Spring Effects on Workspace and Stiffness of a Symmetrical Cable-Driven Hybrid Joint
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CDHJ Description and Kinematic Analysis
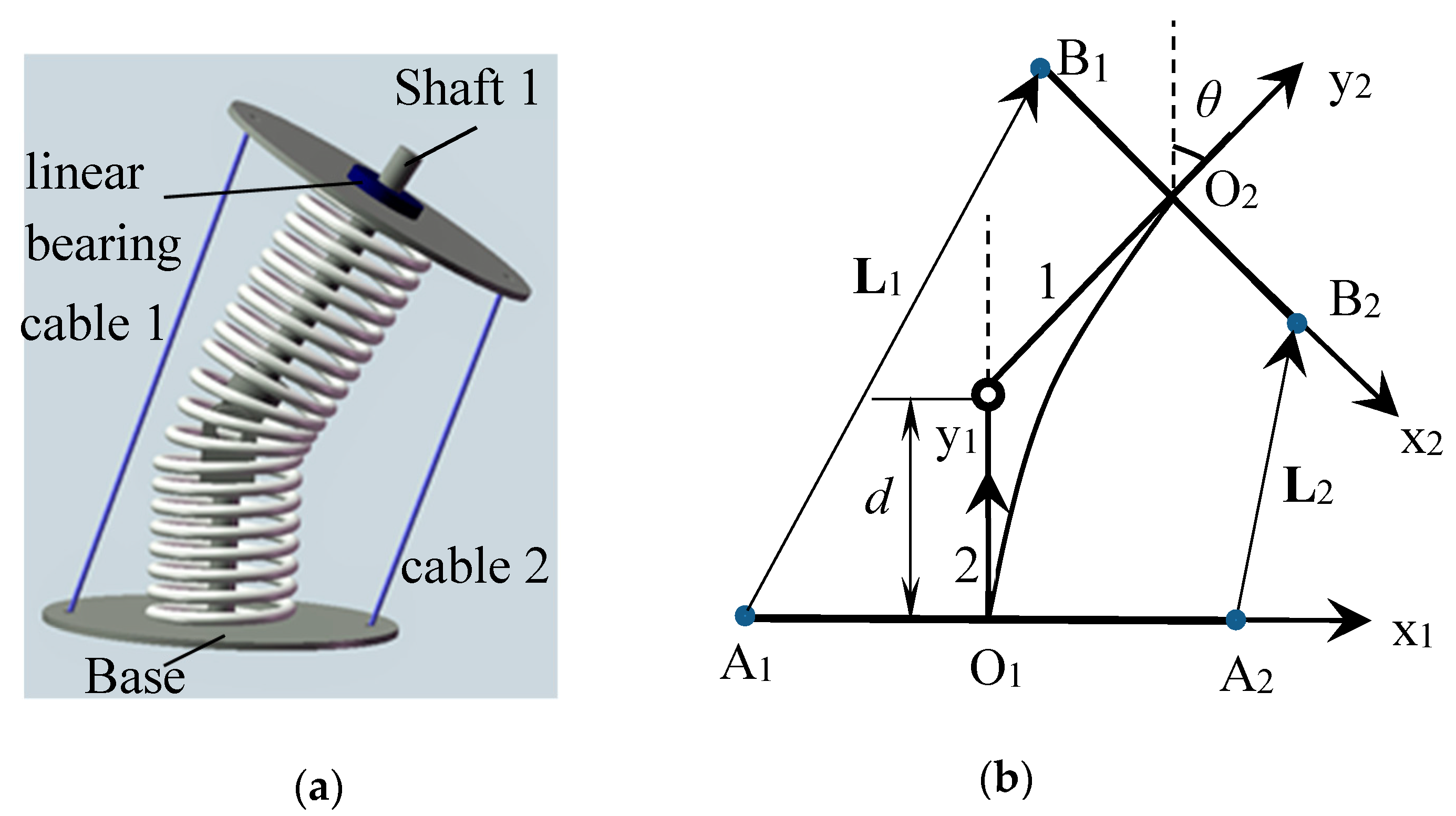
2.1. CDHJ Description
2.2. Kinematic Analysis
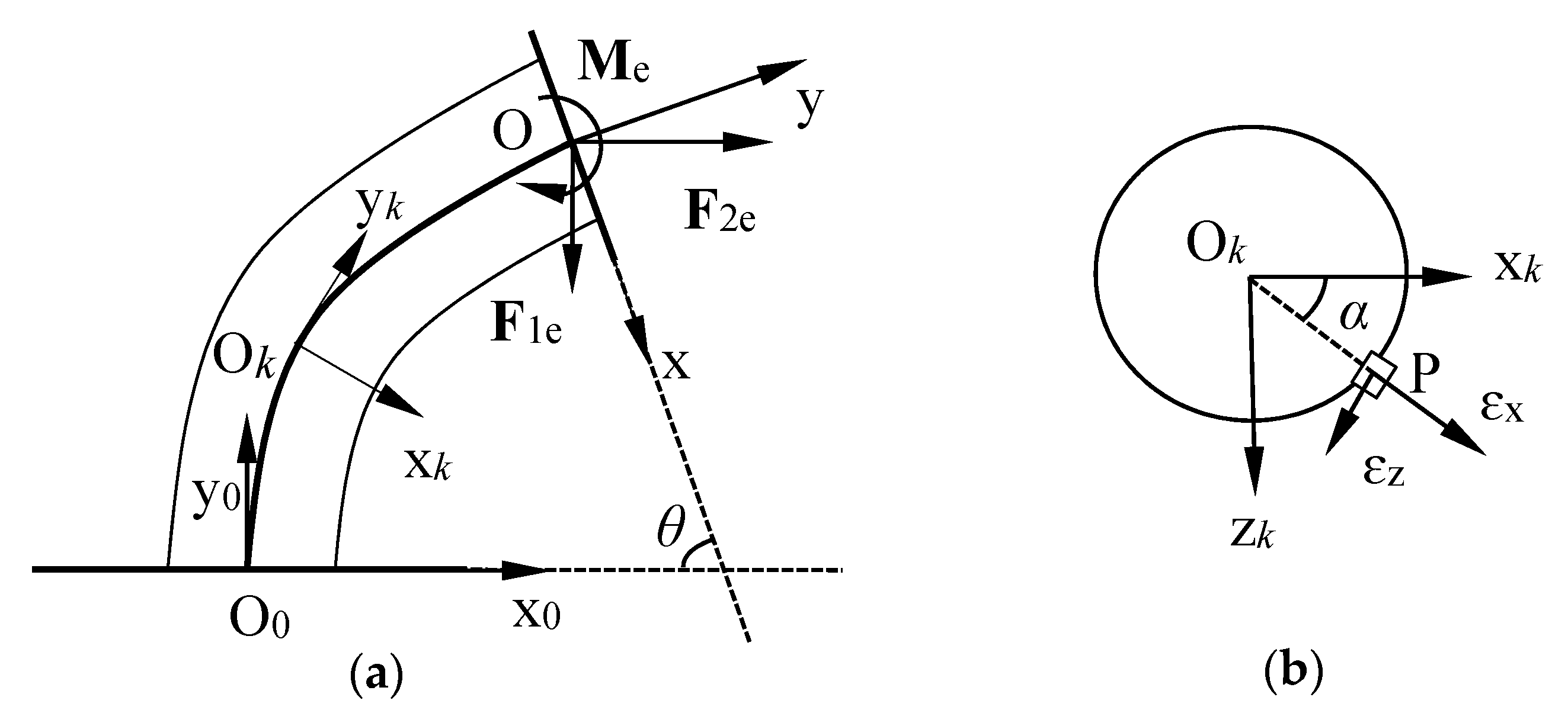
3. Modeling of Spring Lateral Bending and Compression
4. Workspace and Stiffness Index of CDHJ
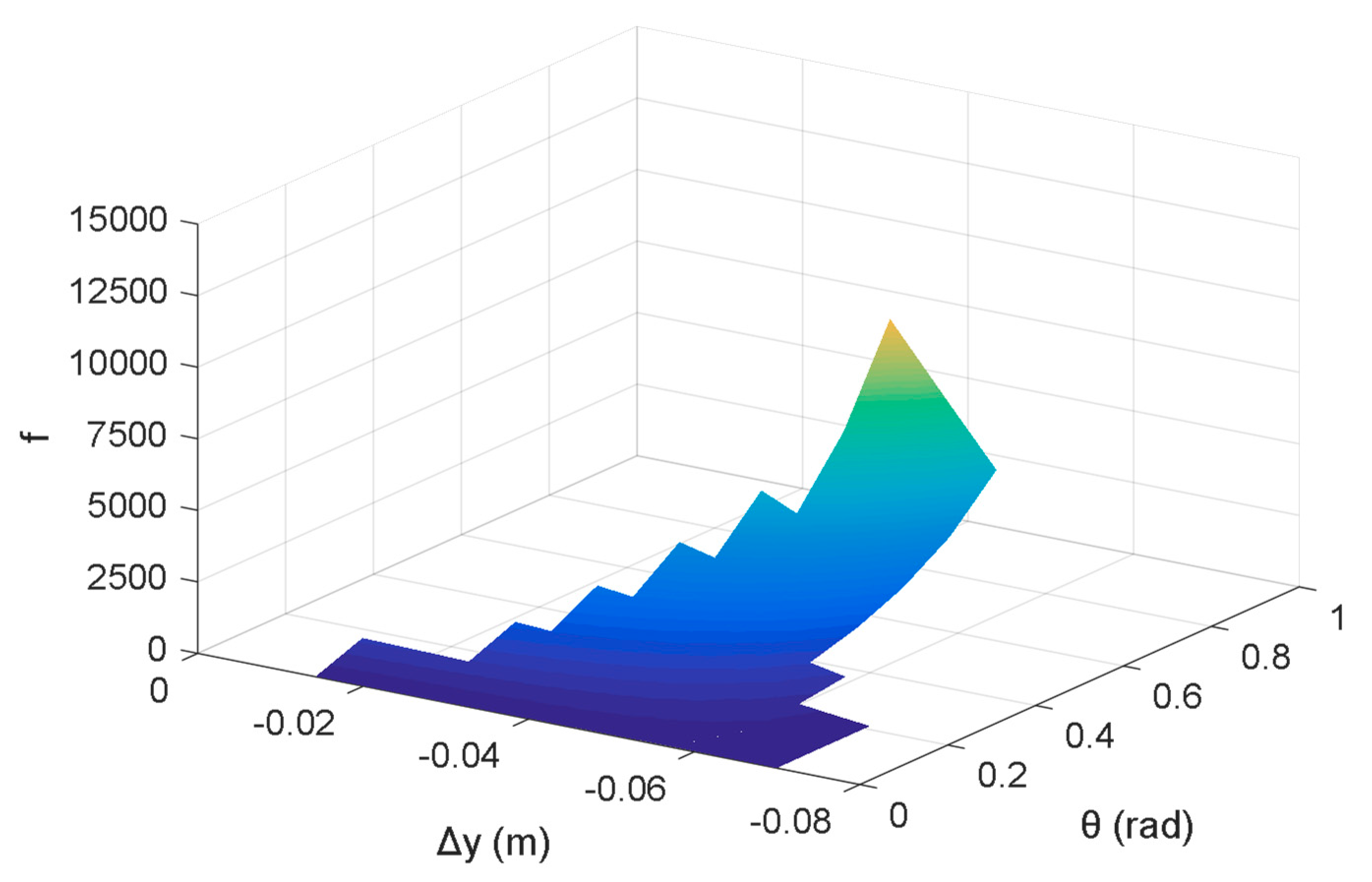
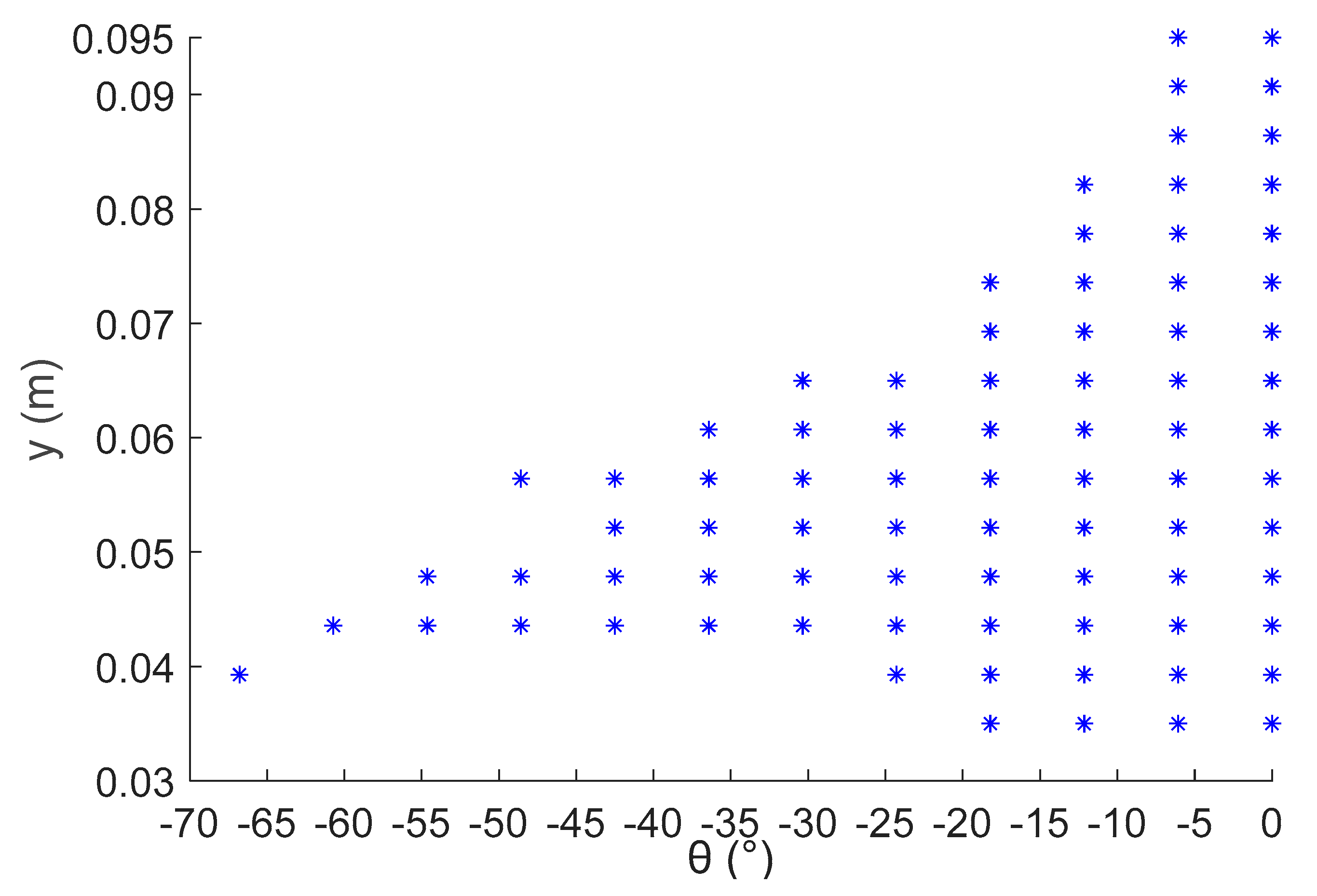
4.1. Workspace Index
4.2. CDHJ Stiffness Index
5. Numerical Simulation
5.1. Cable Parameters
5.2. Numerical Analysis of Spring Effects on CDHJ Workspace and Stiffness
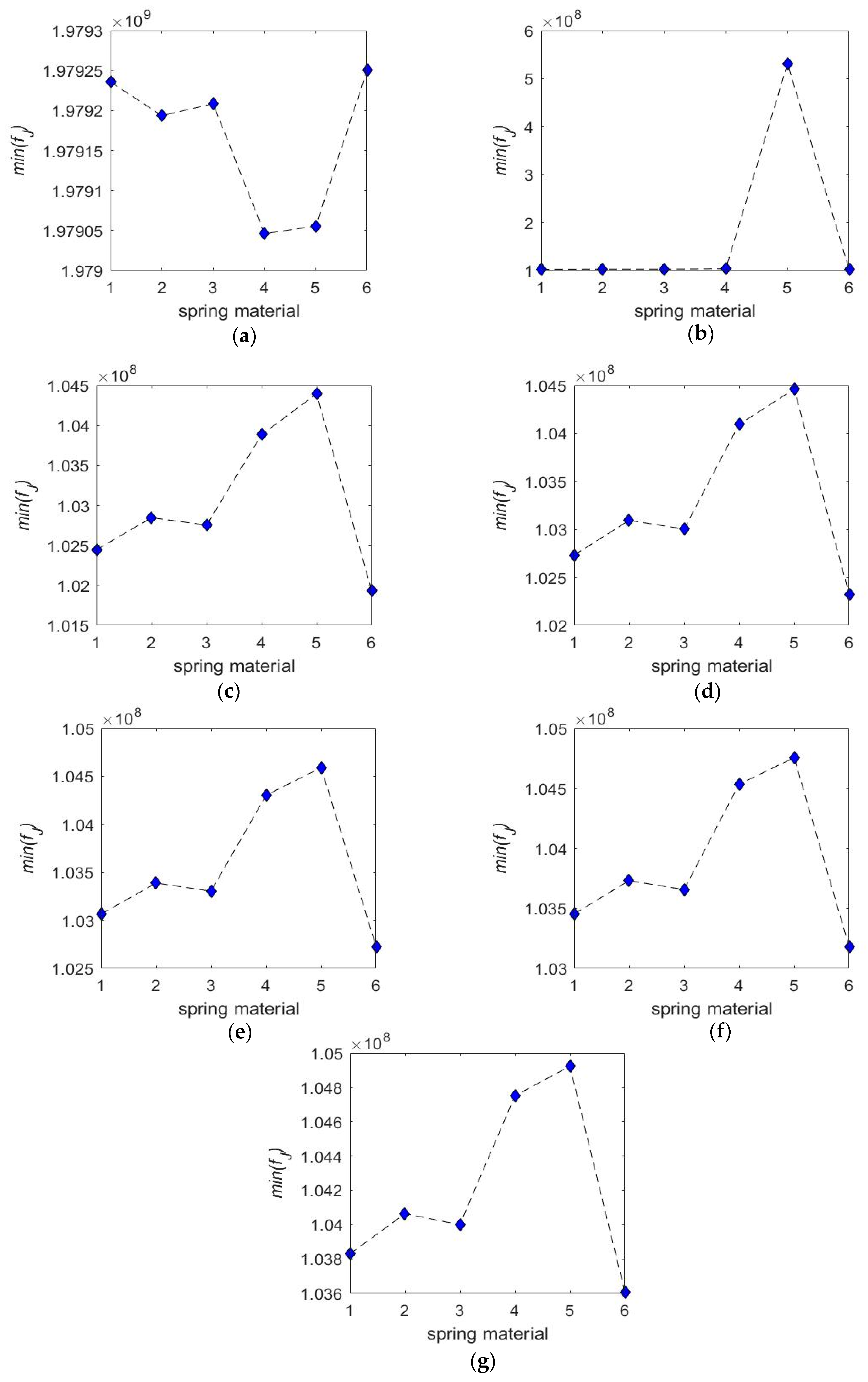
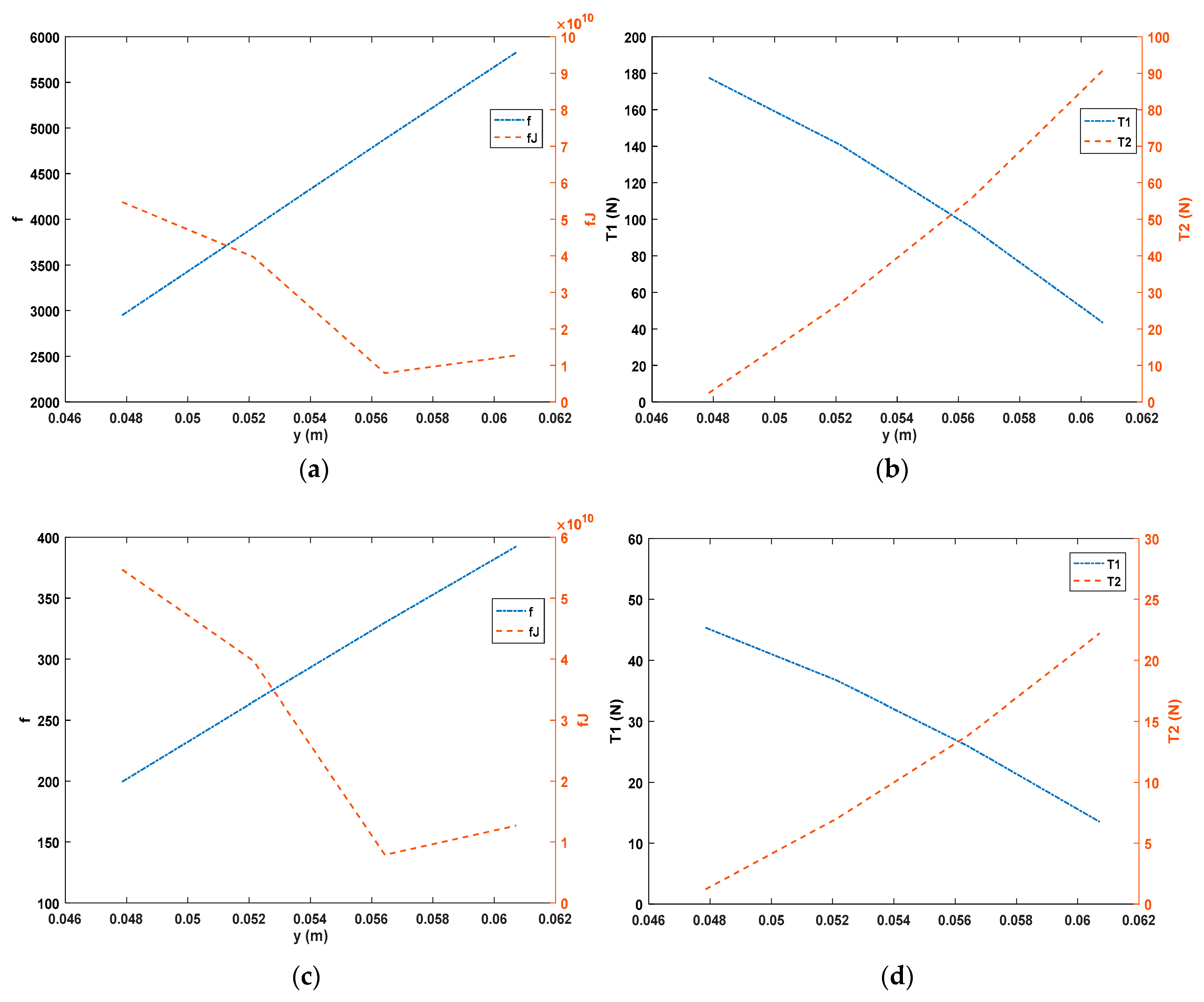
5.2.1. Spring Parameters (n, E/G) on CDHJ Workspace and Stiffness
5.2.2. Variable Stiffness Spring Effects on the CDHJ Stiffness
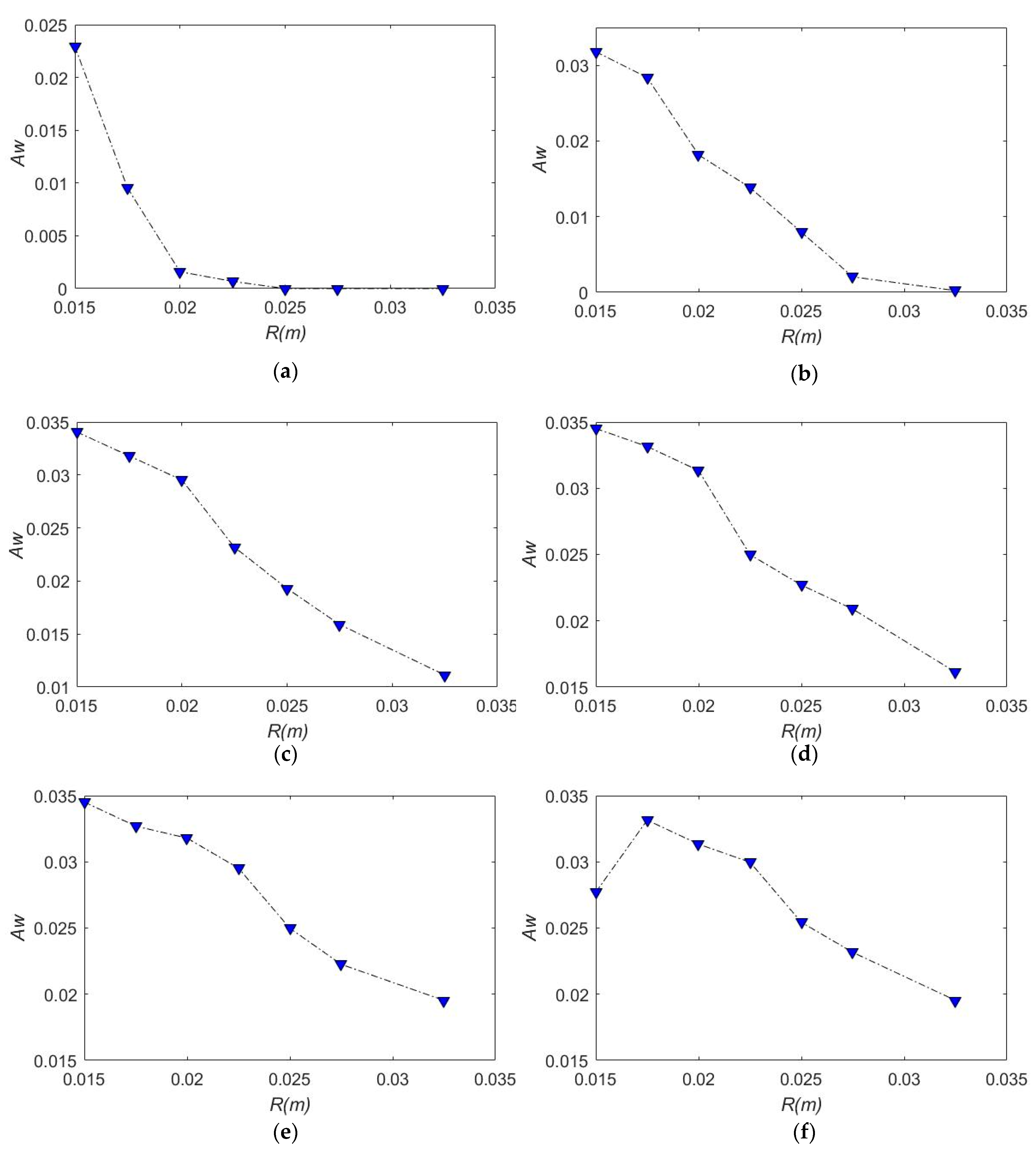
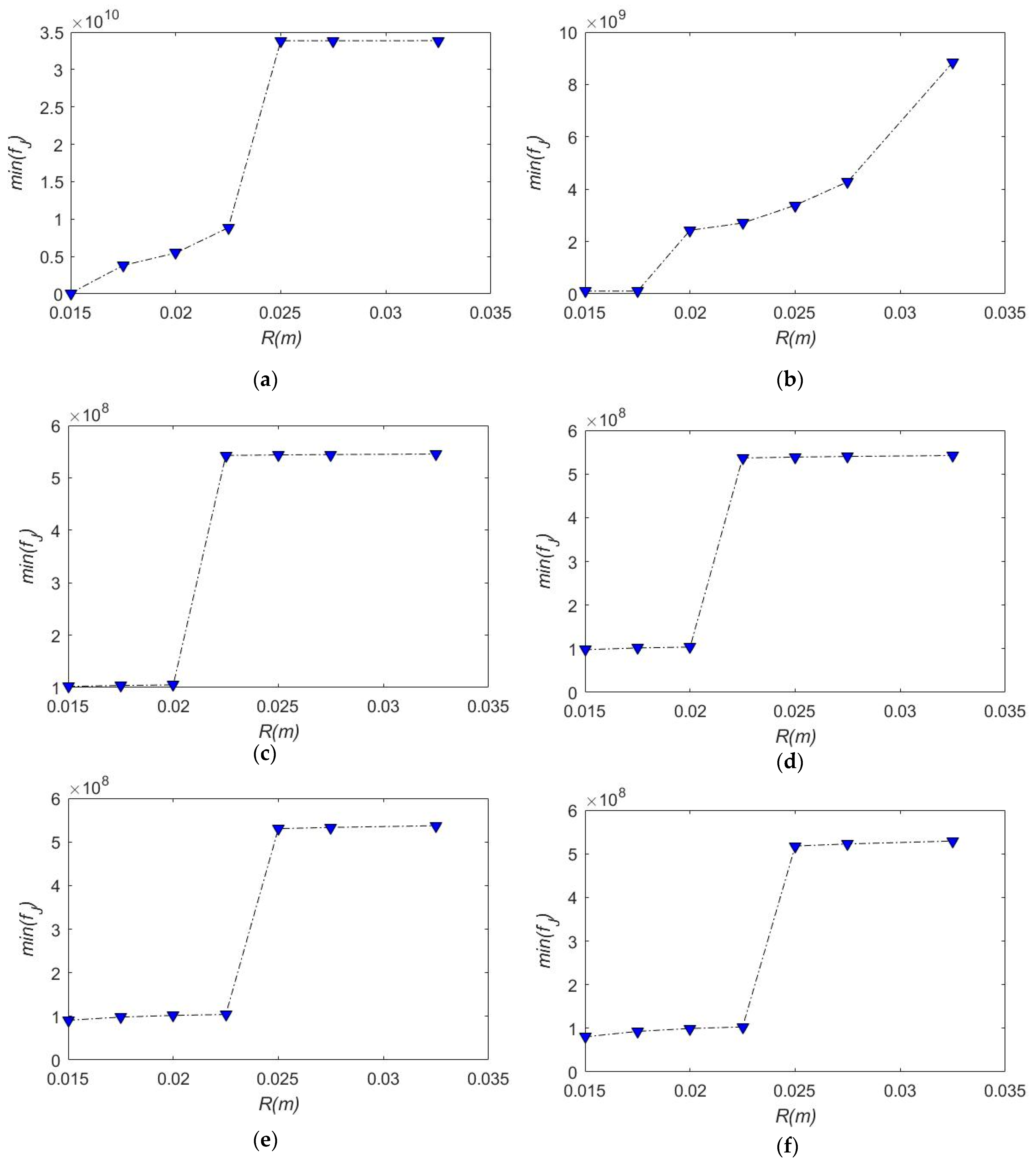
5.2.3. Spring Parameters (R, r) on CDHJ Workspace and Stiffness
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, C.S.; Wang, H.; Cooper, R.A. Functional assessment and performance evaluation for assistive robotic manipulators: Literature review. J. Spinal. Cord. Med. 2013, 36, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersh, M. Overcoming Barriers and Increasing Independence–Service Robots for Elderly and Disabled People. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2015, 12, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.R.; Zhang, T.; Wachs, J.P.; Duerstock, B.S. Enhanced control of a wheelchair-mounted robotic manipulator using 3-D vision and multimodal interaction. Comput. Vis. Image Und. 2016, 149, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilyea, A.; Seth, N.; Nesathurai, S.; Abdullah, H.A. Robotic assistants in personal