Abstract
Micromixers are significant segments inside miniaturized scale biomedical frameworks. Numerical investigation of the effects of galloping cylinder characteristics inside a microchannel Newtonian, incompressible fluid in nonstationary condition is performed. Governing equations of the system include the continuity equation, and Navier–Stokes equations are solved within a moving mesh domain. The symmetry of laminar entering the channel is broken by the self-sustained motion of the cylinder. A parameter study on the amplitude and frequency of passive moving cylinder on the mixing of tiny particles in the fluid is performed. The results show a significant increase to the index of mixing uses of the galloping body in biomedical frameworks in the course of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) devices.
1. Introduction
Micromixers are significant segments inside miniaturized scale biomedical frameworks [1]. The use of micro-magneto-fluidics in microfluidic systems is reviewed by Yang et al. [1]. A literature search shows a thorough survey of the fundamental innovative uses of micromixers in biomedical microreactors in recent years [2]. The biomedical uses of micromixers are then portrayed concerning their use especially for (1) test fixation, (2) substance combination, (3) compound response, (4) organic examination, (5) refinement and extraction, (6) polymerization, and (7) emulsion/bead procedures and micro-distillation [3].
Microfluidic gadgets have significantly affected the field of biomedical diagnostics, and are generally used all through the medication advancement, tranquilizer conveyance, and bio-therapeutic research businesses for immobilized enzyme characterization division [4]. The minor size of the stream directions in microfluidic frameworks expands the area-to-volume proportion, which is accordingly beneficial in some engineering such as for sulfur dioxide detection [5]. Be that as it may, the low Reynolds number routines created in such microchannels result in the laminar stream, and subsequently species blending happens for the most part because of dissemination, which is an inalienably moderate procedure [6]. Pulsatile micromixing research done by Li and Kim showed the case comprehensively [6], since productive micro-fluidic blending plans are required to expand the throughput of biomedical micro-systems and make conceivable the advancement of miniaturized scale all-out investigation frameworks for detecting particle population in microfluidic device [7] and lab on a chip (LOC) devices [8].
Mixed microfluidic chips as a platform for glucose assays [9], carcinoembryonic antigen detection [10], and mixer of blood plasma [11] are commonly based on the chaotic motion within the liquid irregularly causing random variation of velocity and pressure in time and space. A riotous shift in weather conditions can be produced by blending the stream for blood plasma mixing [12], and this is exceptionally successful at low Reynolds numbers [12] because of the subsequent parting, extending, collapsing, and separating of the species streams [13]. In any case, other than a confusing shift in weather conditions, sub-atomic dissemination additionally assumes a key job in achieving mass movement in micromixers [14] where the role of catalysis is important. In fact, in-stream routines where the stream is carefully laminar, species blending happens for the most part because of atomic dispersion between layers of various fixations [15].
Fixation angles of diffusible substances assume a significant job in organic example development and angiogenesis [16]. In any case, notwithstanding the significance of fixation angles in science, moderate couplings of strategies are accessible for creating and keeping up inclinations in low liquid stream rate routines. Pessoa et al. [17] built a microfluidic contribution, in which diffusive blending was upgraded by a disordered shift in weather condition impact created by a lopsidedness in the application of the micromixer [18]. Blending is an exceptionally significant unit task in the chemical procedure, and subsequently, the scholastic investigation of blending in synthetic reactors is of extraordinary simple importance [19]. Smaller-scale blending works at the same time with full-scale blending in the substance reactors used in procedural businesses and assumes a key job in accomplishing the ideal selectivity concerning the ideal items [20]. Micromixing measurement by the chemical probe in homogeneous and isotropic turbulence [20], mixing performance [21], and combined E-model and CFD is done by Duan et al. [22]. Their result shows that CFD plays an important role in mixing analysis. The legitimacy of the numerical model was approved using trial information announced in the literature. The recreation results demonstrated that the micromixing execution and response are performed by CFD method in the Microreactor [23] and four-way micromixers [24]. The effect of the magnetic force was investigated by Jamalabadi et al. [25,26,27,28]. The study of [28] is useful for recent advances and pharmacology advancements in blood flow [29]. Dissimilar to the continuum portrayal of particulate frameworks in a Eulerian approach, the Lagrangian approach sees singular particles and tracks them each time step. The notable Lagrangian approach applied broadly in recreations of granular materials is the Discrete Element Method (DEM) that is used to construct static packs, or to break down the elements of molecule blends. The complex components are characterized with no cover between the components. It is contended in that paper that it is not at all like FEM as a continuum approach, and warm discrete component technique as a discrete methodology. The CFD can depict both continuum and discrete perspectives in the issue. At the end of the day, this model takes after the FEM, where the temperature step changes at contact interfaces are remembered for the model, as well [30].
