Abstract
The eye blink rate, a major human physiological response, directly affects ocular diseases, such as keratitis and dry eye syndrome. It has been shown that the eye blink rate in normal eyes has a certain frequency for individuals, from 6–30 times/min. It was suggested in a previous study that the eye blink rate can be decreased during the viewing of high-intensity and realistic content. Therefore, in this paper, we examine the change of the eye blink rate during the HMD (head-mounted display) viewing of VR (virtual reality) contents; accordingly, we propose an algorithm to measure the eye blink rate as well as compare and analyze this rate in three different environments (natural, monitor, and HMD). We confirmed that IPD (interpupillary distance) and phoria affected the eye blink rate in each environment. In this experiment, 21 subjects (28.38 ± 6.87 years) were selected, and a paired t-test was performed for changes in the eye blink rate over 1 min for each environment. The IPD and phoria effects on the eye blink rate were confirmed using the Spearman’s correlation coefficient. In this experiment, the eye blink rate was decreased in the monitor and HMD environments compared with the natural environment, while that in the HMD environment was decreased compared with the monitor environment. The results of the correlation analysis of far IPD and the eye blink rate show no statistical significance or correlation. The correlation analysis of near IPD and the eye blink rate showed a strong positive correlation of the eye blink rate in the monitor environment. The correlation analysis of distance phoria and the eye blink rate showed a strong negative correlation of the eye blink rate in the HMD environment. The correlation analysis of near-field phoria and the eye blink rate showed a strong negative correlation of the eye blink rate in the HMD environment. It is expected that the results of this study will be used as a VR-viewing recommendation.
1. Introduction
Humans accept information from the external environment through various sensory organs. Among them, vision is higher than the other senses and plays an important role in the support of the other senses. Human beings’ acquisition of external information frequently occurs via eye transmission [1,2].
Eye blinking, one of the main human physiological reactions, is caused by the interaction between the levator palpebrae superioris muscle, which lifts the palpebral; and the orbicularis oculi muscle, which closes the eyelid. When the normally activated levator palpebrae superioris muscle is deactivated, and the orbicularis oculi muscle contracts, the eye closes. When the contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle ceases and the levator palpebrae superioris muscle contracts, a mechanism that opens the eye results in eye blinking [3,4,5].
In the normal vision of individuals, spontaneous eye blinking occurs at a certain frequency. The influential factors affecting eye blinking are eyelid condition, eye condition, disease status, contact-lens presence, psychological state, surrounding environment, drugs, and other stimuli. The blinking frequency is from 6–30 times/min [6,7].
The eye blink response directly affects ophthalmic diseases, such as keratitis and dry eye [8,9,10]. In addition to the ophthalmic factors, the tear film on the surface of the eyeball is evenly dispersed to remove corneal irregularities and prevent corneal dehydration and conjunctiva. Furthermore, the eye blink rate is decreased during the viewing of realistic content; therefore, it is necessary to study the relationship between the viewing of such realistic media and eye blink patterns.
In general, the eye blink rate tends to decrease during work rather than at rest [11,12]. In addition, the eye blink rate tends to decrease during reading or demanding tasks, as these are more visually strict than the typical visual activities [13]. The higher the focal degree regarding an object, the lower the eye blink rate [14,15]. An increase in the interest induction from media viewing can result in a decrease in the eye blink rate, and this can cause ocular pathological effects.
In the study of Sheedy et al., ocular dryness is suggested as one of the external symptoms of stable fatigue [16], and xerophthalmia can be induced by a reduced eye blink rate [8]. Ocular dryness is accompanied by visual disturbances, inflammation of the ocular surface, and ocular discomfort [17], thereby causing symptoms such as irritation, burning sensation, and pink eye (also called conjunctivitis) [9]. This paper proposes an algorithm for the measurement of the eye blink rate, and the authors also studied the effects of each of the realistic media environments on the eye blink pattern in the following three environments: natural, monitor, and head-mounted display (HMD).