care: A scoping review. Med. Eng. Phys. 2017, 49, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, D.X.; Li, S.; Min, H.; Fan, F. Inverse kinematic tension analysis and optimal design of a cable-driven parallel-series hybrid joint towards wheelchair-mounted robotic manipulator. J. Eur. Syst. Autom. 2018, 51, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.S.; Yang, G.L.; Chen, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Z.J.; Zheng, T.J.; Wang, C.C. Study on stiffness-oriented cable tension distribution for a symmetrical cable-driven mechanism. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardini, L.; Caro, S.; Gouttefarde, M.; Girin, A. Discrete reconfiguration planning for cable-driven parallel robots. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 100, 313–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, B.; Lin, J.; Qian, S. Localization, obstacle avoidance planning and control of a cooperative cable parallel robot for multiple mobile cranes. Robot. Comput. Int. Manuf. 2015, 34, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluarachchi, M.M.; Ho, J.H.; Yahya, S. Design of a single motor, tendon driven redundant manipulator with reduced driving joint torques. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2018, 46, 591–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zi, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.S. Design and development of a new cable-driven parallel robot for waist rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, J.M.; Ben-Tzv, P. A cable length invariant robotic tail using a circular shape universal joint mechanism. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 051005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforoua, E.G.; Phocasb, M.C.; Matheoub, M.; Müller, A. Experimental implementation of the ‘effective 4-bar method’ on a reconfigurable articulated structure. Structures 2019, 20, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.L.; Guo, H.W.; Liu, R.Q.; Deng, Z.Q. Self-adaptive grasp process and equilibrium configuration analysis of a 3-DOF UACT robotic finger. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 133, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seriani, S.; Gallina, P.; Scalera, L.; Lughi, V. Development of n-DoF preloaded structures for impact mitigation in cobots. J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 051009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckerle, P.; Salvietti, G.; Ünal, R.; Prattichizzo, D.; Rossi, S. A Human-robot interaction Perspective on Assistive and rehabilitation robotics. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, M.; Behzadipour, S.; Faulkner, G. Antagonistic variable stiffness elements. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 1746–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, Q.; Vedrines, M.; Abdelaziz, S.; Poignet, P.; Renaud, P. Synthesis method for the design of variable stiffness components using prestressed singular elastic systems. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 121, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.H.; Kim, B.S.; Song, J.B. Compliant actuation of parallel-type variable stiffness actuator based on antagonistic actuation. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, F.; Friedl, W.; Hoppner, H.; Grebenstein, M. Analysis and synthesis of the bidirectional antagonistic variable stiffness mechanism. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.H.; Yang, G.L.; Lim, W.B. Design and analysis of cable-driven manipulators with variable stiffness. