Exploring the Gobi Wall: Archaeology of a Large-Scale Medieval Frontier System in the Mongolian Desert
Abstract
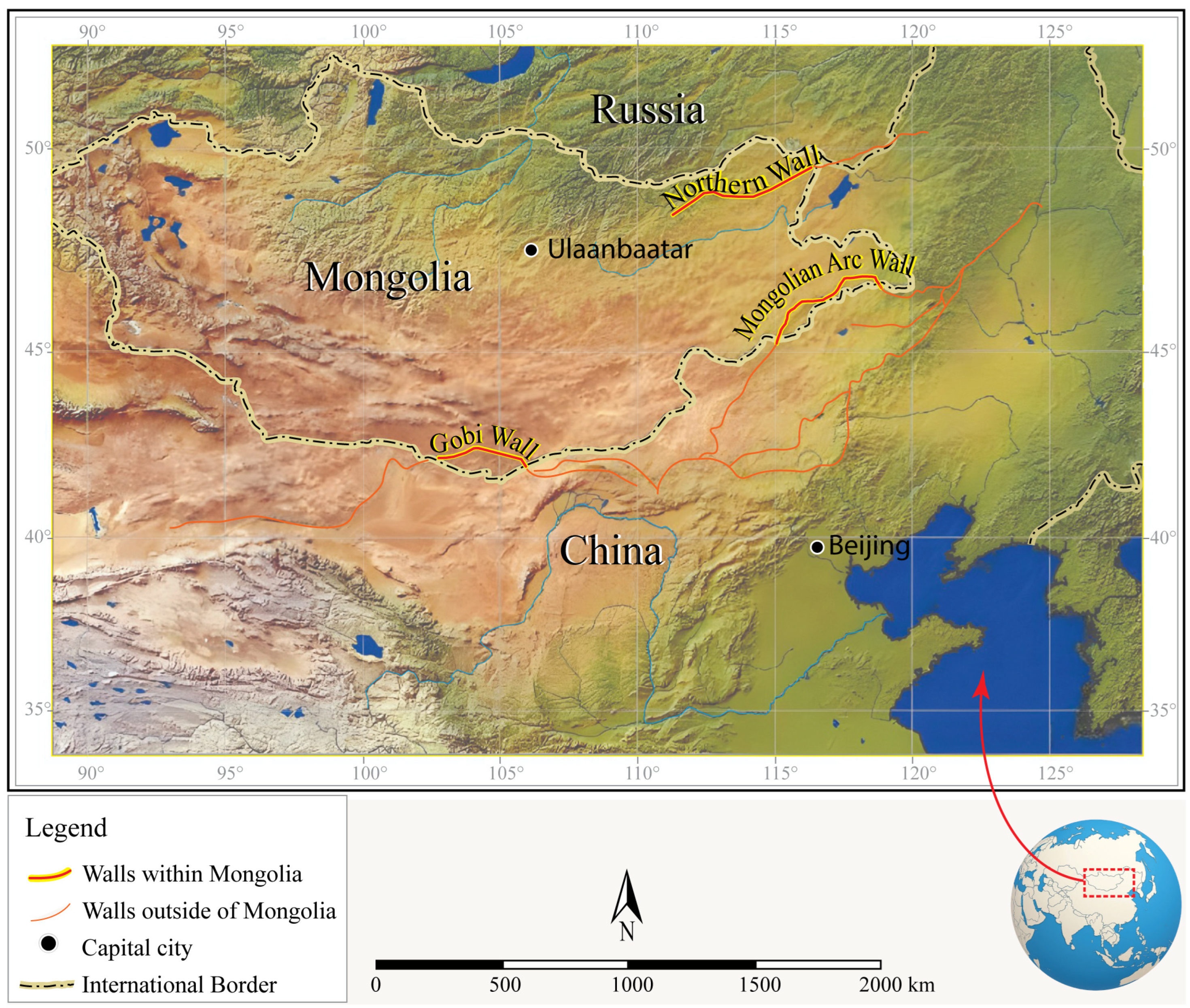
1. Introduction
2. Previous Research
3. Methodology
3.1. Geospatial Analysis and Remote Sensing
3.2. Systematic Archeological Field Survey
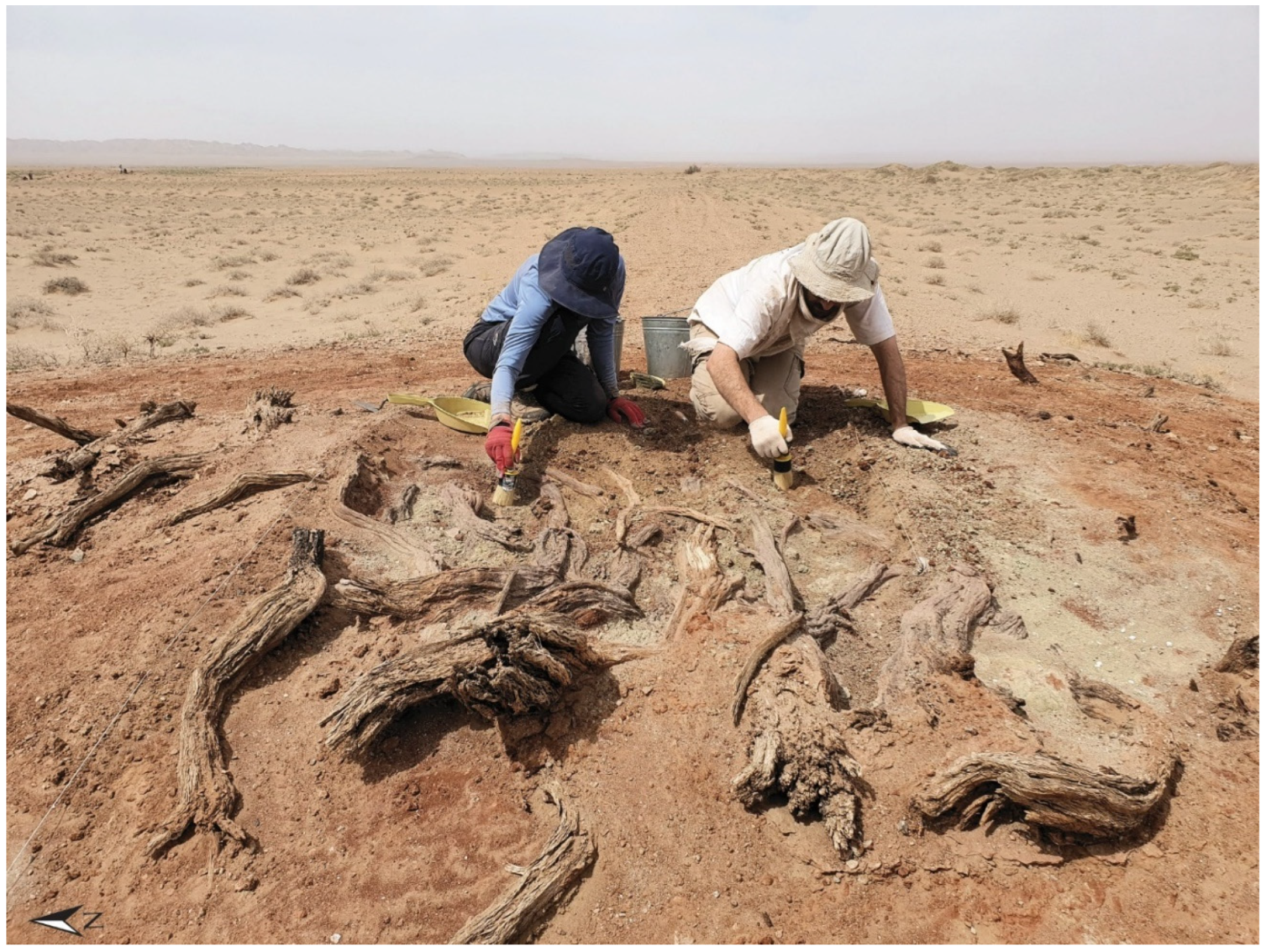
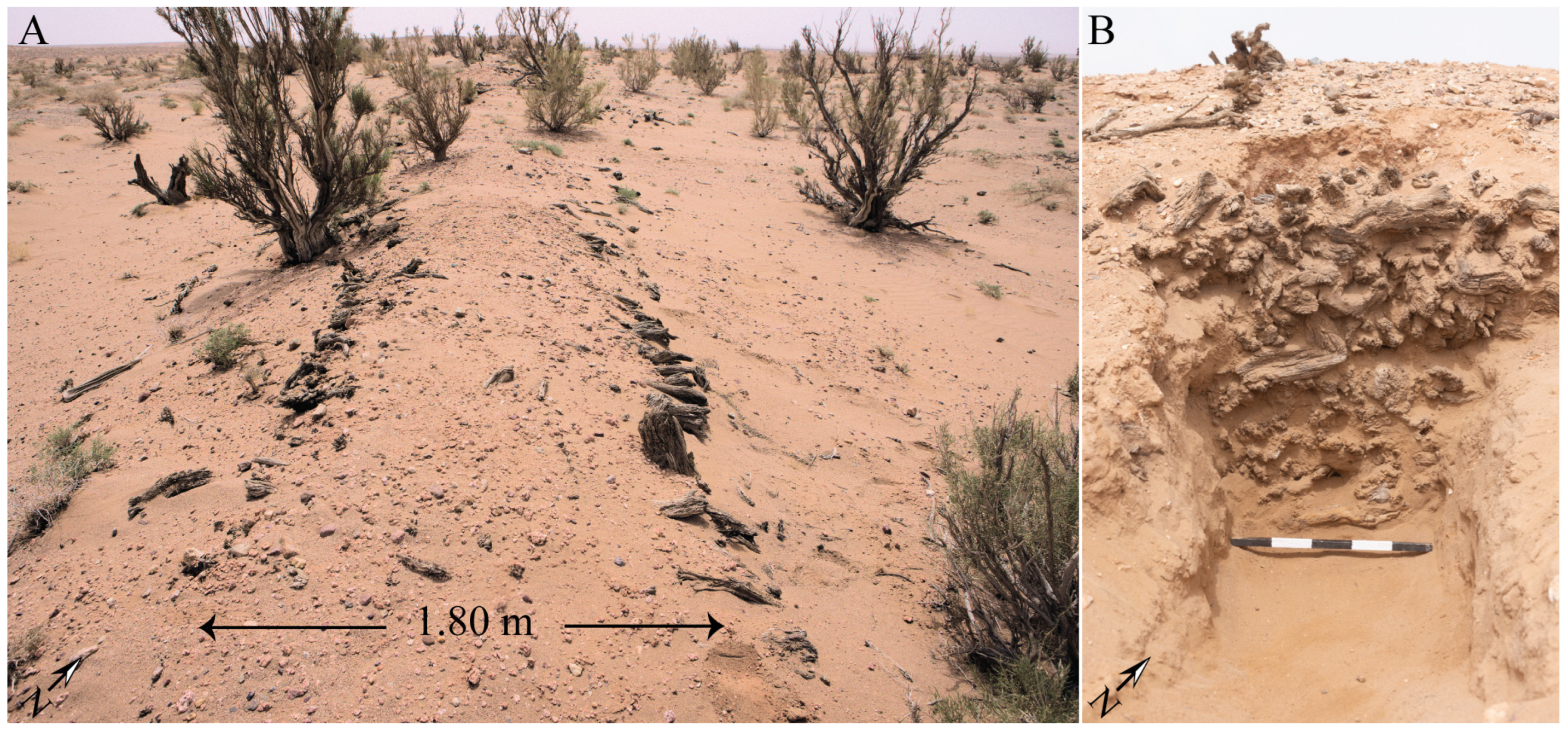
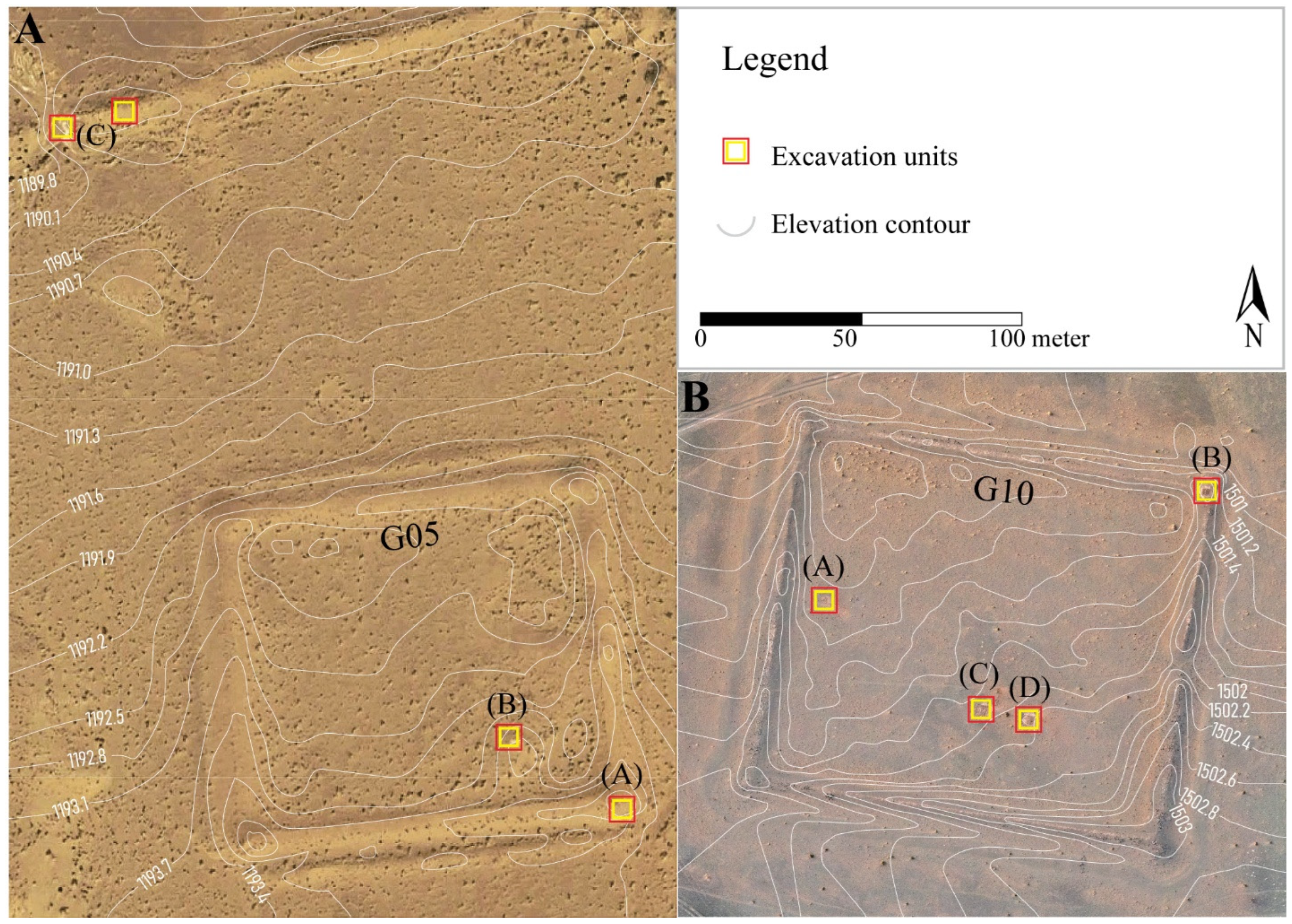
3.3. Targeted Excavations
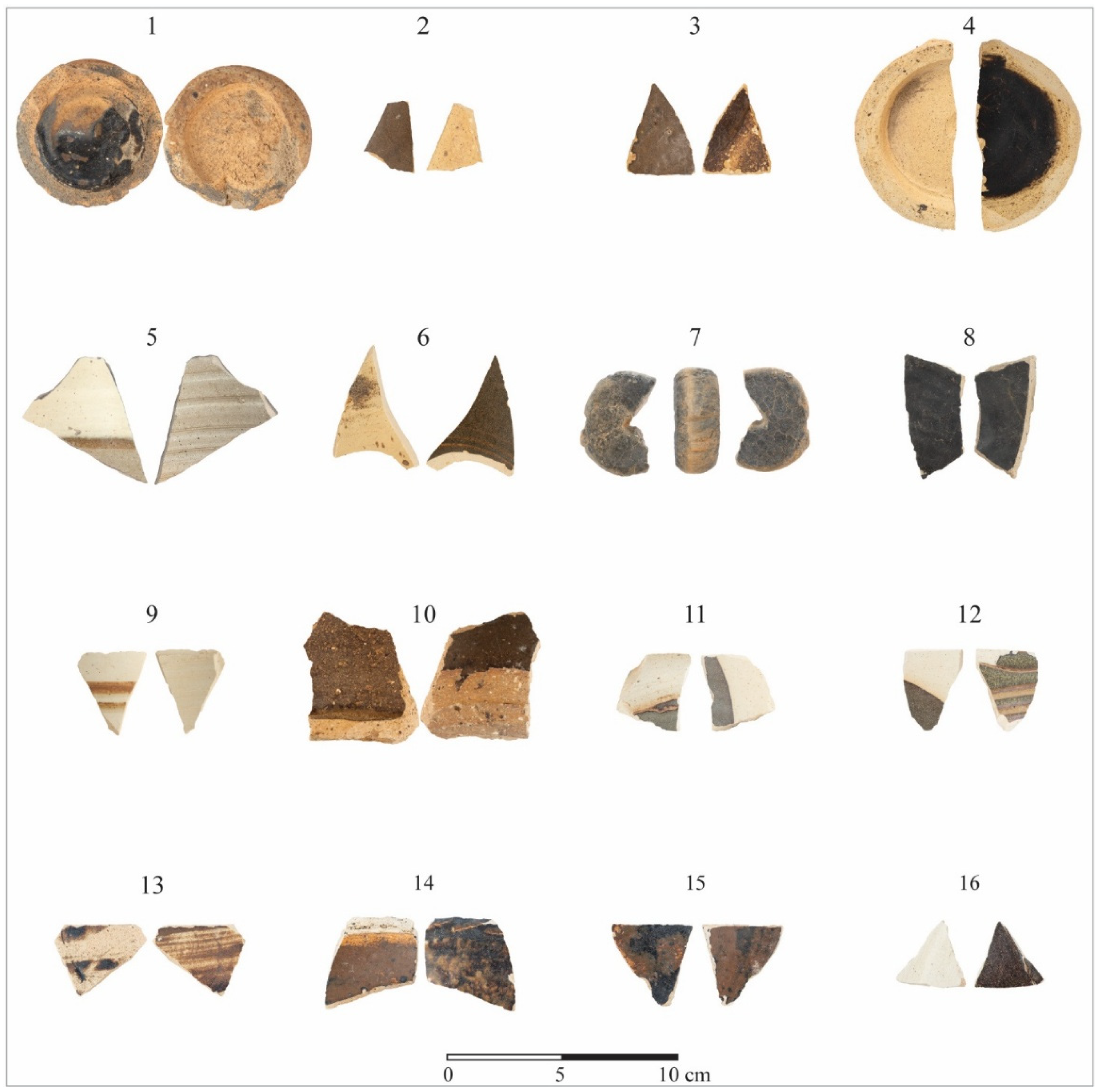
3.4. Laboratory Analyses
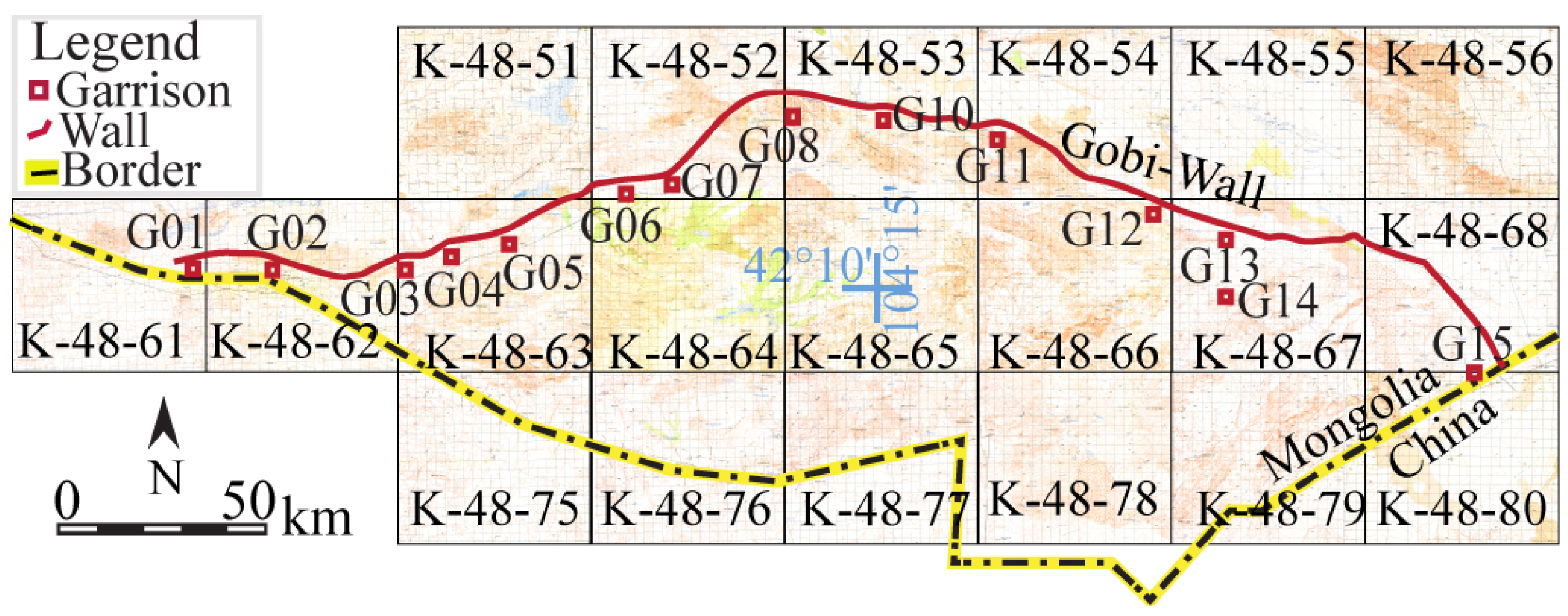
4. Archeological Research of the Gobi Wall System
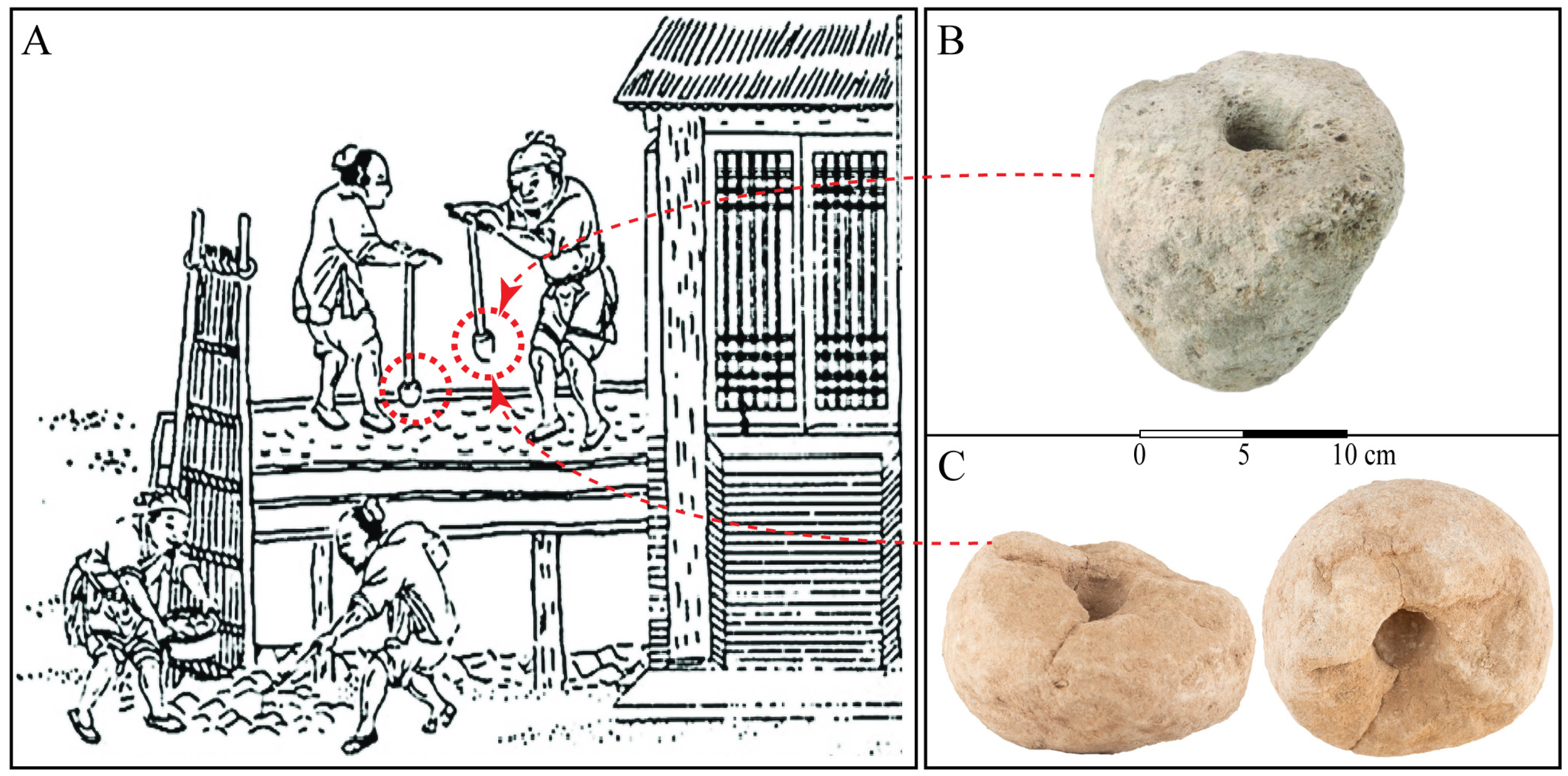
4.1. Wall Construction and Typology
4.2. Garrison Structure
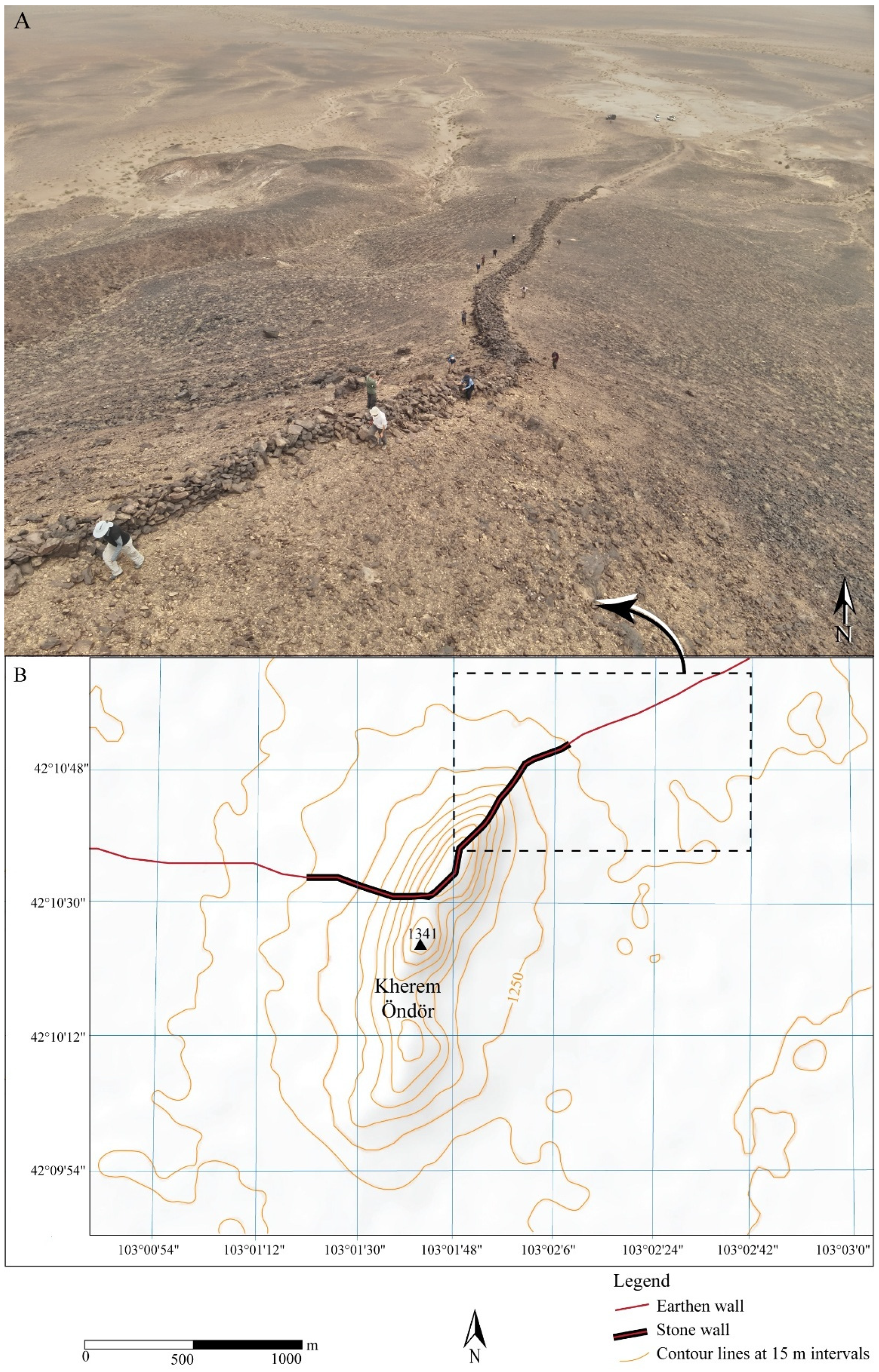
4.3. Mountain Pass Fortifications and Strategic Points
5. Chronology
5.1. Coins
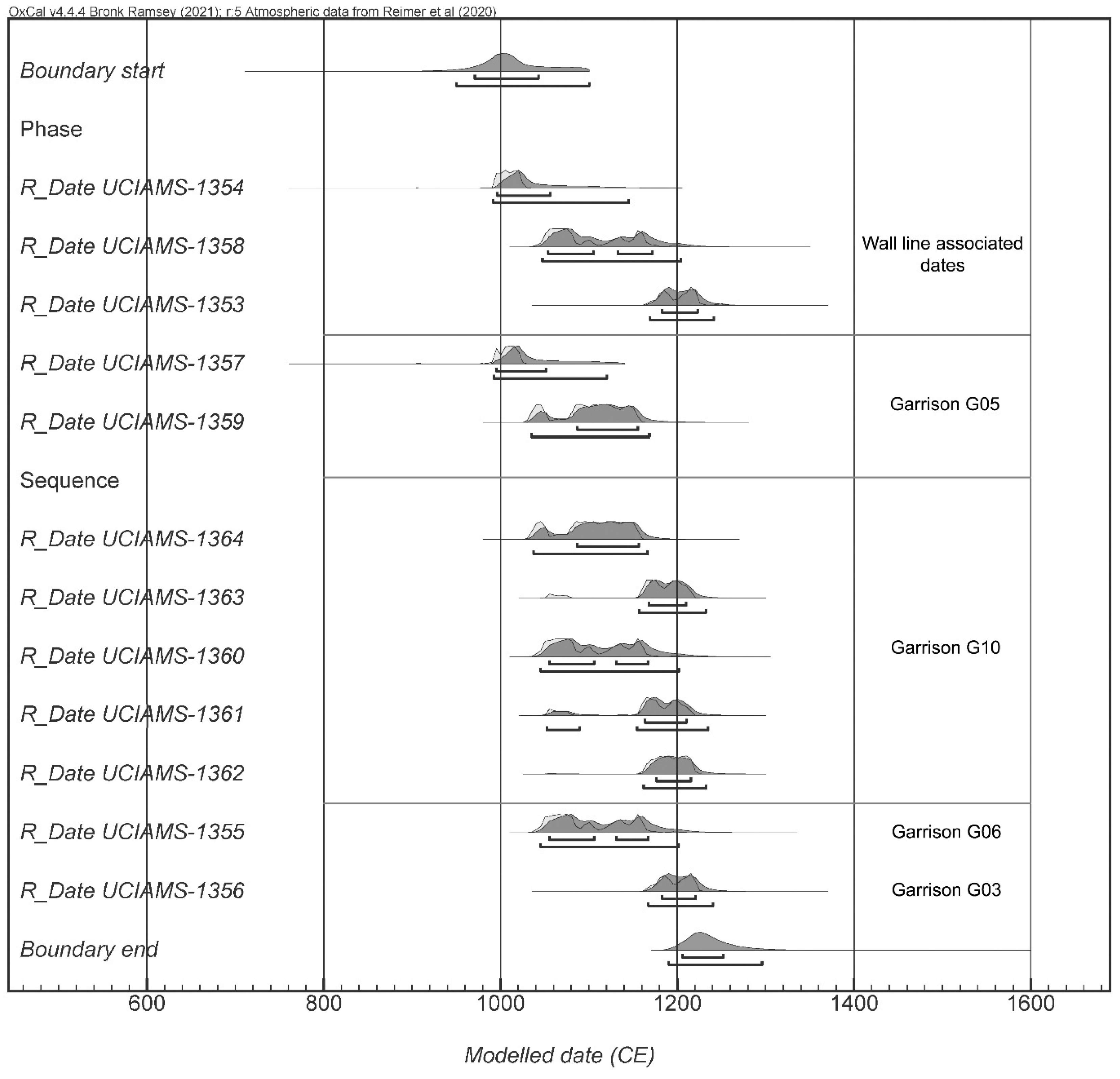
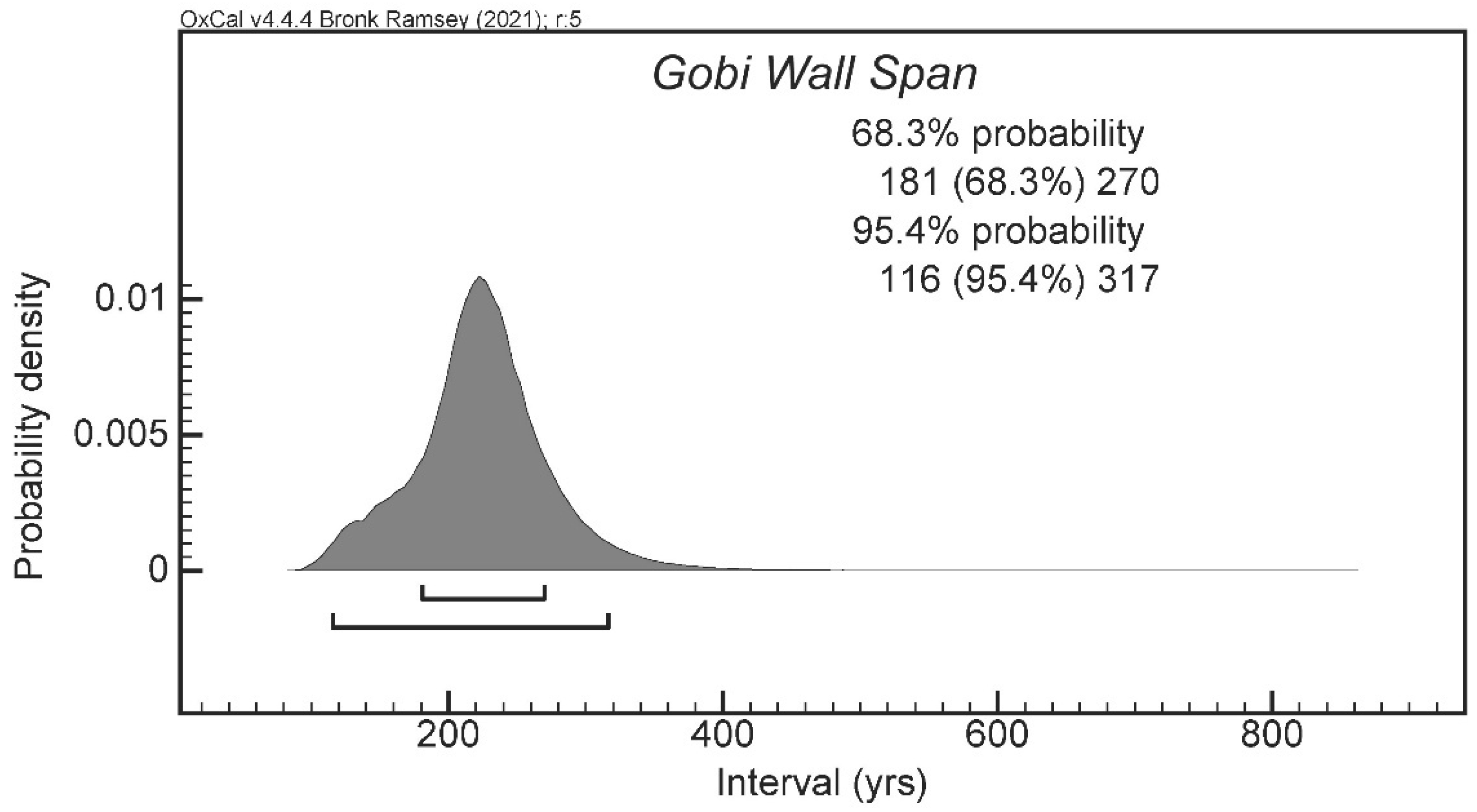
5.2. Radiocarbon Dating Results
6. Analysis and Discussion
6.1. Topographical and Ecological Analysis
6.2. Functional Analysis of the Defensive System
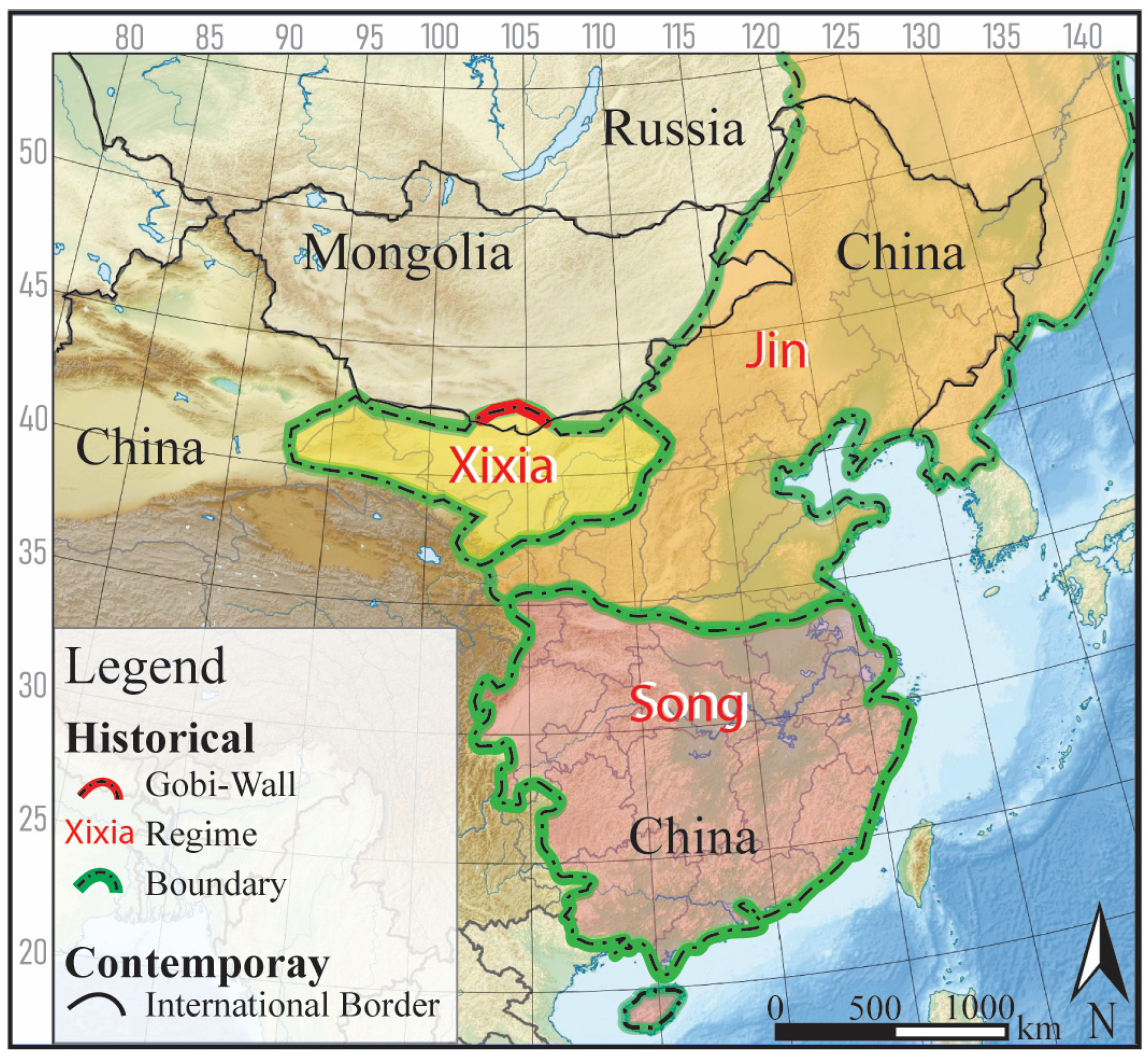
6.3. Historical Context and Implications
7. Conclusions
8. Future Research Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fung, Y.T.; Gantumur, A.; Wachtel, I.; Chunag, A.; Zhang, Z.; Fenigstein, O.; Golan, D.; Shelach-Lavi, G. Unraveling the Mongolian Arc: A field survey and spatial investigation of a previously unexplored wall system in eastern Mongolia. J. Field Archaeol. 2024, 49, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kradin, N.N.; Prokopets, S. The Great Wall of Khitan: North Eastern Wall of Chinggis Khan. Nauka—Vostochnaya Literatura. 2019. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/43375401/The_Great_Wall_of_Khitan_North_Eastern_Wall_of_Chinggis_Khan_Великая_киданьская_стена_Северo_вoстoчный_вал_Чингис_хана (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Shelach-Lavi, G.; Honeychurch, W.; Chunag, A. Does extra-large equal extra-ordinary? The ‘Wall of Chinggis Khan’ from a multidimensional perspective. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelach-Lavi, G.; Wachtel, I.; Golan, D.; Batzorig, O.; Amartuvshin, C.; Ellenblum, R.; Honeychurch, W. Medieval long-wall construction on the Mongolian Steppe during the eleventh to thirteenth centuries AD. Antiquity 2020, 94, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelach-Lavi, G.; Amartuvshin, C.; Heimberg, D.; Wolin, D.; Angaragdulguun, G.; Rogovski, T.; Chen, J.; Fenigstein, O.; Steiner, T.; Honeychurch, W. Life along the medieval frontier: Archaeological investigations of the southeastern long wall of Mongolia. Antiquity, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Storozum, M.; Golan, D.; Wachtel, I.; Zhang, Z.; Lotze, J.S.; Shelach-Lavi, G. Mapping the medieval wall system of China and Mongolia: A multi-method approach. Land 2021, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danda’er. The Typological Research of the Fortified Towns on the Sides of Jin Jiehao. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Defense System and Military Settlements of the Jin Great Wall; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hanks, B.K.; Shelach-Lavi, G.; Bermann, M.; Eklund, E.; Greaves, A.; Amartuvshin, C.; Tserendash, N.; Goldsmith, Y.; Burentogtokh, J.; Erdenebat, U. Examining medieval long-wall frontier systems (11th–12th centuries AD) through archaeological geophysics in the eastern Mongolian steppe region. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2024, 60, 104860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amartuvshin, C.; Shelach-Lavi, G.; Honeychurch, W.; Byambatseren, B.; Shamir, O.; Munkhtur, U.; Wolin, D.; Wang, S.; Shamir, N. An elite grave of the pre-Mongol period, from Dornod Province, Mongolia. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2024, 39, 100537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, A.A.; Erdenebaatar, D. The northern border of the Tangut state, XiXia: According to the archaeological evidence and written sources. Archaeol. J. Kanazawa Univ. 2021, 80, 49–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalev, A.A.; Erdenebaatar, D. Reconsideration about Great wall of Xi Xia and Shouxiangcheng fortress of the Western Han in Ömnögov’ aimag, Mongolia. Inn. Mong. Cult. Relics Archaeol. 2008, 2008, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Perlee, K. Archaeological Exploration Done on the Gobi Steppe in Ömnögovi and Övör Khangai Aimag (1962). In Erdem Shinzhilgeenii Ögüüllüüd; Perlee, K., Ed.; Mongolian Academy of Sciences: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 270–280. [Google Scholar]
