Stability Analysis of the Magnetized Casson Nanofluid Propagating through an Exponentially Shrinking/Stretching Plate: Dual Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
3. Stability Analysis
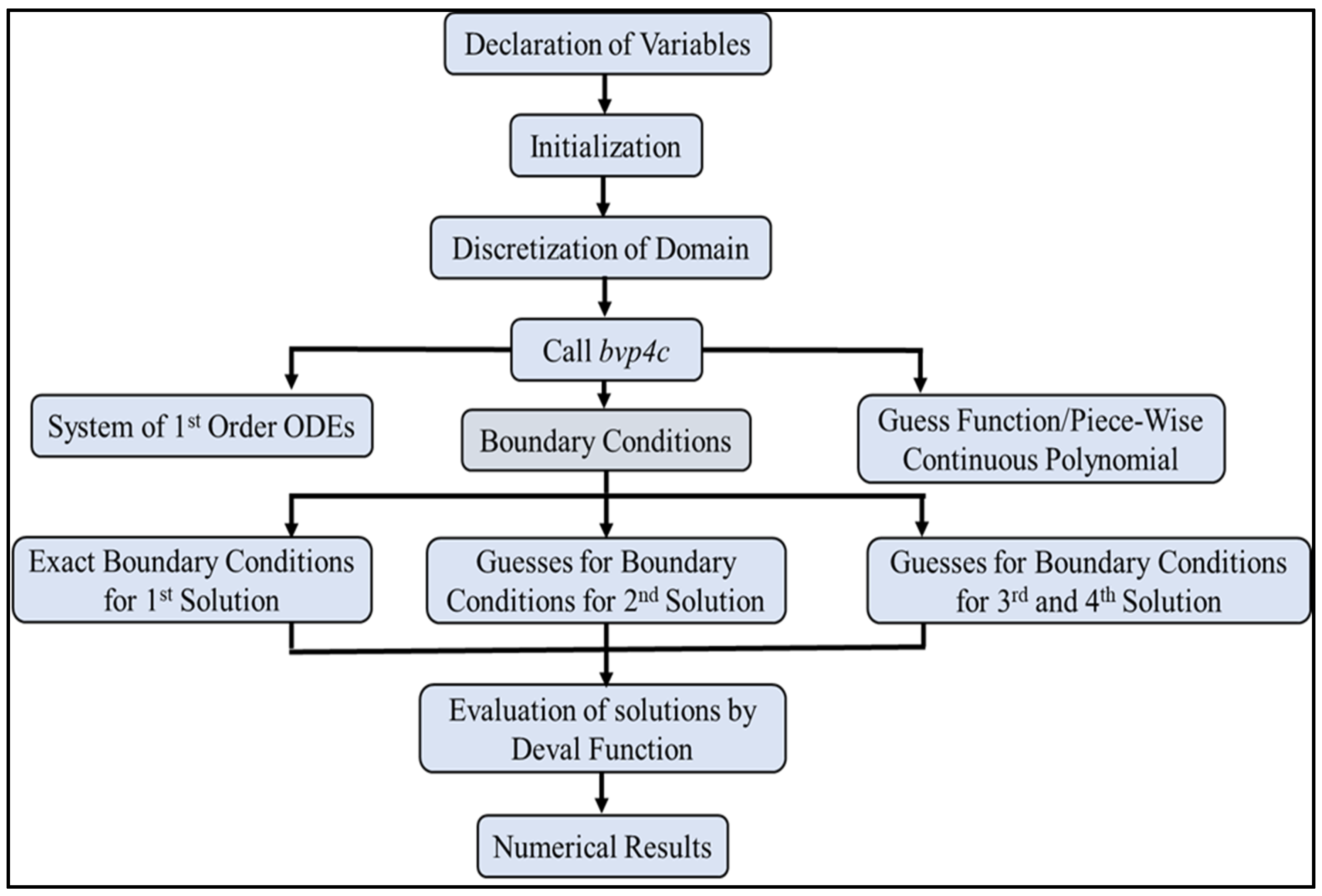
4. Numerical Methods
4.1. Shooting Method
4.2. Three-Stage Lobatto IIIA Formula
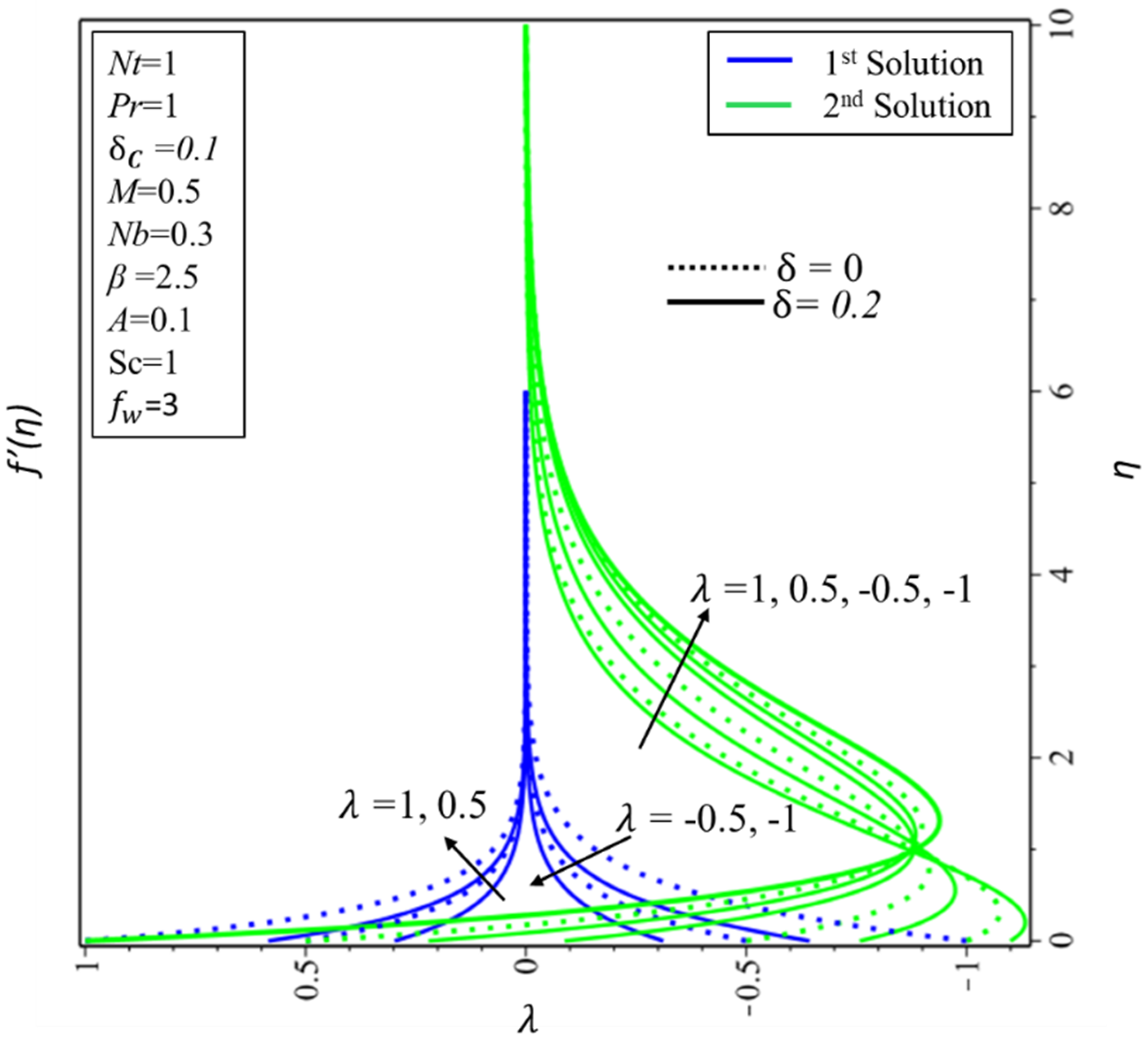
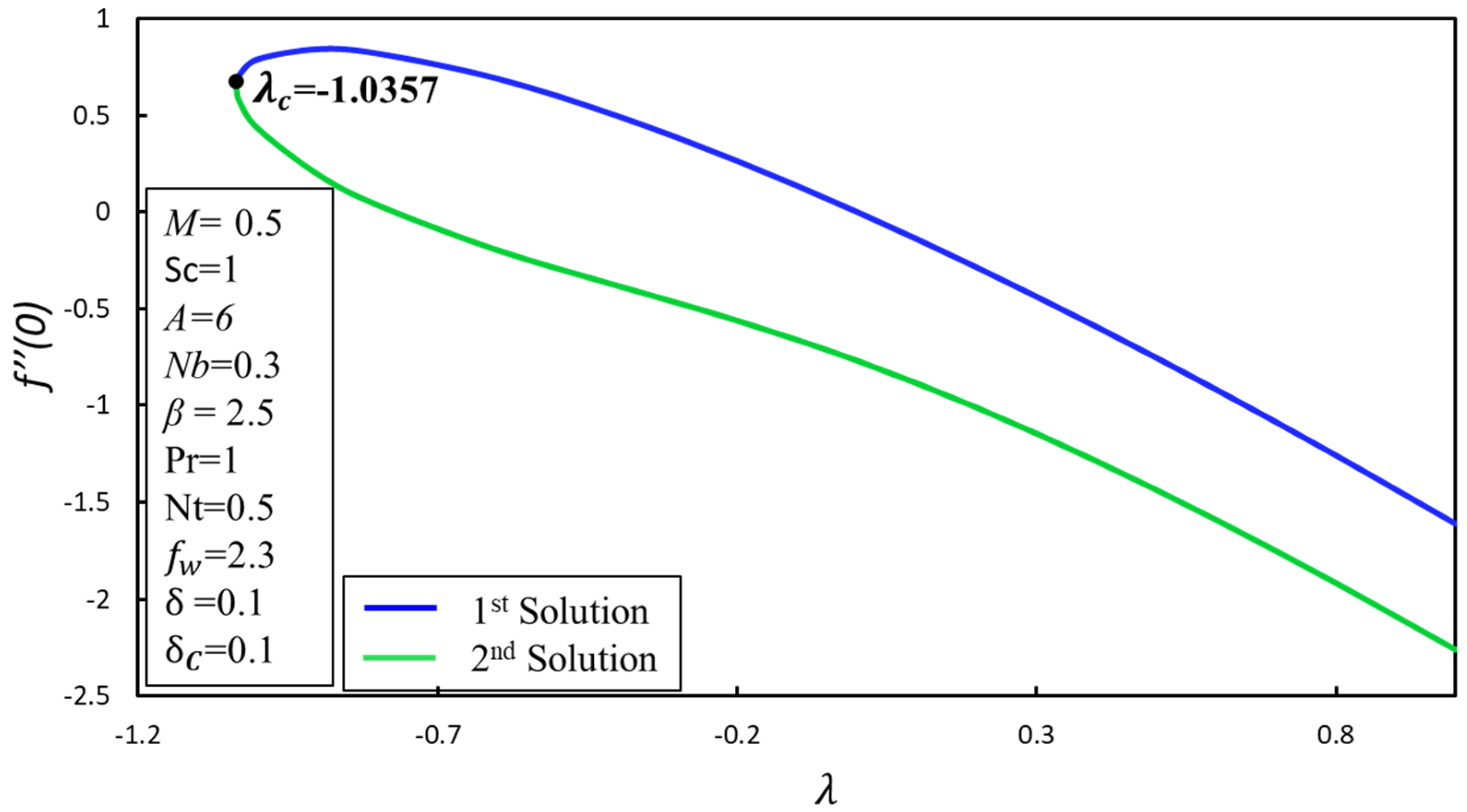
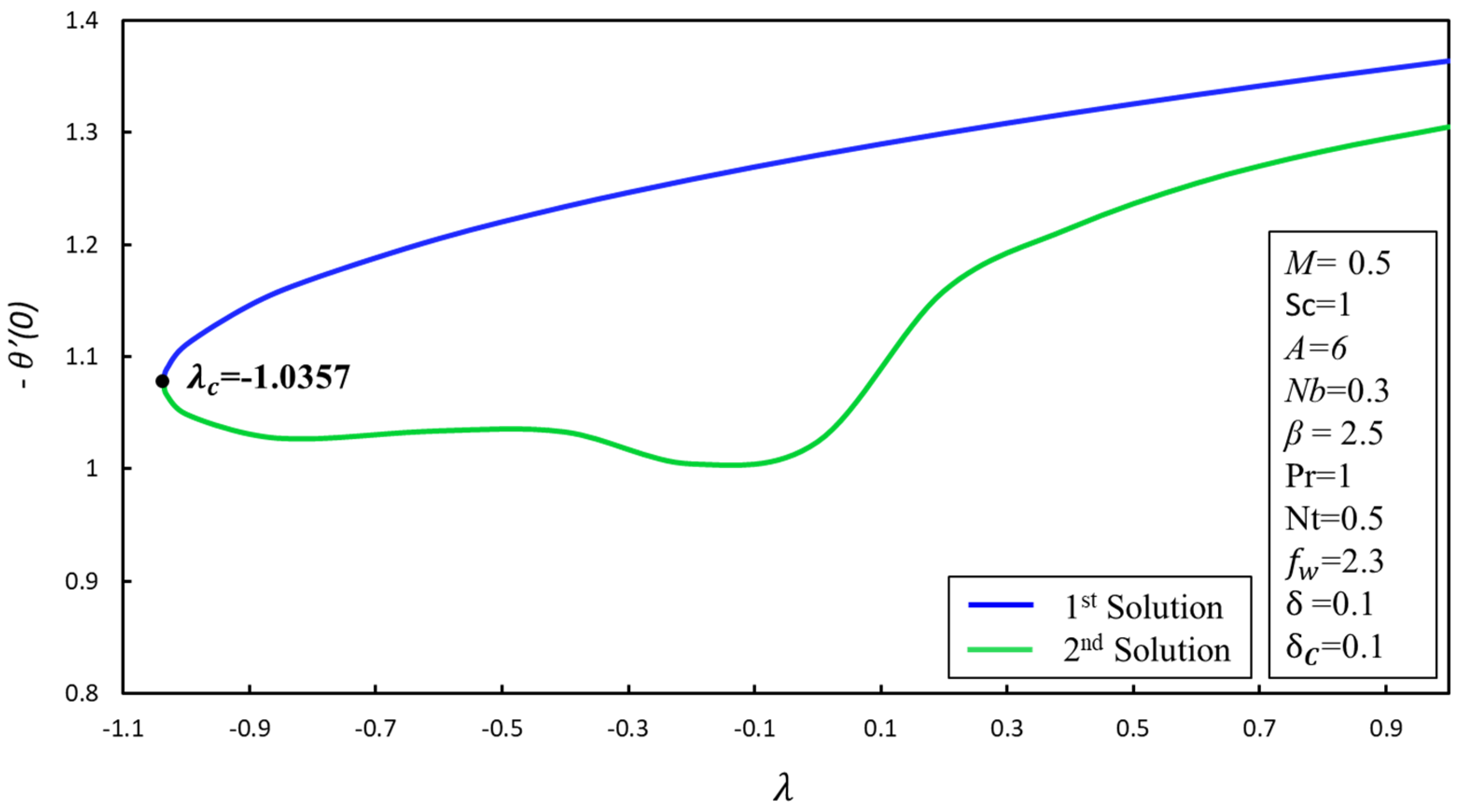
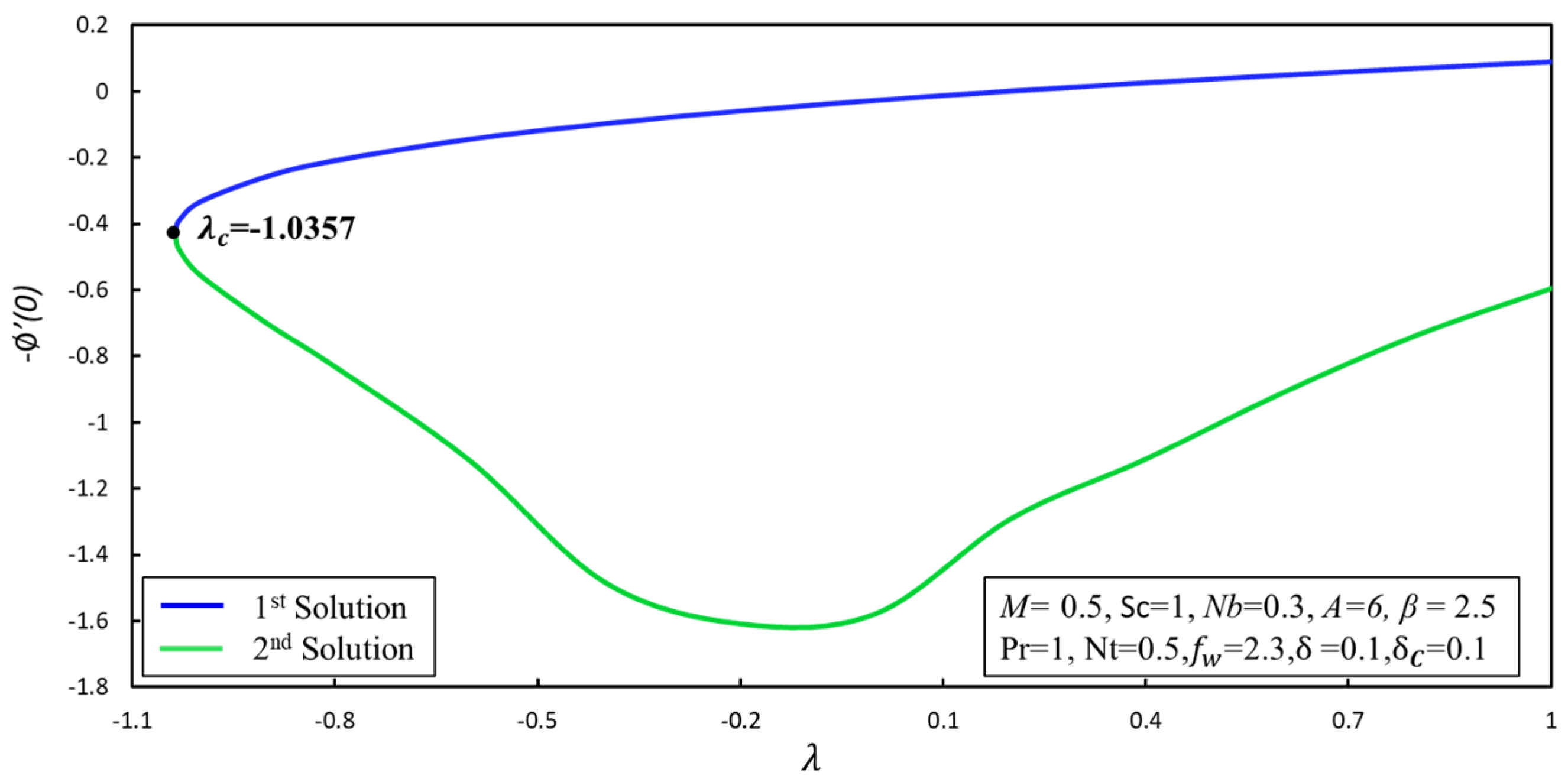
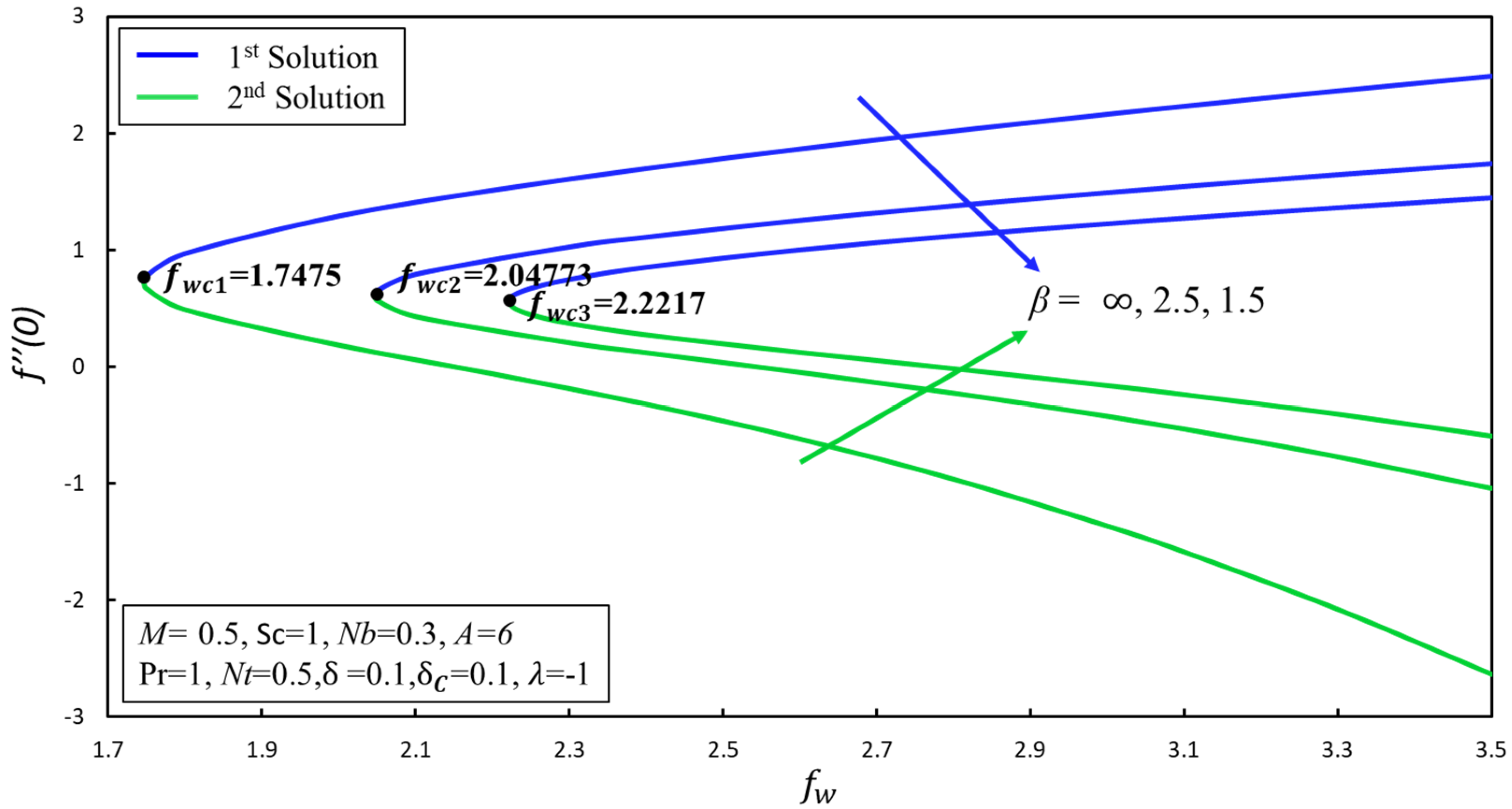
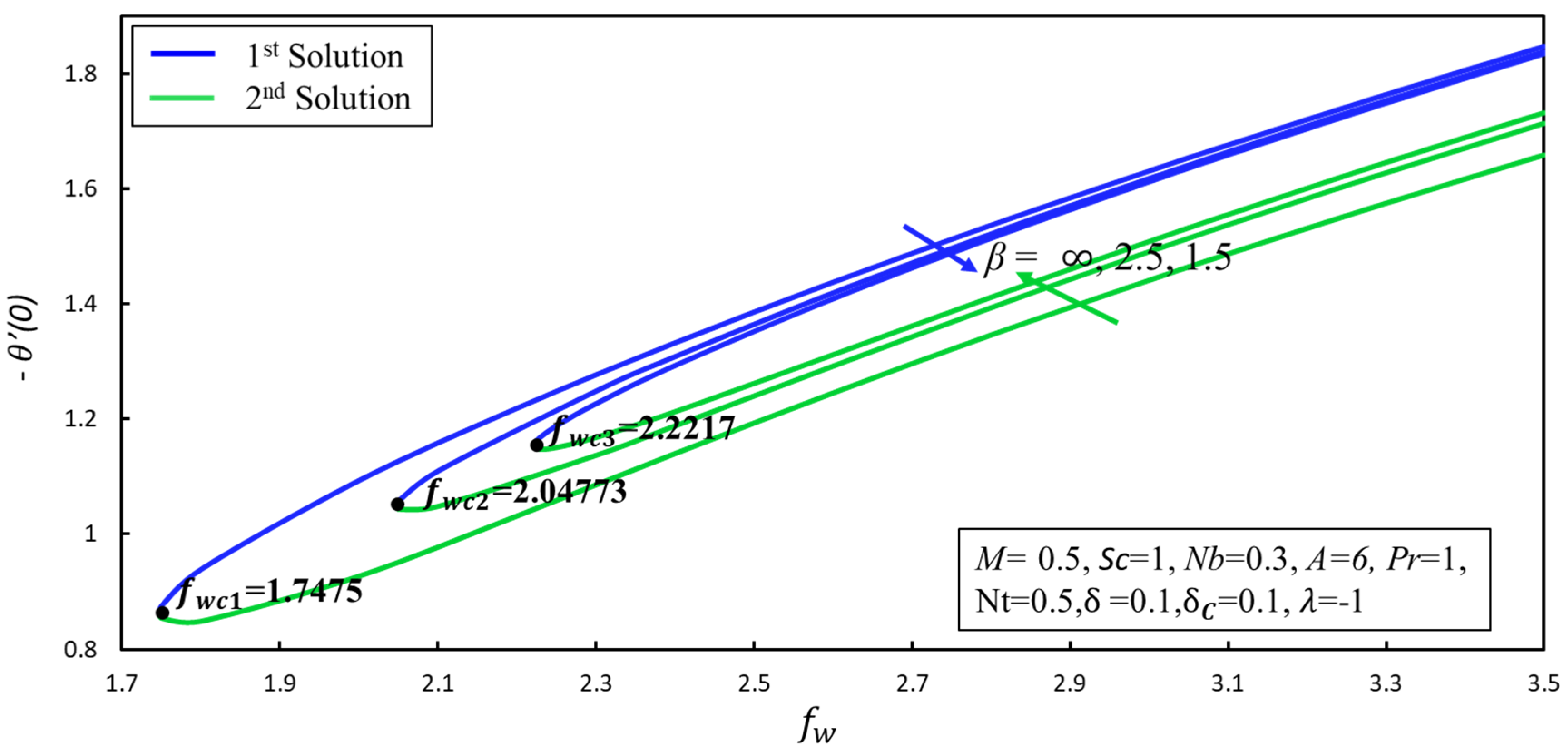
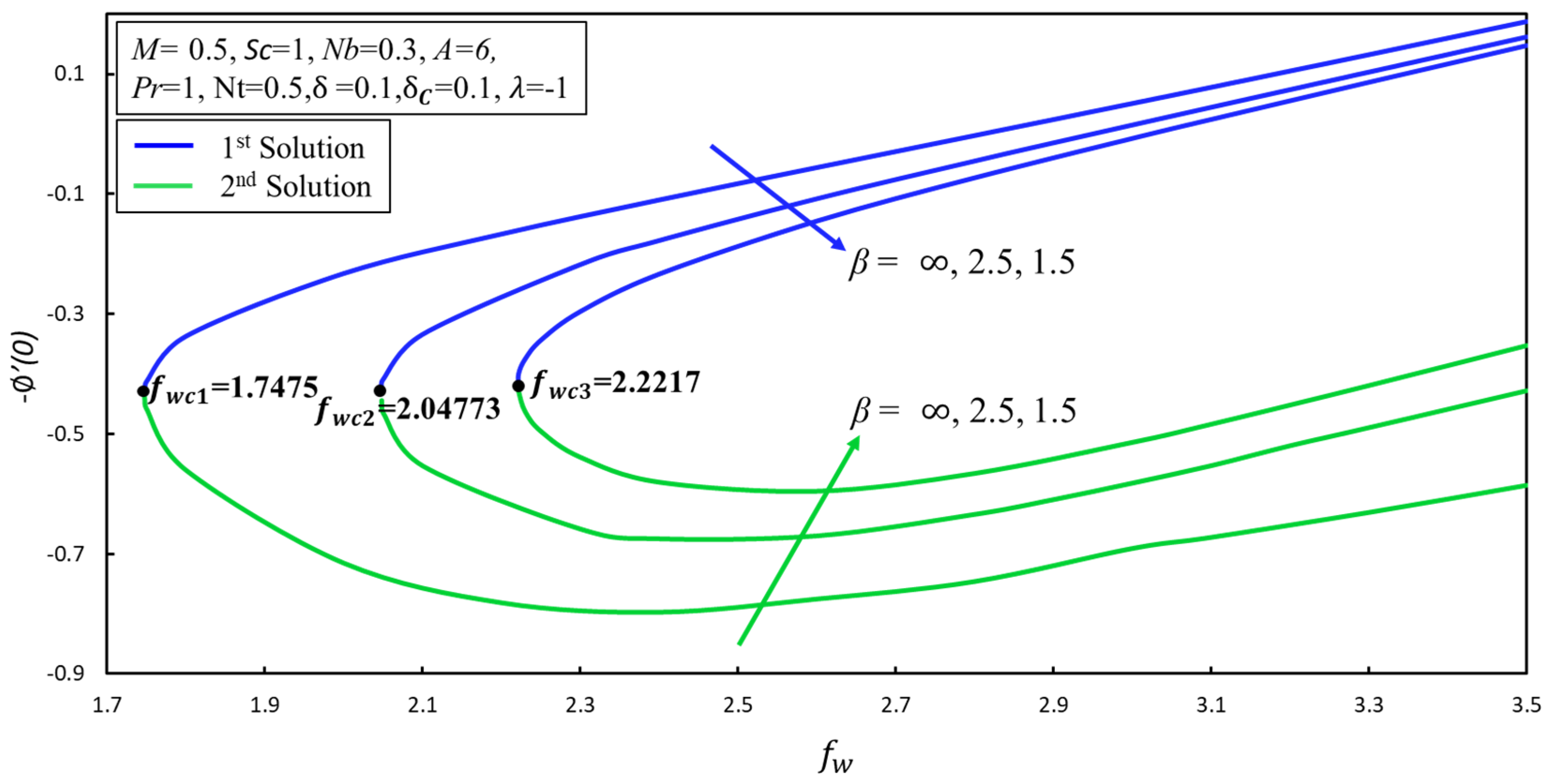
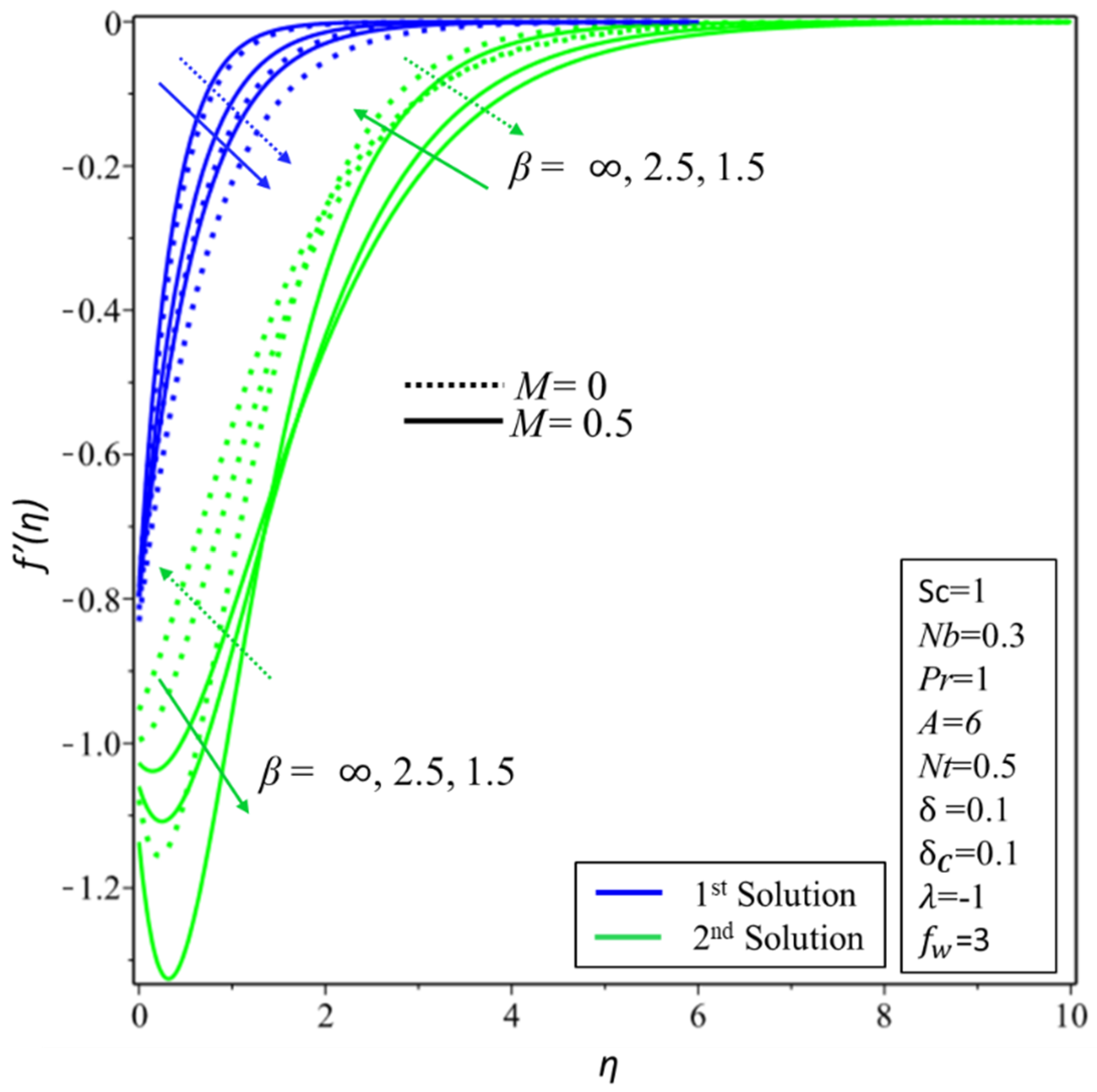
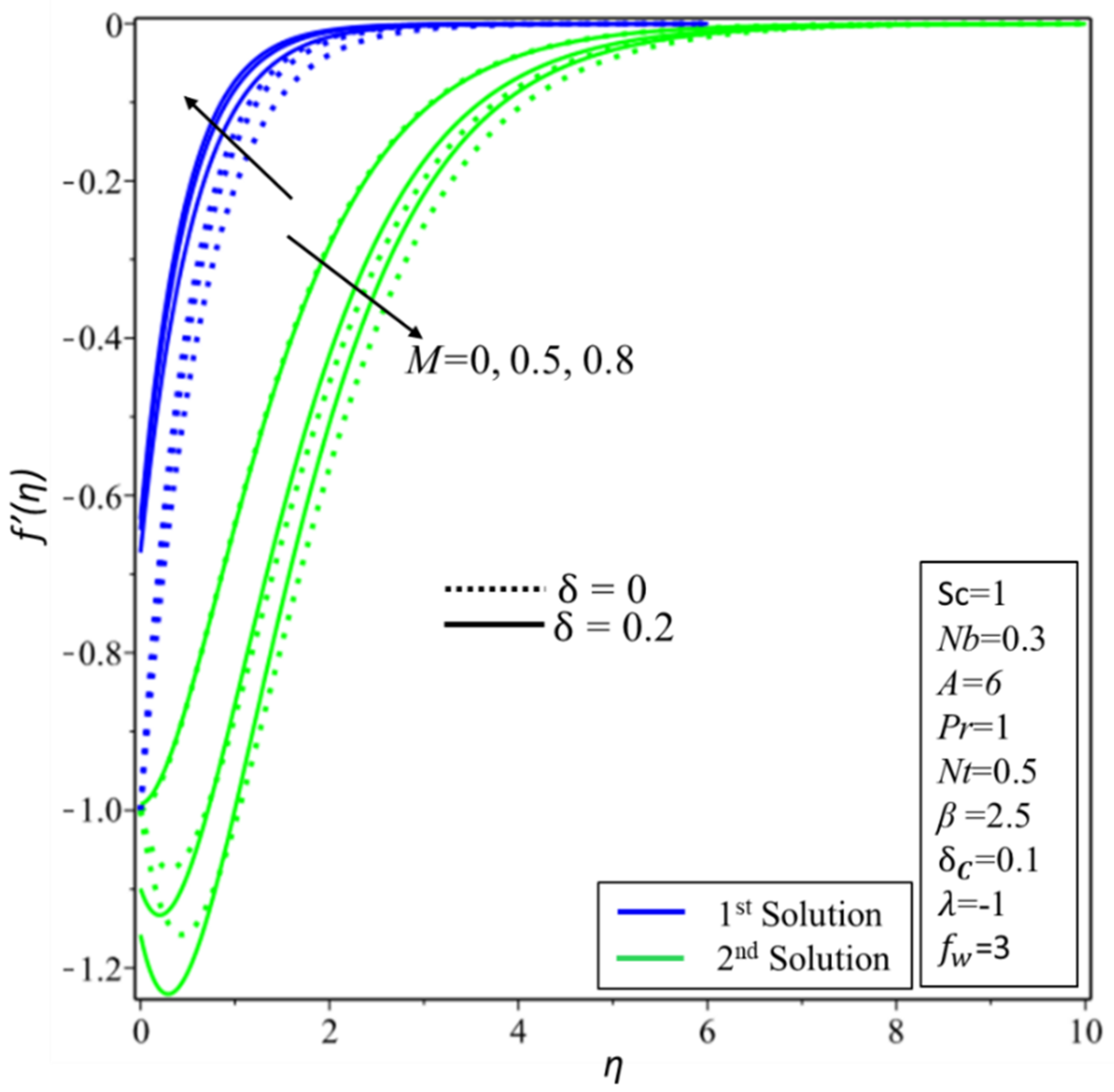
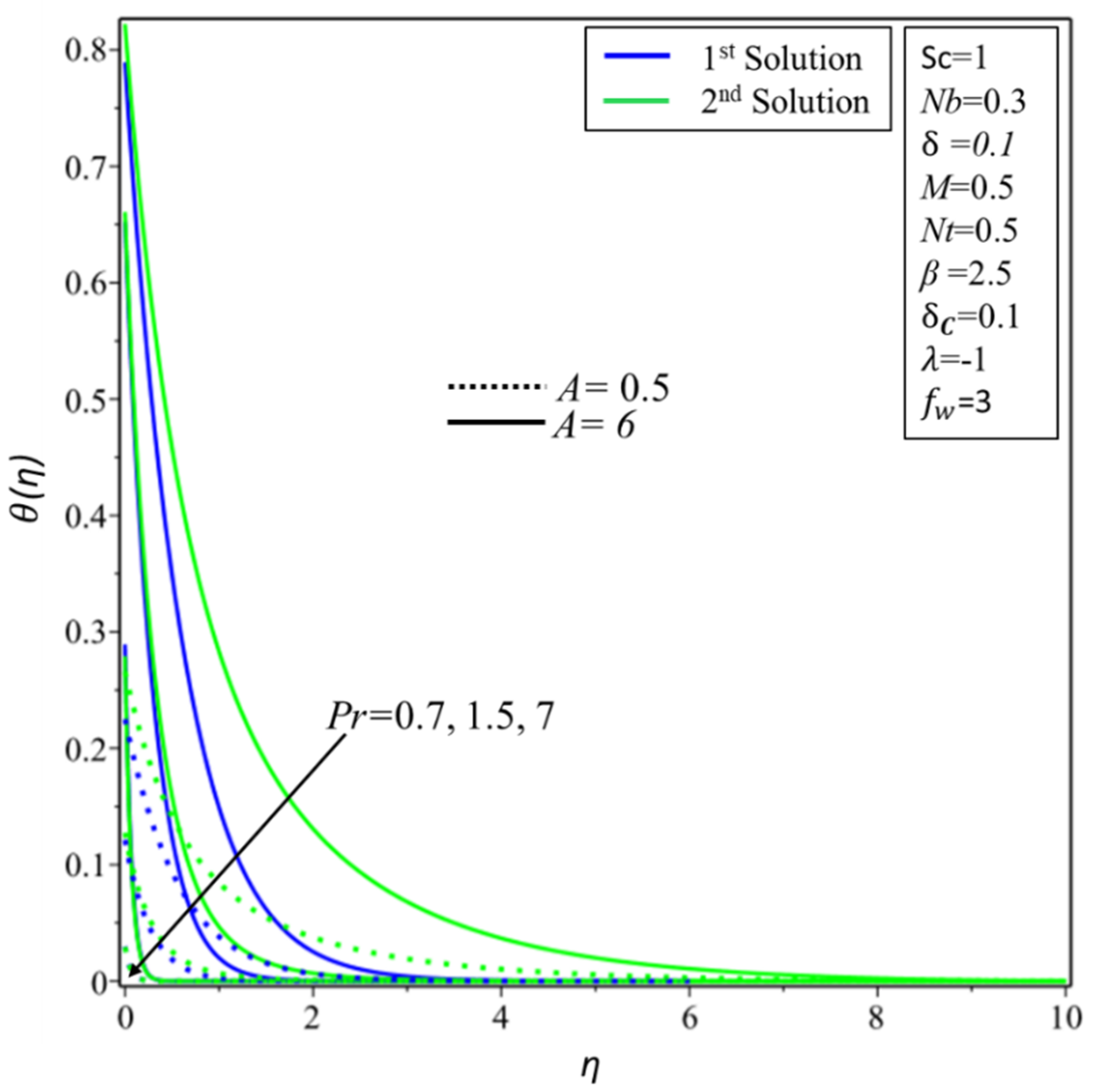
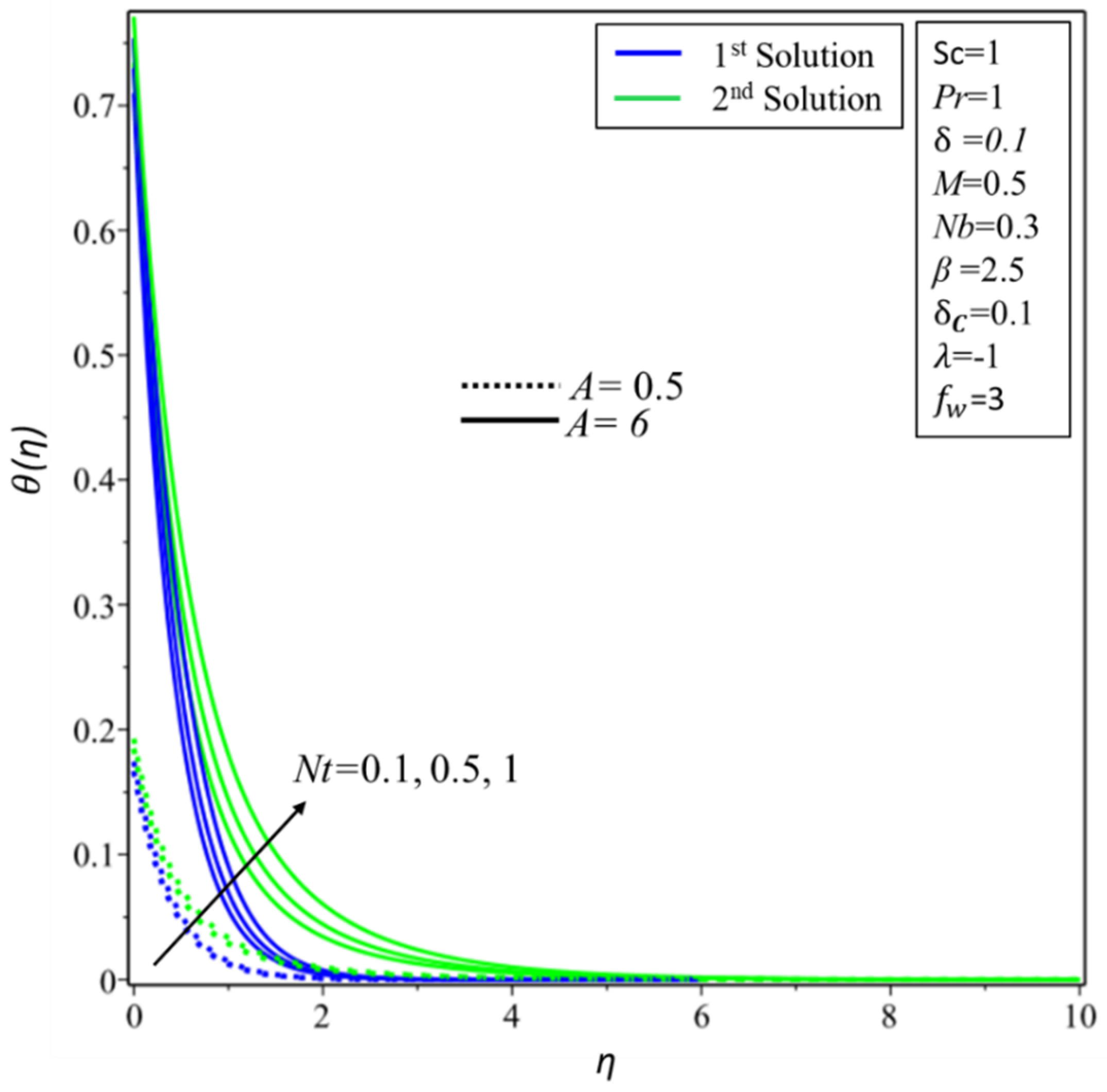
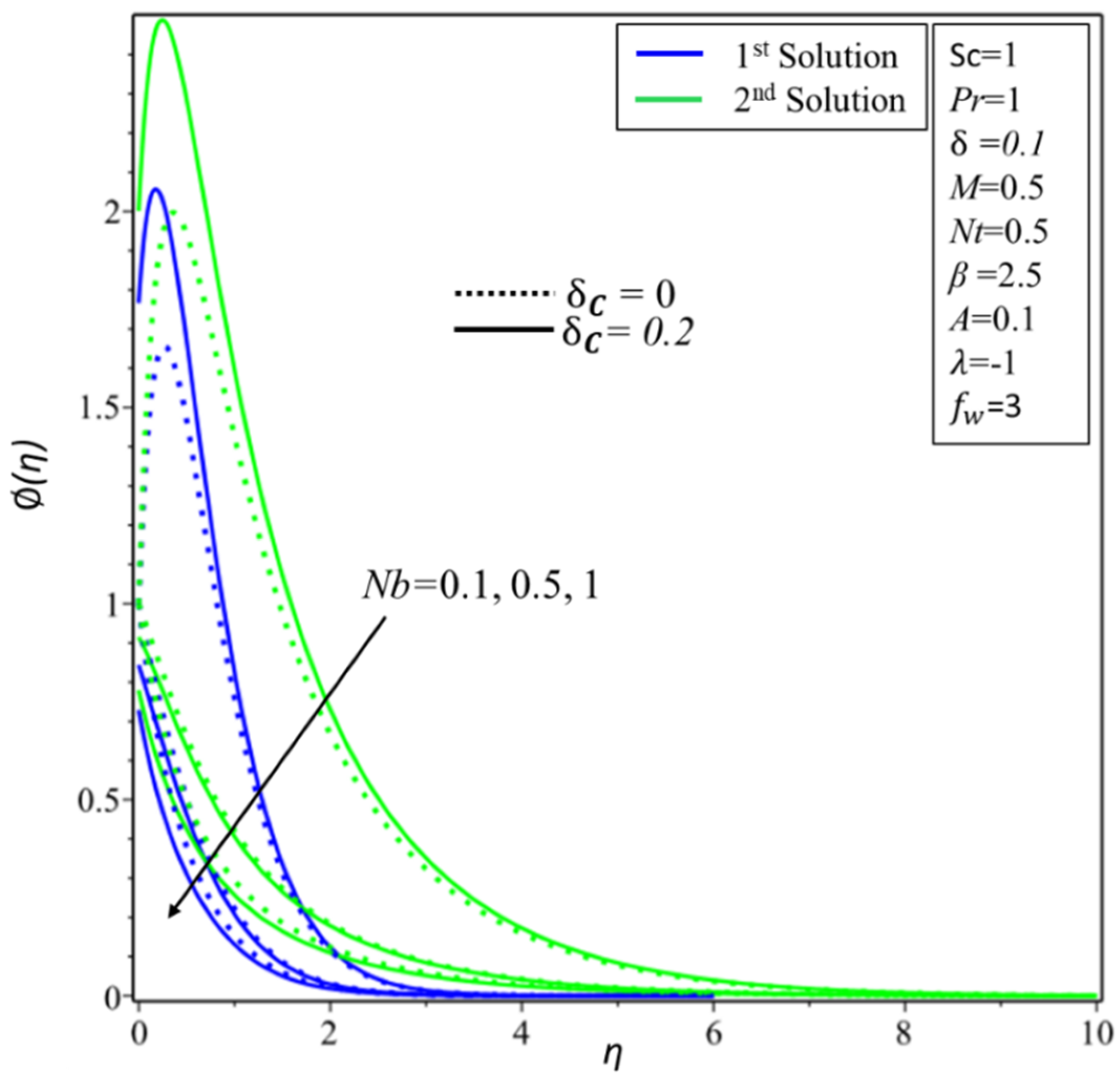
5. Result and Discussion
6. Conclusion Remarks
- For both surfaces, there are dual solutions;
- For the stable solution, the velocity profile decreases for higher values of Casson parameter and the magnetic field ;
- With a rise in the intensity of the convection parameter , the thermal boundary layer is enhanced. Yet, the Prandtl number has the inverse relationship with the temperature profile in both solutions.
- Stability analysis reveals that an unstable (/stable) solution is a second (/first) solution.
- Dual solutions vary, and no solution depends on the parameters involved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| u, v | Velocity components | Biot number | |
| T | Temperature | Dimensionless velocity | |
| Reference temperature | Local Reynolds number | ||
| Temperature of the hot fluid below the surface | Skin friction coefficient | ||