Development of high-performance mixers has been performed by Domínguez and Gamse [31]. The study shows that a staggered herringbone micromixer attains a trapping efficiency around 50% higher than that obtained by a smooth and straight channel [32]. Zhang et al. [33] showed that Koch fractal curve induces the role of diffusion intensity. Santana et al. [34] performed optimization of a micromixer with triangular baffles for chemical processes in mili devices. A high mixing index was observed with more than 90% of conversion. Experimentation and modeling was performed by Adrover et al. [35]. The summary of the vortex type micromixer (passive) for various applications is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summery of vortex type micromixer (Passive) for various applications.
Considering all the above, the use of galloping effect in micromixers was not addressed previously. The aim of the current research is to establish galloping mixer design parameters in a transient incompressible flow over moving circular cylinder obstructions on the mixing model of the particle species. Based on that, a novel micromixer design is proposed using passive control in the mixing.
2. Governing Equations
The progression of liquid behind a dull body—for example, a car—is a complex problem because of the shaky streams. Conversely, the disturbance in the flimsy limit layers beside the streamlined assemblages of airplane and fish make unsettling influences of the stream just powerless. A special case of this happens in a moderate stream when whirlpools compose. A circulation road appears with an anticipated recurrence and includes whirlpools from opposing sides. Ordinary models of this phenomenon incorporate singing phone wires and vehicle radio reception apparatus. From a design outlook, it is imperative to foresee the recurrence of oscillating different liquid rates and in this way maintain a strategic distance from unfortunate strong vortexes. To better understand such impacts, by using a winding top piece of smoke, the subsequent variety perfection restricts the helpful impedance of the circulation components.
To show these concentrate impacts, accompanying analyses were undertaken of precarious stream-back of a chamber set in a channel point-approaching liquid. With a symmetric delta speed profile, the stream needs some sort of asymmetry to trigger vortex generation. This can be accomplished by setting the chamber with a little balance from the focal point of the stream. For this situation, unstructured work is used, and the little asymmetry in the work is sufficient to trigger the vortex creation. The reenactment time is vital for an occasional stream example to show up, but it is hard to anticipate. However, the stream remains not completely violent. The recurrence and abundance of motions are steady highlights, yet stream subtleties are incredibly sensitive to change.
The geometry of current is shown in Figure 1. In Cartesian coordinates the continuity is:
where is the mesh motion velocity vector in the fluid domain and is fluid vector. The Eulerian description is obtained by setting . Furthermore, the Lagrangian description is obtained by setting . The momentum equation is:
where p is the fluid pressure and the material constants are presented in Table 2. The attained velocity field is used to calculate diluted species concentration transport field using a convectional equation. The mass transfer governing equation is:
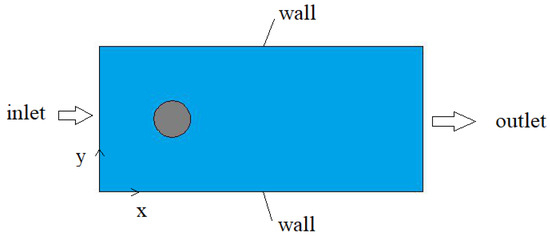
Figure 1.