2. Participants and Methods
2.1. Participants
The subjects of the experiment possessed a near-far correctional visual acuity of 0.8 or greater, had not been diagnosed with any special ophthalmologic, systemic, or mental illnesses, and were not inhibited by the Worth four-dot test. Twenty-one subjects in the age segments of the 20 s and 30 s (28.38 ± 6.87 years old) were selected after they demonstrated that they understood and agreed with the experiment contents.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Detection for Eye Blink
Natural and Monitor: The measurement of the eye blink rate can be evaluated using visual observation after the completion of a video recording. In this case, however, there is a probability that mistakes will occur when measuring eye blink rate in visual observation. Therefore, in this paper, we propose an algorithm for efficient experiments in the natural and monitor environments, as shown in Figure 1.
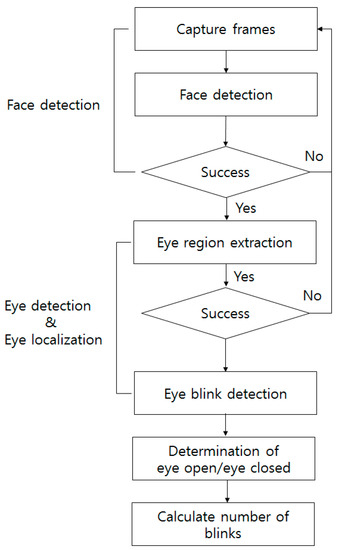
Figure 1.
Proposed algorithm flowchart for Natural and Monitor environments.
• Face Detection
The Haar cascade classifier [18] and optical flow algorithms were applied for face detection and face tracking, respectively [19].
Figure 2 shows the Haar features for face detection. The image frame with templates of different sizes and orientations is convolved for the Haar feature computation.
where local movement X and local movement Y are the local changes in the x coordinate and the y coordinate for slight facial movements, respectively; x and y are the actual changes that lead to changes in local movement; and the global movements of X and Y are achieved using the optical-tracking method.
Local movement X = local movement X + f_xy × x,
Local movement Y = local movement Y + f_xy × y,
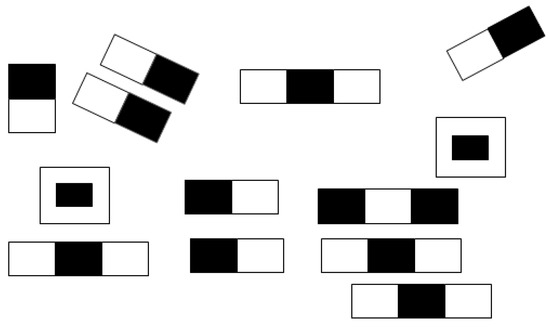
Figure 2.
Rectangular masks used for edge feature (Haar feature) object detection.
• Eye-Region Extraction
In this step, the ocular region of the facial image is identified on the basis of certain geometrical dependencies and then divided into these boxes according to the traditional proportion rules [20], as shown in Figure 3. The located ocular region is subsequently extracted from the face and used as a template for further eye tracking by means of template matching.
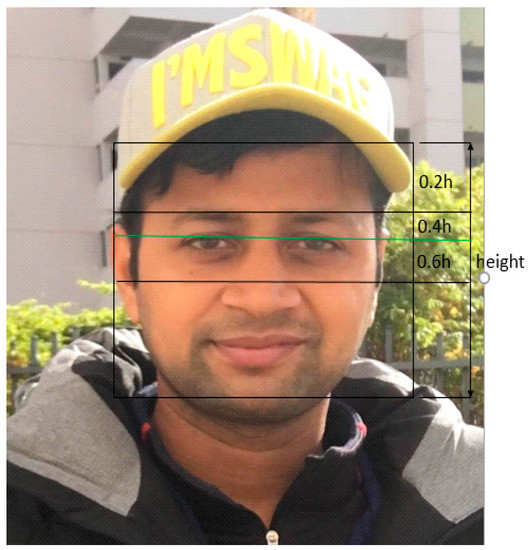

Figure 3.
Rules of human face proportions.
