Exploring the Effects of Climate Change on Farming System Choice: A Farm-Level Space-for-Time Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
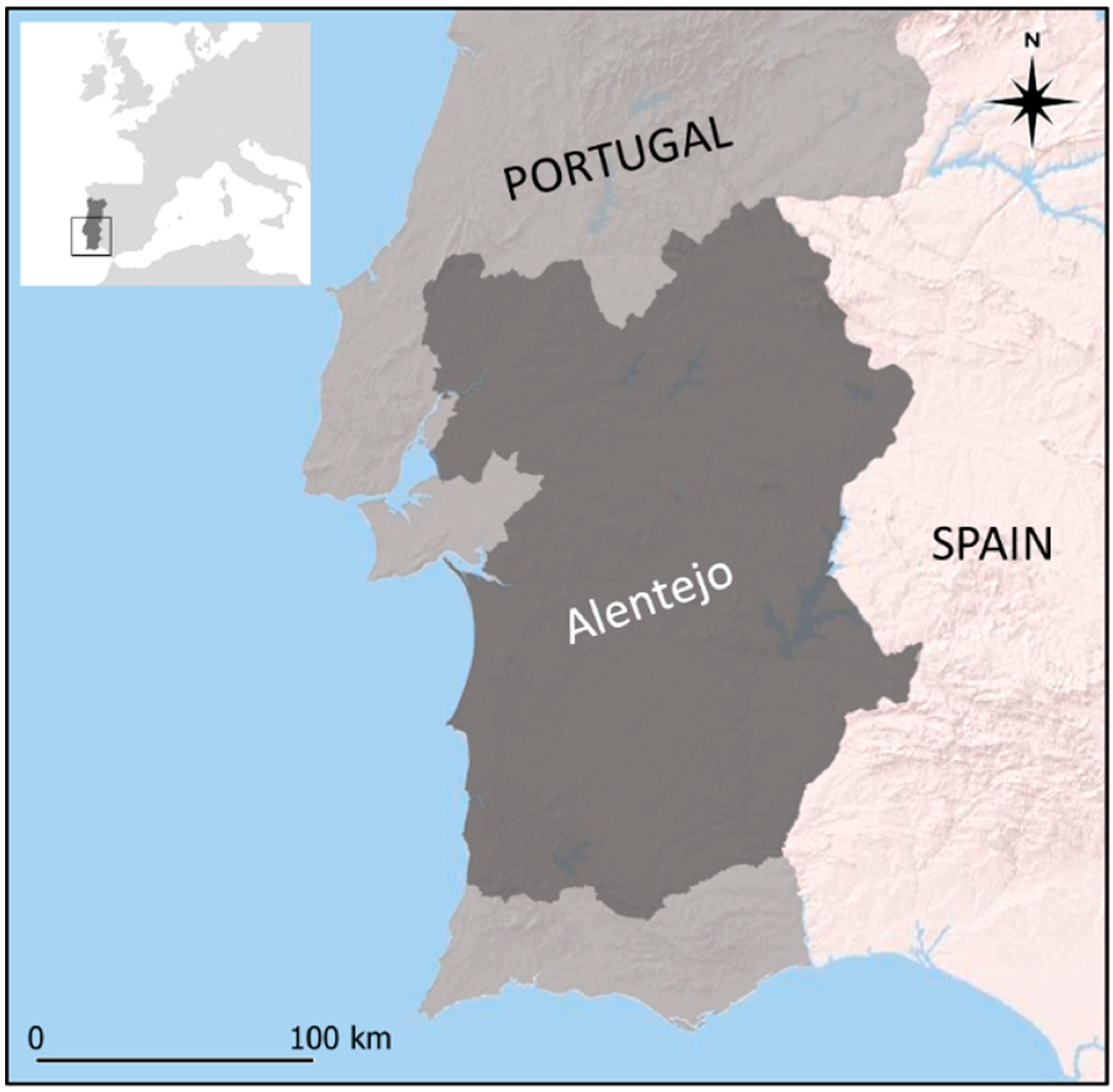
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Baseline Data
2.2.1. Farming Systems Information
2.2.2. Farming Systems Predictive Model
2.2.3. Climate Scenarios
2.3. Scenario Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Climate Change Predictions
3.2. Effects of Climate Change on Farming System Choice
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate Change and Farming System Choice
4.2. Comparing Farming System and Crop-Modelling Approaches
4.3. Strengths and Weaknesses of the Proposed Approach
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environment Agency. Climate Change Adaptation in the Agriculture Sector in Europe—Publications Office of the EU, EEA Rep. No 04/2019, Publ. Off. 2019. Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/fb9bf9af-0117-11ea-8c1f-01aa75ed71a1/language-en/format-PDF/source-265745439 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare-Nuamah, P.; Botchway, E. Understanding climate variability and change: Analysis of temperature and rainfall across agroecological zones in Ghana. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayinu, Y.T.; Ayal, D.Y.; Zeleke, T.T.; Beketie, K.T. Impact of climate variability on household food security in Godere District, Gambella Region, Ethiopia. Clim. Serv. 2022, 27, 100307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, L.T.; Kassa, G.A.; Gandorfer, M. Impact of climate change on farms in smallholder farming systems: Yield impacts, economic implications and distributional effects. Agric. Syst. 2017, 152, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, S.; Ullah, K.; Gao, S.; Khosa, A.H.; Wang, Z. Shifting of agro-climatic zones, their drought vulnerability, and precipitation and temperature trends in Pakistan. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglar, A.; Zampieri, M.; Toreti, A.; Dentener, F. Observed Northward Migration of Agro-Climate Zones in Europe Will Further Accelerate Under Climate Change. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotoks, A.; Smith, P.; Dawson, T.P. Impacts of land use, population, and climate change on global food security. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, S.A.; Cobbina, S.J.; Obiri, S. Climate Change, Land, Water, and Food Security: Perspectives From Sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 680924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Moreira, F.; Ribeiro, P.F.; Canadas, M.J.; Novais, A.; Lomba, A. A farming systems approach to linking agricultural policies with biodiversity and ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 19, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayman, P.; Rickards, L.; Eckard, R.; Lemerle, D. Climate change through the farming systems lens: Challenges and opportunities for farming in Australia. Crop Pasture Sci. 2012, 63, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidsma, P.; Ewert, F.; Lansink, A.O.; Leemans, R. Adaptation to climate change and climate variability in European agriculture: The importance of farm level responses. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 32, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidsma, P.; Wolf, J.