Study on the Impact of Land Transfer on Farmers’ Welfare: Theoretical and Empirical Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Mechanism Discussion
2.1. Theoretical Analysis
2.2. Mechanism Discussion
3. Materials and Data
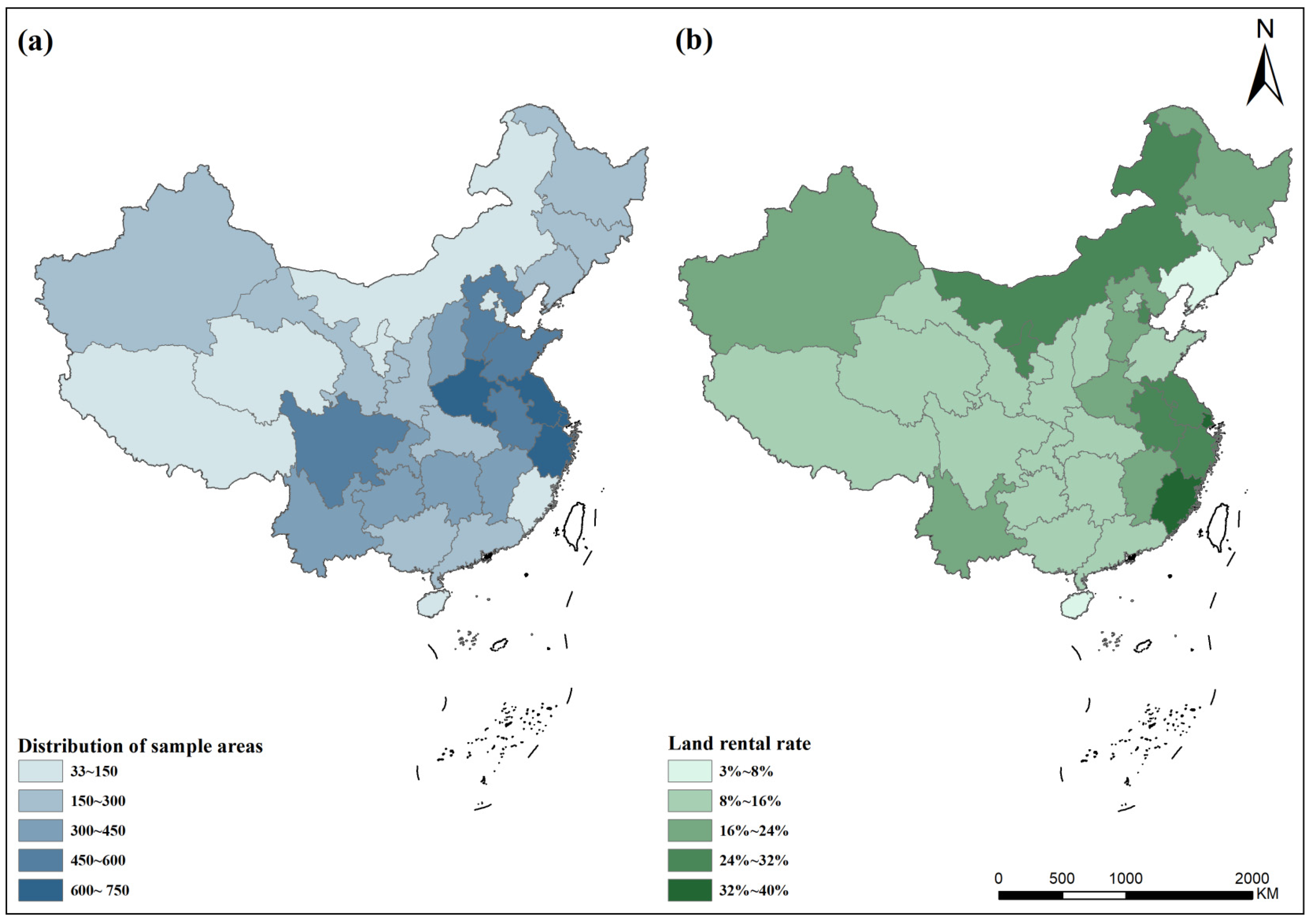
3.1. Sampling and Data Collection
3.2. Variables
3.3. Method
3.4. Descriptive Statistics
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Baseline Results
4.2. Path Analysis
4.3. Discussion on Heterogeneity
4.4. Robustness Check
5. Discussion
5.1. Regional Differences in Land Transfer and Farmers’ Welfare
5.2. Policy Implications
5.3. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chamberlin, J.; Ricker-Gilbert, J. Participation in rural land rental markets in sub-Saharan Africa: Who benefits and by how much? Evidence from Malawi and Zambia. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2016, 98, 1507–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengle, S.A. Local effects of the new land rush: How capital inflows transformed rural Russia. Governance 2018, 31, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Chung, C.C. Evolution of land system reforms in China: Dynamics of stakeholders and policy transitions toward sustainable farmland use (2004–2019). Heliyon 2024, 10, e37471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Policy Research Office of the Communist Party of China, Office of Rural Fixed Observation Points of the Ministry of Agriculture. Compilation of Survey Data from Fixed Observation Points in Rural Areas Across the Country; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.J. Strategies for Farmland Abandonment Governance: An Analysis Based on a “Market−Organization−Government” Framework. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2025, 1, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Shi, H.; Li, B.; Xu, D. The Impact of Whole Region Comprehensive Land Consolidation on Ecological Vulnerability: Evidence from Township Panel Data in Zhejiang Province. Land 2025, 14, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdiningtyas, R.; Wei, Y.; Western, A.W. The evolution of policy instruments used in water, land and environmental governances in Victoria, Australia from 1860–2016. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 112, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Land Expansion and Green Rural Transformation in Developing Countries: A Kaya Identity Approach. Land 2025, 14, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.J.; Yan, Z.H.F.; Wu, F.W. Does return of rural labor inhibit agricultural land transfer?—Also on the relationship between employment distance and agricultural land transfer. Rural. Econ. 2024, 1, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ricardo, T.S. Unlocking Agricultural Productivity: The Role of Land Rental Markets in Reducing Resource Misallocation. Agric. Econ. 2025, 56, 1058–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker-Gilbert, J.; Chamberlin, J.; Kanyamuka, J.; Jumbe, C.B.L. How do informal farmland rental markets affect smallholders’ well-being? Evidence from a matched tenant-landlord survey in Malawi. Agric. Econ. 2019, 50, 595–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Cai, D.; Han, K.; Zhou, K. Understanding peasant household’s land transfer decision-making: A perspective of financial literacy. Land Use Policy 2022, 119, 106189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, X.; Qin, Y. Exploring the Effects of Farmland Transfer on Farm Household Well-Being: Evidence from Ore–Agriculture Compound Areas in Northwest China. Land 2024, 13, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lin, J.; Sexton, R.J. The Transition from Small to Large Farms in Developing Economies: A Welfare Analysis. