EU Framework Programme Horizon 2020. S.C. acknowledges INFN for partial support. R.P. would like to thank the TH division in CERN and BLTP in JINR, Dubna for hospitality.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Appendix A. Path Integral and Quantum Biology Theory
New definition of a Dirac operator for the gene expression can be written with the help of Hamiltonian as
where is an eigenvalue of transition energy with a transition state , in DNA. The operator D has two parts. The kinetic part is the source of energy and the momentum tensor in the genetic code. The potential part is the source of an RNA state or a copy state of DNA to RNA. The first part is the momentum square of protein–protein interaction, , where is an behavior field in the protein folding structure; p is a momentum in protein . The imaginary number means a hidden state in DNA structure associated with the protein. The second part is the potential part of RNA molecule. The interaction of RNA to DNA is expressed in this part analogically with potential energy in the Dirac operator.
The path integral [37] in loop braid group can reproduce the Schrödinger equation for gene expression. We can derive following well known result in quantum mechanics; it is true also in quantum biology because the quantum concept in this work proves the validation of a biological system of gene expression in the form of a path integral over a loop braid group.
Let , , and be three alphabet letters of the anti-codons of t-RNA. They are associated with the smallest elements of proteins as the momentum component for the component of angular momentum in the gene expression:
We have , and with
We have energy and momentum tensor defined by Lagrangian , , and q DNA state or RNA state . Since in an equivalent relation, q is the generalized coordination of the configuration space of a Lagrangian. It maps from the tangent of a super manifold of living organism to a scalar field as a source of energy and momentum tensor in the genetic code. If the path integral along the configuration space is parametrized by a path as a functional f, we have
We generalize three angular momenta , of three states of as the unification of central dogma from with the flow of energy and momentum tensor along the gene expression in every possible direction of path integral. Let be states of four genetic codes in DNA; it is an element of . Let be a protein state as the momentum vector and let be a rate of an evolutional field. The angular momentum tensor is analogous with a source of gene expression in DNA state. That blends the molecular structure of DNA into curve
where
If we rewrite the relation in a scalar field to a vector field with a cross product analogous to a vector field in Lie algebra, we will get the induced field of transition state in DNA as the interaction between RNA and the protein (the behavior of interaction between two docking proteins) with for the induced ncRNA in ancient virus t-RNA with their associated amino acids in proteins for the codon alphabet in the DNA template.
If is an evolutional field in the behavior field of host cell DNA, we can formulate the so-called uncertainty principle in the gene expression
Let p be momentum of protein in active layer of docking system and let be a protein in passive layer; we have the interaction as transition state in DNA as kinetic energy in gene expression
The explicit form of a wave function in DNA contains the momentum for three states of momentum in one amino acid as a linear combination
where .
Appendix Largangian of Path Integral Formalism for System of DNA–RNA Transcription
We start from the formulation of Lagrangian of the system of DNA–RNA transcription with extended central dogma. Let Lagragian be a map from the tangent of the supermanifold of a living organism with eight spinor states with a fiber of . It is a source of Hopf fibration as pa ath integal line and it is exactly a line of the loop braid group in genetic code parametrized by . We choose the coordinates satisfying the equation
Definition A1.
We have the Euler–Lagrange equation for gene expression in the system of extended central dogma with given by
The action of path integral to minimize the geodesic curvature of the path in DNA is . It is a flow of genetic code as a line in braid group in genetic code. In this work we choose and d is a time variable.
The path in quantum biology theory means the string of protein folding which can deform continuously from primary protein structure to secondary protein structure by using homotopy equivalent relation in loop braid group (see Figure A1). If the sequence of protein folding starts from discretized time scale in the path integral, one can choose as a starting point of gene expression in DNA and as an ending point. It is a chosen localized base point in braid group as line in our parameter of localized path in Lagrangian. When these lines intersect each other we have path ordering of Wilson loop [38] in genetic code. The homotopic path is the homotopy equivalent of a line in the path integral from an equivalent class of curve map from the Lagrangian of the tangent of the manifold to the based point of the intersection line between fibration. We define an element of loop braid group in the path integral over loop braid group in genetic code, , if and only if there exists a homotopic path as a map in from .