Problem definition.

Table 2.
Fluid properties.
The diffusion coefficient of the water is 10−9 m2/s. The particle motion in x-direction is modeled by:
The particle motion in y-direction is modeled by:
where the parameter a is defined by
and relative velocity definition is:
here [m]. The boundary conditions are:
- Inlet velocitywhere is average velocity and
- The no-slip boundary at the bottom plate is:
- The no-slip boundary at top plate is:
- Inlet concentrationHere the inlet concentration is Cin = 1 mol/L.
- No flux at bottom plate
- No flux at top plate
- Outlet boundaryi.e., pressure is 0 Pa at the outlet of the microchannel and
- The moving wall boundary on cylinder surface
Before ascertaining the time-differing powers on the chamber, one can approve the technique for calculation. Therefore, one can discover and address basic blunders and mix-ups before the final time-dependent recreation and significant mixing time. The separation generates first-request polynomials when second-request components are used for the speed field. A far superior methodology is to use a couple of response power administrators to process the integrals of the gooey powers, practically identical to second-arrange exact integrals of the thick powers. An elective methodology is to use a couple of frail requirement factors to authorize the no-slip condition. Ideally, the response power administrator is preferred to feeble limitations when processing integrals of response powers or motions in postprocessing. The Reynolds number is the non-dimensional parameter of projected area (product of thickness and height of the geometry) used to determine the flow regime, which is given as:
The of square microchannel is calculated as follows:
where W is the width of the channel.
The Schmidt number is defined by:
Lewis number is defined by:
Mixing index (I) at any cross-section can be calculated by the function of concentration of fully mixed () and unmixed state (), with the maximum standard deviation of concentration of particular species at that cross-section (). Therefore, mixing index parameter is:
3. Results and Discussion
Many studies have been undertaken in similar papers such as [43,44,45,46,47,48]. The cylinder moves under the influence of the steady flow that was simulated, not due to externally applied force. When the viscous and pressure force is applied to the cylinder, it makes the motion a self-sustained motion. The results of the study are discussed in this section. The benchmark of [43] by Turek and Hronis used for the validation of commercial software is used here as well as [43,44,45]. A grid study is revealed in Table 3. The comparison of various results with the current study is discussed in Table 4. Our occurrence of an article moving around inside a region is actually a breaking-point regard issue. All cutoff points have known movements, and these breaking-point expulsions can be used to describe the mutilation of the work inside the two zones.

Table 3.
Grid-independence study.

Table 4.
Validation with another benchmark.
There are four approaches for calculating the distortion of the work inside each space. Here, we will address only the least troublesome case, implied as a Laplace smoothing, and display how this strategy is sufficient for most cases. The Laplace smoothing approach understands the inadequate differential condition inside the space. Since the migrations at all cutoff points are known, this is a commonly introduced issue, and theoretically, the response for this condition will give us the misshaping of the work. In any case, before long, we may run into circumstances where the prepared distortion field is not particularly significant. This is sketched out in the figure below, which shows the primary work on the main space, and the distorted work, as the part is moved along the slanting. Watch the highlighted territory and note that the work becomes uncommonly ruined around the moving part edges, especially at sharp corners. This high bowing shields the model from comprehending the above condition past a particular proportion of mutilation.
Spatial pressure distribution for t = 0 and t = 27 seconds are shown in Figure 2. At the initial time, the pressure constant lines are perpendicular to fluid flow. At the final time, the maximum pressure is 0.05 Pa while the pressure is 0 Pa at the outlet. The pressure constant lines are perpendicular to the surfaces of the channel. As the speed increases, with the Reynolds number augmentation, the liquids experience short contact times, and after that, the sub-atomic dissemination turns out to be less powerful in the blending procedure. Nevertheless, the speed increase advances unsettling influences on the smooth movement, upgrading the compound species association, counterbalancing the proficiency loss of dispersion component. After that, the shift in weather conditions prevalence zone was watched. In Figure 6, this shift in weather conditions zone advanced an expansion in the blending list up to a limit of 0.99 for all channel statures.
