Groundwater Storage Assessment in Abu Dhabi Emirate: Comparing Spatial Interpolation Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Description
2.2. Interpolation Techniques for Groundwater Level Estimation
2.3. Ordinary Kriging
2.4. Local Polynomial Interpolation
2.5. Spatial Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Level
- Cross-validation is a statistical approach that verifies the precision of an interpolation model by dividing the initial data into a training set and a validation set. The validation set is then utilized to test the model created from the training set, providing indicators to assess its accuracy. The model with the lowest error is considered the most suitable interpolation model [32].
- Descriptive Statistics: calculating basic statistics of groundwater level data such as the mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. These statistics provide initial insights into the central tendency, shape, and dispersion of the data [46].
- Visual Inspection: creating time series plots and histograms visualizes the data to provide insights into normality, potential patterns, and outliers [47].
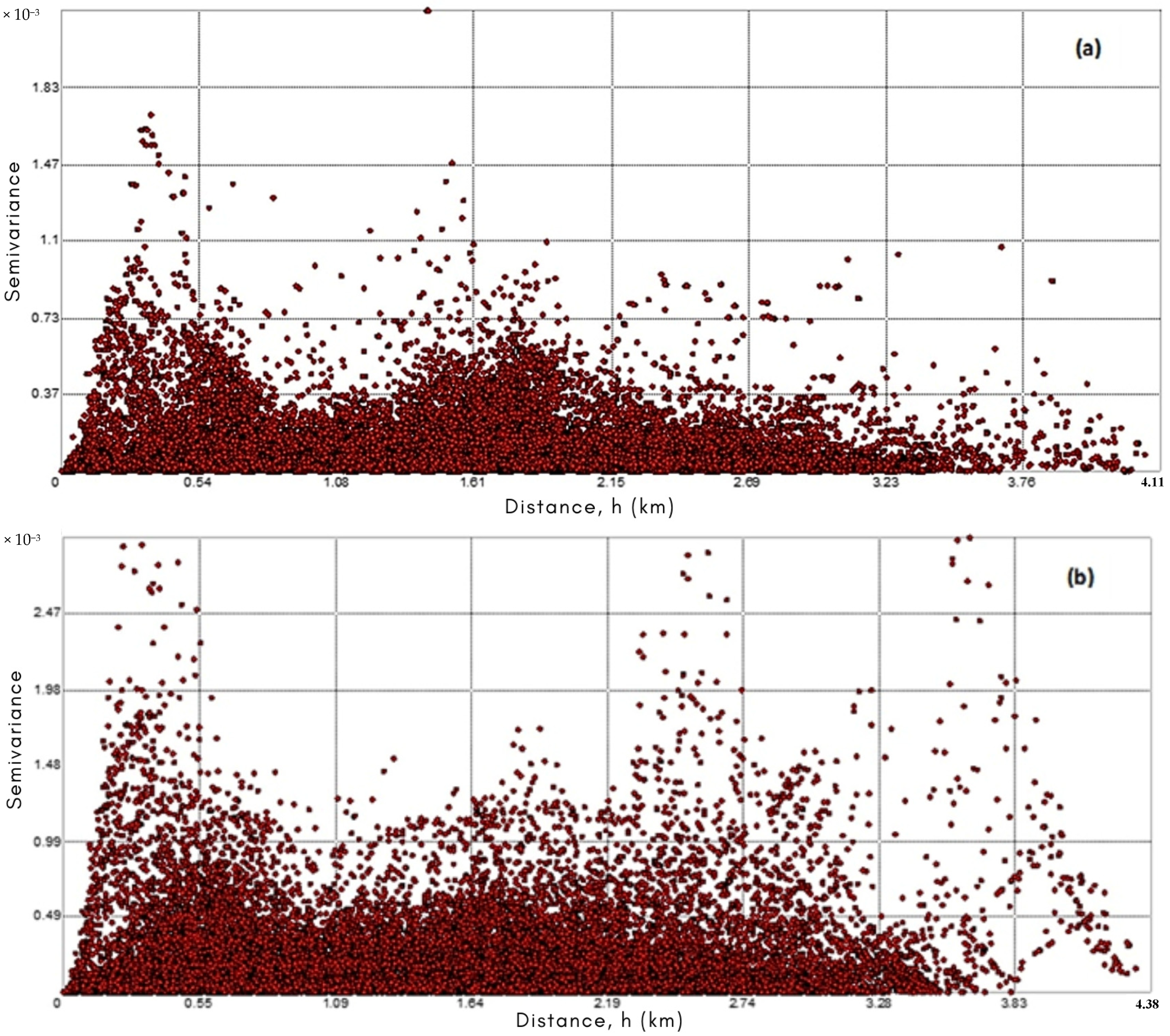
- Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA): conducting a semivariogram, which is a graphical representation that shows the semi variance values for pairs of points at different distances. Essentially, it plots the squared difference between the values of each pair of points on the “y” axis against the distance separating them on the “x” axis. This tool is useful for understanding the spatial autocorrelation of a set of sample points, which assumes that points nearby are more similar to each other [48].
