Planning for Dynamic Connectivity: Operationalizing Robust Decision-Making and Prioritization Across Landscapes Experiencing Climate and Land-Use Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
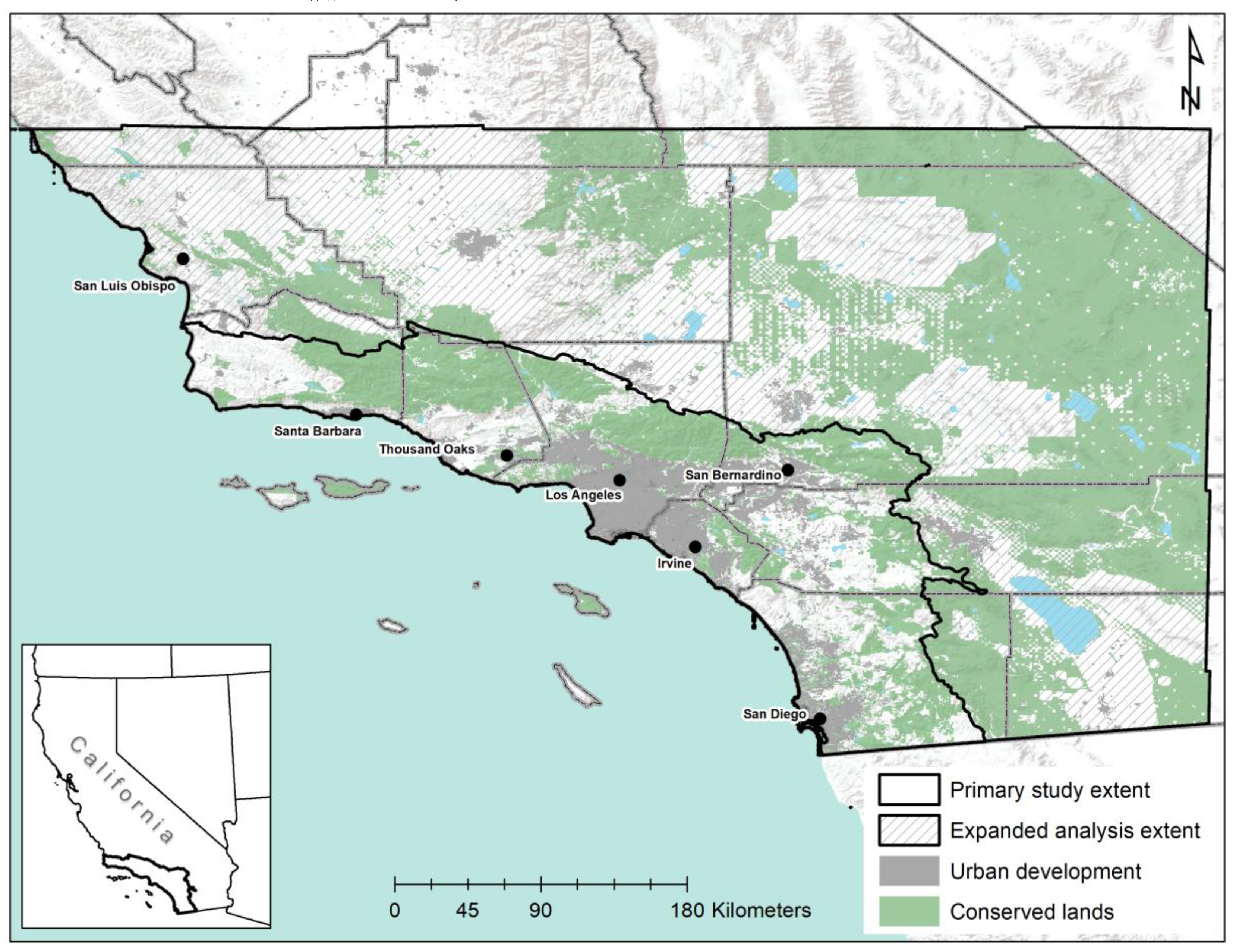
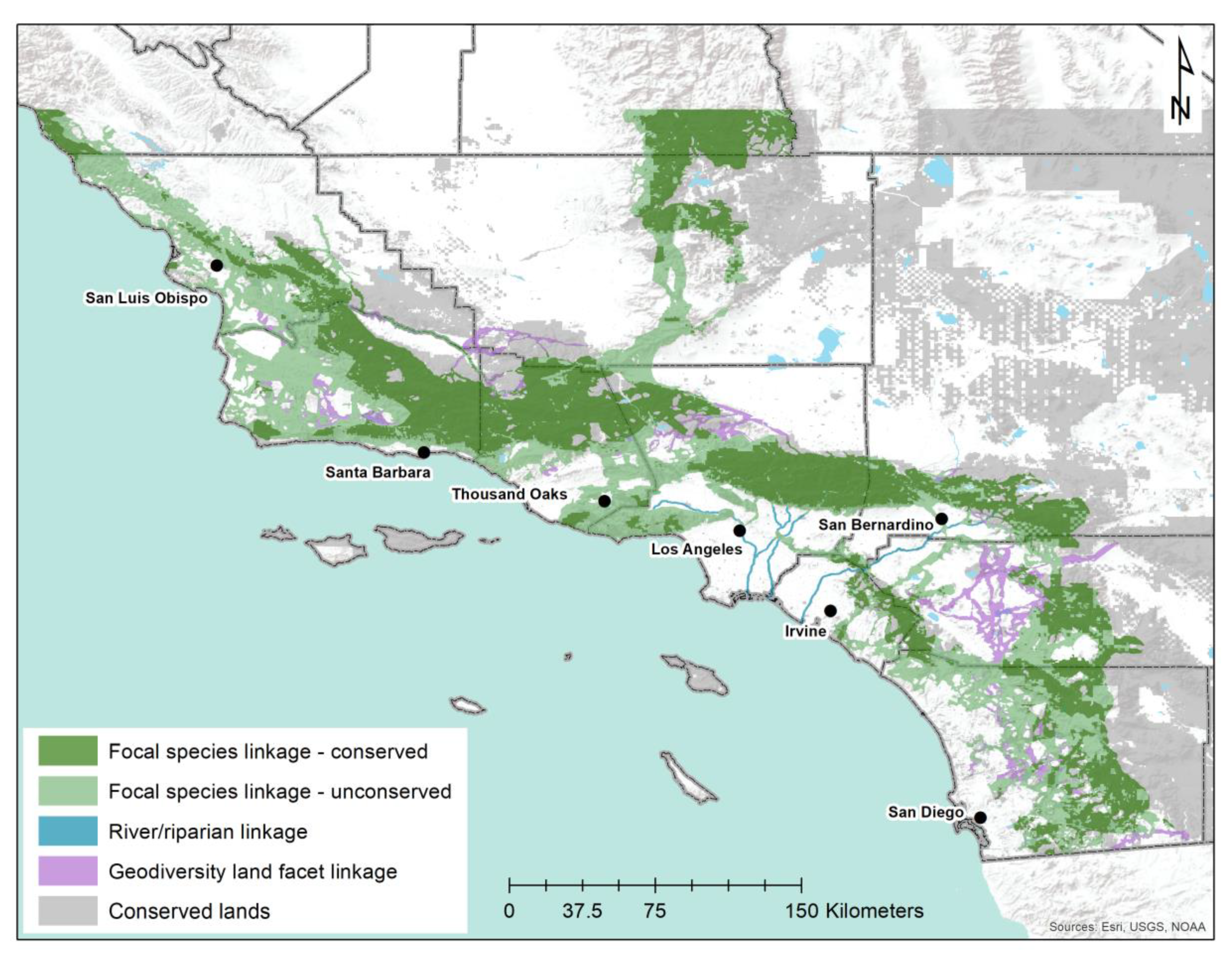
2.1. Study Area
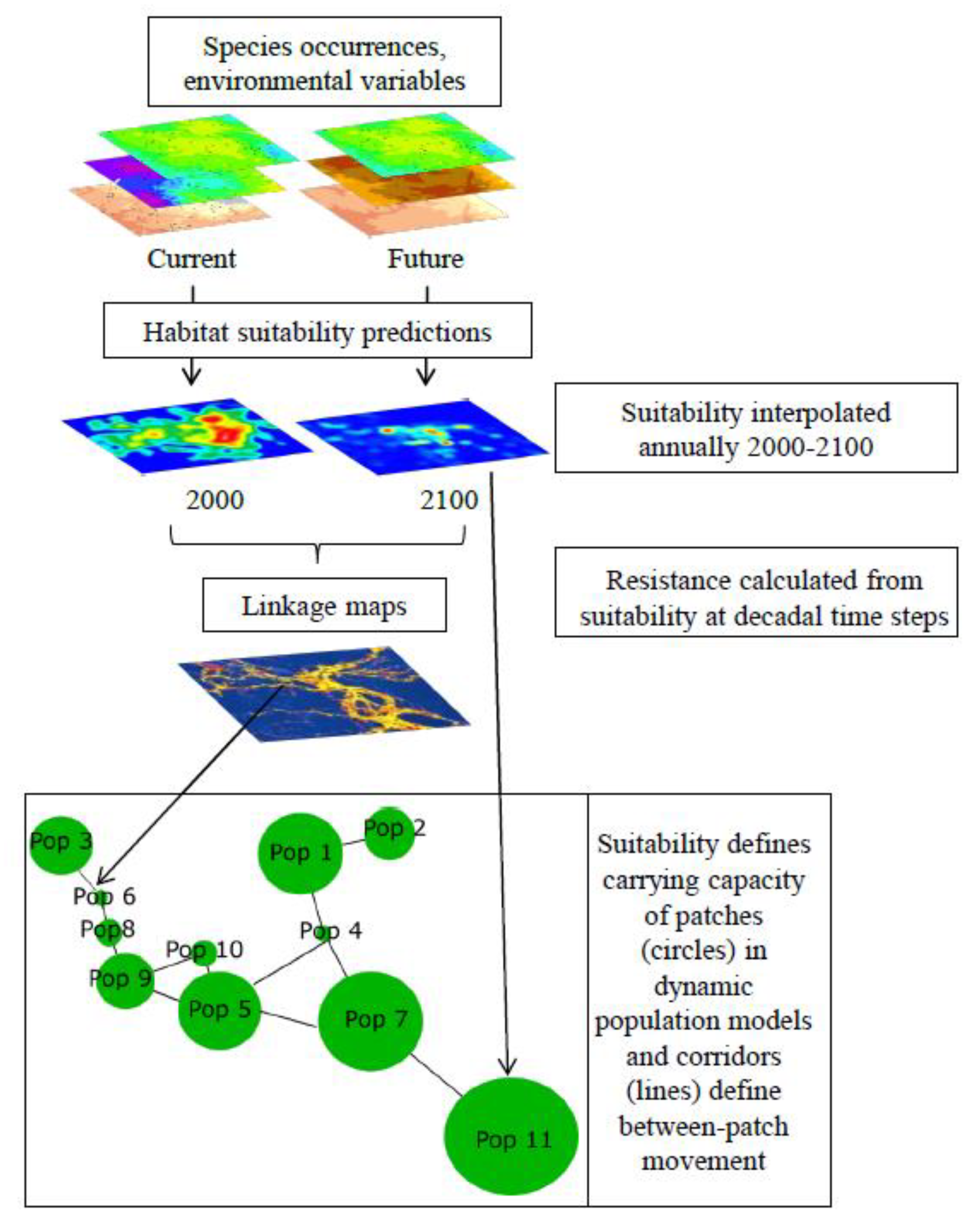
2.2. Modeling Approach
2.2.1. Habitat Suitability, Resistance, and Core Area Modeling
2.2.2. Linkage Modeling
2.2.3. Metapopulation Modeling
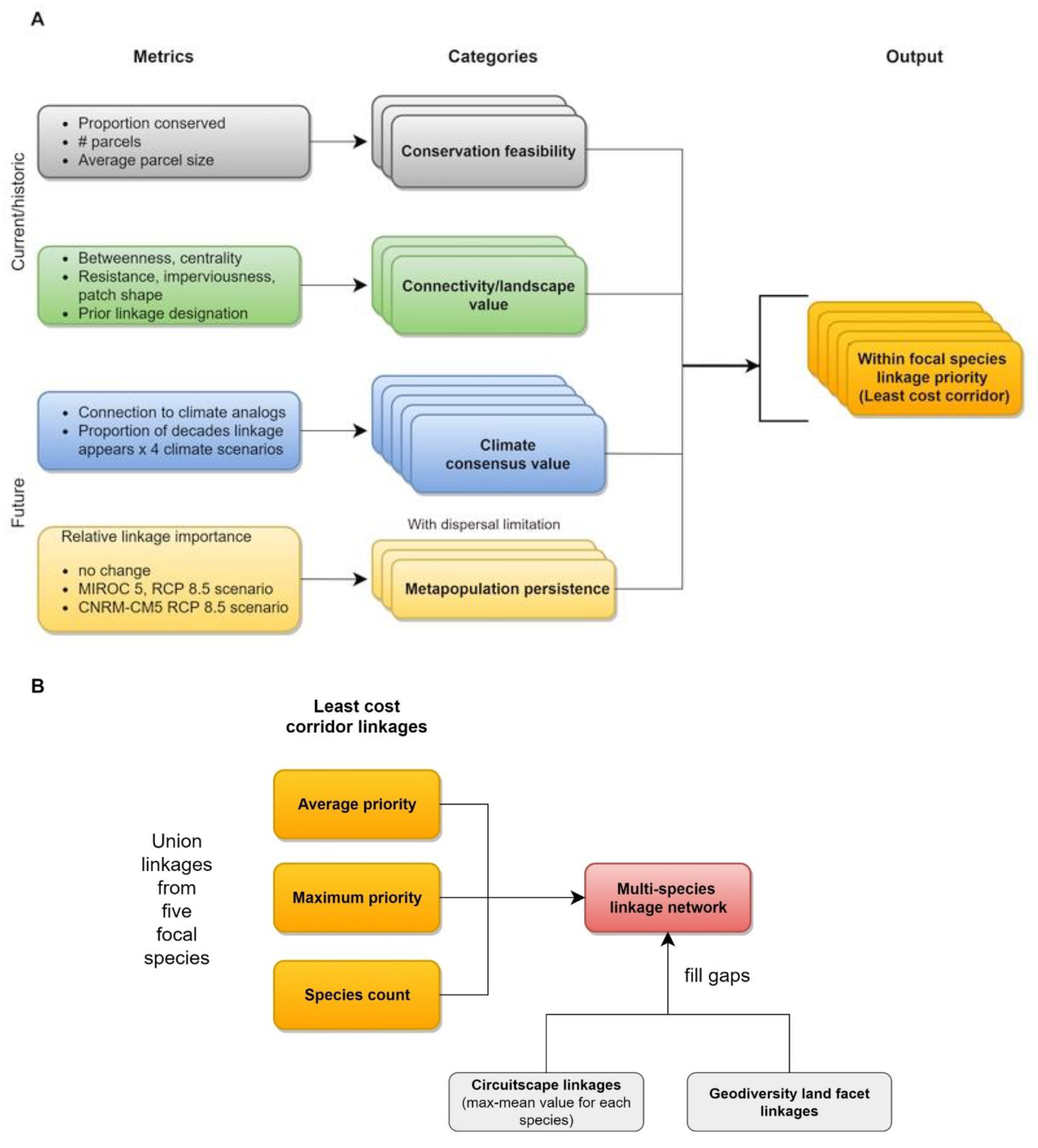
2.3. Prioritizing a Multispecies Linkage Network
2.3.1. Within-Species Prioritization
2.3.2. Multispecies Prioritization
3. Results
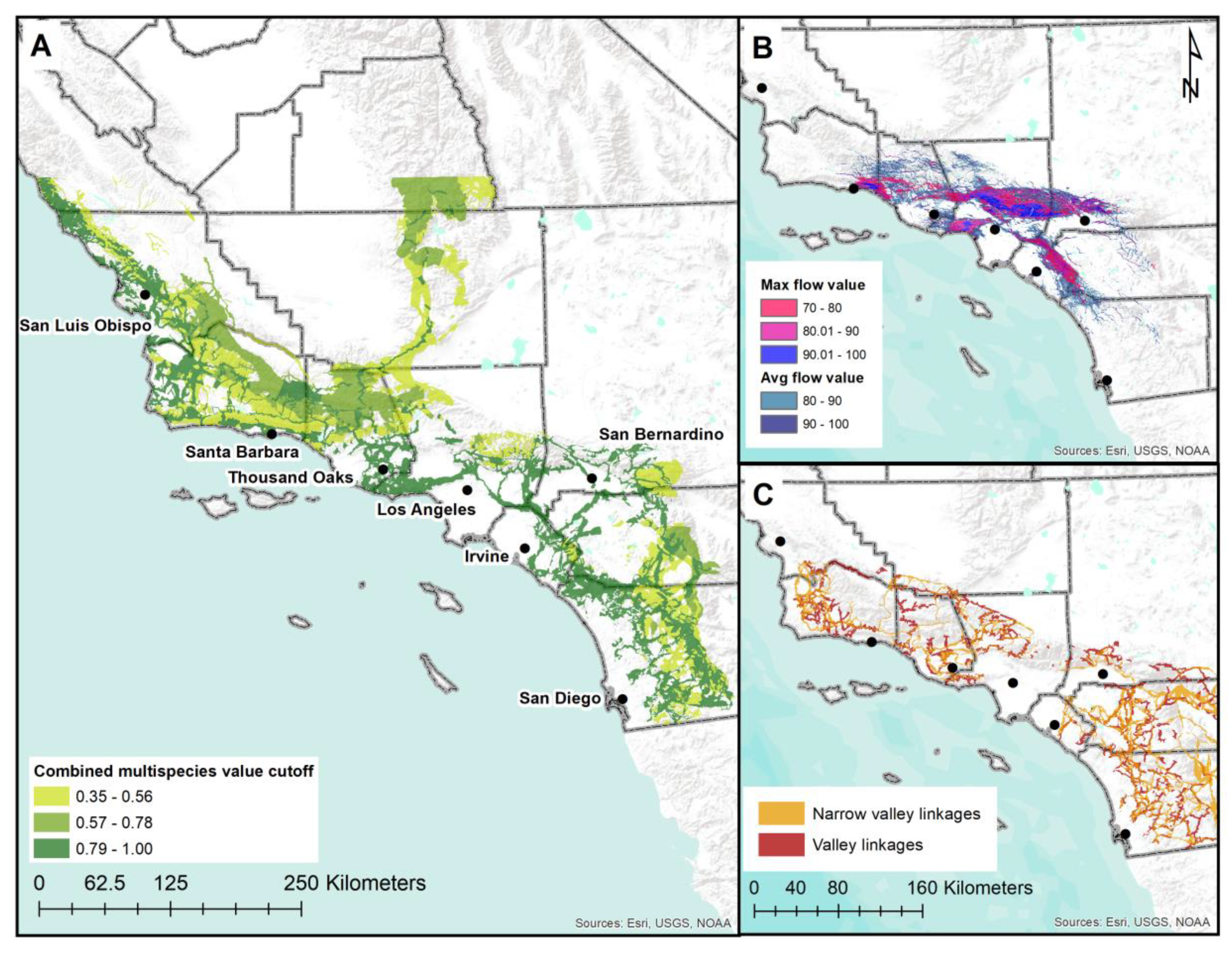
3.1. Habitat Suitability, Linkage, and Metapopulation Modeling
3.2. Prioritizing a Multispecies Linkage Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Parmesan, C. Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 37, 637–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Hall, S.A.; Beier, P.; Theobald, D.M. Where to Restore Ecological Connectivity? Detecting Barriers and Quantifying Restoration Benefits. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, N.E.; Zavaleta, E.S. Biodiversity management in the face of climate change: A review of 22 years of recommendations. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, A.T.H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Cameron, D.R.; Heller, N.E.; Huber, P.R.; Schloss, C.A.; Thorne, J.H.; Merenlender, A.M. New concepts, models, and assessments of climate-wise connectivity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 073002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, P.; Gregory, A.J. Desperately seeking sTable 50-year-old landscapes with patches and long, wide corridors. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noss, R.F. Landscape connectivity: Different functions at different scales. In Landscape linkages and Biodiversity; Hudson, W.E., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hilty, J.A.; Lidicker, W., Jr.; Merenlender, A.M. Corridor Ecology: The Science and Practice of Linking Landscapes for Biodiversity Conservation; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; ISBN 1559630477. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.H.; Kodric-Brown, A. Turnover Rates in Insular Biogeography: Effect of Immigration on Extinction. Ecology 1977, 58, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D.; Farr, J.A.; Cox, J.; Mehlman, D.W. Movement corridors: Conservation bargains or poor investments? Conserv. Biol. 1992, 6, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, L.; Midgley, G.F.; Millar, D. Climate change-integrated conservation strategies. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2002, 11, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Bertzky, B.; Bastin, L.; Battistella, L.; Mandrici, A.; Dubois, G. Protected area connectivity: Shortfalls in global targets and country-level priorities. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 219, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, A.T.H.; Beier, P.; Creech, T.; Jones, K.; Jongman, R.H.G.; Stonecipher, G.; Tabor, G.M. Thirty years of connectivity conservation planning: An assessment of factors influencing plan implementation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, S.; Saura, S.; Fortin, M.-J. Landscape connectivity analysis for conservation: Insights from combining new methods with ecological and genetic data. Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilkina, B.; Houtman, R.; Gomes, C.P.; Montgomery, C.A.; McKelvey, K.S.; Kendall, K.; Graves, T.A.; Bernstein, R.; Schwartz, M.K. Trade-offs and efficiencies in optimal budget-constrained multispecies corridor networks. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gippoliti, S.; Battisti, C. More cool than tool: Equivoques, conceptual traps and weaknesses of ecological networks in environmental planning and conservation. Land Use policy 2017, 68, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.H.; Rayfield, B.; Dumitru, M.; Gonzalez, A. Applying network theory to prioritize multispecies habitat networks that are robust to climate and land-use change. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brost, B.M.; Beier, P. Comparing linkage designs based on land facets to linkage designs based on focal species. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krosby, M.; Breckheimer, I.; Pierce, D.J.; Singleton, P.H.; Hall, S.A.; Halupka, K.C.; Gaines, W.L.; Long, R.A.; McRae, B.H.; Cosentino, B.L.; et al. Focal species and landscape “naturalness” corridor models offer complementary approaches for connectivity conservation planning. Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, J.L.; Lawler, J.J.; McRae, B.H.; Nuñez, T.A.; Theobald, D.M. Achieving climate connectivity in a fragmented landscape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7195–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanski, I. Metapopulation Ecology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999; p. 313. ISBN 0198540655. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson, J.; Angelstam, P.; Elmqvist, T.; Emanuelsson, U.; Folke, C.; Ihse, M.; Moberg, F.; Nyström, M. Reserves, Resilience and Dynamic Landscapes. AMBIO 2003, 32, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, C.C.; van der Hoek, D.C.J.; Vonk, M. Spatial planning of a climate adaptation zone for wetland ecosystems. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, T.A.; Lawler, J.J.; McRae, B.H.; Pierce, D.J.; Krosby, M.B.; Kavanagh, D.M.; Singleton, P.H.; Tewksbury, J.J. Connectivity Planning to Address Climate Change. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrod, K.; Beier, P.; Garding, E.; Cabañero, C. A Linkage Network for the California Deserts; Technical Report for the Bureau of Land Management and The Wildlands Conservancy: Fair Oaks, CA, USA, February 2012.
- Underwood, E.C.; Viers, J.H.; Klausmeyer, K.R.; Cox, R.L.; Shaw, M.R. Threats and biodiversity in the mediterranean biome. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syphard, A.D.; Radeloff, V.C.; Keeley, J.E.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Clayton, M.K.; Stewart, S.I.; Hammer, R.B. Human influence on California fire regimes. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.; Wejnert, K.E.; Hathaway, S.A.; Rochester, C.J.; Fisher, R.N. Effect of species rarity on the accuracy of species distribution models for reptiles and amphibians in southern California. Divers. Distrib. 2009, 15, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C. Guidelines for assessing the suitability of spatial climate data sets. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey National Elevation Dataset. Sioux Falls, SD: EROS. 2009. Available online: http://viewer.nationalmap.gov/viewer/ (accessed on 15 July 2016).