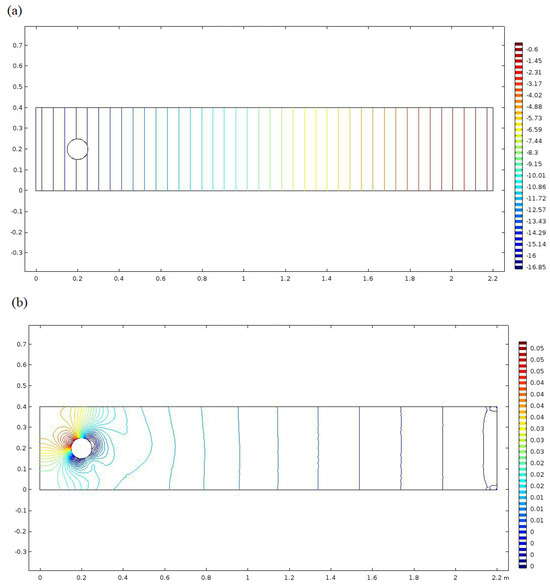
Figure 2.
Pressure distribution at (a) initial and (b) t = 27 (s).
Velocity magnitude and particle distribution at t = 14 (s) and t = 27 (s) is shown in Figure 3. Figure 4 demonstrates the convergence of the micromixer low frequency, and the shading legend demonstrates that the velocity of the fluids changes from 0 to 1.6 m/s. At the point when the liquids simply stream, liquids circulate. At the point when the liquids enter the blended region framed by the galloping, two liquids produce a huge diversion. The phenomena expand the contact territory of the two liquids in microchannel and improves the proficiency of atomic dissemination. Because of the low speed of the liquids, the liquids are blended, streaming huge regions. At the point when is , the living arrangement time that the liquids remain excessively riotous is more fragile; the ideal blending cannot be accomplished only by expanding the contact region of the two liquids. In any case, the avoidance phenomenon is useful to improve the presentation of the micromixer. At low Reynolds number, the solid disorganized convection and huge diversion of the liquids brought about by the bewilders.
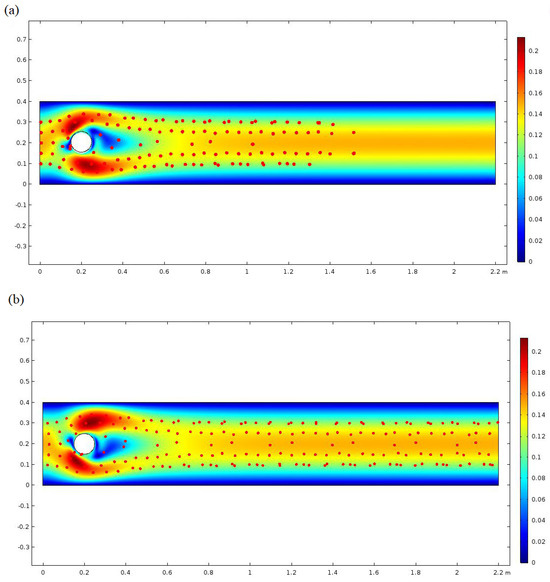
Figure 3.
Velocity magnitude and particle distribution for lower frequency at (a) t = 14 (s) and (b) t = 27 (s).
