International Inland Waterways in Poland: Current State and Their Importance in EU Transport Policy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Inland Water Transport in Poland Compared to the European Union
2.1. EU Inland Water Transport in 2010–2021
2.2. Inland Waterways in Poland and Their Importance in EU Inland Transport
- -
- Waterway E30, connecting the Baltic Sea to the Danube in Bratislava;
- -
- Waterway E40, connecting the Baltic Sea in Gdańsk to the Dnieper and the Black Sea;
- -
- Waterway E70, connecting the Netherlands to Russia and Lithuania.
3. Materials and Methods
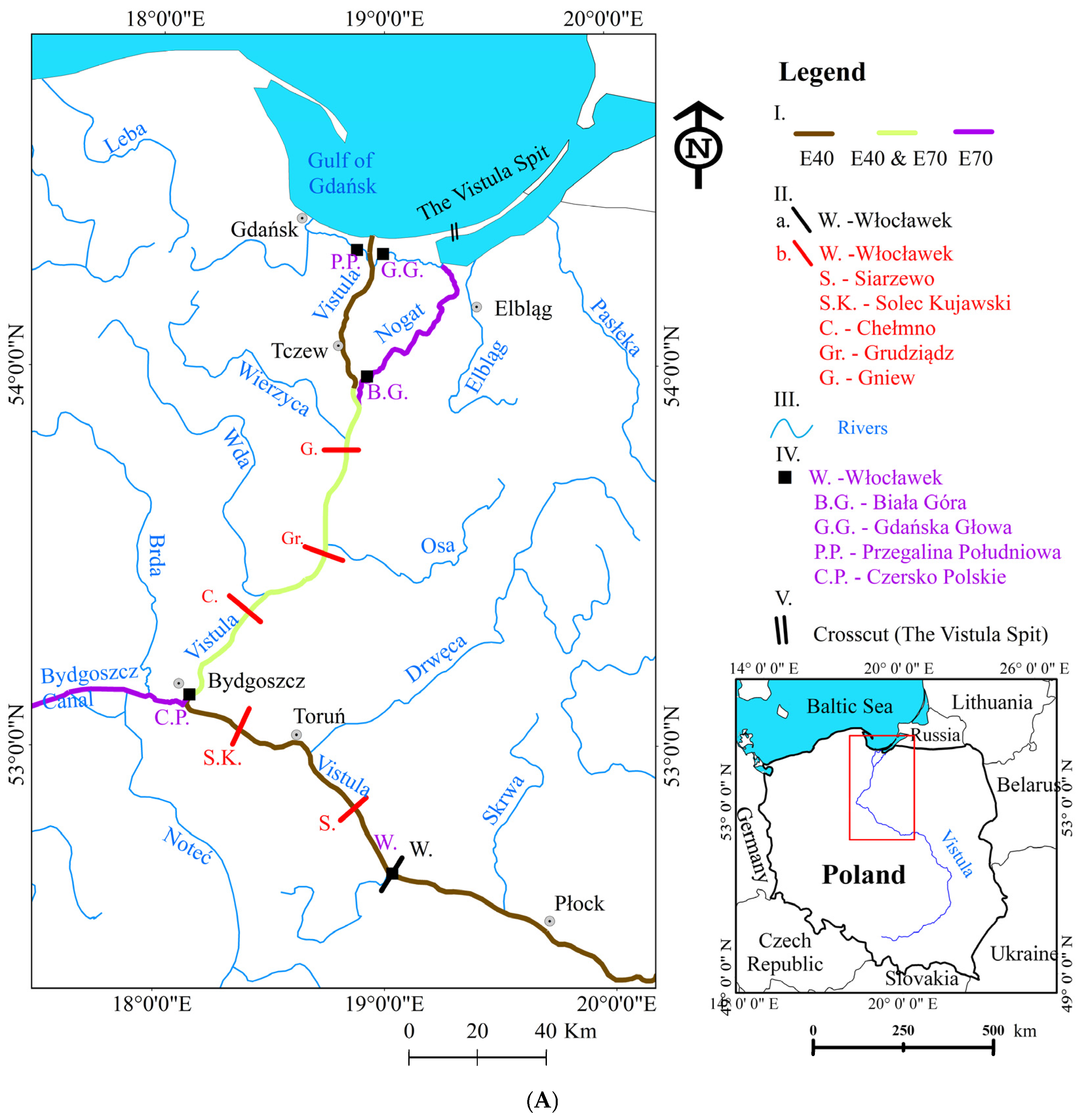
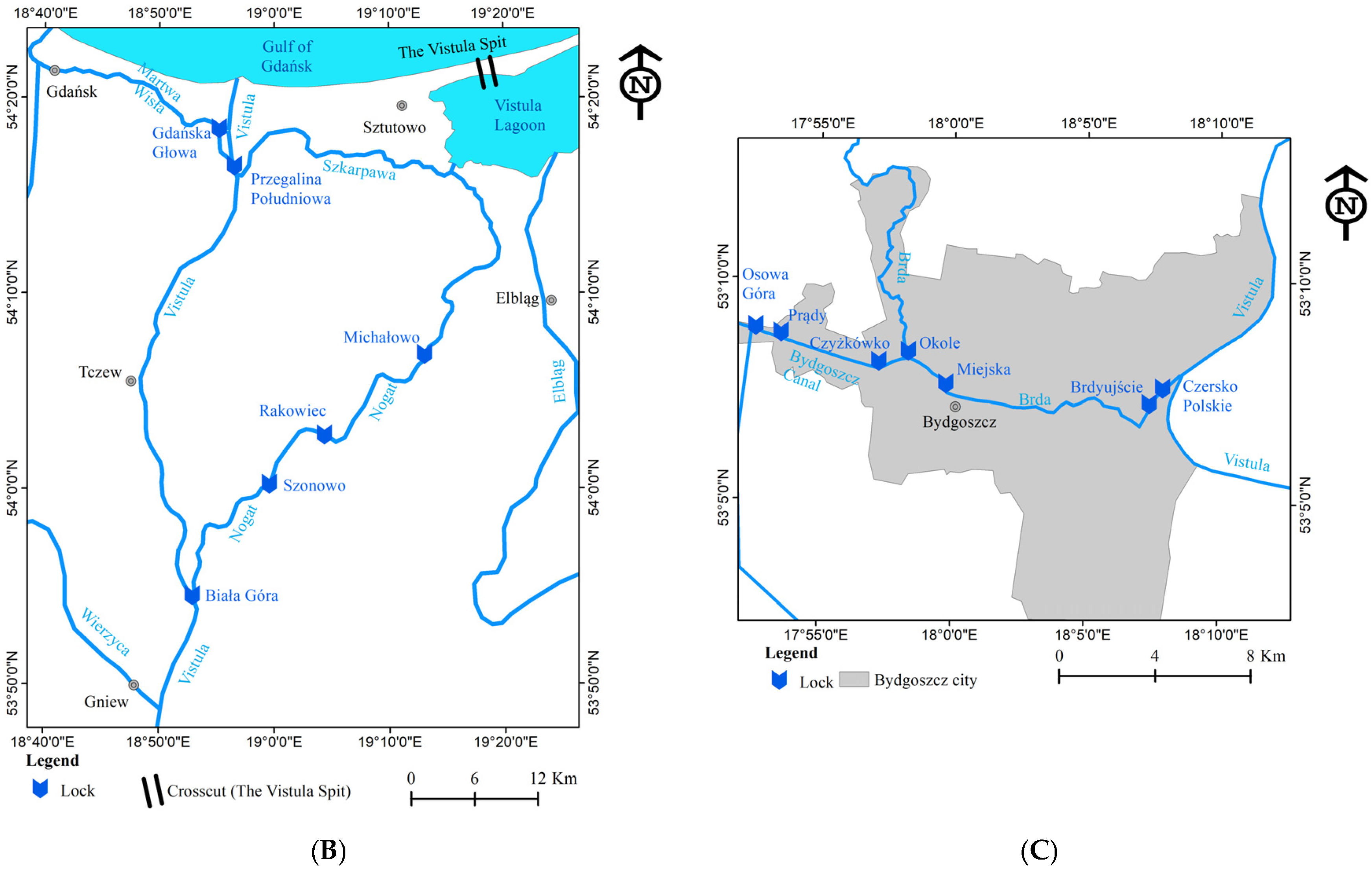
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data and Methods
4. Results
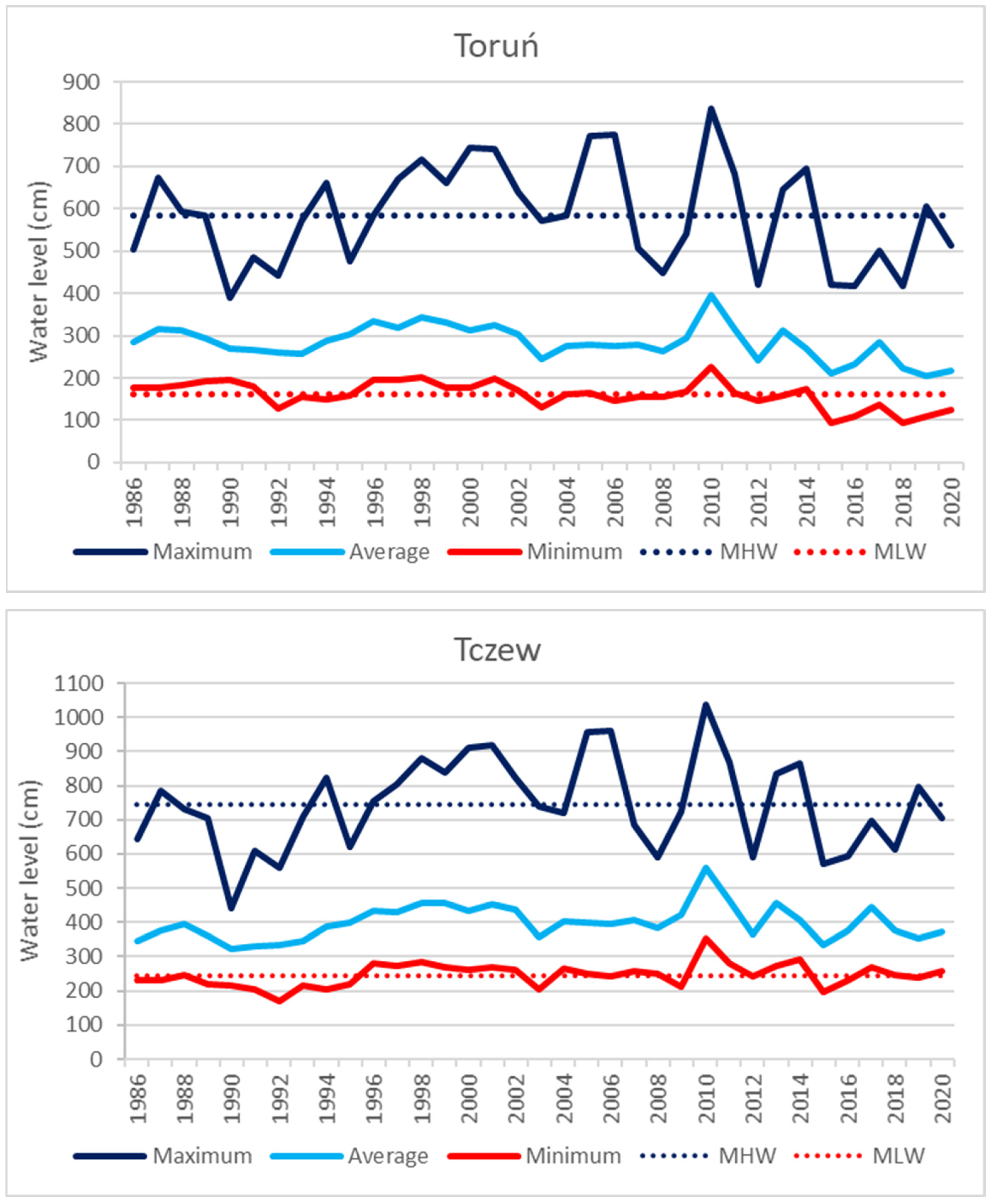
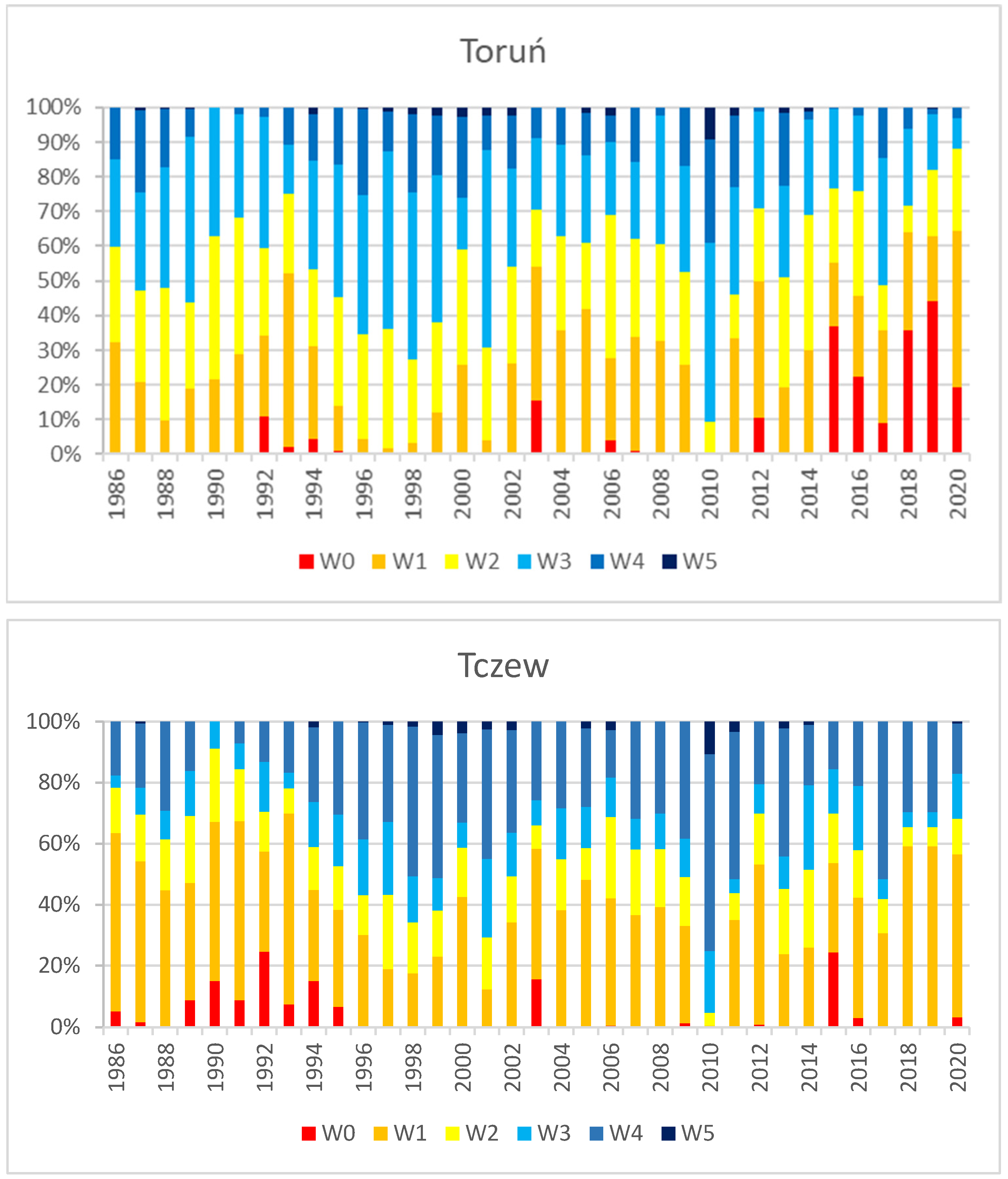