- Baasan, T. What Are the Chinggis Walls? Admon: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Moriya, K.; Shiraishi, N.; Odsuren, D.; Buyanhishig, T.; Batbold, G.; Souma, H. Survey Report of the Great Wall and Castle Ruins in South Gobi Province, Mongolia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Archaeology of Ancient Settlements and Cities in Northern Asia; Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Q. The Historical Atlas of China; Cartographic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1982; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- National Cultural Heritage Administration. The Atlas of the Cultural Heritage of Inner Mongolia; Xi’an Ditu Chubanshe: Xi’an, China, 2003.
- Li, Y. The long walls of the Northern frontier of China. Neimenggu Wenwu Kaogu 2001, 2001, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y. “Remote observation” of the fortress ruins along the southern line of the Han Great Wall in Inner Mongolia. Perspect. Anc. Mod. Hist. 2020, 34, 78–118. [Google Scholar]
- Department of the Army. Soviet topographic map symbols (Technical Manual 30-548). U.S. Government Printing Office. 1958. Available online: https://s3.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/redatlas/TM30-548_1958.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Aylmer, C. Soviet military maps of China. Cartogr. J. 2022, 59, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruickshank, J.L. The evolution of Soviet topographic maps as revealed by their published supporting documentation. Cartogr. J. 2021, 59, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondelli, B.; Stride, S.; García-Granero, J.J. Soviet military maps and archaeological survey in the Samarkand region. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Tian, F.; Li, F.; Gaillard, M.J.; Rudaya, N.; Xu, Q.; Herzschuh, U. Pollen-based quantitative land-cover reconstruction for northern Asia covering the last 40 ka cal BP. Clim. Past 2019, 15, 1503–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, X.; Scuderi, L.A.; Hu, F.; Liang, P.; Jiang, Q.; Buylaert, J.P.; Wang, X.; Du, J.; Kang, S.; et al. East Gobi megalake systems reveal East Asian Monsoon dynamics over the last interglacial-glacial cycle. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülle, D.; Hilgers, A.; Radtke, U.; Stolz, C.; Hempelmann, N.; Grunert, J.; Felauer, T.; Lehmkuhl, F. OSL dating of sediments from the Gobi Desert, Southern Mongolia. Quat. Geochronol. 2010, 5, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banning, E.B. Archaeological Survey (Manuals in Archaeological Method, Theory and Technique); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southon, J.; Santos, G.M.; Druffel-Rodriguez, K.; Druffel, E.R.M.; Trumbore, S.; Xu, X.; Griffin, S.; Ali, S.; Mazon, M. The Keck Carbon Cycle AMS Laboratory, University of California, Irvine: Initial operation and a background surprise. Radiocarbon 2004, 46, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, F. Ancient Chinese Coins: From Origins to the End of the Empire; Les Belles Lettres: Paris, France, 2017; ISBN 978-2-251-44686-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. The Complete Collection of Chinese Ancient Coins; Southwestern University of Finance and Economics Press: Chengdu, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, D.; Niu, Z. Discoveries and research of Xi Xia coins. Tangut Res. 2013, 2013, 88–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Archaeological Research on the Coins of the Western Xia Dynasty. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Normal University, HohHot, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shelach-Lavi, G. The Archaeology of Early China: From Prehistory to the Han Dynasty; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q. Yingzao Fashi: Twelfth-century Chinese building manual. Archit. Hist. 1998, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, J. Science and Civilisation in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology, Part 3, Civil Engineering and Nautics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Wang, R. Design of Xi Xia flat pot and change of nomadic culture. J. Ceram. 2024, 45, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Excavation Report of the Lingwu Kiln in Ningxia; Zhongguo Da Baike Quanshu Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W. Lingwu Kiln in Ningxia; Palace Museum Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ningxia Archaeological Institute. Excavation of the Hui Lane Kiln in