Cosmological Consequences of New Dark Energy Models in Einstein-Aether Gravity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Einstein-Aether Theory
3. Cosmological Parameters
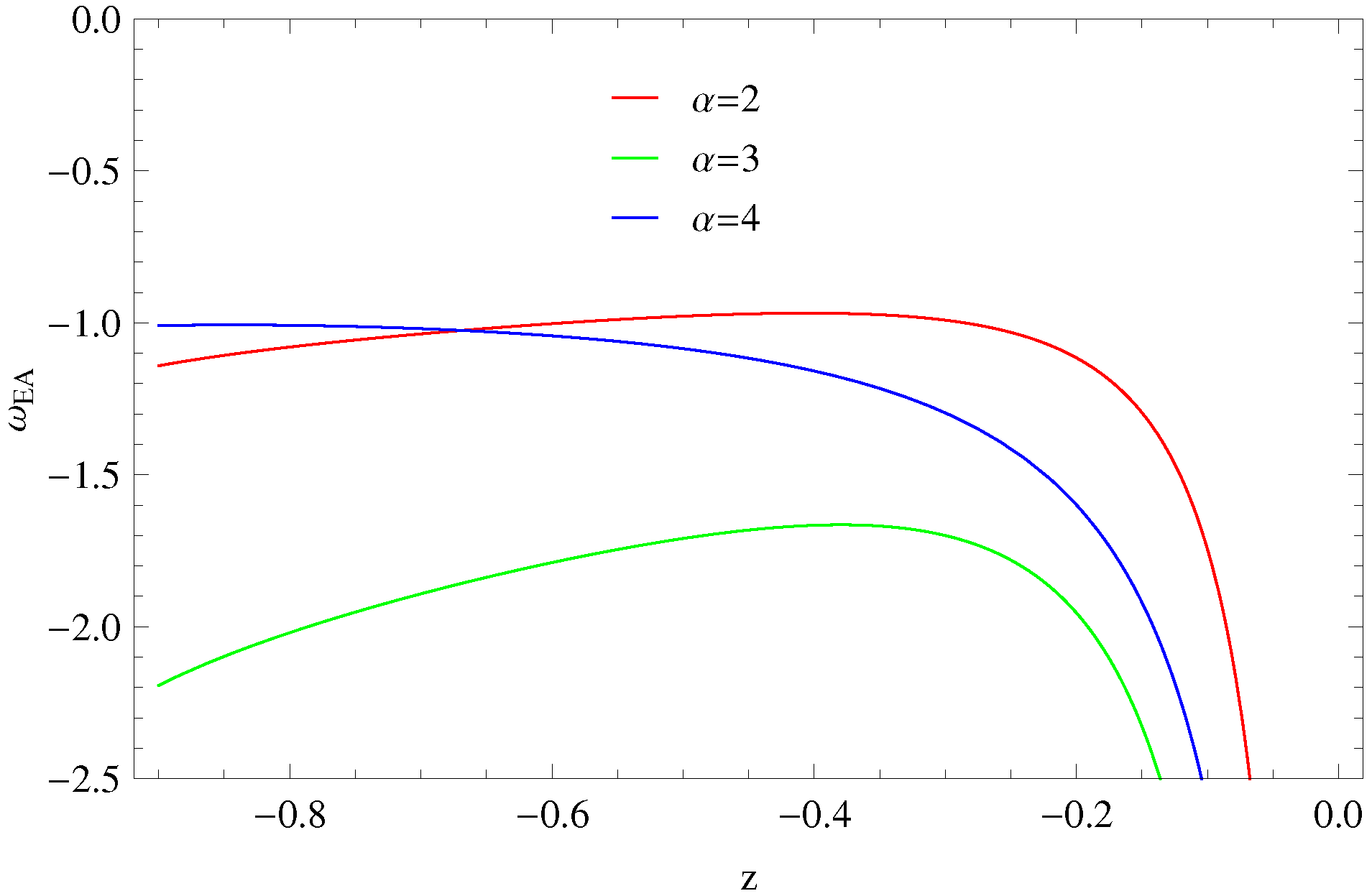
3.1. Equation of State Parameter
- In the decelerated phase, the radiation era and cold DM era are included.
- The accelerated phase of the universe has following eras: cosmological constant, quintessence and phantom era of the universe.
3.2. Squared Speed of Sound
3.3. - Plane
3.4. Scale Factor
4. Reconstruction from the Tsallis Holographic Dark Energy Model
5. Reconstruction from Rényi Holographic Dark Energy Model
6. Reconstruction from the Sharma-Mittal Holographic Dark Energy Model
7. Summary
- EoS parameter for power-law scale factor:
- THDE ⇒ phantom behavior,
- RHDE ⇒ quintessence phase,
- SMHDE ⇒ transition from quintessence to phantom phase for , phantom era for .
- EoS parameter for exponential scale factor:
- THDE ⇒ transition from quintessence to phantom era for , phantom behavior for , CDM model for ,
- RHDE ⇒ phantom phase for , quintessence phase for
- SMHDE ⇒ cosmological constant behavior for , phantom behavior for .