The localized path in loop braid group can be divided into n smaller subintervals , where . We can permute this path ordering by using Wilson loop over loop braid group. The source of mutation is
and it is called a source of uncertainty principle in so-called quantum biology theory, and a source of evolutional field in the form of three types of behavior fields in the genetic code.
An approximation for the path integral can be computed to be proportional to number of gene expression in tRNA. The codes of DNA (codon state) and tRNA (in anticodon state) are assumed to be the same length (without exon and intron involved) in this simple system of DNA–RNA transcription. We have
We define a probability amplitudes of gene expression as a source of protein folding by . It is a spectrum of gene expression with the probability to find the gene particle (geneon) at in the initial state of RNA and at in the final state . In the simple case of Lagrangian we have
The wave propagation obtained from the path integral so-called geneon wave function in gene expression with eigenvalues as transition states in protein folding structure is
where denotes integration over all paths , with and Z is a normalization factor. Here S is the action, given by . We obtain the exponential of the action by
and we can use the approximation
Then, after the rearrangement of the terms properly, we get
which is the Schrödinger equation for the gene expression.
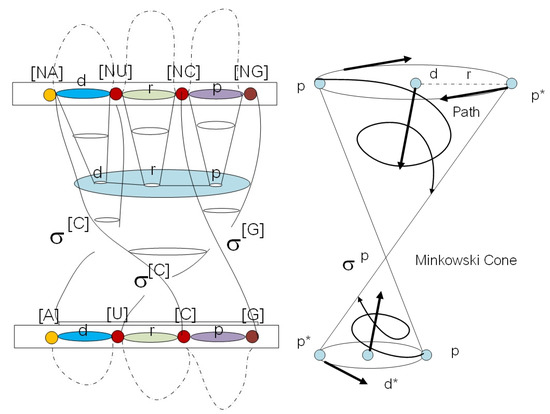
Figure A1.
The path of cocycle of behavior field in loop braid group for genetic code.
Appendix B. The Source of Protein Folding Structure
The protein transition state is a Fermi–Dirac superdistribution of 20 geneonic transition states. The behavior fields of coupling between their evolutional parameters in a cell cocyle are given by as a transition of to future state .
Let cell cocycle be a function of behavior in the genetic code of living organism denoted by
There exists a question about the smallest subunit of genotypes as a pair of alleles in the pair of chromosomes. The smallest subunit should exist in two DNAs, one from a mother’s chromosome and other from a father chromosome. It is the appearance of four states from one DNA inactive part of allele and other four hidden states from a passive part of other one from father DNA, denoted as , , , . The induced four states from homozygous and heterozygous to other four states in the proof is a Hodge star operator in type-III Yang–Mills field . It is a source of a supersymmetry and it answers why the base in DNA molecule has only right-hand chiral symmetry. The left-hand one is in the hidden state of passive layer , , , . Let the Yang–Mills field induced from the interaction of hidden evolutional field be . This field comes from an adaptive behavior field in the genetic code in the form of a mutation.
Definition A2.
For immature behavior field, we use finite state for physiology of time series to accepted protein folding pattern defined by
where is a Pauli spin matrix along y-axis.
Definition A3.
For a maturing behavior field, we use a finite state for the physiology of a time series for the accepted folding pattern defined by
where is a Pauli spin matrix along z-axis.
Definition A4.
Let ω be a instinct behavior of "junk" DNA. From the well known induced relationship between spinor fields we have
where W is a Wilson loop (knot state of an evolution between genetic code and expected genetic code of protein) in biological time series data and is an inverse of Wilson loop (unknown state between transition in protein folding). We have an entanglement with knot state induced from hidden adaptive behavior field of twist for plane of D-brane in protein–protein interaction with state to anti-D-brane in the immature state explained by
Definition A5.