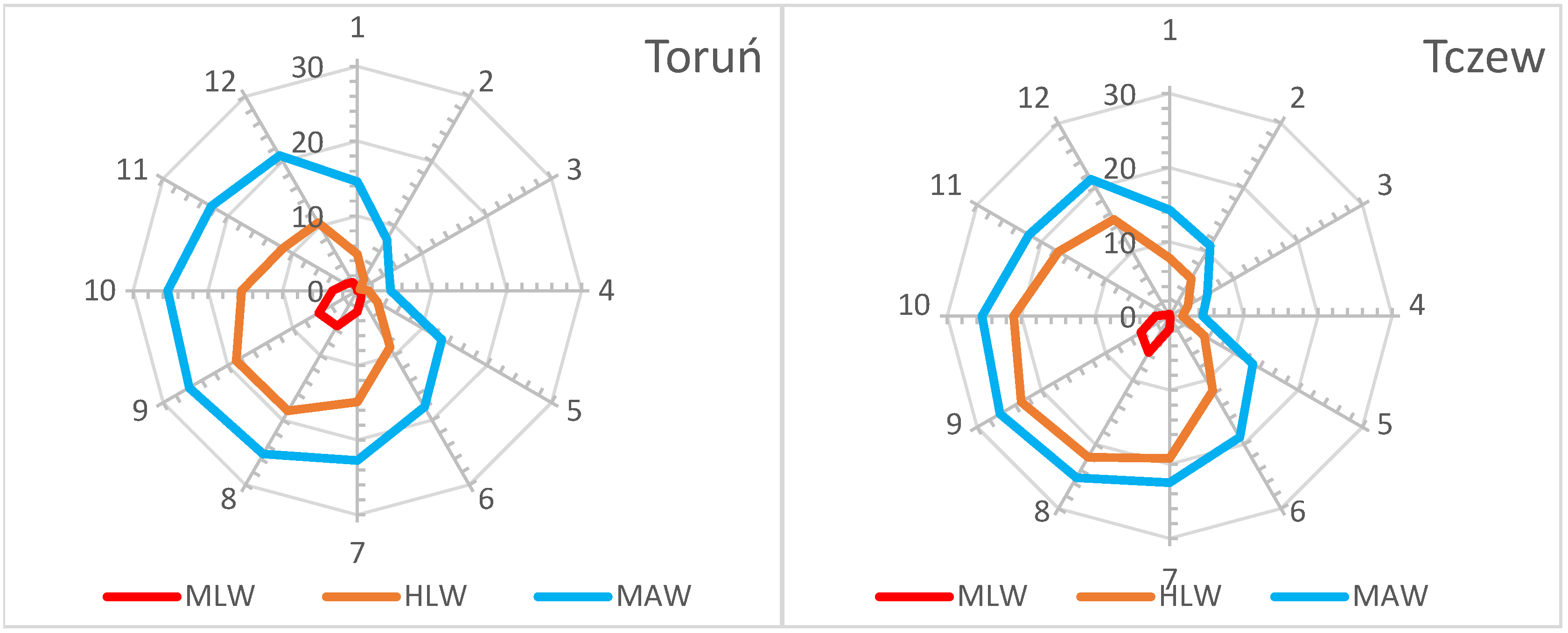
4.1. Hydrological Conditions of the Vistula River
- W0: number of days with water levels below the MLW;
- W1: number of days with water levels between MLW and HLW;
- W2: number of days with water levels between HLW and MAW;
- W3: number of days with water levels between MAW and LHW;
- W4: number of days with water levels between LHW and MHW;
- W5: number of days with water levels above MHW.