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2022, 104, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, M.; Holden, S.T.; Tilahun, M. Tenants’ land access in the rental market: Evidence from northern Ethiopia. Agric. Econ. 2019, 50, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemare, M.F. Insecure land rights and share tenancy: Evidence from Madagascar. Land Econ. 2012, 88, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, H.-J.; Popov, A. Reorganization of Agricultural Land Leases as a Tool for Sustainable Land Use: Comparative Insights from Ukraine and Germany. Land 2025, 1, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorchuk, M.; Popov, A.; Fedorchuk, V. Addressing the spatial shortcomings of agricultural land use: Legal aspects and obstacles. Stud. Iurid. Lublinensia 2024, 33, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Ma, X.; Rao, F. How to Prevent Farmland Rental Breaches in Large-scale Farmland Market: A Case Study from Jinhu County, Jiangsu Province. Agric. Econ. 2025, 6, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, G.; Yu, H. Has rural depopulation reduced agricultural land use efficiency? Mediating roles of cropland abandonment, scale operation, and cultivation structure. Land Use Policy 2025, 159, 107821. [Google Scholar]
- Grabska-Szwagrzyk, E.; Khiabani, P.H.; Pesoa-Marcilla, M.; Chaturvedi, V.; de Vries, W.T. Exploring land use dynamics in rural areas. An analysis of eight cases in the Global North. Land Use Policy 2024, 144, 107246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Hsu, L.Y. Is income catch-up related to happiness catch-up? Evidence from eight European countries. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, I.; Lago-Penas, S. Rural decline and spatial voting patterns. Parliam. Aff. 2024, 78, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, V.; Holl, A. Growth and decline in rural Spain: An exploratory analysis Eur. Plan. Stud. 2023, 32, 430–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L. Neighborhood harmony, neighborhood governance, and the construction of neighborhood communities. Theory J. 2024, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, D.; Irwin, D.D.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y. Predictors of the Prevalence and Importance of the Observed Trinary Control System in Rural China. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Cui, Y.; Cao, H. Formal and Informal Institutions in Farmers’ Withdrawal from Rural Homesteads in China: Heterogeneity Analysis Based on the Village Location. Land 2022, 11, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.F. Neighborhood Does Matter: Farmers’ Local Social Interactions and Land Rental Behaviors in China. Land 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.; Deaton, B.; Weersink, A. Do landlord-tenant relationships influence rental contracts for farmland or the cash rental rate? Land Econ. 2015, 91, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, B. Social Networks, Informal Finance and Residents’Happiness: An Empirical Analysis Basedon Data of CFPS in 2016. J. Shanghai Univ. Financ. Econ. 2018, 20, 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.Z.H.; Li, J.S.H.; Zhou, L. Welfare or Pressure: How does Household Debt Affect Residents’ Sense of Happiness—Evidence from the Micro Data of Chinese Households. J. Shanxi Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022, 44, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, M.; Willis, R. Utility and Happiness. NBER Working Paper, 25 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrera, S.; Moro, M. On the Use of Subjective Well-Being Data for Environmental Valuation. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2010, 46, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, S.W.; Fu, H.Q. The Impact of Health Shocks on Household Welfare: Evidence from Chinese Households. Nankai Econ. Stud. 2023, 12, 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lagakos, D.; Mobarak, A.M.; Waugh, M.E. The Welfare Effects of Encouraging Rural—Urban Migration. Econometrica 2023, 91, 803–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, M.; Lane, N.; Querubin, P. The Historical State, Local Collective Action, and Economic Development in Vietnam. Econometrica 2018, 86, 2083–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skevas, T.; Skevas, I.; Swinton, S.M. Does Spatial Dependence Affect the Intention to Make Land Available for Bioenergy Crops? J. Agric. Econ. 2018, 69, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyantakyi-Frimpong, H. What lies beneath: Climate change, land expropriation, and zaï agroecological innovations by smallholder farmers in Northern Ghana. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamineh, A.S. The political-economy of communal land distribution for rural youths in Amhara region, Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 2025, 157, 107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villavicencio-Pinto, E. The geography of property rights: Land concentration, irrigation access and rural poverty under climate change in Chile. Land Use Policy 2025, 156, 107578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.E.; Fernandez-Gimenez, M.E.; Balgopal, M.M. An integrated livelihoods and well-being framework to understand northeastern Colorado ranchers’ adaptive strategies. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26, 675–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.; Ishtiaque, A.; Agarwal, A.; Gray, J.M.; Lemos, M.C.; Moben, I.; Singh, B.; Jain, M. The role of rural circular migration in shaping weather risk management for smallholder farmers in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. Glob. Environ. Change 2024, 89, 102937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, D. The impact of non-farm employment on the stable land contracting willingness of farm households: Evidence from rural China. Land Use Policy 2025, 157, 107688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, K.; Savastano, S.; Xia, S. Smallholders’ land access in sub-Saharan Africa: A new landscape. Food Policy. 2017, 67, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, B.; Win, M.T.; Zhang, X.; Filipski, M. The rapid rise of agricultural mechanization in Myanmar. Food Policy 2021, 101, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, J. Property rights and land quality. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2024, 106, 1619–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, X. Can Land Transfer-In Improve Farmers’ Farmland Quality Protection Behavior? Empirical Evidence from Micro-Survey Data in Hubei Province, China. Land 2025, 14, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Definition | Mean | Std. Dev. | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjective Well-Being | 1 = Extremely unhappy; 2 = Unhappy; 3 = Neutral; 4 = Somewhat happy; 5 = Happy; 6 = Extremely happy | 4.81 | 1.12 | 9819 |