Let d be a ground state of localized genetic material in DNA. We defined a sequence of gene expression in DNA as a linear compact operator in a superspace D with its copy of sequence in another superspace R. Let r be RNA operator in R. A Wigner ray of biological state at an equilibrium in protein state is a point where such that there exists a ray of unitary operator λ in SU(2) = Spin(3)
We introduce three evolutional behavior fields of adaptive behavior of changing curvature in the protein folding
where + means a positive adaptive behavior of a protein, − is negative adaptive behavior, m is a maturing behavior, is an immature behavior, and ω is an instinct behavior. is a connection behavior of a maturing protein, is a connection behavior field of an immature protein, is a connection behavior field of the instinct-adaptive behavior field of the protein.
Using the definitions above we have , , , , , . It is a vierbien of a transition of cell cocycles in two rounds with the active and passive side of the DNA–RNA transcription (see Figure A2). In order to compute the interaction of the behavior field in the genetic code in terms of evolution, we simplify by analogy a multiplication of a predefined number with vierbein:
We use the well-known formula for the connection for the enegy-momentum tensor in the genotype. It is the transition between the ghost field and anti-ghost field in the active and passive layer of the DNA–RNA transcription. With the existence of a knot protein, the underlying knot of quantum observation over a superspace of genetic code is a modified Wilson loop. It is a hyperbolic knotted-over loop space in biological time series data. The allele in the genotype is a partition function of the active site in DNA. The partition function of a lattice gauge theory for biology is
If we compare this expression with an effective action of Josephson junction in a biological system with critical Chern–Simons current in biology given by
where is a supercurrent, is a phase difference between D-brane and anti-D-brane sheet in the DNA–RNA transcription with underlying two-child manifolds of knot state with partition function ; the free energy of our system is measured by a holomony of Wilson loop inside the Chern–Simons current. We have expansion of the Wilson loop over Green function by
The invariance of Wilson loop can be obtained from the Laurant polynomial in Witten invariance with an explicit form of the Chern–Simons current in which the closed form of sine is an analogy with the phase shift in a current of energy-momentum tensor, so we have with a strong coupling constant . We have a cell cocycle over behavior field by
The path integral in a superspace of genetic code is a Green function of the propagator of a behavior field in an immune system along a principle fiber space in secondary protein structure. Let be a time series of gene expression at time and let et be a biological time series at time . The path integral defines a gene expression equation with the coupling state between geneonic eight states between active and passive layers of a behavior field with parallel transport .
Let be an active codon state and be a passive anti-codon state. Let be a Green function of a propagator for gene expression. We have path integral along a fiber space with extraproperty of knot and link between each sections of fiber by using a path integral over transition between the hidden trash DNA states in Khovanov cohomology, the homotopic path in knotten time series data
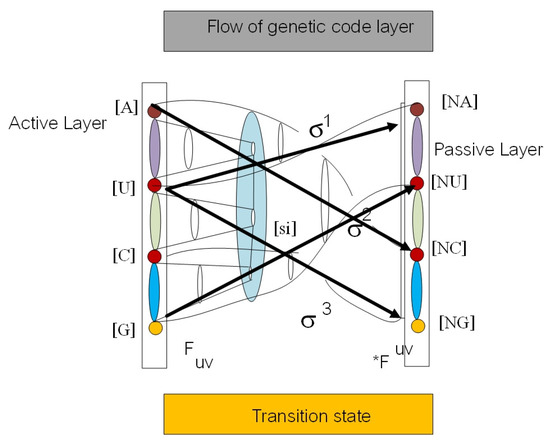
Figure A2.
The source of hidden eight states in genetic code comes from the intersection of a line as an element of loop braid group.