- - plane for power-law scale factor:
- THDE ⇒ freezing region for , thawing region for ,
- RHDE ⇒ freezing region,
- SMHDE ⇒ freezing region.
- - plane for exponential scale factor:
- THDE ⇒ freezing region to thawing region,
- RHDE ⇒ freezing region,
- SMHDE ⇒ thawing region.
- Squared speed of sound for power-law scale factor:
- THDE ⇒ unstable,
- RHDE ⇒ unstable,
- SMHDE ⇒ stable for , unstable for .
- Squared speed of sound for exponential scale factor:
- THDE ⇒ unstable,
- RHDE ⇒ stability for higher values and instability for lower values,
- SMHDE ⇒ unstable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Komatsu, E.; Dunkley, J.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Larson, D.; Limon, M.; Page, L.; et al. Five-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy probe Observations: Cosmological Interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2009, 180, 330–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolta, M.R.; Dunkley, J.; Hill, R.S.; Hinshaw, G.; Komatsu, E.; Larson, D.; Page, L.; Spergel, D.N.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; et al. Five-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy probe Observations: Angular Power Spectra. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2009, 180, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcall, N.; Ostriker, J.P.; Perlmutter, S.; Steinhardt, P.J. The Cosmic Triangle: Revealing the State of the Universe. Science 1999, 284, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, P.G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae. APJ 1999, 517, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Valle, M.D.; Deustua, S.; Ellis, R.S.; Fabbro, S.; Fruchter, A.; Goldhaber, G.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Discovery of a Supernova Explosion at Half the Age of the Universe and its Cosmological Implications. Nature 1998, 391, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiattia, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Strolger, L.G.; Tonry, J.; Casertano, S.; Ferguson, H.C.; Mobasher, B.; Challis, P.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jha, S.; Li, W.; et al. Type Ia Supernova Discoveries at z > 1 from the Hubble Space Telescope: Evidence for Past Deceleration and Constraints on Dark Energy Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 665–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, B.; Esposito-Farese, G.; Polarski, D.; Starobinsky, A.A. Reconstruction of a Scalar-Tensor Theory of Gravity in an Accelerating Universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spergel, D.N.; Bean, R.; Dore, O.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Dunkley, J.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Komatsu, E.; Page, L.; et al. Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Three Year Results: Implications for Cosmology. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2007, 170, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.L. Quintessence and the Transition to an Accelerating Universe. Nucl. Phys. B 2005, 707, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, J.P. Transition from Decelerated to Accelerated Cosmic Expansion in Braneworld Universes. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2006, 38, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.V. Kinematic Constraints to the Transition Redshift from Supernovae Type Ia Union Data. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 047301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, M. Introduction to Cosmology; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, A.; Majeed, A. Ghost Dark Energy Models in Specific Modified Gravity. Astrophy. Space Sci. 2015, 356, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A. Cosmological Analysis of Pilgrim Dark Energy in Loop Quantum Cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2015, 75, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Pasqua, A. A Holographic Reconstruction of the Modified f(R) Horava-Lifshitz Gravity with Scale Factor in Power-law form. Astrophy. Space Sci. 2013, 346, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Pasqua, A. Reconstruction of f(G) Gravity with the New Agegraphic Dark-energy Model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2013, 128, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Pasqua, A. Reconstruction of f() models via well-known scale factors. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Pasqua, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Correspondence between f(G) gravity and holographic dark energy via power-law solution. Astrophy. Space Sci. 2013, 344, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Pasqua, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Holographic reconstruction of f(G) gravity for scale factors pertaining to emergent, logamediate and intermediate scenarios. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2013, 128, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A. New Agegraphic Pilgrim Dark Energy in f(T,TG) Gravity. Astrophy. Space Sci. 2014, 353, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Iqbal, A. Modified Cosmology through Renyi and logarithmic Entropies. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2018, 15, 1850130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Iqbal, A. Cosmological Implications of Non-canonical Scalar Field Model in Fractal Universe. Phys. Dark Univ. 2018, 22, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Jawad, A. Thermodynamics of Ricci-Gauss-Bonnet Dark Energy. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018, 6139430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Bamba, k.; Younas, M.; Qummer, S.; Rani, S. Tsallis, Rényi and Sharma-Mittal Holographic Dark Energy Models in Loop Quantum Cosmology. Symmetry 2018, 10, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, M.; Jawad, A.; Qummer, S.; Moradpour, H.; Rani, S. Cosmological Implications of the Generalized Entropy Based Holographic Dark Energy Models in Dynamical Chern-Simons Modified Gravity. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2019, 2019, 1287932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.B.; Nelson, A.E. Effective Field Theory, Black Holes, and the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 73, 4971–4974. [Google Scholar]
- Moradpour, H.; Sheykhi, A.; Corda, C.; Salako, I.G. Energy Definition and Dark Energy: A Thermodynamic Analysis. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 783, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, H.; Bonilla, A.; Abreu, E.M.C.; Neto, J.A. Einstein and Rastall Theories of Gravitation in Comparison. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 123504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, H. Necessity of Dark Energy from Thermodynamic Arguments. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2016, 55, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavayef, M.; Sheykhi, A.; Bamba, K.; Moradpour, H. Tsallis holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 781, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.A.; Lobo, I.P.; Morais Graca, J.P.; Jawad, A.; Salako, I.G. Thermodynamic approach to holographic dark energy and the Rényi entropy. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.02195. [Google Scholar]