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 69, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Au, K.W.S.; Chen, W.; Miao, Y. Underwater dynamic modeling for a cable-driven soft robot arm. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 2726–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, W.F.; Huang, H.L.; Ning, Y.H. Design and analysis of a high payload manipulator based on a cable-driven serial-parallel mechanism. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 11, 051006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalera, L.; Palomba, I.; Wehrle, E.; Gasparetto, A.; Vidoni, R. Natural motion for energy saving in robotic and mechatronic systemsand. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, R.V.; Sugar, T.G.; Vanderborght, B.; Hollander, K.W.; Lefeber, D. Compliant actuator designs. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2009, 16, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, B.; Albu-Schaeffer, A.; Bicchi, A.; Burdet, E.; Caldwell, D.G.; Carloni, R.; Catalano, M.; Eiberger, O.; Friedl, W.; Ganesh, G.; et al. Variable impedance actuators: A review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 1601–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Lan, C.C. Linear variable-stiffness mechanisms based on preloaded curved beams. J. Mech. Des. 2014, 136, 122302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Martínez, J.; Blanco-Claraco, J.L.; García-Vallejo, D.; Giménez-Fernández, A. Design and analysis of a flexible linkage for robot safe operation in collaborative scenarios. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 92, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.; Oetomo, D.; Halgamuge, S. Wrench-Closure Workspace Generation for Cable Driven Parallel Manipulators using a Hybrid Analytical-Numerical Approach. ASME J. Mech. Des. 