Appendix C. Amino Acids Sequence of Noncoding RNA Sequence in Telomerase
Homo sapiens telomerase RNA component (TERC), telomerase RNA
NCBI Reference Sequence: NR_001566.1
FASTA Graphics
Go to:
LOCUS NR_001566 451 bp RNA linear PRI 21-OCT-2018
DEFINITION Homo sapiens telomerase RNA component (TERC), telomerase~RNA.
ncRNA 1..451
/ncRNA_class="telomerase_RNA"
/gene="TERC"
/gene_synonym="DKCA1; hTR; PFBMFT2; SCARNA19; TR; TRC3"
/product="telomerase RNA component"
/db_xref="GeneID:7012"
/db_xref="HGNC:HGNC:11727"
/db_xref="MIM:602322"
exon 1..451
/gene="TERC"
/gene_synonym="DKCA1; hTR; PFBMFT2; SCARNA19; TR; TRC3"
/inference="alignment:Splign:2.1.0"
misc_feature 46..55
/gene="TERC"
/gene_synonym="DKCA1; hTR; PFBMFT2; SCARNA19; TR; TRC3"
/note="template for telomere repeat TTAGGG"
ORIGIN
1 gggttgcgga gggtgggcct gggaggggtg gtggccattt tttgtctaac cctaactgag
61 aagggcgtag gcgccgtgct tttgctcccc gcgcgctgtt tttctcgctg actttcagcg
121 ggcggaaaag cctcggcctg ccgccttcca ccgttcattc tagagcaaac aaaaaatgtc
181 agctgctggc ccgttcgccc ctcccgggga cctgcggcgg gtcgcctgcc cagcccccga
241 accccgcctg gaggccgcgg tcggcccggg gcttctccgg aggcacccac tgccaccgcg
301 aagagttggg ctctgtcagc cgcgggtctc tcgggggcga gggcgaggtt caggcctttc
361 aggccgcagg aagaggaacg gagcgagtcc ccgcgcgcgg cgcgattccc tgagctgtgg
421 gacgtgcacc caggactcgg ctcacacatg~c
programmed cell death protein 1 precursor [Homo sapiens]
ORIGIN
1 mqipqapwpv vwavlqlgwr pgwfldspdr pwnpptfspa llvvtegdna tftcsfsnts
61 esfvlnwyrm spsnqtdkla afpedrsqpg qdcrfrvtql pngrdfhmsv vrarrndsgt
121 ylcgaislap kaqikeslra elrvterrae vptahpspsp rpagqfqtlv vgvvggllgs
181 lvllvwvlav icsraargti garrtgqplk edpsavpvfs vdygeldfqw rektpeppvp
241 cvpeqteyat ivfpsgmgts sparrgsadg prsaqplrpe~dghcswpl
Appendix D. Amino Acide Sequence of Telomoerase
/product="telomerase reverse transcriptase isoform~2"
Region 460..594
/region_name="telomerase_RBD"
/note="telomerase ribonucleoprotein complex - RNA binding
domain; smart00975"
/db_xref="CDD:214948"
Region 618..>729
/region_name="RT_like"
/note="RT_like: Reverse transcriptase (RT, RNA-dependent
DNA polymerase)_like family. An~RT gene is usually
indicative of a mobile element such as a retrotransposon
or retrovirus. RTs occur in a variety of mobile elements,
including retrotransposons; cl02808"
/db_xref="CDD:295487"
Region 825..>884
/region_name="TERT"
/note="TERT: telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT).
telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) that synthesizes
telomeric DNA repeats. The~telomerase RNA subunit provides
the template for synthesis of these repeats. The~catalytic
subunit of RNP is known as...; cd01648"
/db_xref="CDD:238826"
Site 834
/site_type="other"
/note="putative nucleic acid binding site [nucleotide
binding]"
/db_xref="CDD:238826"
CDS 1..1069
/gene="TERT"
ORIGIN
1 mpraprcrav rsllrshyre vlplatfvrr lgpqgwrlvq rgdpaafral vaqclvcvpw
61 darpppaaps frqvsclkel varvlqrlce rgaknvlafg falldgargg ppeafttsvr
121 sylpntvtda lrgsgawgll lrrvgddvlv hllarcalfv lvapscayqv cgpplyqlga
181 atqarpppha sgprrrlgce rawnhsvrea gvplglpapg arrrggsasr slplpkrprr
241 gaapepertp vgqgswahpg rtrgpsdrgf cvvsparpae eatslegals gtrhshpsvg
301 rqhhagppst srpprpwdtp cppvyaetkh flyssgdkeq lrpsfllssl rpsltgarrl
361 vetiflgsrp wmpgtprrlp rlpqrywqmr plflellgnh aqcpygvllk thcplraavt
421 paagvcarek pqgsvaapee edtdprrlvq llrqhsspwq vygfvraclr rlvppglwgs
481 rhnerrflrn tkkfislgkh aklslqeltw kmsvrdcawl rrspgvgcvp aaehrlreei
541 lakflhwlms vyvvellrsf fyvtettfqk nrlffyrksv wsklqsigir qhlkrvqlre
601 lseaevrqhr earpalltsr lrfipkpdgl rpivnmdyvv gartfrrekr aerltsrvka
661 lfsvlnyera rrpgllgasv lglddihraw rtfvlrvraq dpppelyfvk vdvtgaydti
721 pqdrltevia siikpqntyc vrryavvqka ahghvrkafk shvstltdlq pymrqfvahl
781 qetsplrdav vieqssslne assglfdvfl rfmchhavri rgksyvqcqg ipqgsilstl
841 lcslcygdme nklfagirrd glllrlvddf llvtphltha ktflsyarts irasltfnrg
901 fkagrnmrrk lfgvlrlkch slfldlqvns lqtvctniyk illlqayrfh acvlqlpfhq
961 qvwknptffl rvisdtaslc ysilkaknag mslgakgaag plpseavqwl chqafllklt
1021 rhrvtyvpll gslrtaqtql srklpgttlt aleaaanpal~psdfktild
Appendix E. Cipher Text for Encryption in ALX1 Gene
-Encryption-
Ciphertext:
2984 3181 2990 22 2639 3181 1680 2990
2112 22 1680 2639 180 180 2639 1680 1993 2639
403 2990 260 2984 1091 2112 1091 1091 180 22
3181 3192 2526 2984 3181 3544 22 403 1993 3181
2639 2990 260 2639 1680 2112 2639 2112 1091 1680
1675 2526 1221 2112 2990 1091 180 22 180 2275
2112 3181 3192 3192 2526 2275 22 3181 2275 3544
2639 180 1675 1221 403 2639 2639 2526 1993 260
1091 3756 3544 1680 2526 3181 1091 1221 180 22
3192 3544 3181 22 1993 2275 2112 2984 403 1993
1675 1993 2639 22 2275 2984 2639 180 2526 1680
1091 2984 1221 3181 1680 1091 3181 22 403 3181
22 1091 403 1680 1675 403 2639 1993 2526 2639
2639 2639 1680 1680 2275 2275 3192 2275 3544 3544
2990 3544 2639 22 1221 22 3181 3181 22 3181
1680 2526 2990 1221 1680 3544 3192 260 180 403
2526 260 2526 2275 3181 1221 22 2112 22 2275
3544 3181 22 3544 3181 2112 2275 2526 1221 2526
1956 2990 1221 1993 2275 2275 2112 1680 1956 2275
1680 2275 3181 2275 260 1091 1221 3756 1221 1221
2112 1680 2639 3192 2990 2112 2112 3544 260 403
3756 2639 2526 22 180 2275 3544 403 2639 260
180 1221 3756 1221 1993 1993 22 1956 2112 1091
1993 2112 2639 1091 1091 2639 2526 2526 3544 2639
1675 2984 22 180 2275 403 3544 2639 2639 1675
2984 3544 180 260 2639 3192 2639 180 2275 3544
403 2639 2639 260 3544 1091 2990 2639 1993 3192
1221 1993 1221 2990 2639 3192 2526 180 22 1993
1993 2990 2990 3544 403 2639 22 22 3544 1091
2112 3544 1993 1091 3192 2112 2990 3181 3544 1680
180 3181 2990 3181 2275 2275 2639 2639 2639 3756
2112 2526 22 2275 2984 1680 2112 1680 3181 3192
3544 2112 1993 3756 2639 1956 2112~2984
encrypt message in nucleotide sequence:
Restored Message: ’MEFLSEKFALKSPPSKNSDFYMGAGGPLEHVMET
LDNESFYSKASAGKCVQAFGPLPRAEHHVRLERTSPCQDSSVNYGITKVEGQPLHTELNR
AMDNCNSLRMSPVKGMQEKGELDELGDKCDSNVSSSKKRRHRTTFTSLQLEELEKVFQKTH
YPDVYVREQLALRTELTEARVQVWFQNRRAKWRKRERYGQIQQAKSHFAATYDISVLPRTDS
YPQIQNNLWAGNASGGSVVTSCMLPRDTSSCMTPYSHSPRTDSSYTGFSNHQNQFSHVPLNNF
FTDSLLTGATNGHAFETKPEFERRSSSIAVLRMKAKEHTANISWAM’
-Key Pair-
Modulus: 3953
Public Exponent: 5
Private Exponent: 2297
-Signing-
Signature: 2338 2587 1861 1967 974 2587 2926
1861 3376 1967 2926 974 3839 3839 974 2926 2172 974
3686 1861 3292 2338 1882 3376 1882 1882 3839 1967 2587