- Flint, L.E.; Flint, A.L. Downscaling future climate scenarios to fine scales for hydrologic and ecological modeling and analysis. Ecol. Process. 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.W.; Cayan, D.R.; Thrasher, B.L. Statistical Downscaling Using Localized Constructed Analogs (LOCA)*. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 2558–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Yang, L.; Danielson, P.; Homer, C.; Fry, J.; Xian, G. A comprehensive change detection method for updating the National Land Cover Database to circa 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.K.H.; Carlisle, D.M.; May, J.T.; Klausmeyer, K.R.; Grantham, T.E.; Brown, L.R.; Howard, J.K. Patterns and magnitude of flow alteration in California, USA. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenness, J. DEM Surface Tools. Available online: http://www.jennessent.com/arcgis/surface_area.htm (accessed on 15 July 2016).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/biomod2/index.html (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Phillips, S.; Leathwick, J.; Elith, J. Package ‘dismo’’-Species Distribution Modeling’. Circles 2017, 9, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shirk, A.; McRae, B.H. Gnarly Landscape Utilities: Core Mapper User Guide; The Nature Conservancy: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Adriaensen, F.; Chardon, J.P.; De Blust, G.; Swinnen, E.; Villalba, S.; Gulinck, H.; Matthysen, E. The application of ‘least-cost’ modelling as a functional landscape model. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 64, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, A.T.H.; Beier, P.; Gagnon, J.W. Estimating landscape resistance from habitat suitability: Effects of data source and nonlinearities. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, A.M.; Walters, J.R.; Morris, W.F.; Sexton, J.; Moody, A. Empirical estimation of dispersal resistance surfaces: A case study with red-cockaded woodpeckers. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Sánchez, M.C.; Balkenhol, N.; Cushman, S.; Pérez, T.; Domínguez, A.; Saura, S. A comparative framework to infer landscape effects on population genetic structure: Are habitat suitability models effective in explaining gene flow? Landsc. Ecol. 2015, 30, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Kavanagh, D.M. Linkage Mapper Connectivity Analysis Software; The Nature Conservancy: Seattle, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McRae, B.H.; Dickson, B.G.; Keitt, T.H.; Shah, V.B. Using Circuit Theory to Model Connectivity in Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. Ecology 2008, 89, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezanson, J.; Edelman, A.; Karpinski, S.; Shah, V.B. Julia: A fresh approach to numerical computing. SIAM Rev. 2017, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, R.; Hall, K.; Shah, V.; Edelman, A. Circuitscape in Julia: High performance connectivity modelling to support conservation decisions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.03542. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, P.J.; Pressey, R.L.; Hunter, M.L.; Schloss, C.A.; Buttrick, S.C.; Heller, N.E.; Tirpak, J.M.; Faith, D.P.; Cross, M.S.; Shaffer, M.L. Incorporating geodiversity into conservation decisions. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, D.M.; Harrison-Atlas, D.; Monahan, W.B.; Albano, C.M. Ecologically-relevant maps of landforms and physiographic diversity for climate adaptation planning. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, P.; Brost, B. Use of land facets to plan for climate change: Conserving the arenas, not the actors. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brost, B.M.; Beier, P. Use of land facets to design linkages for climate change. Ecol. Appl. 2012, 22, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenness, J.; Brost, B.; Beier, P. Land Facet Corridor Designer: Extension for ArcGIS; Jenness Enterprises: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2013; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Akçakaya, H.R.; Root, W.T. Linking Landscape Data with Population Viability Analysis (Version 5.0); Applied Mathematics: Setaukey, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, T.; Gough, M. A platform-independent fuzzy logic modeling framework for environmental decision support. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 34, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GreenInfo Network California Protected Areas Database. 2018. Available online: https://www.calands.org/cpad/ (accessed on 31 October 2018).