2011, 133, 071004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.J.; Duan, X.C. Workspace Classification and Quantification Calculations of Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 358727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phama, C.B.; Yeo, H.S.; Yang, G.L.; Chen, M. Workspace analysis of fully restrained cable-driven manipulators. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosscher, P.; Riechel, A.; Ebert-Uphoff, I. Wrench-feasible workspace generation for cable-driven robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Courteille, E.; Deblaise, D. Static and dynamic stiffness analyses of cable-driven parallel robots with non-negligible cable mass and elasticity. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 85, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, Z.; Zi, B.; Qian, S.; Du, J.L.; Ge, Q.J. Three-dimensional static and dynamic stiffness analyses of the cable driven parallel robot with non-negligible cable mass and elasticity. Mech. Based Des. Struct. 2017, 46, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.Q.; Gouttefarde, M.; Company, O.; Pierrot, F. On the Simplifications of Cable Model in Static Analysis of Large-Dimension Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 928–934. [Google Scholar]
- Rogier, D.R.; Mitchell, R.; Amir, K. Out-of-plane vibration control of a planar cable-driven parallel robot using a multi-axis reaction system. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2018, 23, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, D.X.; Hou, B.; Li, S.; Min, H.; Zhang, X.L. Analysis on variable stiffness of a cable-driven parallel-series hybrid joint toward wheelchair-mounted robotic manipulator. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.Q.; Gouttefarde, M. Stiffness Matrix of 6-DOF Cable-Driven Driven Parallel Robots and Its Homogenization Advances in Robot Kinematics. In Advances in Robot Kinematics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Khalilpour, S.A.; Taghirad, H.D.; Habibi, H. Wave-Based Control of Suspended Cable Driven Parallel Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th International Conference on Control Instrumentation and Automation, Shiraz, Iran, 21–23 November 2017; pp. 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadipour, S.; Khajepour, A. Stiffness of cable-based parallel manipulators with application to stability analysis. ASME J. Mech. Des. 2006, 128, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Stiffness analysis and optimization of a co-axial spherical parallel manipulator. Model. Ident. Control 2014, 35, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoevenaars, A.G.L.; Lambert, P.; Herder, J.L. Jacobian-based stiffness analysis method for parallel manipulators with non-redundant legs. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 230, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, M.; Alamdari, A.; Krovi, V. Orientation workspace and stiffness optimization of cable-driven parallel manipulators with base mobility. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9, 031011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Courteille, E.; Gouttefarde, M.; Hervé, P. Vibration analysis of cable-driven parallel robots based on the dynamic stiffness matrix method. J. Sound. Vib. 2017, 394, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.J.; Vashista, V.; Agrawal, S.K. Effect on wrench-feasible workspace of cable-driven parallel robots by adding springs. Mech. Mach. Theory 2015, 86, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.K.; Agrawal, S.K. Force-Closure of Spring-Loaded Cable-Driven Open Chains: Minimum Number of Cables Required & Influence of Spring Placements. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 1482–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Taghavi, A.; Behzadipour, S.; Khalilinasab, N.; Zohoor, H. Workspace Improvement of Two-Link Cable-Driven Mechanisms with Spring Cable. In Cable-Driven Parallel Robots; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.T.; Song, H.G.; Zhao, J.G.; Guo, S.X.; Sun, L.X.; Tang, Y. Inverse kinematics and workspace analysis of a cable-driven parallel robot with a spring spine. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 76, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, C.B.; Boyraz, P. Design and modeling of a cable-driven parallel-series hybrid variable stiffness joint mechanism for robotics. Mech. Sci. 2017, 8, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krużelecki, J.; Życzkowski, M. On the concept of an equivalent column in the stability problem of compressed helical springs. Arch. Appl. Mech. 1990, 60, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, A.R. A Study of the Deformation of Helical Springs under Eccentric Loading. Ph.D. Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.; Gere, J. Theory of Elastic Stability; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961; p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, A.M.; Snyman, J.A. Optimization of a planar tendon-driven parallel manipulator for a maximal dextrous workspace. Eng. Optimiz. 2005, 37, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolboli, J.; Khosravi, M.A.; Abdollahi, F. Stiffness feasible workspace of cable-driven parallel robots with application to optimal design of a planar cable robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 114, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiss, P.; Rettig, O.; Wolf, S.; Loew, M.; Kasten, P. Range of Motion of Shoulder and Elbow in Activities of Daily Life in 3D Motion Analysis. Z. Orthop. Unfall. 