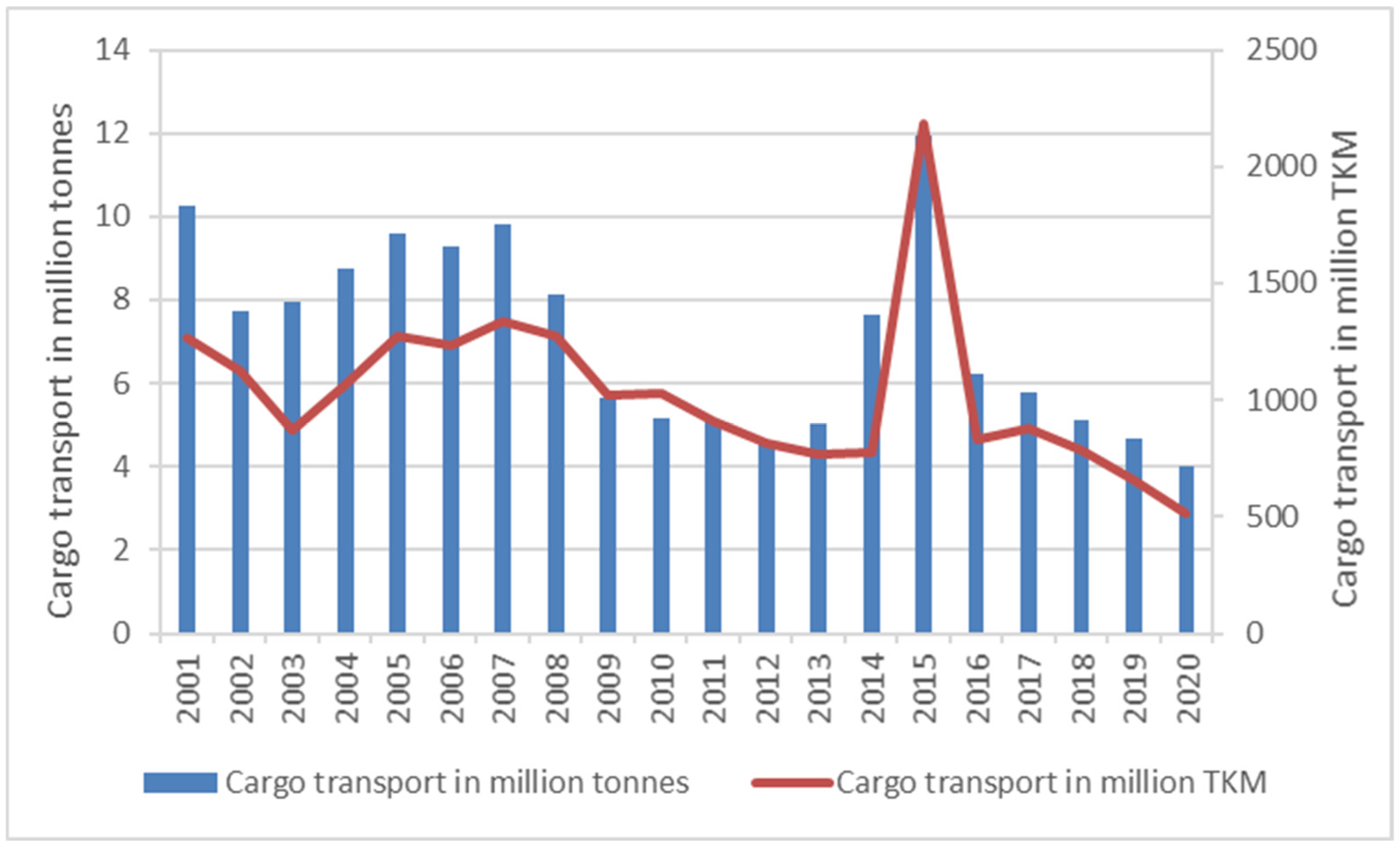
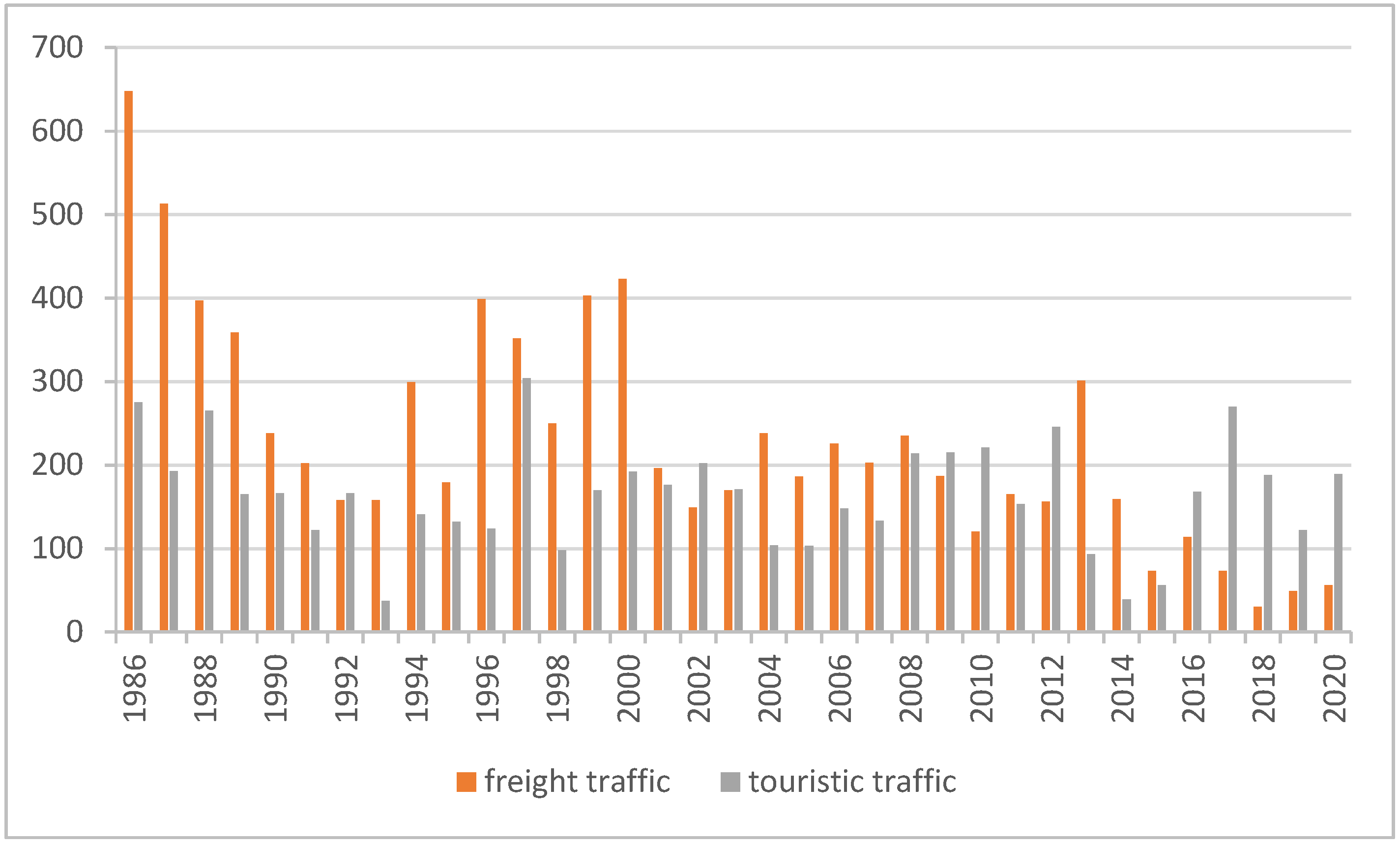
4.2. Volume of Inland Transport in Poland in 2001–2020
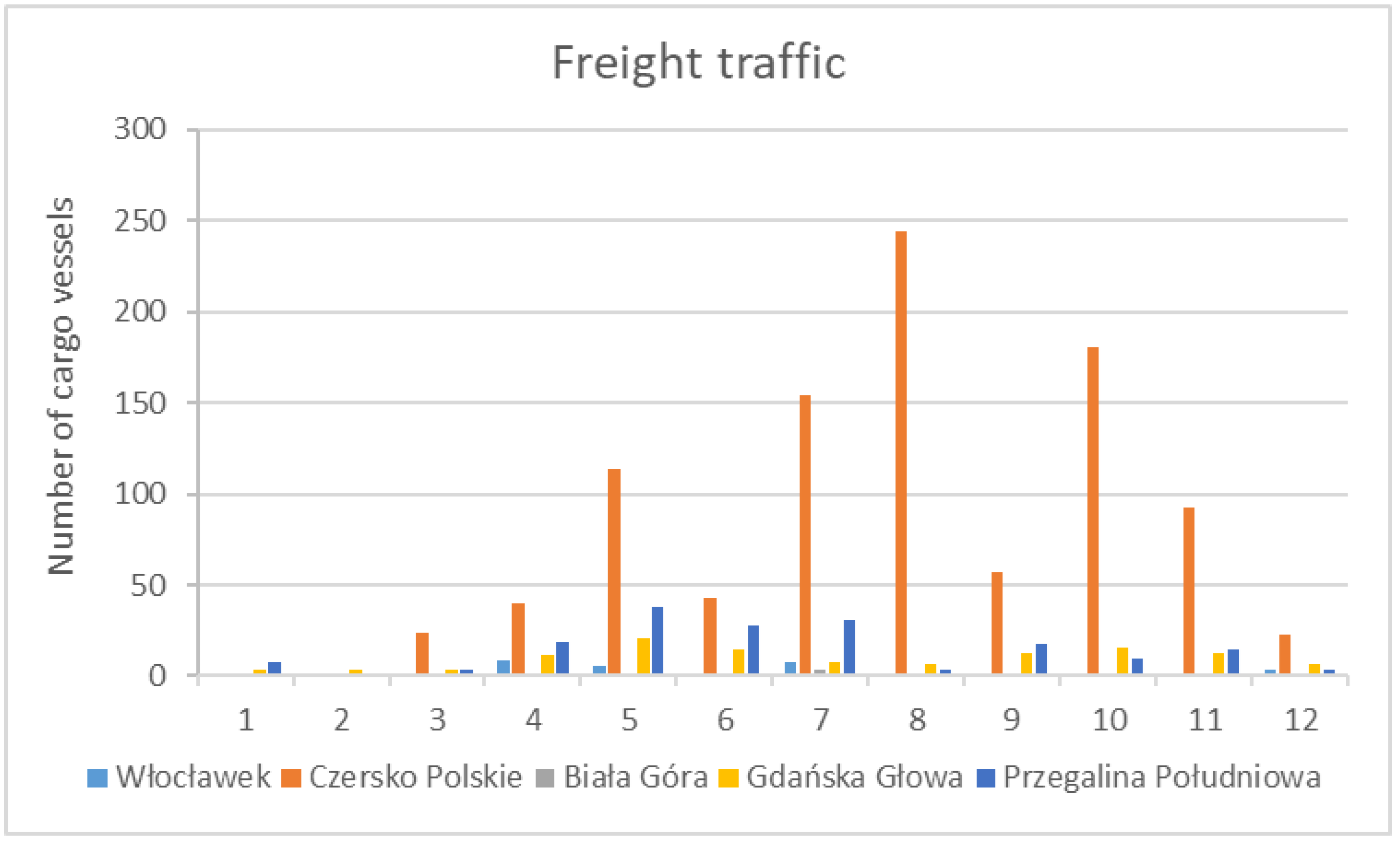
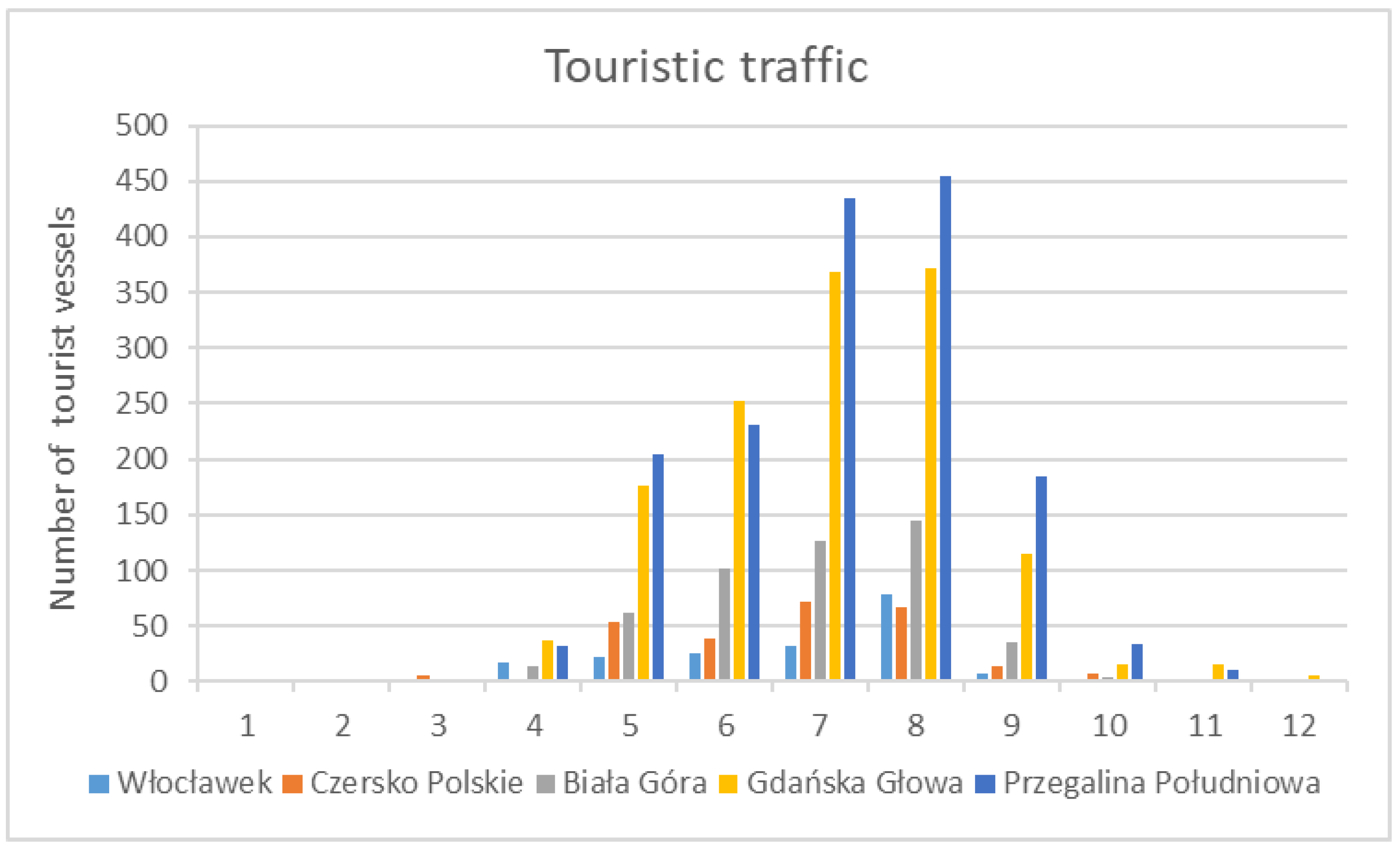
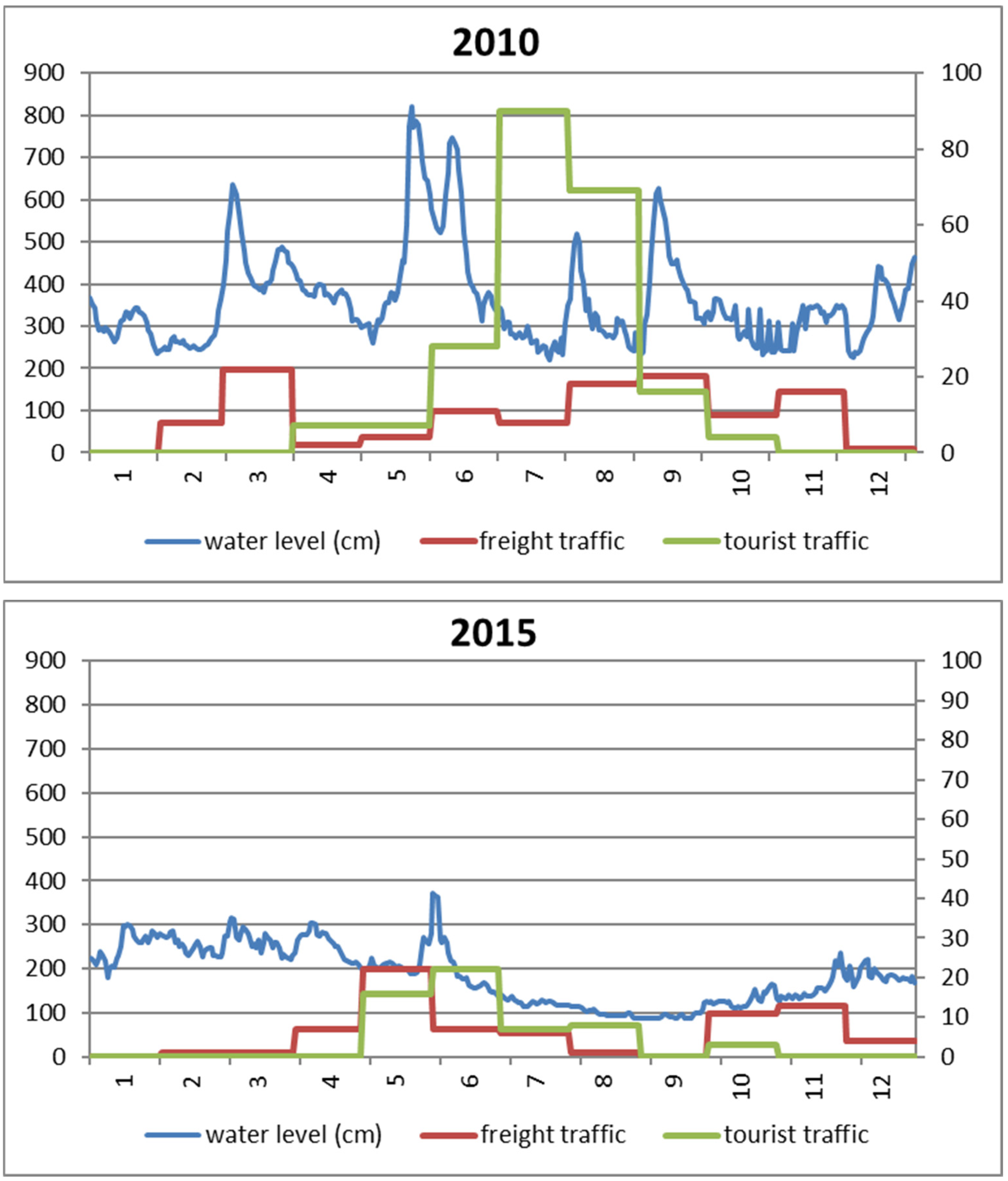
4.3. Lower Vistula Shipping Traffic Intensity
5. Discussion
5.1. Assessment of the Inland Navigation Conditions on the Lower Vistula Against the Background of Hydrological Conditions
5.2. Possibilities for Future Improvement of Inland Navigation on the Lower Vistula
6. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stefaniec, A.; Hosseini, K.; Xie, J.; Li, Y. Sustainability assessment of inland transportation in China: A triple bottom line-based network DEA approach. Transport. Res. Transp. Environ. 2020, 80, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Borthwick, A.G.L.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Zheng, C.; Xu, J.; Ni, J. Sustainability of global Golden Inland Waterways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Barros, B.R.C.; de Carvalho, E.B.; Brasil, A.C.P., Jr. Inland waterway transport and the 2030 agenda: Taxonomy of sustainability issues. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 8, 100462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.D.; Pokhrel, Y.; Chaudhari, S.; Mesquita, A.L.A.; Nascimento, A.; Filho, W.L.; Biato, M.F.; Schneider, P.S.; Lopes, M.A. Challenges and opportunities for a South America Waterway System. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 11, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoiu, V.-M.; Craciun, A.-I.; Kubiak-Wójcicka, K.; Antonescu, M.; Olariu, B. An Eco-Study for a Feasible Project: “Torun and Its Vistula Stretch—An Important Green Navigation Spot on a Blue Inland Waterway”. Water 2022, 14, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolbiecki, R.; Wojewódzka-Król, K. Changes in the transport capacity of Polish inland waterways against the background of European waterway use for transport. Transp. Econ. Logist. 