• Eye Blink Detection and Contours
Generally, an interval of 2 –10 seconds occurs between each adult eye blink, and after face detection, the system will detect the eye and wait for its disappearance, followed by a calculation of the time interval between the disappearance and the next appearance of the pupil in the frame. The eye-detection algorithm only detects both of the eyes if they have been opened and closed. Using this information, it is possible to assess whether the user’s eyes are closed or open and to count the number of times the user blinks; a single eye is sufficient for the detection of the eye blink rate.
HMD (head-mounted display): The accuracy of our proposed algorithm for HMD is much more efficient than the traditional algorithm [21,22,23]. For HMD, the FOVE HMD infrared camera (FOVE, Inc., San Mateo, CA, USA) is used. There are various applications of a histogram [24], and our method uses a histogram for eye blink detection using HMD. The flow chart of the proposed algorithm in HMD is shown in Figure 4. The proposed algorithm works according to a series of steps for HMD environments, which are as follows:
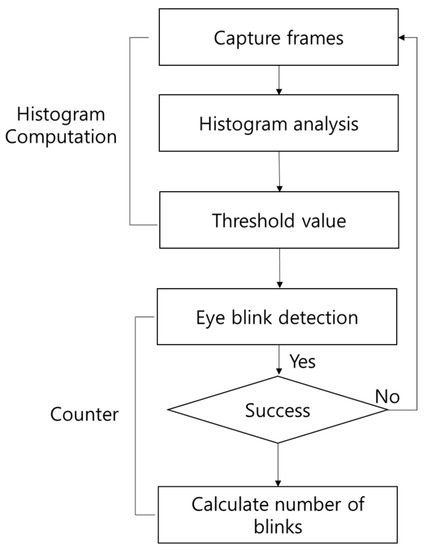
Figure 4.
Proposed algorithm flowchart for HMD (head-mounted display).
• Frame Capture and Histogram Analysis
First, the recorded video was captured by HMD, and image frame of HMD was converted into gray scale using Visual Studio C++. Next, histogram analysis was performed on the opened eye and closed eye image frames, as shown in Figure 5. We compared the open eye histogram in Figure 5a with the closed eye histogram in Figure 5c and observed that the number of pixels at higher pixel values were greater in the closed eye than in opened eye. This is because the black pupil always lowers the number of pixels at higher pixel levels.
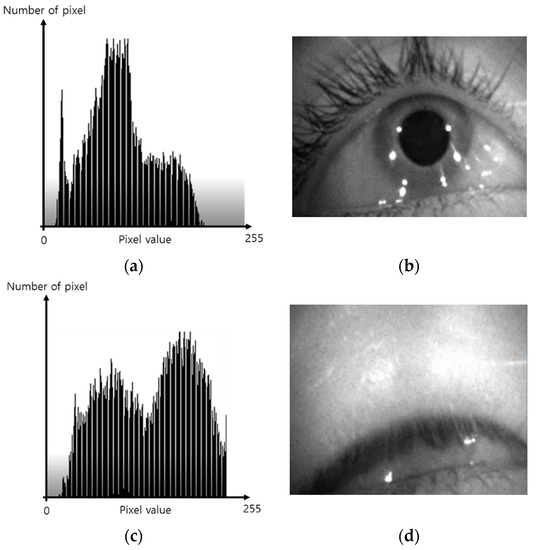
Figure 5.
Histogram example: (a) histogram of open eye; (b) open eye; (c) histogram of closed eye; (d) closed eye.
• Eye Blink Detection and Counter
We adjusted the threshold value between the histogram of the closed eye and that of the open eye. If the value exceeds the threshold, a blink was detected, and if the pixel was lower than the threshold, the same process was repeated. Using this information, it is possible to assess whether the user’s eyes are closed or open. Finally, after successful blink detection, the number of blink detections was counted.
2.2.2. Experiment Environment
Before the participation of the subjects in the experiment, the subject factors that could affect the experiment were checked in a preliminary interview. The experiment conditions were measured in the natural, monitor, and HMD viewing environments, and the experiment order was set randomly to prevent the order effects. Before the measuring of the eye blink rate, the subjects’ far and near interpupillary distances (IPD) and near phoria were measured. The IPDs were measured using the BRT-II pupillary distance (PD) meter, and the phoria was measured using the Howell phoria card (Bernell Corporation, Mishawaka, IN, USA). The eye blink rate was measured for a total of 2 min for stabilization and then for 1 min, except for 30 s before and afterward. For measurement accuracy, the subject was not informed about the measurement of the eye blink rate. The eye blink rate was evaluated using the proposed algorithm.