- Moosavi, S.A.; Moradpour, H.; Morais Graça, J.P.; Lobo, I.P.; Salako, I.G.; Jawad, A. Generalized entropy formalism and a new holographic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 780, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified non-local-F(R) gravity as the key for the inflation and dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 659, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Barrow, J.D. Cosmology of f(R) gravity in the metric variational approach. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified f(R) gravity consistent with realistic cosmology: From matter dominated epoch to dark energy universe. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 086005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunsby, P.K.S.; Elizalde, E.; Goswami, R.; Odintsov, S.; Gomez, D.S. On the LCDM universe in f(R) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 023519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Odintsov, S.D.; Pozdeeva, E.O.; Yu, S.; Vernov, J. Cosmological attractor inflation from the RG-improved Higgs sector of finite gauge theory. J. Cosmo. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 1602, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.C.B.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Consistent modified gravity: Dark energy, acceleration and the absence of cosmic doomsday. Class. Quantum Gravity 2005, 22, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.V. Einstein’s other gravity and the acceleration of the Universe. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 127301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerzhanov, K.K. Emergent Universe in Chameleon, f(R) and f(T) Gravity Theories. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1006.3879v1. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified Gauss-Bonnet theory as gravitational alternative for dark energy. Phys. Lett. B 2005, 631, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, I.; Rizos, J.; Tamvakis, K. Singularity-free cosmological solutions of the superstring effective action. Nucl. Phys. B 1994, 415, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horava, P. Membranes at Quantum Criticality. JHEP 2009, 903, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brans, C.; Dicke, H. Mach’s Principle and a Relativistic Theory of Gravitation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: From F(R) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 59–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; de Laurentis, M. Extended Theories of Gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, V.; Capozziello, S. Beyond Einstein Gravity: A Survey of Gravitational Theories for Cosmology and Astrophysics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bamba, K.; Odintsov, S.D. Inflationary cosmology in modified gravity theories. Symmetry 2015, 7, 220–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Capozziello, S.; de Laurentis, M.; Saridakis, E.N. f(T) teleparallel gravity and cosmology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Modified Gravity Theories on a Nutshell: Inflation, Bounce and Late-time Evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Dark energy cosmology: The equivalent description via different theoretical models and cosmography tests. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2012, 342, 155–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.; Mattingly, D. Gravity with a dynamical preferred frame. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, T.; Mattingly, D. Einstein-aether waves. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, J.D. Errata for cosmological magnetic fields and string dynamo in axion torsioned spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 85, 047503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Du, X. Einstein-aether theory as an alternative to dark energy model. Phys. Lett. B 2012, 710, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Du, X. A Specific Case of Generalized Einstein-aether Theories. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2012, 57, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achucarro, A.; Gong, J.O.; Hardeman, S.; Palma, G.A.; Patil, S.P. Features of heavy physics in the CMB power spectrum. JCAP 2011, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, M. Repulsive gravity in the very early Universe. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 1998, 30, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlosnik, T.G.; Ferreira, P.G.; Starkman, G.D. Modifying gravity with the Aether: An alternative to Dark Matter. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 044017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlosnik, T.G.; Ferreira, P.G.; Starkman, G.D. On the growth of structure in theories with a dynamical preferred frame. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 084010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.R.; Linder, E.V. The Limits of Quintessence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 141301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Introduction to Modified Gravity and Gravitational Alternative for Dark Energy. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2007, 4, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, H.; Moosavi, S.A.; Lobo, I.P.; Graca, J.P.M.; Jawad, A.; Salako, I.G. Tsallis, Rényi and Sharma-Mittal Holographic Dark Energy Models in Loop Quantum Cosmology. Eur. Phys. J. C 2018, 829, 78. [Google Scholar]

















© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rani, S.; Jawad, A.; Bamba, K.; Malik, I.U. Cosmological Consequences of New Dark Energy Models in Einstein-Aether Gravity. Symmetry 2019, 11, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040509
Rani S, Jawad A, Bamba K, Malik IU. Cosmological Consequences of New Dark Energy Models in Einstein-Aether Gravity. Symmetry. 2019; 11(4):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040509
Chicago/Turabian StyleRani, Shamaila, Abdul Jawad, Kazuharu Bamba, and Irfan Ullah Malik. 2019. "Cosmological Consequences of New Dark Energy Models in Einstein-Aether Gravity" Symmetry 11, no. 4: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040509
APA StyleRani, S., Jawad, A., Bamba, K., & Malik, I. U. (2019). Cosmological Consequences of New Dark Energy Models in Einstein-Aether Gravity. Symmetry, 11(4), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11040509