| Ambient temperature | Local Nusselt number | ||
| Casson parameter | Injunction/suction parameter | ||
| C | Concentration | Convective heat transfer coefficient | |
| Reference concentration | Velocity of surface | ||
| Ambient concentration | γ1 | Smallest eigen value | |
| B | Magnetic field | Stability transformed variable | |
| M | Hartmann number | Stretching/shrinking parameter | |
| Pr | Prandtl number | Stream function | |
| Brownian diffusion | A constant | ||
| Thermophoretic diffusion | Velocity slip condition | ||
| Suction/injection velocity | Electrical conductivity | ||
| Local Sherwood number | Thermal buoyancy parameter | ||
| Thermal conductivity of the nanofluid | |||
| Brownian motion parameter | Unknown eigenvalue | ||
| Thermophoresis parameter | Transformed variable | ||
| Schmidt number | Thermal diffusivity | ||
| Velocity slip factor | Slip factor of velocity | ||
| Concentration condition | Slip factor of concentration | ||
| Variable concentration at the sheet | Dimensionless temperature | ||
| Heat capacity of the nanofluid and the effective heat capacity of the nanoparticle material | Dimensionless concentration |
References
- Li, Z.; Barnoon, P.; Toghraie, D.; Dehkordi, R.B.; Afrand, M. Mixed convection of non-Newtonian nanofluid in an H-shaped cavity with cooler and heater cylinders filled by a porous material: Two phase approach. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2666–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabpour, A.; Karimipour, A.; Toghraie, D.; Akbari, O.A. Investigation into the effects of slip boundary condition on nanofluid flow in a double-layer microchannel. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 2975–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnoon, P.; Toghraie, D. Numerical investigation of laminar flow and heat transfer of non-Newtonian nanofluid within a porous medium. Powder Technol. 2018, 325, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, S.; Asghar, S.; Anjum, H.J.; Ehsan, T. Analysis of Hartmann boundary layer peristaltic flow of Jeffrey fluid: Quantitative and qualitative approaches. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2019, 76, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I. Steady incompressible magnetohydrodynamics Casson boundary layer flow past a permeable vertical and exponentially shrinking sheet: A stability analysis. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2019, 48, 3538–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I. Mathematical analysis of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) flow of micropolar nanofluid under buoyancy effects past a vertical shrinking surface: Dual solutions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dero, S.; Rohni, A.M.; Saaban, A. MHD micropolar nanofluid flow over an exponentially stretching/shrinking surface: Triple solutions. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2019, 56, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Sawada, T. Numerical study on the flow of a non-Newtonian fluid through an axisymmetric stenosis. J. Biomech. Eng. 1988, 110, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Hayat, T.; Pop, I.; Aziz, A. Unsteady boundary layer flow of a Casson fluid due to an impulsively started moving flat plate. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2011, 40, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.; Haq, R.U.; Lee, C. MHD flow of a Casson fluid over an exponentially shrinking sheet. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, M.; Khan, H.; Khan, O. Slip analysis at fluid-solid interface in MHD squeezing flow of casson fluid through porous medium. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Dero, S.; Khan, I. Linear stability analysis of MHD flow of micropolar fluid with thermal radiation and convective boundary condition: Exact solution. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2020, 49, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniali, O.A.; Toghraie, D.; Eftekhari, S.A. Thermo-hydraulic and economic optimization of Iranol refinery oil heat exchanger with Copper oxide nanoparticles using MOMBO. Phys. A:Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 540, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Ullah, I.; Waqas, M.; Alsaedi, A. Attributes of Activation Energy and Exponential Based Heat Source in Flow of Carreau Fluid with Cross-Diffusion Effects. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 2019, 44, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabood, F.; Das, K. Outlining the impact of melting on MHD Casson fluid flow past a stretching sheet in a porous medium with radiation. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagendra, N.; Amanulla, C.H.; Reddy, M.S.; Prasad, V.R. Hydromagnetic Flow of Heat and Mass Transfer in a Nano Williamson Fluid Past a Vertical Plate with Thermal and Momentum Slip Effects: Numerical Study. Nonlinear Eng. 2019, 8, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Kumar, D.; Devakar, M. Electrokinetically modulated flow of couple stress magneto-nanofluids in a microfluidic channel. Heat Transf. Asian Res. 2019, 48, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbasifar, B.; Akbari, M.; Toghraie, D. Mixed convection of Water-Aluminum oxide nanofluid in an inclined lid-driven cavity containing a hot elliptical centric cylinder. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 116, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, B.B. Magnetohydrodynamic-hypersonic flow past a blunt body. J. Aerosp. Sci. 1958, 25, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- William, B.B. The stagnation-point boundary layer in the presence of an applied magnetic field. J. Aerosp. Sci. 1961, 28, 610–611. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, T.E.; Hones, E.W.; Bame, S.J.; Asbridge, J.R. The magnetospheric boundary layer: Site of plasma, momentum and energy transfer from the magnetosheath into the magnetosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1976, 3, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A. Viscous and Joule Heating Effects on MHD Free Convection Flow with Variable Plate Temperature (No. IC--90/265); International Centre for Theoretical Physics: Trieste, Italy, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K.V.; Vaidya, H.; Makinde, O.D.; Setty, B.S. MHD Mixed Convective Flow of Casson Nanofluid over a Slender Rotating Disk with Source/Sink and Partial Slip Effects. Defect Diffus. Forum 2016, 392, 92–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghraie, D.; Abdollah, M.M.D.; Pourfattah, F.; Akbari, O.A.; Ruhani, B. Numerical