- Maps Generation: producing groundwater level maps along with prediction standard error maps to interpret spatial patterns and temporal fluctuations, along with critical zones [46].
2.6. Groundwater Storage Calculation from In Situ Data
- Accuracy of Measurements: The equation is heavily dependent on the accuracy of the measurements of water level changes (∆h) and Sy. Any errors or inaccuracies in these measurements can greatly impact the calculation of groundwater storage change (ΔS).
- Assumption of Homogeneity: The method assumes that the aquifer is homogeneous and isotropic, meaning that the properties of the aquifer, including the Sy, are uniform in all directions. However, in reality, aquifers often have variable properties.
- Limitations of Specific Yield: The Sy is a difficult parameter to determine accurately. However, this value can change based on various factors, including soil properties, saturation levels, and even the rate of withdrawal. In this research, the chosen average value of specific yield is based on several published studies conducted in the same region by [49,51,52]. These studies utilized a specific yield that varied between 0.01 and 0.32.
3. Results
3.1. Cross-Validation
3.2. Descriptive Statistics
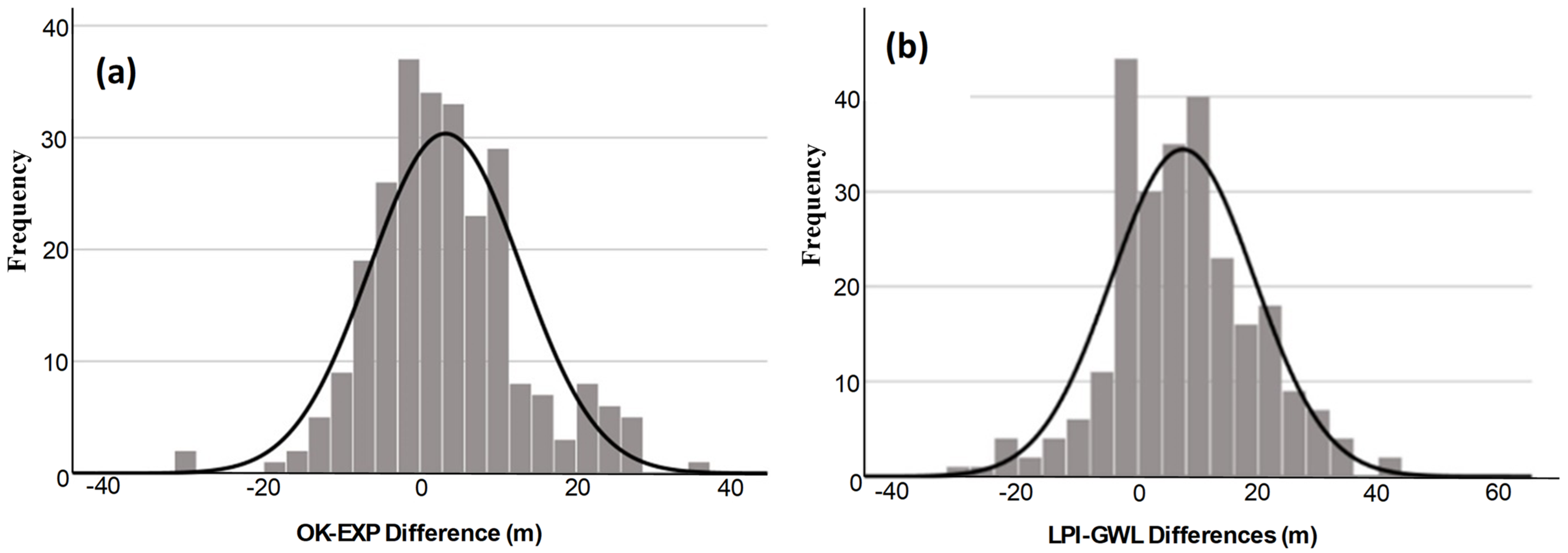
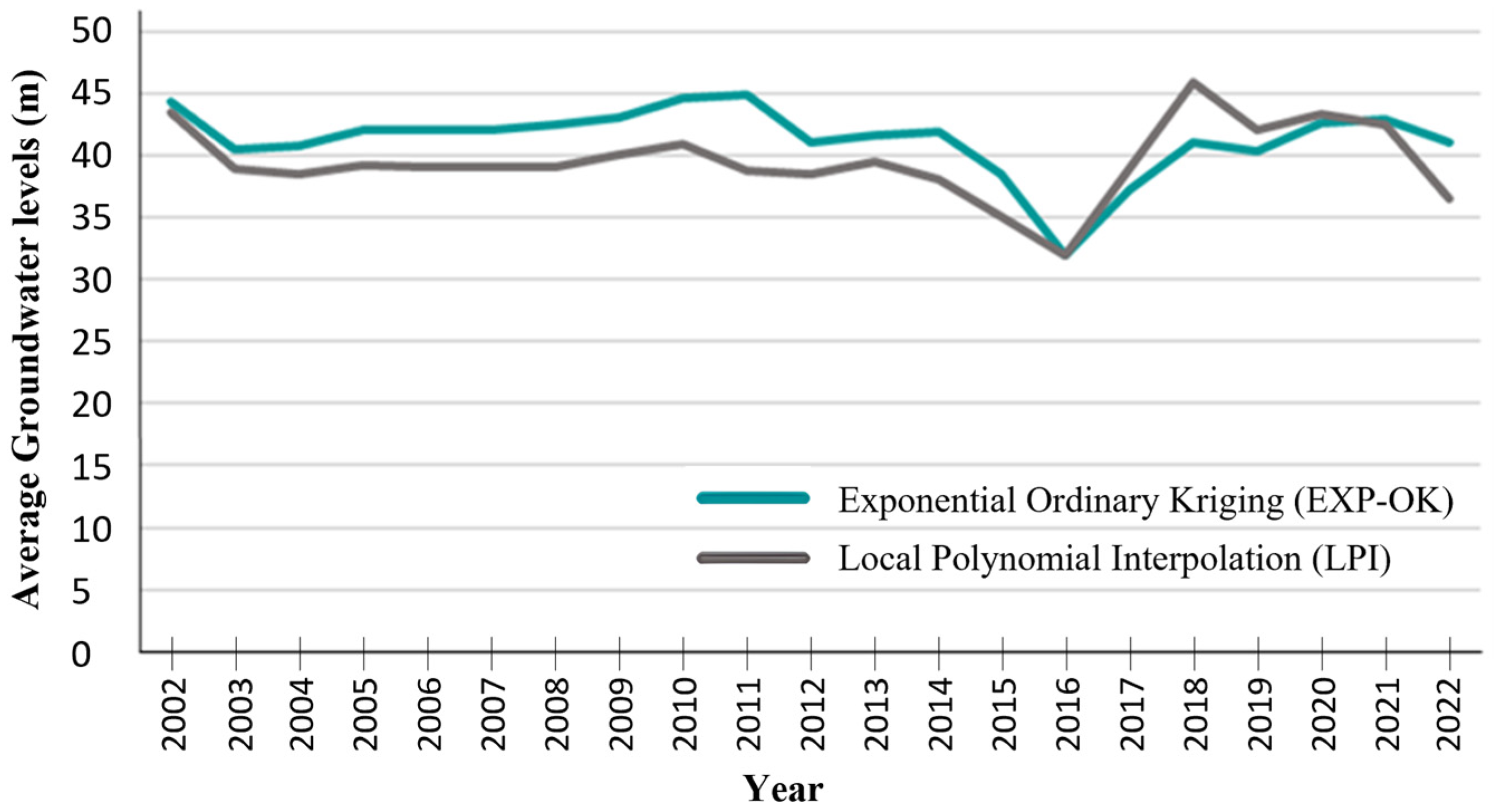
3.3. Histograms and Time-Series Plot
3.4. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis (ESDA)
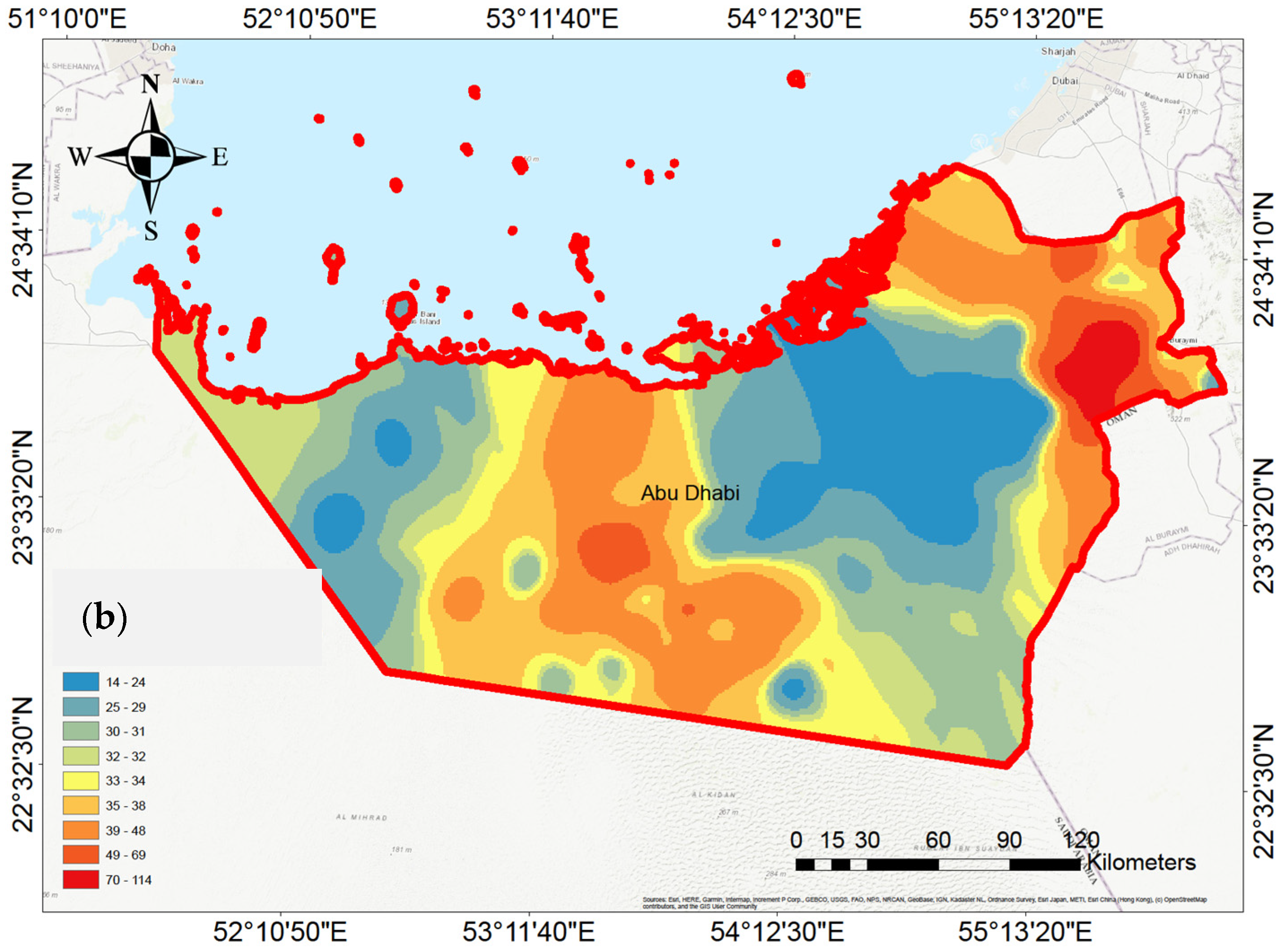
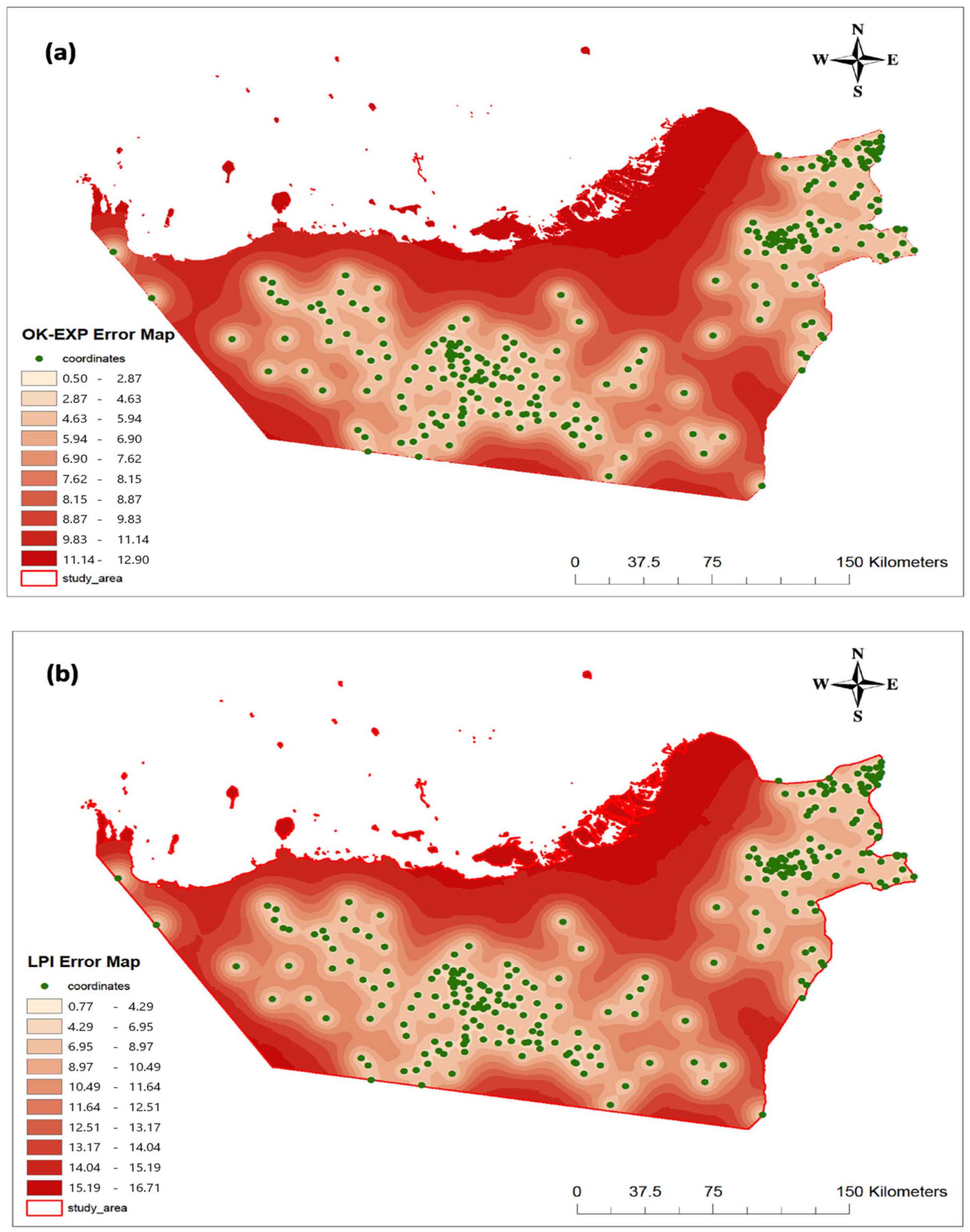
3.5. Groundwater Interpretation Maps
3.6. Change in Groundwater Storage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPI | Local Polynomial Interpolation |
| EXP-OK | Exponential Ordinary Kriging |
| GPI | Global Polynomial Interpolation |
| OK | Ordinary Kriging |
| SPH-OK | Spherical Ordinary Kriging |
| Guass-OK | Gaussian Ordinary Kriging |
| SK | Simple Ordinary Kriging |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| UK | Universal Kriging |
| CoOk | Cokriging |
| ESDA | Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis |
| Sy | Specific yield |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| GWL | Groundwater Level |
References
- UNESCO. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2021: Valuing Water; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, K.; Khan, Q.; Mohamed, M. Selection Criteria of Best Sites for Aquifer Storage and Recovery in the Eastern District of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M.; Parimalarenganayaki, S.; Khan, Q.; Murad, A. Review on the Use of Environmental Isotopes for Groundwater Recharge and Evaporation Studies in the GCC Countries. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Kantoush, S.A.; Saber, M. Wadi Flash Floods: Challenges and Advanced Approaches for Disaster Risk Reduction; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dawoud, M.A. Groundwater Economics in Arid Regions: Abu Dhabi Emirate Case Study. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, Proceedings of the Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration, Sousse, Tunisia, 22–25 November 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Alyaarbi, Y.; Camkin, J.; Neto, S.; Wegener, P. Knowledge, Attitudes, Skills, and Aspirations of Farmers in Abu Dhabi and Western Australia on Groundwater Management: A Comparison Study. World Water Policy 2019, 5, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.M.; Bonsor, H.C.; Dochartaigh, B.É.Ó.; Taylor, R.G. Quantitative Maps of Groundwater Resources in Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 024009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, B.; Gunduz, O. Evaluation of the Temporal Variations of Groundwater Storage and Its Interactions with Climatic Variables Using GRACE Data and Hydrological Models: A Study from Turkey. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koïta, M.; Yonli, H.F.; Soro, D.D.; Dara, A.E.; Vouillamoz, J.-M. Groundwater Storage Change Estimation Using Combination of Hydrogeophysical and Groundwater Table Fluctuation Methods in Hard Rock Aquifers. Resources 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Gupta, S.; Nepal, S. Groundwater Dynamics in North Bihar Plains. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 2482–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, H.; De Oliveira, V.; Kedem, B. Multivariate Geostatistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arkoc, O. Modeling of Spatiotemporal Variations of Groundwater Levels Using Different Interpolation Methods with the Aid of GIS, Case Study from Ergene Basin, Turkey. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Chen, S.; Liang, Y.; Hou, M.; Chen, J. Infilling the Missing Values of Groundwater Level Using Time and Space Series: Case of Nantong City, East Coast of China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 1445–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.M.; Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Hao, K.Z.; Xiaosheng, Q.; Sham, A.W.L. Investigation of Groundwater Table Distribution Using Borehole Piezometer Data Interpolation: Case Study of Singapore. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteraa, O.; Mebarki, A.; Bouaicha, F.; Nouaceur, Z.; Laignel, B. Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Multivariate Analysis, Geostatistical Modeling, and Water Quality Index (WQI): A Case of Study in the Boumerzoug-El Khroub Valley of Northeast Algeria. Acta Geochim. 