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. Inter J. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- South Coast Wildlands. South Coast Wildlands South Coast Missing Linkages: A Wildland Network for the South Coast Ecoregion; South Coast Wildlands: Fair Oaks, CA, USA, 2008; 67p. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, W.D.; Beier, P.; Penrod, K.; Paulman, K.; Rustigian-Romsos, H.; Strittholt, J.; Parisi, M.; Pettler, A. California Essential Habitat Connectivity Project: A Strategy for Conservation a Connected California; Prepared for California Department of Transportation, California Department of Fish and Game, and Federal Highways Administration: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2010; p. 313.
- Flint, L.E.; Flint, A.L.; Thorne, J.H.; Boynton, R. Fine-scale hydrologic modeling for regional landscape applications: The California Basin Characterization Model development and performance. Ecol. Process. 2013, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J.A.; Greene, R. Connectivity Analysis Software for Estimating Linkage Priority; Conservation Biology Institute: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- GreenInfo Network California Conservation Easements Database. 2018. Available online: https://www.calands.org/cced/ (accessed on 31 October 2018).
- Peterson, G.D.; Cumming, G.S.; Carpenter, S.R. Scenario planning: A tool for conservation in an uncertain world. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn; Elissa; Schwarz, A.; Anderson, J.; Correa, M. Perspectives and Guidance for Climate Change Analysis; Technical Report for California Department of Water Resources (DWR) and Climate Change Technical Advisory Group (CCTAG): Sacramento, CA, USA, August 2015.
| Name | Description and Source | Time Variant | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate | Source: Downscaled (to 90 m) PRISM, MIROC5 RCP4.5, MIROC5 RCP8.5, CNRM CM5 RCP4.5, CNRM CM5 RCP8.5 | ||
| Bioclim 1 | Mean temperature | Yes | |
| Bioclim 2 | Mean diurnal range (mean of monthly (max temperature-minimum temperature)) | Yes | |
| Bioclim 4 | Temperature Seasonality (Monthly standard deviation *100) | Yes | |
| Bioclim 6 | Minimum temperature of the coldest month | Yes | |
| Bioclim 12 | Mean precipitation | Yes | |
| Bioclim 14 | Precipitation of the driest month | Yes | |
| Bioclim 15 | Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation across months) | Yes | |
| Land- use | Source: National Land Cover Database 2011 [33] | ||
| Impervious surfaces | Used as a proxy for urban land cover | No | |
| Water Resources | Source: [34] | ||
| Distance to seasonal streams | Euclidean distance to streams with low probability of year-round flow | No | |
| Distance to perennial streams | Euclidean distance to streams with high probability of year-round flow | No | |
| Stream density | Density of all streams within a 5-km moving window | No | |
| Topography | Source: National Elevation Dataset [30] | ||
| Roughness Index | Total curvature calculated with DEM Surface Tools [35] | No | |
| Percent Slope | Derived from National Elevation Dataset | No | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jennings, M.K.; Haeuser, E.; Foote, D.; Lewison, R.L.; Conlisk, E. Planning for Dynamic Connectivity: Operationalizing Robust Decision-Making and Prioritization Across Landscapes Experiencing Climate and Land-Use Change. Land 2020, 9, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9100341
Jennings MK, Haeuser E, Foote D, Lewison RL, Conlisk E. Planning for Dynamic Connectivity: Operationalizing Robust Decision-Making and Prioritization Across Landscapes Experiencing Climate and Land-Use Change. Land. 2020; 9(10):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9100341
Chicago/Turabian StyleJennings, Megan K., Emily Haeuser, Diane Foote, Rebecca L. Lewison, and Erin Conlisk. 2020. "Planning for Dynamic Connectivity: Operationalizing Robust Decision-Making and Prioritization Across Landscapes Experiencing Climate and Land-Use Change" Land 9, no. 10: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9100341
APA StyleJennings, M. K., Haeuser, E., Foote, D., Lewison, R. L., & Conlisk, E. (2020). Planning for Dynamic Connectivity: Operationalizing Robust Decision-Making and Prioritization Across Landscapes Experiencing Climate and Land-Use Change. Land, 9(10), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/land9100341