The eye blink rate in the natural state was measured using a TD20 camera (Sony Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) in a situation where the subject did not recognize the measurement. The measurement of the eye blink rate in the viewing monitor was performed using 24-in Ultron 2457 Ultra monitor (Hansung, Seoul, South Korea) The experiment was conducted at a viewing distance of 1.0 m. The eye blink rate in the viewing HMD was measured using the FOVE0 HMD (FOVE, Inc., San Mateo, CA, USA). The use of the FOVE0 HMD in the experimental environment is shown in Figure 6. In this experiment, we used a VR demo game, called “Grandmother’s Doll”, provided by Fove. This game was used for both the monitor and HMD.

Figure 6.
Measurement environment of the HMD eye blink rate.
2.3. Data Analysis
The data analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon signed-ranked test and a simple correlation analysis (Spearman’s correlation coefficient) of the SPSS software, ver. 18.0 for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). In this analysis, the 95% confidence interval was considered to have a statistical significance of p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results
3.1.1. Comparison of the Blink Rate in the Natural State and with the Viewing Monitor
Table 1 and Figure 7 shows a comparison of the measured eye blink rate per minute in the natural state and with the viewing monitor. The eye blink rate was comparatively decreased (Z = −3.218, p = 0.001) at a statistically significant level during the monitor viewing.

Table 1.
Comparison of the blink rate in the natural state and with the viewing monitor (N = 21).
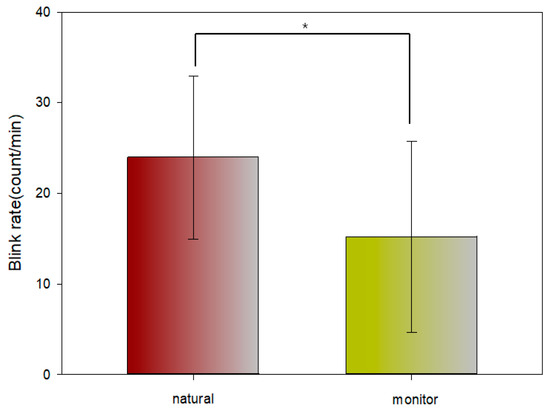
Figure 7.
Comparison of the blink rate in the natural state and with the viewing monitor (*: p < 0.05).
3.1.2. Comparison of the Blink Rate in the Natural State and with the Viewing HMD
Table 2 and Figure 8 shows a comparison of the measured eye blink rate per minute in the natural state and with the viewing HMD. The eye blink rate was comparatively decreased (Z = −3.984, p < 0.001) at a statistically significant level during the HMD viewing.

Table 2.
Comparison of the blink rate in the natural state and with the viewing HMD (N = 21).
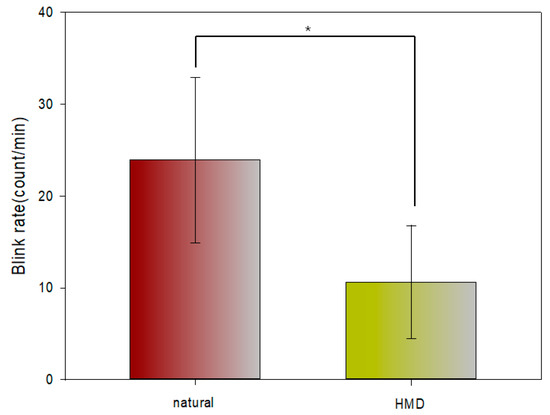
Figure 8.
Comparison of the blink rate in the natural state and with the viewing HMD (*: p < 0.05).
3.1.3. Comparison of the Blink Rate with the Viewing Monitor and the Viewing HMD
Table 3 and Figure 9 shows the measurement results of the eye blink rate per minute with the viewing monitor and the viewing HMD. The comparison of the results shows that the eye blink rate decreased at a statistically significant level (Z = −2.214, p = 0.027) during the HMD viewing.