2019, 38, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohammadi-Kalalagh, S.; Taran, F. Evaluation of the Classical Statistical, Deterministic and Geostatistical Interpolation Methods for Estimating the Groundwater Level. Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2021, 5, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, M.O.; Atikpo, E. Spatial Dependency of Groundwater Quality in Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria Using Semi-Variogram Models. World J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2021, 2, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Huo, Z.; Feng, S.; Mao, X.; Kang, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Steenhuis, T.S. Evaluation of Spatial Interpolation Methods for Groundwater Level in an Arid Inland Oasis, Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowot, M.; Alexander, A.C.; Mulungu, D. Assessment of Spatial Variability of Groundwater Levels in Moroto District, Uganda. Tanzan. J. Eng. Technol. 2023, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakos, A.; Lambrakis, N. Spatial Interpolation for the Distribution of Groundwater Level in an Area of Complex Geology Using Widely Available GIS Tools. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 993–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajari, M.; Mozayyan, M.; Mokarram, M.; Chekan, A.A. Relationship between Groundwater Quality and Distance to Fault Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) and Geostatistical Methods (Case Study: North of Fars Province). Spat. Inf. Res. 2019, 27, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodnia, A.; Mousavi, M.; Kootenaei, F.G.; Asadi-Ghalhari, M. The Performance of Several Current Interpolation Methods for Variability of Cations in Groundwater in Esfarayen Plain, Iran: A Case Study. Avicenna J. Environ. Health Eng. 2022, 9, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, C.J.; Adhikary, P.P.; Lenka, J. Assessment of Groundwater Salinity Risk in Coastal Belt of Odisha Using Ordinary Kriging and Its Management. In Case Studies in Geospatial Applications to Groundwater Resources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Rakib, M.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Ramanathan, A.L. Assessment of Groundwater Quality of Lakshimpur District of Bangladesh Using Water Quality Indices, Geostatistical Methods, and Multivariate Analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.; Moteallemi, A.; Joulaei, F.; Peirovi, R. A Spatial Variation Study of Groundwater Quality Parameters in the Gonabad Plain Using Deterministic and Geostatistical Models. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 103, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, K.S.; Yashwant, B.K. Optimization of Groundwater Level Monitoring Network Using GIS-Based Geostatistical Method and Multi-Parameter Analysis: A Case Study in Wainganga Sub-Basin, India. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, G.; Khorasani, N.; Ghodousi, J.; Panahi, M. Application of Geostatistical Models to Identify Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Quality Parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36512–36532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, G.H.; Lin, Q.G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.R. Comparison of Interpolation Methods for Estimating Spatial Distribution of Precipitation in Ontario, Canada. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bameri, A.; Khaleghi, M. Monitoring and Predicting the Groundwater-Level Fluctuations for Better Management of Groundwater Resource in Lowlands Using Geographic Information System (GIS). J. Radar Opt. Remote Sens. GIS 2021, 4, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bodrud-Doza, M.D.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Ahmed, F.; Das, S.; Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S. Characterization of Groundwater Quality Using Water Evaluation Indices, Multivariate Statistics and Geostatistics in Central Bangladesh. Water Sci. 2016, 30, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, R.J.; Lai, S.H.; Loh, W.S.; Ling, L.; Soo, E.Z.X. Assessment of Inverse Distance Weighting and Local Polynomial Interpolation for Annual Rainfall: A Case Study in Peninsular Malaysia. Eng. Proc. 2023, 38, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, X.; Yin, S.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, Y. Geostatistical Interpolation Model Selection Based on ArcGIS and Spatio-Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Level in Piedmont Plains, Northwest China. Springerplus 2016, 5, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Gu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, W.; Pan, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Q. Geostatistics-Based Spatial Variation Characteristics of Groundwater Levels in a Wastewater Irrigation Area, Northern China. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2017, 17, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooteh Rigi, M.; Shafiee, P.; Fatehi, S.M. Assessment and Zoning of Groundwater Quality in Shiraz Plain Using GIS. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2019, 16, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katipoğlu, O.M.; Acar, R. Space-Time Variations of Hydrological Drought Severities and Trends in the Semi-Arid Euphrates Basin, Turkey. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 4017–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Barati, R.; Baghani, M.; Sakhdari, S. Interpolation methods for spatial distribution of groundwater mapping electrical conductivity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzì, I. Modeling Groundwater in Data-Scarce Environments: A Systematic Review of Approaches, Challenges, and Future Directions. Hydrology 2025, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Blooshi, L.S.; Ksiksi, T.S.; Aboelenein, M.; Gargoum, A.S. The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural and Livestock Production and Groundwater Characteristics in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2020, 19, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M.A.; Saleh, N.E.; Sherif, M.M. Modeling in Situ Benzene Bioremediation in the Contaminated Liwa Aquifer (UAE) Using the Slow-Release Oxygen Source Technique. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M.; El-Shorbagy, W.; Kizhisseri, M.I.; Chowdhury, R.; McDonald, A. Evaluation of policy scenarios for water resources planning and management in an arid region. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, M.; Tadakuma, N.; Asaue, H.; Koike, K. Characterizing the Regional Pattern and Temporal Change of Groundwater Levels by Analyses of a Well Log Data Set. Front. Earth Sci. 2011, 5, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamoori, S.K.; Al-Maliki, L.A.; Al-Sulttani, A.H.; El-Tawil, K.; Al-Ansari, N. Statistical Analysis of the Best GIS Interpolation Method for Bearing Capacity Estimation in An-Najaf City, Iraq. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmer, M.; Liesch, T.; Goeppert, N.; Goldscheider, N. On the Optimal Selection of Interpolation Methods for Groundwater Contouring: An Example of Propagation of Uncertainty Regarding Inter-Aquifer Exchange. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 109, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. An Introduction to Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sunila, R.; Kollo, K. A Comparison of Geostatistics and Fuzzy Application for Digital Elevation Model. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2007, 36. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/253685839_A_COMPARISON_OF_GEOSTATISTICS_AND_FUZZY_APPLICATION_FOR_DIGITAL_ELEVATION_MODEL (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Yarus, J.M.; Chambers, R.L. Stochastic Modeling and Geostatistics; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994; Volume 231. [Google Scholar]