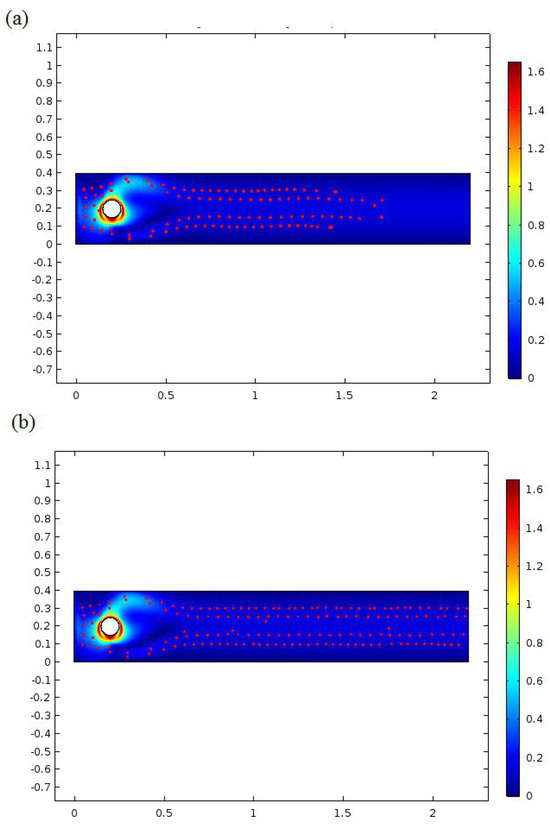
Figure 4.
Velocity magnitude and particle distribution for higher frequency at (a) t = 14 (s) and (b) t = 27 (s).
Essentially improve the blending execution, and the liquids are near finished blending. At the middle time, the von Karman vortexes are formed but the particles do not mix yet. At the final time, the von Karman vortexes are formed, and the particles are mixed. The cylinder moves under the influence of the steady flow that is simulated, not due to externally applied force. When the viscous and pressure force is applied on cylinder, it makes a motion as a self-sustained motion. As shown, the maximum diversion of particles is found at the von Karman vortexes, while, in the back of the cylinder, rare particles exist. The regime extends to the end of the microchannel while the rare number of particles are shown in the mid-line of the channel. These phenomena can be used for bead separation in microchannels. Total normal force versus time applied to the moving cylinder is illustrated in Figure 5.
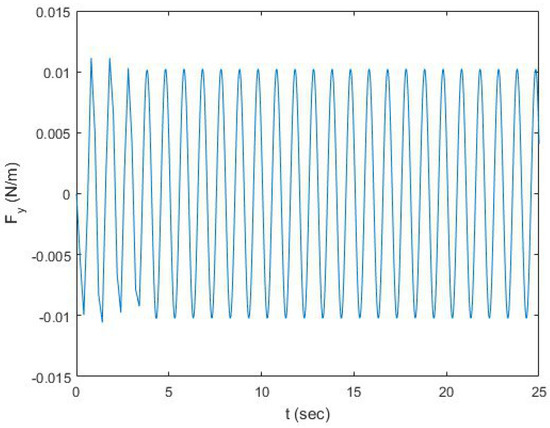
Figure 5.
Total normal force versus time applied on the moving cylinder.
Particle concentration at t = 3 (s) and t = 7 (s) is shown in Figure 6. Notwithstanding the stream unsettling influences, the blending effectiveness upgrade is also an outcome from the nearness of roundabout impediments in the blending channel. The round impediments alter the stream heading. That heading converts the circulation arrangement, improving the blending proficiency. The vortex age in the galloping is the reliant speed. In the primary distinction, galloping configuration age as of now begins at t = 7, as shown in Figure 6. As seen in Figure 7, the mixing performance of the system is studied as a function of amplitude of vibration and natural frequency of the galloping. Figure 7 shows the index of mixing for a galloping micromixer under various conditions. As shown, the galloping micromixer presents a higher mixing index than the vortex micromixer. To look at and dissect the blending productivity of the galloping micromixers, we establish their blending effectiveness using reproduction examination. Figure 7 shows the consequences of the blending effectiveness of two Koch fractal bewilders, distinctive redirection points, and various separations of contiguous two frequencies at an amplitude of 0.01, 0.5, and 0.1. As shown by the increase of amplitude and frequency of the galloping motion, the mixing index is increased.