Table 3.
Comparison of the blink rate with the monitor and the viewing HMD (N = 21).
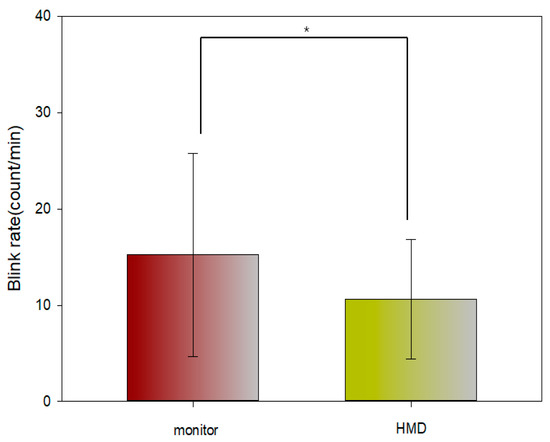
Figure 9.
Comparison of the blink rate with the monitor and the viewing HMD (*: p < 0.05).
3.1.4. Analysis of the Correlation between Far IPD and the Eye Blink Rate
The results of the analysis of the correlation between far IPD and the eye blink rate in Table 4 and Figure 10 show the correlation between remote IPD and the eye blink rate in each environment. The correlation results of far IPD and the eye blink rate are as follows: A weak positive correlation (0.3 ≥ r ≥ 0.1) in the natural environment, a strong positive correlation (0.7 ≥ r ≥ 0.3) in the monitor environment, and a strong positive correlation (0.7 ≥ r ≥ 0.3) in the HMD environment. However, there is no statistical significance (r = 0.193, 0.393, and 0.319; p = 0.402, 0.078, and 0.159).

Table 4.
Analysis of the correlation between far IPD (interpupillary distance) and the eye blink rate (N = 21).
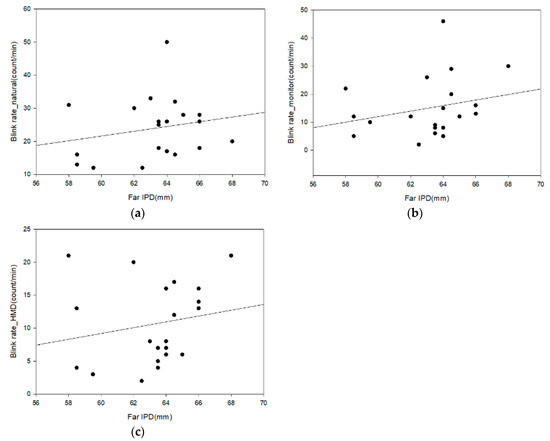
Figure 10.
Analysis of the correlation between far IPD and the eye blink rate: (a) natural; (b) monitor; and (c) HMD.
3.1.5. Analysis of the Correlation between Near IPD and the Eye Blink Rate
Table 5 and Figure 11 shows the correlation between near IPD and the eye blink rate in each environment. The correlation analysis results of the near IPD and the eye blink rate are as follows: a weak positive correlation (0.3 ≥ r ≥ 0.1) in the natural environment, a strong positive correlation (0.7 ≥ r ≥ 0.3) in the monitor environment, and a strong positive correlation (0.7 ≥ r ≥ 0.3) in the HMD environment. The statistical significance in the blink rate was identified (r = 0.280, 0.526, and 0.307; p = 0.220, 0.014, and 0.176).

Table 5.
Analysis of the correlation between near IPD and the eye blink rate (N = 21).
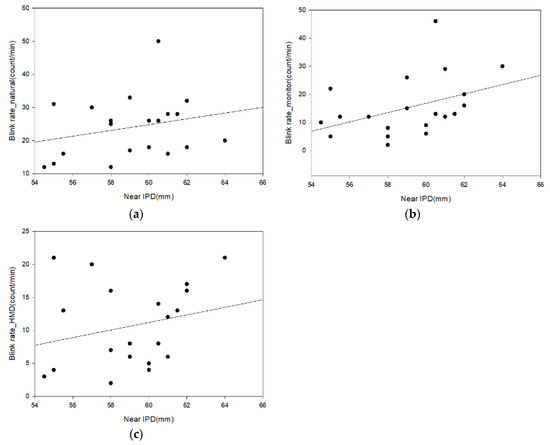
Figure 11.