Lingwu City, Ningxia. Archaeology 2002, 8, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsutdinova, E.; Shamsutdinov, Z. Biological features and forage performance of black saxaul (Haloxylon Aphyllum (Minkw) Iljin) in the Central Asian Desert. BIO Web Conf. 2022, 43, 01023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, C. Long-term effects of xerophytic shrub Haloxylon ammodendron plantations on soil properties and vegetation dynamics in Northwest China. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0168000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Jeschke, M.; Zhang, X.; Lang, P. Stand structure and productivity of Populus euphratica along a gradient of groundwater distances at the Tarim River (NW China). J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 10, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, M.; Bronk Ramsey, C. High-precision Bayesian modeling of samples susceptible to inbuilt age. Radiocarbon 2014, 56, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronk Ramsey, C. OxCal (Version 4.4.4) (Computer Software). 2021. Available online: https://c14.arch.ox.ac.uk/oxcal.html (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.N.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Bronk Ramsey, C.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 cal kBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronk Ramsey, C. Dealing with outliers and offsets in radiocarbon dating. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 1023–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulyk, V.; Shevchenko, L.; Cherniyavskyi, V.; Davydov, A.; Boborykin, O. About the concept of improving border defense lines by means of landscape architecture. Landsc. Archit. Art 2024, 24, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altantungalag, D.; Buyankhishig, N.; Altangadas, E.; Purevsuren, U. Groundwater recharge estimation in Undai watershed area, southern Mongolia [Poster presentation]. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2020: Sharing Geoscience Online, Online, 4–8 May 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayanzul, B.; Nakamura, K.; Machida, I.; Watanabe, N.; Komai, T. Construction of a conceptual model for confined groundwater flow in the Gunii Khooloi Basin, Southern Gobi Region, Mongolia. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsukh, K.; Zlotnik, V.A.; Nasta, P. Analysis of groundwater recharge in Mongolian drylands using composite vadose zone modeling. Front. Water 2022, 4, 802208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amartuvshin, N. The Family Chenopodiaceae vent. in Mongolia: Phylogeny, Historical Development, Range, Distribution, Ecology, Taxonomy; Toonot Print: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Skaggs, T.H.; Lü, H.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fang, X. Simulation of Populus euphratica root uptake of groundwater in an arid woodland of the Ejina Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimore, O. Studies in Frontier History: Collected Papers, 1928–1958; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Nie, H.; Bai, B. Revised and Newly Endorsed Law Code of the Tiansheng Era; Falü Chubanshe Law Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R. Some discussions on the Silk Road of Xi xia. J. Chin. Hist. Geogr. 2003, 18, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnell, R.W. The rise of Chinggis Khan and the United Empire, 1206–1260. In The Cambridge history of the Mongol Empire (Volume 1: Political History, pp. 19–106); Biran, M., Kim, H., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Standen, N. Unbounded Loyalty: Frontier Crossings in Liao China; University of Hawai’i Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dunnell, R. Xi Xia: The First Mongol Conquest. In Genghis Khan and the Mongol Empire; Fitzhugh, W., Rossabi, M., Honeychurch, W., Eds.; Arctic Studies Center, Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- de Rachewiltz, I. The Secret History of the Mongols: A Mongolian Epic Chronicle of the Thirteenth Century; Brill: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J. Relationship between Xixia and Neighbors; Gansu Cultural Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J. Research on Xixia Military Documents; Gansu Cultural Publishing House: Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Frachetti, M.D.; Berner, J.; Liu, X.; Bevan, A.; Hritz, C.; Williams, T. Large-scale medieval urbanism traced by UAV–lidar in highland Central Asia. Nature 2024, 634, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalona, J.; Reynolds, A.J. (Eds.) Scale and Scale Change in the Early Middle Ages: Exploring Landscape, Local Society, and the World Beyond; in The Medieval Countryside; Brepols: Turnhout, Belgium, 2011; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