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Schaap, B.F.; Mandryk, M.; Verhagen, J.; Van Ittersum, M.K. Climate change impact and adaptation research requires integrated assessment and farming systems analysis: A case study in the Netherlands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J. Concept and Classifications of Farming Systems. Encycl. Food Secur. Sustain. 2019, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etwire, P.M. The impact of climate change on farming system selection in Ghana. Agric. Syst. 2020, 179, 102773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRibeiro, F.; Santos, J.L.; Canadas, M.J.; Novais, A.M.; Moreira, F.; Lomba, Â. Explaining farming systems spatial patterns: A farm-level choice model based on socioeconomic and biophysical drivers. Agric. Syst. 2021, 191, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovidis, D.; Gadanakis, Y.; Park, J. Farm-level sustainability assessment in Mediterranean environments: Enhancing decision-making to improve business sustainability. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 15, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, D.; Jayet, P.A.; de Noblet-Ducoudré, N. Farm-level Autonomous Adaptation of European Agricultural Supply to Climate Change. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 87, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, M.P.M.; Feindt, P.H.; Spiegel, A.; Termeer, C.J.A.M.; Mathijs, E.; de Mey, Y.; Finger, R.; Balmann, A.; Wauters, E.; Urquhart, J.; et al. A framework to assess the resilience of farming systems. Agric. Syst. 2019, 176, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zonneveld, M.; Turmel, M.S.; Hellin, J. Decision-Making to Diversify Farm Systems for Climate Change Adaptation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wogan, G.O.U.; Wang, I.J. The value of space-for-time substitution for studying fine-scale microevolutionary processes. Ecography 2018, 41, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzkämper, A.; Calanca, P.; Fuhrer, J. Analyzing climate effects on agriculture in time and space. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 3, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Nussbaum, M.; Wright, M.N.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gräler, B. Random forest as a generic framework for predictive modeling of spatial and spatio-temporal variables. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Riahi, K.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Kriegler, E.; Edmonds, J.; O’Neill, B.C.; Fujimori, S.; Bauer, N.; Calvin, K.; Dellink, R.; Fricko, O.; et al. The Shared Socioeconomic Pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: An overview. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 42, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba, N. Research note: Sankey diagrams for visualizing land cover dynamics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 139, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Girón, J.C.; Díaz-Varela, E.R.; Álvarez-Álvarez, P. Climate-driven variations in productivity reveal adaptive strategies in Iberian cork oak agroforestry systems. For. Ecosyst. 2022, 9, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acácio, V.; Dias, F.S.; Catry, F.X.; Rocha, M.; Moreira, F. Landscape dynamics in Mediterranean oak forests under global change: Understanding the role of anthropogenic and environmental drivers across forest types. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, I.H.; Torralba, M.; Quintas-Soriano, C.; Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Plieninger, T. Linking Cork to Cork Oak Landscapes: Mapping the Value Chain of Cork Production in Portugal. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 787045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Carvalho-Santos, C.; Diogo, P.; Beça, P.; Keizer, J.J.; Nunes, J.P. Impacts of climate change on reservoir water availability, quality and irrigation needs in a water scarce Mediterranean region (southern Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, A.; Palma, P.; Fialho, S.; Lima, A.; Alvarenga, P.; Potes, M.; Salgado, R. Spatial and temporal dynamics of irrigation water quality under drought conditions in a large reservoir in Southern Portugal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acácio, V.; Dias, F.S.; Catry, F.X.; Bugalho, M.N.; Moreira, F. Canopy Cover Loss of Mediterranean Oak Woodlands: Long-term Effects of Management and Climate. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 1775–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Lazo, J.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; Ruíz-Gómez, F.J. Assessment of the future stability of cork oak (Quercus suber L.) afforestation under climate change scenarios in Southwest Spain, For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 409, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, N. Predicting agronomical and ecological effects of shifting from sheep to cattle grazing in highly dynamic Mediterranean dry grasslands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, B.; Andueza, D.; Niderkorn, V.; Lüscher, A.; Porqueddu, C.; Picon-Cochard, C. A meta-analysis of climate change effects on forage quality in grasslands: Specificities of mountain and mediterranean areas. Grass Forage Sci. 2015, 70, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Fraga, H.; Van Ieperen, W.; Santos, J.A. Modelling climate change impacts on early and late harvest grassland systems in Portugal. Crop Pasture Sci. 2018, 69, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Moriondo, M.; Leolini, L.; Santos, J.A. Mediterranean olive orchards under climate change: A review of future impacts and adaptation strategies. Agronomy 2021, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Pinto, J.G.; Santos, J.A. Olive tree irrigation as a climate change adaptation measure in Alentejo, Portugal. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasijevic, L.; Todorovic, M.; Pereira, L.S.; Pizzigalli, C.; Lionello, P. Impacts of climate change on olive crop evapotranspiration and irrigation requirements in the Mediterranean region. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 144, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, A.; Petacchi, R. Climate Change and Major Pests of Mediterranean Olive Orchards: Are We Ready to Face the Global Heating? Insects 2021, 12, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branquinho, S.; Rolim, J.; Teixeira, J.L. Climate change adaptation measures in the irrigation of a super-intensive olive orchard in the south of portugal. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Fraga, H.; van Ieperen, W.; Trindade, H.; Santos, J.A. Effects of climate change and adaptation options on winter wheat yield under rainfed Mediterranean conditions in southern Portugal. Clim. Change 2019, 154, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettori, M.; Cesaraccio, C.; Duce, P. Simulation of climate change impacts on production and phenology of durum wheat in Mediterranean environments using CERES-Wheat model. Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.T.A. Space-for-Time Substitution as an Alternative to Long-Term Studies. In Long-Term Studies in Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 110–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, R.S.L.; Collins, S.; Martin, S.H.; Pigot, A.L.; Phillimore, A.B. Space-for-time substitutions in climate change ecology and evolution. Biol. Rev. 2023, 98, 2243–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Kros, J.; Webber, H.; Zhao, G.; Britz, W.; Reinds, G.J.; Ewert, F.; De Vries, W. Combined analysis of climate, technological and price changes on future arable farming systems in Europe. AGSY 2015, 140, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Baseline (1971–2000) | Anomalies | Legends (Baseline|Anomalies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Emission Scenario (SSP 1-2.6) | Moderate Emission Scenario (SSSP 3-7.0) | High Emission Scenario (SSP 5-8.5) | |||
| Minimum temperature of the coldest month (°C) |  |  |  |  | 
 |
| Maximum temperature of the warmest month (°C) |  |  |  |  | 
 |
| Annual precipitation (mm) |  |  |  |  | 
 |
| Farming System | Area in 2017 (Predicted) | Expected Relative Changes in Area in Each 2081–2100 Scenario | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ha | % | Low (SSP 1-2.6) | Moderate (SSP 3-7.0) | High (SSP 5-8.5) | |
| Cattle grazing–CO | 495,655 | 25.2 | −22% | −62% | −72% |
| Cattle grazing–HO | 580,656 | 29.5 | 44% | 80% | 89% |
| Cattle grazing–forages | 168,219 | 8.5 | −3% | 17% | 23% |
| Grazing goats | 21,075 | 1.1 | −12% | 8% | 6% |
| Mixed cattle and sheep–irrigated forages | 20,090 | 1.0 | −1% | −13% | −18% |
| Sheep grazing–CO | 132,621 | 6.7 | −55% | −89% | −93% |
| Sheep grazing–HO | 100,952 | 5.1 | −11% | 4% | 5% |
| Sheep grazing–pastures | 32,734 | 1.7 | −48% | −62% | −66% |
| Sheep grazing–pastures and forages | 36,330 | 1.8 | −45% | −61% | −63% |
| Sheep grazing–forages | 18,602 | 0.9 | −23% | −48% | −59% |
| Rainfed olive groves with sheep | 13,396 | 0.7 | 3% | −22% | −28% |
| Rainfed olive groves | 15,472 | 0.8 | −15% | −12% | −7% |
| Irrigated olive groves | 89,647 | 4.6 | 11% | 42% | 46% |
| Vineyards | 21,947 | 1.1 | −45% | −58% | −64% |
| Fruit trees | 10,256 | 0.5 | −8% | −33% | −37% |
| Stone pine | 54,665 | 2.8 | −11% | −26% | −29% |
| Rice | 22,220 | 1.1 | 7% | −9% | −12% |
| Irrigated cereals and horticultural crops | 50,042 | 2.5 | −9% | −22% | −21% |
| Rainfed cereals and oilseeds | 39,694 | 2.0 | 9% | −9% | −12% |
| Rainfed cereals | 19,182 | 1.0 | 7% | 14% | 22% |
| Pastures without livestock | 12,775 | 0.6 | −75% | −84% | −84% |
| Fallows | 12,700 | 0.6 | −13% | −5% | −1% |
| Total | 1,968,929 | 100.0 | – | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, P.F.; Santos, J.L. Exploring the Effects of Climate Change on Farming System Choice: A Farm-Level Space-for-Time Approach. Land 2023, 12, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122113
Ribeiro PF, Santos JL. Exploring the Effects of Climate Change on Farming System Choice: A Farm-Level Space-for-Time Approach. Land. 2023; 12(12):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122113
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Paulo Flores, and José Lima Santos. 2023. "Exploring the Effects of Climate Change on Farming System Choice: A Farm-Level Space-for-Time Approach" Land 12, no. 12: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122113
APA StyleRibeiro, P. F., & Santos, J. L. (2023). Exploring the Effects of Climate Change on Farming System Choice: A Farm-Level Space-for-Time Approach. Land, 12(12), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12122113