Analysis of the correlation between near IPD (interpupillary distance) and the eye blink rate: (a) natural; (b) monitor; and (c) HMD.
3.1.6. Analysis of the Correlation between Far Phoria and the Eye Blink Rate
Table 6 and Figure 12 shows the correlation between far phoria and the eye blink rate in each environment. The correlation analysis results of far phoria and the eye blink rate are as follows: no correlation in the natural environment (0.1 ≥ r ≥ −0.1), a strong negative correlation in the monitor environment (−0.3 ≥ r ≥ −0.7), and a strong negative correlation (−0.3 ≥ r ≥ −0.7) in the HMD environment. Among them, the HMD blink rate is statistically significant (r = −0.011, −0.302, and −0.470; p = 0.964, 0.183, and 0.031).

Table 6.
Analysis of the correlation between far phoria and the eye blink rate (N = 21).
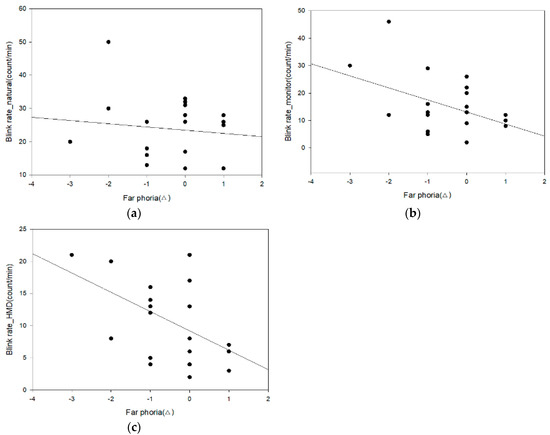
Figure 12.
Analysis of the correlation between far phoria and the eye blink rate: (a) natural; (b) monitor; and (c) HMD.
3.1.7. Analysis of the Correlation between Near Phoria and the Eye Blink Rate
Table 7 and Figure 13 shows the correlation between near phoria and the eye blink rate in each environment. The correlation analysis results of the near phoria and the eye blink rate are as follows: a negative correlation (−0.1 ≥ r ≥ −0.3) in the natural environment, a weak negative correlation (−0.1 ≥ r ≥ 0.3) in the monitor environment, and a strong negative correlation (−0.3 ≥ r ≥ −0.7) in the HMD environment. Among them, the HMD blink rate showed statistical significance (r = −0.102, −0.248, and −0.493; p = 0.659, 0.278, and 0.023).

Table 7.
Analysis of the correlation between near phoria and the eye blink rate (N = 21).
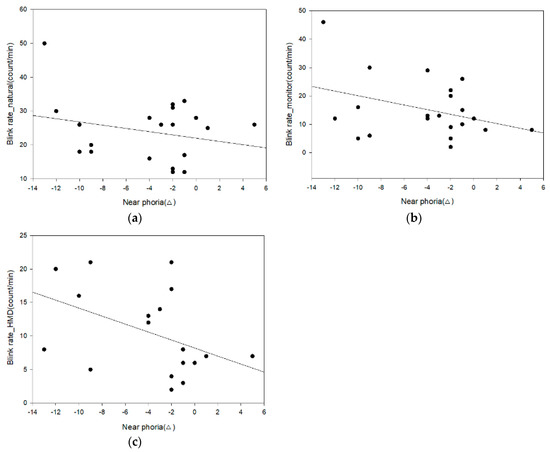
Figure 13.
Analysis of the correlation between near phoria and the eye blink rate: (a) natural; (b) monitor; and (c) HMD.