| Life Satisfaction | 1 = Extremely dissatisfied; 2 = Dissatisfied; 3 = Neutral; 4 = Somewhat satisfied; 5 = Satisfied; 6 = Extremely satisfied | 4.81 | 1.13 | 9819 |
| Land Rental | 1 means the land is rented-out; 0 implies that the land is not rented-out | 0.16 | 0.36 | 9819 |
| Non-Farm Income | Logarithmic value after adding 1 to the annual Non-Farm Income | 1.74 | 1.26 | 9819 |
| Local Social Acceptance | 1 = Very poor; 2 = Poor; 3 = Fair; 4 = Good; 5 = Very good; 6 = Excellent | 4.63 | 0.79 | 9819 |
| Agricultural Operating Income | Logarithmic value after adding 1 to the annual Farm Income | 0.46 | 0.70 | 9819 |
| Household Size | Logarithmic value of Household Size (in Persons) | 1.20 | 0.49 | 9819 |
| Household Wealth | Logarithmic value of Household Wealth (in Yuan) | 1.86 | 1.52 | 9819 |
| Household Contracted Cultivated Land | logarithm of (current household contracted cultivated land area in mu) | 1.59 | 1.14 | 9819 |
| Children’s Health Status | 1 = Disability Grade 1–3; 2 = Disability Grade 4–6; 3 = Disability Grade 7–10; 4 = Very Poor; 5 = Poor; 6 = Fair; 7 = Good; 8 = Excellent | 7.56 | 0.64 | 9819 |
| Parents’ Health Status | 1 = Disability Grade 1–3; 2 = Disability Grade 4–6; 3 = Disability Grade 7–10; 4 = Very Poor; 5 = Poor; 6 = Fair; 7 = Good; 8 = Excellent | 6.46 | 1.10 | 9819 |
| Social Harmony Index | 1 = Very low; 2 = Somewhat low; 3 = Neutral; 4 = Somewhat high; 5 = Very high; 6 = Quite high | 4.48 | 1.07 | 9819 |
| Satisfaction with Rural Governments | 1 = Extremely dissatisfied; 2 = Dissatisfied; 3 = Neutral; 4 = Somewhat satisfied; 5 = Satisfied; 6 = Extremely satisfied | 4.26 | 1.13 | 9819 |
| Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Land Rental | 0.281 *** | 0.157 *** | 0.132 *** | 0.143 *** | 0.291 *** | 0.156 *** | 0.121 ** | 0.130 *** |
| (0.046) | (0.048) | (0.049) | (0.050) | (0.046) | (0.048) | (0.049) | (0.050) | |
| Non-Farm Income | 0.192 *** | 0.126 *** | 0.131 *** | 0.237 *** | 0.143 *** | 0.153 *** | ||
| (0.017) | (0.020) | (0.020) | (0.017) | (0.020) | (0.020) | |||
| Local Social Acceptance | 0.825 *** | 0.793 *** | 0.625 *** | 0.756 *** | 0.725 *** | 0.560 *** | ||
| (0.026) | (0.026) | (0.026) | (0.026) | (0.026) | (0.027) | |||
| Agricultural Operating Income | 0.022 | −0.015 | −0.011 | 0.070 *** | 0.007 | 0.003 | ||
| (0.027) | (0.028) | (0.029) | (0.027) | (0.028) | (0.029) | |||
| Household Size | 0.359 *** | 0.263 *** | 0.299 *** | 0.201 *** | ||||
| (0.030) | (0.030) | (0.030) | (0.030) | |||||
| Household Wealth | 0.155 *** | 0.125 *** | 0.167 *** | 0.133 *** | ||||
| (0.018) | (0.018) | (0.017) | (0.018) | |||||
| Household Contracted Cultivated Land | 0.038 ** | 0.002 | 0.043 ** | 0.015 | ||||
| (0.017) | (0.019) | (0.017) | (0.019) | |||||
| Children’s Health Status | 0.041 | 0.127 *** | −0.017 | 0.076 * | ||||
| (0.039) | (0.041) | (0.039) | (0.041) | |||||
| Parents’ Health Status | 0.067 *** | 0.069 *** | 0.116 *** | 0.124 *** | ||||
| (0.016) | (0.016) | (0.016) | (0.016) | |||||
| Social Harmony Index | 0.411 *** | 0.404 *** | ||||||
| (0.021) | (0.021) | |||||||
| Satisfaction with Rural Governments | 0.311 *** | 0.287 *** | ||||||