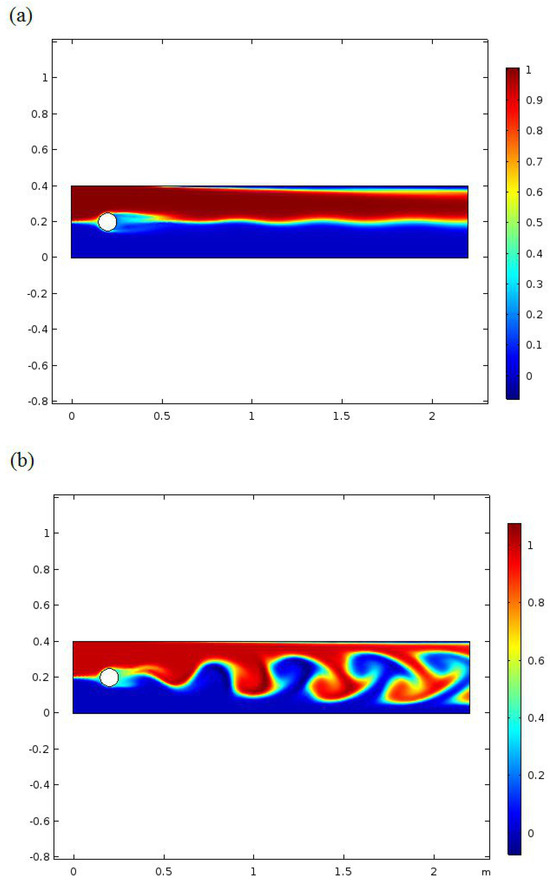
Figure 6.
Particle concentration at (a) t = 3(s) and (b) t = 7 (s).
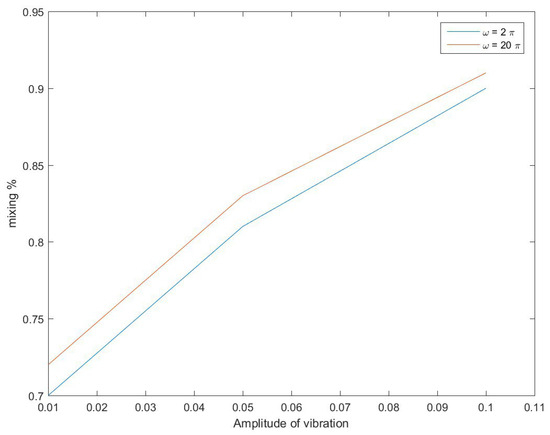
Figure 7.
Index of mixing for galloping micromixer under various conditions.
4. Conclusions
Numerical investigation of the effects of galloping cylinder characteristics inside a Newtonian microchannel, incompressible fluid in nonstationary condition was examined. Governing equations of the system include the continuity equation, and Navier–Stokes equations were solved within a moving mesh domain. The symmetry of laminar that entered the channel is broken by the self-sustained motion of the cylinder. A parameter study on the amplitude and frequency of a passive moving cylinder on the mixing of tiny particles in fluid was performed. Concentration mixing, bio-reactors, droplet formation, and the design of efficient micromixers were examined. A parameter study on the amplitude and frequency of the passive moving cylinder and on the mixing of tiny particles in a fluid is performed. The results show a significant increase in the index of mixing uses of the galloping body in biomedical frameworks during MEMS devices. The mixing performance of the system is studied as a function of amplitude of vibration and natural frequency of the galloping.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, and Writing—original draft were done by M.Y.A.J. and Z.A. worked on Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DEM | Discrete Element Method |
| MEMS | Micro-electromechanical systems |
| MHD | Magneto Hydro Dynamics |
| CFD | computational fluid dynamics |
Nomenclature
| D | diffusion coefficient | m2/s |
| inlet concentration | K | |
| u | velocity component in the x direction | m/s |
| v | velocity component in the y direction | m/s |
Greek Symbol
| standard deviation | ||
| fluid density | kg/m3 | |
| viscosity of the fluid | Pa·s |
References
- Yang, R.J.; Hou, H.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M. Micro-magnetofluidics in microfluidic systems: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Lei, Q.; Shen, R.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L. The continuous kilogram-scale process for the synthesis of 2,4,5-trifluorobromobenzene via Gattermann reaction using microreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.J.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Hou, H.H.; Fu, L.M. Heat transfer A comprehensive review of micro-distillation method. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, K.; Szumski, M.; Buszewski, B. Microfluidic reactors with immobilized enzymes-Characterization dividing, perspectives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M.; Yang, D.Y. Rapid integrated microfluidic paper-based system for sulfur dioxide detection. Chem. Eng. J 2017, 316, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kim, S. Pulsatile micromixing using water-head-driven microfluidic oscillators. Int. Commun. Heat Transf. 2017, 313, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Floquet, C.F.A.; Sieben, V.J.; MacKay, B.A.; Mostowfi, F. Determination of boron concentration in oil field water with a microfluidic ion exchange resin instrument. Talanta 2016, 154, 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarlucea, B.; Munoz-Berbel, X.; Ortiz, P.; Büttgenbach, S.; Fernández-Sáncheza, C.; Llobera, A. Self-validating lab-on-a-chip for monitoring enzyme-catalyzed biological reactions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 237, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Estala, L.; Gaines, M.; Gomez, F.A. Mixed thread/paper-based microfluidic chips as a platform for glucose assays. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar]