3.2. Discussion
The eye blink rate was decreased as the observation degree was strengthened beyond the typical natural state. Decreases in the eye blink rate require great care because they lead to ocular pathological effects. The experiment of this study showed that the eye blink rate was decreased during the monitor and HMD viewing compared with the natural state. Moreover, the comparison of the monitor and HMD conditions shows that the eye blink rate was decreased during the HMD viewing, thereby showing that the interest rates of the monitor and HMD videos were increased along with the increase of the observation degree.
The eye blink rate directly affects ocular diseases, such as keratitis and dry eye. In addition, tears are evenly distributed on the surface of the eyeball to form a tear film. This removes the irregularities of the cornea and allows the light to refract. It is also an important factor in preventing the dehydration of the cornea and conjunctiva. Because the individual's eye blink rate habit is so important in eyeball physiology, observation of the eye blink rate, which can be changed by using realistic content, should be observed as a major visual item.
The results of this study show the same tendency as previous studies; that is, the eye blink rate was decreased during activities with a higher attention intensity compared with those with the typical visual activity. In general, near-field work, such as reading, leads to visual fatigue, and the degree of fatigue varies depending on the environment; in this paper, the same tendency was observed for the eye blink rate in the HMD environment, near the physical viewing distance. It is known that the eye blink rate is affected by the cognitive load as well as visual fatigue. In Kim’s study [25], regarding the change in the eye blink rate according to the reading environment, the eye blink rate was decreased with longer reading time. The use of monitors and the HMD for long durations may cause a decrease in the eye blink rate, so user breaks are considered necessary.
The larger the IPD, the more convergence is needed when viewing near objects, and the larger the phoria, the greater the eye fatigue. Therefore, in this paper, we hypothesized that IPD and phoria would affect the eye blink rate. Finally, correlation analysis was performed to determine whether the eye blink rate changes as a parameter to induce fatigue and supplemental feedback. The correlation analyses regarding IPD and phoria, and the eye blink rate, showed a correlation between near IPD and the eye blink rate in the Monitor environment, a correlation between far phoria and the eye blink rate in the HMD environment, and a correlation between near phoria and the eye blink rate in the HMD environment. These findings mean that the eye blink rate was increased in the monitor environment as the near IPD increased, while the eye blink rate was increased in the HMD environment as the far/near-distance exophoria increased.
People with near IPD may need to be visually more relaxed during visual activities (video viewing, computer work, etc.) for which general TVs and monitors are used; moreover, children with IPD forms that are relatively narrower than those of adults will likely require adult guidance during such visual activities. The correlation data of phoria and the eye blink rate show that, in the HMD environment, the larger the exophoria, the higher the eye blink rate. In the HMD environment with the near-distance display, the larger the exophoria, the greater the discomfort of the eyeball, and the eye blink rate was increased by the physiological feedback. Therefore, given the eye-fatigue intensification, the exophoria type is stricter than the other type.
4. Conclusions
Recently, the HMD-usage rate has increased due to the development of the virtual/augmented reality (VR/AR) industry. The high immersion and the short distances between the eye and the display during HMD viewing are factors that cause a decrease in the eye blink rate, and the HMD user must recognize this. For adults, if dryness is felt in the eyes during HMD usage, the authors recommend the temporary cessation of HMD usage to rest the eyes; regarding children, it is likely that parental/guardian guidance will be needed. Because individual eye blink rates are very important for eye physiology, the eye blink rate should be observed as a major visual-effect factor with respect to special content.
Factors influencing the eye blink rate include the platform, content characteristics, and external environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity. In this paper, we examined the change of the eye blink rate according to the platform (HMD, monitor, and natural). However, there are limitations associated with not conducting experiments on other factors. Future studies will require the comprehensive study of various factors relating to the eye blink rate.
In this paper, we recommend the following to HMD users. The eye blink rate is closely related to eye diseases, such as dryness and keratitis. Whenever we use HMD, the user should be aware of the eye blink rate. If the user feels subjective symptoms, such as dryness of the eyes, he must take an eye rest. For a safe and comfortable use of the HMD, take a break for some time. It is necessary to determine the resting time in accordance with the personal disturbance compliance and HMD content characteristics. Children who do not recognize the condition of the body properly can be accompanied by an adult.