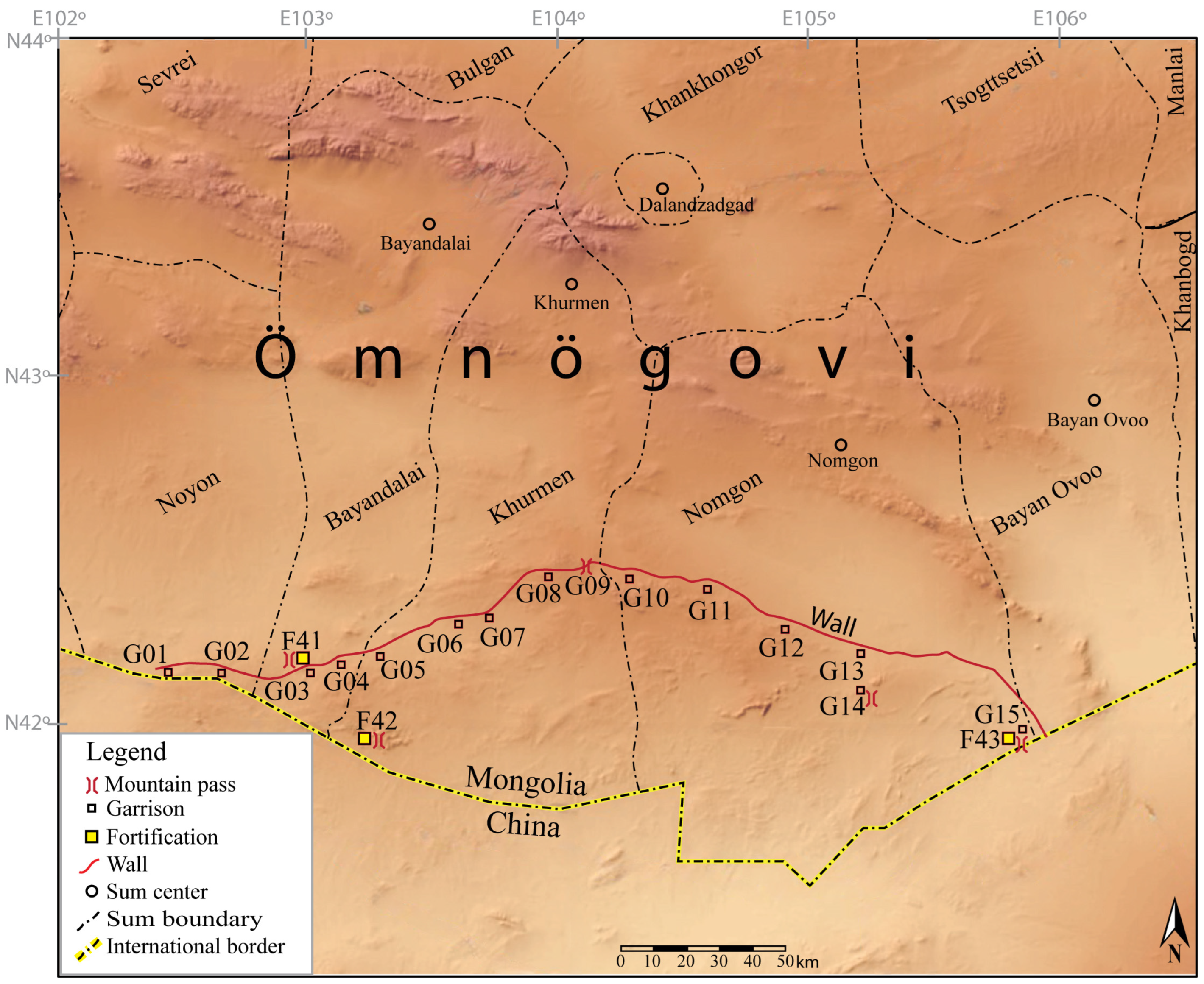


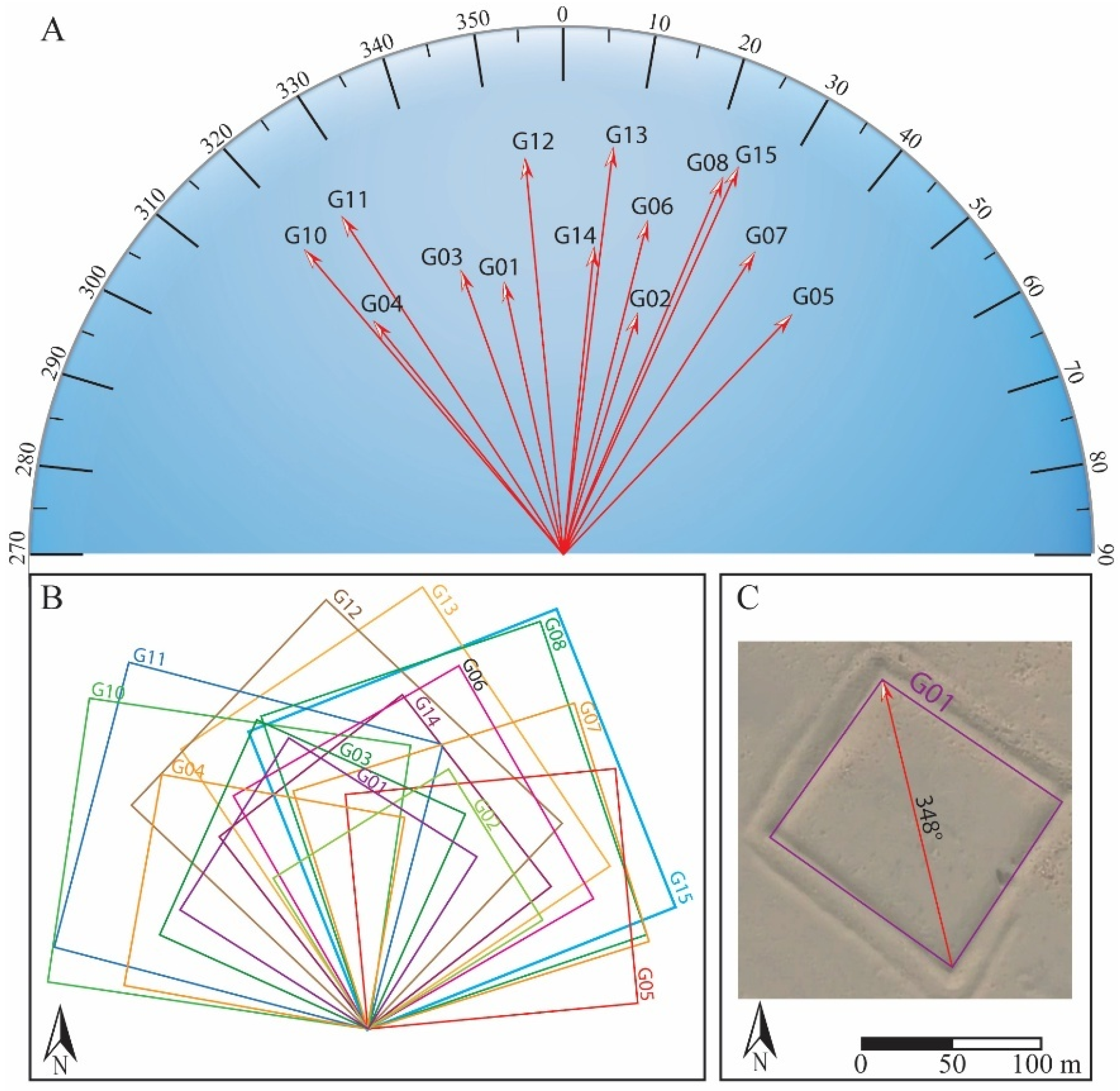











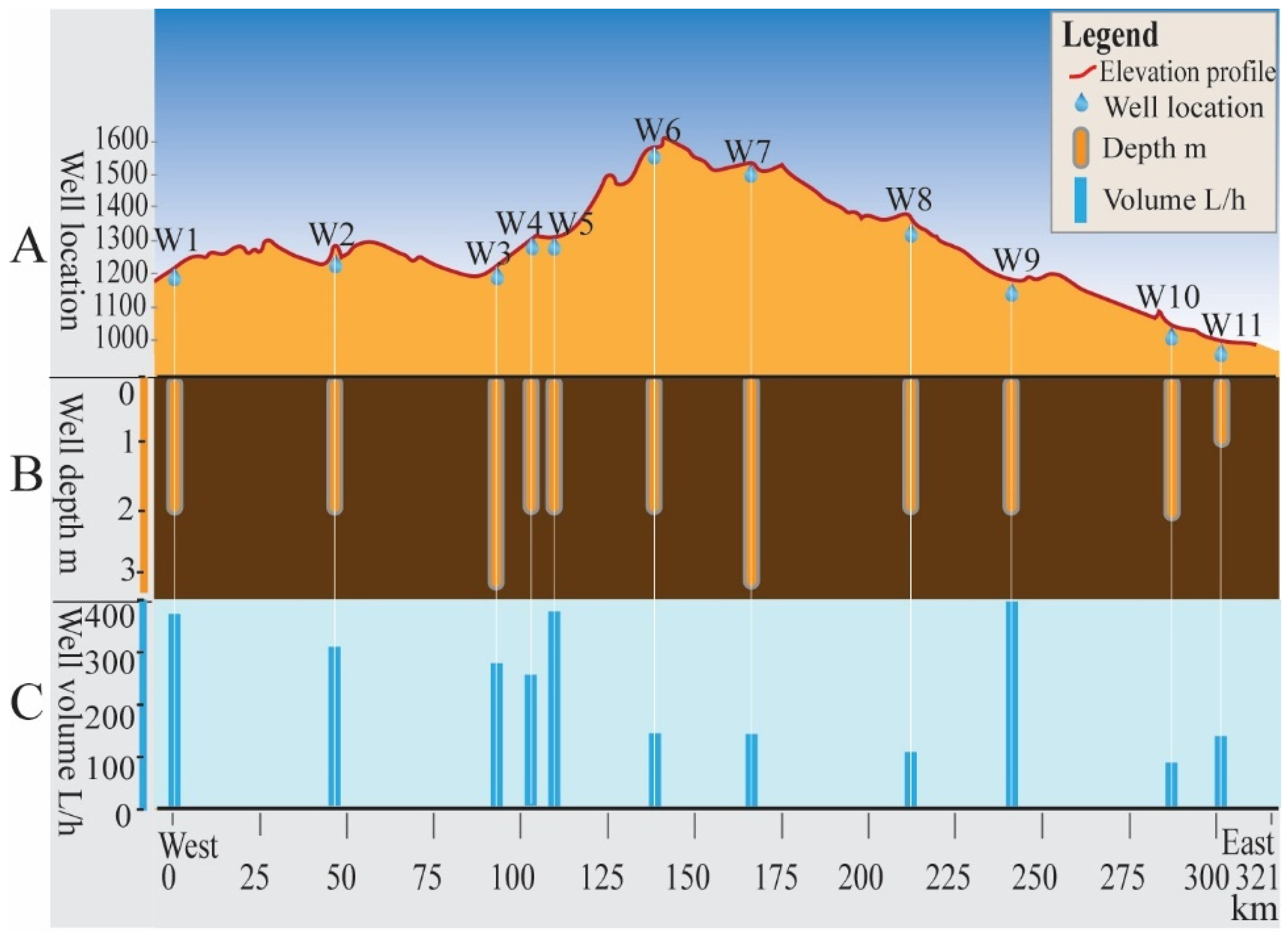

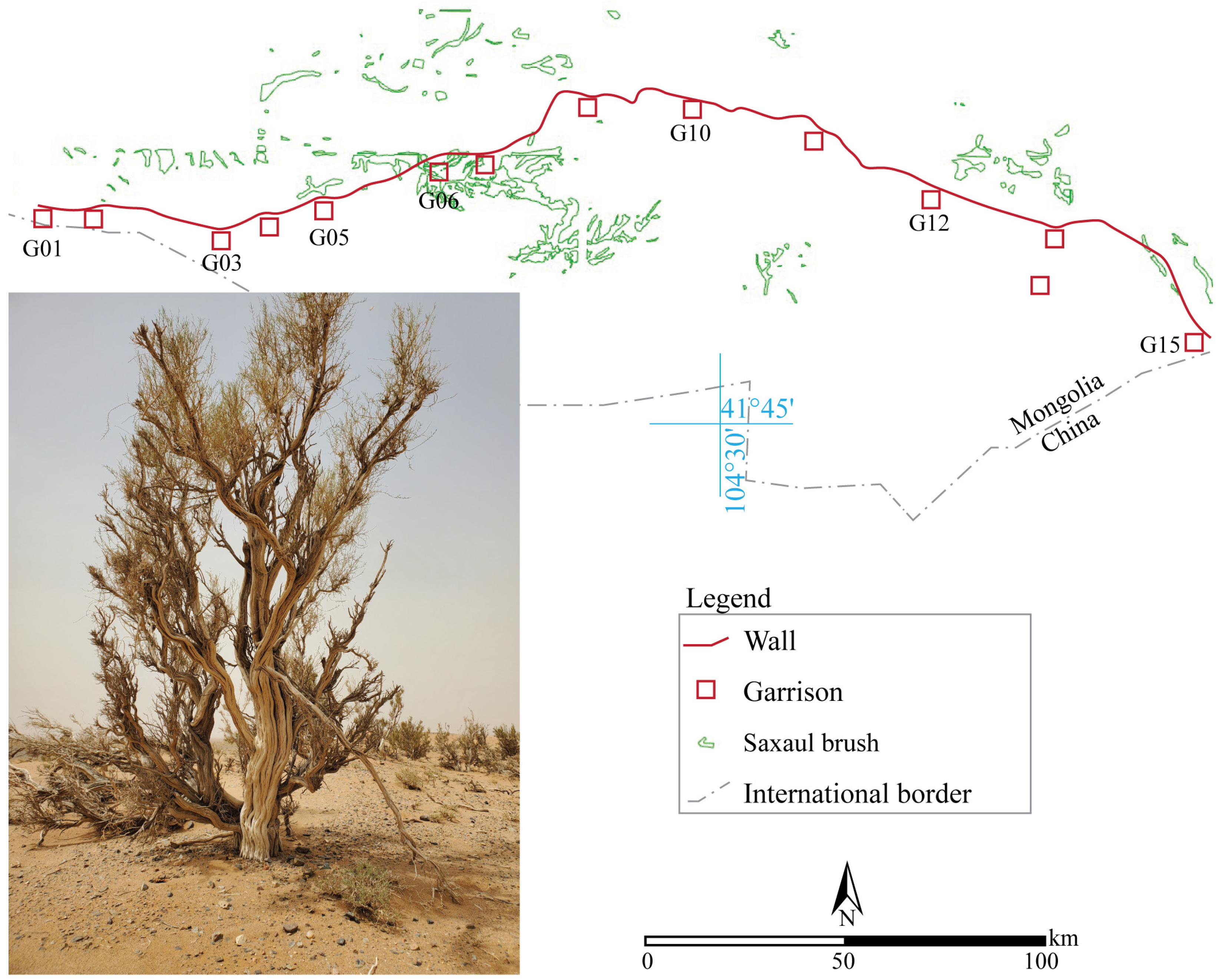
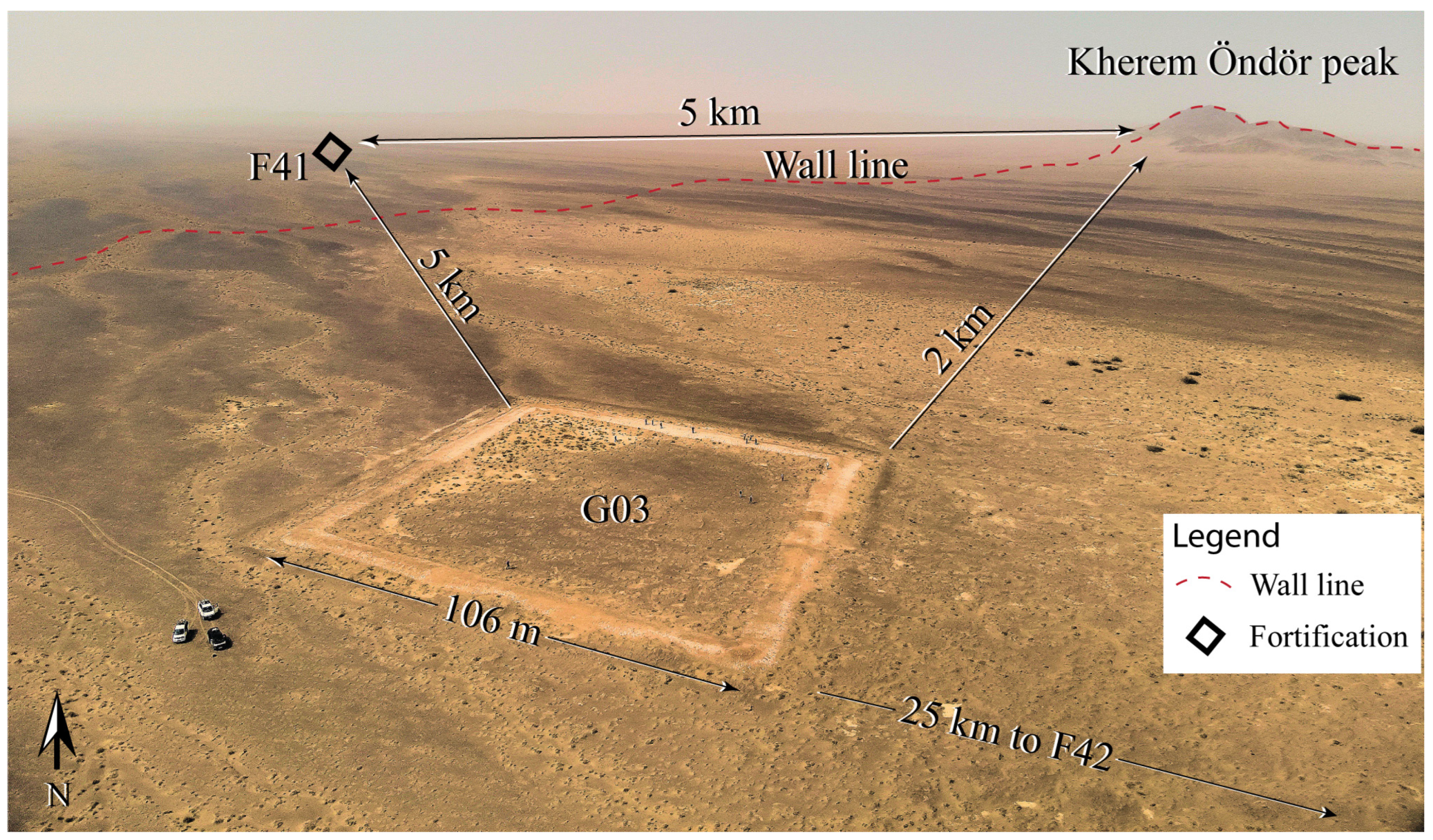
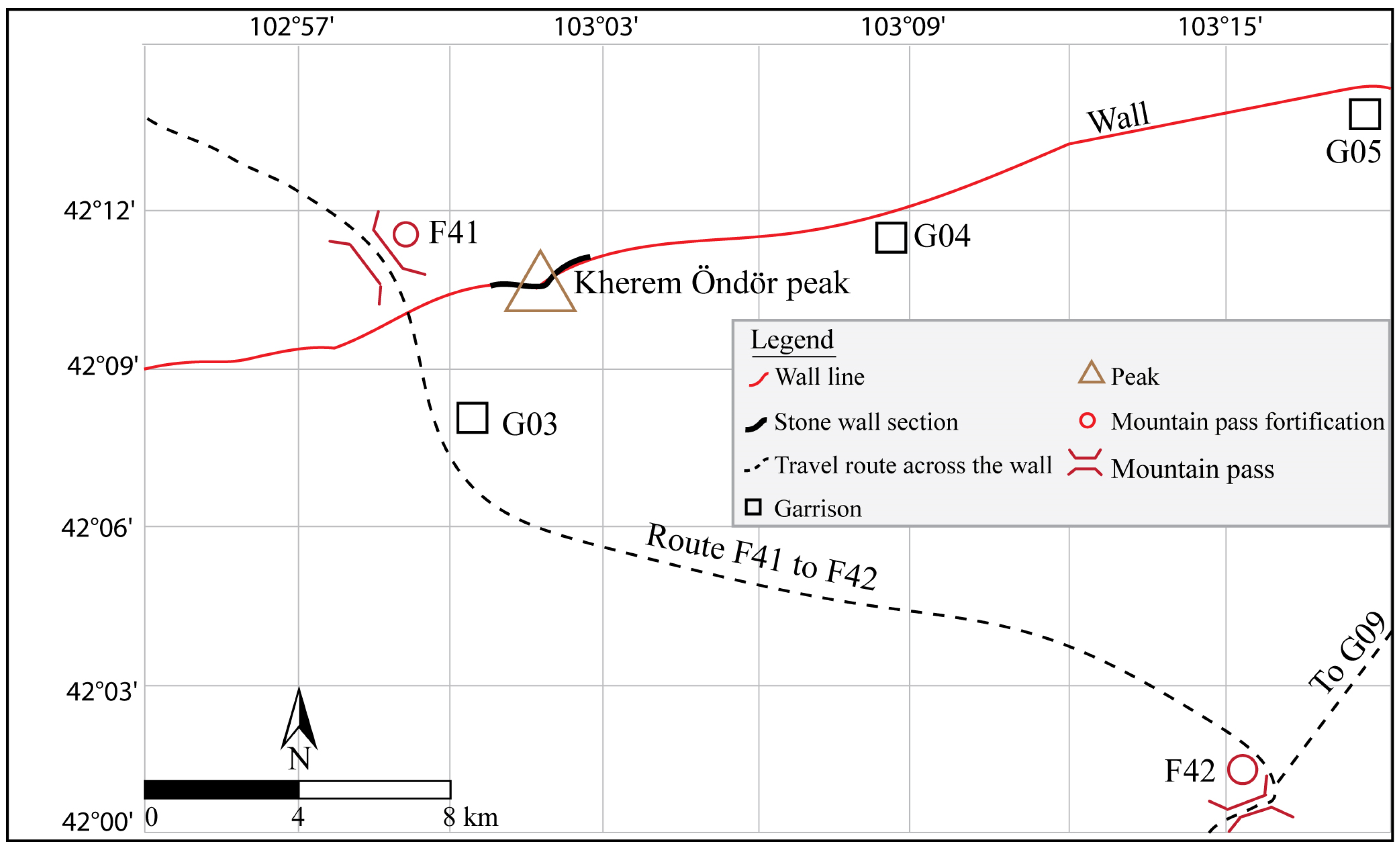
| Site Label | District (Sum) | Coordinates Latitude, Longitude | Research Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| G01 | Noyon | 42.17226, 102.41749 | Satellite observation |
| G02 | Noyon | 42.19049, 102.65412 | Satellite observation |
| G03 | Bayandalai | 42.15132, 103.01183 | Field survey |
| G04 | Bayandalai | 42.19178, 103.14206 | Field survey |
| G05 | Khurmen | 42.23697, 103.28883 | Survey and Targeted excavations |
| G06 | Khurmen | 42.33963, 103.61582 | Field survey |
| G07 | Khurmen | 42.34569, 103.73799 | Field survey |
| G08 | Khurmen | 42.47144, 104.03172 | Field survey |
| G09 | Nomgon | 42.48703, 104.17385 | Field survey |
| G10 | Nomgon | 42.47315, 104.32389 | Survey and Targeted excavations |
| G11 | Nomgon | 42.43807, 104.66517 | Field survey |
| G12 | Nomgon | 42.31544, 104.99789 | Field survey |
| G13 | Nomgon | 42.22180, 105.33192 | Satellite observation |
| G14 | Nomgon | 42.10577, 105.29337 | Satellite observation recorded for the first time |
| G15 | Bayan-Ovoo | 41.97812, 105.74893 | Satellite observation |
| F41 | Bayandalai | 42.19413, 102.97452 | Field survey |
| F42 | Bayandalai | 42.01897, 103.26631 | Field survey |
| F43 | Bayan-Ovoo | 41.97702, 105.74585 | Satellite observation |
| Lab No. | Sample Type | Site and Context | 14C Age (BP) | Error | 2 Sigma (CE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCIAMS 1354 | Wood, saxaul | F42, Hilltop fortification | 1040 | 15 | 992–1025 (95.4%) |
| UCIAMS 1358 | Wood, saxaul | Garrison G05, Area C wall line | 920 | 15 | 1041–1109 (59.6%) |
| 1114–1174 (35.8%) | |||||
| UCIAMS 1353 | Wood, saxaul | Garrison G05, Area C wall line | 850 | 15 | 1164–1228 (95.4%) |
| UCIAMS 1357 | Wood, saxaul | Garrison G05, Area A garrison corner | 1050 | 15 | 988–1026 (95.4%) |