2007, 145, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Tmin (N) | 1 |
| Tmax (N) | 300 |
| lmin (m) | 0.01 |
| xmin (m) | 0 |
| xmax (m) | 0.08 |
| θmin (rad) | −1.48 |
| θmax (rad) | 0 |
| ymin (m) | 0.035 |
| ymax (m) | 0.095 |
| Spring Materials | Mark | E (Gpa) | G (Gpa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| carbon spring steel wire, oil quenched-tempered spring steel wire, alloy spring steel wire, spring steel | 1 | 206 | 78.5 |
| stainless steel wire for spring (A) | 2 | 185 | 70 |
| stainless steel wire for spring (B), (C) | 3 | 195 | 73 |
| copper and copper alloy wire | 4 | 93.1 | 40.2 |
| beryllium bronze wire | 5 | 129.4 | 42.1 |
| spring-tempered steel | 6 | 195 | 81.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L.; Yu, C.; Cao, D. Spring Effects on Workspace and Stiffness of a Symmetrical Cable-Driven Hybrid Joint. Symmetry 2020, 12, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12010101
Zhang S, Sun Z, Lu J, Li L, Yu C, Cao D. Spring Effects on Workspace and Stiffness of a Symmetrical Cable-Driven Hybrid Joint. Symmetry. 2020; 12(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shan, Zheng Sun, Jili Lu, Lei Li, Chunlei Yu, and Dongxing Cao. 2020. "Spring Effects on Workspace and Stiffness of a Symmetrical Cable-Driven Hybrid Joint" Symmetry 12, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12010101
APA StyleZhang, S., Sun, Z., Lu, J., Li, L., Yu, C., & Cao, D. (2020). Spring Effects on Workspace and Stiffness of a Symmetrical Cable-Driven Hybrid Joint. Symmetry, 12(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12010101