2019, 81, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloslavskaya, S.; Plotnikova, E. Current situation and optimization of inland waterway infrastructure financing. Transp. Probl. 2018, 13, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caris, A.; Limbourg, S.; Macharis, C.; van Lier, T.; Cools, M. Integration of inland waterway transport in the intermodal supply chain: A taxonomy of research challenges. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 41, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolliver, D.; Lu, P.; Benson, D. Comparing rail fuel efficiency with truck and waterway. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 24, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkeren, O.; Piet, R.; Van Onnoren, J. Welfare effects of low water levels on the river Rhine through the Inland Waterway Transport Sector. J. Transp. Econ. Policy 2007, 41, 387–411. [Google Scholar]
- Smolnik, P. Assumption of state policy concerning inland waterways in Poland. Sci. J. Marit. Univ. Szczec. 2016, 47, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozerska, M. Inland waterway transport in Poland—The current state and prospects for development. Sci. J. Marit. Univ. Szczec. 2016, 47, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesiński, D.; Sobkowiak, L. Transformation of the Flow Regime of a Large Allochthonous River in Central Europe-An Example of the Vistula River in Poland. Water 2020, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Januchta-Szostak, A.; Nachlik, E.; Pińskwar, I.; Zaleski, J. Challenges for Flood Risk Reduction in Poland’s Changing Climate. Water 2023, 15, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, P. Projections of Climate Change Impact on Stream Temperature: A National-Scale Assessment for Poland. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, B.; Salehi, H.; Przybylak, R.; Pospieszyńska, A. Projection of climate change impact on the occurrence of drought events in Poland. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak-Wójcicka, K.; Pokropski, T. Natężenie ruchu żeglugowego na dolnej Wiśle na podstawie analizy śluzowań we Włocławku w latach 1997-2016 [Intensity of inland navigation on the lower Vistula River based on the analysis of lockage in Włocławek in the years 1997–2016]. Pr. Geogr. 2019, 156, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inland Waterway. 2023. Available online: https://transport.ec.europa.eu/transport-modes/inland-waterways_en (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Inland Waterway Transport in Europe: No Significant Improvements in Modal Share and Navigability Conditions Since 2001. Special Report, 15. 2015. Available online: https://www.eca.europa.eu/Lists/ECADocuments/SR15_01/SR15_01_EN.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Mako, P.; Galieriková, A. Inland navigation on the Danube and the Rhine waterways. 14th International scientific conference on sustainable, modern and safe transport. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 55, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoiu, V.-M.; Craciun, A.-I. Danube river water quality trends: A qualitative review based on the open access web of science database. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat Data. 2023. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Inland_waterways_freight_transport_-_quarterly_and_annual_data (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Informacje sygnalne. In Transport Wodny Śródlądowy w Polsce w 2020 roku [Inland Waterway Transport in Poland in 2020]; Główny Urząd Statystyczny: Warszawa, Poland, 2021.