- Anh, N.V.; Trung, H.V.; Tien, B.Q.; Binh, N.H.; Ha, C.H.; Huy, N.L.; Loc, N.T.; Thu, V.T.; Lam, T.D. Development of a PMMA electrochemical microfluidic device for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, J.N.; Liao, H.S.; Li, X.M. Design optimization of capillary-driven micromixer with square-wave microchannel for blood plasma mixing. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.N.; Li, Y.S. Centrifuge-based micromixer with three-dimensional square-wave microchannel for blood plasma mixing. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 2343–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Xuan, J. Factory-on-chip. Modularised microfluidic reactors for continuous mass production of functional materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensaid, S.; Piumetti, M.; Novara, C.; Giorgis, F.; Chiodoni, A.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. Catalytic oxidation of CO and soot over Ce-Zr-Pr mixed oxides synthesized in a multi-inlet vortex reactor: Effect of structural defects on the catalytic activity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, Y.; Faust, R. Micromixing enhanced synthesis of HRPIBs catalyzed by EADC/bis(2-chloroethyl)ether complex. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 27629–27636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, M.; Knauer, A.; Malsch, D.; Csáki, A.; Henkel, T.; Köhler, J.M.; Fritzsche, W. Combination of microfluidic high-throughput production and parameter screening for efficient shaping of gold nanocubes using Dean-flow mixing. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, A.C.S.N.; Sipoli, C.C.; de la Torre, L.G. Effects of diffusion and mixing pattern on microfluidic-assisted synthesis of Chitosan/ATP nanoparticles. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.; Nazar, R. Laminar boundary layer flow along a stretching cylinder. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 36, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, M.; Lamarque, N.; Lebaigue, O.; Plasari, E.; Ducros, F. Micromixing characterisation in rapid mixing devices by chemical methods and LES modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 283, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemenand, T.; della Valle, D.; Habchi, C.; Peerhossaini, H. Micromixing measurement by chemical probe in homogeneous and isotropic turbulence. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Q.; Dang, X.; Li, W.; Lei, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J. Geometrical improvement of inline high shear mixers to intensify micromixing performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.X.; Feng, X.; Yang, C.; Mao, Z.-S. Numerical simulation of micro-mixing in stirred reactors using the engulfment model coupled with CFD. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 140, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, E.; Roberge, D.M.; Macchi, A. Microreactor mixing-unit design for fast liquid–liquid reactions. J. Flow Chem. 2016, 6, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Mohammadi, F.; Basiri, M.; Parsamoghadam, M.A.; Masahi, M.M. Transesterification of soybean oil in four-way micromixers for biodiesel production using a cosolvent. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 64, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalabadi, M.Y.A. Electromagnetohydrodynamic two-phase flow-induced vibrations in vertical heated upward flow. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2019, 6, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalabadi, M.Y.A. EMHD effects on subcooled boiling in a Vertical annulus. Multiph. Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalabadi, M.Y.A.; Park, J.H. Thermal radiation, joule heating, and viscous dissipation effects on MHD forced convection flow with uniform surface temperature. Open J. Fluid Dyn. 2014, 4, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mae, K.; Maki, T.; Hasegawa, I.; Eto, U.; Mizutani, Y.; Honda, N. Development of a new micromixer based on split/recombination for mass production and its application to soap free emulsifier. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 101, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.A.V. The initiation of blood flow and flow induced events in early vascular development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Paul, A.; Taylor, M.D.; Banerjee, R.K. Pulsatile arterial wall-blood flow interaction with wall pre-stress computed using an inverse algorithm. Biomed. Eng. Online 2015, 14, S1–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, C.C.; Gamse, T. Utilization of micro-mixers for supercritical fluid fractionation: Influence of the residence time. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 132, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Fu, L. Recent advances and applications of micromixers. Sensors Actuators Chem. 2018, 259, 677–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Y. Numerical study on stagger Koch fractal baffles micromixer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 133, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, H.S.; Silva, J.L.; Taranto, O.P. Optimization of micromixer with triangular baffles for chemical process in millidevices. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, A.; Varani, G.; Paolicelli, P.; Petralito, S.; Di Muzio, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Tho, I. Experimental and Modeling Study of Drug Release from HPMC-Based Erodible Oral Thin Films. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.M.; Ju, W.J.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, R.J.; Wang, Y.N. Integrated microfluidic array chip and LED photometer system for sulfur dioxide and methanol concentration detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.C.; Zahn, J.D. Droplet enhanced microfluidic-based DNA purification from bacterial lysates via phenol extraction. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.Y.; Hyun, K.A.; Kim, S.I.; Jung, H.I. An integrated microfluidic chip for one-step isolation of circulating tumor cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillo, G.; Deorsola, F.A.; Bensaid, S.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. MoS2 nanoparticle precipitation in turbulent micromixers. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 207–208, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbino, T.A.; Azzoni, A.R.; de la Torre, L.G. Microfluidic devices for continuous production of pDNA/cationic liposome complexes for gene delivery and vaccine therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Lin, H.I.; Wang, J.H.; Shiesh, S.C.; Lee, G.B. An integrated microfluidic system for C-reactive protein measurement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3091–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.X.; Hyun, K.A.; Moon, H.; Sim, T.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Jung, H. Continuous labeling of circulating tumor cells with microbeads using a vortex micromixer for highly selective isolation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turek, S.; Hron, J. Proposal for numerical benchmarking of fluid-structure interaction between an elastic object and laminar incompressible flow. In Fluid-Structure Interaction; Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 53, p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.-B.; Dai, H.; Luo, H.; Doyle, F.; Rousseau, B. Fluid–structure interaction involving large deformations: 3D simulations and applications to biological systems. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 258, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Mittal, R. Benchmarking a coupled immersed-boundary–finite-element solver for large-scale flow-induced deformation. AIAA J. 2012, 50, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadloo, M.S. Numerical Simulation of Compressible Flows by Lattice Boltzmann Method. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A 2018, 75, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Ellahi, R.; Sait, S.M.; Sarafraz, M.M.; Shadloo, M.S.; Waheed, I. Enhancement of heat transfer in peristaltic flow in a permeable channel under induced magnetic field using different CNTs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, F.; Shadloo, M.S.; Hadjadj, A.; Ozbulut, M.; Tofighi, N.; Yildiz, M. Numerical simulations of multi-phase electro-hydrodynamics’ flows using a simple incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).