| (0.020) | (0.020) | |||||||
| Other control variables | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Regional fixed effects | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| N | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 |
| Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Laborers Return to Rural Areas Due to Urban-Related Factors | Others | Laborers with Low Skills | Others | Laborers Return to Rural Areas Due to Urban-Related Factors | Others | Laborers with Low Skills | Others | |
| Land Rental | 0.041 | 0.165 *** | 0.017 | 0.156 *** | −0.054 | 0.175 *** | −0.094 | 0.162 *** |
| (0.123) | (0.055) | (0.124) | (0.055) | (0.123) | (0.055) | (0.124) | (0.055) | |
| Non-Farm Income | 0.155 *** | 0.125 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.195 *** | 0.145 *** | 0.127 *** | 0.159 *** |
| (0.050) | (0.023) | (0.048) | (0.023) | (0.050) | (0.023) | (0.048) | (0.023) | |
| Local Social Acceptance | 0.621 *** | 0.627 *** | 0.698 *** | 0.605 *** | 0.546 *** | 0.566 *** | 0.576 *** | 0.553 *** |
| (0.064) | (0.029) | (0.062) | (0.029) | (0.064) | (0.029) | (0.062) | (0.030) | |
| Agricultural Operating Income | 0.105 | −0.034 | 0.036 | −0.02 | 0.056 | −0.011 | −0.019 | 0.008 |
| (0.066) | (0.032) | (0.070) | (0.032) | (0.066) | (0.032) | (0.070) | (0.032) | |
| Other variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Regional fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 1706 | 8108 | 1852 | 7962 | 1706 | 8108 | 1852 | 7962 |
| Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Villages with the Presence of “Village Tyrant”-like Groups | Villages Without the Presence of “Village Tyrant”-like Groups | Villages with the Presence of “Respected and Prestigious Group”-like Entities | Villages Without the Presence of “Respected and Prestigious Group”-like Entities | Villages with the Presence of “Village Tyrant”-like Groups | Villages Without the Presence of “Village Tyrant”-like Groups | Villages with the Presence of “Respected and Prestigious Group”-like Entities | Villages Without the Presence of “Respected and Prestigious Group”-like Entities | |
| Land Rental | 0.111 | 0.166 *** | −0.042 | 0.238 *** | 0.236 * | 0.129 ** | 0.026 | 0.175 *** |
| (0.130) | (0.055) | (0.087) | (0.062) | (0.132) | (0.055) | (0.087) | (0.062) | |
| Non-Farm Income | 0.194 *** | 0.117 *** | 0.155 *** | 0.127 *** | 0.272 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.182 *** | 0.145 *** |
| (0.051) | (0.022) | (0.036) | (0.025) | (0.053) | (0.022) | (0.036) | (0.025) | |
| Local Social Acceptance | 0.649 *** | 0.621 *** | 0.671 *** | 0.604 *** | 0.495 *** | 0.572 *** | 0.587 *** | 0.551 *** |
| (0.068) | (0.029) | (0.046) | (0.033) | (0.069) | (0.029) | (0.046) | (0.033) | |
| Agricultural Operating Income | −0.01 | −0.013 | 0.031 | −0.031 | 0.112 | −0.024 | 0.04 | −0.02 |
| (0.069) | (0.032) | (0.049) | (0.036) | (0.070) | (0.032) | (0.050) | (0.036) | |
| Other variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Regional fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 1442 | 8377 | 3263 | 6556 | 1442 | 8377 | 3263 | 6556 |
| Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Households with Middle-Upper Social Status | Households with Lower Social Status | Opinions Carry Significant Weight in the Village’s Major Events | Opinions Carry Little Weight in the Village’s Major Events | Households with Middle-Upper Social Status | Households with Lower Social Status | Opinions Carry Significant Weight in the Village’s Major Events | Opinions Carry Little Weight in the Village’s Major Events | |