Author Contributions
J.K.—data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, visualization, and writing–original draft; Y.S.K.—data curation, formal analysis, software, and writing—original draft; J.Y.—funding acquisition, project administration, and supervision; S.K.—conceptualization, funding acquisition, investigation, supervision, and writing—review and editing.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1A6A3A01007041) and the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (MSIP) of the Korea Government (no. NRF-2017R1C1B5015194).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Harald, K. Schule der Farben: Grundzüge der: Farbentheorie fur Computeranwender und andere; DuMont Reiseverlag: Ostfildern, Germany, 1992; pp. 1–187. [Google Scholar]
- Jason, J. The VR Book: Human-Centered Design for Virtual Reality, 1st ed.; Morgan & Claypool: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 85–109. [Google Scholar]
- Evinger, C.; Shau, M.D.; Peck, C.K.; Manning, K.A.; Baker, R. Blinking and associated eye movements in humans, guinea pigs, and rabbits. J. Neurophysiol. 1984, 52, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibony, P.A.; Evinger, C.; Manning, K.A. Eyelid movements in facial paralysis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evinger, C.; Manning, K.A.; Sibony, P.A. Eyelid movements: mechanisms and normal data. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1991, 32, 387–400. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, F.W. Ophthalmology, 6th ed.; C. V. Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 1986; pp. 201–202. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D.-E. System of Ophthalmology, Vol 4, The Physiology of the Eye and of Vision; C. V. Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 1968; pp. 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Gowrisankaran, S.; Nahar, N.K.; Hayes, J.R.; Sheedy, J.E. Asthenopia and blink rate under visual and cognitive loads. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.J.; Hong, J.H.; Jung, D.I.; Park, M.J. A study on the confidence of dry eye diagnosis methods. J. Korean Ophthalmic Opt. Soc. 2008, 13, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Doughty, M.J. Consideration of three types of spontaneous eyeblink activity in normal humans: During reading and video display terminal use, in primary gaze, and while in conversation. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2001, 78, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himebaugh, N.L.; Begley, C.G.; Bradley, A.; Wilkinson, J.A. Blinking and tear break-up during four visual tasks. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2009, 86, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlote, T.; Kadner, G.; Freudenthaler, N. Marked reduction and distinct patterns of eye blinking in patients with moderately dry eyes during video display terminal use. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Henderson, R.; Bradley, L.; Galloway, B.; Hunter, L. Effect of visual display unit use on blink rate and tear stability. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1991, 68, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackintosh, J.H.; Kumar, R.; Kitamura, T. Blink rate in psychiatricillness. Br. J. Psychiatr. 1983, 143, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdulmunem, M.; Briggs, S.T. Spontaneous blink rate of a normal population sample. ICLC 1999, 26, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, J.E.; Hayes, J.N.; Engle, J. Is all asthenopia the same? Optom. Vis. Sci. 2003, 80, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biljana, M.; Reza, D.; David, A.S.; Debra, A.S. Impact of Dry Eye Syndrome on Vision-Related Quality of Life. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V.; Michael, J. Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V.; Michael, J. Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2001, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, O. The proportion of the face in younger adults using the thumb rule of Leonardo da Vinci. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1996, 18, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.K.; Yoo, J.S.; Kwon, S.C. Implementation and Performance Evaluation of Eye-blink Rate Detection Algorithms for Natural and HMD Environment. In Proceedings of the Advanced Engineering and ICT-Convergence, Seoul, Korea, 12–14 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zeeshan, A.H.; Ziaul, H. Eye-Blink rate detection for fatigue determination. In Proceedings of the 1st India International Conference on Information Processing, Delhi, India, 12–14 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Matjaz, D. Eye blink based fatigue detection for prevention of Computer Vision Syndrome. In Proceedings of the IAPR Conference on Machine Vision Applications, Yokohama, Japan, 20–22 May 2009; pp. 350–353. [Google Scholar]
- Harpreet, K.; Neelofar, S. A Study for Applications of Histogram in Image Enhancement. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 6, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Park, M.J.; Kim, S.R. Relationship between Reading Speed and Blinking Rate according to Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration during Book Reading. J. Korean Ophthalmic Opt. Soc. 2015, 20, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).