- Tanjung, M.; Syahreza, S.; Rusdi, M. Comparison of Interpolation Methods Based on Geographic Information System (GIS) in the Spatial Distribution of Seawater Intrusion. J. Nat. 2020, 20, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyan, M.; Cay, T. Spatial Analyses of Groundwater Level Differences Using Geostatistical Modeling. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2013, 20, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasel, H.M.; Alam, S.; Hasnat, A.; Hossain, I.; Hasan, M.; Ahsan, A. Geospatial Analysis of Groundwater Level Variations Using Kriging Method. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2019, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Verma, P. A Comparative Study of Spatial Interpolation Technique (IDW and Kriging) for Determining Groundwater Quality. In GIS and Geostatistical Techniques for Groundwater Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghafli, K.; Shi, X.; Sloan, W.; Shamsudduha, M.; Tang, Q.; Sefelnasr, A.; Ebraheem, A.A. Groundwater Recharge Estimation Using In-Situ and GRACE Observations in the Eastern Region of the United Arab Emirates. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K.; Mays, L.W. Groundwater Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 0471059374. [Google Scholar]
- Sathish, S.; Mohamed, M.M. Assessment of Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Feasibility at Selected Sites in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, UAE. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, K.; Khan, Q.; Mohamed, M. Modeling Aquifer Storage and Recovery in the Eastern District of the United Arab Emirates Using MODFLOW. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obroślak, R.; Dorozhynskyy, O. Selection of a Semivariogram Model in the Study of Spatial Distribution of Soil Moisture. J. Water Land Dev. 2017, 35, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.-G.; Diana, E.M.; Germán, T.; David, B.; Laurent, P.; Eulogio, J.B. Spatial Distribution of N-Cycling Microbial Communities Showed Complex Patterns in Constructed Wetland Sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 340–351. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Q.; Kalbus, E.; Alshamsi, D.M.; Mohamed, M.M.; Liaqat, M.U. Hydrochemical analysis of groundwater in Remah and Al Khatim regions, United Arab Emirates. Hydrology 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, M.U.; Mohamed, M.M.; Chowdhury, R.; Elmahdy, S.I.; Khan, Q.; Ansari, R. Impact of land use/land cover changes on groundwater resources in Al Ain region of the United Arab Emirates using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Q.; Liaqat, M.U.; Mohamed, M.M. A comparative assessment of modeling groundwater vulnerability using DRASTIC method from GIS and a novel classification method using machine learning classifiers. Geocart. Int. 2021, 37, 5832–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdy, S.I.; Marghany, M.M.; Mohamed, M.M. Application of a weighted spatial probability model in GIS to analyze landslides in Penang Island, Malaysia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2013, 7, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