| Land Rental | 0.129 ** | 0.147 | 0.152 *** | 0.048 | 0.103 * | 0.166 | 0.123 ** | 0.141 |
| (0.054) | (0.145) | (0.055) | (0.133) | (0.054) | (0.146) | (0.055) | (0.132) | |
| Non-Farm Income | −0.143 * | 0.078 | −0.141 * | 0.001 | −0.023 | 0.281 * | −0.068 | 0.276 ** |
| (0.079) | (0.139) | (0.083) | (0.123) | (0.080) | (0.150) | (0.084) | (0.129) | |
| Local Social Acceptance | 0.100 *** | 0.141 ** | 0.110 *** | 0.282 *** | 0.121 *** | 0.157 ** | 0.122 *** | 0.343 *** |
| (0.022) | (0.063) | (0.022) | (0.057) | (0.022) | (0.063) | (0.022) | (0.057) | |
| Agricultural Operating Income | 0.610 *** | 0.515 *** | 0.643 *** | 0.594 *** | 0.546 *** | 0.428 *** | 0.590 *** | 0.475 *** |
| (0.029) | (0.070) | (0.030) | (0.061) | (0.029) | (0.070) | (0.030) | (0.061) | |
| Other variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Regional fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 8485 | 1334 | 8262 | 1557 | 8485 | 1334 | 8262 | 1557 |
| Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | Subjective Well-Being | Life Satisfaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changing Method | Modifying Variables | Adjusting Sample | Outlier Elimination | |||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Land Rental | 0.079 *** | 0.076 *** | 0.088 * | 0.064 | 0.112 ** | 0.096 * | 0.237 *** | 0.220 *** |
| (0.027) | (0.027) | (0.046) | (0.046) | (0.053) | (0.053) | (0.069) | (0.069) | |
| Non-Farm Income | 0.067 *** | 0.082 *** | 0.099 *** | 0.103 *** | 0.146 *** | 0.174 *** | 0.130 *** | 0.140 *** |
| (0.011) | (0.011) | (0.019) | (0.018) | (0.021) | (0.021) | (0.030) | (0.030) | |
| Local Social Acceptance | 0.290 *** | 0.261 *** | 0.288 *** | 0.247 *** | 0.627 *** | 0.555 *** | 0.607 *** | 0.547 *** |
| (0.013) | (0.014) | (0.023) | (0.023) | (0.027) | (0.027) | (0.035) | (0.034) | |
| Agricultural Operating Income | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.021 | 0.012 | −0.001 | 0.02 | 0.056 | 0.067 * |
| (0.015) | (0.015) | (0.026) | (0.025) | (0.030) | (0.030) | (0.039) | (0.039) | |
| Other variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Regional fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| cons | 0.25 | 0.699 *** | −3.919 *** | −3.433 *** | ||||
| (0.226) | (0.229) | (0.274) | (0.274) | |||||
| R2 | 0.237 | 0.229 | - | - | ||||
| N | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9819 | 9168 | 9168 | 5998 | 5998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Kang, J. Study on the Impact of Land Transfer on Farmers’ Welfare: Theoretical and Empirical Evidence from China. Land 2025, 14, 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122384
Deng Z, Kang J. Study on the Impact of Land Transfer on Farmers’ Welfare: Theoretical and Empirical Evidence from China. Land. 2025; 14(12):2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122384
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhituan, and Jiaojiao Kang. 2025. "Study on the Impact of Land Transfer on Farmers’ Welfare: Theoretical and Empirical Evidence from China" Land 14, no. 12: 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122384
APA StyleDeng, Z., & Kang, J. (2025). Study on the Impact of Land Transfer on Farmers’ Welfare: Theoretical and Empirical Evidence from China. Land, 14(12), 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14122384