276 942 2338 2587 2401 1967 3686 2172 2587 974 1861
3292 974 2926 3376 974 3376 1882 2926 2412 942 2318
3376 1861 1882 3839 1967 3839 952 3376 2587 276 276
942 952 1967 2587 952 2401 974 3839 2412 2318 3686
974 974 942 2172 3292 1882 457 2401 2926 942 2587
1882 2318 3839 1967 276 2401 2587 1967 2172 952 3376
2338 3686 2172 2412 2172 974 1967 952 2338 974 3839
942 2926 1882 2338 2318 2587 2926 1882 2587 1967 3686
2587 1967 1882 3686 2926 2412 3686 974 2172 942 974
974 974 2926 2926 952 952 276 952 2401 2401 1861
2401 974 1967 2318 1967 2587 2587 1967 2587 2926 942
1861 2318 2926 2401 276 3292 3839 3686 942 3292 942
952 2587 2318 1967 3376 1967 952 2401 2587 1967 2401
2587 3376 952 942 2318 942 3733 1861 2318 2172 952
952 3376 2926 3733 952 2926 952 2587 952 3292 1882
2318 457 2318 2318 3376 2926 974 276 1861 3376 3376
2401 3292 3686 457 974 942 1967 3839 952 2401 3686
974 3292 3839 2318 457 2318 2172 2172 1967 3733 3376
1882 2172 3376 974 1882 1882 974 942 942 2401 974
2412 2338 1967 3839 952 3686 2401 974 974 2412 2338
2401 3839 3292 974 276 974 3839 952 2401 3686 974
974 3292 2401 1882 1861 974 2172 276 2318 2172 2318
1861 974 276 942 3839 1967 2172 2172 1861 1861 2401
3686 974 1967 1967 2401 1882 3376 2401 2172 1882 276
3376 1861 2587 2401 2926 3839 2587 1861 2587 952 952
974 974 974 457 3376 942 1967 952 2338 2926 3376
2926 2587 276 2401 3376 2172 457 974 3733 3376~2338
References
- Anshel, I.; Anshel, M.; Fisher, B.; Goldfeld, D. New key agreement protocols in braid group cryptography. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2001, 2020, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Birman, J.; Ko, K.; Lee, S. A New Approach to the Word and Conjugacy Problems in the Braid Groups. Adv. Math. 1998, 139, 322–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshel, I.; Anshel, M.; Goldfeld, D. An algebraic method for public-key cryptography. Math. Res. Lett. 1999, 6, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Pincak, R.; Kanjamapornkul, K.; Saridakis, E. The Chern-Simons Current in Systems of DNA-RNA Transcriptions. Ann. Der Phys. 2018, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Pincak, R. The Chern–Simons current in time series of knots and links in proteins. Ann. Phys. 2018, 393, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincak, R.; Kaniamapornkul, K.; Bartoš, E. Forecasting Laurent Polynomial in the Chern–Simons current of V3 Loop Time Series. Annalen der Physik 2019, 1800375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.; Rachakonda, S.; Kumar, R. Telomeres and Telomere Length: A General Overview. Cancers 2020, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, E. Asymptotic Convergence of Soft-Constrained Neural Networks for Density Estimation. Mathematics 2020, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilson-Thompson, S.; Hackett, J.; Kauffman, L.; Wan, Y. Emergent braided matter of quantum geometry. Symmetry Integr. Geom. Methods Appl. 2012, 8, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjamapornkul, K.; Pinčák, R. Kolmogorov space in time series data. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2016, 4463–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, D.; Seiringer, R. Fermionic behavior of ideal anyons. Lett. Math. Phys. 2018, 108, 2523–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, B.; Simula, T. Introduction to topological quantum computation with non-Abelian anyons. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusca, D.; Boaron, A.; Grünenfelder, F.; Martin, A.; Zbinden, H. Finite-key analysis for the 1-decoy state QKD protocol. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 171104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacco, D.; Vagniluca, I.; Da Lio, B.; Biagi, N.; Della Frera, A.; Calonico, D.; Toninelli, C.; Cataliotti, F.; Bellini, M.; Oxenløwe, L.; et al. Field trial of a three-state quantum key distribution scheme in the Florence metropolitan area. EPJ Quantum Technol. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armas, P.; Calcaterra, N. G-quadruplex in animal development: Contribution to gene expression and genomic heterogeneity. Mech. Dev. 2018, 154, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiani, C. A journey through loop braid groups. Expo. Math. 2017, 35, 252–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresnigt, N. Braids, normed division algebras, and Standard Model symmetries. Phys. Lett. Sect. B Nucl. Elem. Part. High-Energy Phys. 2018, 783, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, D. Central dogma or central debate? Physiology 2018, 33, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjamapornkul, K.; Pinčák, R.; Bartoš, E. The study of Thai stock market across the 2008 financial crisis. Physica 2016, A462, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjamapornkul, K.; Pinčák, R.; Bartoš, E. Cohomology theory for financial time series. Physica 2020, A546, 122212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinčák, R.; Kanjamapornkul, K.; Bartoš, E. Cohomology theory for biological time series. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2020, 43, 552–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, B.; Pfeifer, R.; Brennen, G. Phase transitions on a ladder of braided non-Abelian anyons. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 045432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N. A ribonucleopeptide world at the origin of life. J. Syst. Evol. 2018, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, N. Junk DNA. A Journey through the Dark Matter of the Genome; Icon Books Ltd.: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Harley, C.; Futcher, A.; Greider, C. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature 1990, 345, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancich, M.; Schrank, Z.; Wojdyla, L.; Leviskas, B.; Kuckovic, A.; Sanjali, A.; Puri, N. Treating cancer by targeting telomeres and telomerase. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, M.; Ansari, S.; Alqahtani, M.; Shay, J. Roles of telomeres and telomerase in cancer, and advances in telomerase-targeted therapies. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilson-Thompson, S. Braided topology and the emergence of matter. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, 3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Cech, T. Reversing time: Origin of telomerase. Cell 1998, 92, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigner, E. On the quantum correction for thermodynamic equilibrium. Phys. Rev. 1932, 40, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, T.; Sakaguchi, R.; Perlinska, A.; Lahoud, G.; Ito, T.; Taylor, E.; Yokoyama, S.; Sulkowska, J.; Hou, Y.M. Methyl transfer by substrate signaling from a knotted protein fold. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene ID: 7012. TERC Telomerase RNA Component. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2004-[cited 2018]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=7012 (accessed on 14 June 2020).
- Tate, J.G. COSMIC: The Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinčák, R.; Kanjamapornkul, K.; Bartoš, E. A theoretical investigation on the predictability of genetic patterns. Chem. Phys. 2020, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinčák, R.; Bartoš, E. Chemical evolution of protein folding in amino acids. Chem. Phys. 2020, 537, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P.; Hibbs, A.R.; Styer, D.F. Quantum Mechanics and Path Integrals; Dover Books on Physics; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A.P.C. Chern-Simons Path Integrals in S2 × S1. Mathematics 2015, 3, 843–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).