| Study | GPI | LPI | IDW | OK-SPH | EXP-OK | OK-GAUSS | SK | RBF | UK | CoOk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arkoc [12] |  | |||||||||
| He et al. [13] |  | |||||||||
| Nistor et al. [14] |  | |||||||||
| Bouteraa et al. [15] |  | |||||||||
| Shahmohammadi-Kalalagh and Taran [16] |  | |||||||||
| Ezugwu and Atikpo [17] |  | |||||||||
| Yao et al. [18] |  | |||||||||
| Lowot et al. [19] |  | |||||||||
| Antonakos and Lambraki [20] |  | |||||||||
| Aghajari et al. [21] |  | |||||||||
| Mahmoodnia et al. [22] |  | |||||||||
| Dash et al. [23] |  | |||||||||
| Bhuiyan et al. [24] |  | |||||||||
| Moteallemi et al. [25] |  | |||||||||
| Chandan and Yashwant [26] |  | |||||||||
| Farzaneh et al. [27] |  | |||||||||
| Wang et al. [28] |  | |||||||||
| Bameri and Khaleghi [29] |  | |||||||||
| Bodrud-Doza et al. [30] |  | |||||||||
| Chin et al. [31] |  | |||||||||
| Xiao et al. [32] |  | |||||||||
| Yin et al. [33] |  | |||||||||
| Pooteh et al. [34] |  | |||||||||
| Katipoğlu and Acar [35] |  |  | ||||||||
| Salehi et al. [36] |  | |||||||||
| Borzì [37] |  |
| Statistics | EXP-OK GWL Difference (m) | LPI GWL Difference (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum | −30.773 | −29.107 |
| Maximum | 35.566 | 41.915 |
| Mean | 3.281 | 7.467 |
| Standard deviation | 9.686 | 11.904 |
| Skewness | 0.268 | 0.071 |
| Kurtosis | 1.151 | 0.383 |
| Median | 2.489 | 7.552 |
| Range | 66.339 | 71.022 |
| Interquartile range | 11.750 | 15.597 |
| Year | h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 43.47 | −6.60 | 0.01–0.32 | −0.066 | −2.112 |
| 2022 | 36.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maksoud, T.; Mohamed, M.M. Groundwater Storage Assessment in Abu Dhabi Emirate: Comparing Spatial Interpolation Models. Water 2025, 17, 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213078
Maksoud T, Mohamed MM. Groundwater Storage Assessment in Abu Dhabi Emirate: Comparing Spatial Interpolation Models. Water. 2025; 17(21):3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213078
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaksoud, Tala, and Mohamed M. Mohamed. 2025. "Groundwater Storage Assessment in Abu Dhabi Emirate: Comparing Spatial Interpolation Models" Water 17, no. 21: 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213078
APA StyleMaksoud, T., & Mohamed, M. M. (2025). Groundwater Storage Assessment in Abu Dhabi Emirate: Comparing Spatial Interpolation Models. Water, 17(21), 3078. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213078