- Rudnik, S. Ratification by Poland of the European Agreement on major inland waterways of international importance (AGN). Transp. Overv. Prz. Komun. 2017, 10, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzielskia, P.; Durajczykb, P.; Drop, N. Utilizing the RIS system to improve the efficiency of inland waterway transport companies. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 192, 4853–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, S.; Tutaj, J. Reasons for stagnation in river transport in Poland at the turn of the 20th and 21st centuries. Econ. Environ. 2024, 88, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inland Waterways Transport in Poland in 2024. News Releases 2025. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/en/topics/transport-and-communications/transport/inland-waterways-transport-in-poland-in-2024,10,15.html (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Woś, K. Plany rozwoju polskich śródlądowych dróg wodnych [Development plans for Polish inland waterways]. Probl. Transp. I Logistyki 2017, 1, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strategia Zrównoważonego Rozwoju Transportu do 2030 roku [Sustainable Transport Development Strategy Until 2030]. 2019. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/attachment/e268e9f9-d7ca-473e-a7b1-8731348155d9 (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- Kenc, J.; Szostak, E. Decarbonisation of Transport—A Challenge for Inland Navigation. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2022, XXV, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durajczyk, P.; Drop, N. Possibilities of Using Inland Navigation to Improve Efficiency of Urban and Interurban Freight Transport with the Use of the River Information Services (RIS) System—Case Study. Energies 2021, 14, 7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durajczyk, P.; Drop, N.; Maruszczak, M. Possibilities of Implementation of the System of Automatic Indication of Safe Clearance under the Bridge in Poland. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2021, XXIV, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port Szczecin. 2023. Available online: https://www.port.szczecin.pl/biznes/glebokowodny-terminal-kontenerowy (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Absalon, D. New inland waterways in heavily invested areas—Conditions and hazards. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2186, 120002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegowski, J.; Robakiewicz, M.; Woś, K.; Wrzosek, K. Sediment Transport Management Using the Planned Construction of the Lower Vistula Cascade as an Example. Energies 2022, 15, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port Gdańsk. 2023. Available online: https://www.portgdansk.pl/biznes/informacje-ogolne/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Breś, J.; Lorens, P. Shaping the New Vistula Spit Channel: Political, Economic, and Environmental Aspects. Urban Plan. 2023, 8, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiński, J.; Zdulski, W. Hydropower potential of the Vistula. Acta Energetica 2013, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiński, Z.; Habel, M. Hydromorphological conditions of the lower Vistula in the development of navigation and hydropower. Acta Energetica 2013, 2, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzosek, K.; Sobiesak, P.; Sikorski, G. Characteristic technical solutions of barrages planned on the Vistula River on the international E-40 waterway. Energetyka Wodna 2021, 3, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kubrak, J.; Kiczko, A.; Kubrak, A. Case Study: Forecasting the Lower Vistula Bed Deformation without and with Development of Dam Cascade. Water 2021, 13, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankiersztejn, I. The Lower Vistula Cascade. Acta Energetica 2013, 3, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerstwo Infrastruktury [Ministry of Infrastructure]. 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/infrastruktura/program-zagospodarowania-dolnej-wisly-przyjety-przez-rade-ministrow (accessed on 16 November 2023).
- Jokiel, P.; Tomalski, P. Zróżnicowanie i zmienność wieloletnia sezonowości przepływu w wybranych przekrojach wodowskazowych Wisły [Differentiation of river flow seasonality and its multiannual changeability in selected cross-sections on the Vistula river]. Pr. Geogr. 2018, 155, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesiński, D.; Sobkowiak, L. Detection of changes in flow regime of rivers in Poland. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2018, 66, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regional Water Management Board in Gdańsk Data. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/wody-polskie-gdansk (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Babiński, Z.; Grześ, M. Monografia Hydrologiczna Zbiornika Stopnia Wodnego Włocławek [Hydrological Monograph of Włocławek Reservoir]; Zeszyty IGiPZ PAN: Warszawa, Poland, 1995; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Meteorology and Water Management National Research Institute Data. Available online: https://danepubliczne.imgw.pl/ (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Rozporządzenie Rady Ministrów z dnia 7 Maja 2002, r. w Sprawie Klasyfikacji Śródlądowych Dróg Wodnych [Regulation of the Council of Ministers of 7 May 2002 on the Classification of Inland Waterways]. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20020770695 (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Central Statistical Office (CSO) Data. Available online: http://stat.gov.pl/obszary-tematyczne/transport-i-lacznosc/transport/transport-wodny-srodladowy-w-polsce-w-2016-roku,4,7.html (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Regional Water Management Board in Warsaw Data. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/wody-polskie-warszawa (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Yevjevich, V. An Objective Approach to Definition and Investigation of Continental Hydrological Droughts; Hydrology Paper, 23; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Scholten, A.; Rothstein, B. Navigation on the Danube—Limitations by Low Water Levels and Their Impacts; JRC Technical Reports; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; ISBN 978-92-79-64798-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, M.; Nagavciuc, V. Extreme Floods in the Eastern Part of Europe: Large-Scale Drivers and Associated Impacts. Water 2021, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeneich, M.; Habel, M.; Szatten, D. Limitation for Inland Ships in the Area of Planned Multimodal Port on Vistula River. TRansNav Int. J. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2020, 14, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorączko, M.; Kubiak-Wójcicka, K. Waterways in Poland: The history, present state and future. In Management of Water Resources in Poland; Zeleňáková, M., Kubiak-Wójcicka, K., Negm, A.M., Eds.; Springer Water: Cham, Germany, 2021; pp. 357–378. ISBN 978-3-030-61964-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Sportu i Turystyki z dnia 9 kwietnia 2013 roku w sprawie uprawiania turystyki wodnej [Regulation of the Minister of Sport and Tourism of April 9, 2013 on Practicing Water Tourism]. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20130000460/O/D20130460.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Kubiak-Wójcicka, K. Water Tourism on the Example of the Brda River (Central Poland). In Proceedings of the Poprad Economic and Management Forum: Conference Proceedings from International Scientific Conference, Poprad, Slovak Republic, 17–18 October 2019; Madzík, P., Askarnia, M., Eds.; Verbum-Vydavatel’stvo Katolíckej Univerzity: Poprad, Slovakia, 2019; pp. 372–382. Available online: https://www.pemf-conference.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/PEMF_2019_Proceedings-1.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Ionita, M.; Tallaksen, L.M.; Kingston, D.G.; Stagge, J.H.; Laaha, G.; Van Lanen, H.A.J.; Scholz, P.; Chelcea, S.M.; Haslinger, K. The European 2015 drought from a climatological perspective. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, A.; Christidis, P.; Bisselink, B. Forecasting the impacts of climate change on inland waterways. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 82, 102159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinke, F.; van Koningsveld, M.; van Dorsser, C.; Baart, F.; van Gelder, P.; Vellinga, T. Cascading effects of sustained low water on inland shipping. Clim. Risk Manag. 2022, 35, 100400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuthe, M.; Urbain, N.; Lingemann, I.; Ubbels, B. Climate change impacts on transport on the Rhine and Danube: A multimodal approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 27, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szépszó, G.; Lingemann, I.; Klein, B.; Kovács, M. Impact of climate change on hydrological conditions of Rhine and Upper Danube rivers based on the results of regional climate and hydrological models. Nat. Hazards 2014, 72, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, K.; Weiler, M.; Van Tiel, M.; Kohn, I.; Haensler, A.; Freudiger, D.; Seibert, J.; Moretti, G.; Gerlinger, K. Climate change impact on rain, snow and glacier melt components of streamflow for the river Rhine: Synthesis of a model experiment and relevance for water use. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022. EGU22-11271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak-Wójcicka, K.; Bąk, B. Monitoring of meteorological and hydrological droughts in the Vistula basin (Poland). Environ. Monit. Assess 2018, 190, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piniewski, M.; Szcześniak, M.; Huang, S.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Projections of runoff in the Vistula and the Odra river basins with the help of the SWAT model. Hydrol. Res. 2018, 49, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak-Wójcicka, K. Variability of Air Temperature, Precipitation and Outflows in the Vistula Basin (Poland). Resources 2020, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grześ, M.; Pawłowski, B. Hydromorfologiczne Uwarunkowania Lodołamania na Wiśle od Stopnia Wodnego we Włocławku do Ujścia, z Uwzględnieniem Sezonu Zimowego 2011/2012; Regionalny Zarząd Gospodarki Wodnej: Gdańsk, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pieron, Ł.; Woś, K.; Wrzosek, K. Water Reservoirs in Plans to Improve Navigability of the Lower Section of the Vistula. Water 2022, 14, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woś, K.; Wrzosek, K.; Kolerski, T. The Energy Potential of the Lower Vistula River in the Context of the Adaptation of Polish Inland Waterways to the Standards of Routes of International Importance. Energies 2022, 15, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macharis, C.; Caris, A.; Jourquin, B.; Pekin, E. A decision support framework for intermodal transport policy. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2011, 3, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rožić, T.; Rogić, K.; Bajor, I. Research Trends of Inland Terminals: A Literature Review. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2016, 28, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krośnicka, K.A.; Lorens, P.; Michałowska, E. Port Cities within Port Regions: Shaping Complex Urban Environments in Gdańsk Bay, Poland. Urban Plan. 2021, 6, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, C. Port City Porosity: Boundaries, Flows, and Territories. Urban Plan. 2021, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.S. Materiality in the Seam Space: Sketches for a Transitional Port City Dome District. Urban Plan. 2021, 6, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piątek, Ł.; Wycisk, A.A.; Parzych, D.; Modrzejewska, K. Floating buildings in the hotel, catering and water tourism industry in Poland—Business environment survey. J. Water Land Dev. 2020, 45, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Hydrological Station | Kilometer of the River | The Catchment Area (km2) | Maximum Flow (m3/s) | Average Flow (m3/s) | Minimum Flow (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warszawa Nadwilanówka | 504.1 | 84,641 | 5740 | 547 | 157 |
| Włocławek | 679.4 | 171,763 | 6540 | 856 | 160 |
| Toruń | 734.7 | 180,391 | 6190 | 911 | 218 |
| Tczew | 908.6 | 193,806 | 6360 | 985 | 266 |
| Operational Parameters | Parameter Values | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | Ia | Ib | II | III | IV | Va | Vb | |
| Minimum dimensions of the navigable route in the river - width of navigable route - transit depth - radius of arc of fairway axis | Units m m m | 15 1.2 100 | 20 1.6 200 | 30 1.8 300 | 40 1.8 500 | 40 2.8 650 | 50 2.8 650 | 50 2.8 800 |
| Minimum channel dimensions - width of navigable route - smallest water depth in the channel - radius of arc of fairway axis | m m m | 12 1.5 150 | 18 2.0 250 | 25 2.2 400 | 35 2.5 600 | 40 3.5 650 | 45 3.5 650 | 45 3.5 800 |
| Minimum dimensions of navigation locks - lock width - lock length - depth at bottom sill | m m m | 3.3 25 1.5 | 5.0 42 2.0 | 9.6 65 2.2 | 79.6 72 2.2 | 12.0 120 3.5 | 12.0 120 4.0 | 12.0 187 4.0 |
| Parameter | Toruń | Tczew |
|---|---|---|
| Zero level of the hydrological station (m a.s.l.) | 31.96 | −0.58 |
| Warning state (cm) | 530 | 700 |
| Emergency state (cm) | 650 | 820 |
| MHW (cm) | 585 | 746 |
| LHW (cm) | 391 | 442 |
| MAW (cm) | 284 | 399 |
| HLW (cm) | 226 | 354 |
| MLW (cm) | 161 | 246 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubiak-Wójcicka, K.; Manoiu, V.-M. International Inland Waterways in Poland: Current State and Their Importance in EU Transport Policy. Water 2025, 17, 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223190
Kubiak-Wójcicka K, Manoiu V-M. International Inland Waterways in Poland: Current State and Their Importance in EU Transport Policy. Water. 2025; 17(22):3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223190
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubiak-Wójcicka, Katarzyna, and Valentina-Mariana Manoiu. 2025. "International Inland Waterways in Poland: Current State and Their Importance in EU Transport Policy" Water 17, no. 22: 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223190
APA StyleKubiak-Wójcicka, K., & Manoiu, V.-M. (2025). International Inland Waterways in Poland: Current State and Their Importance in EU Transport Policy. Water, 17(22), 3190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223190