| UCIAMS 1359 | Charcoal | Garrison G05, Area A garrison corner | 955 | 15 | 1031–1054 (18.2%) |
| 1075–1158 (77.3%) | |||||
| UCIAMS 1364 | Charcoal | Garrison G10, Area D | 950 | 15 | 1033–1054 (16.1%) |
| 1064–1068 (01.1%) | |||||
| 1073–1158 (78.2%) | |||||
| UCIAMS 1363 | Charcoal | Garrison G10, Area D | 885 | 15 | 1053–1073 (05.4%) |
| 1156–1219 (90.1%) | |||||
| UCIAMS 1360 | Wood, saxaul | Garrison G10, Area D | 925 | 15 | 1040–1165 (95.4%) |
| UCIAMS 1361 | Charcoal | Garrison G10, Area C | 890 | 15 | 1053–1076 (12.3%) |
| 1156–1216 (83.2%) | |||||
| UCIAMS 1362 | Charcoal | Garrison G10, Area C | 870 | 15 | 1162–1219 (95.4%) |
| UCIAMS 1355 | Wood, saxaul | Garrison G06 | 925 | 15 | 1040–1165 (95.4%) |
| UCIAMS 1356 | Wood, poplar | Garrison G03 | 855 | 15 | 1165–1224 (95.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golan, D.; Shelach-Lavi, G.; Amartuvshin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wachtel, I.; Chen, J.; Angaragdulguun, G.; Lubel, I.; Heimberg, D.; Cavanagh, M.; et al. Exploring the Gobi Wall: Archaeology of a Large-Scale Medieval Frontier System in the Mongolian Desert. Land 2025, 14, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051087
Golan D, Shelach-Lavi G, Amartuvshin C, Zhang Z, Wachtel I, Chen J, Angaragdulguun G, Lubel I, Heimberg D, Cavanagh M, et al. Exploring the Gobi Wall: Archaeology of a Large-Scale Medieval Frontier System in the Mongolian Desert. Land. 2025; 14(5):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051087
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolan, Dan, Gideon Shelach-Lavi, Chunag Amartuvshin, Zhidong Zhang, Ido Wachtel, Jingchao Chen, Gantumur Angaragdulguun, Itay Lubel, Dor Heimberg, Mark Cavanagh, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Gobi Wall: Archaeology of a Large-Scale Medieval Frontier System in the Mongolian Desert" Land 14, no. 5: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051087
APA StyleGolan, D., Shelach-Lavi, G., Amartuvshin, C., Zhang, Z., Wachtel, I., Chen, J., Angaragdulguun, G., Lubel, I., Heimberg, D., Cavanagh, M., Ullman, M., & Honeychurch, W. (2025). Exploring the Gobi Wall: Archaeology of a Large-Scale Medieval Frontier System in the Mongolian Desert. Land, 14(5), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051087