investigation of flow and heat transfer characteristics in smooth, sinusoidal and zigzag-shaped microchannel with and without nanofluid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, R.; Arasteh, H.; Toghraie, D.; Motaharpour, S.H.; Keshmiri, A.; Afrand, M. Heat transfer enhancement of Water-Al2O3 nanofluid in an oval channel equipped with two rows of twisted conical strip inserts in various directions: A two-phase approach. Comput. Math. Appl. 2019, 79, 2203–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiadis, B.C. Boundary-layer behavior on continuous solid surfaces: I. Boundary-layer equations for two-dimensional and axisymmetric flow. Aiche J. 1961, 7, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, L.J. Flow past a stretching plate. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 1970, 21, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.S.; Gupta, A.S. Heat and mass transfer on a stretching sheet with suction or blowing. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1977, 55, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubka, L.J.; Bobba, K.M. Heat transfer characteristics of a continuous stretching surface with variable temperature. ASME J. Heat Transf. 1985, 107, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.I.; Aarseth, J.B.; Dandapat, B.S. Heat transfer in a liquid film on an unsteady stretching surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidman, P.D.; Kubitschek, D.G.; Davis, A.M.J. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transport. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1986, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roşca, A.V.; Pop, I. Flow and heat transfer over a vertical permeable stretching/shrinking sheet with a second order slip. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 60, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rosca, A.V.; Pop, I. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a permeable exponentially shrinking surface with convective boundary condition using Buongiorno’s model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2015, 25, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafaa, M.; Hayat, T.; Obaidat, S. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid over an exponentially stretching sheet with convective boundary conditions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2013, 23, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavčič, M.; Wang, C. Viscous flow due to a shrinking sheet. Q. Appl. Math. 2006, 64, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhang, J. Closed-form exact solutions of MHD viscous flow over a shrinking sheet. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 2853–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K. Boundary layer flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2011, 28, 074701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| [38] | [37] | Present Results | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 1.28181 | 0.25374 | 0.37525 | 1.28180857 | 0.25373483 | 0.37525393 | 1.28180857 | 0.25373483 | 0.37525393 |
| 0.2 | 1.28181 | 0.25192 | 0.20423 | 1.28180857 | 0.25191722 | 0.20422841 | 1.28180857 | 0.25191726 | 0.20422841 |
| 0.3 | 1.28181 | 0.25008 | 0.03662 | 1.28180857 | 0.25007701 | 0.03660736 | 1.28180857 | 0.25007701 | 0.03660735 |
| 0.4 | 1.28181 | 0.24821 | −0.12757 | 1.28180857 | 0.24821431 | −0.12757046 | 1.28180857 | 0.24821430 | −0.12757045 |
| 0.5 | 1.28181 | 0.24633 | −0.28826 | 1.28180857 | 0.24632922 | −0.28826784 | 1.28180857 | 0.24632921 | −0.28826784 |
| 1st Solution | 2nd Solution | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 2.1 | 0.17016 | −0.15422 |
| −1 | 2.05 | 0.10934 | −0.04286 |
| −1 | 2.048 | 0.03401 | −0.00966 |
| 1 | 2.1 | 1.83592 | −2.63523 |
| −1.03 | 2.1 | 0.07409 | −0.08139 |
| −1.035 | 2.1 | 0.02781 | −0.03149 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Abdo, H.S. Stability Analysis of the Magnetized Casson Nanofluid Propagating through an Exponentially Shrinking/Stretching Plate: Dual Solutions. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071162
Lund LA, Omar Z, Khan I, Sherif E-SM, Abdo HS. Stability Analysis of the Magnetized Casson Nanofluid Propagating through an Exponentially Shrinking/Stretching Plate: Dual Solutions. Symmetry. 2020; 12(7):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071162
Chicago/Turabian StyleLund, Liaquat Ali, Zurni Omar, Ilyas Khan, El-Sayed M. Sherif, and Hany S. Abdo. 2020. "Stability Analysis of the Magnetized Casson Nanofluid Propagating through an Exponentially Shrinking/Stretching Plate: Dual Solutions" Symmetry 12, no. 7: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071162
APA StyleLund, L. A., Omar, Z., Khan, I., Sherif, E.-S. M., & Abdo, H. S. (2020). Stability Analysis of the Magnetized Casson Nanofluid Propagating through an Exponentially Shrinking/Stretching Plate: Dual Solutions. Symmetry, 12(7), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071162








